mental health final
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Grief
loss of a relationship, job, person, experience - emotional reaction to loss
Can be experienced as Physically, Emotionally, Cognitively, Socially, Behaviorally, Spiritually
Bereavement
Reaction to loss that encompasses the emotional and physical reactions of grief and mourning - can be months to years
psychological process of letting go
DSM5 exclusion - Argument — Removing bereavement exclusion will “medicalize” ordinary grief orrr No clinical basis to exclude patients from diagnosis of depression simply because it occurs shortly after death
Mourning
behavioral action and integration of grief and bereavement - culturally driven experience and occupations that foster healing
Routines or tasks that can be a health part of coping with death

4 stages of grief
Emotional Numbing and Disbelief
Yearning and searching
Disorganization and Despair
Reorganization
not linear - can move in and out of stages or overlap
emotional numbing and disbelief - stage 1
cognitive and emotional protective measure - may last short time and becomes a barrier to engagement
typically 1 month after death
Yearning and searching phase 2
mood swings, catatonic/emotional, high energy
preoccupation with thoughts of a loved one
Disorganization and despair - stage 3
death becomes reality - isolate, fatigue, depression - it “hits” them
anger peaks at 5 months post and depression peaks at 6 months
Reorganization - stage 4
gradual and difficult process of reorganizing the deceased place in ones life - making sense and creating new life patterns
all negative symptoms were on the decline 6 mo post
Complicated and prolonged grief
Departure from the normal grief patterns in duration or intensity of emotion, psychological, or physical symptoms of grief— Intrusive thoughts can interfere with daily activities
emotional responses last longer, high anxiety and depression
unexpected death, suicide, law enforcement
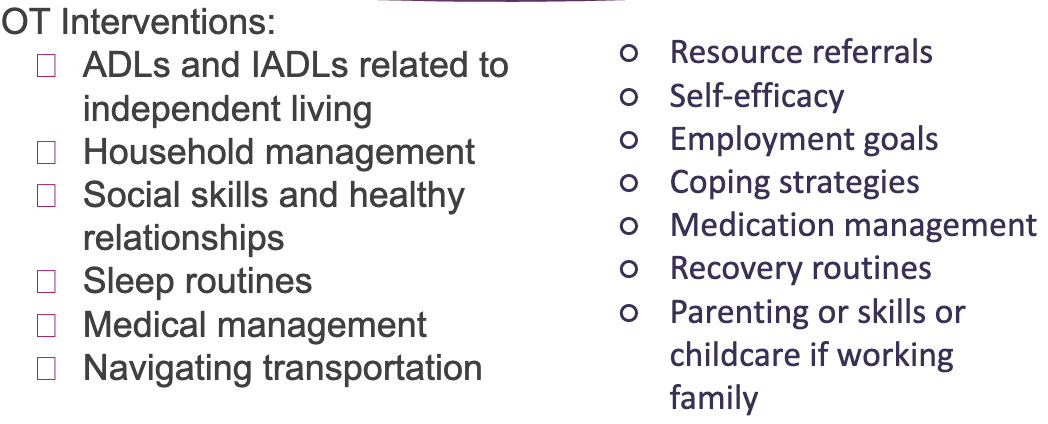
OT role in grief
Addressing the psychosocial impact
VALIDATE the client and his/her concerns, Establish client-centered goals, Be honest about what lies ahead, Provide factual information, Create a partnership, Provide resources for psychosocial healing
Grief interventions
Adults- roles and routines to honor dead, prepare their fav meal, memory walk, foster new self-efficacy (IADLS, support group, coping skills)
Children- open communication, allow questions, give choice to attend funeral, determine support system, encourage artwork, movement, music
Person w mental illness- assist in mourning rituals, evaluate support system, evaluate coping skills and support avoiding substances, referrals to other disciplines
Mental Health Practice Settings
Reference textbook chapters 35, 38-45
Permanent Supportive Housing
individuals who are chronically homeless AND have a serious mental health diagnosis
housing-first model, indefinite lease (federal funding), Rental assistance paired with supportive services
OT- clients are experiencing a significant life transition, variety of complex personal, environmental and occupational factors
Rapid- Re-housing
individuals who are homeless and may or may not have a disability
short-term assistance with intention to move homeless persons and families as rapidly as possible into permanent housing
Time-limited financial assistance, Supported services, Avoid near-term homelessness with emphasis on connecting to long-term resources

Peer-led services
programs and organizations led by individuals who have a mental health or substance use disorder
support for recovery is provided by peers who are in recovery Experience using community, social, and clinical resources
Self-help, community services, peer professional programs, peer-led organization
modeling, self-management strategies, coping skills, problem-solving

Psychosocial clubhouse
community of individuals who share a lived experience with mental health and recovery
similar to peer-led services but consumers and practitioners work together
Emphasis on community, Consumers have opportunities for friendship, housing, education, and employment
OT work closely w clubhouse peers, client centered intervention

Criminal Justice settings
individuals with mental health concerns who have committed a crime
Incarcerated individuals may not find occupations meaningful if they feel no sense of control over their routine or cannot associate cultural meaning to task, Interventions should address community reintegration, Introduce new hobbies for unoccupied time

State hospitals
individuals with serious mental illness; individuals who make direct threats to harm themselves or others, may demonstrate uncontrolled behavior
general public may view them dangerous - treatment mall approach, milieu therapy approach, sensory interventions
voluntary/involuntary admission

Inpatient Mental Health Settings
Acute: patient is hospitalized for a physical health concern, but care is impacted by mental health concerns. possible move to a behavioral health floor for more specialized care
Inpatient Hospitalization: hospitalized on a behavioral health unit to stabilize MH symptoms and discharging into a less restrictive care environment
Specialized Hospitalization: standalone hospitals or hospital units that offer specialized care based on life stage (Ex: child, adolescent, young adult, adult, geriatric or crisis stabilization, co-occurring disorders)
Partial Hospitalization Programs and Intensive Outpatient Programs
individuals with mental illness who can receive care in less restrictive environments - Consumers must be considered safe to live outside the hospital - practice coping skills
HW is beneficial, provide education, address social supports

Inpatient Substance Use and Rehabilitation Facilities
individuals with substance use or co-occurring disorders
Co-occurring disorder: mental health and substance use disorder Comorbidity: presence of one or more diseases
Description: consumers receive intense therapy and other tools for managing addiction
OT should seek additional training in substance abuse, anticipate withdrawl, draw connection between substance abuse and MH

Community-Based Case Management Assertive Community Treatment
individuals diagnosed with mental illness and recovery - case management is a method for providing consumer with needed services
Highly individualized, Advocate for community resources, Multidisciplinary team provides services 24/7, Team is primary service provider to minimize need for numerous providers, Practitioners have small caseloads because demands are high
Facilitate new learning skills, home visits, strengths-based

Integrated Behavioral Health and Primary Care
consideration of mental health and substance abuse conditions, along with any other health conditions within the same episode of care, as well as across a person’s lifespan
mental health and substance abuse is considered “behavioral health”
focus on prevention and focus, social determinants of health, expand chronic disease management

MH eval
client-centered and occupation-focused
occupational profile, baseline level of function, subjective interview, observation, standardized assessments, screenings
Eval- mental capacity, insight, motivation, performance - cognition, mood and affect, home environment, support system, daily routine, functional performance, strengths, motivators

choosing the best source of information
self-report- client preferences or expectations
observation- informal, structured, or standardized assessments
proxy report- info gathered from family, friend, caregiver
dynamic assessment- engage in activities to assess what the person is able to do on their own and where performance can be improved
Resilience
ability to recover and thrive in the face of trauma, stress, adversity
enduring stressful situations without suffering physiological or psychological
Problem-solving, influencing, organization, managing resources
Protective features
work collaboratively with individuals to foster protective features
Positive qualities and skills, Perceived social supports, Safe environment, Ability to problem solve, Physical activity, Connection to community resources, Sense of meaning or purpose, Spirituality or religious values
Benefits of CBT
Clinicians can use CBT to prevent maladaptive behaviors, especially for individuals with anxiety and depression
Examples of thought distortions or errors in thinking
Distortions in how persons perceive, appraise, and process information about themselves and the environment lead to dysfunctional beliefs that can be self-fulfilling.
Dysfunctional beliefs are associated with several psychiatric conditions and psychological problems and often interfere with the process of rehabilitation and recovery
Methods for cognitive restructuring
Belief-oriented CBT typically integrates cognitive, behavioral, and social cognitive intervention methods because they work synergistically to most effectively achieve outcomes related to cognitive content, specifically cognitive beliefs.
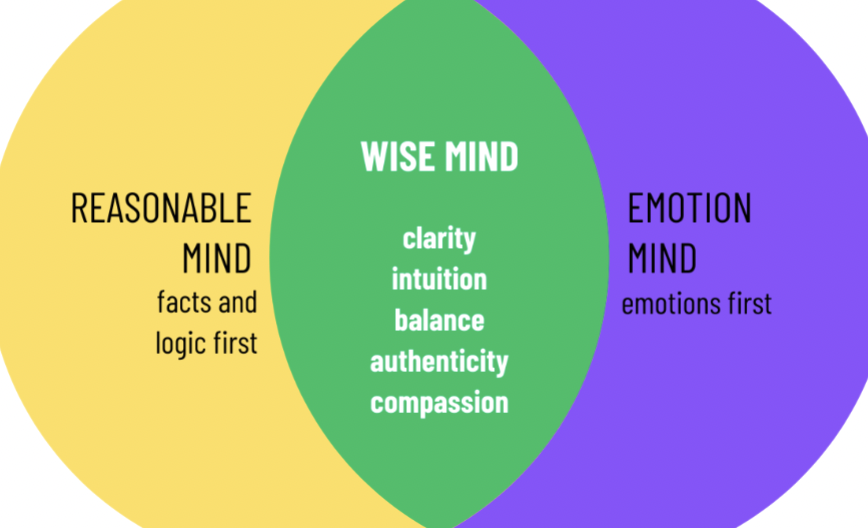
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness - pairs radical acceptance and validation with teaching transformative skills
non-judementally observing experiences without labeling them as good or bad - fully present and not lost in the past
Definition of trauma-informed care
empathy for the lived experience of our patients, recognizing that our interactions with patients are shaped by their unique history,
doesn’t require us to directly address traumas in our patient interaction
Trauma-informed care as a universal precaution (rather than targeted individual interventions)
Instead of focusing interventions only on the internal resources of the person doing the coping, the trauma-informed and healing-centered provider works to address the systems and narratives that discriminate and cause the need to cope
Trauma informed care interventions
Offering information and choice, Identifying strengths, Collaborative approach to treatment and plan of care, Letting go of expectations-progress isn’t linear
Six key principles of trauma informed care
safety (attend to signs of discomfort), trustworthiness and transparency, peer support, collaboration (recognize stage of change), empowerment voice and choice, humility and responsiveness (adjusting approach and address biases)
Substance Use Disorders (SUD)
History- thought to be acute and fixed w detox, residential rehab, short-term outpatient therapy — NOW know it it long-term and chronic
Prevalence- overall population 15-20% - higher for individuals with SMI because symptoms of MI worsen from use, decreased resilience, and cognitive function - risk increases when substances consumed alongside prescribed meds

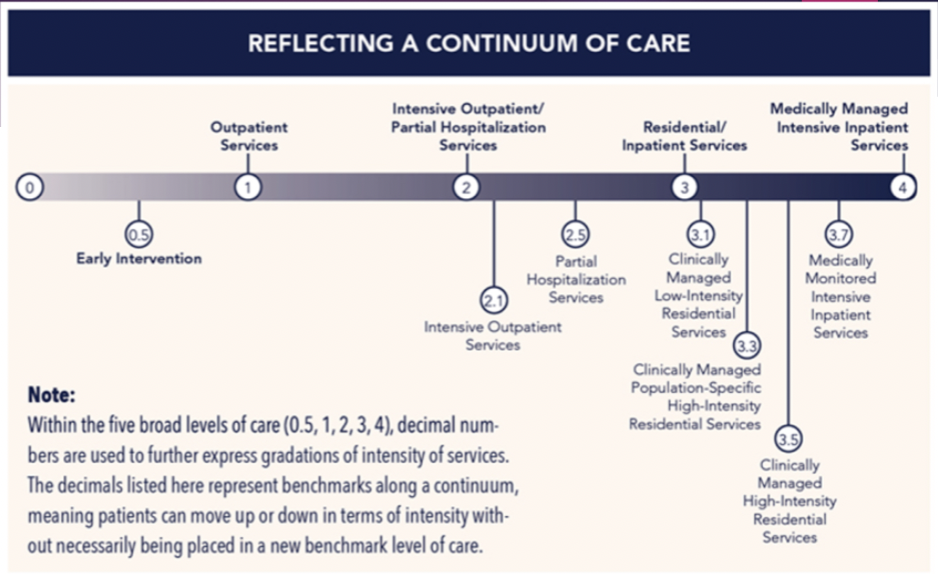
Levels of care - SUD in SMI
determined by - biomedical conditions, readiness to change, recovery/living environment, relapse/continued use, withdrawal potential, emotional, behavioral conditions
Evidence-based practice for substance use disorders (6 types)
Building and maintaining motivation to abstain or reduce use
Constraints (contingency management)
Peers/family
Behaviors to manage cravings/urges
Building a balanced life of meaning with long-term goals and rewards
Twelve Step Programs
Building Motivation to Abstain or Reduce Use -1
motivational interviewing, intervention style not protocol
express empathy, develop discrepancy, avoid argumentation, roll with resistance, support self-efficacy
Constraints -2
Contingency management- recovery housing, self-help meetings, breathalyzer, drug testing
OT- address the overlooked barriers to assist in client in being able to manage contingency
Peers and family -3
Behavioral Couples Therapy (BCT), Theoretical Background - Social Modeling, Family Involvement in Treatment, Community Reinforcement Approach (CRA)
OT- Social skills training, Developing routine surrounding ability to access positive support network, Promoting ability to engage in specific treatment
Managing urges/cravings -4
Distraction: reading, hobbies, exercise, eating, etc., Contact with sober support, “Urge Surfing”
OT- Development of important leisure pursuit, Increase knowledge of preparing health food to use as replacement or craving strategy, Educating on relaxation or exercise routines
Building a balanced life -5
engage in activities that hold meaning and purpose
OT- assess and train in meaningful life skills - develop healthy relationships, taking care of their home, returning to a job
Twelve step programs -6
self-help groups, AA, [Substance Name] Anonymous, Dual Diagnosis Anonymous
WRAP
Wellness recovery action plans - identify triggers and wellness tools and help people create a daily management plan
OT- strength based - incorporate coping strategies, sensory processing, task analysis, habits, routines
Discharge key points
The client/patient should be discharged to the home and community, not just from the facility or therapist
Follow-up and continued support in the community are the keys to ensuring a successful transition

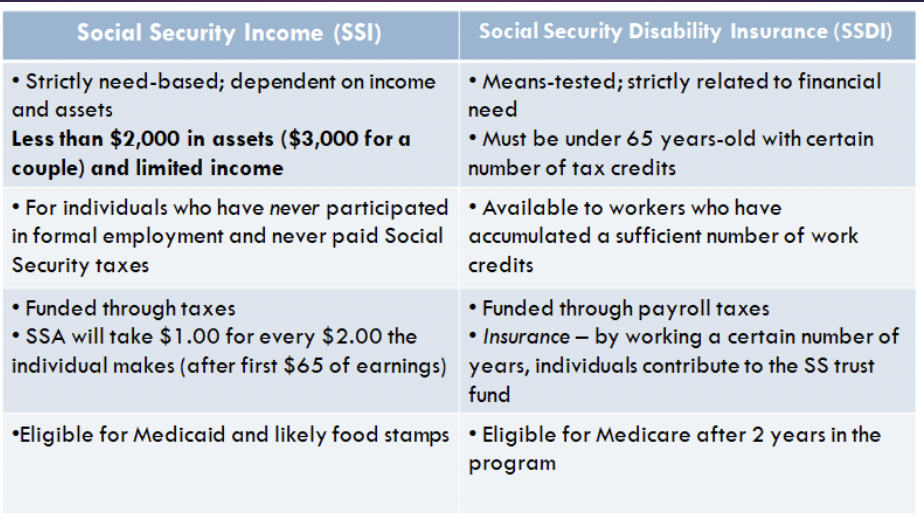
Difference between SSI and SSDI
Discharge financial resources
Third Party Payee- court ordered, individual or organization who assist w managing money
ABLE accounts and trusts
Discharge housing options
Skilled Nursing Facility, Intermediate care facility, residential care facility, permanent supportive housing, supportive housing, independent housing
most intensive to least intensive
Ethics and discharge planning
