Menstruation: Normal and Amenorrhea
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Menarche
Onset of menstruation
-Median age is 12.4 years old
bleeding, least, low, thins, decreased, prostaglandin, myometrium
Menstrual Cycle: Early Follicular Phase
-Starts with the onset of ___________
-Early follicular phase
Menstruation
Ovarian cycle → ovary is _____ active, hormones are ___
Endometrial cycle → menstruation occurs, endometrium _____
-Degeneration and sloughing of endometrial lining due to ____________ estrogen and progesterone
-Causes release of uterine ________________, which stimulates rhythmic contractions of uterine ______________
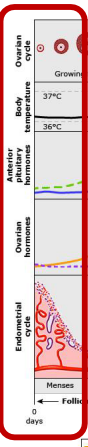
end, FSH, follicles, proliferation, thickens, mucus, lubricates
Mid-Follicular Phase
-___ of menstruation
-___ stimulates folliculogenesis and estradiol production
-Ovarian cycle → several _________ start to develop
-Endometrial cycle → __________ of endometrial glands
Endometrium _________ and regenerates
Endocervical glands produce thin, clear _______
__________ vagina and facilitates sperm transport

dominant, developing, thickens, egg white, mucin, sperm, LH, 36
Late Follicular Phase
-Ovarian cycle → one follicle is selected as the __________ follicle, while the rest of the growing follicles stop ____________ (atresia)
-Endometrial cycle → endometrium ___________ more and the cervical mucus becomes more “stringy” (also known as “____ _______ cervical mucus”)
-_____ protein in this cervical mucus is important for _____ transit to the uterus
-__ surges, also known as the midcycle surge → ovulation occurs ~__ hours later
-Monitoring for a LH surge is often used to help detect ovulation

released, fallopian, uterine, 14
Ovulation
-The oocyte is _________ from the follicle at the surface of the ovary, where it then travels down the ___________ tube to the uterine cavity
-Typically occurs around day __ in the average menstrual cycle
ovulation, not, corpus luteum, progesterone, pregnancy, suppresses, increase, 6
Luteal Phase: Early
-Begins with __________ and ends with new cycle if the oocyte is ___ fertilized
-Usually lasts 14 days
-Ovarian Cycle:
Follicle changes to form ________ ________, which produces large amounts of ___________ to prepare the body for __________
Progesterone _________ growth of new follicles
Causes ________ in basal body temperature
Progesterone _ or more ng/mL confirms ovulation
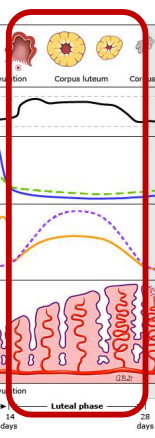
hCG, corpus albicans, fertilized, progesterone
Luteal Phase: Late Luteal Phase & Ovarian Cycle
-If ___ is not produced by an embryo, the corpus luteum declines and becomes the _______ ________ before resolving completely
-If the oocyte becomes __________, the early embryo begins to make hCG, which maintains the corpus luteum and ___________ production
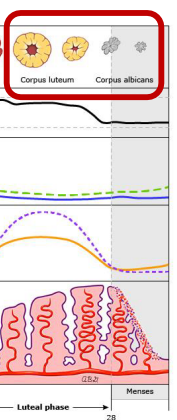
implants, decline, meses, 14
Late Luteal Phase: Endometrial Cycle
-If the oocyte becomes fertilized, it _______ in the endometrium several days after ovulation
-If there is no implantation, the uterus throws a hissy fit
-_______ in estradiol and progesterone results in the loss of endometrial blood supply → endometrial sloughing and onset of ______ approximately __ days after LH surge, therefore restarting the cycle
irregular, 24-38, 2-8, interfere, spotting, between, scheduled, common
Normal Menstrual Cycle in Young Females
-Frequency → during the first 2 years after menarche, cycles may be _________
Normal is every __-__ days (after first 2 years)
-Duration → flow length is approximately _-_ days
-Regularity → cycle variation depends on the age range, however, anything greater than 9 days is considered abnormal
-Volume → subjective, but normal menstrual blood loss should not ______ with a patient’s physical, social, emotional, and/or material quality of life
3-6 pads/tampons per day (on average)
-Intermenstrual bleeding → _______ at the beginning of the cycle is normal, but bleeding _______ regular cycles is not considered normal
-Unscheduled bleeding → should be no bleeding on hormonal contraceptives except for ________ withdrawal bleeding (placebo pills), however, irregular bleeding is a _________ side effect of hormonal contraceptives
38, 8, heavy, irregular, primary, breast
When to Evaluate for a Menstrual Problem?
-Cycles are persistently less than 24 days or greater than __ days
-Flow lasts more than _ days
-Flow is subjectively too _____ or light
-Intermenstrual bleeding
-Cycles are initially regular then become _________
-Evaluate ______ amenorrhea when menses have not started within 3 years of _____ development
Primary
What type of amenorrhea is being described?
-Absence of menarche by age 15 years in the presence of normal growth and secondary sex characteristics
Secondary
What type of amenorrhea is being described?
-Absence of menses for more than 3 months in females who previously had regular menstrual cycles
-Absence of menses for more than 6 months in females who had irregular cycles
Pregnancy
What is the most common cause of amenorrhea?
15, absence, breast, 13, secondary, pain, before
Primary Amenorrhea
-Even though the definition is no menses by age __, there are other scenarios that would merit evaluation:
If no menses have occurred and there is a complete _________ of secondary sex characteristics (such as _____ development) by age __
If secondary sex characteristics have developed and there is cyclic pelvic ____ with amenorrhea, even if _______ age 15
pregnancy, TSH, Turner, ultrasound
Primary Amenorrhea: Evaluation
-History and physical
-Labs → hCG (rule out ________), FSH, LH, ___, prolactin
-Karyotype → ________ Syndrome, FMR I premutation
-Pelvic ________
High
In the evaluation of primary amenorrhea in someone with a uterus present, _____ FSH would lead you to ordering a karyotype to test for Turner Syndrome or other genetic disorders
FSH, 2, outflow, endocrine, MRI
-In the evaluation of primary amenorrhea in someone with a uterus present, a low or normal ___ with breast development more than Tanner stage _ warrants an ultrasound.
If there is a uterine anatomic abnormality identified on US, there is likely an ______ tract disorder like an imperforate hymen
If there is no abnormality detected, the amenorrhea is likely due to underlying __________ disorder like PCOS
-In the evaluation of primary amenorrhea in someone with a uterus present, a low or normal FSH with breast development less than Tanner stage 2 warrants a repeat FSH + LH.
Regardless of the lab values, a pituitary ___ to rule out sellar mass in some patients may be indicated
Karyotype, testosterone
In the evaluation of primary amenorrhea in a patient without a uterus, the next steps should be to order a __________ and serum total __________
3, 6, 9, 35, same
Secondary Amenorrhea
-Many women occasionally miss a single period. Further evaluation is indicated when:
_ months of secondary amenorrhea
_ months in women with previously irregular cycles
-Oligomenorrhea
<_ menstrual cycles per year or cycle length greater than __ days
The etiologic and diagnostic considerations for oligomenorrhea are the ____ as for secondary amenorrhea
negative, TSH, MRI, testosterone
Secondary Amenorrhea: Evaluation
-History and physical
-Labs (after checking that hCG is _________) → FSH, prolactin, ___, estradiol
-Pituitary ___ and serum total ____________ may be indicated
fertility, osteoporosis
Secondary Amenorrhea: Management
-Goals of management are:
Correct underlying pathology if present
Help the woman achieve ______ if desired
Prevent complications like ____________
40, estrogen, high, idiopathic, surgery, menopause, 25, low, HRT, donor
Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
-Loss of ovarian function before __ years old, infertility, low ________, ____ FSH and LH
-Causes:
_________ is MC
Genetic = Turner Syndrome, FMRI premutation
Autoimmune = thyroid disease, Addison’s Disease
Iatrogenic = _______ related
-Patients have __________ symptoms
-Labs:
FSH > __ on 2 occasions, > 4 weeks apart
___ estradiol
-Management:
___ until natural menopause age and _____ oocyte if desires pregnancy