Acid And Bases New
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Acid
Acid is a proton donor
Base
Base is a proton acceptor
Monobasic/protic, dibasic/diprotic and tribasic/triprotic
If a substance disassociates in water to produce 1 H+ ions it is monobasic/monoprotic, if 2 are produced, the acid is dibasic/diprotic and if 3 are produced the acid is tribasic/triprotic
Strong acid
Stronger the acid - the more readily it donates the proton
Strong Base
Stronger the base the more readily it accepts the proton
Acid-Base Reactions
An acid-base reaction involves the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base.
HCl (acid) + H₂O (base) → H₃O⁺ (acid) +Cl⁻ (base)
HCl donates a proton to water, forming H₃O⁺ (hydronium ion) and Cl⁻.
Water acts as a base because it accepts the proton.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair
an acid and a base that differ from each other by the presence or absence of a single hydrogen ion.
Conjugate Acid
The species formed when a base gains a proton.
The conjugate acid gains a positive charge
Conjugate Base
The species formed when an acid loses a proton.
The conjugate base gains a negative charge
Amphoretic Behaviour
Amphoteric behavior refers to the ability of a substance to act as both an acid and a base, depending on the circumstances.
Water can act as:
An acid (donates H⁺):
H₂O+NH₃→NH₄⁺+OH⁻
Water donates a proton to ammonia, acting as an acid.
A base (accepts H⁺):
Acid reaction with a metal
Acid+Metal→Salt+H2
It produces salt and hydrogen
Acid reaction with Carbonates and Bicarbonates
Acid+Carbonate/Bicarbonate→Salt+H2O+CO2
It produces salt, water and CO2
Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization reactions are chemical reactions in which an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water
HCl + NaOH = NaCl + H2O
pH
The pH scale measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. The more hydrogen ions, the stronger the acid.
The concentration of H⁺ ions changes by a factor of 10 between pH values.
PH of a solution is the negative logarithm base-10 of the hydrogen ion concentration, measured by moles per liter.
How can pH be measured
The quantity of hydrogen ions in solution can affect the color of certain dyes found in nature. These dyes can be used as indicators to test for acids and alkalis.
PH can be measured using universal indicator paper and solution as well as a pH meter.
pH questions
1. Calculating pH of an acid from hydrogen ion concentrations
-log10[hydrogen ion concentrations (* amount of H+ ions in an acid)
2. Calculating hydrogen ion cocnetration from ph
10-PH
3. Calculating pH of a base
14 -log10[hydroxide ion concentrations (* amount of oh ions in a base)
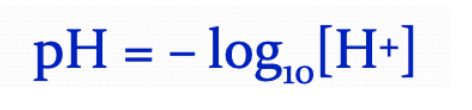
Limitations of pH scale
Temperature dependent
Limited to a range of 0-14, in theory there can be pH values of substances beyond this range.
Do not work well with concentrated solution, due to limited disassociation.
Limited to aqueous reactions, reactions can occur in other types of solution.