PSY 2114 3.2 - Physical Development in Early Infancy
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Stages of vaginal birth
1. Contractions leading to dilation of cervix
2. Delivery
3. Detachment and expulsion of placenta, umbilical cord, and other membranes
On average, how long does it take to deliver first-born child and subsequent children?
- 12-14 hrs for first born
- 4-6 hrs for subsequent children
when does the first stage of birth end?
when the cervix is ~10cm dilated
Delivery usually takes how long?
20-50 mins
Expulsion of the placenta usually takes how long?
5-10 mins
Neonate average length and weight
20" long and 7.5lbs
Neonate appearance
- Large head
- Short, bowed legs
- Round face, large forehead and eyes
Apgar scale use
used to assess vital signs in infant
When is the apgar usually taken?
taken 1-5mins after birth
Apgar scale acronym
A - appearance
P - pulse
G - grimace
A - activity (muscle tone)
R - respiratory effort
Apgar scores
A score from 7-10 is ideal
A score of 3 or under is an emergency
Gestational age terms
Preterm, full-term, postterm
Preterm
born before 36 weeks gestation
Full-term
born between 37 and 42 weeks gestation
Postterm
born after 42 weeks gestation
Birth weight
Low BW, very low BW, extremely low BW
Low BW
less than 2500g
Very low BW
Less than 1500g
Extremely low BW
less than 1000g
Weight is also compared with...?
gestational age
Weight percentile meaning
heavier than --% of your peers
Appropriate for gestational age (AGA)
BW between 10th and 90th percentile
Small for gestational age (SGA)
BW below 10th percentile
Large for gestational age (LGA)
BW above 90th percentile
Birth weight chart
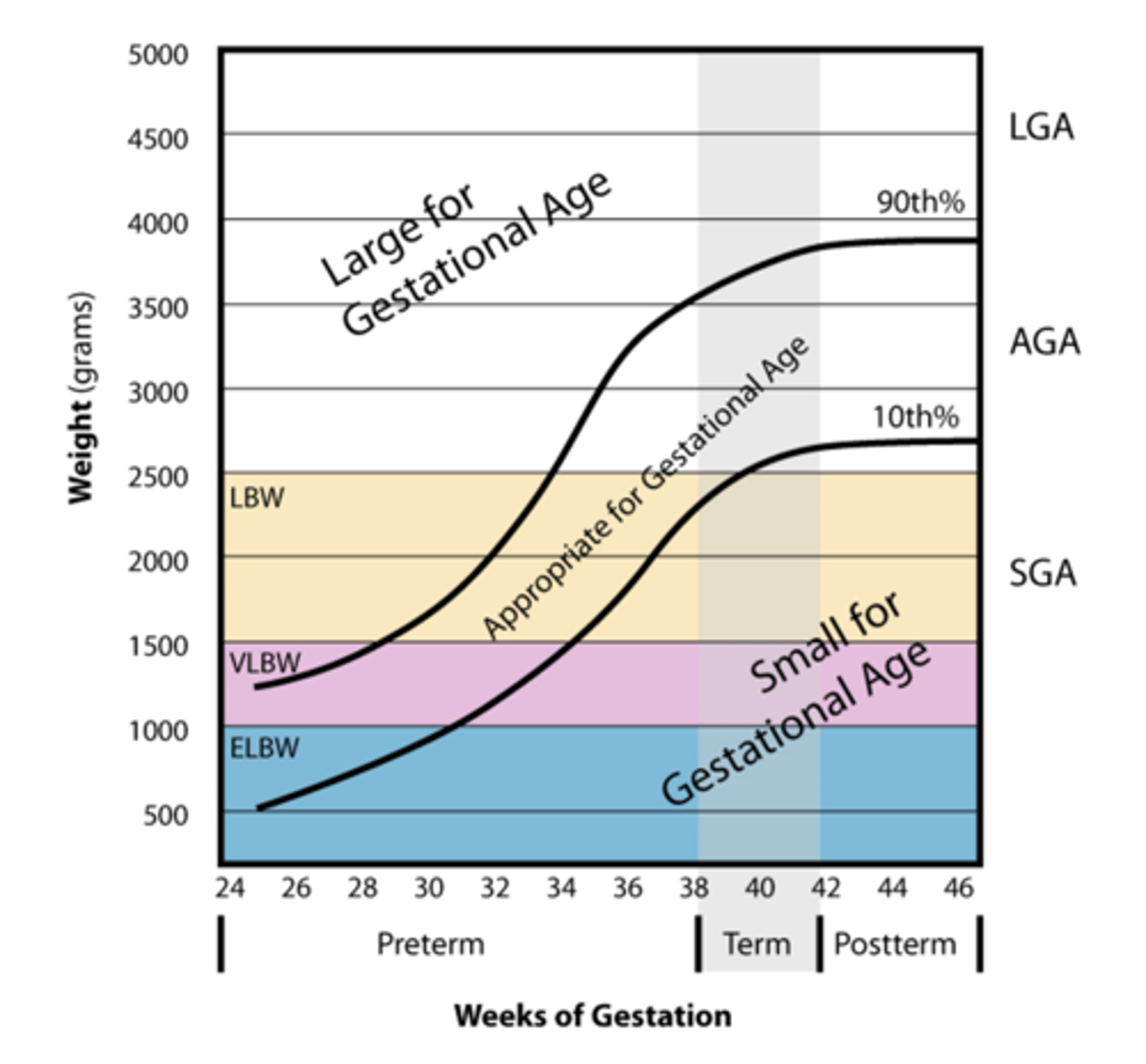
Birth weight in singletons vs. multiples
Multiples (twins/triplets etc.) are usually smaller than singletons
Fetuses are viable after how many weeks gestation?
22 weeks gestation
- 1lb
How many fetuses survive at lowest possible viability age/weight?
9-30% survive (VERY low rate of survival)
50% of those who do survive have major disabilities
Risk factors for preterm birth
- Immature uterus (mom <20yrs)
- Poor nutrition
- Poor prenatal care
- Low SES
- Alcohol, drugs
- High BP
- Fetal malformations
- Stress
Challenges in LBW infants
- 25X more likely to die in first month
- Smaller and younger at birth: increased number and severity of problems
- Increased risk of vision/hearing loss, learning disability, epilepsy, cognitive impairments, anxiety
Factors that improve outcomes for LBW infants
- parental contact (skin-to-skin)
- good nutrition
Issues in preterm infants
- respiratory distress, death
- temperature regulation (lack of fat)
- brain bleeds, heart valve problems
Why is respiratory distress a concern in preterm infants?
Lungs are not fully developed, so they lack surfactant which leads to lung collapse
- surfactant develops ~34 weeks gestation
Kangaroo care
A 'replacement' for incubators for preterm infants, in underdeveloped countries with little access to incubators.
Baby is worn skin-to-skin to baby for 24hrs
Types of reflexes
Adaptive reflexes
Primitive reflexes
Adaptive reflexes
help newborns survive; some adaptive reflexes persist throughout life
- sucking
Primitive reflexes
controlled by primitive parts of the brain; these reflexes mainly disappear by the end of the 1st year
- moro, babinski
Common primitive reflexes
- Babinski (sole of foot)
- Grasping (palm of hand)
- Moro (loss of support, arms and legs out)
- Plantar (curls toes when object under)
- Rooting (cheek touch, opens mouth)
- Tonic neck (on back, flex one side, extend other)
What are primitive reflexes usually used for?
to assess neurological development
Two significant infant states
sleeping and crying
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
the unexplained sudden death of an apparently healthy infant under one year of age
Incidence of SIDS
1/2000 live-born babies in Canada
- rare in the 1st month
- peaks b/w 2-4 months
Disproportionately prevalent in Indigenous communities
SIDS risk factors
- LBW (< 3.5 lbs)
- Sibling died of SIDS
- Exposure to cocaine, heroin, or methadone during pregnancy
- Parental smoking
- Male
- Minor respiratory illness
- Teen mom with previous children
- Short interval between pregnancies (recommended: wait >1 year between pregnancies)
Reducing the risk of SIDS
- healthy pregnancy (increases BW)
- Breast-feed babies whenever possible (antibodies in colostrum)
- No objects in crib
- No smoke
- put babies to sleep on their BACK
Back to Sleep Campaign
Encourage parents to put babies to sleep on back to reduce SIDS risk
Why does stomach sleeping increase risk of SIDS?
Infants are more likely to re-breathe the air they have just exhaled, which can raise their levels of carbon dioxide
Physical skills present at birth (3)
- Looking
- Sucking
- Crying
Looking
infants can direct head and eyes to look at particular stimuli
Sucking
- Quite complex; some babies need practice
- Means of exploration
- Buffers against pain
Why is sucking more than a simple reflex?
- Stops with distraction (visual or auditory stimulus)
- Varies with conditions (changes if amount or type of fluid available changes)
- Can be used to control access to stimuli (non-nutritive sucking paradigm)
Crying
- Complex
- Different types (parents can't actually tell)
- Survival mechanism
- crying method can follow accents
Early motor development
- Postural and locomotor development (control of trunk of body, moving around)
- Prehension (using hands to do tasks)
Patterns of early development
- Proximodistal
- Cephalocaudal
Proximodistal development
Centre of body is controlled before extremities
- Ex: Babies can control their hand before their digits
Cephalocaudal development
Development moves from head to toe
- Ex: Babies can sit up before they stand up
Postural and locomotor milestones...?
have a huge range in what is considered typical