Unit 1 Human Anatomy
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Basic Anatomy Terms, Cytology, and Histology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Anatomy
study of “normal” body structure
Pathology
study of abnormal body structure
Physiology
study of body function
Pathophysiology
study of abnormal body function
Gross anatomy
can be seen by the naked eye
ex. dissection, cadavers, autopsy, and exploratory surgery
Radiography
X-rays - used to look at bones
Computed tomography
CT - used to see soft tissues
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI
Positron emission tomography
PET - used to look at the brain and detect cancer
Sonography
ultrasounds
Clinical procedures
Inspection
Palpation
Percussion
Auscultation
Reflex response
Palpation
used to feel pulse and lymph nodes
Percussion
tapping back or chest and looking for density changes
Auscultation
listening with a stethoscope
Reflex response
used to check for spinal nerve/cord damage
Levels of human structure
microscopic and macroscopic
Microscopic
cellular (cytology) and tissue (histology)
Macroscopic
Organ and organ system
Anatomical position
· Person stands erect with feet flat on the floor
· Arms at sides with forearms supinated
· Palms, face, and eyes facing forward
Dorsal body cavity
includes the cranial cavity and vertebral canal (CNS)
Ventral body cavity
includes the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity (trunk)
Layers of serous membranes
Parietal, serous cavity, and visceral
Parietal
outer wall
Serous cavity
in between parietal and visceral and filled with fluid
Visceral
inner wall
Pericardium
serous membrane around the heart
Pleura
serous membrane surrounding the lungs
Peritoneum
serous membrane surrounding the abdominal organs
Axial
cephalic, cervical, trunk (thorax and abdominopelvic), and back (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral)
Appendicular
upper extremities and lower extremities
Upper extremities
axillary, brachium, antebrachium, carpus, pollex, digits
Lower extremities
inguinal, femoral, patellar/popliteal, crural, tarsus, hallux, digits
Superior/cranial
toward the top of the body
Inferior/caudal
toward the bottom of the body
Anterior
more toward the front of the body
Posterior
more toward the back of the body
Medial
more toward the midline of the body
Lateral
farther from the midline of the body
Proximal
more toward the joint/attachment point
Distal
farther away from the joint/attachment point
Ipsilateral
toward the same side
Contralateral
toward the opposite side
Sagittal plane
divides the body into right and left sides
“getting on the saddle” - in line with the horse
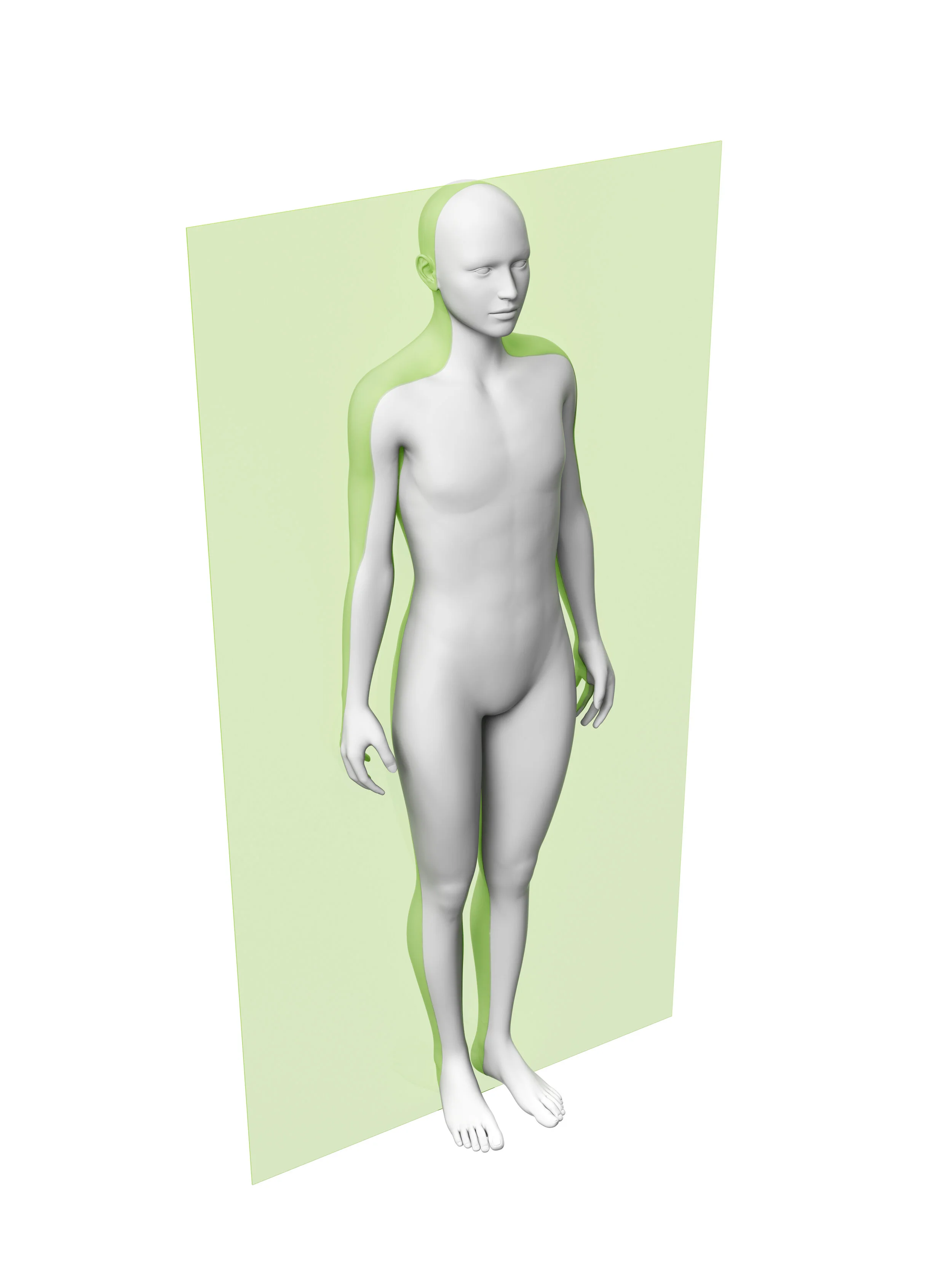
Frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections

Transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior sections
Cells
most basic structural/functional unit of the body
Characteristics of Life
complex organization, metabolism, homeostasis, responsiveness and movement, growth and development, and reproduction
Squamous
thin, flat cells that line airways and the skin
Cuboidal
square-shaped cells found in the liver
Columnar
cells that are taller than wide found in the inner lining of the stomach and intestines
Plasma membrane
unit membrane that encloses a cell and controls the traffic of molecules into and out of it
made up of a lipid bilayer and contains transmembrane proteins, peripheral proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, and glycocalyx
Lipid bilayer
made up of phospholipids with hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic heads
Transmembrane proteins
spans both layers of phospholipids
have different functions and roles
receptor, enzyme, channel, gated channel, cell-identity marker, and cell-adhesion molecule
Receptor
binds to chemical messengers
Enzyme
breaks down a chemical messenger and terminates its effect
Channel
constantly open and allows solutes to pass into and out of the cell
Gated channel
opens and closes to allow solutes through only at certain times
Cell-identity marker
glycoprotein acting as a cell-identity marker distinguishing the body’s own cells from foreign cells
Cell-adhesion molecule (CAM)
binds one cell to another
Peripheral proteins
proteins on one side of the lipid bilayer
Glycoproteins
carbohydrate attached to a protein
Glycolipid
carbohydrate attached to a lipid
Glycocalyx
sugar coating of all cells
Intracellular face
side of the plasma membrane facing the cytoplasm
Extracellular face
side of the plasma membrane facing outward
Filtration
physical pressure forces fluid through a membrane
Simple diffusion
net movement of particles from high concentration to lower concentration
Osmosis
net diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
Facilitated diffusion
movement of a solute through a membrane and down the concentration gradient with the aid of a carrier protein
Active transport
carrier-mediated transport of a solute through a unit membrane up its concentration gradient
Endocytosis
vesicular processes that bring matter into a cell
Exocytosis
vesicular processes that release material from a cell
Microvilli
extensions of the plasma membrane that increase the surface area
Cilia
hairlike processes with sensory functions
Pseudopods
cytoplasm-filled extensions of the cell
Intracellular matrix (ICM)
cytoplasm
organelles + cytosol
Nucleus
contains DNA
contains chromatin and the nucleolus
Golgi body
modifies and packages synthesized proteins and synthesizes carbohydrates
Centriole
short cylindrical assembly of microtubules
Ribosomes
small granules of protein and RNA in the cytosol and mitochondria and on the surface of the rough ER and nuclear envelope
Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes steroids, detoxifies alcohol and other drugs, and manufactures the membranes of the cell
Lysosome
membrane-bounded packets of enzymes
Peroxisome
contain different enzymes than lysosomes
use oxygen to oxidize organic molecules
Proteasome
protein-degrading organelles
Mitochondria
converts glucose into ATP
Cytoskeleton
supports the cell, determines its shape, organizes its contents, and contributes to movement
microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate fibers
Inclusions
either accumulated cell products and granules of glycogen or internalized foreign matter
Hemidesmosome
attaches cell to basement membrane of ECM
Desmosome
attaches cell to cell and provides elasticity
Tight junction
attaches cell to cell and prevent paracellular diffusion
“ziplock”
Gap junction
attaches cell to cell and establishes a passageway
Cellular diversity
shape/size
function
differentiation - development of a more specialized form and function; which genes are turned on
Histones
proteins with DNA wrapped around them
forms nucleosomes → chromosomes
G1
cell synthesizes proteins, grows, and carries out its predestined tasks for the body
S
cell makes duplicate copies of its nuclear DNA and centrioles
G2
cell finishes replicating its centrioles and synthesizes enzymes that control cell division
Mitosis (M)
cell replicates its nucleus, divides its DNA, and forms two identical daughter cells
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Transcription
DNA → mRNA; takes place in the nucleus
mRNA leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore to enter the cytoplasm (rER)
strand is fed through a ribosome and read as a codon
codons translate to amino acids → protein
Post translation
protein enters the golgi body for modification
Newly formed proteins are…
packaged into lysosomes
incorporated into the plasma membrane (ex. transmembrane, peripheral…)
exported by exocytosis