units 0-3 psych final
1/458
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
459 Terms
what is classical conditioning?
learning where the learner is not active
what is behavioral perspective?
behaviors are learned responses to environmental stimuli, focusing on observable actions rather than internal thoughts
what was Ivan Pavlov’s experiment?
“Why did the dogs salivate before anything happened?” the dogs he experimented on always salivated when seeing him because they knew he was going to give them treats eventually
what was Albert Bandura’s experiment?
"Can children learn aggressive behaviors through observational learning (seeing others do it) rather than direct reinforcement?" he showed children an 'aggressive' video of a woman beating up a bobo doll, the children who saw the video were more likely to pick up weapons, cuss, and be more aggressive towards the doll than children who did not see the video (they typically did nothing major to the doll)
what was Wolfgang Kohler’s experiment?
"Do animals (and humans) learn solely through a gradual process of trial and error, or can they solve problems through a sudden understanding of the entire situation?" bananas were put up above multiple crates , how will the chimpanzees get it? chimpanzees first ran around, not knowing what to do before finally stacking the crates together to obtain the bananas.
what are the 4 steps of classical conditioning?
naturally occurring relationship → UCS pairs with UCR → association/acquisition → associative learning
what is UCS?
an unconditioned stimulus that naturally causes a response
what is UCR?
an unconditioned response to stimulus
what is NS?
neutral stimulus is anything outside the naturally occurring relationship
what is being paired in the naturally occurring relationship?
UCR and UCS
what is being paired in association/acquisition?
NS and UCS
what occurs in associative learning?
NS becomes CS and UCR becomes CR
what is the UCS, UCR, NS, CS, and CR of this situation?
You receive shots every 3 months in doctor’s office for back pain. Your back feels better when see the nurse who gives you the shots at the grocery store.
UCS: shots UCR: 😁 NS/CS: nurse CR: 😁
what is the UCS, UCR, NS, CS, and CR of this situation?
Lisandra goes outside to play in her tree house. A swarm of bees has nested near her house, and she gets stung several times when she climbs up the tree house, causing her much pain. This happens 3 times a week. When her father tells her to go up the treehouse, she violently cries.
UCS: bee stung UCR: pain NS/CS: tree house CR: crying
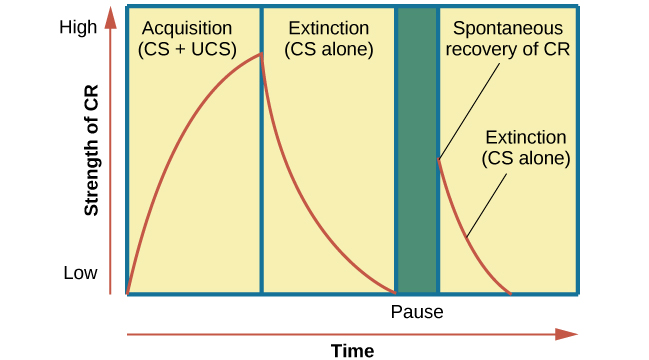
when does extinction occur?
occurs when CS is forgotten most often due to neglect
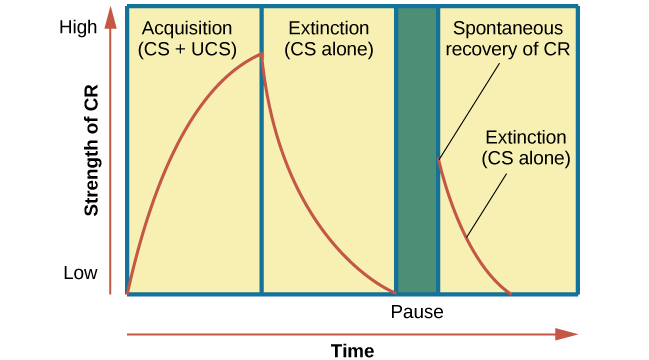
when does spontaneous recovery occur?
after a CS has been extinct, it is much more likely to be remembered quickly.
When does high-order conditioning occur?
after you have a CS, you can pair that CS with NEW NS to create a second CS
what is CS2 and NS2 in this situation? (high-order conditioning)
UCS: time to pack end of class
UCR: packing up belongings
NS1/CS1: the school bell ringing
CR: packing up belongings
backpack zipping
what is generalization?
ex.) bell ringing a few pitches louder
when a NS is similar enough to the CS to get a CR
what is discrimination?
ex.) music bell instead of typical school bell
new NS is not similar to the CS so you don’t get a CR
what is counterconditioning?
when you have a behavior that is unwanted, adding a desirable stimulus can turn the response positive
what concept aligns with this situation?
before: door bell ring → dog bark crazy
treats → happy dog
during: door bell ring + treat → happy dog
after: door bell ring → happy dog
counterconditioning
what is taste aversion? (evolutionary !)
ex.) smell/look of object/item becomes CS
after eating bad food, you become avoidant to the same thing
what is one-trial conditioning?
ex.) trauma/taste aversion
learning a CS with one instance, where a strong association forms after a single, powerful pairing of a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus
why are babies more afraid of snakes than wall sockets?
biological preparedness
what is biological preparedness?
we as humans are more likely to be afraid of things that our ancestors were afraid of than new problems
what is habituation?
when you are introduced to a CS for an extended period of time without consequences, you are most likely going to ignore it
what is this concept called?
crows presented in a corn field → introduction of scarecrow → prolonged exposure to scarecrow → nothing happens → crows continue to be in the cornfield
habituation
the law of effect was created by Edward Thorndike, what was this theory about?
learning stems from consequences
operant conditioning was created by B.F. Skinner, what was this theory about?
learning where the learner is NOT passive (active)
what is reinforcement?
behavior is good and we want it to continue
is this situation PR, NR, PP, NP?
Peter keeps swearing in class, each time he does his teacher asks him to put a dime in a jar, since this policy has been implemented Peter’s swearing has slowed considerably.
NP
what is punishment?
behavior is bad and we do not want it to continue
is this situation PR, NR, PP, NP?
You get 25 cents for sleeping on time
PR
is this situation PR, NR, PP, NP?
brushing the toilet so you don’t have to wash the dishes
NR
is this situation PR, NR, PP, NP?
adding GoGuardian to ensure academic integrity
PP
what was skinner box used for?
controlled environment where Skinner studied how behaviors are shaped by reinforcement; training tool
what is primary reinforces?
things we innately (naturally) know are good
what is secondary reinforces?
something you have to learn has value
what is reinforcement discrimination?
the ability to distinguish between different stimuli and respond appropriately
what is reinforcement generalization?
learning that certain stimuli is useful in a multitude of places
what is this an example of?
raising your hand
reinforcement discrimination
what is this an example of?
being kind
reinforcement generalization
what is shaping?
teaching a new behavior by rewarding small, step-by-step improvements that gradually get closer to final, desired action; building blocks
what is instinctive drift?
animals have a difficult time in learning behaviors outside of their natural instincts and will revert to natural behaviors over time
what is superstitious behavior?
an individual associates behavior with something outside that has nothing to do with it, causing them to believe that they are correlated
what is learned helplessness?
when an individual gives up or doesn’t even try a difficult task because of similar previous failures
what are aversive consequences/conditioning?
using punishment to correct a behavior
European therapists typically give alcoholics a pill and order them to drink right afterwards → pill makes them nauseous → reduction in alcohol craving and long-term abstinence
what concept aligns with this situation?
aversive consequences
what is continuous reinforcement?
every time the individual does the behavior, they get reinforced
because continuous reinforcement can be learned quickly.. what is the outcome of this?
prone to extinction
what is partial reinforcement?
sometimes when the individual does the behavior, they sometimes get reinforced
what is a ratio schedule based on?
of times they do the behavior
what is a fixed ratio?
after a set number of times we do a behavior, we get a reward
what is a variable ratio?
HIGHLY ADDICTIVE!
after a random number of a behavior is done, we get a reward
what is a fixed interval?
after a set amount of time you spend on a behavior, you get a reward
what is a variable interval?
HIGHLY ADDICTIVE!
after a random amount of time you spend on a behavior, you get a reward
what is an interval schedule?
rewarding based on how much time we spend on a behavior
is this FR, VR, FI or VI?
after completing 67 practice problems → 20 minute break
FR
is this FR, VR, FI or VI?
lottery
VR
is this FR, VR, FI or VI?
study for 2 hours → 30 min break
FI
is this FR, VR, FI or VI?
speed traps
VI
the social learning theory was created by Albert Bandura, what was the main idea?
watching other people is imperative to learning, especially for children
what is vicarious learning/conditioning?
learning by the consequences of others
the concept of insight learning was founded by Wolfgang Kohler, what is it?
suddenly knowing the answer, aha moment!
the concept of latent learning was discovered by Edward Toleman, what is it about?
learning something that does not need to be used immediately
what is this an example of?
seeing someone get a haircut you wanted but it turned out poorly → “wow i was gonna get that but never mind”
vicarious learning
what was Edward Toleman’s experiment?
“Does learning require immediate reinforcement, or can it occur internally, without an obvious change in behavior?” he timed rats to go through a maze, incentivized rats were faster than rats without. then when the disincentivized rats were incentivized, they were the fastest overall.
the concept of cognitive maps were founded by Edward Toleman, what is it about?
mental construct of problems in your mind
which concept by Edward Toleman aligns with this situation?
gps to drive to school
latent learning
which concept by Edward Toleman aligns with this situation?
mentally mapping your pathway to T hall, what is the fastest route?
cognitive maps
what is hindsight bias?
when you make an initial prediction that is later proven correct, we WILL overestimate our original assurances (i told you so!)
what do you explore in an experimental research method?
cause and effect
what are the 3 steps for conducting an experimental research?
(specifically our notes bc its typically not js these)
1.) hypothesis 2.) experimental variables 3.) population
there are 3 experimental values… what is an independent variable?
the variable that you can manipulate
there are 3 experimental values… what is a dependent variable?
the variable you can measure
there are 3 experimental values… what is a confounding variable?
the variable outside of the study that impacts it
what is a population sample?
a small group of the population (randomly selected but includes every group)
what is sampling bias?
the person conducting the study pick the people with bias
what is generalizability?
how well the findings connect the real word population
what are the main ethical guidelines for human subjects?
informed consent, freedom to withdraw, protection from harm, debriefing, confidentiality
what are the main ethical guidelines for animal subjects?
justification of research, personnel familiarity, care and housing, acquisition, experimental procedure, field research, educational use
what is an experimental group known for?
receives the independent variable
what is the control group known for?
does not receive the independent variable
what are control measures?
ex.) randomization
tools used to protect us from confounding variables
what is a single-blind study?
the participant does not know what group they are in
what is a double-blind study?
neither the participant nor the experimenter know what group the participant is in
what is a placebo?
a fake to make the participant feel like they’re apart of the experiment
what is a placebo effect?
occurs when the placebo works (confounding variable!!)
what is peer review?
when others review your work
what is replication?
when other experimenters do your study and do it in a different situation
what is operational definition?
an empirical measure of a vague term
what does qualitative research consist of?
observations; answers “why” question, observe and interpret, grouping of non-numerical common data
what does quantitative research consist of?
numbers; answers “how many” or “how much”, statistical result/analysis, measure and test
what is correlational research?
does NOT imply causation!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
comparing 2 sets of data to find their relationship
what is a descriptive research method?
observe and record behavior
what is a naturalistic observation?
observing people in their natural habitat and see what they do,
don’t get caught looking! people tend to change when knowing somebody is watching them
what are case studies?
an in-depth look at a strange phenomenon
what are advantages with surveys?
fast, broad reach, cheap
what are disadvantages with surveys?
potential bias, limited depth, need an incentive