SEROIM LEC ANTIBODY STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Antibody
- Product of B lymphocytes that undergo differentiation upon stimulation by antigen (plasma cells)
- reacts specifically with the inducing antigen in vivo and in vitro
Immunoglobulins
Antibodies are properly called as:
Glycoproteins
What are found in the serum portion of the blood?
Gamma band
electrophoresis @ pH 8.6
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE
What are the 5 major classes of antibodies? (GAMDE)
Humoral immunity
Antibodies confer (is associated) with what type of immunity?
Antigen recognition
Opsonization
Activation of complement
Antibody essential roles: (3) (AOA)
Tetra peptide
What type of structure does immunoglobulin have?
H chains
2 large chains of immunoglobulin
L chains
2 smaller chains of immunoglobulin
Noncovalent forces
Disulfide interchain bridges
The chains of immunoglobulin are held by: (2)
Gerald Edelman and Rodney Porter
Who developed the basic structure of antibodies in 1950 and 1960s? (2)
Analytic centrifuge
To separate immunoglobulins based on molecular weight, what did Edelman use?
7S
The intact IgG molecule had a sedimentation coefficient of:
Svedberg unit
unit that indicates sedimentation rate
7M Urea
To obtain purified preparation of IgG to unfold the molecule, what did Edelman use?
Mercaptoethanol
What is the reducing agent that cleaved the exposed sulfhydryl bonds in Edelman's work?
3.5 S
After ultracentrifugation, the result was 2 fractions.
One fraction at ___________ with a molecular weight of 50000 Daltons and was designated as the H chain.
2.2 S
The other fraction with a Mol. wt. of 20000 daltons
designated as L chain
H2L2
What is the generalized formula for all immunoglobulins?
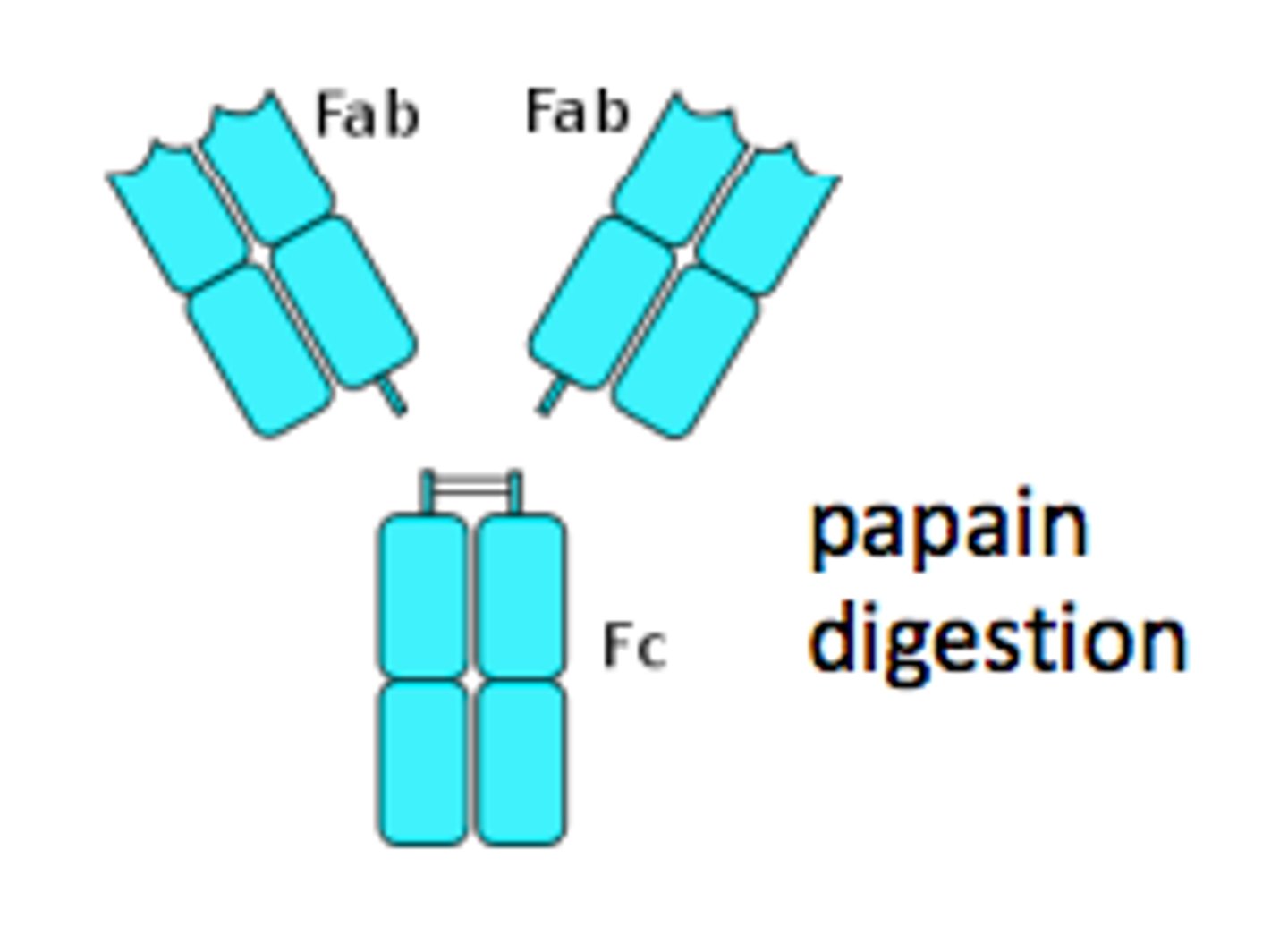
Papain
Porter's work on Igs is based on the use of proteolytic enzyme:
Papain
Enzyme used to cleave IgG into 3 pieces of about equal size
Each piece has 3.5 S
Carboxymethylcellulose Ion Exchange Chromatography
Porter used what type of chromatography to separate material in 2 fragments?
Fc fragment and Fab fragment
2 fragments separated by
Carboxymethylcellulose Ion Exchange Chromatography
Fragment crytallizable
•spontaneously crystallized at 4°C
•no antigen binding ability
•represents the carboxy terminal halves of the two H chains held together by S-S bonding
•important in effector function of Ig
Opsonization
Complement fixation
Fc fragment functions (2) (OpsC fragment)
Fragment antigen-binding
- have antigen binding capacity
- each fragment represents one antigen- binding
- 2 such fragments were present in an intact antibody molecules
1 L chain
1/2 H chain
Each Fab fragment consists of: (2)
Disulfide bonding
The Fab fragment's L chain and H chain are held together by:
Alfred Nisonoff
Used pepsin to obtain additional evidence for the structure of immunoglobulins
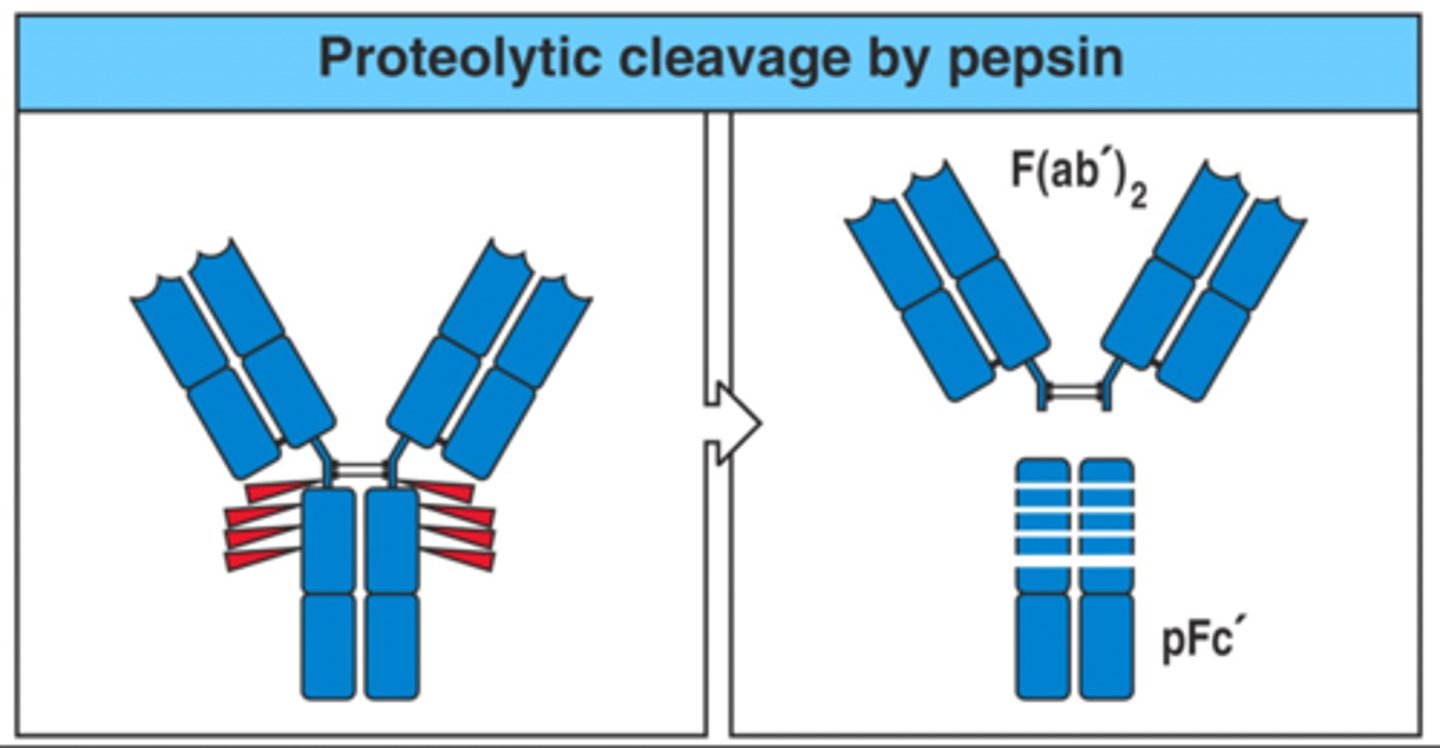
Pepsin
cleaved IgG at the carboxy-terminal side of the interchain disulfide bond
F(ab) squared and Fc
After cleaving IgG using pepsin, what are the results? (2)
F(ab) squared
One piece with all the antigen- binding ability
Fc
Similar to Fc except that it usually disintegrates into several smaller pieces
Bence Jones Protein
What protein is used for amino acid analysis of light chains?
Dr. Henry Bence-Jones
Discovered the BJP
Multiple myeloma
BJP are found in urine of patients with what disease?
60°C - Precipitate
80°C - Dissolve
BJP precipitate when heated to _________ but dissolve on further heating at __________
Kappa and Lambda
BJP analysis revealed 2 main types of L chains:
Constant region
Same sequence
Variable region
amino-terminal end of the immunoglobulin chain; part that recognizes antigen
Kappa L-chains
All ____________ have an almost identical carboxy-terminal end and the same is true of λ chains
Amino acid substitutions
The difference between the K and λ chains lies in the _________________ at a few locations along the chain
Only 1 type
In Igs, only how many types (Kappa or Lambda) can be present in a given molecule?
Heavy chain sequencing
Demonstrated the presence of domains similar to those of L chains
110 amino acids
The first how many amino acids at amino-terminal end constitute the variable domain?
Constant regions of the H chain
What part of the H chain gives each Ig type its name?
Gamma H chain
IgG heavy chain
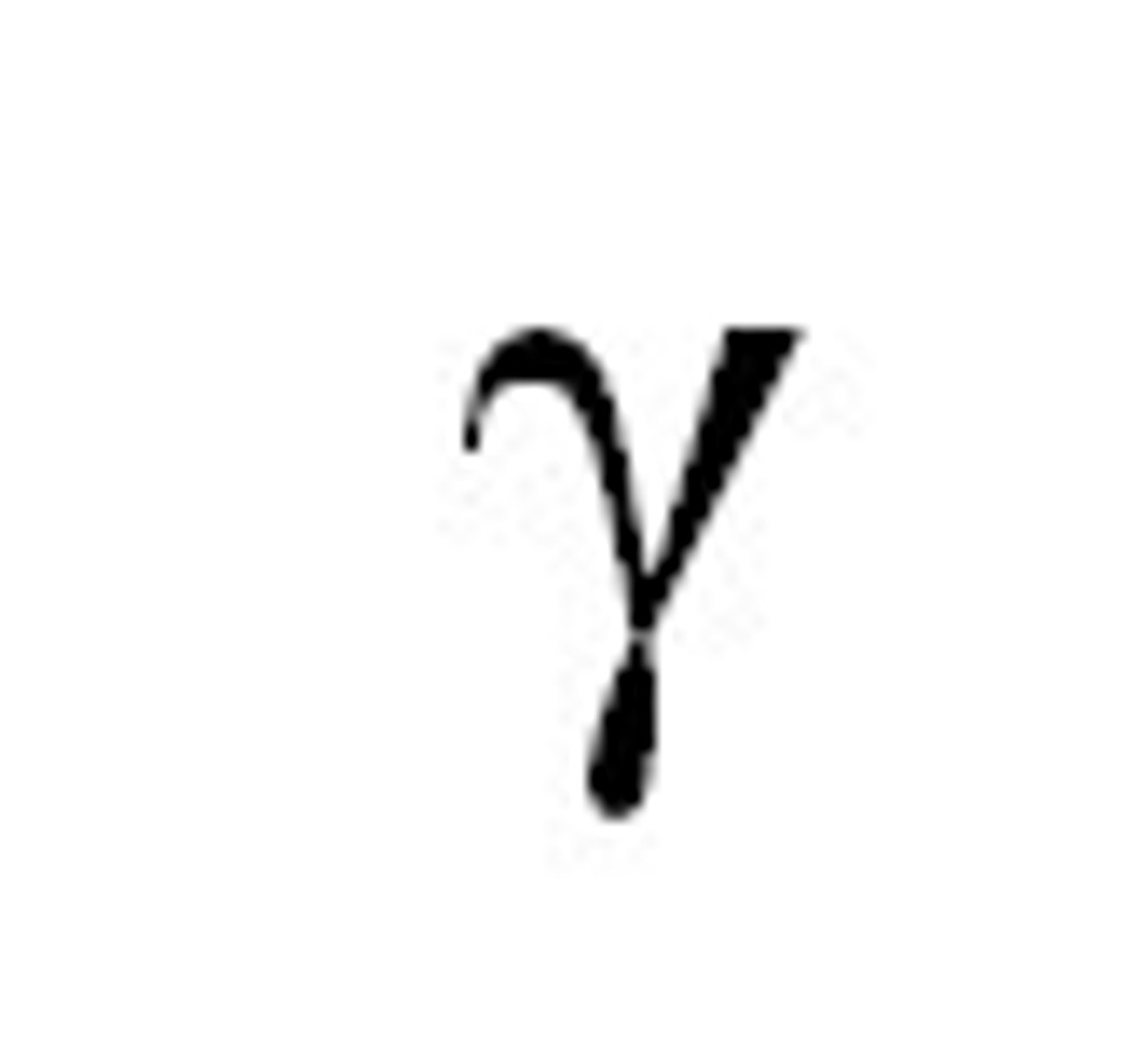
Mu H chain
IgM heavy chain
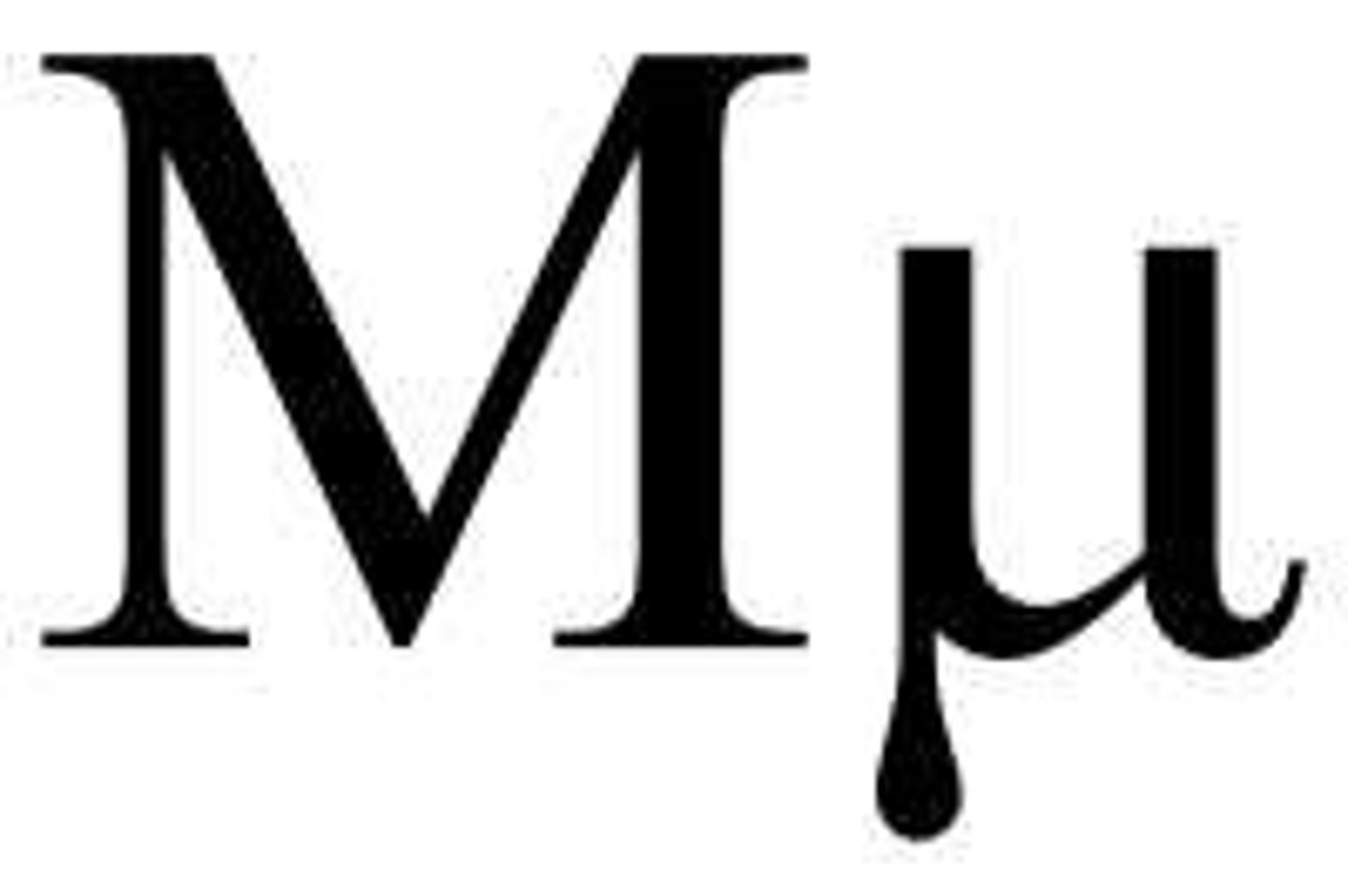
Alpha chain
IgA heavy chain
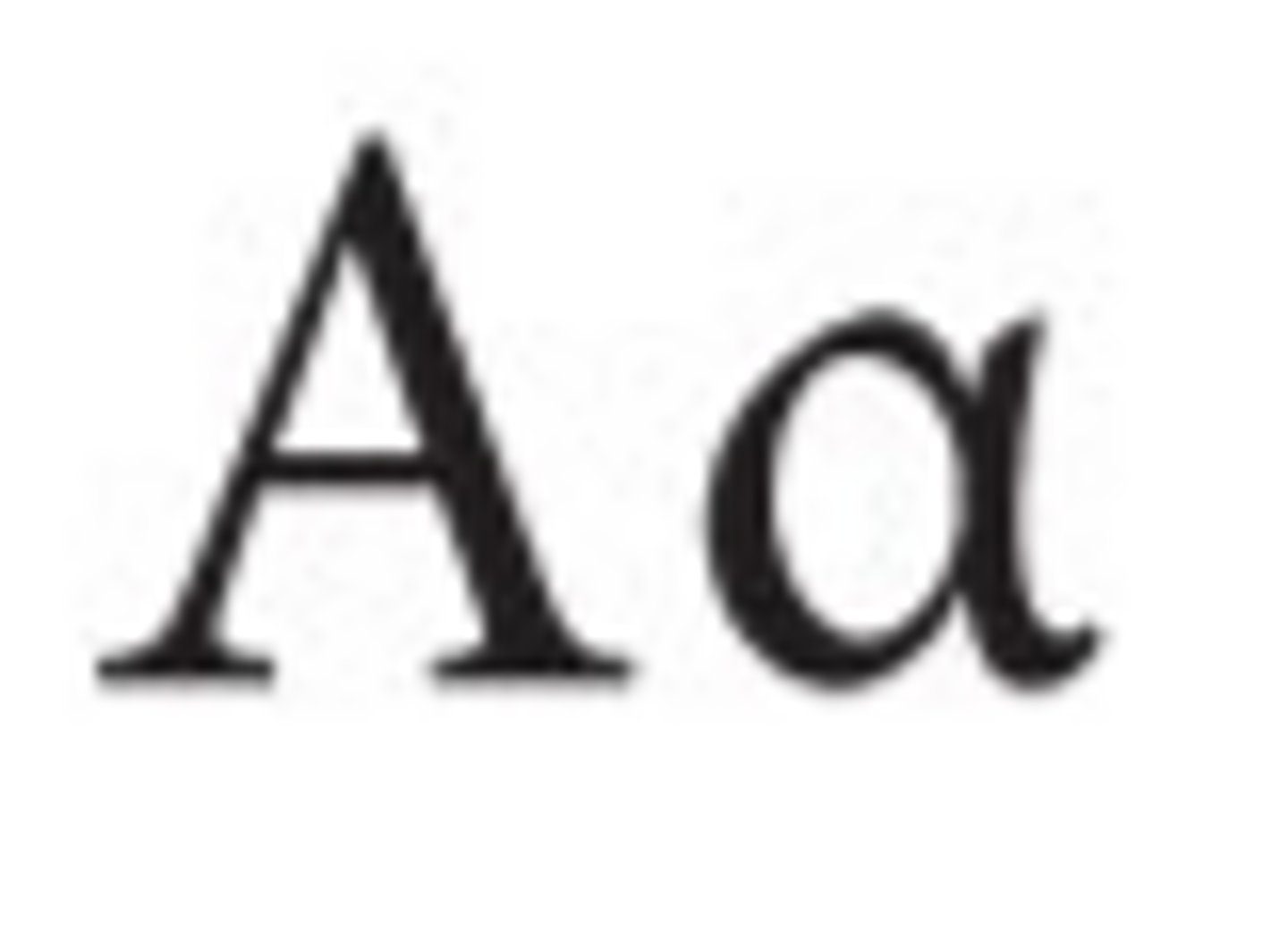
Delta chain
IgD heavy chain
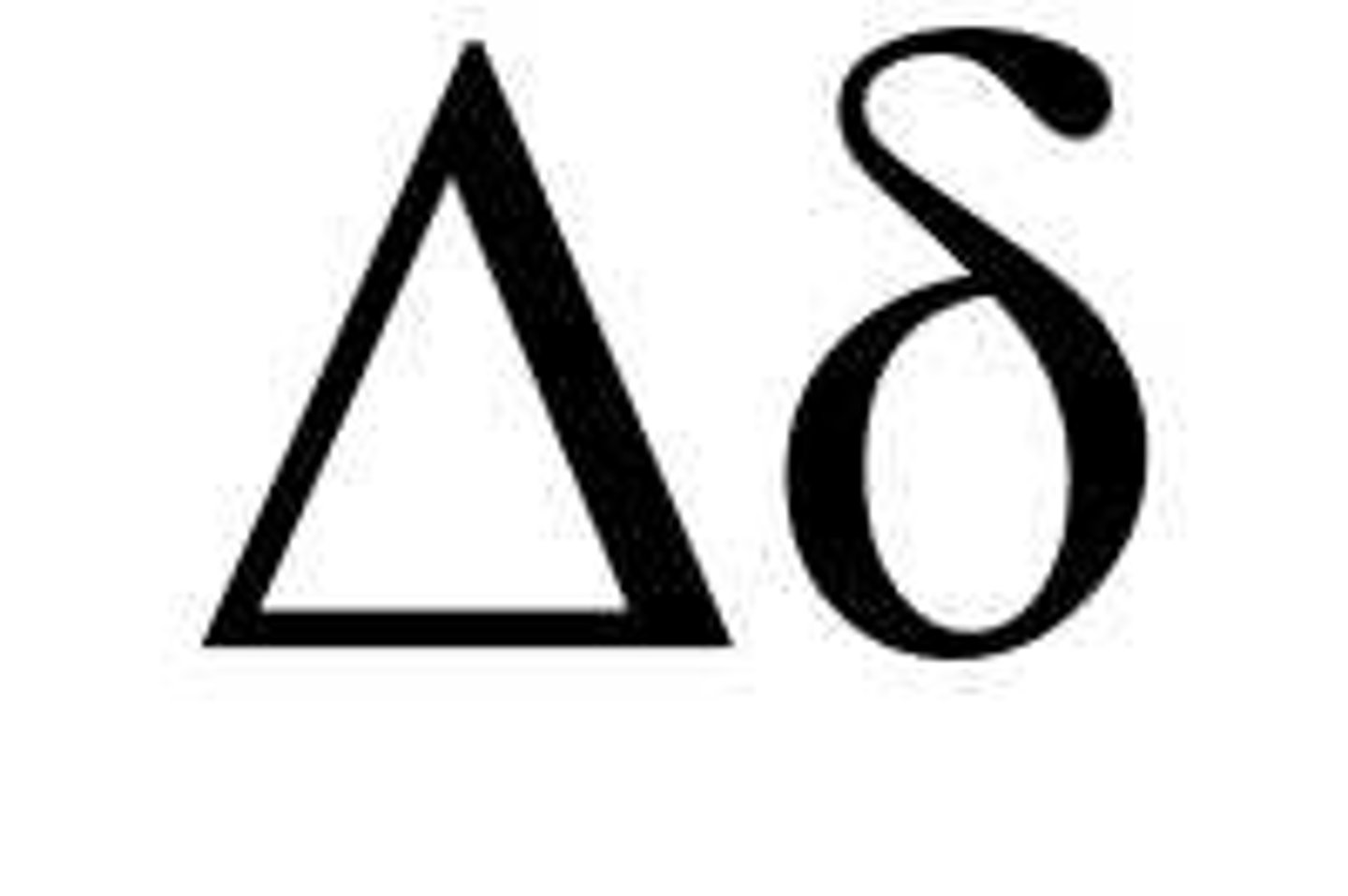
Epsilon chain
IgE heavy chain
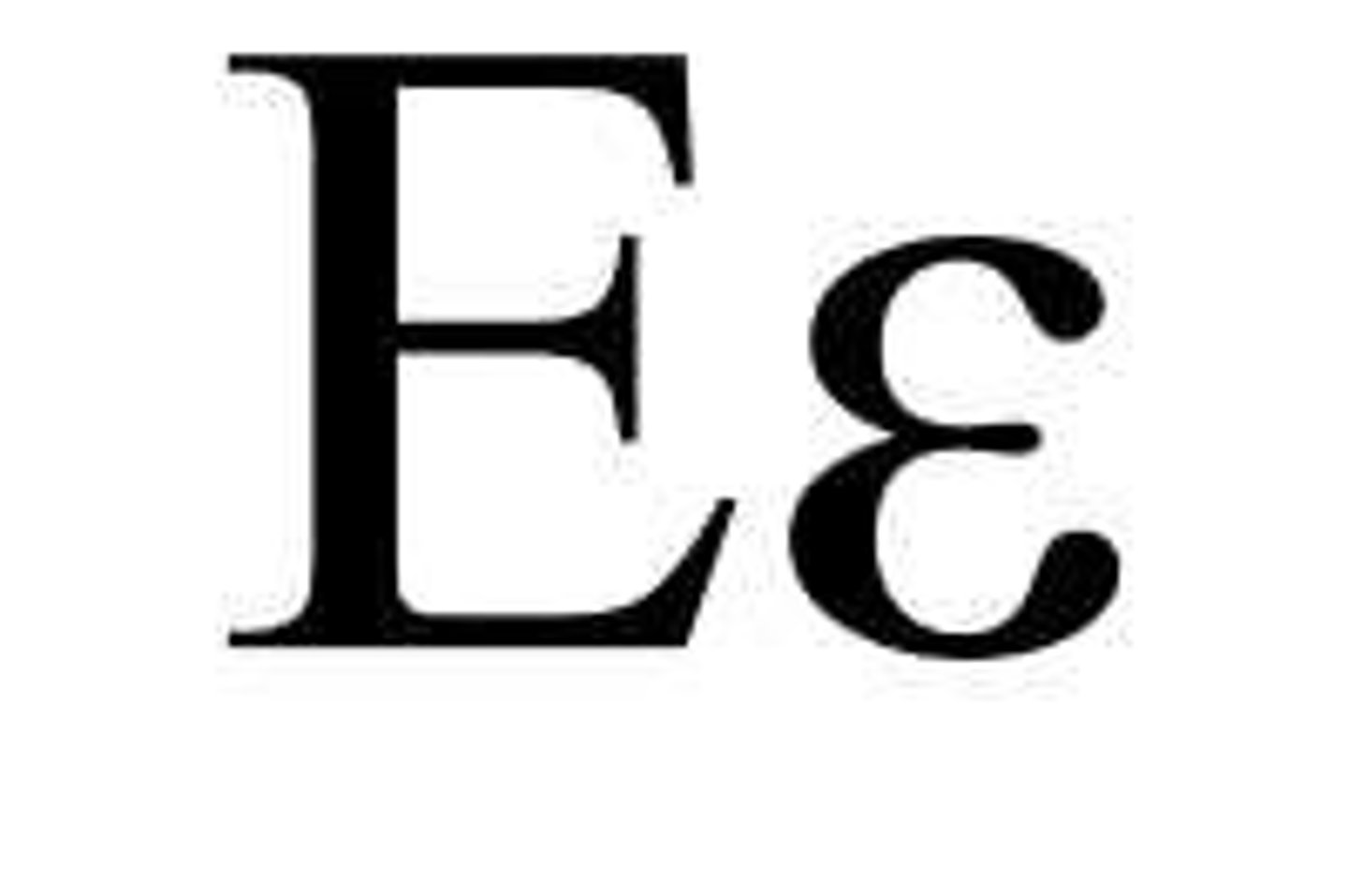
Isotype
A unique amino acid sequence that is common to all immunoglobulin molecules of a given class in a given species
same heavy chain for each class
Allotypes
Minor variations of sequences that are present in some individuals but not to others (constant regions)
Kappa
Alpha
Gamma
Epsilon
Allotypes occur for which types of IgG? (4) (KAGE)
G1m3 and G1m17
Example of an allotype which are the variations of the Gamma chain?
Idiotypes
variations in variable regions
Variable regions
antigen recognition unit
constitute the idiotype of the mole
Hinge region
region that allows flexibility
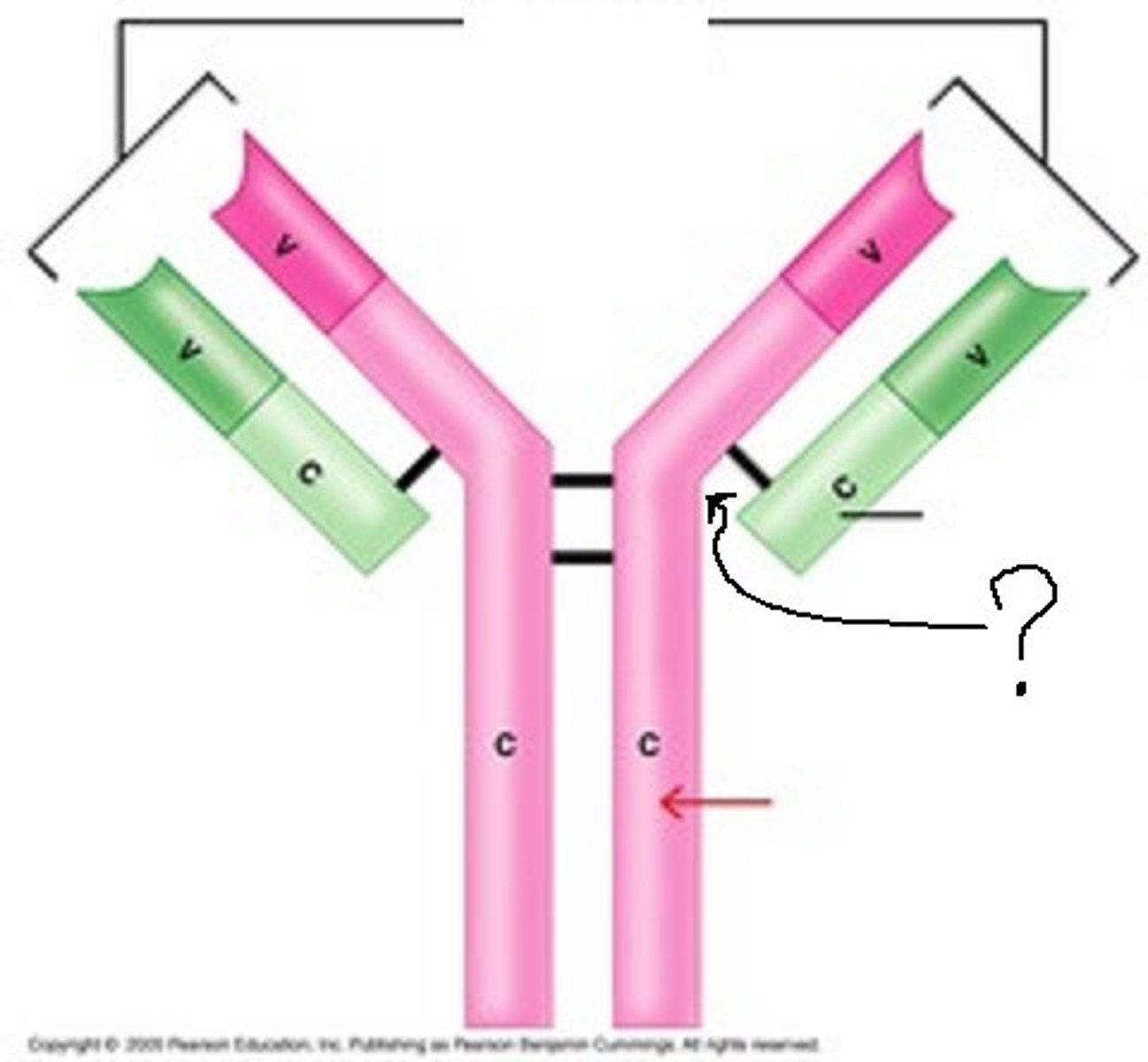
Proline content
Hydrophobic residues
The hinge region is high in: (2)
Flexibility
• the ability to bend allows the two antigen-binding sites to operate independently
• assists in effector functions such as initiation of the complement cascade
Carbohydrate portion
In the hinge region, what is located between CH2 domains of the two H chains?
Balloon-shaped loops
The basic four-chain structure of all immunoglobulin is folded into compact globular subunits, based on the formation of _________________________ at each of the domains
Intrachain disulfide bonds
What stabilizes the globular regions?
Beta-pleated sheet
Within each of these regions or domains, the polypeptide chain is folded back and forth on itself to form a:
Immunoglobulin barrel
The folded domains of the H chains line up with those of the L chains to produce an:
WHERE ANTIGEN IS CAPTURED
Hypervariable regions
found within the variable regions of both heavy and light chains
Complementary determining regions
the acronym for CDR; names given to the hypervariable loops of the heavy chain in receptors in antibodies and lymphocyte receptors
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
molecular recognition or cellular adhesion
other proteins with three-dimensional structure similar to all immunoglobin
Immunoglobulin G
What is the predominant Ig in humans of about 75 to 80%?
23-25 days
half life of IgG
IgG1: 66%
IgG2: 23%
IgG3: 7%
IgG4: 4%
Percentages of the 4 major subclasses of IgG
IgG3
What is the IgG with the largest hinge region and the highest number of interchain disulfide bonds and most efficient at binding complement?
IgG2 and IgG4
Which IgGs have:
shorter hinge segments
poor mediators of complement activation
(2)
Providing immunity for newborn
Fixation of complement
Opsonization
Neutralization of toxins and viruses
Participation in agglutination and precipitation reactions
5 Major functions of IgG
(P-FON-P)
Macroglobulin
other name for IgM
10 days
half life of IgM
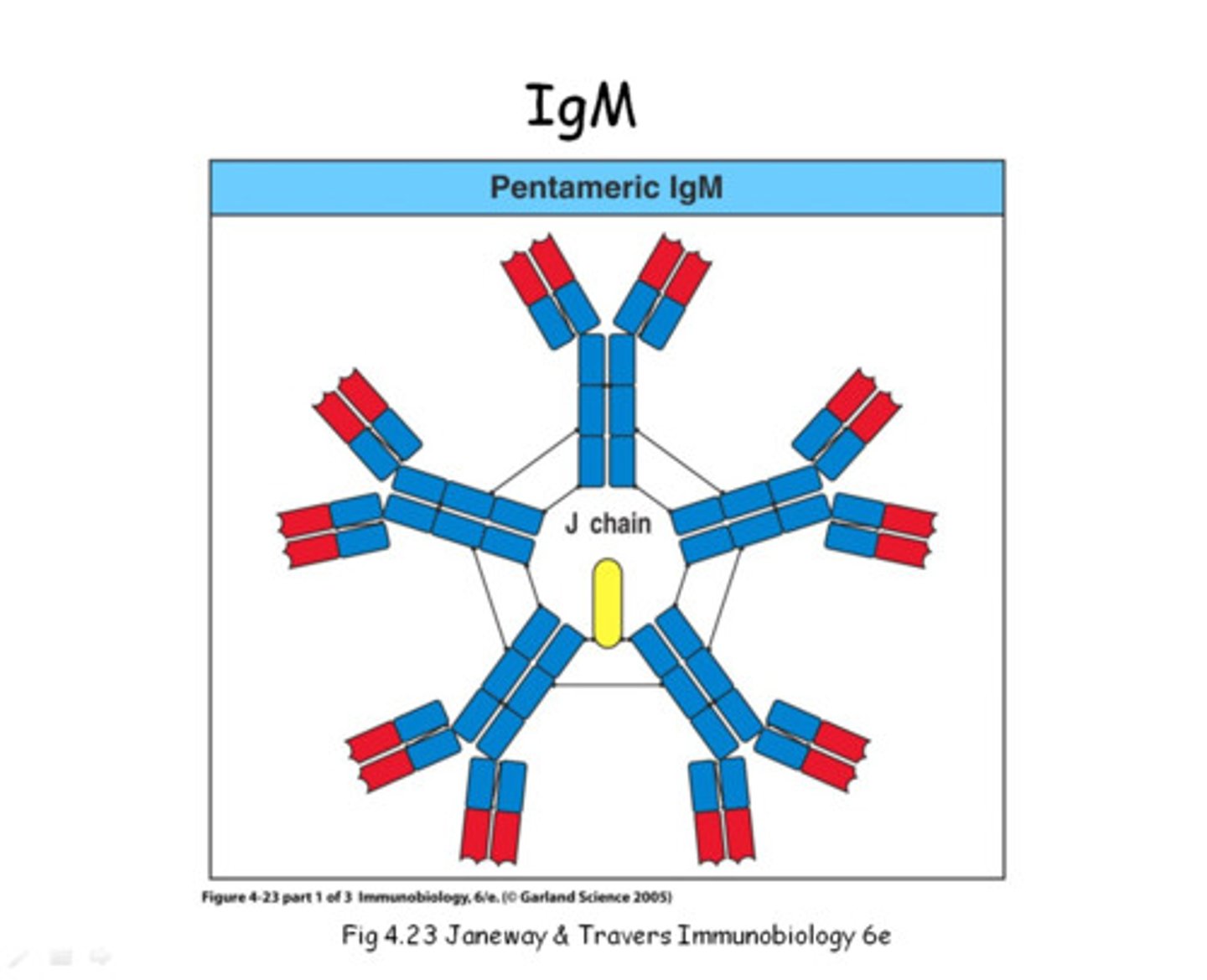
Immunoglobulin M
Mol. wt. of approximately 970,000
Immunoglobulin with the mu chain
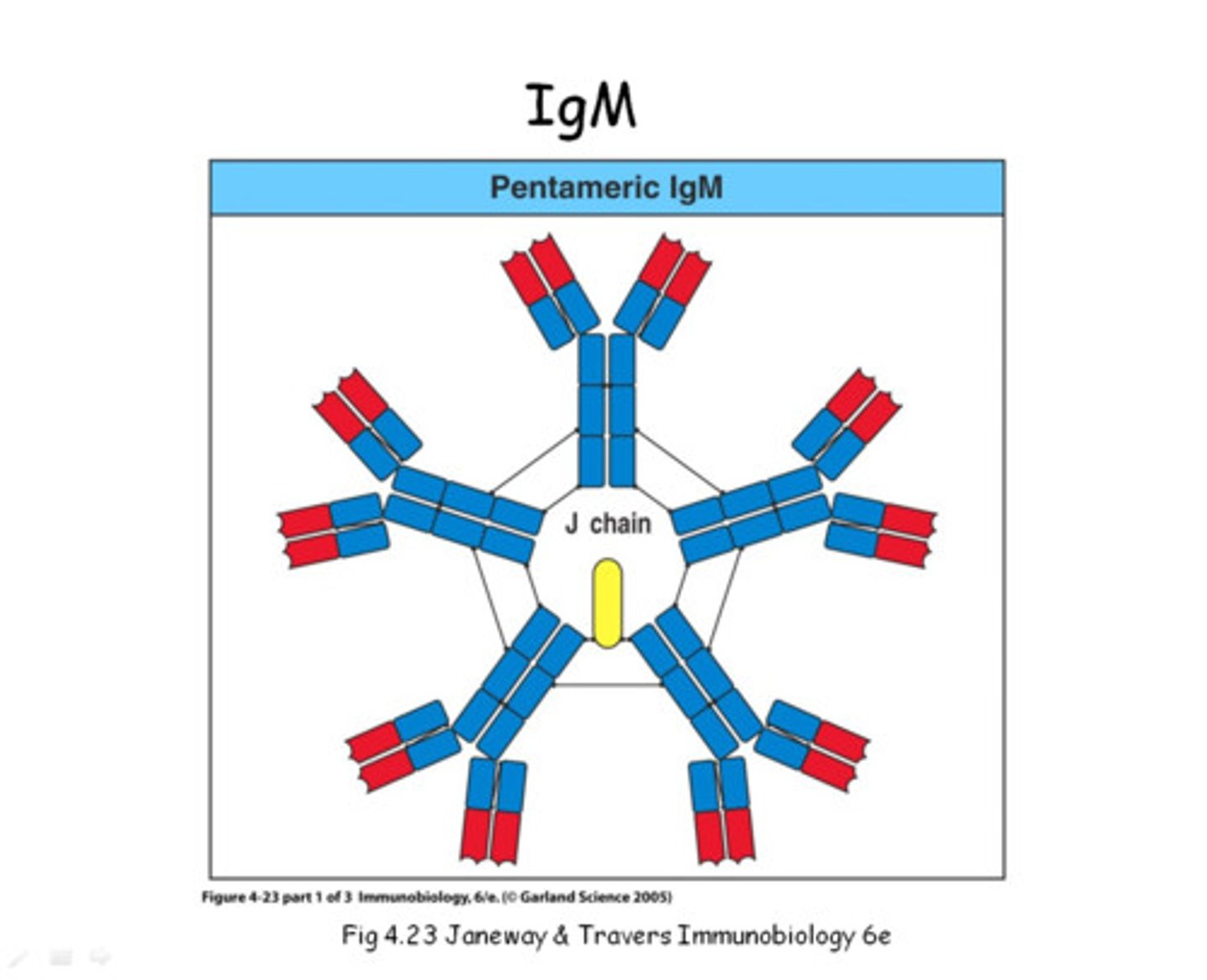
Mu chain
mol. wt. 70,000
576 AAs; one more constant domain than γ chain
Pentameric form
The IgM has 2 forms, pentameric and monomer form.
Which is responsible for secretions?
Monomer form
The IgM has 2 forms, pentameric and monomer form.
Which is present on the surface of B cells?
Joining chain
Cysteine residues that serve as linkage points for disulfide bonds between two adjacent monomers
Holds the five monomeric units together
Star-like shape
Pentameric IgM shape with 10 functional binding sites
Crab-like
3d structure of IgM
What the structure looks like when combined with an antigen
Primary response antibody
The IgM is also called as this because it is the first to appear after antigenic stimulation and first to appear in the maturing infant.
True
T/F
IgM is synthesized only as long as antigen remains present
False, there are no memory cells for IgM
T/F
IgM has memory cells.
Primary response
Which response is predominantly IgM; long lag phase?
Secondary response
Which response is mainly IgG; shortened lag period; more rapid increase in antibody titer?
Complement fixation
Agglutination
Neutralization of toxins
Opsonization
Surface receptor for antigen
Functions of IgM (5) (CANOS)
Complement fixation
The most important function of IgM
Immunoglobulin A
immunoglobulin that migrates between gamma and beta regions on electrophoresis
has the alpha heavy chain
IgA1
primary monomer of IgA found in serum
IgA2
Secretory IgA
more resistant to bacterial proteinases (cleaved IgA1)
has disulfide bond that covalently link together the L chains rather than the H
serves to keep antigens from penetrating further into the bod
Dimer
What is the structure of IgA2?
Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue
IgA2 is made in plasma cells found mainly in:
Secretory component
Later attached to the Fc portion of the α chains
Consists of five immunoglobulin-like domains
Derived from epithelial cells found in close proximity to the plasma cell
Makes dimer resistant to enzymatic digestion
Facilitate transport of IgA to mucosal surfaces
Specific receptor for IgA
3 functions of the secretory component of IgA
(MFS)
Patrol mucosal surfaces, first line of defense
Neutralization of toxins
Prevents bacterial adherence to mucosal surfaces
Functions of IgA (3) (PNP)
Sabin vaccine
Which vaccine demonstrates effectiveness of IgA's protective role on mucosal surfaces?