anatomy lab : tissues
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
4 main tissues in human body
-epithelial tissue
-connective tissue
-muscular tissue
-nervous tissue
epithelial tissue
-covers & lines surfaces of body (skin & digestive tract)
-found in → glandular tissue & pancreas
basement membrane
underlying layers of epithelial tissue
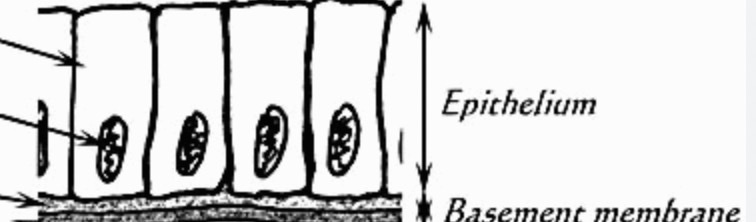
simple
one layer
simple squamous epithelium
-single layer of flat cells (floor tiles)
function → diffusion & smooth lining
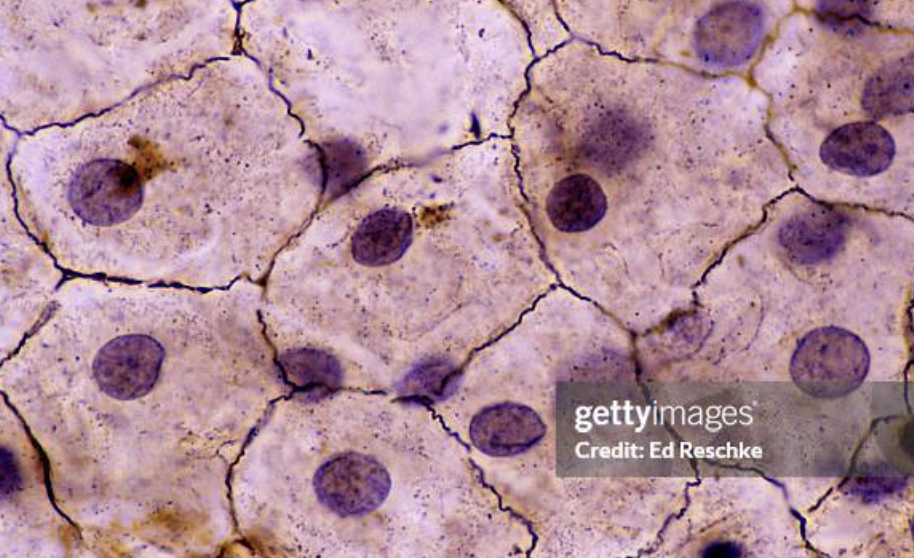
simple squamous location
-inside heart 🫀 & lungs 🫁
simple cuboidal epithelium
-single layer of cube shaped cells
functions → absorption & secretion
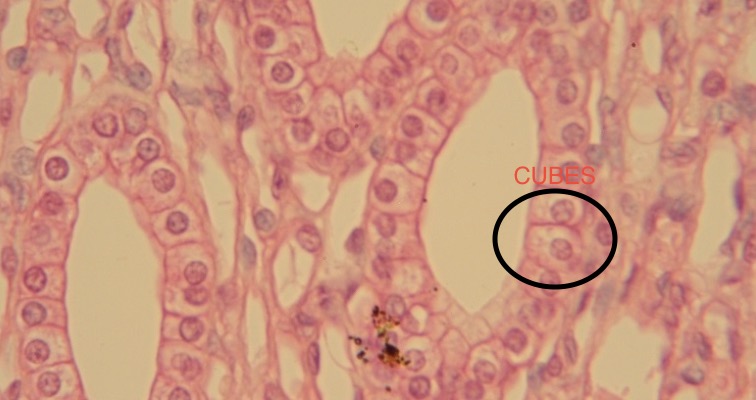
simple cuboidal location
-kidney tubules & liver 🦵
simple columnar epithelium
-tall cells in one layer
-function → absorption & secretion
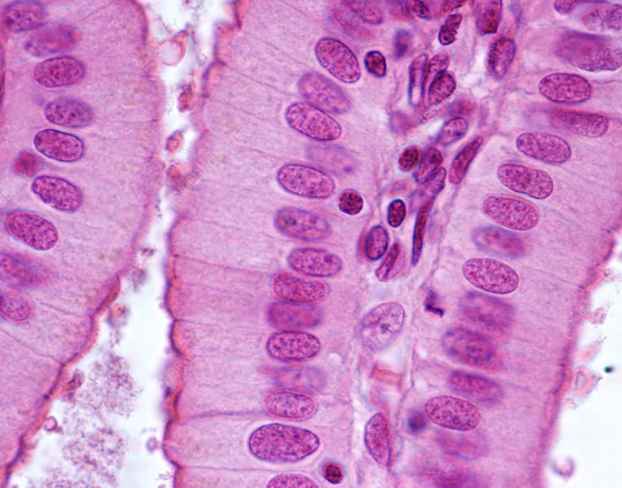
simple columnar location
stomach through intestines & uterine tube
Pseudostratified (fake) columnar epithelium
-multiple layers with varying cell heights
-functions → secretes mucus & traps dust particles, moving them away from lung
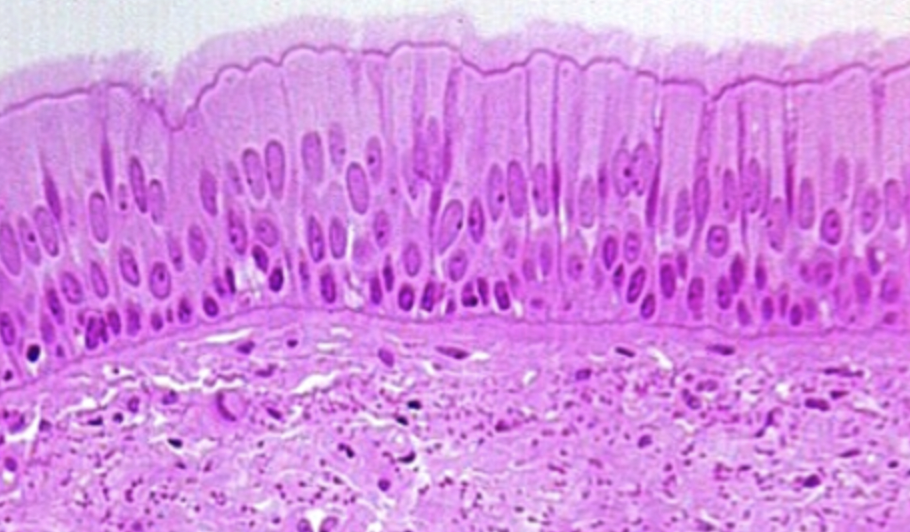
Pseudostratified columnar location
-respiratory passages
stratified squamous epithelium
- multi-layered tissue composed of basal cuboidal & flat, scale-like surface (squamous) cells
function → protective barrier against physical abrasion
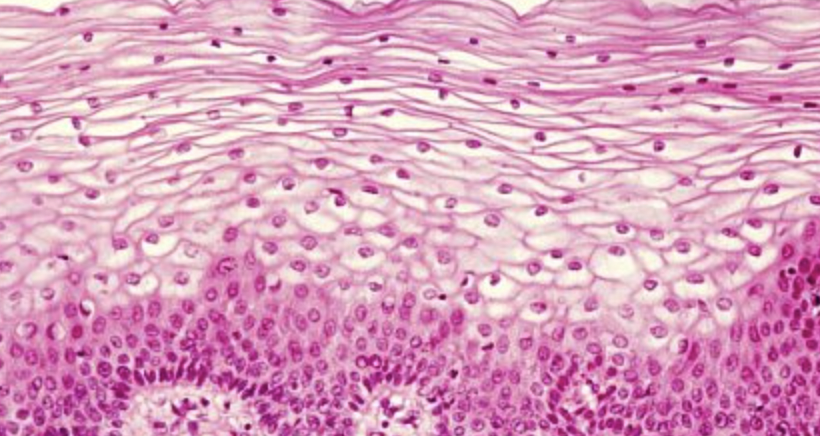
stratified squamous epithelium location
-outermost layer of skin
- lines vaginal & oral cavity
-esophagus
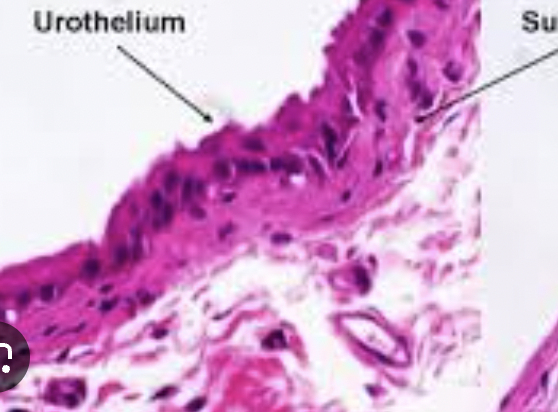
urothelium
-specialized protective lining of the entire urinary tract
-functions → preventing infection & sensory transduction of stimuli
-location → renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder, proximal part of urethra
⭐️allows bladder to expand and fill with urine
muscular tissue
-composed of contractile cells (muscle fibers) that shorten to produce body movement, maintain posture, & move substances through the body
skeletal muscle
-cells are called fibers or myocytes
-has striations (stripe-looking)
-voluntary (conscious control over muscle)
⭐️elongated nuclei
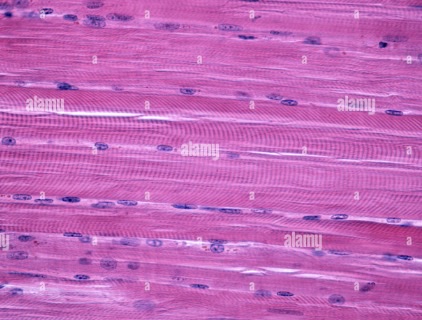
skeletal muscle function
produce voluntary movement, support posture & stabilize joints
skeletal muscle location
arms, legs, abdomen, chest, back & head
cardiac muscle
--found in and makes up the heart 🫀
-less striated than skeletal
-function → generate rhythmic, involuntary contractions that pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen & nutrients & removing waste
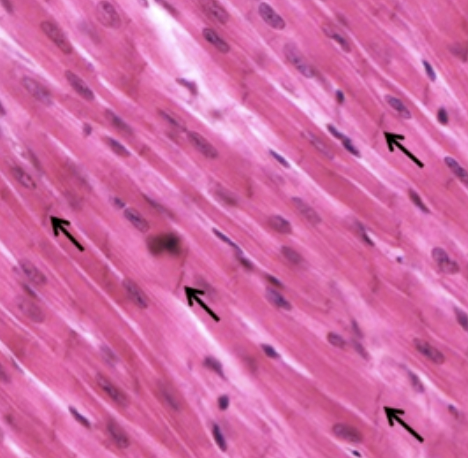
smooth muscle
-non-striated
-involuntary (done without control)
-function → involuntary contraction to move substances through hollow organs & regulate organ size
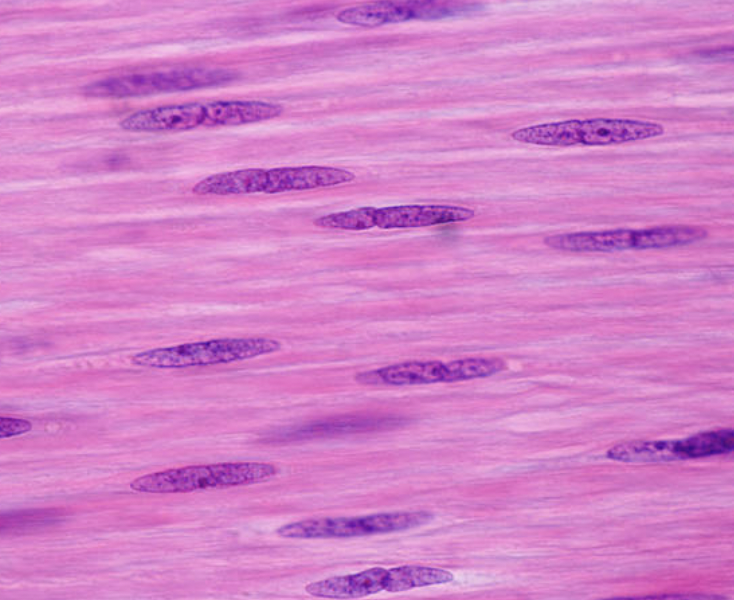
smooth muscle location
-digestive tract, blood vessels & uterus
nervous tissue
-cellular tissue
-⭐️has neuron
-function → communication, control & coordination of body activities through electrical & chemical signals
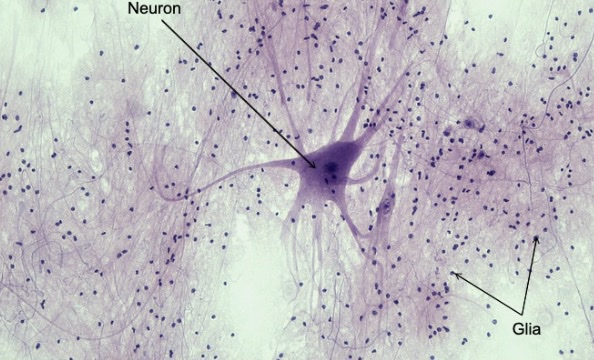
nervous tissue location
brain, spinal cord & peripheral nerves of body
connective tissue
-consists of fibers & fluid ground substance rather than ECM
dense regular connective tissue
-parallel
-made of collagenous fibers
function → provides strength & resistance to stretching in a single direction

dense regular connective tissue location
tendons & ligaments 🦵
dense irregular connective tissue
-run in many directions
-collagenous fibers
-function → provides structural strength, flexibility, & resistance to tearing in multiple directions
dense irregular connective tissue location
deep layers of skin & white of eye
elastic tissue
-cellular component of fibroblasts (collagenous & elastic fibers)
-dark & squiggly lines
-function → provide tissues with stretch & recoil, allowing them to expand & snap back to og shape
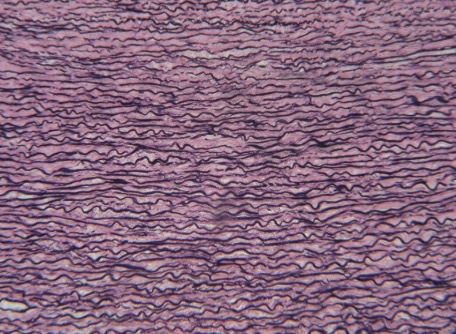
elastic tissue location
-walls of arteries
reticular tissue
-dark staining fibers with scattered pale cells
-function → provide a flexible internal framework for soft organs & supporting cells for fluid
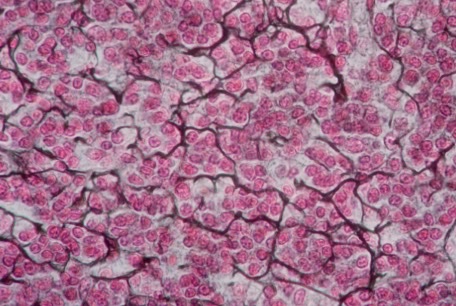
reticular tissue location
-soft internal organs (liver, spleen & lymph nodes)
areolar tissue
-scattered arrangement of collagenous fibers
-function → binds epithelia to lower layers & insulates organs
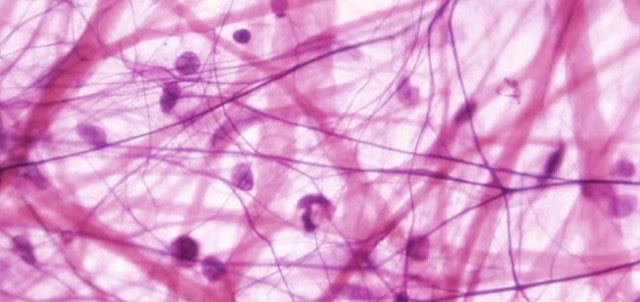
areolar tissue location
wrapping around organs & sheets of tissues between muscles
adipose tissue
-made up of adipocytes
large, pale open cells
-functions →energy storage & physical protection
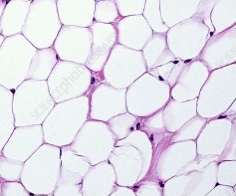
adipose tissue location
under skin, breast tissue & outside heart & kidney
hyaline cartilage
-clear and glassy looking
-function → reduces friction at joints & keeps air passages open
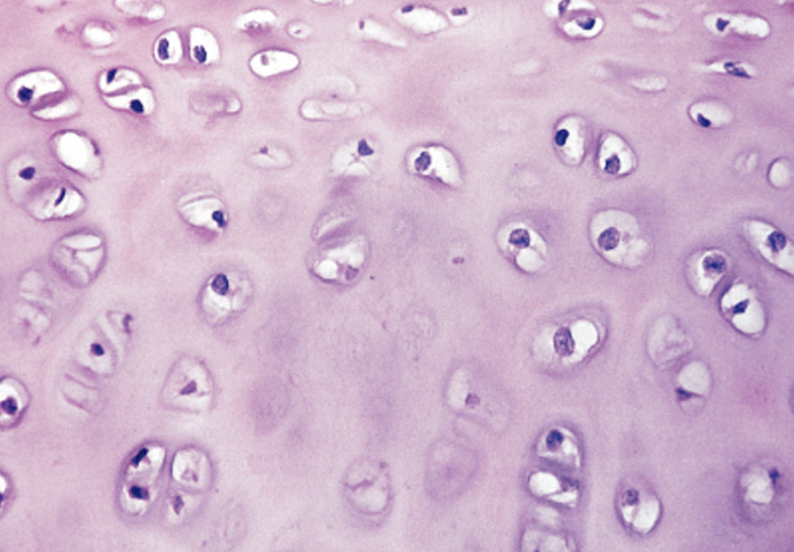
hyaline cartilage location
end of long bones, ribs & trachea
fibrocartilage
-numerous collagen fibers in rows of 4 or 5
-function → protects from wear & tear at weight-bearing or stressed joints
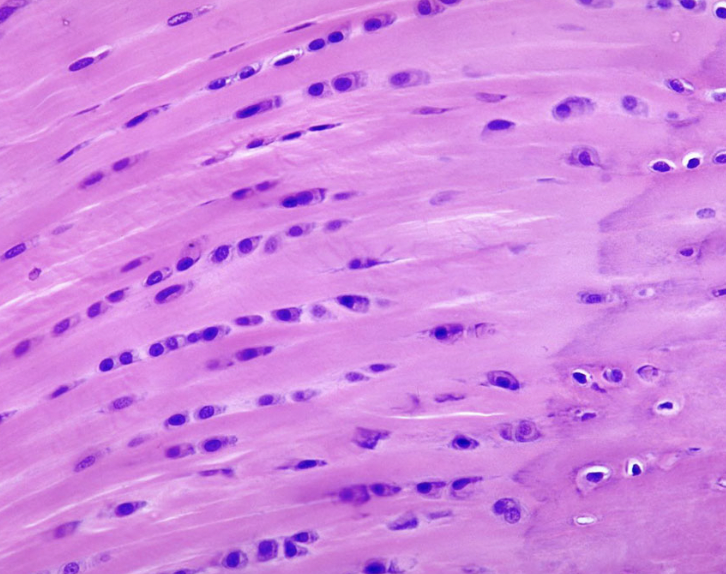
fibrocartilage location
pubic symphysis & intervertebral discs
elastic cartilage
-netlike pattern of fibers
-functions → provides flexible framework
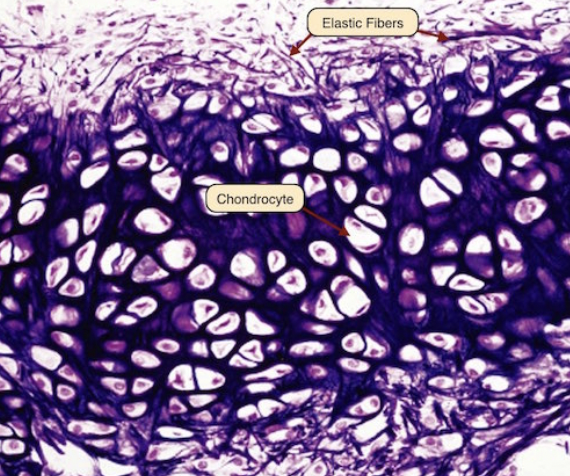
elastic cartilage location
external ear & epiglottis 👂
bone
-cells enclosed in calcium salts
-function → protection of soft organs & support
located in skeleton
blood
-many cells with no nucleus, suspended in plasma
-function → transport gases, nutrients, hormones & water
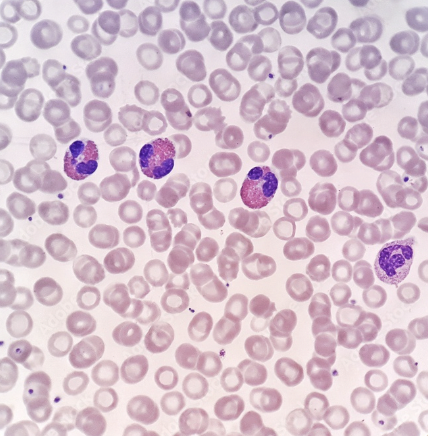
blood location
heart & blood vessels