Genetics and Evolution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
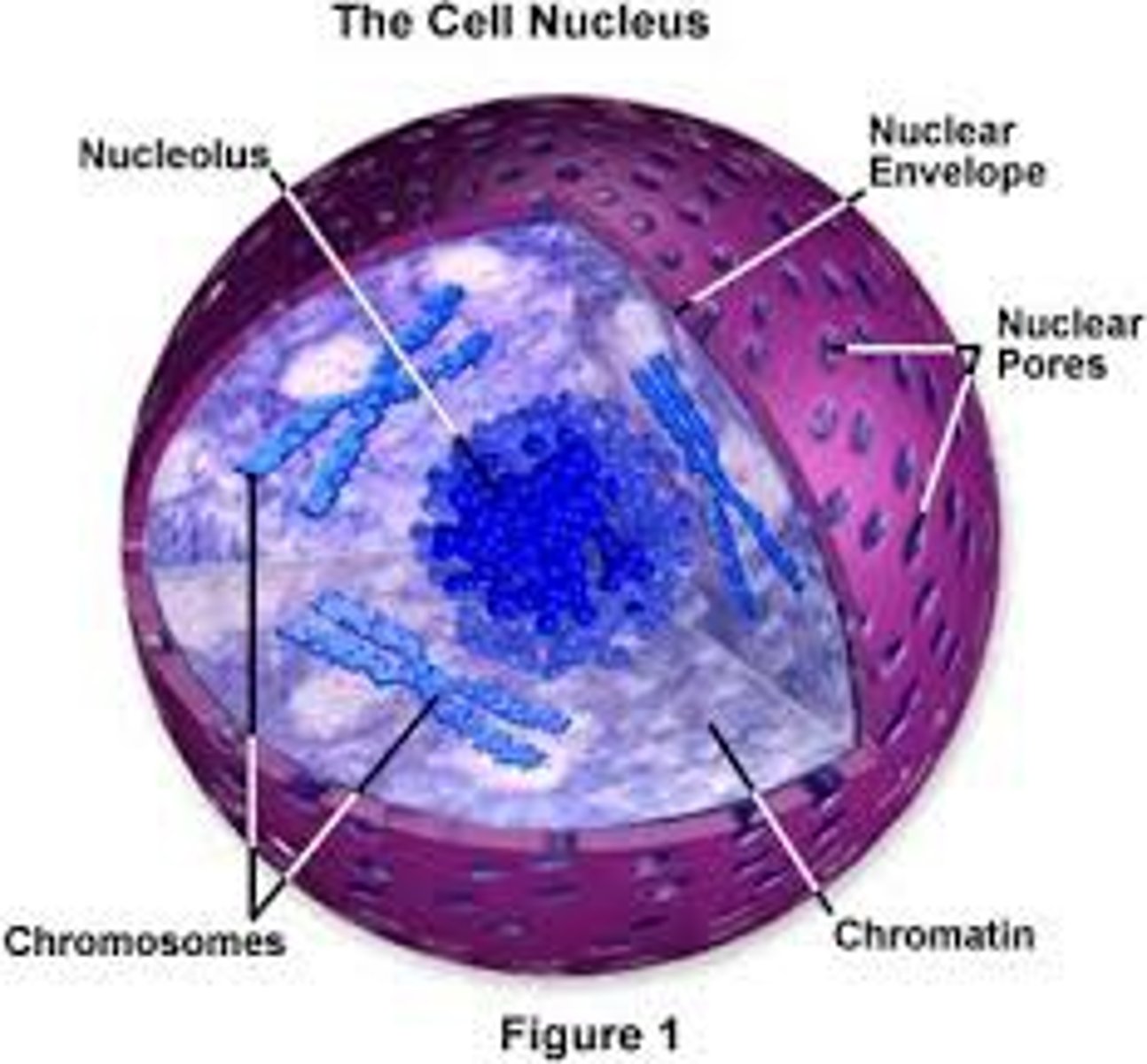
Nucleus
Location where genetic information is stored, located in the center of the cell
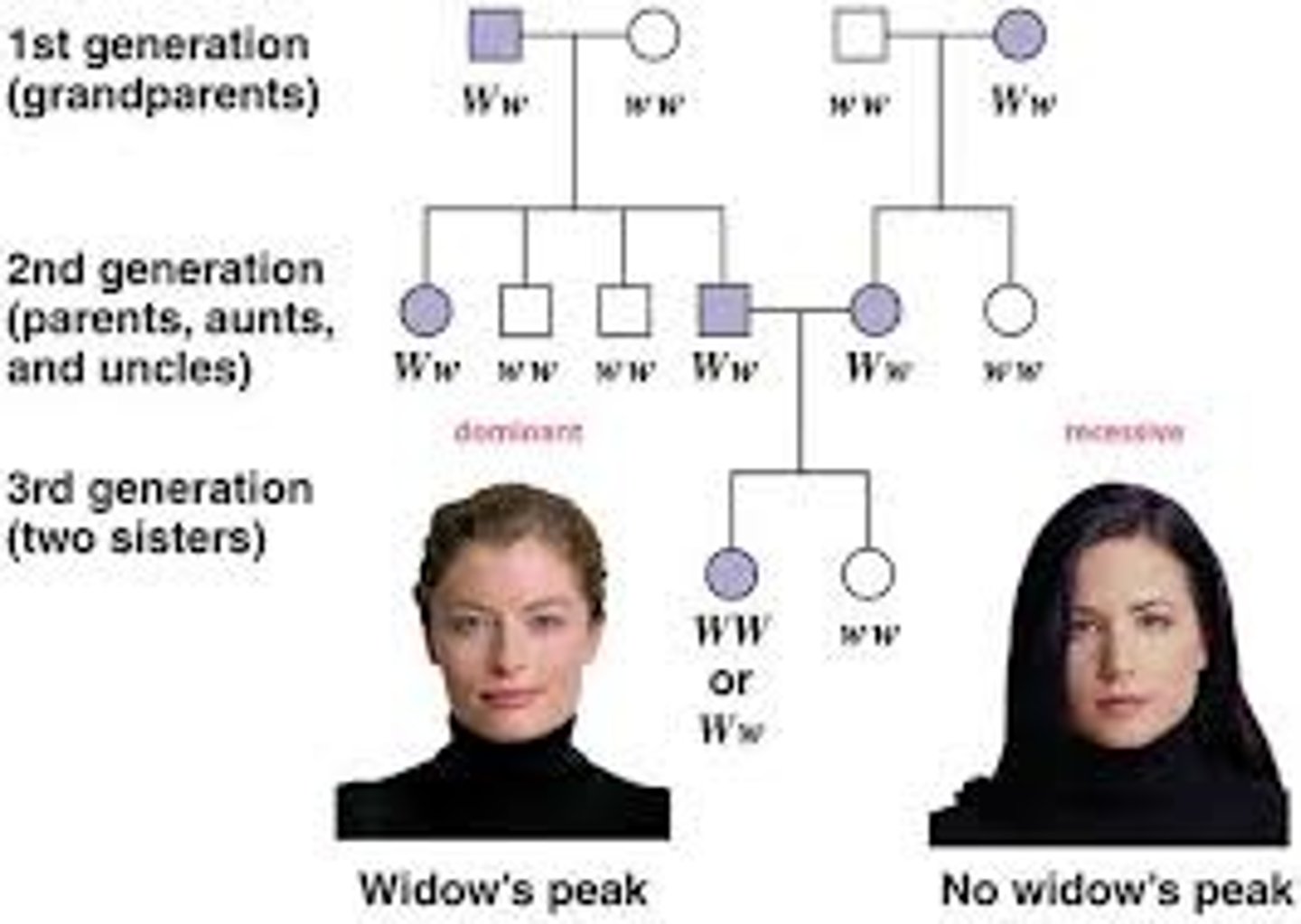
Inheritance
The passing of traits from one generation to the next
Heredity
Passing of features from generation to generation
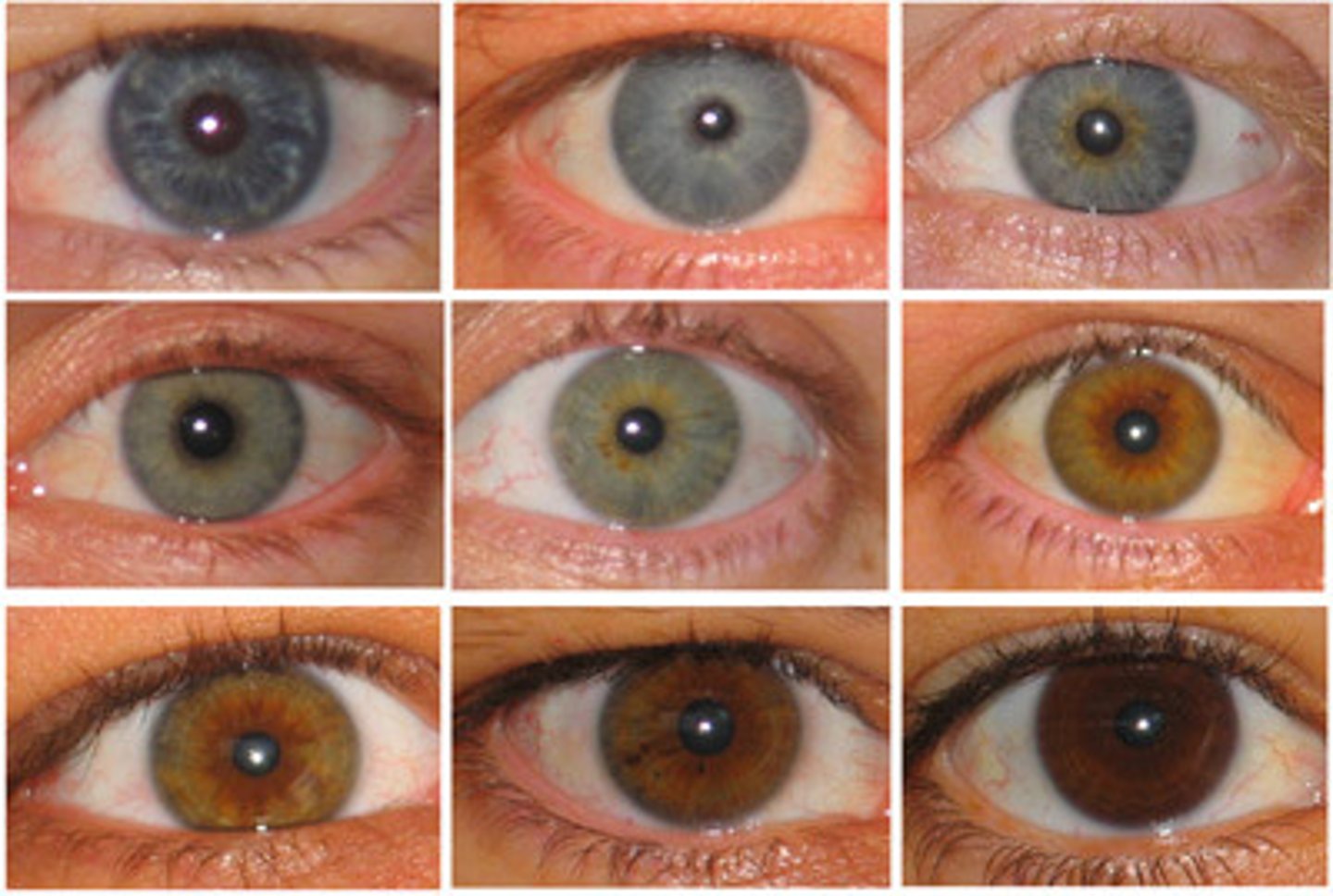
Trait
The way a feature is expressed in an individual
Gene
the basic unit of heredity carried by the chromosome
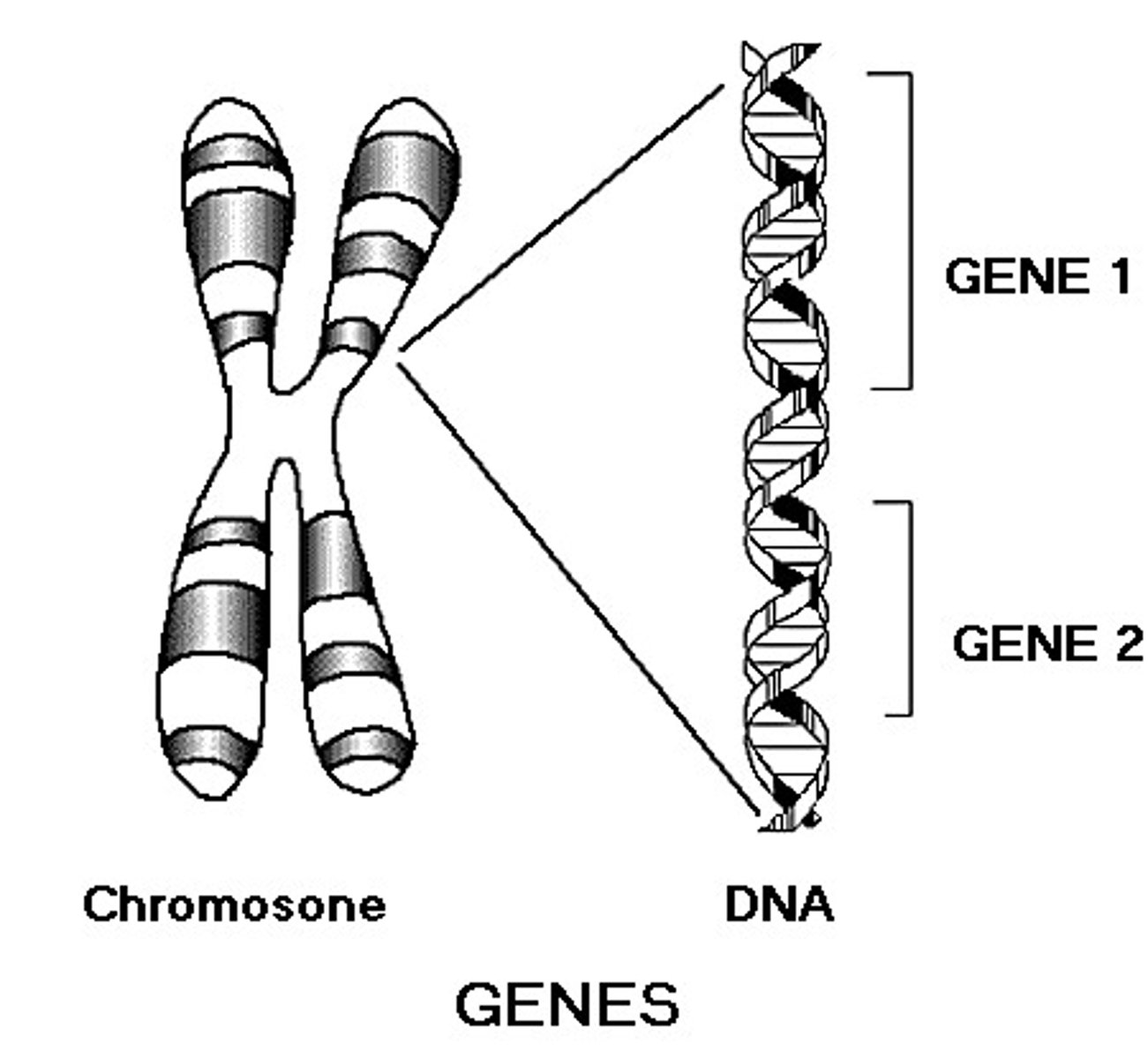
Chromosome
structures that carry heredity information to the next generation. Coiled. DNA found inside the nucleus.
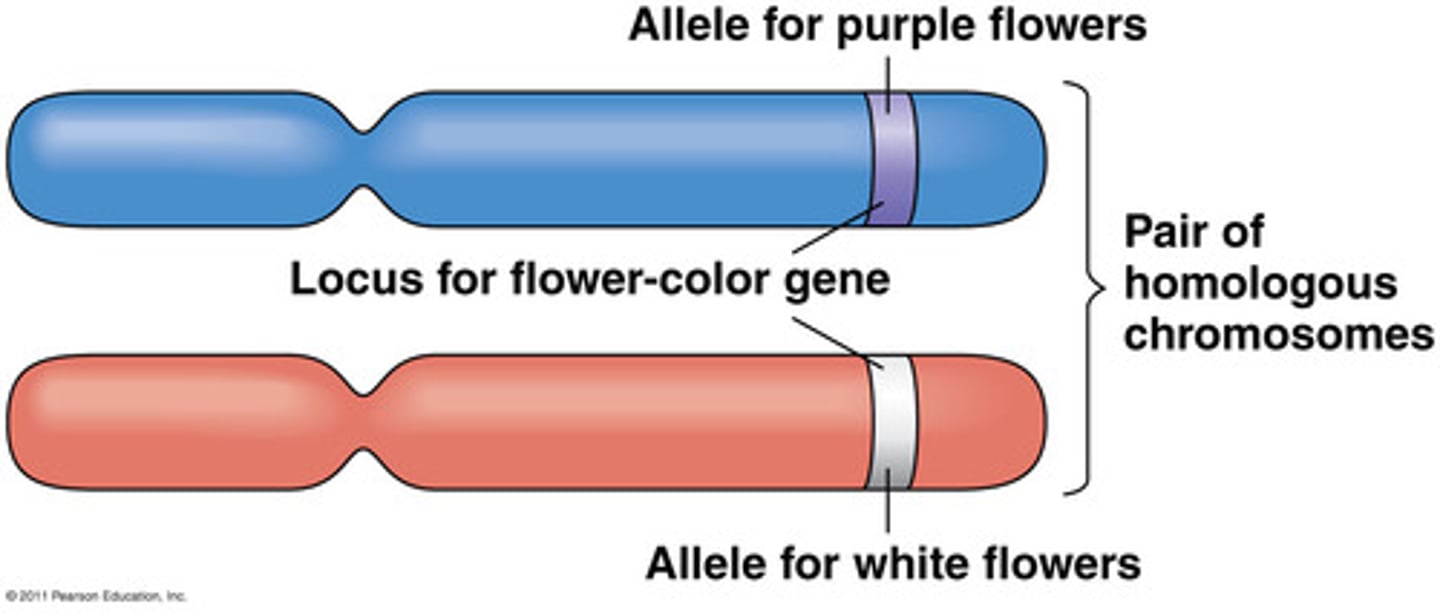
Allele
Variations of genes that determine traits in organisms.
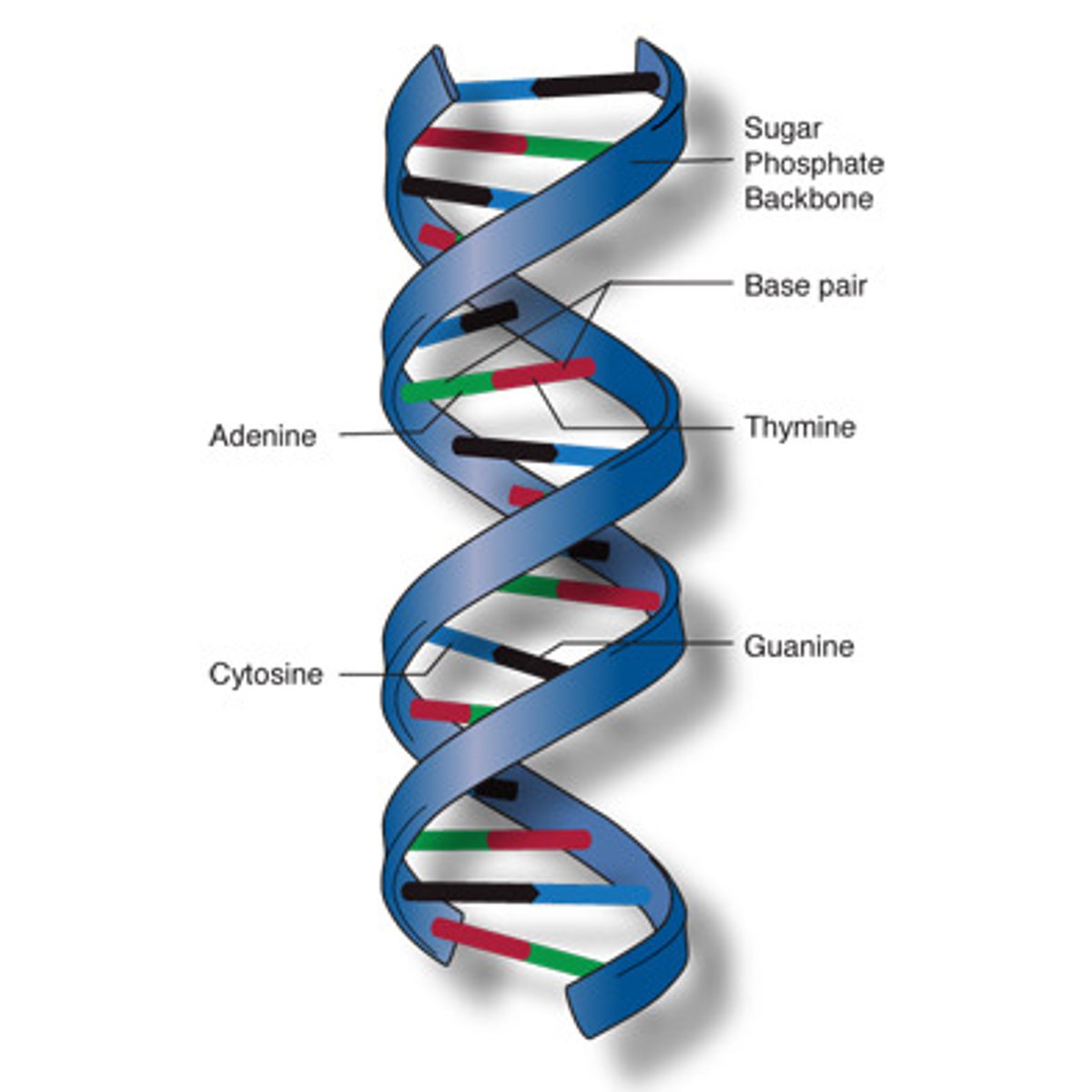
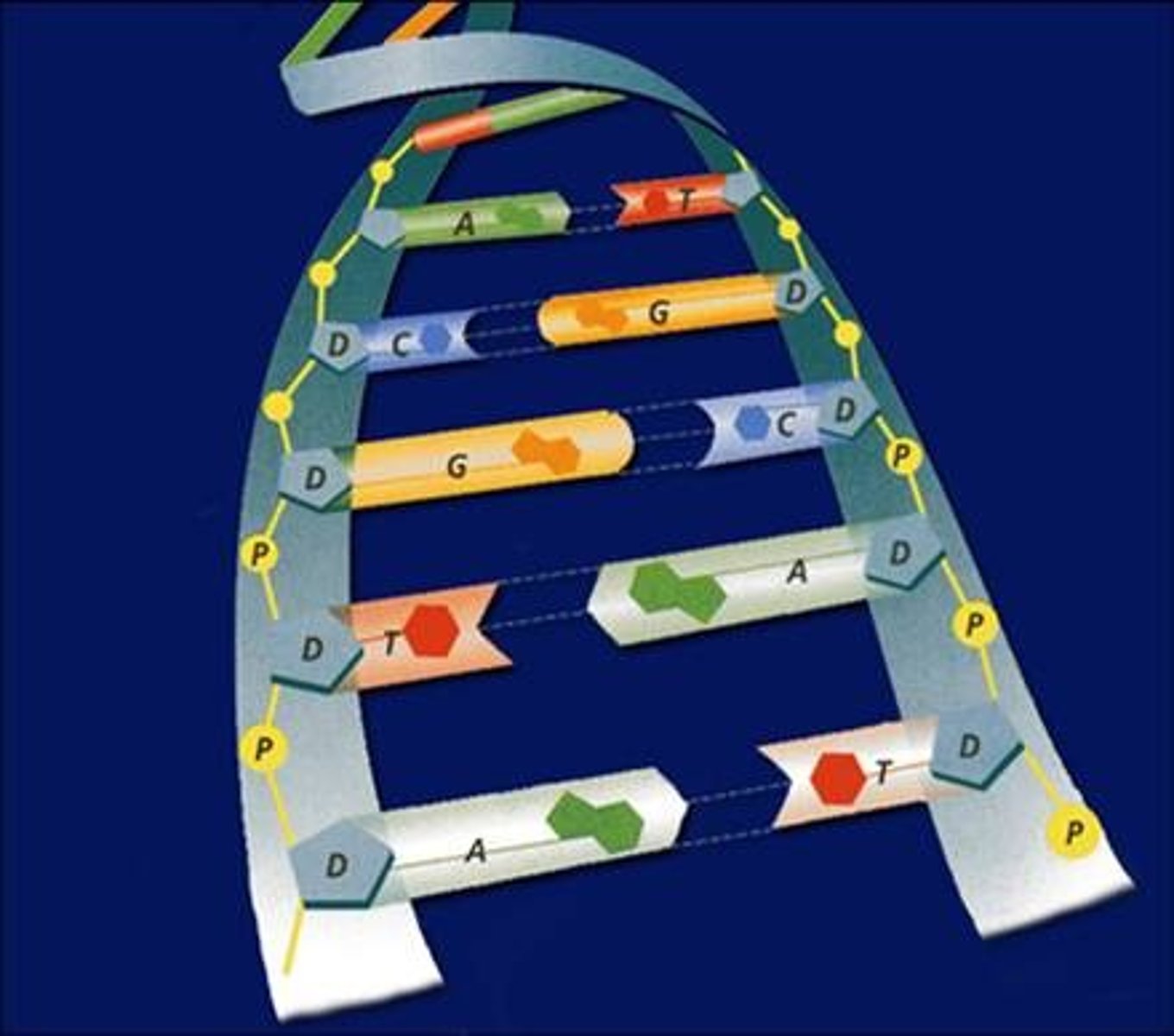
DNA
a long tightly coiled molecule that looks like a twisted ladder inside the cell's nucleus.
Genotype
An organism's particular combination of paired alleles. It is the genetic makeup of an organism.
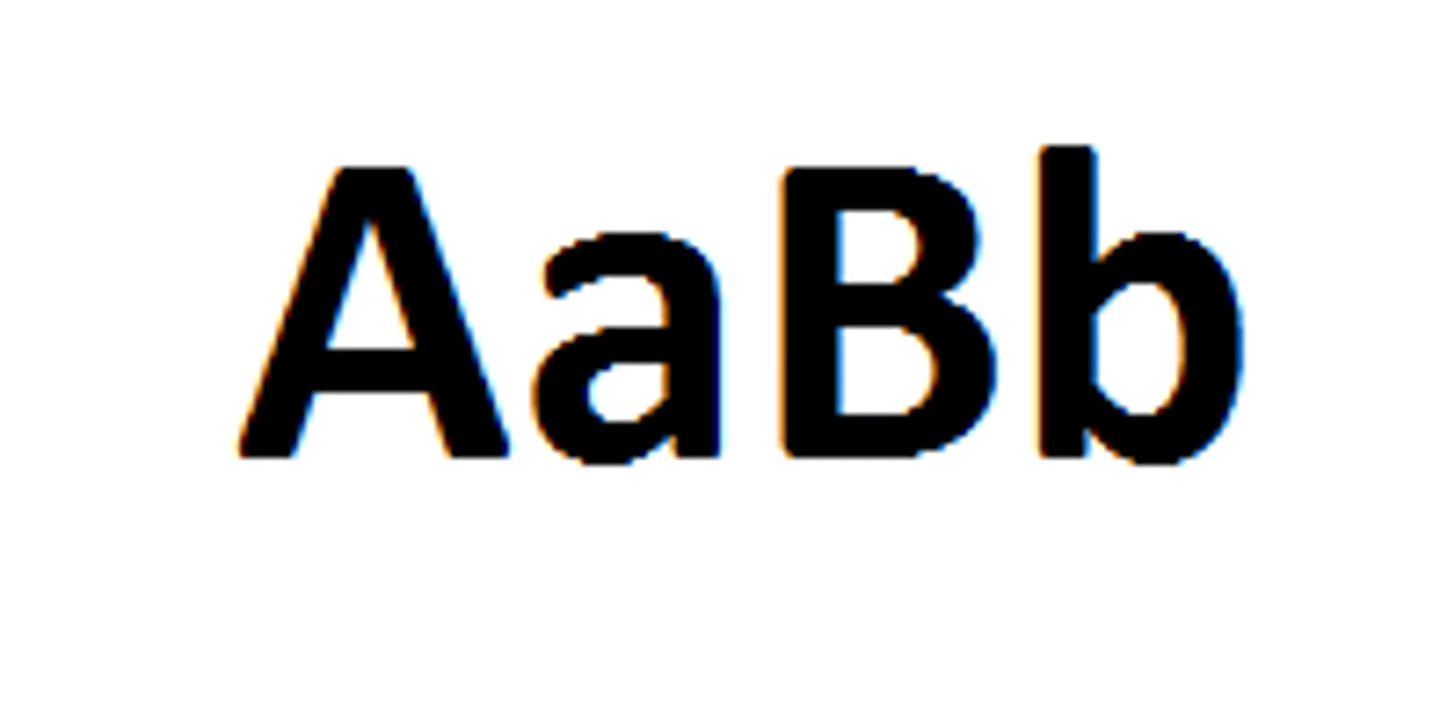
Phenotype
The trait produced by the genotype; the expression of the genes or what the organism looks like.
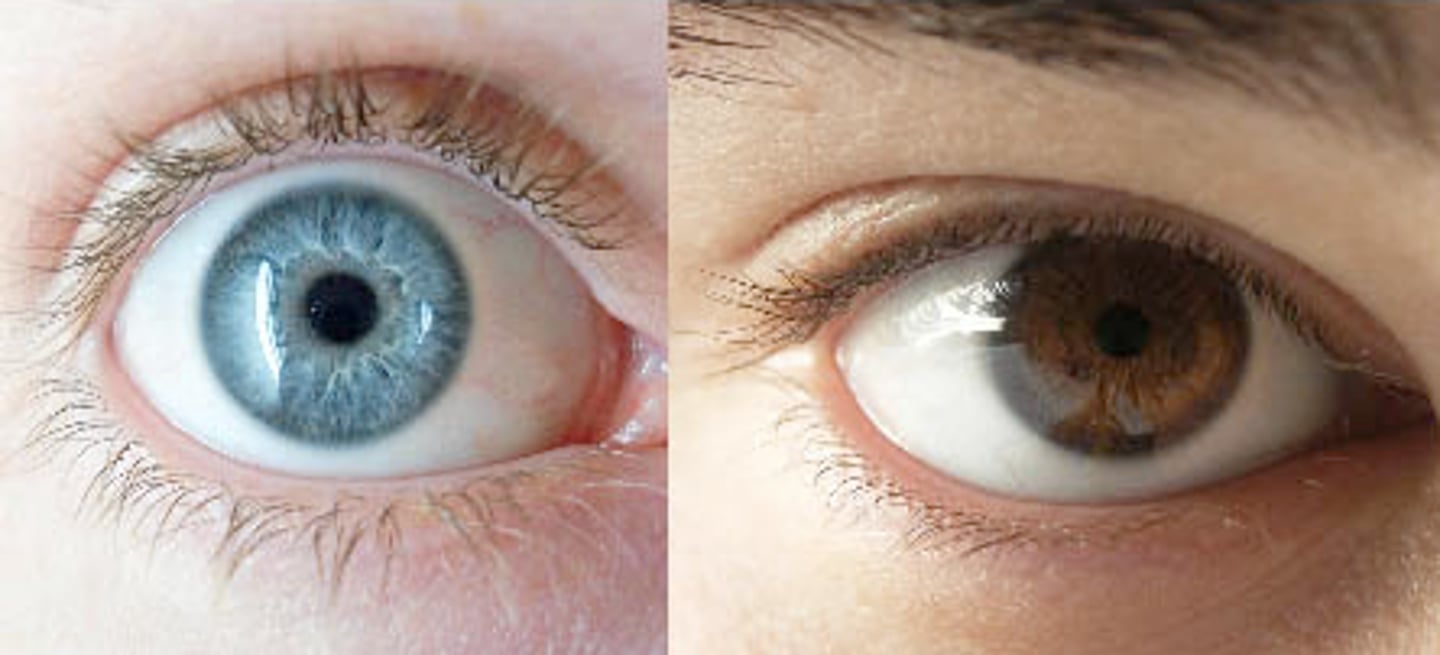
Dominant Trait
A trait that is more likely to appear in the phenotype, hides Recessive Trait

Recessive Trait
A trait that is less likely to appear in the phenotype, hidden by the Dominant Trait
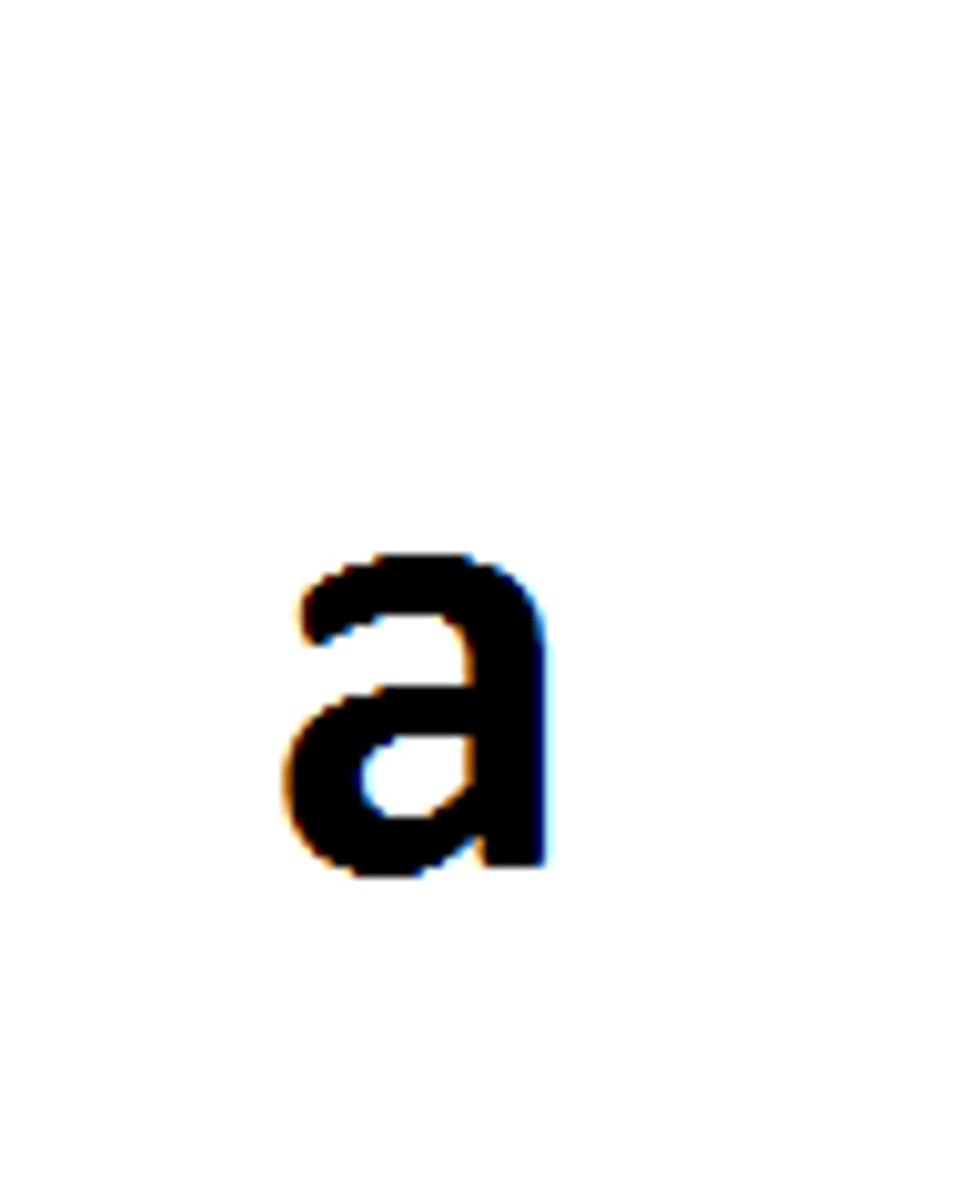
Variation
Any difference between individuals of the same species.
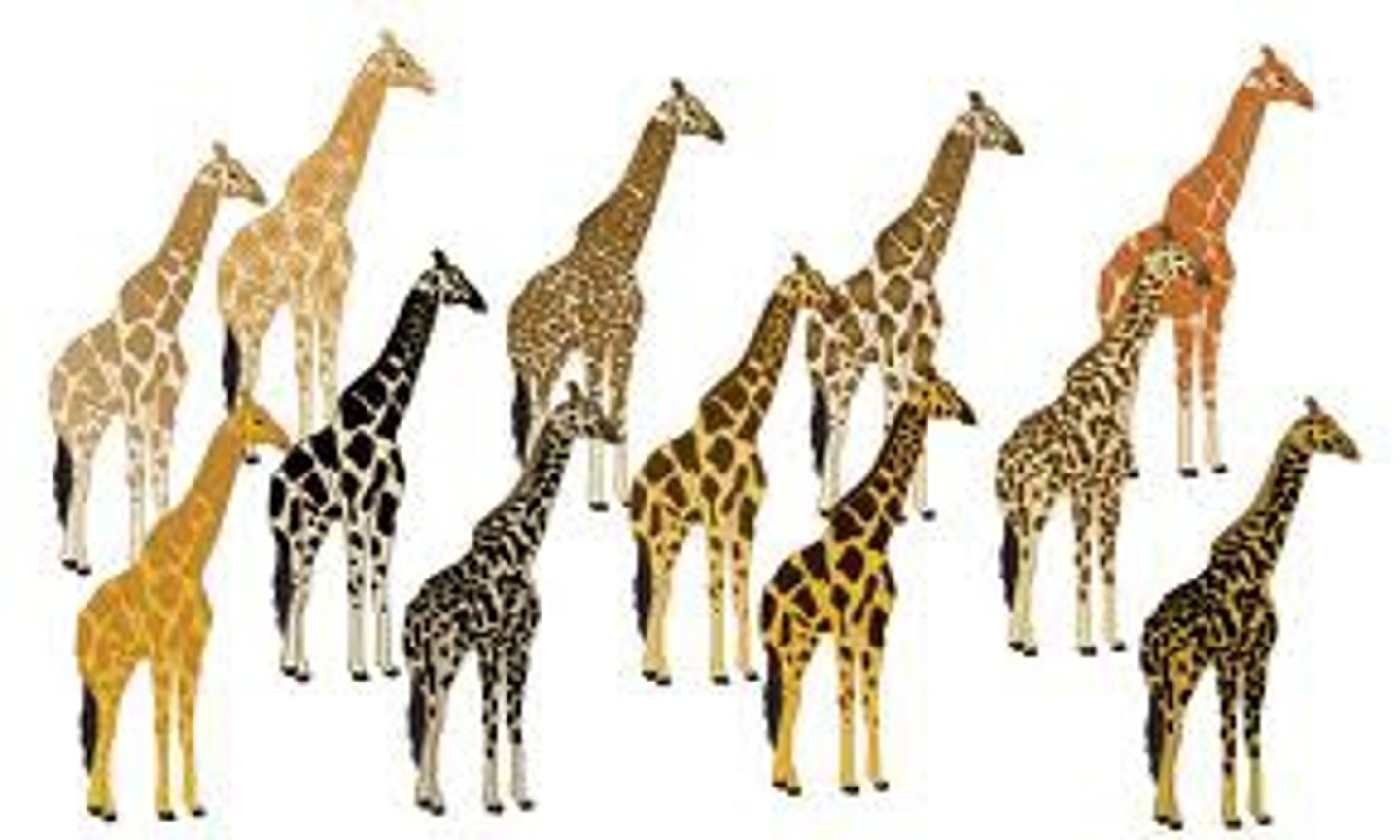

Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene
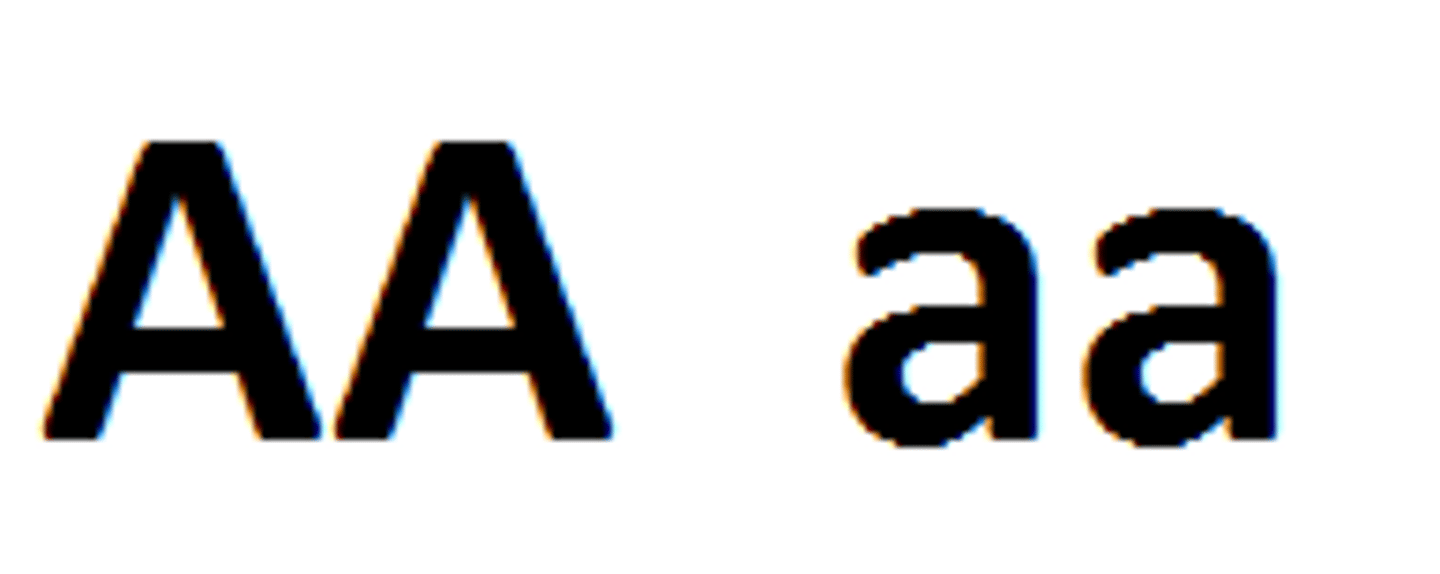
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait

Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce
Gregor Mendel
Discovered the principles of heredity while studying pea plants, Father of Genetics

Watson and Crick
Discovered the structure of DNA

Mitosis
Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
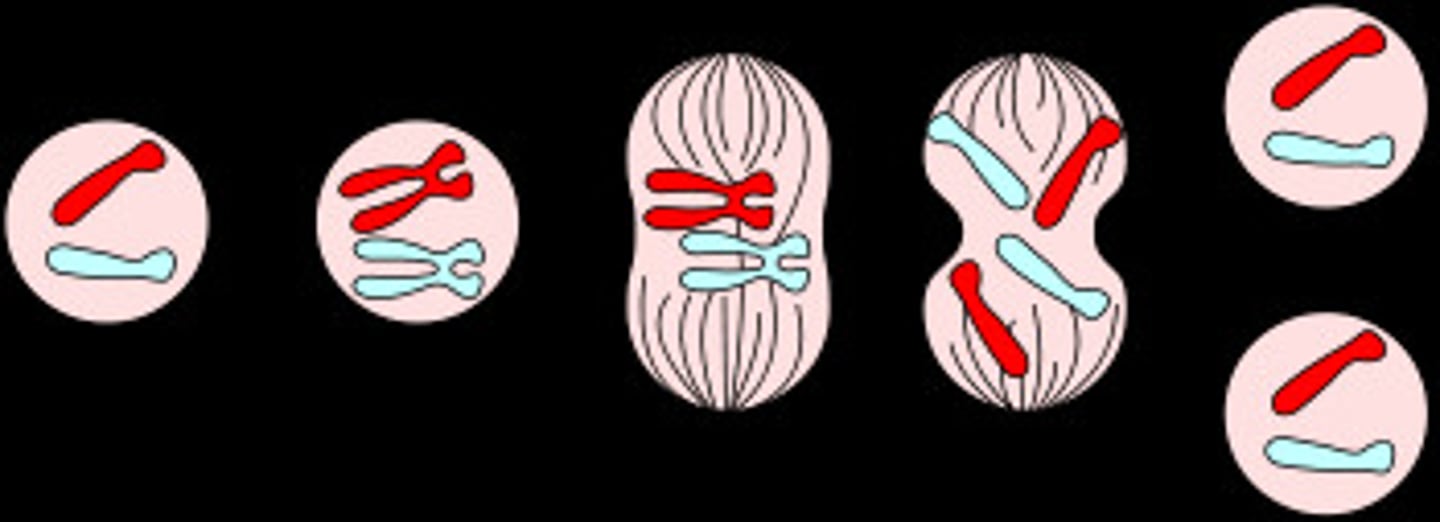
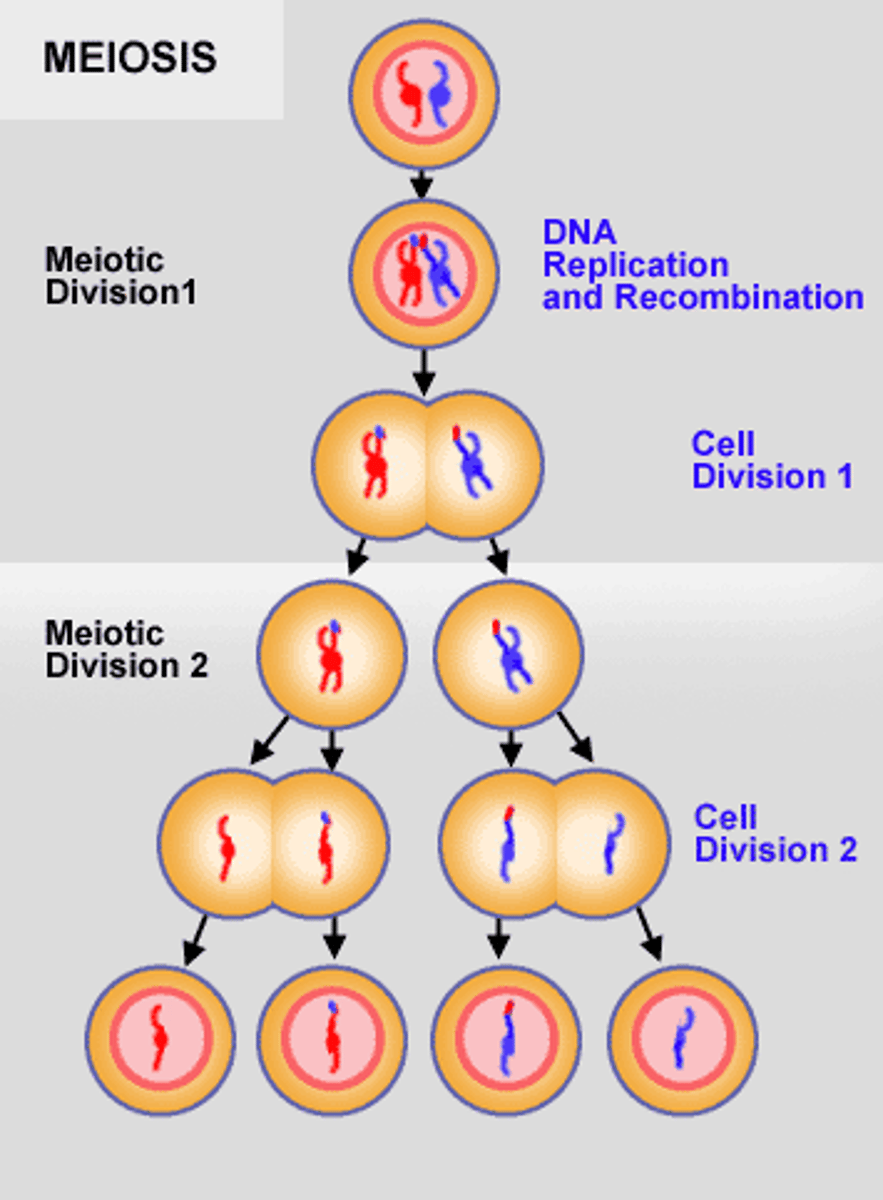
Meiosis
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, more variation.
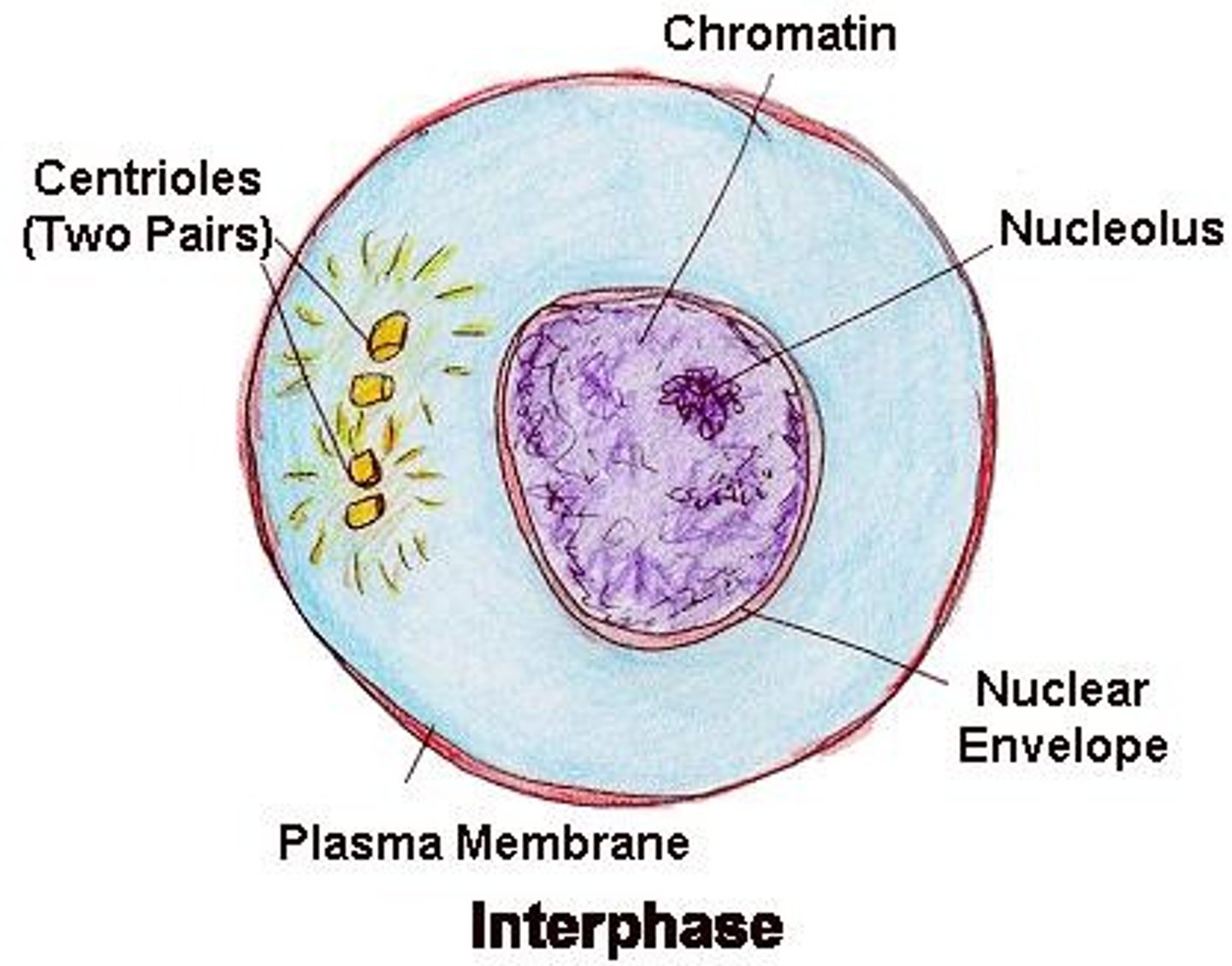
Interphase
Period of the cell cycle between cell divisions in which the cell grows, and DNA is replicated
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelop dissolves.

Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
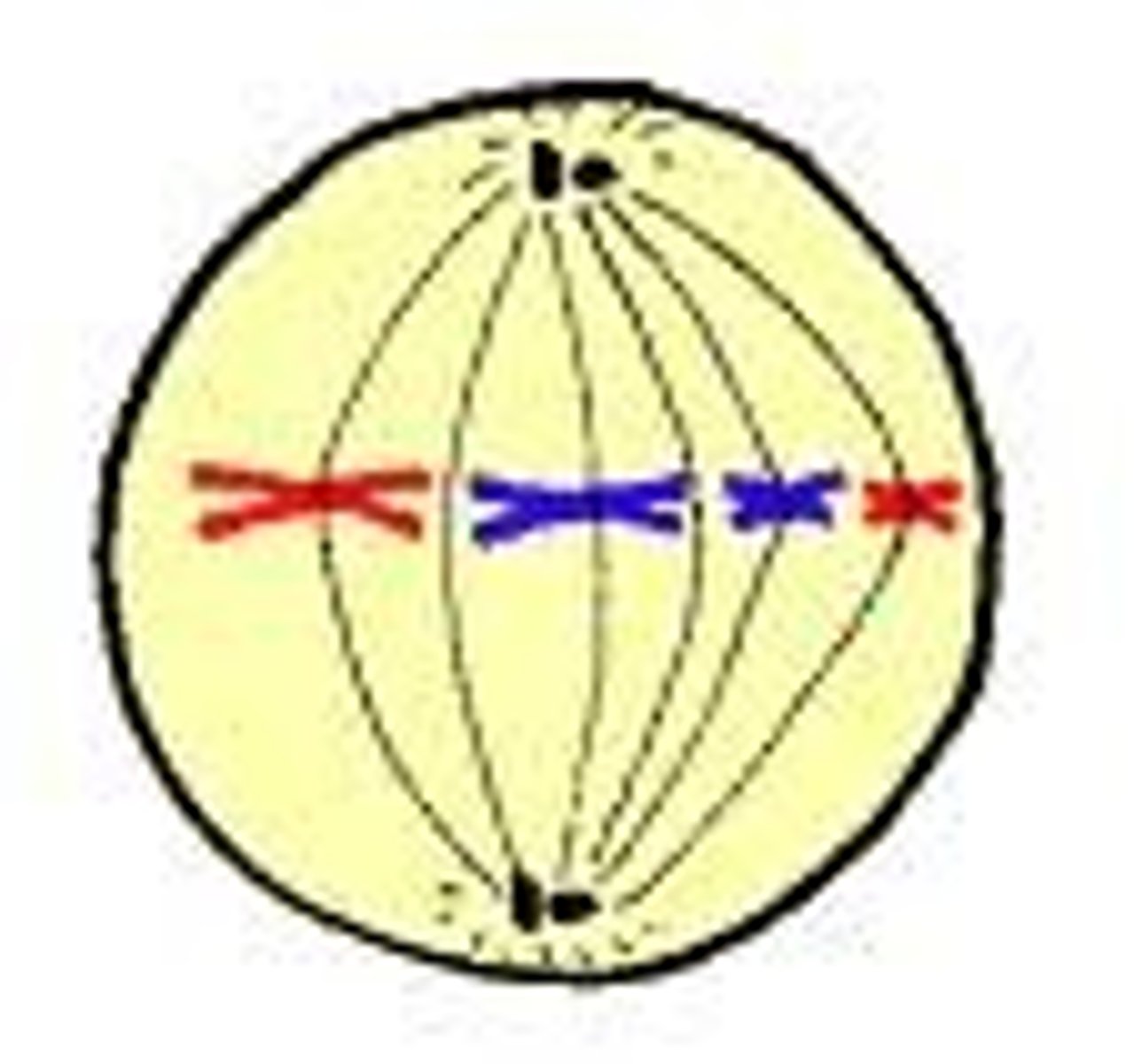
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
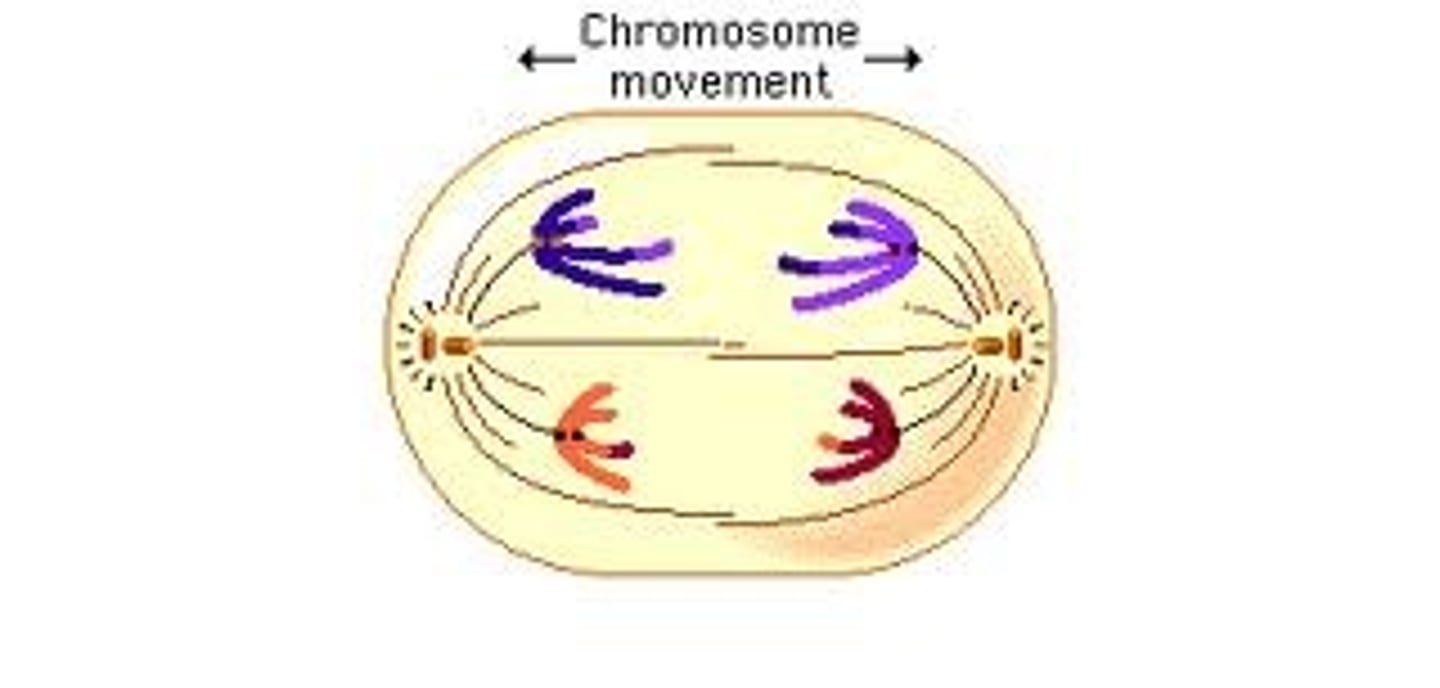
Telophase
New identical nuclei form
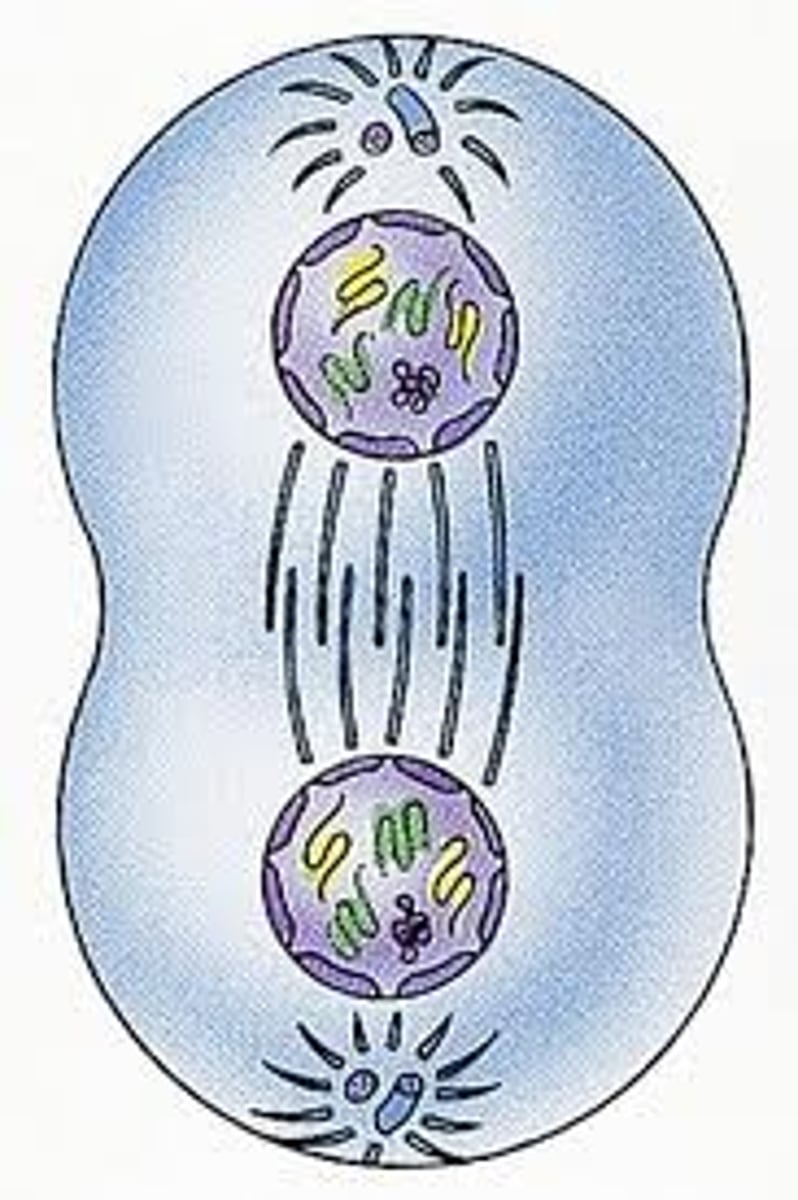
Cytokinesis
Membrane separates cells to form two separate daughter cells
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
The four bases in DNA, A, T, C, and G
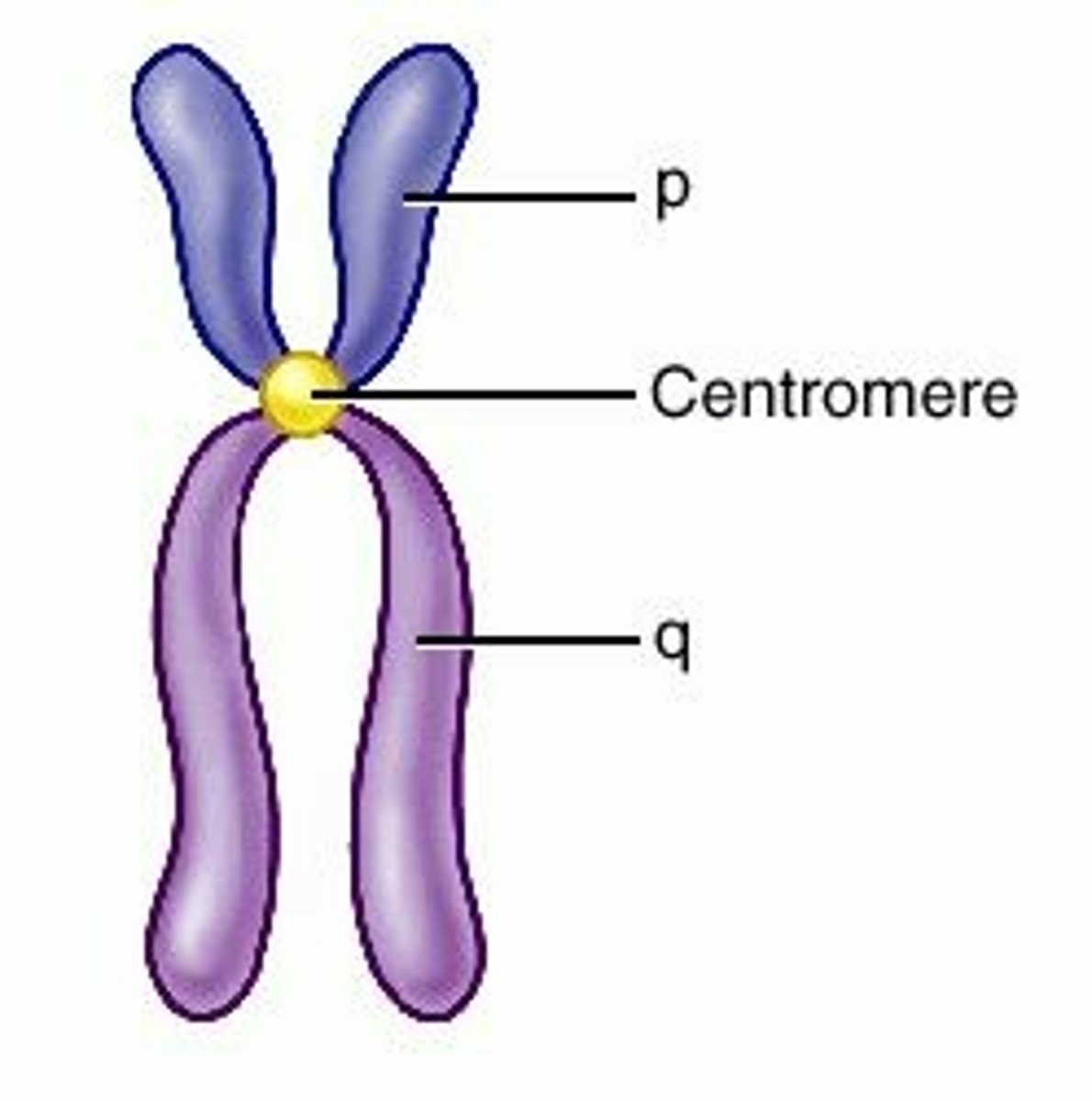
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached, chromosomes are counted by them
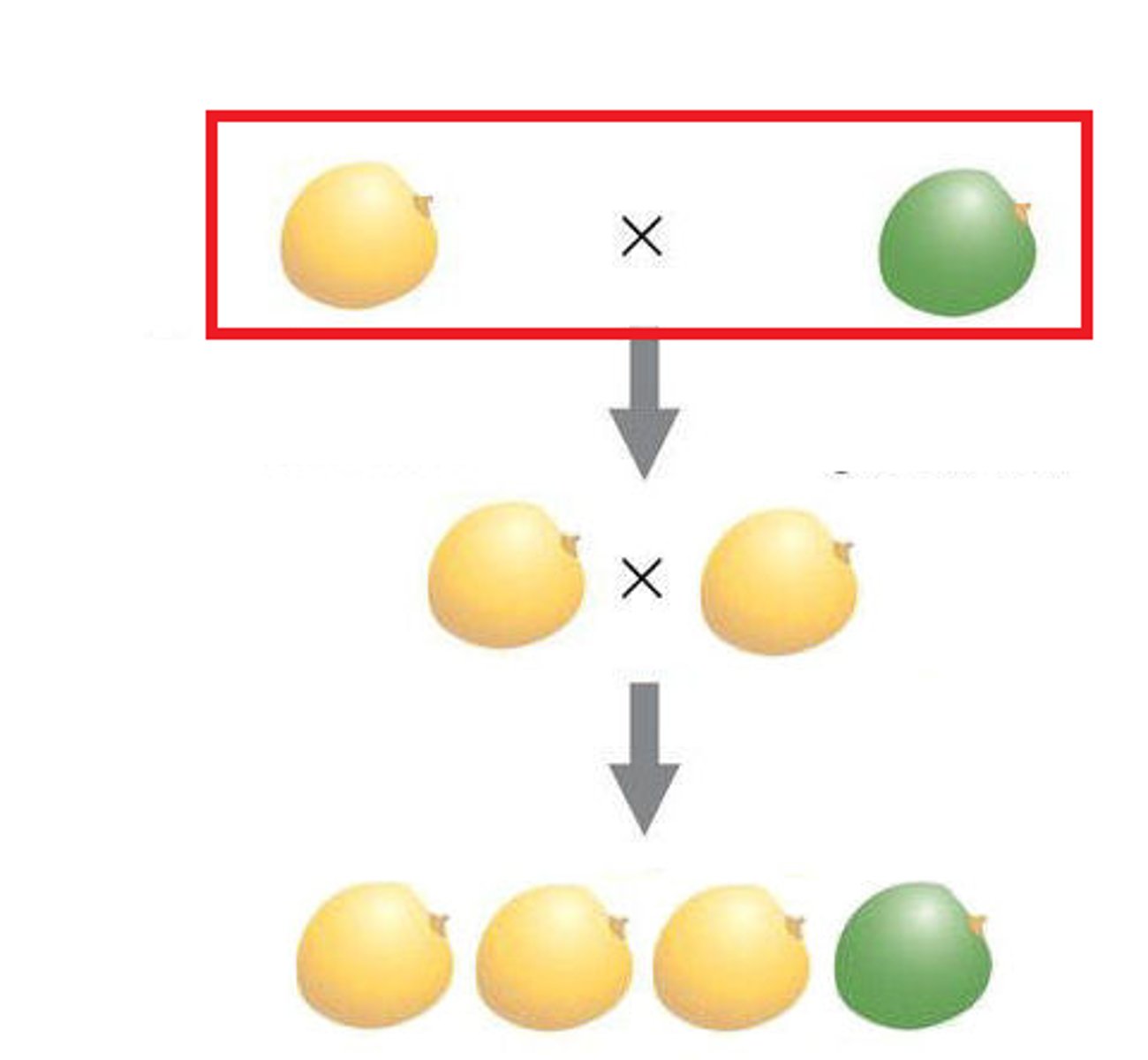
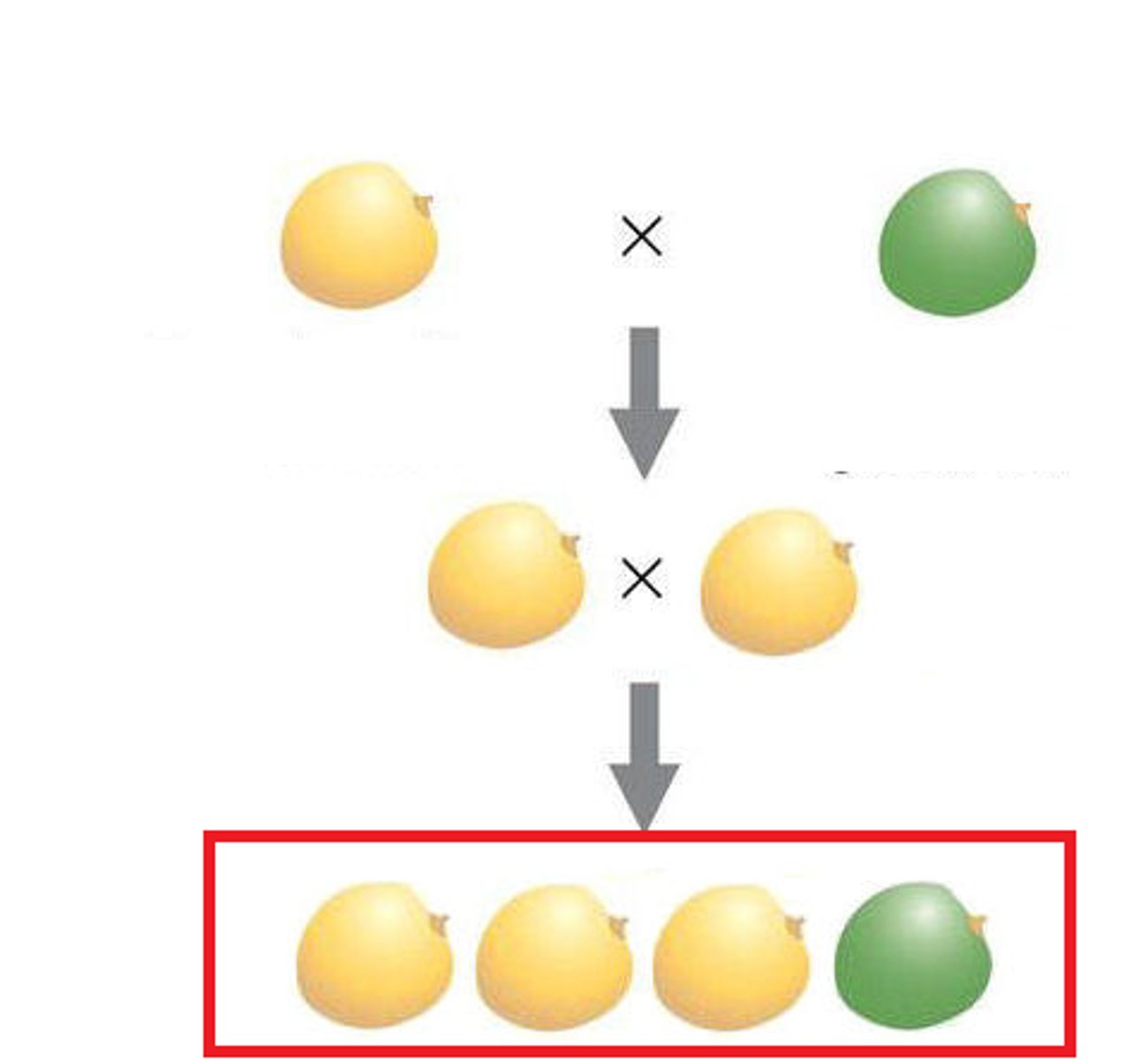
P generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate
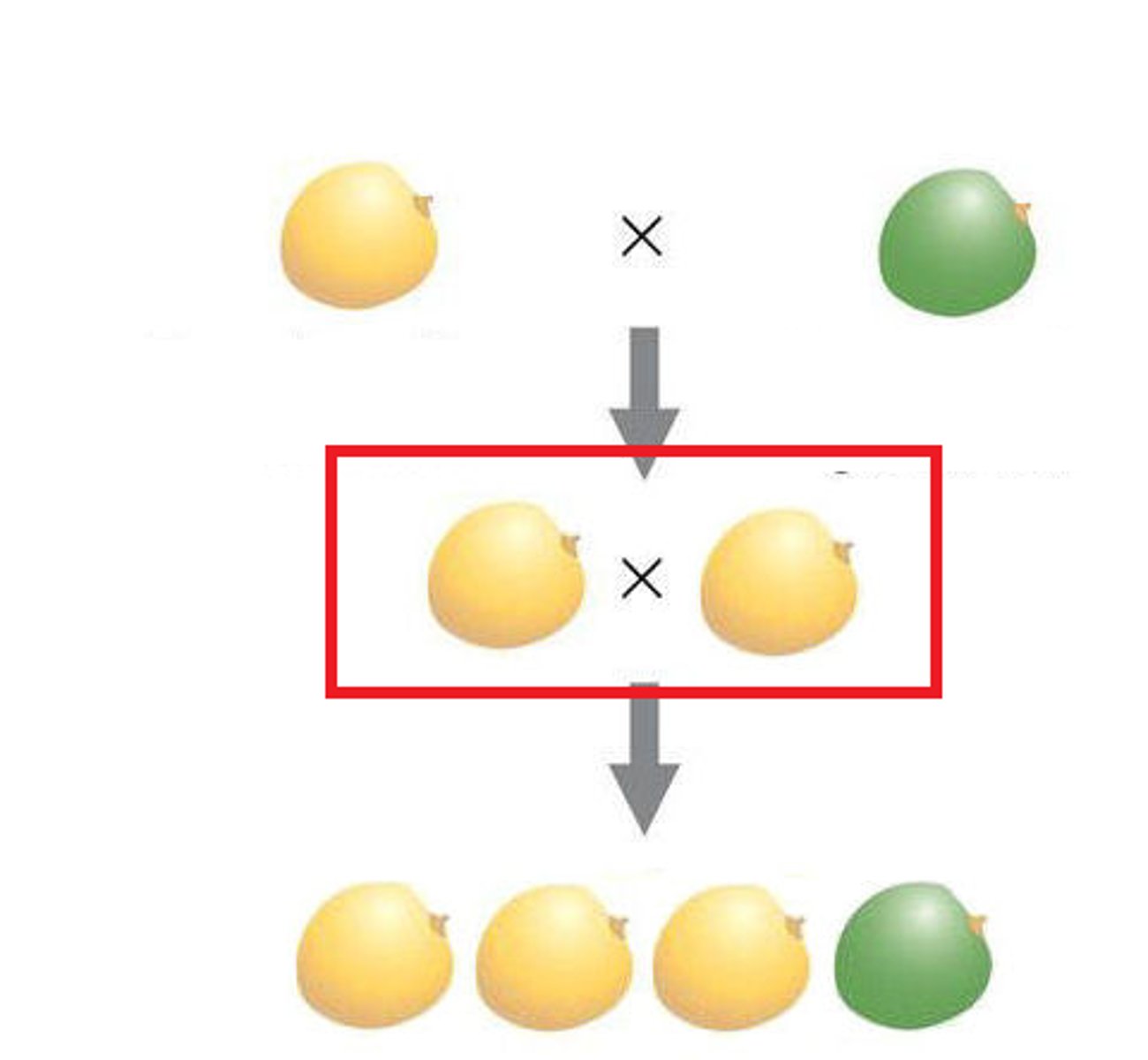
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental breeding of two organisms
F2 generation
Offspring resulting from interbreeding of the hybrid F1 generation.
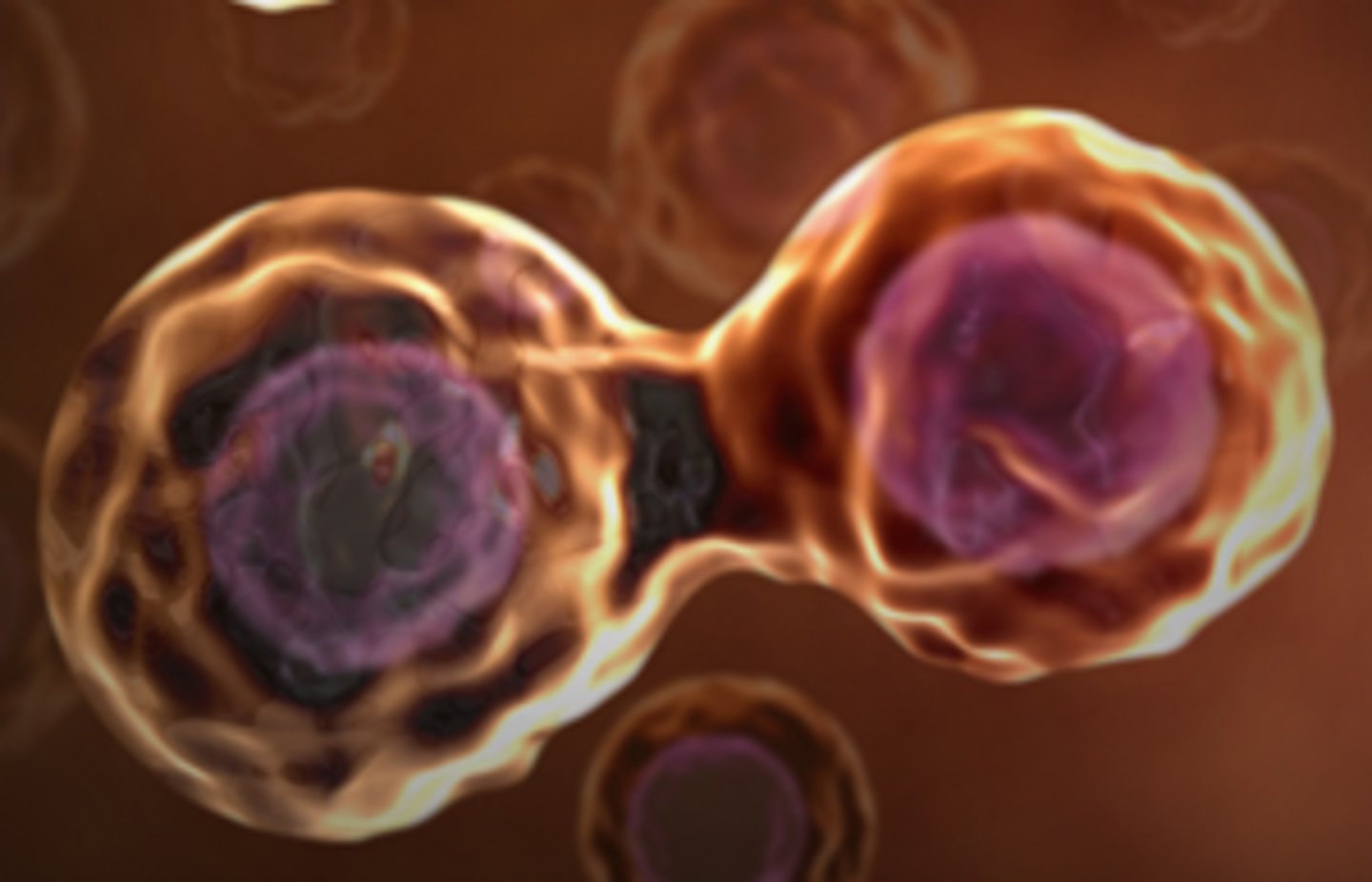
Cell Division
Process by which a cell divides into two new identical daughter cells
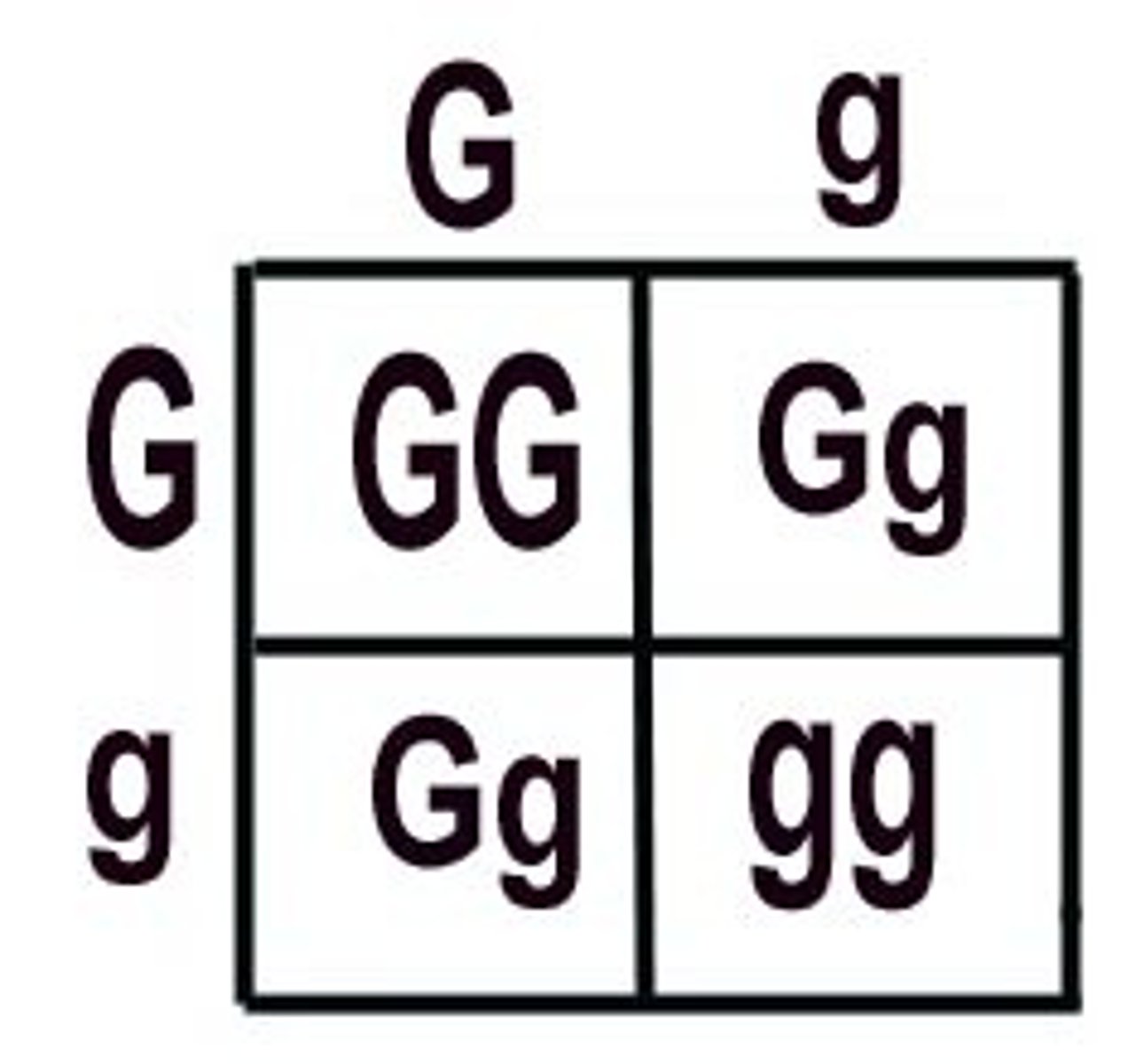
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from reproduction between two given organisms
Mutation
An unexpected alteration in the DNA sequence during replication
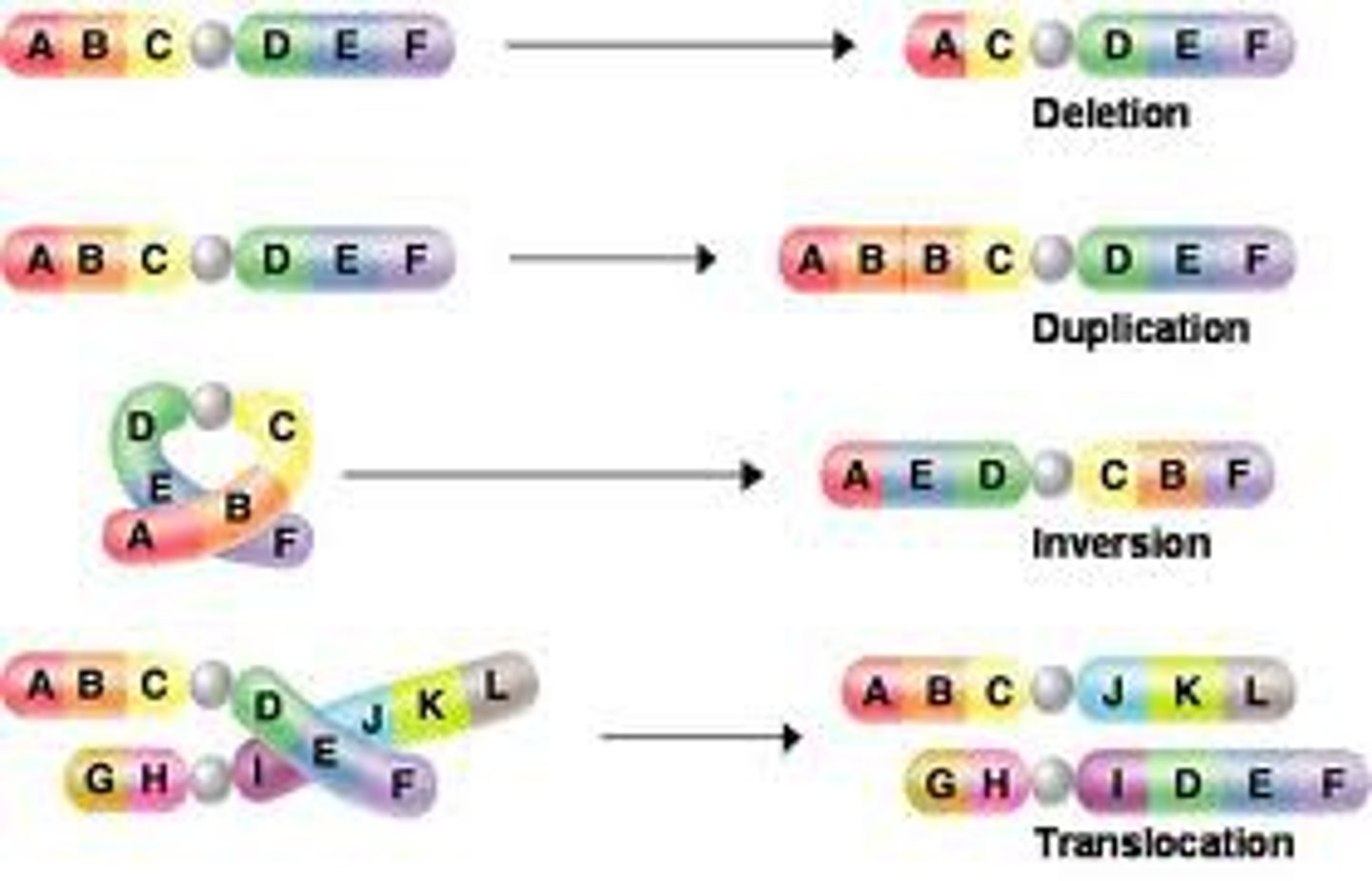
Methods of Mutations
Adding, deletion, or swapping one or more nucleotides
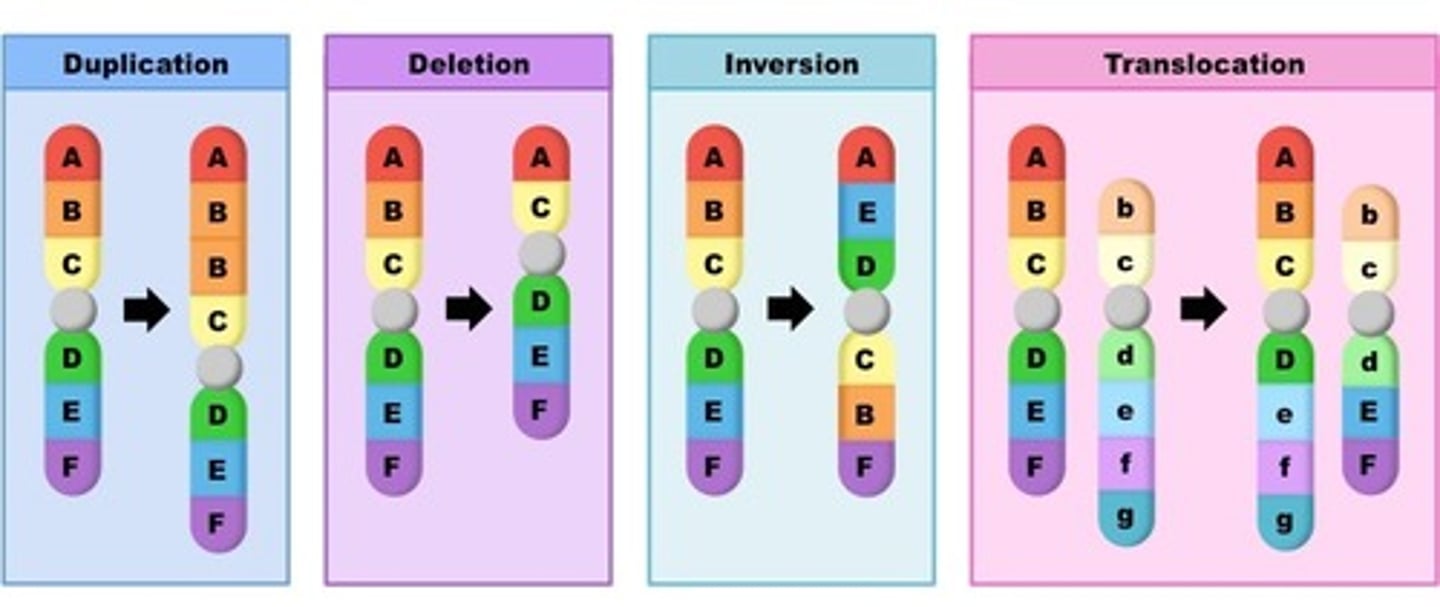
These affect a person's a persons traits
Genetics and Environment

Feature
A characteristic shared by all members of a species
Still learning (5)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!