Endocrine + Reproductive System Overview for TEAS
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Purpose/function of endocrine system
The endocrine system uses hormones (chemical messengers) that travel through the bloodstream to regulate long-term processes such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, stress response, and homeostasis.
Difference between nervous and endocrine systems
Nervous:
Electrical + neurotransmitters
Fast speed
Short duration
Reflexes are an example
Endocrine:
Includes hormones in blood
Slower speed
More long-lasting
Growth and metabolism are examples
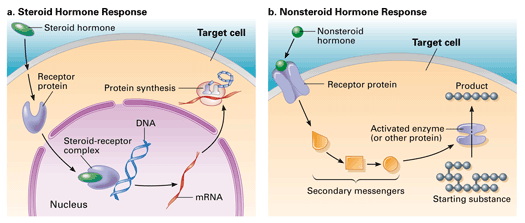
Name the three classifications of hormones, including their chemical structure, solubility, and some examples of each
Steroid hormones:
are derived from cholesterol (four carbon ring structure)
are lipid-soluble and can pass through cell membranes, and
includes cortisol, aldosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
Nonsteroid/peptide hormones:
are composed of amino acid linked together,
are water-soluble and can bind to cell surface receptors, but cannot pass through the lipid bilayer of membranes, and
includes insulin, glucagon, ADH, FSH, and LH
Amine hormones:
derived from a single amino acid
can be water-soluble or lipid-soluble
includes epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and melatonin
What are the functions and receptor locations of the three classifications of hormones?
Think about how they relate to each other.
Steroid hormones:
intracellular receptor (inside cell; in cytoplasm or nucleus)
directly influence gene expression and protein synthesis
long-lasting
Non-steroid hormones:
bind to receptors on the cell surface (extracellular receptors)
they activate second messenger systems inside the cell; leading to a cascade of cellular responses
basically, act through second messengers
fast
Amine hormones:
Receptors in membrane or inside cell (can act as water-soluble or lipid-soluble hormones)
HYPOTHALAMUS main endocrine function
to control pituitary and link the nervous + endocrine systems
What four releasing hormones from the hypothalamus are sent to the anterior pituitary for stimulation of its own hormone release?
TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) → stimulates release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone) → stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) → stimulates follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
PRH (prolactin-releasing hormone) → stimulates prolactin
What inhibiting hormones are released from the hypothalamus?
Somatostatin → inhibits GH (growth hormone)
Dopamine “happy hormone” → inhibits prolactin
The posterior pituitary stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus, what are those hormones?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone), a vasopressin that regulates water balance, kidney function, and BP.
Water reabsorption in kidney; low urine output
Raises BP by constricting blood vessels
Oxytocin, or the “love hormone”, functions in childbirth (uterine contractions), milk ejection, and emotional bonding.
The anterior pituitary gland, or the “master gland”, makes its own hormones.
Name the (6) hormones, its target organ, and main function.
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), which targets the thyroid and increases T3/T4 release
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), which targets the adrenal cortex to increase cortisol
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), which targets the gonads for egg maturation and sperm production
LH (luteinizing hormone), which targets the gonads to trigger ovulation, estrogen/progesterone, and testosterone
GH (growth hormone or somatotropin), targets the liver, bone and muscle, for growth and increase metabolism (increase blood glucose)
Prolactin, which targets the mammary glands for milk production
The thyroid gland contains follicle cells and parafollicular (C) cells. Each secretes and functions differently.
Name these secretions and functions.
Follicle cells → T3 (triiodothyronine) & T4 (thyroxine)
increases metabolism
increases heart rate
increases body temperature
Required for growth and development
Requires iodine
Parafollicular cells (C cells) → Calcitonin
lowers blood calcium
inhibits osteoclasts
increases calcium deposition in bone
Parathyroid glands contain a certain type of cell.
Name this cell, its secretions, and its function.
Chief cells → PTH (parathyroid hormone)
(functions opposite of calcitonin)
raises blood calcium
stimulates osteoclasts
increases calcium reabsorption in kidneys
activates Vitamin D to increase calcium absorption in intestines
The adrenal cortex is composed of three layers, each producing different hormones, and functioning differently.
Name these layers, hormones, and functions.
GFR = salt, sugar, sex!
Zona Glomerulosa → produces aldosterone (mineralocorticoid)
Increases sodium reabsorption
Increases water
Increaes BP
Zona Fasciculata → produces cortisol (glucocorticoid)
Stress hormone
Increases glucose
Anti-inflammatory
Zona Reticularis → produces androgens
Puberty hair and sex drive
The adrenal gland also has the adrenal medulla, which contains a specific cell that releases two hormones.
Name the cell, the hormones, and its function.
Chromaffin cells → Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
fight-or-flight
increase heart rate
increase BP
increase glucose
dilates bronchi
The pancreas has clusters of endocrine cells called Islets of Langerhans, which produces hormones.
Name these cells and their hormone secretions, along with their function.
Alpha cells → produces glucagon to raise blood glucose and breakdown glycogen
Beta cells → produces insulin to lower glucose and promote storage
Delta cells → produces somatostatin to inhibit insulin and glucagon
PP cells → pancreatic polypeptide to regulate pancreas secretion
Insulin and Glucagon are associated with “fasting” and “fed” states.
Which of the following correctly states this relation?
A. Insulin = fed stage; Glucagon = fasting state
B. Glucagon = fed state; Insulin = fasting state
A. Insulin = fed state, glucagon = fasting state.
Name the hormone production and function of the Pineal gland.
Pineal gland produces melatonin
regulates circadian rhythm
released in darkness
There are male and female gonads, each produces and secretes hormones for their respective function.
Name the male and female gonads, the hormones, and functions.
Ovaries in females
Estrogen → female characteristics; endometrial growth
Progesterone → maintains uterine lining/prepares uterus for pregnancy
Inhibin → inhibits FSH
Testes in males
Testosterone → produced by Leydig cells or Interstitial cells; male traits, sperm production
Inhibin → produced by Sertoli cells or Sustentacular cells; inhibits FSH
What does the Thymus produce and what is its function?
The thymus produces thymosin to promote T cell maturation. The thymus is most active in childhood.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback loops?
Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes, which moves the system away from its equilibrium state.
Negative feedback loops work to stabilize a system by counteracting changes and bringing it back to its equilibrium. Negative feedback loops effectively maintain homeostasis.
What is the most common example of a positive feedback loop? List the steps.
Childbirth!
1) The baby’s head pushes against the cervix and creates pressure
2) Oxytocin releases from the pituitary gland
3) Oxytocin triggers stronger uterine contractions
4) Increased pressure of the cervix = INCREASED release of oxytocin
5) Upon birth, the positive feedback loop stops since the stretching of the cervix stops. No more oxytocin and cycle is completed.
Complete this summarized table of hormones.
Hormone | Source | Target | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
ADH | |||
Oxytocin | |||
TSH | |||
ACTH | |||
GH | |||
Calcitonin | |||
PTH | |||
Aldosterone | |||
Cortisol | |||
Epinephrine | |||
Insulin | |||
Glucagon | |||
Estrogen | |||
Progesterone | |||
Testosterone |
Hormone | Source | Target | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
ADH | Posterior pituitary | Kidneys | Water retention |
Oxytocin | Posterior pituitary | Uterus, breasts | Contractions, milk ejection |
TSH | Anterior pituitary | Thyroid | T3/T4 release |
ACTH | Anterior pituitary | Adrenal cortex | Cortisol release |
GH | Anterior pituitary | Bones/muscles | Growth |
Calcitonin | Thyroid C cells | Bone | Lower Ca²⁺ |
PTH | Parathyroid | Bone/kidney | Raise Ca²⁺ |
Aldosterone | Adrenal cortex | Kidneys | Na⁺ retention |
Cortisol | Adrenal cortex | Liver/muscle | Raise glucose |
Epinephrine | Adrenal medulla | Multiple organs | Fight-or-flight |
Insulin | Pancreas beta | Body cells | Lower glucose |
Glucagon | Pancreas alpha | Liver | Raise glucose |
Estrogen | Ovary | Body tissues | Female traits |
Progesterone | Ovary | Uterus | Maintains lining |
Testosterone | Testes | Body tissues | Male trait |
Which hormone lowers blood calcium?
Calcitonin
Which cell produces insulin?
Beta cells
Which hormone is released during dehydration?
ADH
Which gland produces cortisol?
Adrenal cortex
What type of hormone acts on DNA in the nucleus?
Steroid hormones
What gland shrinks after puberty?
Thymus
What does PTH do?
Raises blood calcium
List the types of ovarian follicles in the phases of the ovarian cycle in order.
Follicular Phase
1) Primordial Follicle
Most basic stage
Primary oocyte (stuck in prophase l of meiosis) surrounded by a layer of squamous follicle cells
2) Primary Follicle
Follicle cells become cuboidal granulosa cells
Zona pellucida forms around oocyte
Thecal cells develop
3) Secondary Follicle
Granulosa cells multiply
Antrum starts forming (small cavities filled with follicular fluid)
4) Vesicular (tertiary) Follicle
Primary oocyte finishes meiosis l and becomes secondary oocyte
Large antrum filled with follicular fluid
Ovulation Phase
5) Ruptured Follicle
secondary oocyte is released from the vesicular follicle into fallopian tube
Triggered by LH surge
Oocyte begins meiosis ll, but stops in Metaphase ll until fertilization
Luteal Phase
6) Corpus Luteum
The remnant of the ruptured follicle
Mainly secretes progesterone to support pregnancy; also, estrogen + inhibin
7) Corpus Albicans
The remnant of the corpus luteum after it stops ceases hormone production
Forms when there is no pregnancy; a decline in progesterone indicates menstruation
List and describe the three endometrial changes in the uterine cycle.
The uterine cycle changes the endometrium to prepare for pregnancy.
1) Menstrual Cycle (day 1-5)
Triggered by LOW progesterone and estrogen
Stratum functionalis layer of endometrium is shed → menstruation
2) Proliferative Phase (days 6-14)
Triggered by rising estrogen
Endometrium rebuilds
Endometrial glands form
3) Secretory Phase (days 15-28)
Triggered by progesterone from corpus luteum
Spiral arteries convert stratum functionalis to secretory mucosa + endometrial glands secrete uterine milk
Fill in this summary table of the Ovarian vs Uterine Cycles
System | Phase | Dominant Hormone | Major Event |
|---|---|---|---|
Ovarian | |||
Uterine | |||
System | Phase | Dominant Hormone | Major Event |
|---|---|---|---|
Ovarian | Follicular | FSH → Estrogen | Follicle maturation |
Ovulation | LH surge | Oocyte released | |
Luteal | Progesterone | Corpus luteum active | |
Uterine | Menstrual | Low hormones | Endometrial shedding |
Proliferative | Estrogen | Endometrium rebuilds | |
Secretory | Progesterone | Endometrium ready for implantation |
Function of the ovaries
produce oocytes and estrogen, progesterone, and inhibin
Function of the uterine (Fallopian) tube and structures included
moves oocytes or fertilized ovum toward uterus
site of fertilization and early stages of development
Structures:
fimbriae (finger-like)
infundibulum
ampulla
isthmus
Function of the uterus and its layers
protects and sustains conceptus during pregnancy
cyclic shedding results in menstrual flow
Layers:
Perimetrium → outer
Myometrium → smooth muscle
Endometrium → inner lining
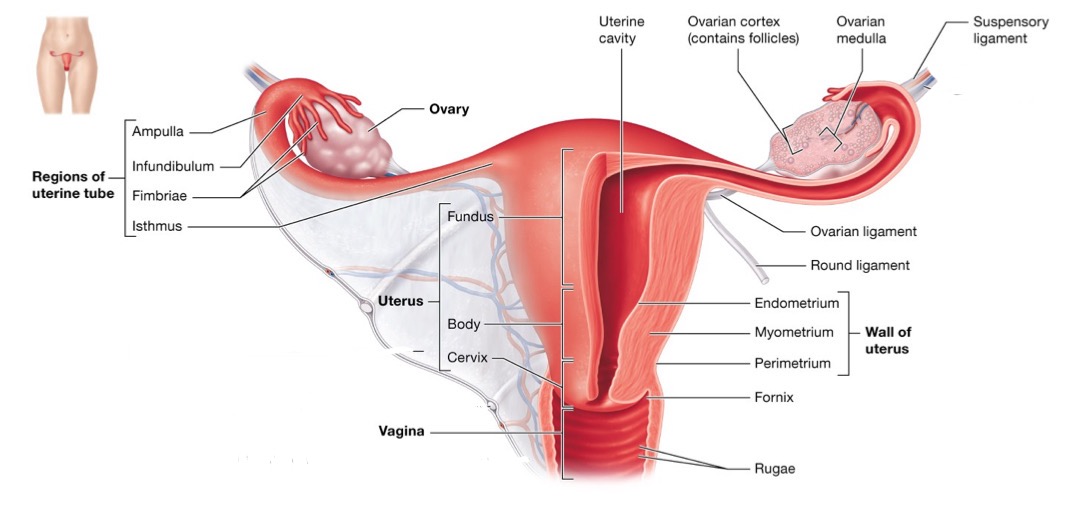
Function of the greater vestibular gland of a female
secretes mucus, which helps lubricate the opening of the vagina
Function of the testis
produces sperm cells as well as testosterone and inhibin
Function of the epididymis
promotes sperm cell maturation
stores sperm until ejaculation
moves sperm to ductus deferens
Function of the ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, and urethra in males
Ductus Deferens
stores sperm
moves sperm to ejaculatory duct
site of vasectomy
Ejaculatory Duct
transports sperm from ductus deferens into urethra
Urethra
transports semen out of penis
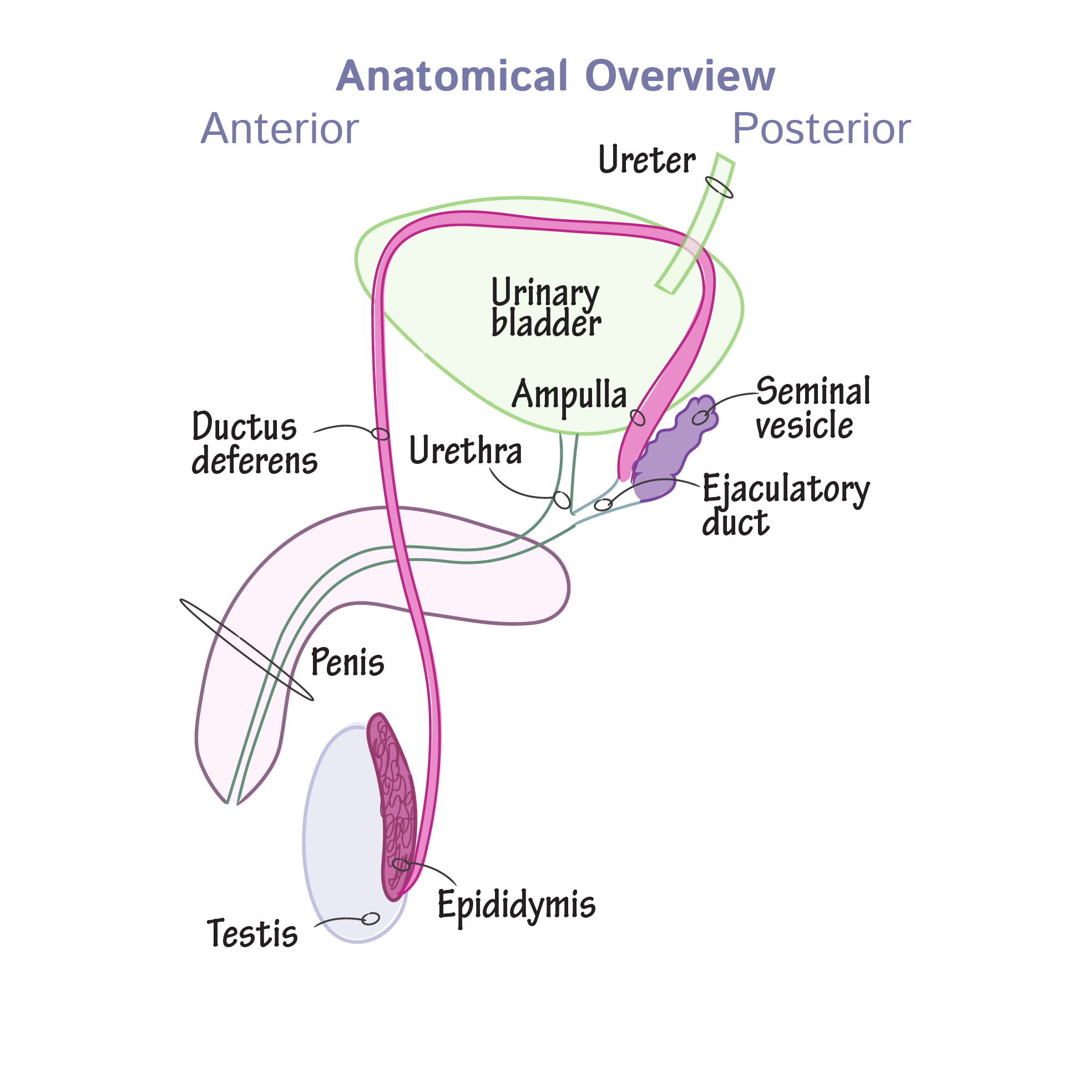
There are 3 accessory glands of the male reproductive system, what are they and what are their functions?
Seminal Vesicles
produce 60% semen and secrete:
alkaline fluid (neutralize vaginal acidity) with nutrients (fructose)
prostaglandins for motility
co-agulating enzyme to clot semen in the vagina
Prostate Gland
secretes fluid that supports sperm, helps activate sperm for fertilization
anti-coagulant and antibacterial
Bulbourethral Glands
secretes mucus to lubricate glans penis
neutralize urine acidity in urethra
Function of the scrotum
encloses, protects, and regulates temperature of testes
When cold, the cremator muscle contract to lift the testes closer to the warmth of the body while the detrusor muscle causes tightening and wrinkles.
When hot, the muscles relax to hang lower from the body to reduce surface area for cooling.
What hormone prepares for implantation in females?
progesterone
What hormone triggers the release of gametes in females?
LH (during ovulation)