Unit 2 Chemistry Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Last updated 5:07 PM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
alkali metals
1st group
1+ charge
1+ charge
2
New cards
alkaline earth metals
2nd group
2+ charge
2+ charge
3
New cards
transition metals
3rd -12th group
varying charges, including Sn and Pb, excluding Ag and Cd and Zn
varying charges, including Sn and Pb, excluding Ag and Cd and Zn
4
New cards
Ag charge
1+
5
New cards
Cd and Zn charge
2+
6
New cards
halogens
17th group
1- charge
1- charge
7
New cards
noble gases
18th group
no/neutral charge
no/neutral charge
8
New cards
metalloids
along the staircase, excluding Al
some of the characteristics of metals
some of the characteristics of metals
9
New cards
metals
left to the staircase
generally solid, shiny, lustrous, ductility, malleable, conductive
generally solid, shiny, lustrous, ductility, malleable, conductive
10
New cards
nonmetals
right to the staircase
opposite/no characteristics of metals
opposite/no characteristics of metals
11
New cards
wavelength
distance between 2 identical points on consecutive waves
λ
λ
12
New cards
frequency
the number of waves that pass a fixed point in unit time
ν
ν
13
New cards
energy
energy of a specific quantum of energy
E=hν
frequency times planck's constant
E=hν
frequency times planck's constant
14
New cards
energy and frequency relationship
directly related
15
New cards
energy and wavelength relationship
inversely related
16
New cards
wavelength and frequency relationship
inversely related
17
New cards
speed of light equation
c=λν
18
New cards
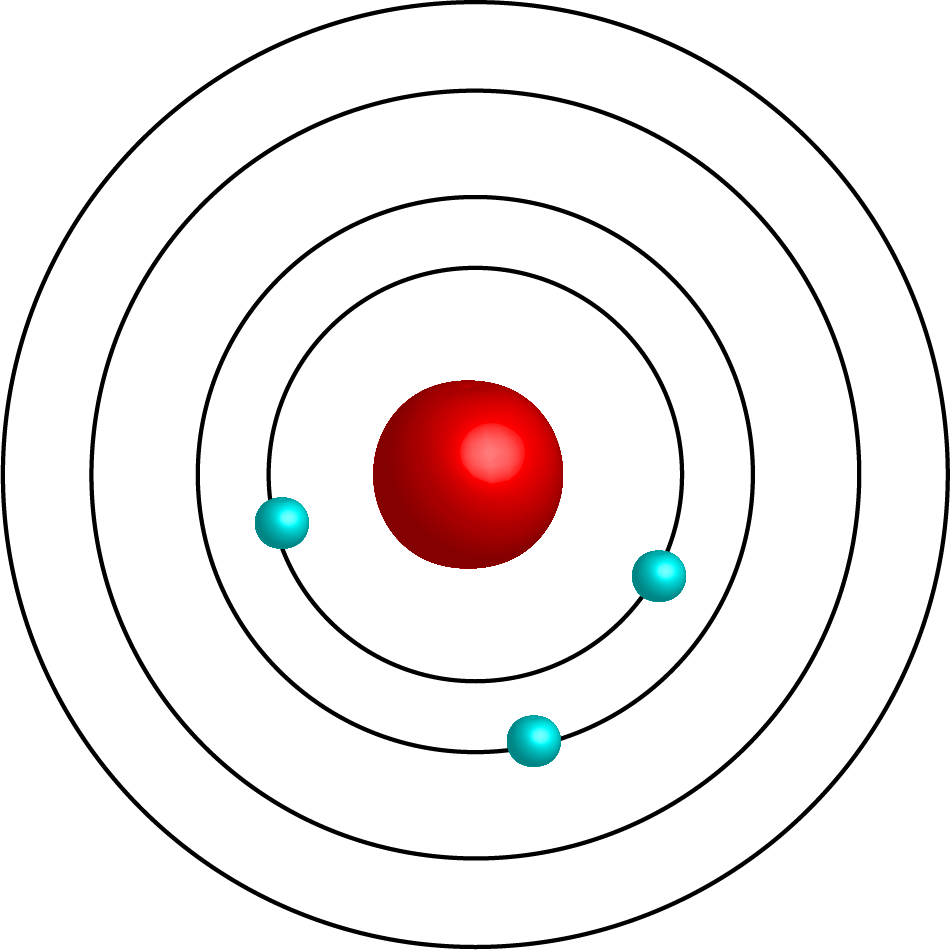
Bohr's Model
circular rings
electrons follow a fixed path
energy levels n=1 to n=7
electrons follow a fixed path
energy levels n=1 to n=7
19
New cards
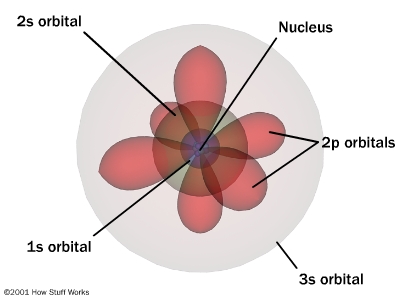
Quantum Mechanical Model (QMM)
different shaped areas with a 90% chance of finding an electron
electrons do not follow fixed path
energy levels n=1 to n=7
electrons do not follow fixed path
energy levels n=1 to n=7
20
New cards
Orbit
21
New cards
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
we cannot know both the position and speed of a particle with perfect accuracy, the more we know about the position the less we know about the momentum and vise versa
22
New cards
Orbital
an area where there is a 90% chance of finding a given electron
different shapes = s, p, d, f
energy levels n=1 to n=7
different shapes = s, p, d, f
energy levels n=1 to n=7
23
New cards
S Orbital
spherical
starts at 1st energy level (n=1)
starts at 1st energy level (n=1)
24
New cards
node
an area with no electrons/low probability of electrons being found
25
New cards
P Orbital
dumbbell/lobe
starts at 2nd energy level (n=2)
each level contains 3 degenerate orbitals
starts at 2nd energy level (n=2)
each level contains 3 degenerate orbitals
26
New cards
degenerate orbitals
orbitals having the same energy levels but they are positioned differently
27
New cards
D Orbital
clover leaf
starts at 3rd energy level (n=3)
each level contains 5 degenerate orbitals
starts at 3rd energy level (n=3)
each level contains 5 degenerate orbitals
28
New cards
F Orbital
starbursts
starts at 4th energy level (n=4)
each level contains 7 degenerate orbitals
starts at 4th energy level (n=4)
each level contains 7 degenerate orbitals
29
New cards
energy levels
the fixed amount of energy that a system described by quantum mechanics
30
New cards
valence electrons
outer electrons in an atom
31
New cards
core electrons
inner electrons in an atom
32
New cards
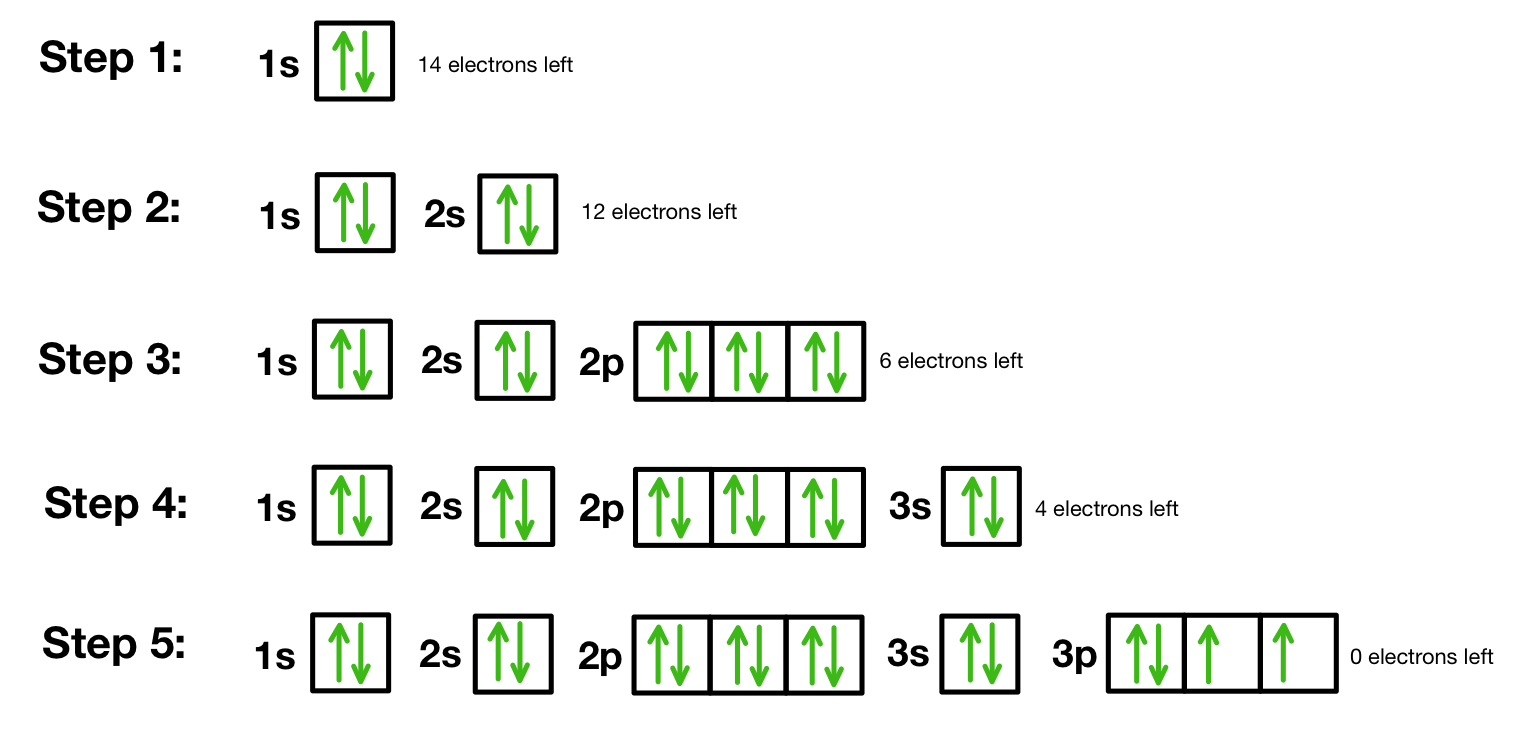
orbital diagram
a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals.
33
New cards
Hund's rule
electrons must be unpaired before they are paired in a sublevel
34
New cards
Pauli Exclusion
no more than two electrons can occupy the same orbital and two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
35
New cards
Aufba Principle
electrons fill from lowest to highest energy
36
New cards
period similarities
same number of core electrons
37
New cards
group similarities
same number of valence electrons
38
New cards
Trends with atomic radius
decreases as you go the the left and increases as you go down
39
New cards
Trends with ionization energy
increases as you go the the left and decreases as you go down
40
New cards
atomic radius and IE relationship
inversely related
41
New cards
atomic radius and reactivity relationship
directly related
42
New cards
reactivity and IE relationship
inversely related