CST IA - SSE
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
what is security engineering
building systems to remain dependable in the face of malice or error
focuses on tools and methods used to design, implement, test complete systems
what is the design hierarchy
policy
define what we are trying to achieve
architecture, protocols
how we achieve this in terms of strategy and architecture
hardware, crypto, access control
which hardware platform to use, etc.
what is a system
equipment or a component
a collection of products, their operating systems, some networking equiment
+applications
+internal staff
+external users
what is dependability
reliability and security
malice is different from error
reliability and security are often strongly correlated
what is a subject, a person, and a principle
subject: a physical person
person: a subject or legal person (e.g. a firm or a charity)
what is secrecy
mechanism to control which principals can access information
what is anonymity
not being able to identify a subject or not being able to link their actions
by restricting access to metadata
what is privacy
control of your own secrets
what is confidentiality
an obligation to protect someone else’s secrets
what is integrity
an object has not been altered since the last authorised modification
what is authenticity
object has integrity plus freshness
you are speaking to the right principal
what is a trusted system
system or component that can break security policy
what is an error vs a failure
error: a design flaw or deviation from the intended tate
failure: nonperformance of the system when inside its specified environmental conditions
what is reliability
probability of failure within a specified period of time
what is an accident
an undesired, unplanned event resulting in a specified kind or level of loss
what is a hazard
a set of conditions in a system or its environment where failure can lead to an accident
what is a critical system
process or component whose failure will lead to an accident
what is risk
probability of an accident
often combined with a unit of exposure, e.g. a micromort
uncertainty is where the risk is not quantifiable
what is a security policy, protection profile, and security target
security policy: a succinct statement of protection goals, typically less than a page of text written in plain language
protection profile: a detailed statement of protection goals, typically dozens of pages written in a semi-formal language
security target: a detailed statement of protection goals applied to a particular system, may have hundreds of pages for both functionality and testing
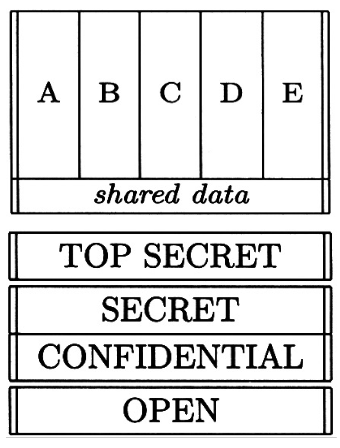
how does a Multilevel Secure System (MLS) work
classify all documents and data with a level, e.g. high and low, or top secret
principals have clearances
clearance must be equal to or exceed classification of any documents viewed
enforce handling rules at each level
information flows upwards only: no read up, no write down, follows BLP model
what is the Bella-LaPadula model (BLP)
simple security policy: no read up
*-policy: no write down
with these two rules, one can prove that a system that starts in a secure state will remain in one
aim is to minimise the Trusted Computing Base
what is the Trusted Computing Base
the hardware and software required to trust to enforce security policy
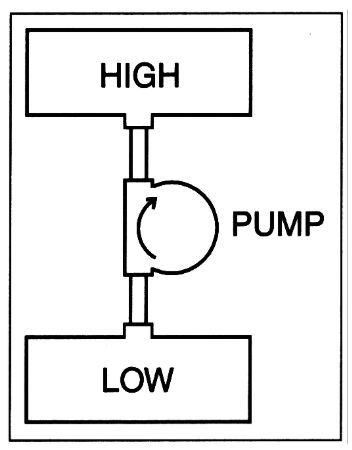
how do covert channels cause problems
a covert channel occurs when the performance of a resource shared between low and high allows information to flow
BLP lets malware move from low to high
if there is low level malware it can be read by a higher level program, copying it into a higher level, infecting that level
but high level programs cannot write down to a low level program so if there is data at that level how can it be stolen?
high level program will use a shared resource, like the CPU, on and off
low level program can detect this as it is a shared resource, and the CPU usage can be used as a binary code to retrieve the data
how to create a high assurance MLS system
add a pump: allows the system to pump information from low to high if needed
what is multilateral security
aims to stop lateral flow
e.g. accounting firms using this to allow them to work for two or more firms competing in the same sector
what is the Biba model
simple integrity policy (no read down)
*-integrity policy (no write up)
dual of the BLP model
why does architecture matter
if there are lots of legacy protocols that trust all network nodes, then it is poor architecture
so many things can be interconnected
e.g. Chrysler Jeep getting hacked and being able to control everything
good architecture has defence in depth
separate subnets, effective firewalls
if you hack into one side of the system, it prevents you from attacking the other aspects
what is the swiss cheese model
risk management model showing how multiple failures align to cause an accident
each layer represents an area of defense, and the holes are potential errors
e.g. layers: hardware, software, policy, human factors, etc.
how do safety policies evolve
industries have their own standards
with architectural assumptions embedded in component design
and lots of safety legislation
sometimes completely new standards, but usually for mature industries, old standards evolve
two basic ways to evolve:
failure modes and effects analysis
fault tree analysis
what do failure modes and effects analysis do
look at each component and list failure nodes
figure out what to do about each failure
use secondary mechanisms to deal with interactions
developed by NASA
what does fault tree analysis do
creates a tree of the system's failures
identifies all possible causes of an undesired event
what are simple things to consider for safety
authorisation
intent
environment
all independent, simple mechanisms
what is double-entry bookkeeping
each entry in one ledger is matched by opposite entries in another
ensure each ledger is maintained by a different subject so bookkeepers must collude to defraud
how does separation of duties work
separating subjects that do different tasks
serial: one thing is done at a time
parallel: authorisation coming from two distinct subjects
what does Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) do
decouples policy and mechanism
helps manage complexity but does not remove it as still have to write a policy for each role
what is security and safety
security: threat model, security policy
safety: harvard analysis, safety standard
why is user behaviour important
many systems fail because users make mistakes
e.g. banks will tell victims of fraud that the system is secure so it is the fault of the victim
however most car crashes are due to user error, but we still have improved cars to have crumple zones
what is the hierarchy of harms
targeted attacks (most sophisticated)
generic malware
bulk compromised password
abuse of mechanism (highest volume of harm)
what are some abuses of mechanism
cyberbullying
doxxing
websites advertising fake rental apartments to get people to pay a rental deposit
protect by having website recommendations from a trusted source
why is usable privacy difficult to implement
traditional approaches such as anonymisation and consent are hard to deliver
even if a device is anonymous, with location samples you can figure out who they are
problem gets worse as systems get larger and using automated data collection like from sensors
how is medical device safety
there are usability problems
biggest killer nowadays are infusion pumps
not standardised
nurses get blamed, not vendors of the devices
give an example of bulk password compromise
June 2012, 6.5m LinkedIn passwords stolen, cracked, posted on a Russian forum
using SQL injection
passwords were reused on other sites
give an example of phishing and social engineering
credit card thieves ring up the number of the card owner pretending to be their bank
make up a story like saying their card has been used and to confirm freezing it they need the PIN
or emails with a URL and a cover story to get the victim to click the URL
from fake authority figure to company emails, can trick 30% of employees
spear phishing is targeting a specific person
what cognitive factors can lead to someone making an error
the ability to automate familiar, frequently encountered actions leads to absent-minded errors
loss aversion, where people are more risk-seeking when it comes to losses, Asian Disease problem shows risk misperception humans have
obeying authority, Milgram experiment showed over 60% of people would electrocute a student against their personal conscience to follow an authority figure in a white coat in a lab setting
obeying the herd, Asch conformity experiments showed 7 actors stating line A shorter than B when it is evidently longer, subjects would follow them
reciprocity bias, built-in social norm of responding to a positive action with another positive action
‘recently’ bias, where people will have more of a bias towards the thing you’ve seen last
UI design having heuristics like button colour to make users more likely to click certain things
time pressure makes people more likely to make mistakes
conditioning to the default choice is what is more likely
people only follow advice that confirms their own worldview
what methods do fraudsters use to scam people
cognitive factors
appealing to the mark’s (person being defrauded) kindness
appealing to the mark’s dishonesty
distracting them so they act automatically
arouse them so they act viscerally
what types of human mistakes are there
forgetting plans, intentions
misidentifying objects, signals
retrieval failures
rule-based mistakes like applying the wrong procedure
knowledge-based mistakes with heuristics and biases
what are aspects to be considered with passwords
will users enter them correctly
will users remember them
will users choose a strong password
will users be tricked into revealing passwords
password recovery is a weak point involving basic info that doesn’t change, accounts for public figures are especially vulnerable
how can we limit brute-force repeatedly guessing passwords
online services and tamper-proof hardware like 3 guesses allowed for ATMs, or timeouts for login attempts to webservices
how to mitigate the worst effects of a stolen password file
use key stretching techniques like PDBKF2, hashing the password with a per-user salt repeatedly to produce a derived key that can be used as a cryptographic key
breach reporting laws state that breaches must be reported to the individuals who have been compromised
Oauth is a potential solution that allows a website to access resources hosted on other sites on behalf of a user using Access Tokens but privacy problem as they are a third party, they will know how often users log in and how long they are on the site
how did Mat Honan get hacked just with his Twitter handle
Twitter: find personal website, Gmail, home address
Gmail: account recovery gave alternative email showing that he had an AppleID account because no 2FA
needed billing address and last 4 digits of credit card for Apple’s tech support to give access
got billing address from searching on personal website
Amazon: call with name, address, email, adding new fake credit card to account
Amazon: call again with name, address, fake credit card number, adding new email to account
Amazon: send password reset to new email, allowing to see last 4 digits of all cards
Apple: call with billing address and last 4 digits of credit card to get temp password for AppleID email
Gmail: reset password for Gmail account sent to AppleID email
Twitter: reset password for Twitter account sent to Gmail