Topic 1.1: The Causes of World War I
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What are the MAIN long-term causes of World War I?
Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, Nationalism (MAIN).
What was the Moroccan Crisis in relation to World War I?
A significant event that exemplified imperialist tensions leading up to World War I.
What event is considered the trigger for World War I?
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
What was the July Crisis?
A series of events following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand that led to the outbreak of World War I.
What does militarism mean in the context of World War I?
The belief that a nation must increase its military capabilities and the glorification of war.
What was the Naval Race between England and Germany?
A competition between the two nations to build the largest and most powerful naval fleet.
What was the purpose of the alliance system before World War I?
To prevent war through a balance of power.
What was the Franco-Russian Alliance and when was it established?
An alliance formed in 1894 between France and Russia.
What was the Triple Entente?
An alliance formed by Britain, France, and Russia, confirmed in 1907.
What was the Triple Alliance?
An alliance formed in 1882 between Austria-Hungary, Germany, and Italy.
What is imperialism in the context of World War I?
The policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization.
What was Weltpolitik?
Germany's policy aimed at expanding its colonies and influence.
What role did nationalism play in the causes of World War I?
Nationalism fostered competition and tensions among nations, contributing to the war's outbreak.
What is the significance of the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand?
It is considered the immediate cause that triggered the outbreak of World War I.
How did the Balkans Crisis contribute to World War I?
It heightened tensions among European powers and set the stage for conflict.
What percentage of people owed allegiance to the British Empire on the eve of WW1?
1 in 4 people owed allegiance to the British Empire.
What is nationalism in the context of World War I?
Nationalism is an extreme form of patriotism, characterized by a strong love for one's country.
What does Max Hastings argue about responsibility for the outbreak of war?
He states that 'NO ONE NATION DESERVES ALL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE OUTBREAK OF WAR'.
What was the First Moroccan Conflict?
In 1912, France established a protectorate over Morocco, which angered Germany when Kaiser Wilhelm II visited Morocco in 1905 to support the Sultan.
What was the outcome of the First Moroccan Conflict?
The crisis was resolved at the Algeciras Conference in 1906, reaffirming French control over Morocco.
What triggered the Second Moroccan Conflict?
In 1911, Germany sent a naval cruiser to Morocco in response to a tribal revolt, believing France was using it as a pretext to seize control.
What was the outcome of the Second Moroccan Conflict?
Germany was forced to accept French control of Morocco following the Agadir Conference.
What is the definition of a protectorate?
A relationship between two countries where one country has more control over another, often relying on the stronger for defense.
What was the Anglo-Franco Entente?
An agreement between Britain and France that strengthened their alliance, particularly during the Moroccan crises.
What historical interpretation is often associated with Germany regarding WWI?
Germany is often blamed for starting WWI, leading to discussions about the validity of this interpretation.
What was the purpose of the Moroccan Crisis in the context of WWI?
It heightened tensions between European powers, particularly between France and Germany.
What is the significance of the quote attributed to Otto von Bismarck regarding the cause of World War I?
It suggests that European speculation indicated that the war would arise from a seemingly trivial incident in the Balkans.
What was the trigger event for World War I?
The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
What does the term 'Eastern Question' refer to?
Concerns Western European nations had about the Balkans following the decline of the Ottoman Empire.
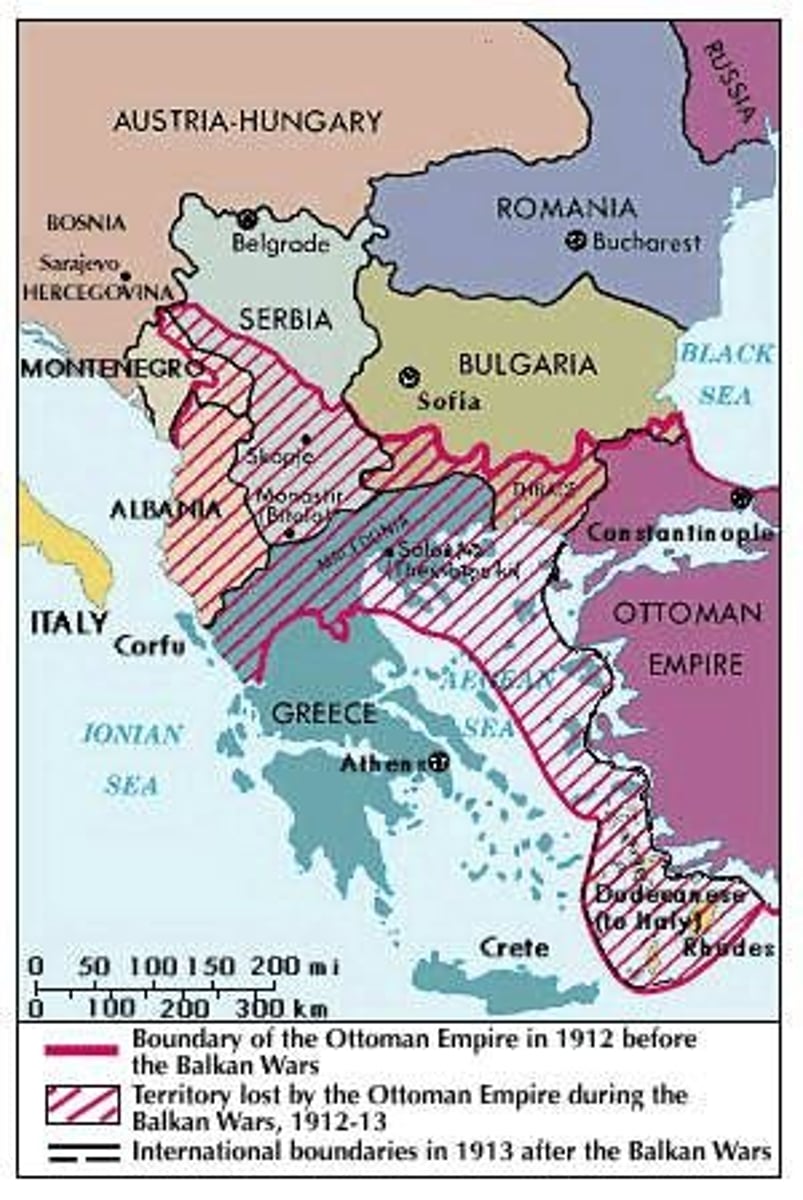
What was the objective of the Balkans League in 1912?
To incite cooperation among Balkan states against the Ottoman Empire.
What was the outcome of the Balkan War declared in October 1912?
The war aimed to weaken the Ottoman Empire and resulted in territorial gains for the Balkan League.
What geographical significance did the Balkans have before World War I?
The Balkans were becoming geographically important in Europe due to their strategic location and accessible waterways.
What does the term 'strategic location' imply about the Balkans before WWI?
It suggests that the Balkans were not initially seen as desirable but became important due to geopolitical interests.
What were the main concerns of Russia regarding the Balkans?
Russia aimed to gain control of the Bosporus to connect with ports in the Black Sea.
What did Western Europeans hope to achieve in the Balkans?
They sought to expand their influence and control over the region, particularly following the decline of the Ottoman Empire.
What was the primary objective of Russia in inciting the Balkan League in 1912?
To remove the Ottoman Empire from the Balkans and gain control of the Bosporus for access to Black Sea ports.
What significant event occurred in October 1912 regarding the Ottoman Empire?
The Balkan League was victorious over the Ottoman Empire in the First Balkan War, resulting in the Ottomans losing all remaining territory in Europe.
What was the outcome of the Second Balkan War in 1913?
Bulgaria attacked the Balkan League but lost.
How did Serbia benefit from the Balkan Wars?
Serbia emerged as the main beneficiary of the conflicts, gaining territorial advantages.
What impact did the Balkan Wars have on Russia's position in the region?
Russia viewed Serbia as its last buffer against Austria-Hungary and sought to strengthen its influence.
What event in 1908 escalated Serbian nationalism?
Austria-Hungary annexed Bosnia-Herzegovina from Serbia, increasing Serbian hostility towards Austria-Hungary.
What was the significance of Serbia's territorial gains after the Balkan Wars?
These gains were a significant outcome that fueled Serbian nationalism and aspirations.
What was the relationship between Serbia and Austria-Hungary before World War I?
Austria-Hungary believed it could defeat Serbia, which was seen as a growing threat.
What was the role of Germany in the context of the Ottoman Empire?
Germany sought to acquire Ottoman colonies during the decline of the Ottoman Empire.
What was the geographical significance of the Balkans?
The Balkans had several accessible waterways that were strategically important.
What was the primary concern of Western European nations regarding the Balkans?
The decline of the Ottoman Empire raised concerns about stability and power dynamics in the region.
What did Russia aim to achieve by controlling the Bosporus?
Russia aimed to connect with ports in the Black Sea.
How did the Balkan Wars affect the Great Powers?
The wars shifted power dynamics and heightened tensions among the Great Powers, particularly between Austria-Hungary and Russia.
What was the consequence of the Balkan Wars for Austria-Hungary?
Austria-Hungary faced territorial losses and increased tensions with Serbia.
What was the significance of pan-Slavism in the context of Serbian nationalism?
Pan-Slavism emerged as a movement that sought to unite Slavic peoples, influencing Serbian nationalism.
What did Russia realize about Serbia's role in the Balkans?
Russia recognized that Serbia was its last buffer against the influence of Austria-Hungary.
What was the strategic importance of the waterways in the Balkans?
The accessible waterways facilitated trade and military movement, making the region strategically valuable.
What was the outcome of the First Balkan War for the Ottoman Empire?
The Ottoman Empire lost all its remaining territory in Europe.
What did the term 'Balkan League' refer to?
An alliance formed by Balkan states to oppose and defeat the Ottoman Empire.
How did the Balkan Wars contribute to the onset of World War I?
The conflicts heightened tensions between the Great Powers and set the stage for further hostilities.
What was Germany's interest in the Ottoman Empire during the Eastern Question?
Germany wanted Ottoman colonies.
What was the outcome for the Ottoman Empire after the First Balkan War?
The Ottomans lost nearly all their remaining territory in Europe.
What happened in 1913 involving Bulgaria and the Balkan League?
Bulgaria attacked the Balkan League and lost.
Who declared independence for Bulgaria during the Balkan conflicts?
Ferdinand I of Bulgaria.
What territory did Austrian Emperor Franz Joseph I annex during the Balkan tensions?
Bosnia and Herzegovina.
What does the term 'primary source' mean?
An original document or firsthand account used in historical research.
What is a 'secondary source'?
A document or recording that relates or discusses information originally presented elsewhere.
What does 'historiography' refer to?
The study of historical writing and perspectives.
What is 'Pan Slavism'?
A political and cultural movement aimed at uniting all Slavic peoples.
What does the term 'Black Hand' refer to in the context of World War I?
A secret society that aimed to unify all South Slavs and was involved in the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
What ultimatum did Austria-Hungary issue to Serbia?
An ultimatum that was deliberately unacceptable, demanding Serbia's compliance or face military action.
What was Germany's response to Austria-Hungary's needs during the July Crisis?
Germany offered unconditional support to Austria-Hungary, referred to as a 'blank cheque'.
What was the outcome of Serbia's response to Austria-Hungary's ultimatum?
Serbia met almost all demands, but Austria-Hungary broke off diplomatic relations and declared war.
What was the significance of the 28th of July 1914?
Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia.
What action did Tsar Nicholas II take on the 30th of July 1914?
He authorized Russian mobilization.
What was the Schlieffen Plan?
Germany's military strategy to quickly defeat France and then turn to fight Russia.
What was the response of Britain to Germany's invasion of Belgium?
Britain declared war on Germany.
What did Britain propose on the 26th of July 1914?
A mediation conference, which was ignored by Germany and Austria-Hungary.
What did the Austro-Hungarian Ministerial council decide on the 7th of July 1914?
To issue a deliberately unacceptable ultimatum to Serbia.
What happened on the 1st of August 1914?
Germany declared war on Russia, and France began to mobilize.
What was the significance of the 3rd of August 1914?
Germany invaded Belgium and declared war on France.
What was the significance of the 25th of July 1914 in the context of the ultimatum?
Serbia replied to the ultimatum, but Austria-Hungary chose to escalate tensions.