AP Calculus AB Midterm Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
General Power Rule
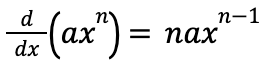
d/dx (sin x)
cos x
d/dx (cos x)
-sin x
d/dx (tan x)
sec2x
d/dx (cot x)
-csc2x
d/dx (sec x)
secxtanx
d/dx (csc x)
-cscxcotx
d/dx (arcsinx)

d/dx (arccosx)
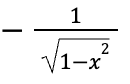
d/dx (arctanx)

d/dx (arccotx)
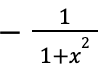
d/dx (arcsecx)

d/dx (arccscx)

d/dx (af(x))
(af(x))(f’(x))(ln a)
d/dx (ex)
ex
d/dx (loga f(x))
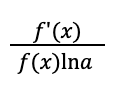
d/dx (ln x)
1/x
Product Rule
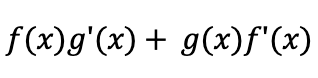
Quotient Rule
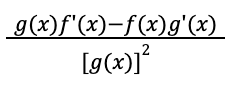
Chain Rule
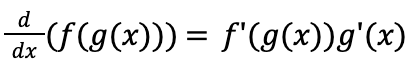
Squeeze Theorem
If g(x)≤f(x)≤h(x) and if g(x) = L and h(x) = L then f(x) = L
Intermediate Value Theorem
If a function f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b], then f takes on every value between f(a) and f(b) on the interval [a,b].
Extreme Value Theorem
If a function is continuous on [a,b], then there is an absolute max and an absolute min on [a,b].
Mean Value Theorem
If a function is continuous and differentiable on [a,b], there is a point c in between a and b such that
![<p>If a function is continuous and differentiable on [a,b], there is a point c in between a and b such that</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2928cf28-d0ea-4d7d-9395-9045b9f4fb9b.png)
Continuity
lim f(x)x→a exists
f(a) exists
lim f(x)x→a = f(a)
Average Rate of Change (AROC)
The average range at which a quantity changes over a given interval
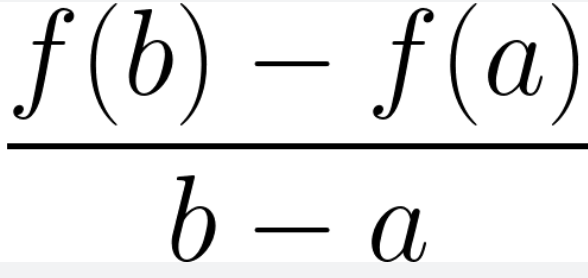
Instantaneous Rate of Change
The exact or precise rate at which a quantity is changing at an instant or specific point
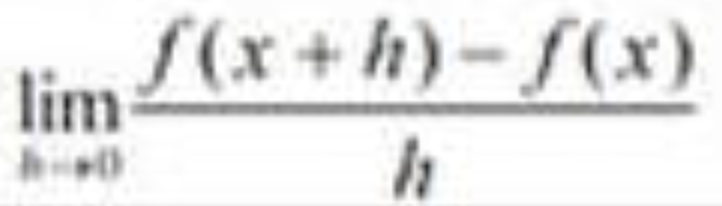
Limit of a Forward Difference Quotient
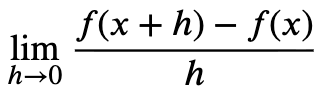
Limit of a Backwards Difference Quotient

Limit of a Symmetric Difference Quotient
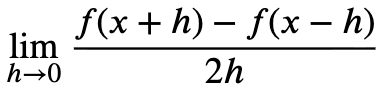
Limit at a Specific Point
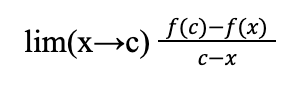
Point-Slope Form
y-y1 = m(x-x1)
Normal Slope
Negative reciprocal of the tangent slope
Implicit Differentiation
Write dy/dx next to every y-variable & solve for dy/dx
Position
Original/Given Function
Velocity
f’(x) = rate of change of position (average velocity uses position)
Acceleration
f’’(x) = rate of change of velocity (average acceleration uses velocity)
Average Velocity
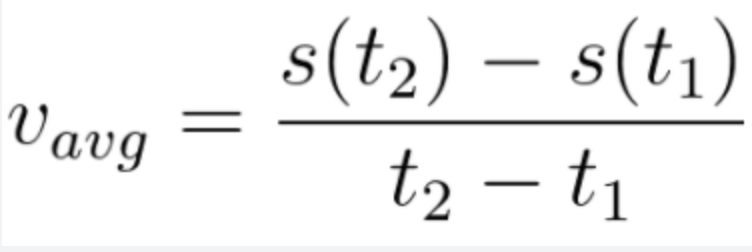
L’Hôpital’s Rule
If limx→a f(x)/g(x) yields either of the indeterminate forms 0/0 or ± ∞/∞, then limx→a f(x)/g(x) = limx→a f’(x)/g’(x)
1/∞
0
e0
1
Critical Points
When f’(x) = 0 or f’(x) = DNE
Absolute Maximum
Highest y-value that occurs on a closed function
Absolute Minimum
Lowest y-value that occurs on a closed function
Rolle’s Theorem
If a function is continuous and differentiable on [a,b] and f(a) = f(b) then there exists at least one value, c, in (a,b) such that f’(c) = 0 (AROC = IROC)
Local Minimum
Where f’(x) changes from negative to positive
Local Maximum
Where f’(x) changes from positive to negative
Related Rates
Multiple variables changing at one time and they are related to each other. Always taken in terms of time (dx/dt)
First Derivative Test
Take f’(x) and set equal to zero and DNE values to find x-values of critical points
Put critical point x-values on a sign chart to find where the slope of f(x) is increasing/decreasing and where the local max/local min are
Second Derivative Test
Take f’’(x) and set equal to zero and DNE values
Put x-values of f’’(x) on sign chart to find concavity and points of inflection
Point of Inflection
A point where f’’(x) changes sign & halfway between local min and local max
When f’(x) is positive, then f(x) is
Increasing
When f’(x) is negative, then f(x) is
Decreasing
When f’’(x) is positive, then f(x) is
Concave up
When f’’(x) is negative, then f(x) is
Concave down
When f’’(x) is positive, then f’(x) is
Increasing
When f’’(x) is negative, then f’(x) is
Decreasing
When f’(x) is increasing, then f(x) is
Concave Up
When f’(x) is decreasing, then f(x) is
Concave down