Totonchy Study Guide - work in progress
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What does the suffix "-ximab" indicate about a monoclonal antibody?
It is chimeric
What does the suffix "-zumab" indicate about a monoclonal antibody?
It is humanized
What does the suffix "-omab" indicate about a monoclonal antibody?
It is mouse-derived
What does the suffix "-umab" indicate about a monoclonal antibody?
It is fully human
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Chimeric
Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Humanized
Muromonab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Mouse-derived
Adalimumab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Fully human
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Humanized
Cetuximab is a monoclonal antibody. What type is it based on its name?
Chimeric
Which applications of mAb therapeutics require the Fc region?
TNF alpha therapeutics
Infliximab
Adalimumab
Etanercept
What is one stability advantage of nanobodies compared to mammalian immunoglobulins?
Nanobodies are more resistant to pH changes and denaturation
Nanobodies are easier to manufacture because they are composed of only ______
one protein
True or False: Nanobodies have a longer half-life than mammalian immunoglobulins
False. Nanobodies have a shorter half-life compared to mammalian immunoglobulins
What is one drawback of the small size of nanobodies as therapeutics?
Reduced bioavailability
True or False: Nanobodies do not require an identified target for their use.
False. Nanobodies require an identified target for therapeutic applications
The Fc region of a monoclonal antibody is required for applications such as ______ therapeutics
TNF alpha
What does an antibody with an Fc region look like?
See image
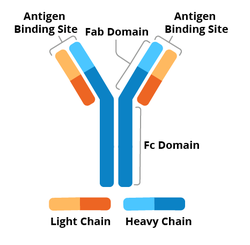
Name three monoclonal antibodies used as TNF alpha therapeutics.
Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Etanercept
Which applications require two antigen binding sites and what are these antibodies
called?
Cross linking
Emicizumab
Bispecific antibody
Which applications require a small structure like a fragment?
Single Chain mAb application
Nanobody
What terms are used for therapeutics that use the patient’s own cells?
Autogenic/autologous
What terms are used for therapeutics that use other people’s cells?
Allogenic/heterologous
What is a major limiting factor for the development of CAR T cell therapeutics?
The need for a defined protein target
Why must CAR T cell targets be highly specific?
To avoid off-target toxicities
True or False: CAR T cell therapy can target any protein regardless of its specificity
False. CAR T cell therapy requires a specific target to minimize off-target toxicities
What is an example of "on-target but off-tumor" toxicity in CAR T cell therapy?
Targeting CD19 in tumor cells but also destroying normal B cells that express CD19, leading to immunosuppression
What systemic toxicity is commonly associated with CAR T cell therapy?
Cytokine storm caused by the activation and proliferation of CAR T cells
The systemic cytokine toxicities in CAR T cell therapy result from the activation of the ______
immune system
What is the goal of gene silencing in gene therapy?
To reduce or prevent the expression of a protein from a mutated gene
True or False: Gene silencing is a permanent solution to fix defective genes
False. Gene silencing is temporary and requires continuous therapy
What is the advantage of gene silencing in gene therapy?
It eliminates overactive defective genes without causing permanent alterations
What is the purpose of genome editing in gene therapy?
To fix the mutated gene directly
True or False: Genome editing in gene therapy has no risks of unintended effects.
False. Genome editing can cause off-target mutations
What is ectopic expression in gene therapy?
Adding a good copy of the mutated gene to restore function
Ectopic expression often uses ______, which can be dangerous
viral vectors
What is a disadvantage of ectopic expression in gene therapy?
It may not result in long-term effects for all applications
What are the three approaches for gene therapy?
Gene silencing
Genome editing
Ectopic expression
Which type of virus used in gene therapy is mostly episomal but can also integrate?
Adeno-associated virus (AAV)
True or False: Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is always an integrating vector.
False. AAV is mostly episomal but can sometimes integrate
What type of vector is lentivirus in gene therapy?
Integrating vector
The ______ platform is an episomal vector used in gene therapy
HSV1 STAR-D
True or False: Lentivirus is an episomal vector.
False. Lentivirus is an integrating vector
What is the only FDA approved oncolytic therapeutic (only specific therapeutic
mentioned on the exam)
Imlygic
What are the ethical and practical reasons behind placebo choice for vaccine clinical trials.
Should mimic the same side effects but still not put the patient at risk. Patients
should still have equal protection from the disease.
Which vaccine types require specific target antigens to be selected during development?
Subunit
Recombinant
mRNA
Viral vector
Conjugate