Ligand gated ion channels
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Ligand gated ion channels definition
integral membrane proteins that contain a pore which allows regulated flow of selected ions and a receptor for binding of an agonist
2 different types of ligand gated channels
Excitatory (pass (+) ions like sodium, potassium, calcium)
nicotinic acetylcholine
seratonin
ionotropic glutamate
AMPA, NMDA, Kainate
Inhibitory (pass (-) ions like chloride)
GABA(A)
Glycine
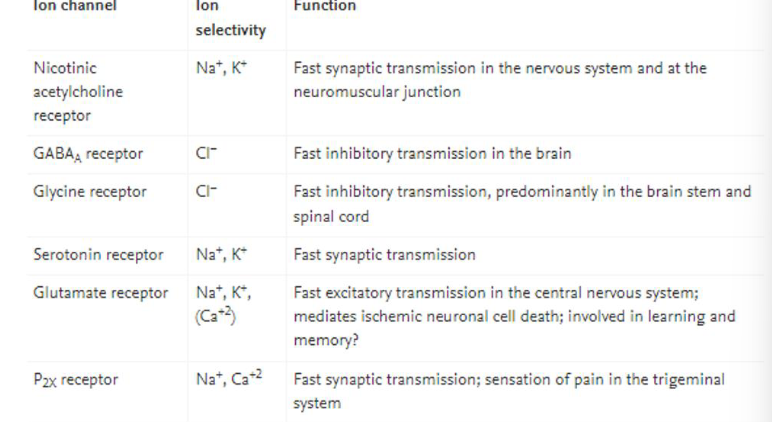
List examples of ligand gated ion channels and the ion selectivity of the channel (image)
List the three different types of receptors
Cys-loop receptor (nicotinic ACh) superfamily
Glutamate receptor family
P2X receptor family
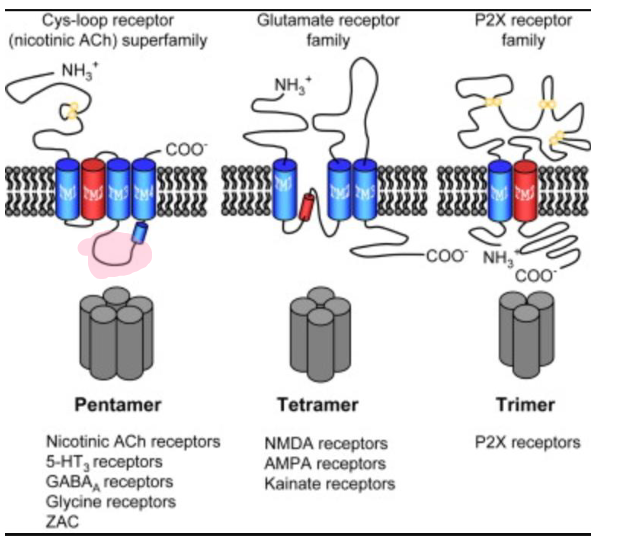
Cys-loop receptor (nicotinic ACh) superfamily
pentamer
nicotinic ACh receptors
5-HT3 receptors
GABA(A) receptors
ZAC
Glutamate receptor family
tetramer
NMDA receptors
AMPA receptos
Kainate receptors
P2X receptor family
trimer
P2X receptors
AMPA Receptors
part of the glutamate receptor family
mediator of fast excitory synaptic transmission
permeabile to sodium, potassium, calcium
4 subunits consisting of 2 dimers
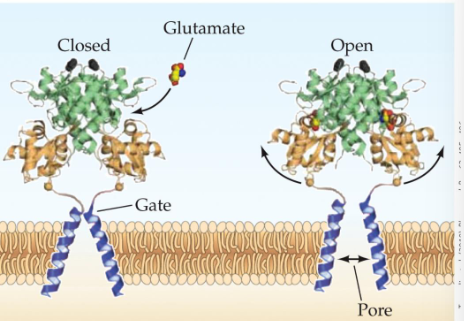
NMDA receptors
ionotropic glutamate receptor
permeable to sodium, potassium, calcium
critical for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory
involved in nic addiction and ischemic stroke
GABA(A) Receptor
part of the Cys-loop receptor (nicotinic ACh) superfamily
inhibitory receptor
permeable to chloride ions - results in hyperpoarization of the membrane and inhibits neuron depolarization
interacts with G-coupled receptors - dopamine D5
Gating mechanisms (3)
Activation (binding of agonist)
transition of channels from closed to open states
Deactivation (removal of agonist)
transition of channels from open to closed states
Desenitization
fraction of channels in an open state in the maintained presence of an agonist
non-conducing states - do not respond to activating stimuli
Describe the use of blocking agents to understand gating of ion channels
channel blockers are used as analytical probes in studies of channel gating
most channel blockers enter and bind to the channel in an open state
use dependent
requires activation of the channel
channel blocker unbinding - depends on gating transitions
blocker may become trapped in the channel
“foot in the door” channel blockers physically occlude closure of the channel gate
Describe potential clinical application of ligand gated ion channels
LGIC interactions for Neuroprotection
glutamate receptors have critical roles in brain functions
interactions between ionic glutamate receptors and other proteins could lead to potential therapuetic
AMPA activation increases the formation of GluR2-GAPDH complex and promotes cellula internalization - blocking formation of this complex protects cells against glutamatergic excitoxicity and ischemia induced neural damage
interaction between NMDA NR2 subunit and PSD95 cuases nitric oxide neurotoxicity - blocking this interaction could protect neurons from excitoxicity and ischemic brain damage