Biochem CH. 9
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
hemoglobin (Hb)
oxygen-binding, transport protein
what kind of protein is hemoglobin
tetrameric transport protein
allosteric
RBC
myoglobin, Mb
func = store
transports oxygen in MUSCLE
facilitates O2 diffusion for high respiration
hemoglobin carries oxygen from where to where
from LUNGS —> TISSUES
how is hemoglobin an allosteric protein
it displays cooperativity in oxygen binding/release
where does myoglobin bind oxygen? what type of bind?
in MUSCLES
binding is NOT COOPERATIVE
oxygen binding in Hb & Mb is measured as
a function of the partial pressure of O2
YO2, (fractional saturation by O2) describes what?
how much O2 bound
YO2 = [HbO2] / [HbO2] + [Hb]
myoglobin structure
single polypeptide chain
consists of many alpha helices
arranged to form globular structure
myoglobin & hemoglobin bind oxygen at what location
at a heme
heme
a bound prosthetic group
2 things heme groups consists of
protoporphyrin
central iron ion (Fe2+)
protoporphyrin
org. component in heme group
heme structure
iron (Fe) in middle, bound to 4 Nitrogens
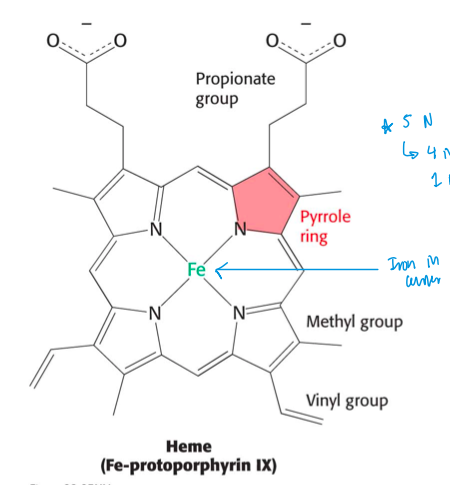
iron can form…
2 additional bonds
called 5th & 6th coordination series
iron’s 2 additional bonds it can form are called what?
5th & 6th coordination series
the 5th coordination site is occupied by what
proximal histidine
(imidazole ring of histidine)
proximal histidine
occupies 5th coordination sie; imidazole ring of histidine
what does the 6th coordination site bind
oxygen
O2 binding causes iron to move into the plane of protoporphyrin ring
hemoglobin structrue
tetramer
2 alpha subunits
2 beta subunits
EACH subunit has a bound heme
the quaternary structure in Hb is best described as….
a pair of identical alphabeta dimers (a1 B1 a2 B2)
each subunit in Hb has what?
a bound heme
deoxyhemoglobin corresponds to what state
T state of allosteric enzymes
(inactive/low binding affin)
oxyhemoglobin is what state
R state
what causes the transition from deoxyhemoglobin (T state) to oxyhemoglobin (R state)
oxygen binding
iron moves into the plane of the heme
proximal histidine (a helix) moves w/ iron
two aB dimers rotate, forming R state
strucutural changes of Hb protein from O2 binding affects what
quaternary strucuture
what does the first O2 binding in Hb allow for
allows binding of additional oxygens to be 10x greater
cooperativity
when O2 binds in Hb the contacts between what are disrupted?
alpha beta subunits
a1 & B2
a2 & B1
what 3 new interactions are made from O2 binding in Hb
hydrophobic, ionic, H bonding
O2 binding in Hb affects solvent channel how
narrower solvent channel
2-3 Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)
stabilizes T state of Hb —> facilitates release of O2
where does 2,3-BPG (bisphosphoglycerate) bind to in Hb
a pocket in Hb tetramer that only exists when Hb is in T state
how Hb oxygen affinity is adjusted for fetal/mother
fetal hemoglobin has higher O2 affinity than adult
binds O2 when mom’s Hb releases
fetal Hb does not bind 2,3-BPG (reducer) well
func of 2,3-BPG
reduces O2 binding
what kind of amino acid change happens for fetal/mom Hb
histidine —> serine
(his = mom, ser = fetus; ser reduces BPG affin, alllows to bind O2 more tightly)
Bohr effect
Hb releases protons upon O2 binding
what role do CO2 and H+ have in hemoglobin
enhance O2 release
(both are produced by actively respiring tissues)
when pO2 is low in TISSUES
H+ binding releases O2
when pO2 is high in LUNGS
O2 binding releases H+
H+ binding releases O2 when
pO2 is low in tissues
O2 binding releases H+ when
pO2 is high in lungs
when low pO2 what is pCO2
pCO2 is high
when high pO2 what is pCO2
low pCO2
low pH allows for what interactions? this enhances…
allows formation of ionic interactions —> stabilize T state of Hb —> enhances O2 release
CO2 reacts w/ what to form what?
terminal amino groups
form neg charged carbamate groups
neg charged carbamate groups do what
form salt bridges that stabilize T state
how CO2 & H+ regulate O2 binding by Hb
CO2: reacts w/ terminal amino groups —> form carbamate groups —> form salt bridges that stabilize T state
H+: low pH allows ionic interactions —> stabilize T state
(T state stabilize = more O2 release)
why does T state favor carbamate formation more than R state
T state Hb has more avail amine sites
CO2 is transported to lungs as
bicarbonate
what facilitates formation of bicarbonate ions
carbonic anhydrase
sickle cell anemia is caused by
mutation in Hb
sub valine instead of glutamate at position 6 of B chains
when is sickle cell anemia fatal
when both alleles of the B chain are mutated
(one mutated/one normal = asymptomatic)
hemoglobinopathies (abnormal Hb)
general Hb region altered
change in:
surface residues
internally located residues
stabilizing metHb
changes at alpha beta contacts
thalassemia (abnormal Hb)
diseases of globin synthesis & processing
effect of CO on Hb O2 transport
CO binds Hb at O2 binding site —> shifts Hb to R-state —> O2 is not released
COHb almost always fatal
hemoglobin structure 2.0
4 subunits
allosteric
cavity
hemoglobin oxygen binding
4 & cooperative
hemoglobin func
oxygen delivery
4 negative effectors in hemoglobin
BPG
CO
H+
CO2
(decrease O2 affin; release O2 to tissues)
myoglobin sturcture 2.0
1 subunit
myoglobin oxygen binding
1
myoglobin func 2.0
diffusion & storage
myoglobin negative effectors
CO