Biology 173 Exam 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Qualitative Data
recorded descriptions
Quantitative data
numerical measurement, organized into graphs and tables
hypothesis
a possible explanation that leads to a testable prediction and motivates experiments. NOT an if-then statement and must be falsifiable
prediction
description of an expected outcome in the test (experimental) group and in each control group
controlled experiment
single variable is changed in an experimental group and compared with a control group
independent variable
the factor being manipulated by researchers
dependent variable
the one predicted to be affected in response to the independent variable
controls
set up so the researcher knows in advance what result should be expected if everything in the study is working properly
negative control
a variable is not changed and you don’t expect a reponse/effect from that lack of change (ie. not adding an enzyme to the catechol)
positive control
a variable with a known effect is being introduced and you expect a certain effect (ie. swabbing the known bacteria onto plate to show that the agar is working properly)
Serial dilutions
a method used to create a range of concentrations of a substance. One with full concentration is diluted stepwise, to obtain lower concentrations for experimental analysis.
spectrophotometer
an instrument used to measure the intensity of light at different wavelengths which we used to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution by measuring the absorbance of light
absorbance
the amount of light absorbed by a sample, varies by concentration of substances
transmittance
the amount of light passing through a sample, proportional to absorbance
species interactions- competition
(-/-)when individuals (of the same/different species) share the use of a resource that limits the growth, survival, or reproduction of each (can be interspecific or intraspecific, interference or exploitation)
intraspecific competition
competition between individuals of the same species
interspecific competition
competition between individuals of different species
interference competition
individuals that are competing are directly interacting with each other (ie fighting)
exploitation competition
organisms compete through the consumption of a limited resource (ie food/sunlight/nesting habitats)
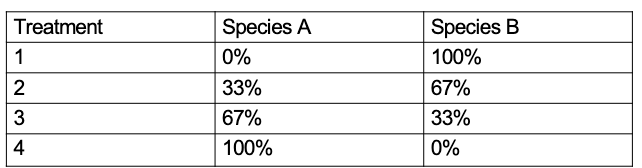
de Wit Replacement Series
experimental design technique used in ecology lab pt1, used to examine resource use and productivity between competing species, also looks at interspecific vs intraspecific
null hypothesis
a hypothesis which assumes no result and that the control and experiment groups will be identical
monoculture
cultivation of a single species in a plot
mutualism
(+/+) an interaction which causes beneficial outcomes for each organism
amensalism
(-/0) an interaction which causes a negative reaction for one organism and a neutral reaction in the other organism
predation/herbivory/parasitism
(+/-) interactions where one organisms is benefitted while the other is harmed
commensalism
(+/0) a relationship where one is benefited and the other is neutral
neutralism
(0/0) a relationship which neither organism benefits nor harms from
enzyme
a protein (chain of polypeptides) that catalyze (make go faster) biological reactions, in lab we used polyphenoloxidase as our enzyme
form= function
the form (meaning shape, size, etc) of an enzyme is crucial to its functioning properly because the shape of the active site allows it to break/build the substrate properly, also means an enzyme only works on one substrate
RNA and enzymes
only other macromolecule that can carry out catalysis (ribosomes)
the catalytic cycle
1) substrate binds to enzyme in active site 2) induced fit- active site changes shape slightly to properly hold substrate 3) substrate has stress put on bonds/ positioned to react 4) Enzyme holds substrate in intermediate state to make it more likely to transition to product 5) enzyme lowers activation energy of reaction 6) allows substrate to become product more easily
initial rate
in lab, the increase in absorbance over the first two minutes of spectrophotometer readings divided by 2
generally, product at start- product formed/ time passed
rate of enzyme reaction is determined by ____
substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, temperature, pH, reaction order, product concentration, inherent inefficiency of enzyme, factors that affect enzyme shape
polyphenoloxidase’s substrate is __
catechol, which it breaks down into orthoqionine, which has a red-brown color
what concentration usually determines the reaction rate (ie. what is limiting)?
enzyme
Vmax
the maximum rate of reaction, all enzyme active sites are filled all the time, the higher the better
KM
the substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half-maximal, vary with conditions, is used as a measure of the affinity of enzyme for the substrate, the lower the better (bc its more likely to be at Vmax)
What graph do you use to find Vmax and KM?
rate vs. concentration of substrate
Cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers needed to bind or position the substrate and may help with catalysis, may be inorganic (like metal ions) or organic (which are coenzymes, think vitamins)
competitive inhibition
a molecule with a similar shape as the substrate competes for access to the active site, may be a chemical cousin of the true substrate, has less of an effect on rate at high substrate concentrations, Vmax will be the same as w/o inhibitor but Km will be higher
non-competitive inhibition
the competitor acts not on the active site but the allosteric site changing the shape of the active site and lowering Vmax. may or may not change Km, inhibitor is EQUALLY effective at inhibition regardless of substrate concentrations
percent inhibition
[(Activity without inhibitor - Activity with inhibitor) / Activity without inhibitor] x 100, constant when noncompetitive
gene regulation
the process of controlling when, where, and how much a gene is expressed
human microbiome
all the microorganisms that live on or in the human body, the colon is the largest repository for microorganisms
gut microbiome
4×103 organisms present, 200-1000 species, all three domains of life. roughly equivalent to the number of human cells in the body, but with 1000x more unique genes. Aid in digestion and nutrition, also help with immune system, susceptibility to infection, mood, aging, and drug interactions
fermentation
the chemical breakdown of a substance by bacteria, yeasts, or other microorganisms in the absence of oxygen
Metabolite
a substance created when the body breaks down food, drugs, chemicals, or its own tissues, created during metabolism
Fermentable/non-fermentable carbohydrates
those that can be broken down and "fermented" by gut bacteria in the large intestine, producing short-chain fatty acids and gases
Inulin
a natural, soluble dietary fiber found in various plants, including chicory, Jerusalem artichoke, garlic, and onion, It stays in the bowel and helps certain beneficial bacteria to grow.
Butyrate
Butyrate, a four-carbon short-chain fatty acid, is produced through microbial fermentation of dietary fibers in the lower intestinal tract.
streak plating
to obtain isolated colonies from an inoculum by creating areas of increasing dilution on a single plate
gene
a stretch of DNA which codes for a useful biological product (protein or RNA), region of a chromosome, including termination and activation sequences
chromosome
a long DNA double helix with proteins bound to it (human has 100-200 mil basepairs, bacteria has 0.5-10 mil)
DNA replication
separates parental strand, then creates a corresponding copy using helicase (unwinds), DNA polymerase (enzyme that synthesizes DNA through replication), primase (an enzyme that creates short RNA sequences called primers, which are essential for DNA replication), and ligase (acts as an enzyme that joins together fragments of newly synthesized DNA strands)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
DNA replication without the cells, produces many copies of a specific target segment of DNA (one gene) so it can be used for further analysis, three steps (heating/denaturation, cooling/annealing, and replication/extension), only uses polymerase compared to DNA replication
Needed for PCR
Template DNA
PCR master mix: Taq polymerase (which is heat stable DNA polymerase), pair of primers (DNA or RNA used to start DNA synthesis)(some amplify genes like the ones in lab for 16S rRNA), nucleotides (dNTPs)
and a thermocycler
PCR uses
to amplify a gene
providing a template for sequencing the DNA
makes it possible to detect whether a gene is present or not
Sanger DNA sequencing
a method used to determine the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA fragment by incorporating special chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides during DNA replication, allowing for the identification of the sequence based on the different lengths of DNA fragments generated
ddNTPs are used and labelled with a florescent tags according to their identity (T=red, C=blue, A=green, G=yellow) on a 1:100 ratio with regular dNTPs
gel electrophoresis
separates DNA based on size (largest strands travel the shortest distance from the well)
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) Analysis
looks at a chromatogram and compares it to known samples to determine a best match