CT
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Anode
positively charged electrode that attracts electrons; in CT this is where the accelerated electrons from the cathode will strike to produce x-rays; large amounts of heat are generated from this process.
Beam Current
stream of electrons traveling from the cathode to the anode; measure in mA.
Beam Hardening Artifacts
Artifacts such as streaks, blurs and shadows which result from the lower energy photons that are preferentially filtered by the intervening tissues being absorbed more than high energy photons as the beam passes through the patient; effect is dependent on the composition of the tissue and the path of the beam thus these artifacts are commonly observed in larger patients.
Bowtie Filter
Pre-patient filter that reduces the dynamic range of the data acquisition system and improves noise. Reduces x-ray beam intensity, improve homogeneity, reduces skin dose.
Bremsstrahlung
x-ray emitted when a high energy electron is slowed down and/or deflected by a positively charged nucleus; major source of x-rays in CT.
Cathode
negatively charged electrode that acts as a source of electrons; in CT this heated filament boils off electrons and accelerates them towards the anode.
Characteristic X-Ray
Monoenergetic x-rays that are produced by electrons dropping to a lower energy shell in the atom. These x-rays may result from ionization of the atom by a process that removes an inner shell electron such as a photoelectric interaction. High speed electrons from cathode interact with an inner shell electron of tungsten of anode. Inner electron is ejected, outer electron moves in, releasing energy.
Cone Beam
Used in 3rd generation CT machines. Increases the speed of the exam by increasing the area imaged by being able to reach multiple detectors in the fan beam array and multiple rings while constantly moving.
CTDI
Computed tomography dose index. The average dose imparted by a single axial acquisition to a standard 100mm pencil chamber dosimeter inside a PMMA phantom over the width of 14 CT slices.
Dose Length Product (DLP)
Represents the integrated dose in terms of the total scan length. This is an indicator of biologic risk.
Flat Filter
Pre-patient filter that removes low energy x-rays that would otherwise be absorbed by the patient.
Fluence
The total number of photons integrated over time. It is defined by the current and exposure time.
Focal Spot
The area on the anode of an x-ray tube or the target that is struck by electrons and from which the resulting x-rays are emitted.
Geometry
center-to-center spacing of detector elements decreases as the distance from the ring center increases; geometric corrections make the spacing uniform across the field of view.
Helical CT
Continuously rotating x-ray tube and detector.
High Contrast (Spatial) Resolution
The ability of the system to resolve high contrast objects of increasingly smaller size. Can be influenced by pixel size, reconstruction filters, and geometric resolution limits.
Hounsfield Unit
A unit of measured value placed into the pixels of a CT image. The value represents a relative density to water, which has a value of zero on the Hounsfield scale, with densities lower than water having a negative number (air=-1000) and densities higher than water having a positive number (bone 100-3000)
Kernel
The image filter used in the CT reconstruction algorithm to calculate the sharpness of a reconstructed image.
Kilovolt Potential (kVp)
The peak voltage that can be applied between the cathode and anode of an x-ray tube; the potential difference between the cathode and anode.
Low Contrast Resolution
The ability of a system to resolve objects having small difference from background.
Low Dose CT
x-ray beam energy and beam current are set low to minimize radiation exposure to the patient.
Milliampere (mA)
A unit of electric current that describes the flow of charge per second. Used to measure the number of photons generated by the x-ray tube in CT imaging.
Partial Volume Effect
When the size of an object begins to approach the resolution limits of an imaging system, resulting in a voxel containing more than one type of tissue.
Pitch
The ratio of table movement per revolution over the collimated slice thickness of one row of a multi-slice CT detector.
Postpatient Collimator
It removes scattered x-rays that would lead to image degradation.
Prepatient Collimator
It reduces the x-ray flux in the z-direction, and in single slice CT scanners it defines the slice thicknes
Scout Scan
An x-ray examination performed with the CT gantry in a fixed position to generate a planar image. Used to define the body region to be imaged during the CT scan. This is sometimes referred to as a topogram.
Segmentation
replace tissue values in transmission or CT scans with known tissue values in order to reduce noise in the transmission attenuation correction maps
Sinogram
A collection of projections for one slice that are arranged by radial distance and angle.
Slip Ring Technology
Allows for continuous rotation of x-ray tube and eliminates the need for cables
Thermoionic Emission
A boiling off of electrons at the filament"; the process by which charge carriers, such as electrons or ions, move over a surface or some sort of energy barrier by the induction of heat.
Window/Level
represents the central Hounsfield unit of all the numbers within the window width.
Window Width
Range of Hounsfield Units displayed on an image
Explain the process of x-ray production that occurs in the x-ray tube of a CT scanner.
Within the x-ray tube, is the cathode which includes a filament or coil of wire. When a current is applied to the filament, it is heated, electrons are boiled off and are then accelerated toward the anode assembly which includes a tungsten target. The electrons interact with the target and produced via Bremsstrahlung and characteristic x-rays. The x-ray beam then exits the tube from a window. There is a tremendous amount of heat that is produced from this process and only about 1% of the energy applied to the system results in the production of x-rays that exit the tube window. The remaining 99% of the energy creates heat.
Compare the purpose of the filter to that of the pre-patient collimator
The purpose of the filter is to absorb most of the low-energy Bremsstrahlung x-rays that do not contribute to the quality of the image and therefore only increase radiation exposure to the patient. The filter is made of a low atomic material such as aluminum. A bowtie filter may also be used to ensure a more uniform energy distribution and thus improves noise homogeneity. The pre-patient collimator is used to shape the beam and reduce scatter radiation, therefore reducing unnecessary dose to patients as well as improving image contrast resolution.
Pitch increases
noise
Pitch <1
indicates overlap from one rotation to the next
Pitch = 1
table movement per rotation equals the slice width, such that tissues exposed to radiation are contiguous
Pitch >1
gaps are present between rotations; not all tissues are exposed to radiation
kVp and image quality
pertains to the maximum potential energy of the x-rays being emitted during a CT scan; x-ray energy needs to be high enough to pass through the patient and be detected as opposed to being absorbed within the patient; quality of x-rays
mA and image quality
pertains the number of x-rays being emitted during a CT scan; quantity of x-rays
Compare high contrast resolution and low contrast resolution.
High contrast resolution affords the ability to differentiate objects or organs with a significant density difference such as a calcified lesion in the lung.
Low contrast resolution refers to the ability to see small objects with little density differences such as a liver mass.
beam hardening artifact
Lower energy x-rays are more easily and readily absorbed than higher energy x-rays. In a CT scan, this means that the x-ray beam beyond an absorbing material (such as a metal implant) is harder and therefore has different absorption properties than other parts of the x-ray beam not being attenuated in this manner.
CT voxel values are given in terms of
Hounsfield units
CT voxel values are given in terms of Hounsfield Units, which express the attenuation of a given tissue relative to that of
water
F18DG decays by
positron emission
Explain positron emission
proton loses an e- and becomes a neutron and gives off a positron
FDG gamma energy
511 keV
FDG half life
110 mins
Producing FDG
one of the hydroxyl groups in a glucose molecule gets replaced with a fluorine atom through a series of chemical reactions. The resulting FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) molecule is capable of undergoing glycolysis in cells throughout the body, mimicking a glucose molecule.
F18 FDG MOL
passive transport (High to low conc.), facilitated diffusion via GLUT protein glucose transporters
How is FDG trapped in cells
phosphorylates in first step of glycolysis.
What is F18 FDG ideal to image?
cancer/inflammatory cells due to high metabolic rate due to glycolysis.
FDG Indications
Oncology, neurology, infection/inflammation
Oncologic FDG indications
Lymphoma, Breast Cancer, Head and Neck Cancer, Melanoma, Myeloma, Sarcoma, Leukemia
Neurological FDG indications
Alzheimer’s, Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD), Epilepsy
Infection/inflammatory FDG indications
Graft Infection, Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO), Endocarditis, Sarcoidosis
FDG Contraindications
Food in < 4 hours, Physical Exertion within 24 hours (subjective), BGL > 250 mg/dl. For Diabetic patients: Not off rapid-acting insulin for at least 2 hours, or Not off regular-acting insulin for at least 4 hours.
FDG Normal Distribution
Brain, bladder, salivary glands, myocardium, liver, spleen, kidneys, thyroid, muscles, blood vessels, thymus, brown fat.
FDG Body dose
10 mCi
FDG Body dose for Quadra
0.06 mCi/kg, 8 mCi max
FDG Brain dose
5 mCi
FDG Peds dose
0.1 mCi/kg (min of 1 mCi)
FDG uptake
body- 60 mins
brain- 30 mins
FDG Scan Prep
• NPO for 4-6 hours (water is okay)
•Tube Feeding (TPN) off for 6 hours
•Nutritional Supplements (Ensure, Boost) off for 8 hours
• No workout for at least 24 hours
• For Diabetic patients:
• Off insulin for 2-4 hours depending on type taken
Cardiac Sarcoidosis
inflammatory conditioning affecting heart. Formation of granulomas in myocardium
Why does cardiac sarcoid scan prep include keto diet (no carbs high fat/protein)?
• When patients are on a high fat/protein diet, the body relies more on ketone bodies for energy (aka keto diet)
•This include cardiac myocytes
• Thus, we need to have patients follow dietary restrictions of carbohydrates to have the cardiac muscle rely heavily on ketone bodies and not on carbohydrates for energy
• This would limit cardiac muscle uptake, while immune cells’ metabolism remain unaltered and they will still take in FDG
How Can FDG Scan Detect Cardiac Sarcoidosis?
• Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is capable of getting transported into the immune cells because they are actively causing the inflammatory condition, needing energy in the source of FDG.
• However, cardiac myocytes (muscle cells) are also demanding FDG for metabolic processes.
FDG Prep Questions
• Fasting within last 4 hours?
• Diabetic?
•Taking Insulin?
• Vaccines within last 2 months?
• Superficial medical devices on skin?
• GLP-1 Medications?
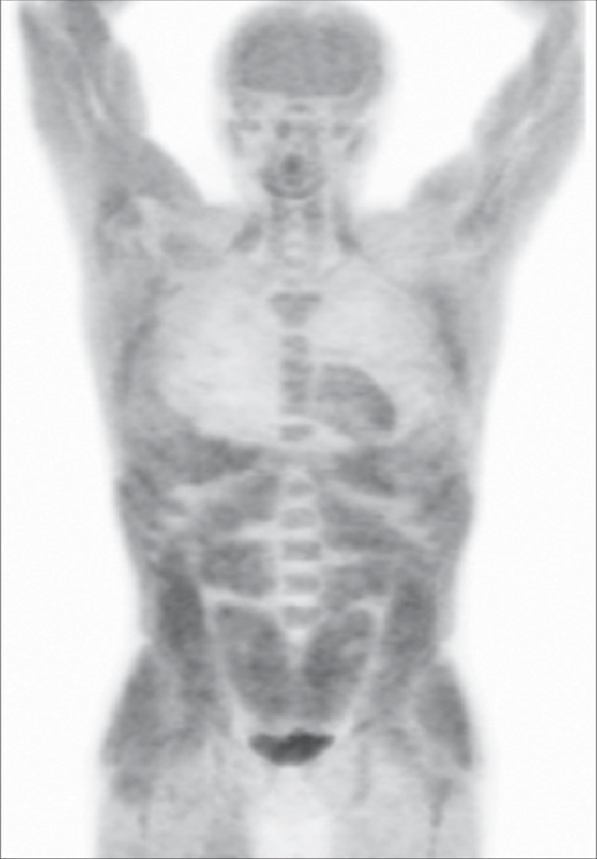
Non-fasting patient
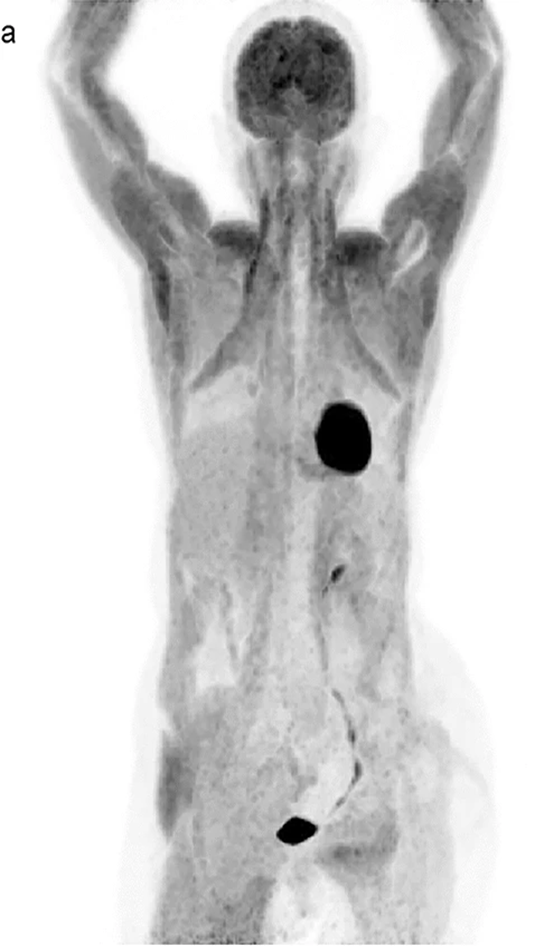
Non-fasting patient
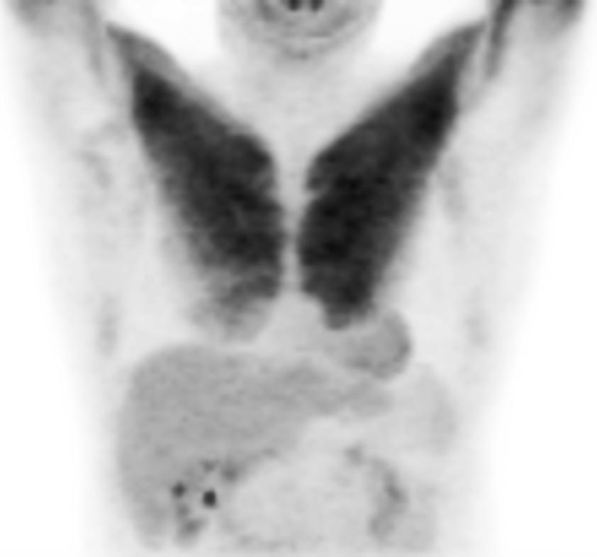
chest workout prior
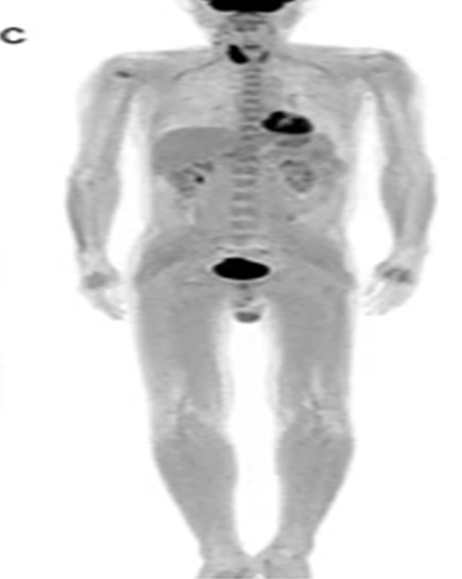
Rapid acting insulin 90min before FDG injection in diabetic patient with fasting bgl over 160 mg/dL
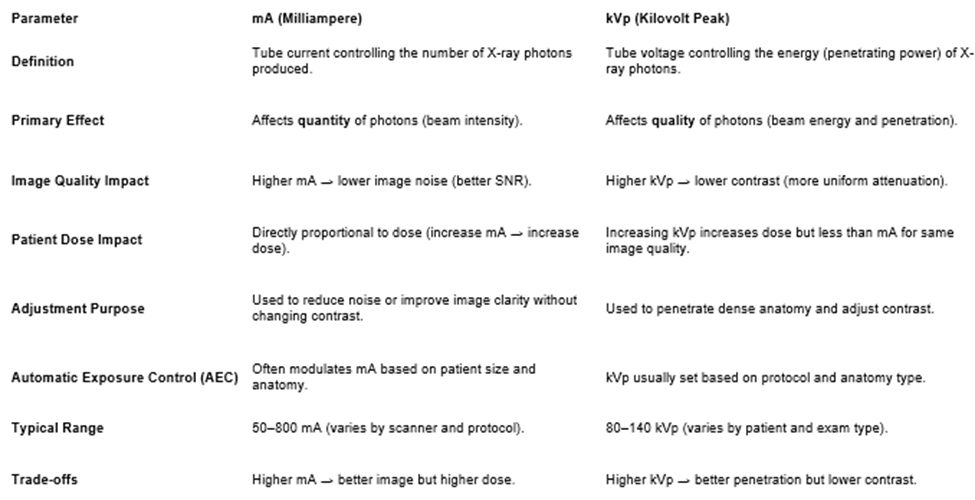
know this
mA effect
quantity of photons (bean intensity)
kVp
kilovolt peak
kVp effect
effects quality of photons (beam energy)
Image quality mA
higher = lower noise
Image quality kVp
higher = lower contrast
mA range
50-800 (CT 10-440)
kVp range
80-140
Computed tomography
combines X-rays images taken from different angles to create cross sectional images. spatial resolution reduced by an order of magnitude over radiography.
3 components of CT
Gantry
Operating Console
Computer and Array Processor
Gantry of CT
frame housing of the x-ray tube, collimators, detectors, DAS, slip rings
Data Acquisition system in gantry
Measures transmitted intensity of radiation beam, turns data into digital signal via analog to digital converter ADC, sends binary data to computer.
Operating console functions:
Select protocol, change image factors, move table, patient info. Post process images.
Computer and Array Processor functions
Image reconstruction system. Receives info from the DAS and creates image.
the opening of the gantry is called
the Aperture
Typical generator power
20-100 kW
total collimation =
beam width
Purpose of CT Filters
remove unnecessary low energy photons, produce uniform distribution.
Inherent + added = total
3 CT scanning methods
CT localizer radiography, axial/conventional, helical/spiral
CT localizer radiography scan
scout, tube stationary and patient moves.
Axial/conventional scan
better special resolution. Bed is stationary, tube rotates. Data can be overlapping, contiguous, or with gaps.
What is a projection
view, set of ray sums at fixed angle
What is a ray and ray sum
ray=one x ray path
Ray sum= line integral, total attenuation along one ray
Helical/spiral scan
Tube and bed in motion. Needs interpolation to reconstruct image.
Effective mA:
mAs per slice, mAs divided by pitch
average photon energy (keV) is
30-40% of applied kilovoltage.
Focal spot size
0.5-1.2 mm