Amides Slides
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Orgo 2 3rd Partial
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Characteristics of Amides
They are very abundant organic compounds in Nature
that have the formula as a functional group
R – CO – NH2, are considered derivatives of the acids
carboxylic acids because the –OH has been replaced by a
amino group (NH2).
Boiling points (lowest → highest)
Alkanes < Alkenes < Esters < Amines < Alcohols < Carboxylic acids < Amides
Amides have the strongest hydrogen bonding (N–H and C=O) and extensive resonance stabilization of the carbonyl makes them cluster strongly.
Melting points (lowest → highest)
Alkanes < Alkenes < Esters < Amines < Alcohols < Carboxylic acids < Amides
Amides commonly have strong intermolecular H-bonding networks in the solid state → very high melting points.
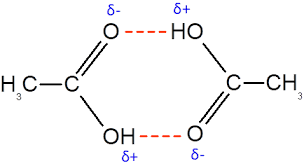
Dimers
A dimer is usually not a new chemical compound, just a pair held together by intermolecular forces (often hydrogen bonds): Ex:
Two acids hydrogen-bond to each other:
the carbonyl oxygen of one bonds to the OH of the other
and vice versa
This “pairing” greatly increases boiling point.
properties of Amides 1
• Low-molar-mass amides are water- and alcohol-soluble
• Solubility decreases as molar mass increases
• The amide group is polar
• Except formamide (liquid), most amides are colorless crystalline solids
• Amides have high melting and boiling points
Properties of Amides 2
• Resonance restricts rotation of the C–N bond
• This restricted rotation is important for protein structure
• Tertiary amides lack N–H bonds and cannot form hydrogen bonds
• Amides behave as weak bases (practically Neutral)
Amide Synthesis: CH3-COOH + NH4OH →
Ethanamide CH3-CONH2
Acid hydrolysis of Amides
Amides can be hydrolyzed in an acidic
medium and heat to form carboxylic acids.
Ethanamide + H2SO4 + H2O + Heat →Ethanoic acid + NH4+
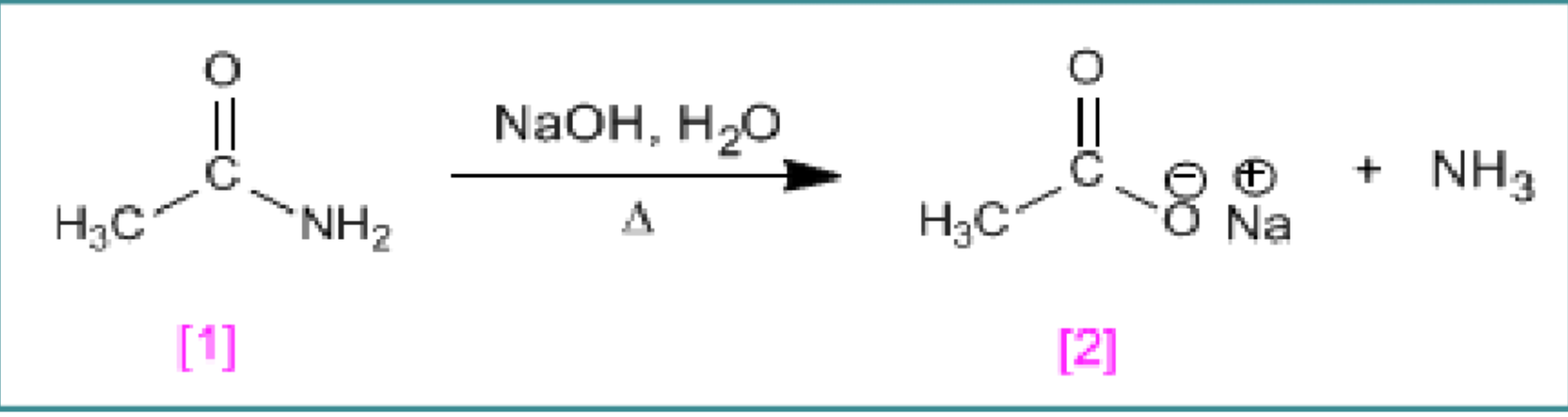
Amide reaction with NaOH
Amides react with strong bases and heat to form salts
Ethanamide + NaOH + H2O + Heat → Sodium Ethanoate + NH3
Amide Reaction with Alcohols
Amides react with alcohols to form Esters
Ethamide + Ethanol → Ethyl Ethanoate + NH3
Reduction of Amides
Propanamide + LIAlH4 → propylamine
Hoffmann Transposition
Propanamide + NaOH + Br2 + H2O → ethyl amine + CO2
Uses of Amides
In the pharmaceutical industry for the
production of anesthetics.Production of Nylon is done with amide.
Allow the links of the amino acids in the
proteins.Used as foaming agents
Acrylamine are used in the production of
paper, metal extraction, textile industry,
cooling and synthesis of other amides