Brain Functions and neurotransmitters
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
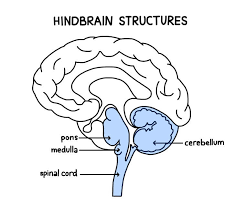
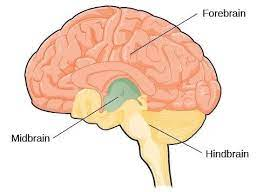
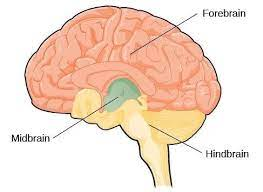
Hindbrain
-L: located on top of our spinal cord: cerebellum, pons, and medulla
-F: controls basic biological structures
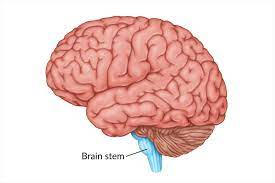
Brainstem
-L: base of the brain at the top of the spinal cord
-F: automatic, survival functions:
sends and receives info
severe damage to brainstem results in death
-oldest and innermost part
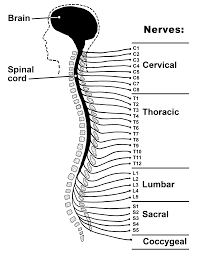
Spinal Cord
-L: starts at the base of brain and runs down the spine
-F: pathway for nerve fibers to carry info
connects brain to rest of body
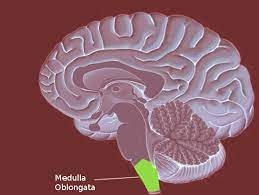
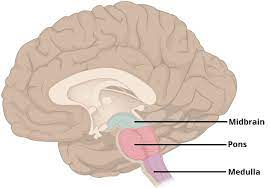
Hindbrain-Medulla (oblongata)
-L: above spinal cord, below pons
-F: heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
reflexes (sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and swallowing)
Hindbrain- pons
-L: above medulla on brainstem
-F: controls sleep, dreams, and facial expressions
connects multiple brain areas (medulla and cerebellum)
info processing
involved in control of breathing
coordinates movement
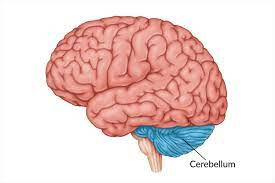
Hindbrain-cerebellum
-”little brain”
-L: base of the brain, size of baseball
-F: balance of smooth and coordinated movements, fine motor movements
procedural (implicit) memory
judgements, emotions, discriminate, sounds/textures
Midbrain
-L: above the hindbrain, very small in humans
-F: coordinates simple movement with sensory info
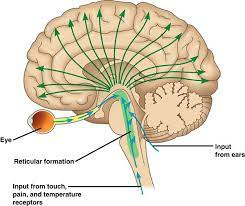
Midbrain- Reticular Formation
-L: finger-line shape through the brain stem
-F: arousal/consciousness to stimuli (awake-sleep cycle, not sexual)
-damage will put you in coma
-reflexes, breathing, and pain perception
Forebrain
-L: all brain parts except for brainstem and cerebellum
-largest part of the brain-most of it
-F: allows for the complex thoughts and behaviors unique to humans
-Tip: foremost of importance
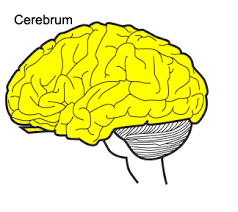
Cerebrum
-L: all brain parts except for brainstem and cerebellum (85% of the brain)
-F: all brain processes except for basic survival functions
the internal layer of the cerebrum is made up of the axons of neurons and glial cells
white matter
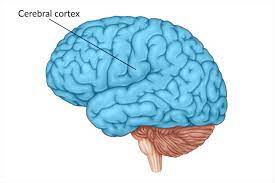
Cerebral Cortex
-L: ¼ inch wrinkled outer layer of the whole brain; 20-30 billion nerve cells are located here
-F: all higher mental functions (thought and planning)
ultimate control and info processing
-made up of the cell bodies of neurons called gray matter
-like a helmet
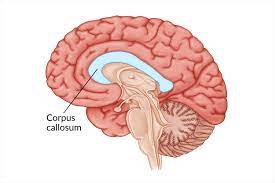
Corpus Callosum
-L: rainbow shape, like a bridge from back and front of brain
-F: bundle of neurons (axons) connecting the two cerebral hemispheres for communication
Limbic system
a system of brain structures and neural networks involved in processing emotion and long term memory
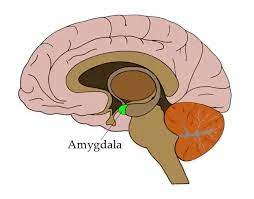
Amygdala
processes emotion especially fear and aggression
triggers flight or fight in response to danger
helps read other people’s emotions
helps store memories from emotional situations
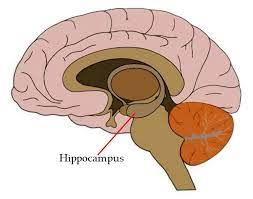
Hippocampus
stores information into long-term memory
stores spatial memory (navigation + location of objects)
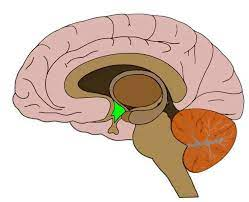
Hypothalamus
regulates autonomic nervous system
monitors + regulates body temp, hunger, thirst, and sexual responses
hormones alert hypothalamus of bodily states
directs other glands to release hormones in response
Lateral Hypothalamus
regulates feelings of hunger
-damage can cause you to never feel hungry
Ventromedial hypothalamus
regulates feelings of satiety (fulness)
-damage can cause you to never feel full
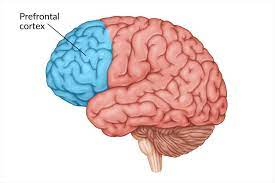
prefrontal cortex
judgement
planning
reasoning
problem solving
involved in personality
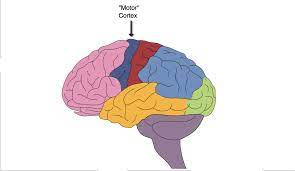
Motor cortex
L: in the rear of the frontal lobes
F: Controls voluntary movement
areas with more precise movement occupy more cortical space
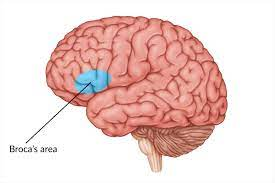
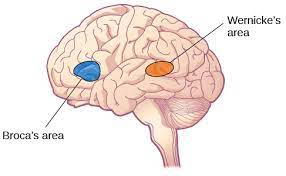
Broca’s area
-L: in the left frontal lobe next to motor cortex
-F: speech production
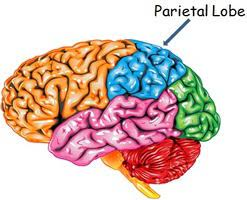
Parietal lobes
processes somatosensory input (touch, pressure, temp, and pain)
helps with spatial orientation (where you are and how you’re positioned)
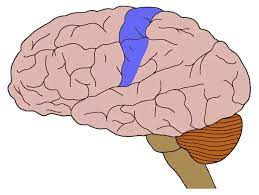
Somatosensory cortex
L: behind motor cortex
F: processes body movement and sensations
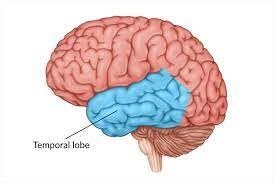
Temporal lobe
-L: behind ears
-F: involved in hearing, language processing, and storage of long-term memory
connects to the limbic system
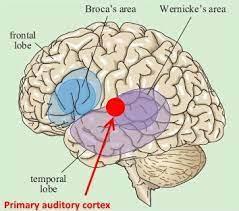
Primary Auditory Cortex
-L: in the frontal lobe
-F: main site of auditory perception and processing
Wernicke’s area
-L: in temporal lobe
-F: involved in comprehension of written and spoken language
Right Fusiform gyrus
-L: temporal lobe
-F: allows us to recognize human faces
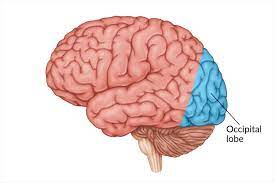
Occipital lobe
-L: back of brain
-F: processes visual info from eyes
norepinephrine
-Type: excitatory
-Function: helps control alertness and arousal, fight or flight
-Surplus: anxiety
-Deficit: depression
dopamine
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
-Surplus: schizophrenia
-Deficit: parkinson’s disease
endorphins
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: influences perceptions of pain and pleasure
-Surplus: artificial highs and inadequate responses to pain
-Deficit: depression, potential involvement in addiction
acetylcholine
-Type: Excitatory
-F: activates skeletal muscles and carries our voluntary movements
involved in memory formation and learning.
-deficit: lead to alzheimer’s disease or paralysis- limited mobility
-surplus- violent muscle spasms and contractions
serotonin
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: regulates mood, sleep, digestion
-Surplus: seizures and hallucination
-deficit: depression, mood disorders
Glutamate
-Type: excitatory
-Function: main excitatory neurotransmitter and involved in memory
-Surplus: overstimulate the brain, migraines, or seizures
-Deficit: none
GABA
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: major inhibitory neurotransmitter, regulates sleep-wake cycle
-surplus: sleep and eating disorder
-Deficit: seizures, tremors, insomnia, and huntington’s disease