I: Bacteriology
1/274
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
275 Terms
Taxonomy
classification of organisms into categories based on genotypic and phenotypic characteristics
Domain
Kingdom
Division
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Hierarchy of classification
Subspecies
same species but differ phenotypically
Biotype
same species, same genetic makeup, but different physiologic characteristics
Serovar
same species but differ serologically
Strain
same species, but different subtype or genetic variant
Subspecies
Biotype
Serovar
Strain
What are under species
eukaryotic
cells of human & plant
Prokaryotic
cells of bacteria & fungi
T
Prokaryotic (t/f)
they have no organelles; no membrane-enclosed structure
F
do not have nucleus
Prokaryotic (t/f)
have nucleus
T
Prokaryotic (t/f)
have 70s ribosomes & are haploid with a single chromosome
mycoplasma & ureaplasma
Prokaryotic
cell wall: with peptidoglycan expect
carbohydrate & sterol
Prokaryotic
cytoplasmic membrane: fluid phospholipid bilayer with
cytoplasmic membrane
Prokaryotic
site of energy production
free ribosomes
Prokaryotic
site of protein synthesis
F
unicellular
Prokaryotic (t/f)
multicellular
F
unicellular; contains DNA & RNA
Prokaryotic (t/f)
unicellular; contains DNA only
0.2 - 5.0 µm
Prokaryotic
average size
Mycoplasma spp.
Prokaryotic
smallest
Bacillus spp.
Prokaryotic
largest
binary fission
Prokaryotic multiplies by
Bacilli
Comma
Cocci
Spiral
4 Morphology of Prokaryotic
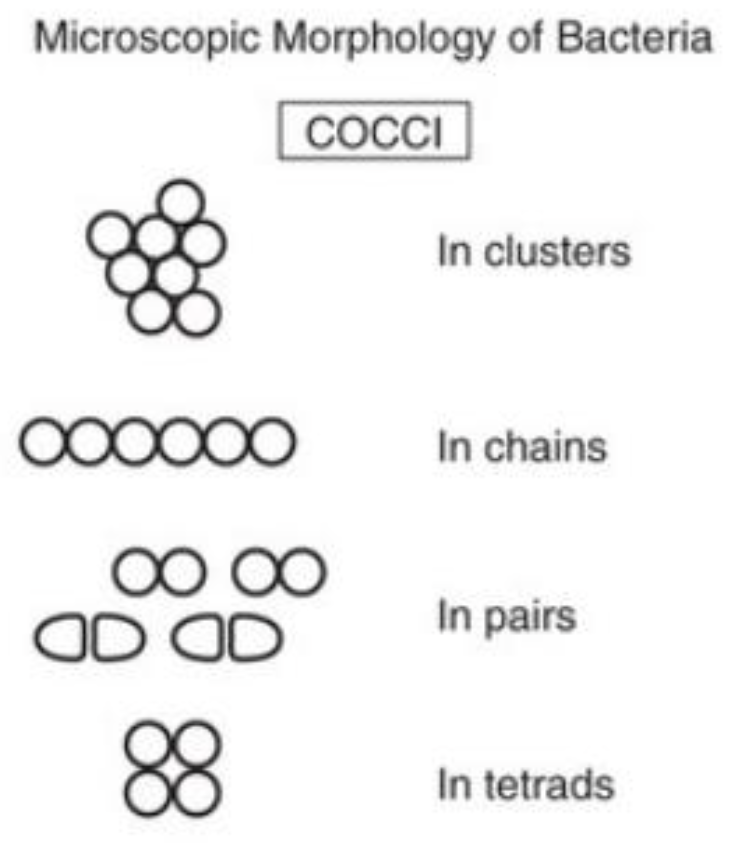
In clusters
In chains
In pairs
In tetrads
Microscopic Morphology of Bacteria
Cocci
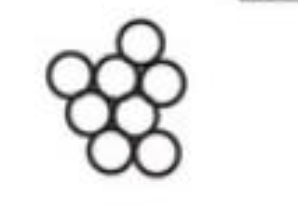
cocci: in clusters
identify

cocci: in chains
identify

cocci: in pairs
identify

cocci: in tetrd
identify
bacilli
rod-shaped
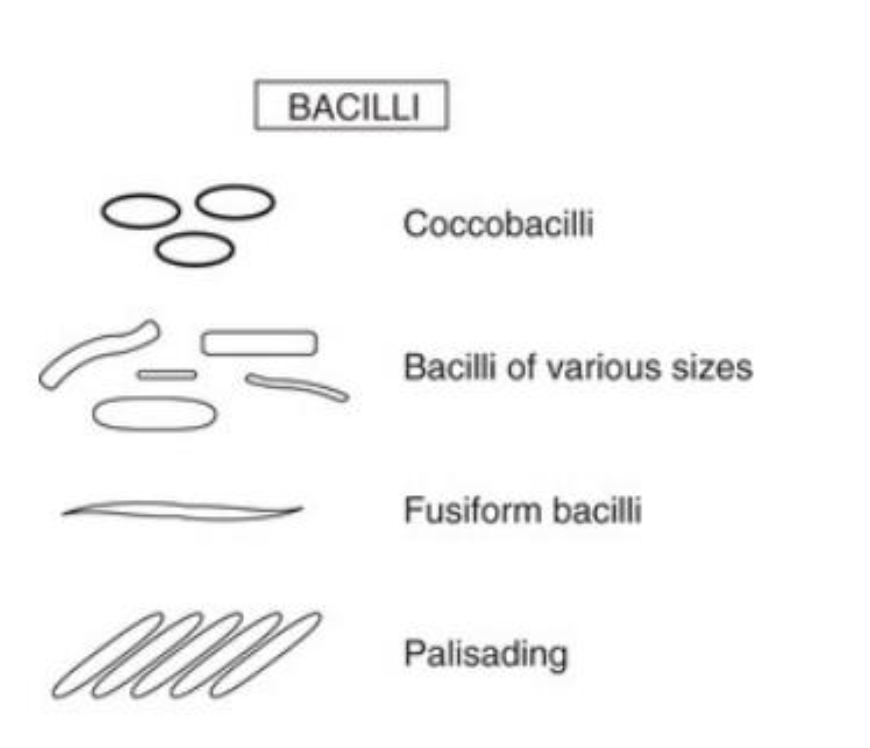
Coccobacilli
Bacilii of various sizes
Fusiform bacilli
Palisading
Microscopic Morphology of Bacteria
Bacilli

bacilli: coccobacilli (slightly curved edges)
identify
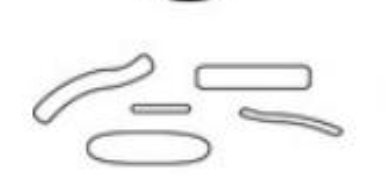
bacilli: bacilli of various sizes
identify

bacilli: fusiform bacilli (sickle shaped)
identify

palisading
identify

Spirochetes
spiral
Biofilm
property of bacteria to attach to a solid surface
Pathogenicity
the ability of a microbe to produce disease in a susceptible individual
Virulence
relative ability of microorganisms to cause disease or the degree of pathogenicity; usually measured by the number of microorganisms necessary to cause infection in the host
adherence factors
Virulence
_- pili/fimbriae
Anti-phagocytic factors
Virulence
_ - capsule and self-component of cell wall
Enzymes
Virulence
_ - i.e. Coagulase: S. aureus; Fibrinolysin- sp
0.20 - 2.0 um
Size of the cell of prokaryotes
F
usually present
Cell wall of prokaryotes is usually absent (t/f)
T
Nucleus of prokaryotes (t/f)
absence of nuclear membrane or nucleoli
in the nucleoid, at the mesosomes
genome location of prokaryotes
without histones
Chromosomes of prokaryotes
Single, singular chromosomes; _
Absent
membrane-bounded organelles of prokaryotes
70s
ribosomes of prokaryotes
Present; smaller size -
T
PRESENT
Pili and Fimbriae of prokaryotes is Present (t/f)
10-100um
Size of the cell of eukaryotes
T
Cell wall of of eukaryotes is usually absent, except for fungi (t/f)
T
Nucleus of eukaryotes (t/f)
True nucles of nuclear membrane or nucleoli
in the nucleus
genome location of eukaryotes
with histones
Chromosomes of eukaryotes
Multiple liner chromosomes; _
PRESENT
membrane-bounded organelles of eukaryotes is present (t/f)
80s
ribosomes of eukaryotes
Present; larger size -
Absent
Pili & fimbriae of eukaryotes
gram +
Producer of Exotoxin
released by all major gram
living bacteria
DOES NOT require cell death for release
Manner of excretion of Exotoxin
Exotoxin is excreted by ___________ and it __________ ____________; the metabolic product of bacteria
F
mainly protein in nature
Composition of Exotoxin (t/f)
polysaccharide and lipids
High
Toxicity of Exotoxin
unstable at 60
Stability to heating of Exotoxin
Exotoxin
Stimulates antitoxin production: Yes (can be converted into toxoid; easily neutralized by anti- toxin)
Exotoxin
Specificity
Binds to specific receptors
Exotoxin
Synthesis: Controlled by extrachromosomal gene
Local
Composition of Exotoxin
“________”- one area not associated with fever
gram -
Producer of Endotoxin
usually produced by gram
cell death
Manner of excretion of Endotoxin
It requires ________________ for release (cell wall disintegration)
F
polysaccharide and lipids
Composition of Endotoxin (t/f)
mainly protein in nature
Systemic
Composition of Endotoxin
“___________”- all over the body
low
Toxicity of Endotoxin
Stable
Stability to heating of Endotoxin
Endtoxin
Stimulates antitoxin production: No (cannot be converted into toxoid, not easily neutralized by anti- toxin)
Endotoxin
Specificity
Specific receptors not found on cells
Endotoxin
Synthesis directed by chromosomal genes (inside the cell)
Cell Envelope
Capsule
Cell wall
Plasma membrane
Pili / Fimbriae
Endospores
Flagella
Metachromatic Granules / Cytoplasmic Granules/Inclusion Bodies
Ribosomes
Mesosomes
Cytosol
Nucleoid
Bacterial Cell Structure
Cell envelope
Composed of layers (capsule, cell wall, cell membrane) that surround the bacterium
T
NOT ALL organisms have a cell wall, responsible for mucoid colonies (t/f)
polysaccharide / polypeptide
Cell envelope
Capsule is usually made of
T
Cell envelope (t/f)
Capsule prevents phagocytosis and is considered a virulence factor
Quellung reaction
Cell envelope
Capsule is antigenic; based on serotyping by
Neufeld-Quellung capsular Ag
Cell envelope
Capsule
what serologic test is (+) capsular swelling due to Ag-Ab complex
Somatic O Ag
Cell envelope
Capsule
_: heat stable
Vi Ag (salmonella)
K Ag (E.coli)
Cell envelope
Capsule
_: heat labile
animal tissues & fluids
Cell envelope
Capsule
Demonstration:
milk & serum
Cell envelope
Capsule
Media containing
mucoid & slimy
Cell envelope
Capsule
Colonies often
MUIR
ANTHONY’S
TYLER
HISS
WELCH’S
GRIN’S
Cell envelope
Capsule
Stains are
Cell wall
defines the shape of the bacteria
Cell wall
point of anchorage for flagella, site of attachment, and antibiotic action
M Protein of Streptococcus pyogenes
Cell wall
Pathogenicity:
_ - major virulence factor and prevents phagocytosis
Mycolic acid
responsible for acid fastness of Mycobacterium spp. and prevents digestion during phagocytosis
Poly-d-glutamic acid
Cell wall
Pathogenicity:
_- Bacillus spp.
Chitin
Cell wall
Pathogenicity:
_- fungi
L-forms
Cell wall
Pathogenicity:
_ are organisms that have temporarily lost their cell wall as a result of environmental condition
N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (NAG) & N-acetyl-d-muramic acid (NAM)
Cell wall
Peptidoglycan (murein layer) consists of glycan chains of alternating - and
-
Mycoplasma & Ureaplasma
Cell wall
- lack cell wall, and only contains sterol; making them pleomorphic and sensitive to osmotic pressure
sterol
Cell wall
Mycoplasma & Ureaplasma lack cell wall, and only contains _ ; making them pleomorphic and sensitive to osmotic pressure
F
Gram-positive and gram-negative cells can lose their cell walls and grow as L- forms in media supplemented with serum or sugar to prevent osmotic rupture of the cell membrane
Cell wall (t/f)
Gram-positive and gram-negative cells cannot their cell walls and grow as L- forms in media supplemented with serum or sugar to prevent osmotic rupture of the cell membrane