NBCE Part 4 Boards - Orthopedics
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Foraminal Compression Test
The patient is seated and actively rotates head from side to side. Then the doctor exerts downward pressure and the head is rotated to each side with pressure.
Positive Radicular Pain -> Nerve Root Compression
Positive Local Pain -> Foraminal Encroachment
Jackson's Compression Test
The patient is seated and the doctor laterally flexes the patient head to the left and the right and applies downward pressure.
Postive Radicular Pain -> Nerve Root Compression
Distraction Test
The patient is seated and the doctor holds under the mastoid and pulls the patient's head superior, removing the weight of the head.
"What did you experience?"
Decreased Pain -> Nerve Root Compression
Increased Pain -> Sprain/Strain
O'Donohue's Test is for....
Determining whether it is a SPRAIN or STRAIN
O'Donohue's Test Performed
1) Patient actively moves part against resistance.
2) Then the doctor moves part passively through a full ROM.
Pain Active: STRAIN (damage in mm tissue)
Pain Passive: SPRAIN (damage I'm ligamentous tissue)
Valsalva's Maneuver
The doctor asks the patient to take a deep breath and hold while bearing down.
Postive Radicular Pain -> SOL
Maximal Cervical Compression Test
Patient is seated and actively rotated and extended head. If no pain the patient is asked to maximally laterally flex head in the same direction. Repeat on the other side. No compression applied.
Postive Radicular pain -> Nerve Root Compression
Shoulder Depression Test
Patient is seated, the doctor depressed the patient's shoulder while laterally flexing the cervical spine away from the shoulder. Repeat on other side.
Postive Pain -> Nerve Root Adhesion
Soto Hall Sign
Patient supine and the doctor places one hand on the patient's stream and passively flexes the patient's head towards his/her chest.
Positive localized pain -> ant: fracture/ post: ligament tear
Bakody's Test AKA Shoulder Abduction Test
Patient is seated and placed affected arm's palm on top of their head. The elbow should be at the level of the head.
Postive Relief of Pain -> IVF encroachment
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome AKA
Neurovascular Compression Syndrome
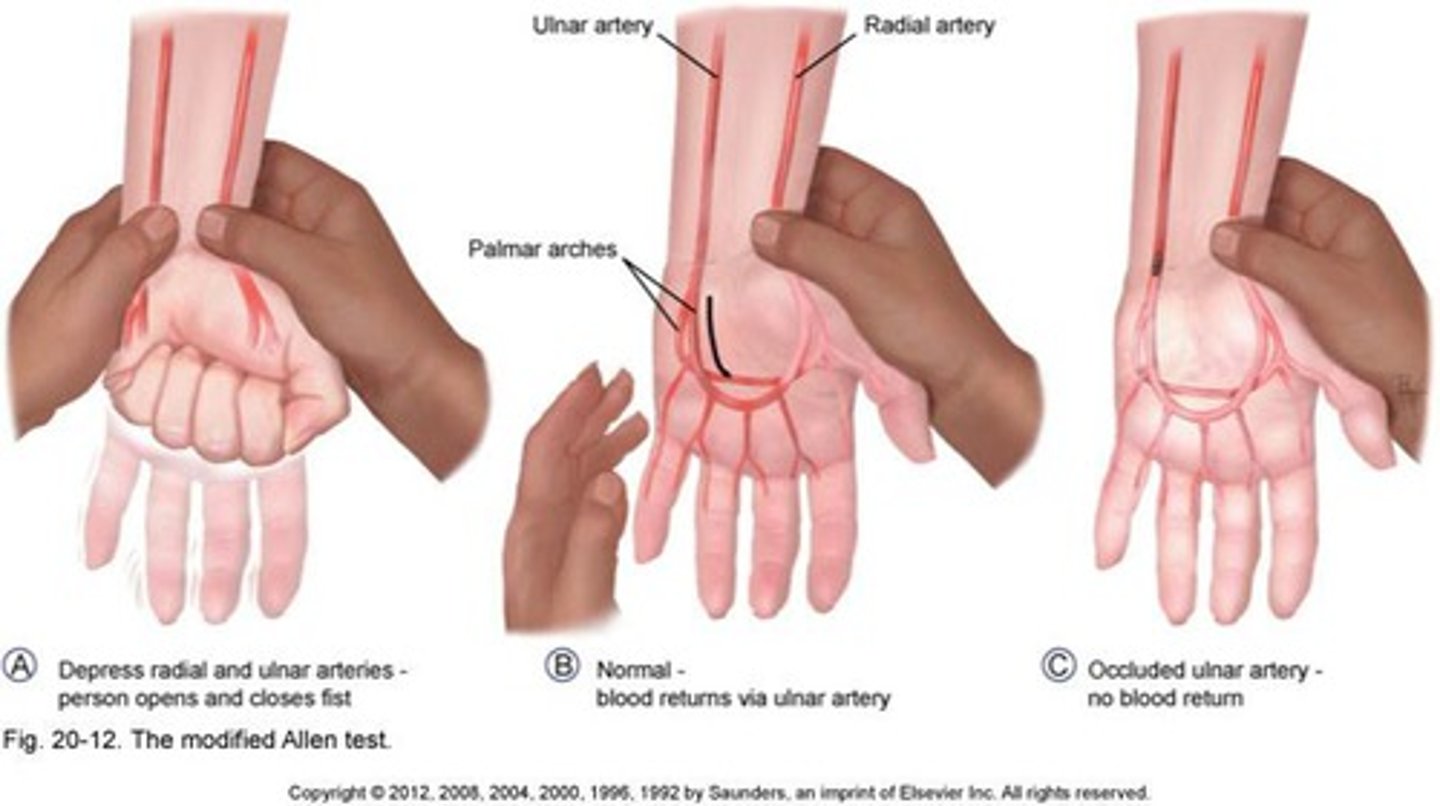
Allen's Test
Patient is seated with their elbow flexed and forearm supinated. Ask patient to pump their hand while doctor occludes the radial and ulnar arteries until hand whitens. The patient the opens hand and doctor releases on artery, recording fill time (until hand regains color). Repeat for other artery.
Postive for delay more than 10 seconds -> occlusion of the tested artery
Costoclavicular Maneuver AKA
Eden's Test
Eden's Test Performed
Patient is seated and doctor palpated for the radial pulse. Patient brings shoulder down and back and then flexes chin to their chest.
Positive if alteration to amplitude of radial pulse -> compression between first rib and clavicle
Adson's Test AKA
Scalenus Anticus Test
Scalenus Anticus Test Performed (MUST KNOW)
Patient is seated and doctor abducts, extends and externally rotates arm while taking the radial pulse. Patient rotates head TOWARDS the tested side and extends head. Patient takes a deep breath and holds it.
Postive if alteration to amplitude of radial pulse -> Scalenus Anticus Syndrome (Cervical "Halstead" rib)
Modified Adson's Test AKA
Scalenus Medius Test
Scalenus Medius Test Performed (MUST KNOW)
Patient is seated and doctor abducts, extends and externally rotates arm while taking the radial pulse. Patient rotates head AWAY from the tested side and extends head. Patient takes a deep breath and holds it.
Positive if alteration to amplitude of radial pulse -> Scalenus medium syndrome (Subclavian Artery)
Wright's Test AKA
Hyperabduction Maneuver
Hyperabduction Maneuver Performed (MUST KNOW)
Patient is seated and doctor palpated radial pulse. Both arms are abducted 180degrees. The doctor notes at what angle the radial pulse diminishes or disappears.
Positive f pulses are lost greater than 10degrees difference -> Pectorals Minor Syndrome (Axillary Artery)
Reverse Bakody Maneuver
Patient is seated and patient actively placed palm on top of their head.
Positive is pain is increased -> TOS
Halstead's Test
Patient is seated and extends their head backwards. The examiner exerts downward traction and slight abduction on arm while taking patient's pulse.
Positive if alteration in the amplitude of the radial pulse -> cervical rib
Rotator Cuff Injury...is muscle or tendon more commonly injured?
TENDONS
Which Rotator cuff tendon is most likely injured?
SUPRASPINATUS
How do you diagnosis and treat a Rotator Cuff Tear?
Diagnosis: MRI
Treatment: Codman's Exercises
Apley's Scratch Test
Patient is seated and actively moves hand behind head in attempt to touch the superior angle of the scapula. The patient then moves hand behind back to touch the inferior angle of the same scapula.
Positive decreased ROM -> Degenerative tendonitis of the Rotator Cuff
Cowman's Drop Arm Test
The doctor passively abducts the patient's arm to above 90 degrees and suddenly removes support. This will cause a firing of the deltoid muscle.
Positive: Patient unable to maintain arm position -> supraspinatous tear
Apprehension Test
The doctor abducts and slowly externally rotates the affected shoulder.
Positive: Patient shows signs of apprehension that the arm will re-injure -> Chronic Shoulder Dislocation
Dugas' Test
The patient places the hand of the affected shoulder on the opposite shoulder and attempts to touch the elbow to the chest.
Positive: unable to perform -> Shoulder Dislocation (Active & Acute)
Yergason's Test
The patient flexes their elbow to 90 degrees while seated. The doctor palpates the biceps tendon and actively resists the patient's attempt to actively supinate the hand and flex the elbow.
Positive: Audible click or snap in bicipital groove -> Bicipital Tendon Instability
Dawbarn's Sign
The doctor palpates the subacromial bursa and elicits pain. The doctor passively abducts patient's shoulder without moving his/her fingers off of the subacromial bursa.
Positive: Reduction of pain in second maneuver -> Subacromial Bursitis
Impingement Sign
The patient slightly abducts their arm and the doctor passively moves their arm through a full flexion. This causes a jam of the greater tuberosity against the lacrimal surface.
Positive: Pain -> Tendonitis (overuse of tendons)
Supraspinatus Press Test AKA
Empty Can Test
Empty Can Test Performed
Patient abducts shoulders to 90degrees and the doctor apple resistance. The patient flexes shoulders to 30 degrees and points thumbs downward and resistance is applied again. (Hold & push the proximal elbow).
Positive: Weakness -> Supraspinatus Tear
Speed's Test
Patient is seated with elbow slightly flexed and palm up. The doctor resists the patient's attempt to flex shoulder while extending and supinating the forearm.
Positive: Pain -> Bicipital Tendonitis
Subacromial Push Button Test
Doctor applies a deep pressure over the subacromial bursa.
Postive: Pain -> Supraspinatus degeneration OR Subacromial bursitis
Passive Shoulder Approximation
Patient is standing and the doctor asks patient to lift shoulders up and back (squeeze the shoulder blades together).
Positive: Pain in scapular region -> T1 or T2 Nerve Root problem on side of pain
Bryant's Test
Doctor observed patient standing and notes the heights of axillary folds.
Positive: lower axillary fold on involved side -> Shoulder Dislocation
Brachial Plexus Tension Test
Patient is seated. Patient places both hands behind his/her head and pulls elbows posteriorly.
Positive: Pain -> C5 Nerve Root Lesion and/or TOS
Lateral Epicondylitis AKA
Radiohumeral Bursitis
Radiohumeral Bursitis AKA
Tennis Elbow
Lateral Epicondylitis Affects
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Pain in extension of wrist and pronation of elbow (overhand swing)
Medial Epicondylitis AKA
Little Leaguer's Elbow
or
Golfer's Elbow
Medial Epicondylitis Affects
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Pain at elbow with flexion of the wrist
Cozen's Test
(C6 Biker Chicks)
Patient's elbow is flexed to 90degrees with forearm pronated and fist dorsiflexed. Doctor stabilizes patient's elbow and resists patient's dorsiflexed wrist.
Postive: Pain in the lateral elbow-> Lateral Epicondylitis
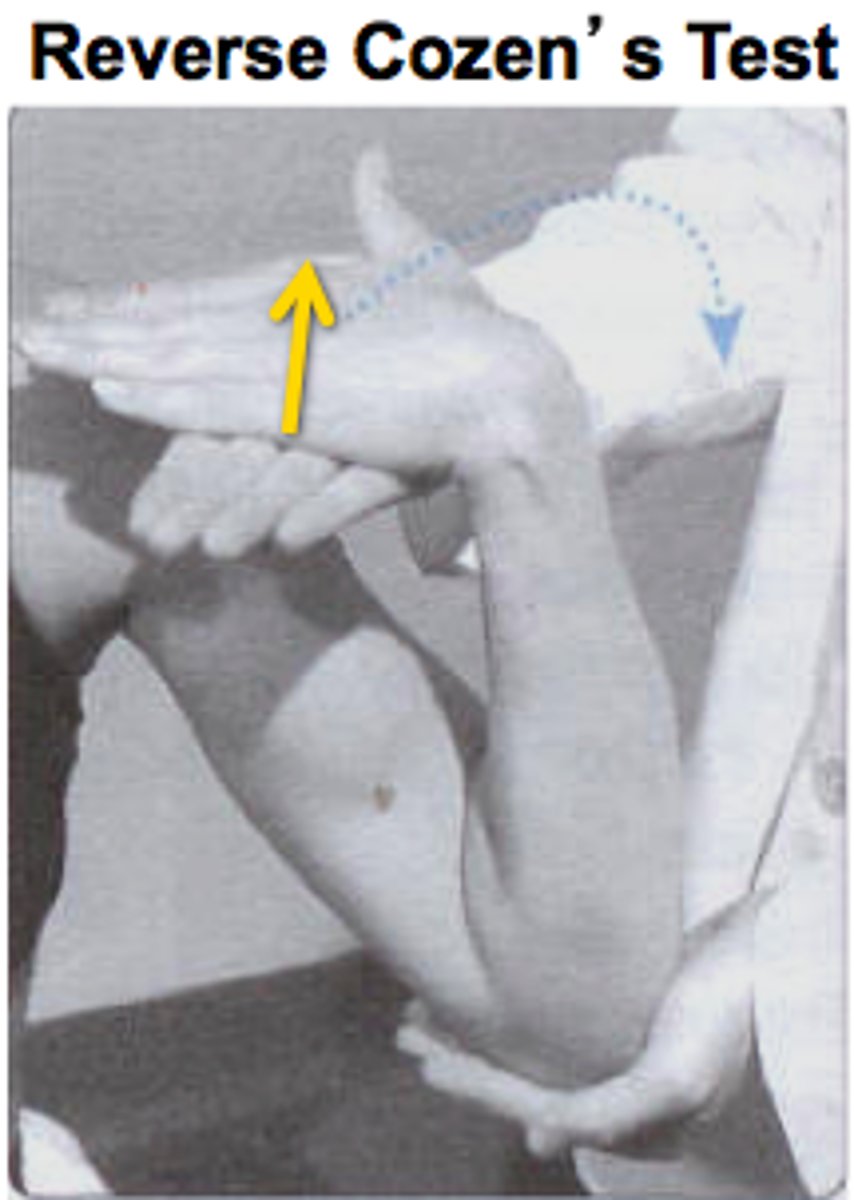
Reverse Cozen
Same except arm is supinated and doctor pulled on flexed wrist.
Positive: Pain in medial elbow->Medial Epicondylitis
Mill's Test
Doctor passively flexes patient's fingers, wrist, elbow and the brings elbow around and into max pronation and extension.
Positive: Pain in Lateral Elbow -> Lateral Epicondylitis
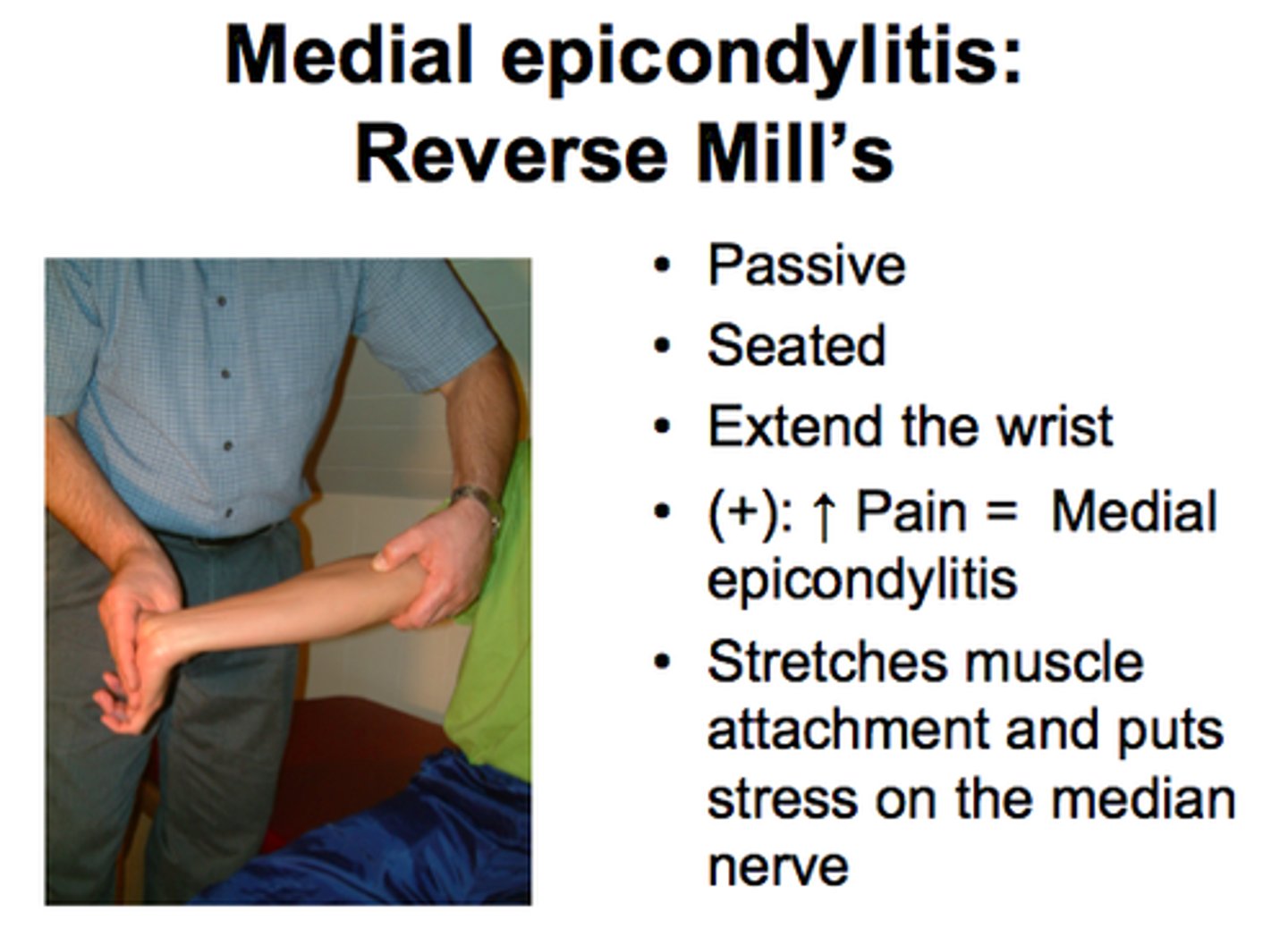
Reverse Mill's
Patients hand is flat, patient flexes and doctor resists.
Postive: Pain in Medial Elbow -> Medial Epicondylitis
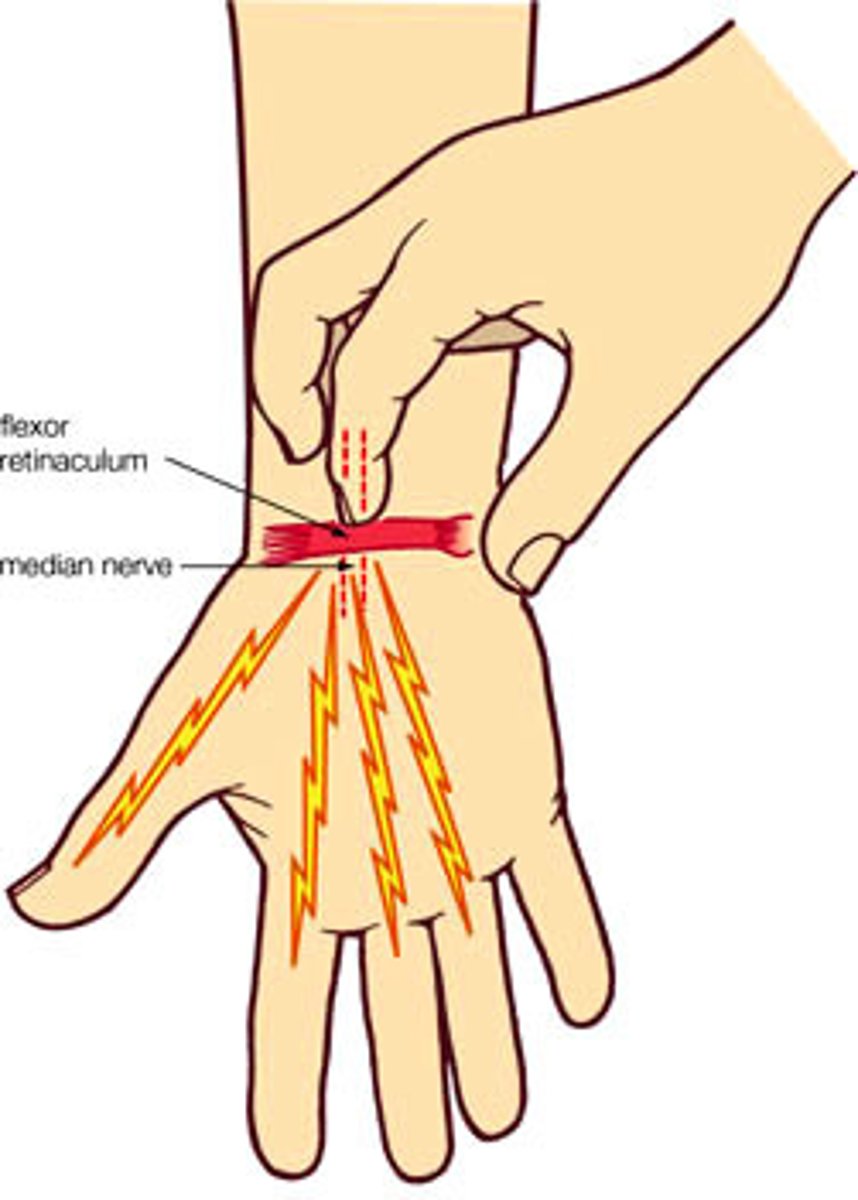
Tinel's Sign (wrist)
Percuss over the flexor retinaculum (anterior portion of the wrist where a watch would sit) and the Tunnel of Guyon (most medial portion of above)
Postive: Tingling in the lateral 3 fingers (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) of medial two fingers (Ulnar Impingement)
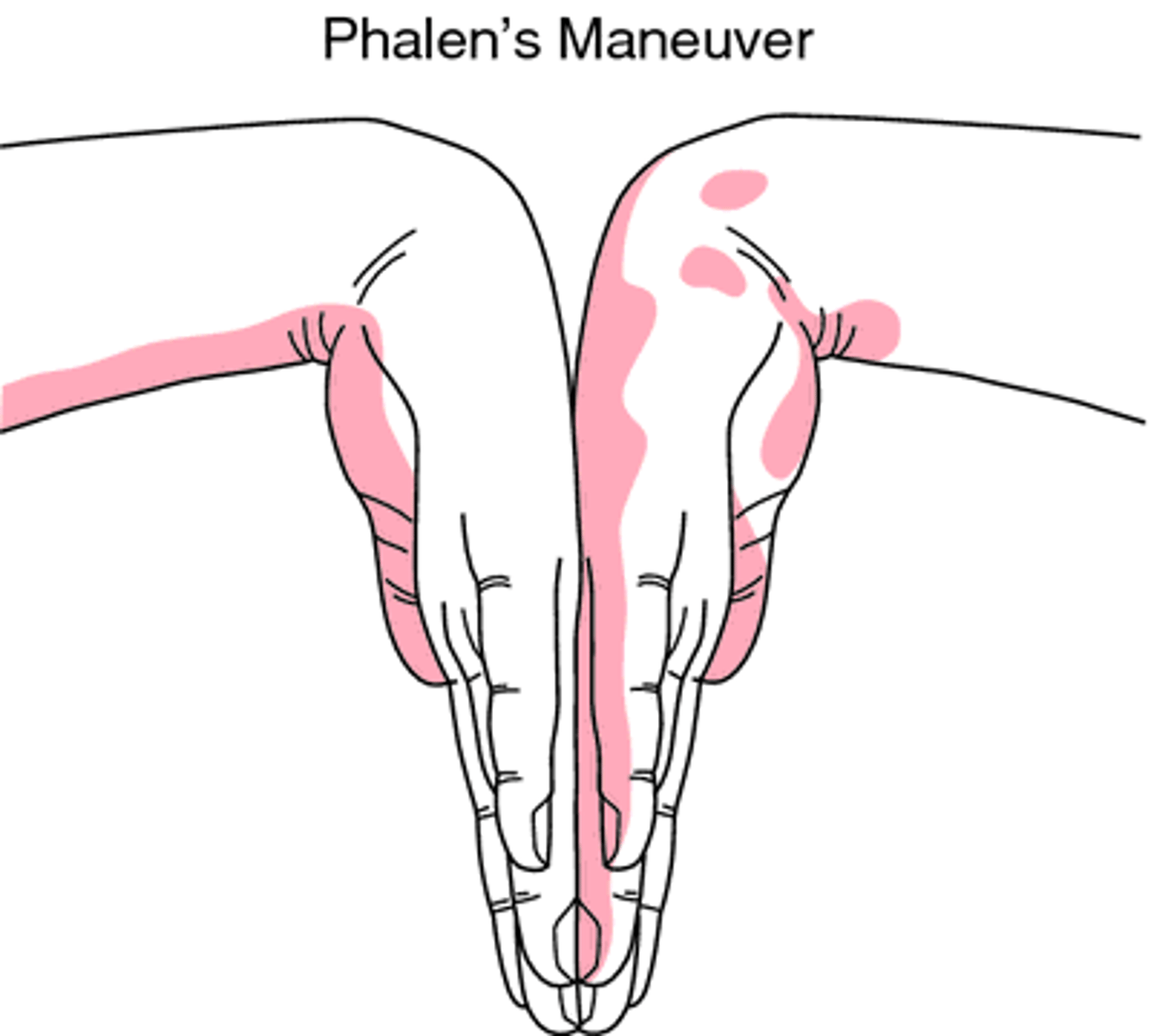
Phalen's Sign
The patient flexes writs maximally and holds position for one minute, pushing hands together.
Positive: tingling into lateral 3 fingers of hand -> Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
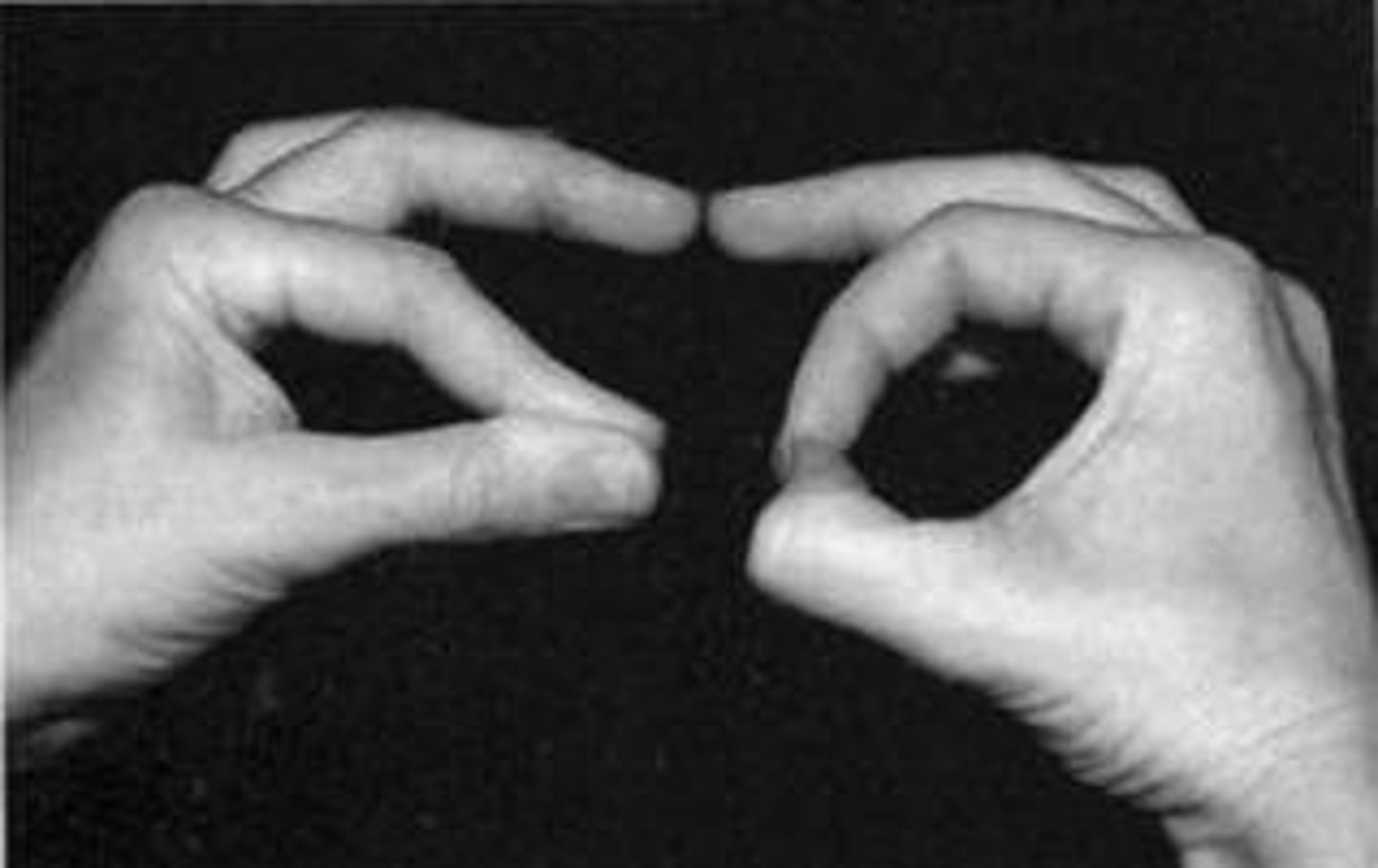
Pinch Grip Test
Ask the patient to put the tip of their thumb to the tip of their index finger.
Positive: if they put the pads of their thumb and forefinger together -> Ant. Interosseous N. Syndrome -> Median N. Lesion
Front's Paper Sign
Doctor places a piece of paper between the patient's thumb and index finger (all other fingers too) and attempts to pull it out.
Positive: Cannot hold paper-> Ulnar N. Palsy
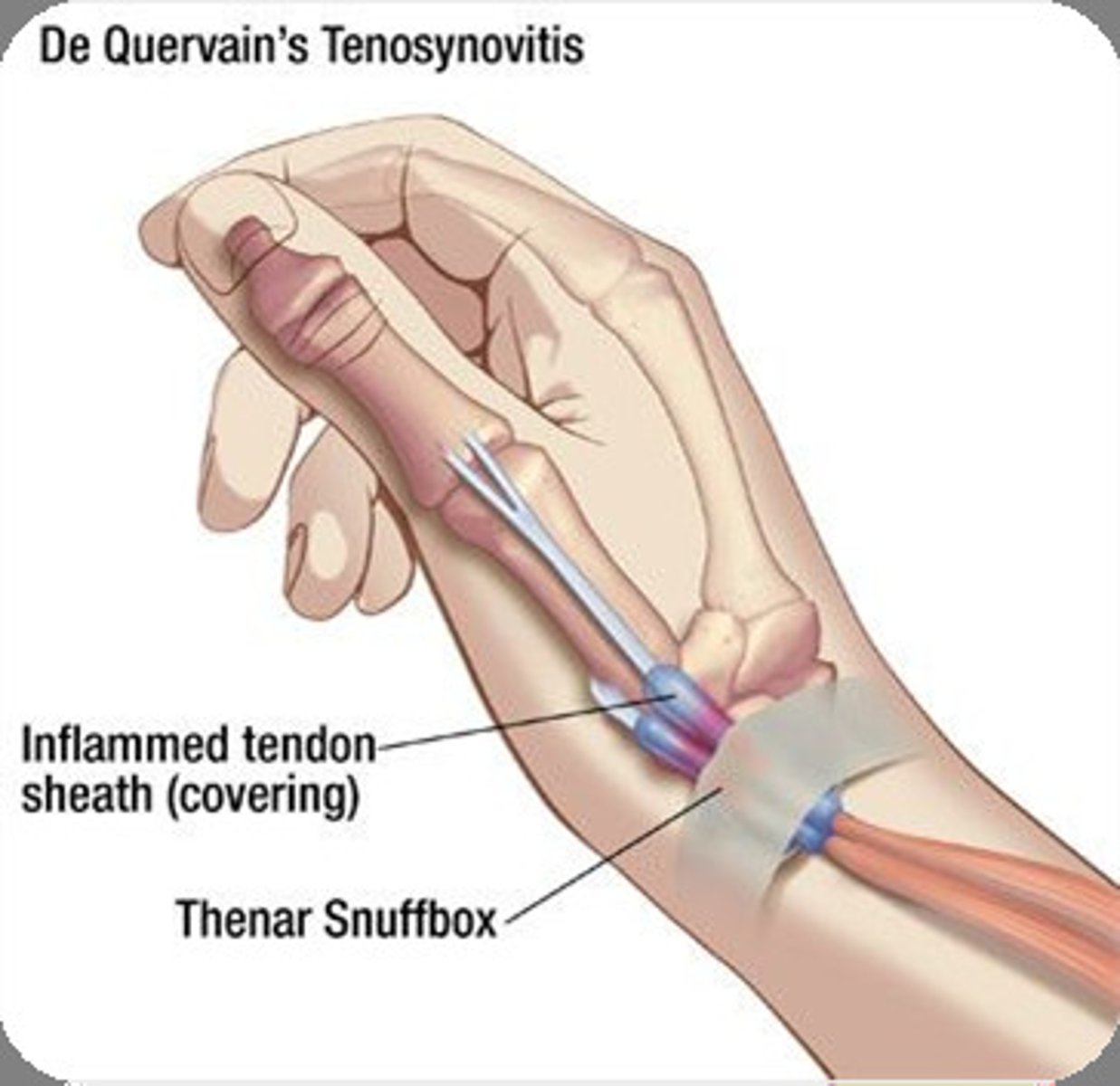
Finkelstein's Test
Patient makes a fist with thumb inside fist; then fist is passively ulnar deviated.
Positive: Pain over the anatomical snuff box -> DeQuervain's Disease AKA Stenosing Tenosynovitis.
Stenosing Tenosynovitis
Bracelet Test
Doctor applies compression around patient's wrist like a bracelet.
Positive: Pain -> RA (if bilateral) or Strain/Sprain (if unilateral)
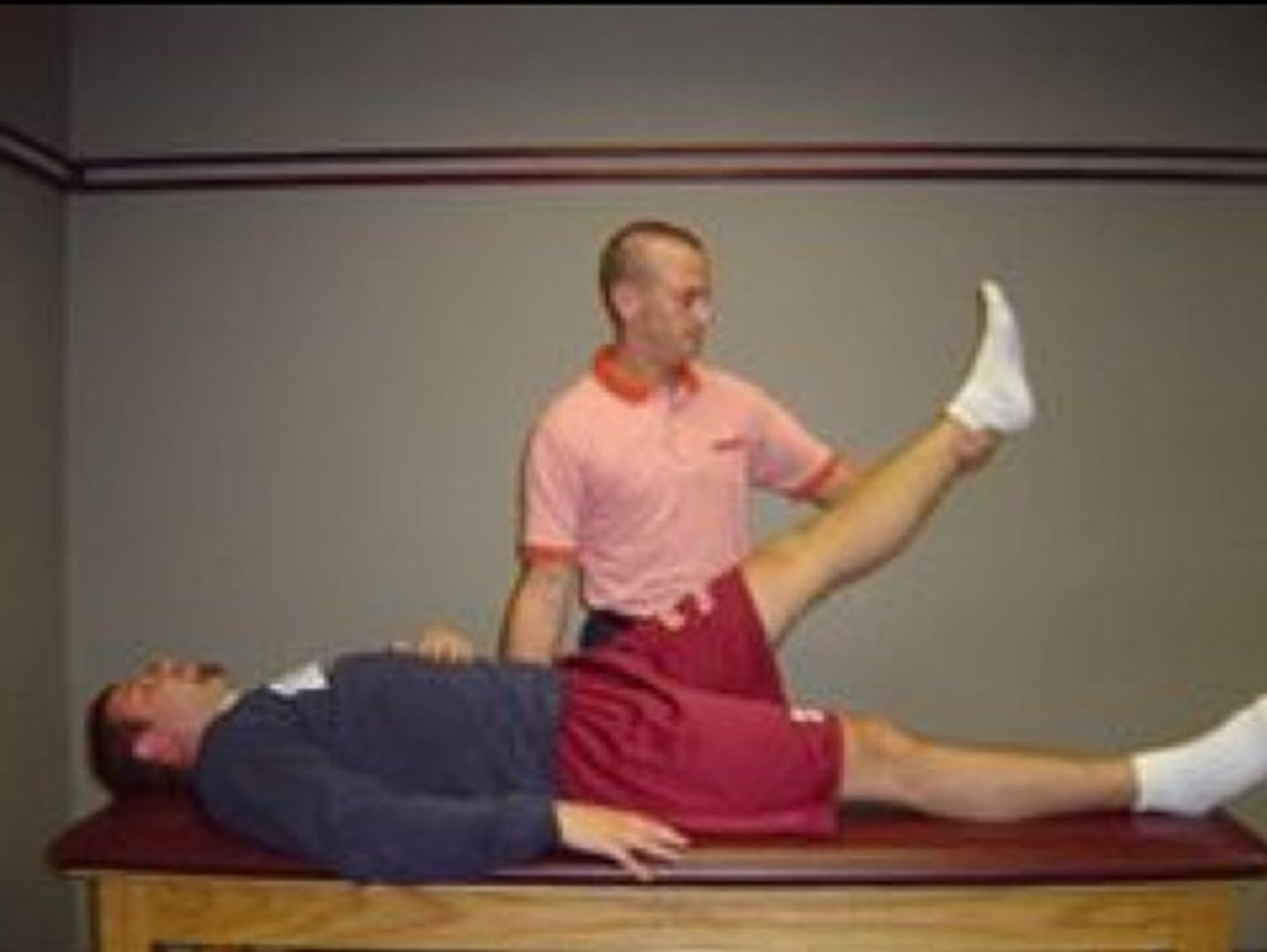
Straight Leg Test
Patient is supine. Doctor places one hand under heel and the other over the knee and slowly, passively raises patient's leg.
Positive: Pain down affected side -> Sciatica, Disc, lumbar lesion
Lasegue Rebound Test
Positive SLR + Drop
Positive: increased pain -> Sciatica, disc, and muscle spasm
Bragard's Sign
SLR + lower 5degrees + Foot flexed
Postitive: Pain in affected leg -> Sciatica
Sicard's Sign
SLR + lower 5degrees + Flex Big Toe
Positive: Pain in affected leg -> Sciatica
Turyn's Sign
Patient supine, Doctor flexes the big toe.
Positive: Pain in affected leg -> Sciatica
WLR AKA
Fajerstazn's
WLR/ Fajerstazn's
Doctor performs a SLR on asymptomatic side with dorsiflexion of the foot.
Positive: pain in symptomatic side ->medial disc lesion
Millgram's Test
Patient supine. Asked toe actively elevate legs off the table 6 inches. Hold for 30seconds.
Positive: Pain -> SOL
Leg Lowering Test
Patient supine. Doctor moves patient's legs passively to 90degrees and ask's patient to bring legs back down to the table.
Positive: LBP -> SOL
Bilateral SLR
SLR on L, SLR on R, SLR bilaterally
Positive: Pain occurs earlier on bilateral than unilateral -> Lumbosacral Joint Lesion
Goldthwait's Sign
SLR with hand under lumbar section of the spine.
Positive: Pain
0-30degrees: SI joint
30-60degrees: Lumbosacral joint
60-90degrees: Lumbar spine or contralateral SI joint

Linder's Sign
Passively flex patient's head to chest.
Positive: Pain the lumbar spine -> Root Sciatica
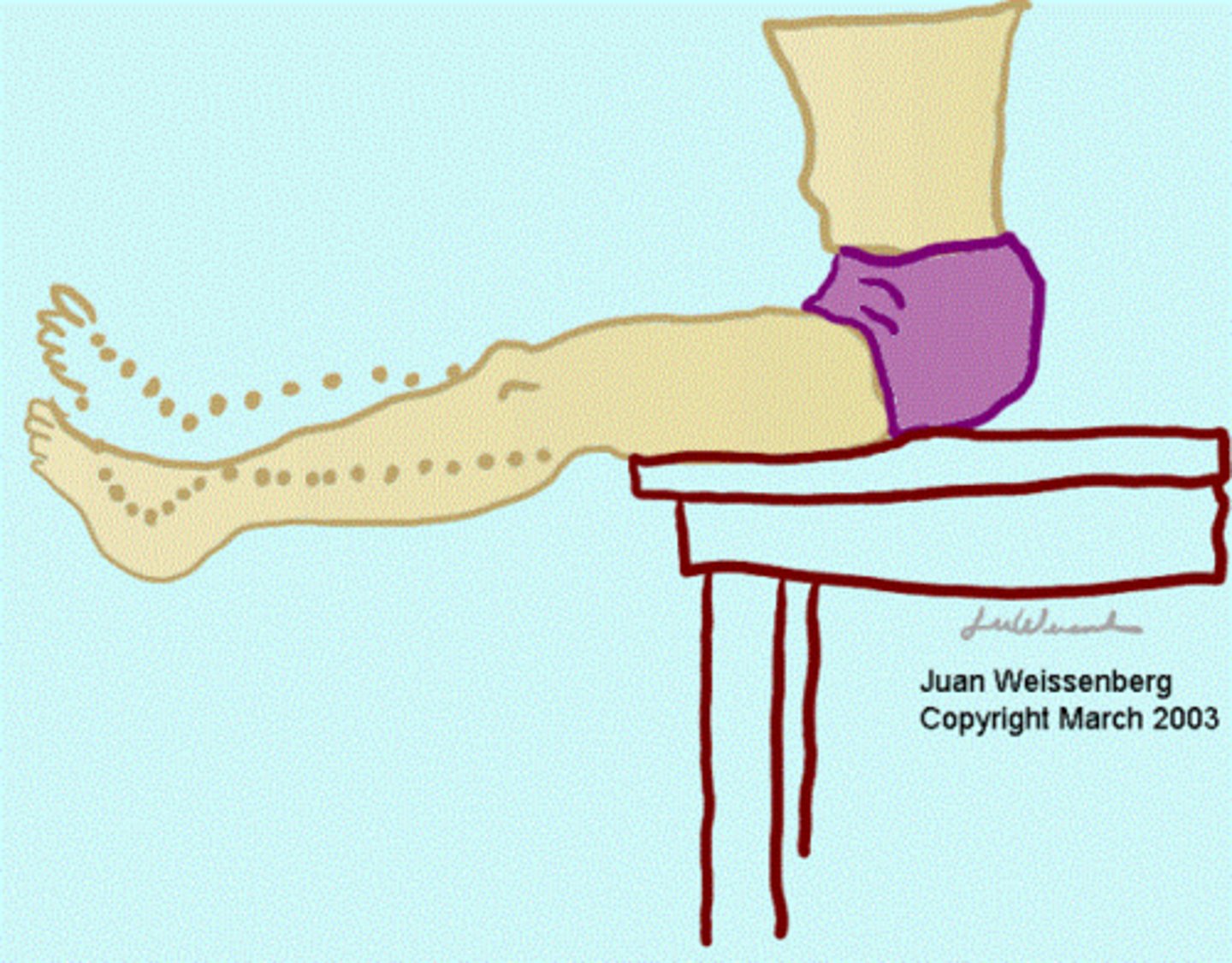
Bowstring Sign
SLR to point of pain + flex knee to Doctor's shoulder + pressure in popliteal fossa
Positive: Pain in lumbar region or radiculopathy -> Sciatica (BEST TEST)
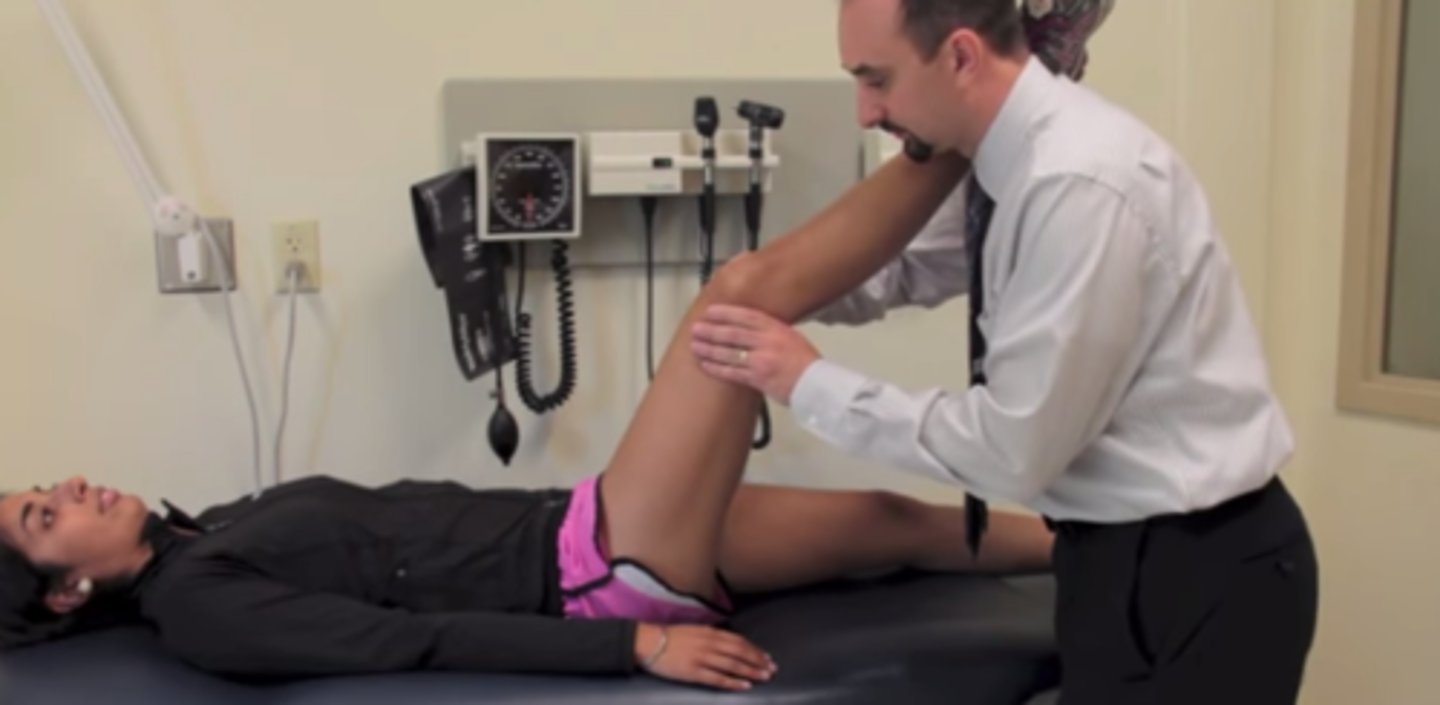
Bonnet's Sign
Patient supine. Doctor internally rotates, abducts leg and the performs SLR .
Positive: Radicular pain -> Piriformis Syndrome
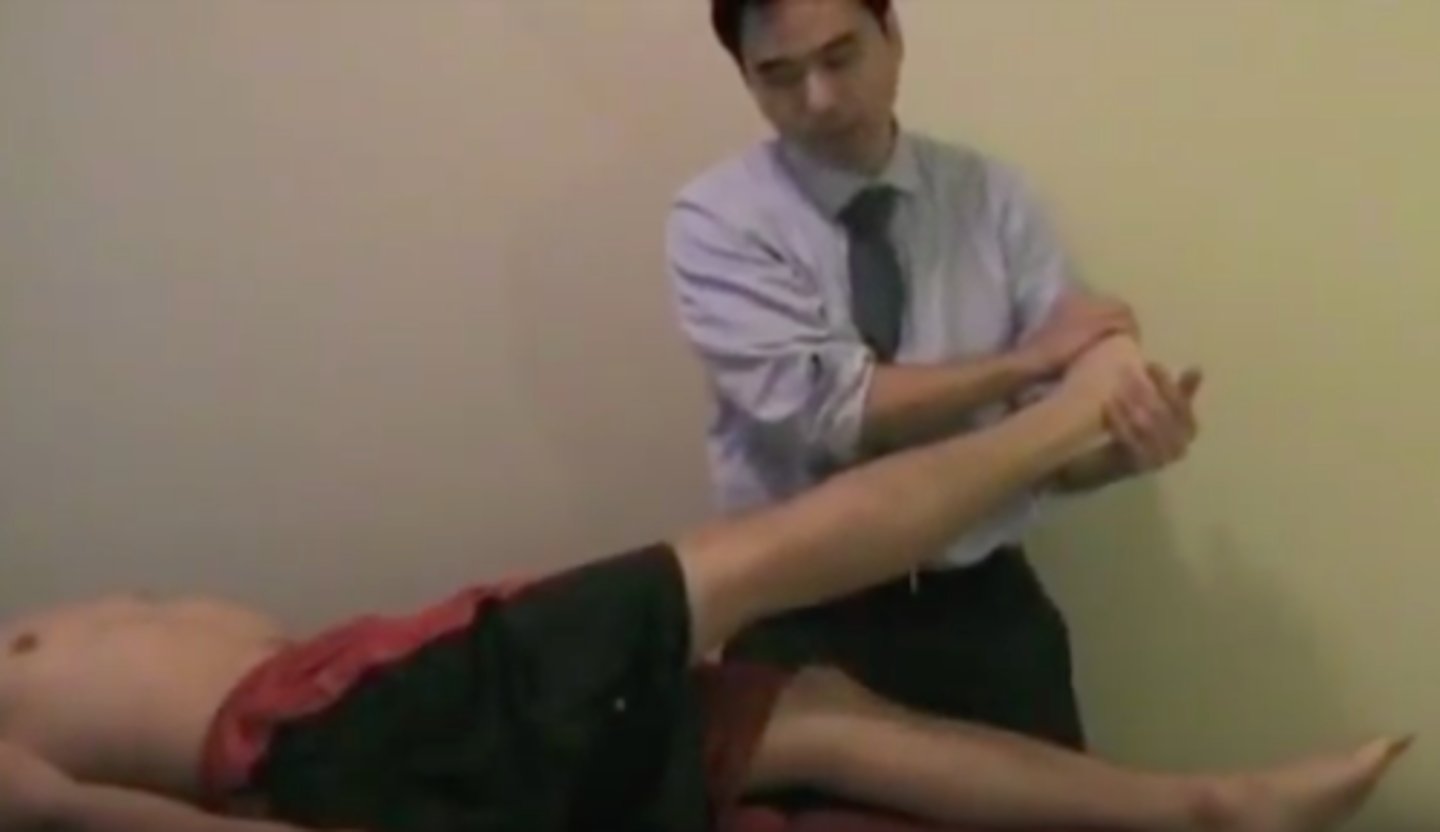

Becterew's Test
Patient seated. Doctor stabilizes thighs and patient attempts to extend both legs.
Positive: pain or leaning back -> Disc (posteromedial disc IF pain when good leg is raised)
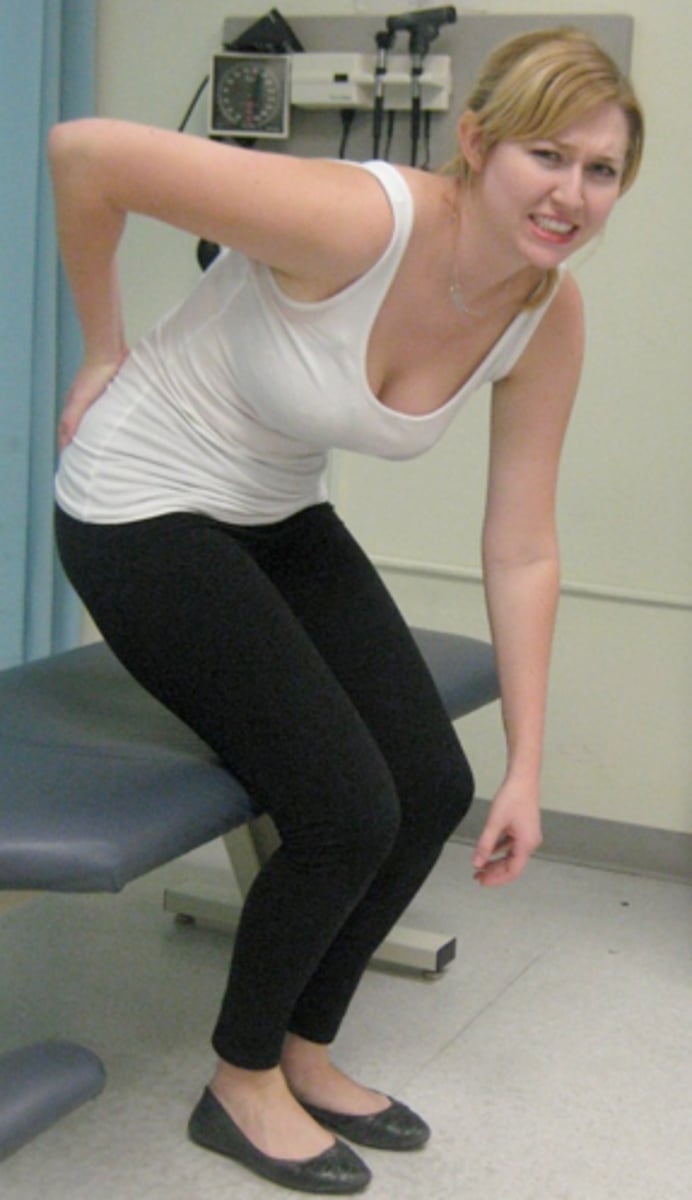
Minor's Sign
Ask patient to rise from a seated position.
Positive: support body with good side -> sciatica
Kemp's Test
Patient seated. Doctor rotates patient's trunk and laterally bends towards and then away from affected side.
Positive: Sciatica pain in involved side -> Disc
Local pain -> Facet
Heel Walk
minimum of 7 steps
Patient walks on heels
DOCTOR WALKS WITH PATIENT (in case they fall).
Positive: unable to perform -> L5 lesion
Toe Walk
minimum of 7 steps
Patient walks on toes
DOCTOR WALKS WITH PATIENT (in case they fall).
Positive: unable to perform -> S1 lesion
Belt Test AKA
Supported Adam's Test
Belt Test
1) Patient bend forward (note when pain occurs)
2) Doctor applies L-M pressure on SI joints and patient bends forward again
Positive: Pain in 1 & 2 -> Lumbar lesion
Pain in only 1 -> SI joint lesion
Stork Test
Patient stands making a yoga tree pose. Extends.
Positive: Pain -> Spondy or SI lesion
Gaenslen's Test
Patient supine with involved side near exam table edge. The opposite knee and thigh are fully flexed against abdomen of patient. Involved leg is slowly lowered off table by Doctor. The Doctor then applies downward pressure against clasped knee and extended hip.
Positive: SI pain -> SI lesion
Lewin-Gaenslen's Test
Patient lie on unaffected side and pulls (table contacting) lower knee to chest. Doctor stabilizes pelvis and hyper extends top thigh.
Positive: SI pain -> SI lesion
Iliac Compression
Patient lies on unaffected side. Doctor contacts upper iliac crest and exerts downward pressure.
Positive: SI pain -> SI lesion
Hip Abduction Stress Test (KNOW)
Patient lies on unaffected side. Patient actively abducts top leg and the doctor exert downward pressure on proximal to knee.
Positive:
Pain at PSIS -> SI lesion
Weakness ->Glut Med weakness
Femoral Nerve Traction Test (KNOW)
Patient lies on unaffected side. Patient extends knee and Doctor brings hip to 15degrees of extension...if no pain, increase extension and flex knee.
Positive: Pain in anterior thigh -> L2, L3, L4 N. root lesion
Hibbs Test
Patient is prone. Doctor stabilizes hip on side she is standing. Doctor take opposite ankle and flexes knee to 90degrees. Doctor slowly pushes leg laterally away producing internal rotation of the hip.
Positive: SI pain -> SI joint lesion
Nachlas Test
Pain prone. Heel is approximated to same buttock. Doctor stabilizes hip.
Positive: SI Pain-> SI lesion
Yeoman's Test
Doctor stabilizes SI joint. Flexes affected knee and hyperextends the thigh by lifting leg off the table.
Positive SI pain -> SI lesion
Prone Hyperextension Test (KNOW)
Patient is prone. Doctor stabilizes the lumbosacral area. Doctor lifts legs while the knee remains extended.
Positive: Localized lumbar pain with anterior thigh pain -> L3, L4 N root lesion
Patrick's Test AKA
Fabere's Test
Patrick Fabere
Patient is supine. Thigh is flexed, abducted and externally rotated and extended with downward pressure is placed on the opposite ASIS and same knee.
Positive: pain in hip -> hip lesion
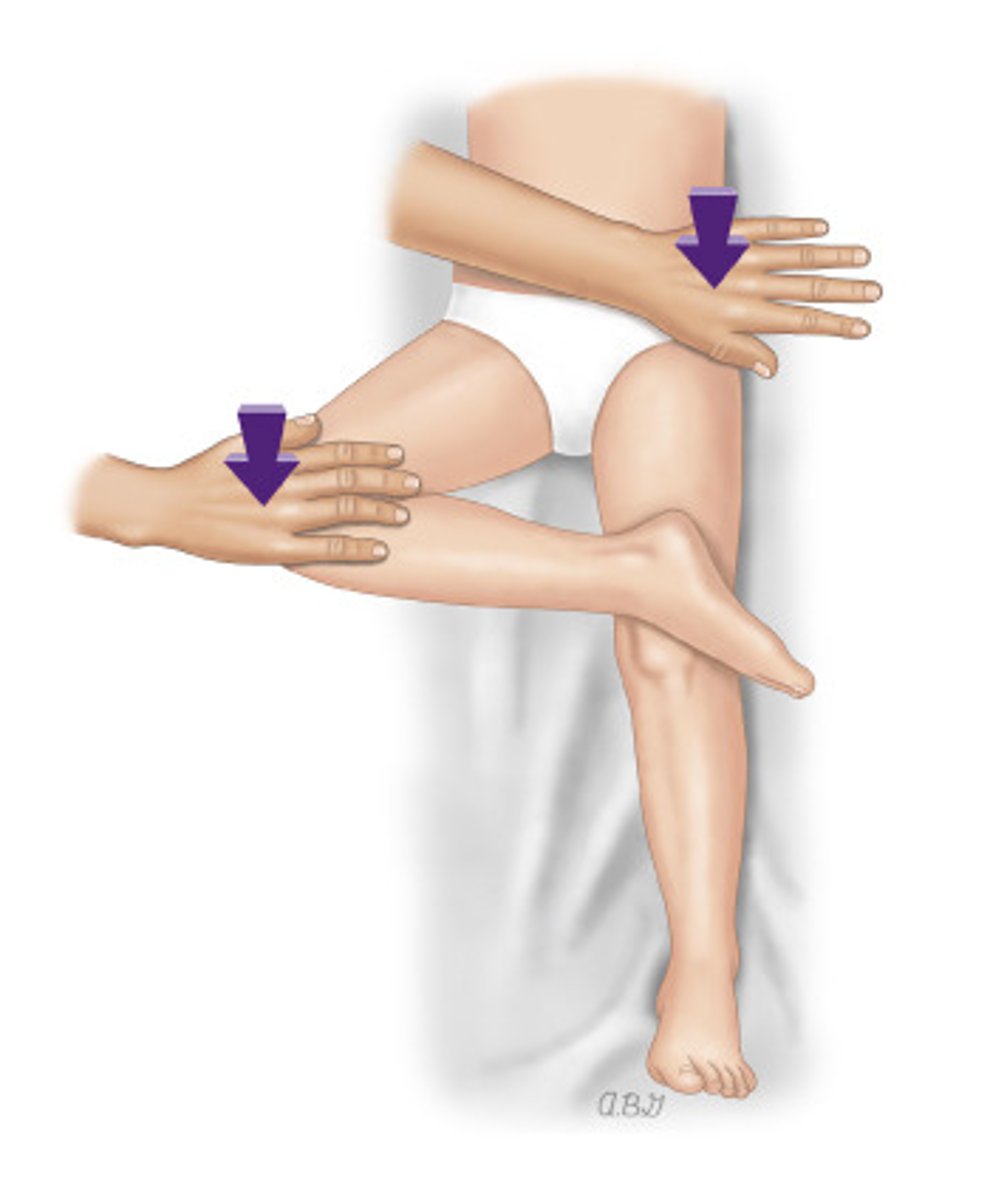
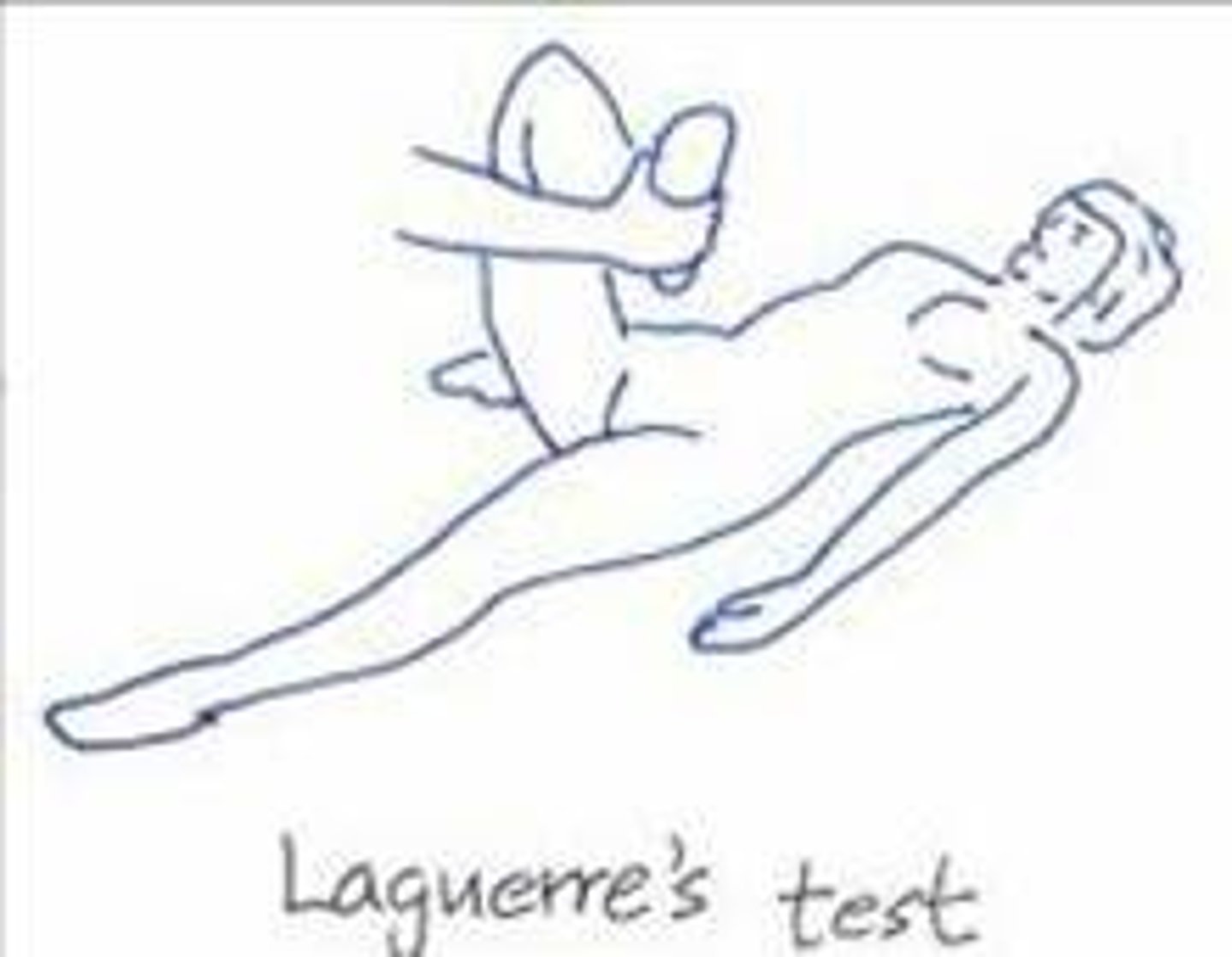
Laguerre's Test
Patient is supine. Doctor flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates hip. Doctor than applies pressure over the opposite ASIS with one hand and other hand on knee.
Positive: pain in hip -> hip lesion
Thomas Test
Patient is supine. Thigh is flexed with the knee bent upon the abdomen.
Positive: Opposite thigh/knee rises off the table -> Hip flexure contracture
Anvil Test
Patient is supine. Doctor raises leg and strikes the heel with their fist.
Positive: pain in the hip -> hip pathology or fracture
Ely's Sign
Patient prone. Heel to buttock.
Postitive: hip elevated -> Hip flexor contracture
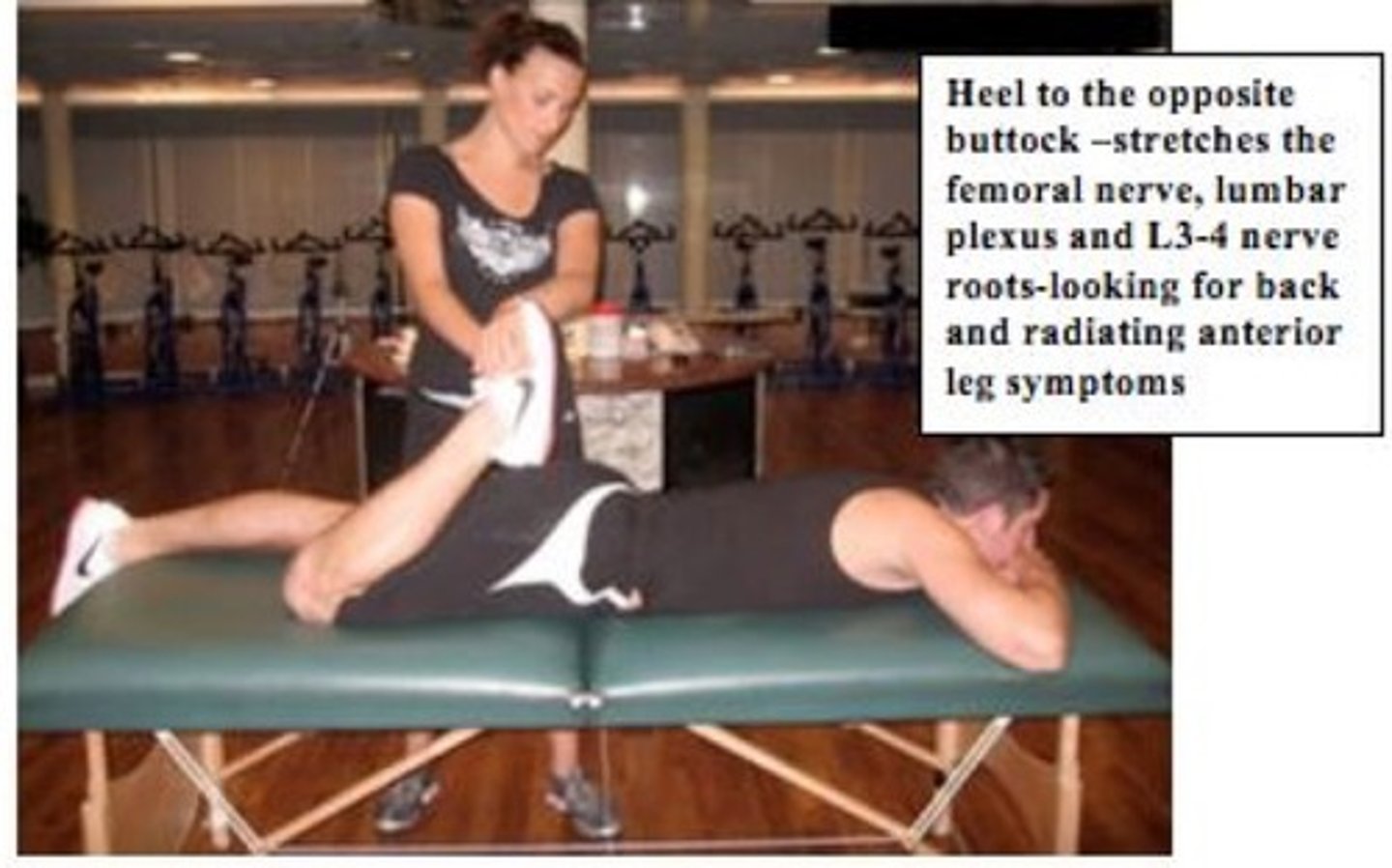
Ely's Test
Patient prone. Heel to opposite buttock.
Positive: Pain -> Hip Lesion
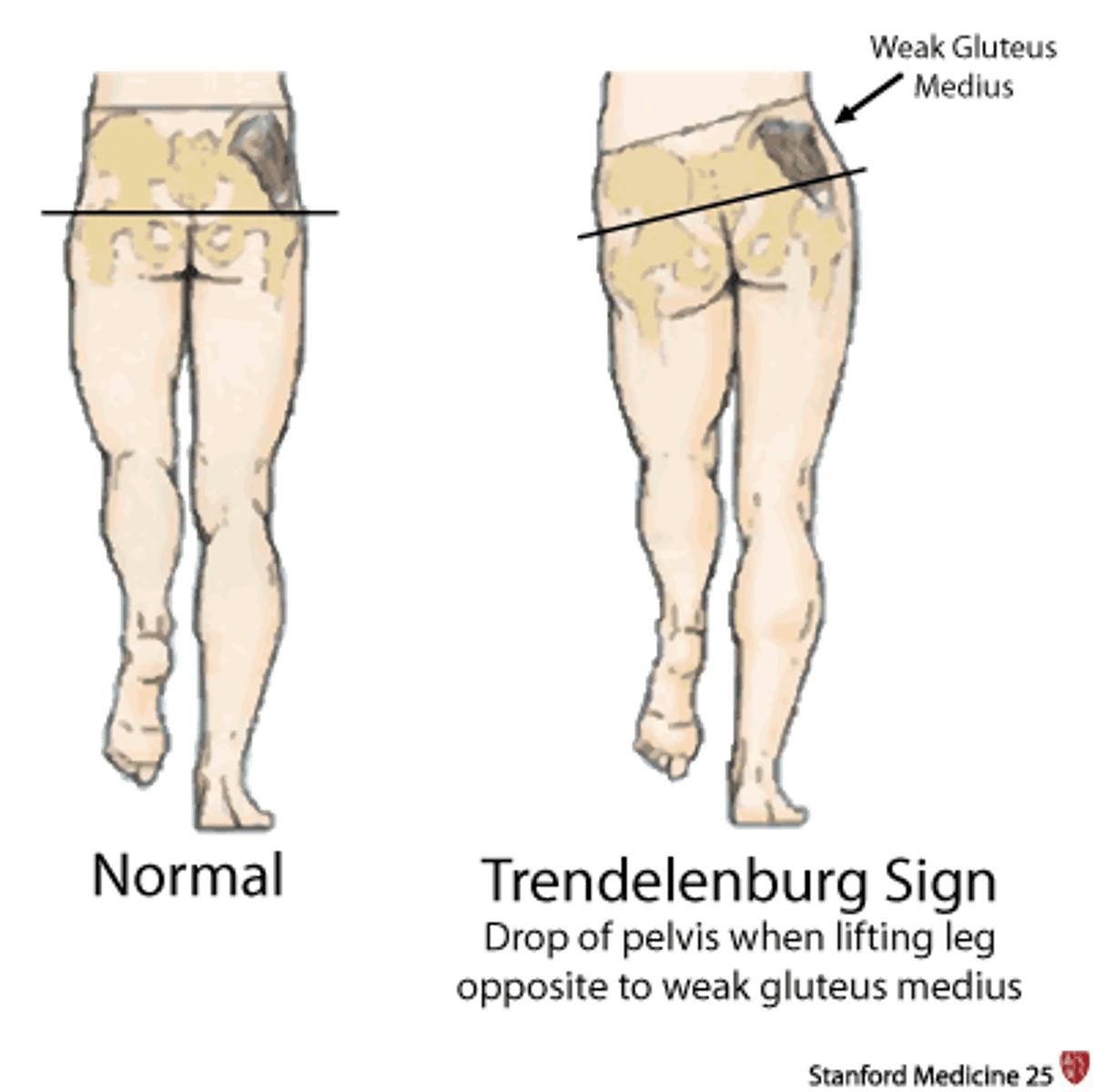
Trendelenburg's Test
Patient is standing and lifts on leg.
Positive: Hip falls on side that is lifted -> glut med weakness on standing side
Neri's Sign
Standing patient bends forward at waist.
Positive: Knee buckles -> Tight hamstrings
Lewin-Gaenslen's Test (KNOW)