**Geology ALL QUIZES** (quiz 12 is research summary)
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Q14 and Q2 have one identical question with the same answer so I skipped the duplicate on the flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
(Q1) Stars are just like ___, but they lie farther away from Earth
the Sun
(Q1)These are relatively small rocky or metallic objects that orbit the Sun
Asteroids
(Q1)The formation of the first atoms in the Universe is called ___ nucleosynthesis
Big Bang
(Q1)Using simple observations, reason, and math, Eratosthenes determined that Earth was spherical and its ___ was approximately 40,000 km
Circumference
(Q1)In the context of scientififc cosmology, there are two basic entities: _____ and ___
Matter and energy
(Q2)Analyses suggests that the inner core is most likely primarily composed off ____ and ___
Iron and nickel
(Q2)The boundary between the crust and mantel, called the ___, may be detected by changes in seismic wave velocity
Moho
(Q2)Temperature and pressure at Earth’s center probably reaches ___ and ___
6,000C and 3.6 million atmospheres
(Q2)The terms lithosphere and crust are not synonymous; most of the lithosphere actually consists of ___ rock
mantle
(Q2)The mantle experiences upwards flow in warm regions and downwards flow in cooler regions; a process known as_____
convection
(Q3)Harry Hess proposed that the old ocean floor sinks into the mantle through the process of____
subduction
(Q3)Wegner predicted the existence of a supercontinent called ______
Pangea
(Q3)The broad flat regions of the seafloor that lie at a depth of 4-5km below sea level are known as_____
abyssal plains
(Q3)Glaciers leave evidence of their direction of flow by creating ____ in the substrate over which they flow
striations
(Q3)In the pacific ocean, we see many ____ that border all of the deep sea trenches
volcanic arcs
(Q4)For seafloor rocks, a ____ describes magnetic signatures that are stronger than expected
positive magnetic anomaly
(Q4)Rocks retain a record, known as _____, of Earth’s magnetic field that existed when the rock formed
paleomagnetism
(Q4) Drilling of the seafloor indicates that the oldest seafloor rock can be found ____
closer to continental slopes
(Q4)If a geologists knows the age of the seafloor rocks at a particular distance from a mid-ocean ridge, then she can calculate _____
spreading rate
(Q4) The primary support for Hess’s mechanism of seafloor spreading came from the interpretation of_______
marine magnetic anomalies
(Q5) The basin and Range province is an example of a continental rift in_____
western US
(Q5)___ is an example of a majestic rift valley volcano
My. Kilimanjaro
(Q5)An example of acient collisional mountains in the US would be ____
Appalachian
(Q5)____ Is an outward-directed force that contributes to moving plates away from a mid-ocean ridge axis
ridge push force
(Q5)The sinking of dense lithosphere at a subduction zone creates this force that moves plates apart at midocean ridges
slab pull force
(Q6)The banded iron formations of northern Michigan are examples of ___ mineral deposits
sedimentary
(Q6) In these mineral deposits, groundwater leaches metal from a rock and deposits them nearby, usually at at the water table
Secondary enrichment
(Q6) In these mineral deposits, ground water leaches elements from a rock, but it is the material left behind that is of value
residual
(Q6) In these mineral deposits, moving water in streams concentrates dense metal grains
(Q6) In these mineral deposites, circulation hot water concentrates minerals, normally in veins
hydrothermal
(Q7) Ignous rocks freezes at temperatures between ___ and ___
650C & 1100C
(Q7)Fragmental material explosively ejected during a volcanic eruption is known as
pyroclastic debris
(Q7) earth would be a cold solid mass if not for the heat continually generated by ___
decay of radioactive elements
(Q7)molten rock beneath earth’s surface is known as __
magma
(Q7) Four compositional types of molten rock are
Felsic, mafic, intermediate, ultramafic
(Q8) Igneous rocks with this texture are known to have cooled slowly
phaneritic
(Q8)Igneous rocks with this texture are known to have cooled very fast, almost immediently
glassy
(Q8)mafic scoria shows this texture
vesicular
(Q8)the Andes of South America formed in this tectonic setting
subduction ocean to continent
(Q8)The Aleutian Arc of Alaska formed in this tectonic setting
subduction ocean to ocean
Q9) In Hawaii, this hazard associated with recent eruptions of Kilauea has destroyed homes and shut down a geothermal powerplant.
lava flows
(Q9)Many volcanoes are topped with glaciers. The volcanic hazard killed 25,000 people in Amero, Colombia, 60km from Nevado del Ruiz.
lahars
(Q9)this volcanic hazard resulted in the death of 1742 people in Nyos, Cameroon. (came from lake Nyos)
toxic gas clouds
(Q9)In the Mediterranean, this civilization likely disappeared as a result of the eruption in Santorini
minoan
(Q9)All human evolution may have been altered by the eruption of ___ Volcano in Indonesia about 73,000 years ago
Mt. Toba

(Q10) Does Photo A show a fissure eruption or a summit crater eruption?
fissure
(Q10)What a effusive eruption?
when magma rises up through a volcano and simply flows out

(Q10)Which type of eruption does Photo B show?
summit crater
(Q10)What is an explosive eruption?
when magma rises through a volcano, but then explodes pyroclastic material out of the volcano due to pressure and gas. D:
(Q10)What is a Shield Volcano?
volcanoes that SOMETIMES have viscous lava being emitted from a central vent. They are large and look flat-topped. They can also sometimes have a collapsed caldera.
(Q10)What is a stratovolcano?
taller than a shield volcano and it emits explosive and pyroclastic debris from its central vent
(Q10)What is a Cinder Cone volcano?
volcano can be characterized by its bowl-shaped crater at the summit. They rarely grow more than a thousand fee above their surroundings
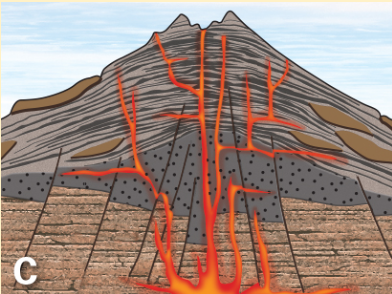
(Q10)What type of volcano does diagram C represent?
cinder cone
(Q10)What phenomena causes volcanic explosions?
The buoyancy of magma, the pressure from gasses in the magma, and the injection of magma into a magma chamber can all cause a volcanic eruption
(Q10) How does a caldera form?
the collapse of the ground that forms a large depression following a volcanic eruption.
(Q10)How does a super volcanic eruption differ from other eruptions?
volcanoes that has had an eruption with a volcanic explosivity index of 8
(Q10)What forces drive debris motion in a gas-thrust jet
characterized by large velocities and decelerations and is dominated by momentum

(Q10) What locations in photo D shows a pyroclastic flow?
X
(Q10) forces drive debris motion in a pyroclastic flow
a fast-moving avalanche-like mixture of hot gasses, ash, and volcanic rock fragments that flows downhill.
Q11)This chemical rock is formed from the calcium carbonate that precipitates directly from ground water
travertine
(Q11) this organic rock contains 15-30% organic material called kerogen
oil shale
(Q11) the burial and lithification of gravel-sized, angular (round) clasts produces
conglomerate
(Q11) Mud, when deposited in thin layers, is lithified and breaks into thin sheets, becomes ___
shale
(Q11) this biochemical rock is formed from the silica shells of plankton
chert
(Q11 Bonus)The transformation of loose sediment into solid rock
lithification
((Q10))What forces drive debris motion in a air fall ash
process where the pyroclastic dust which is carried to far away places by wind and later settles due to gravity
((Q10))What forces drive debris motion in a connective cloud
when volcanic ash and gasses are injected high into the atmosphere during an eruption.
(Q13) This rock type forms from the metamorphism of mafic rocks like basalt and gabbro
Amphibolite
(Q13)This rick type is a fine-grained nonfoliated metamorphic rock
Hornfels
(Q13) This foliated rock forms from the metamorphism of shale
Slate
(Q13) this rock type is characterized by light and dark compositional banding
Gneiss
(Q13)The soft, uniform texture of this rock was exploited by Michelangelo
Marble
(Q14) Within the lower portion of the upper mantle is the ____, an area of successive seismic discontinuities
Transition one
(Q14)Refers to areas where warmer and les dense mantle is rising
mantle upwelling
(Q14)within the upper portion of the upper mantle is the ____, an area where 1%-6% of peridotite melts
low velocity zone
(Q14) Gutenberg identified the core mantle boundary using ___
seismic waves
(Q15) The ____ of an earthquake is a measure of several wave amplitudes, dimension of slip, and total displacement
moment magnitude
(Q15)A magnitude (Mw) of 6 earthquakes results in ground motion that is____ times greater than a magnitude (Mw) of 5 earthquakes
Ten (10)
(Q15)A magnitude (Mw) of 8 earthquakes results in energy release is approximately____ times greater than a magnitude (Mw) of 7 earthquakes
Thirty-two (32)
(Q15) The San Francisco earthquake of 1906 is an example of ____ seismicity
transform plate boundary
(Q15) The New Madrid earthquakes of 1811-12 are an example of ___ seismicity
intraplate
(Q16) The term describes a thin film of runoff that flows down the land surface
Sheetwash
(Q16) This drainage network forms on the surface of conical mountains
Radial
(Q16) this feature of the landscape is also called the catchment
Watershed
(Q16) this drainage network forms across a landscape of parallel valleys and ridges
trellis
(Q16)This drainage network exhibits channels that form along pre-existing surface fractures, streams join one another at right angles
rectangular
(Q17) The relatively flat, shallow marine area off the Georgia coast is an example of a ____
Passive continental margins
(Q17) The nearly flat, deep marine area far off the Georgia coast is an example of a
abyssal plain
(Q17)____ form by erosion in areas offshore of major rivers along the east coast
submarine canyons
(Q17)Refers to the sediment that covers basalt on the deep ocean floor
pelagic
(Q17) A___ forms where a oceanic volcano sinks beneath the waves due to isostasy
seamount
(Q18) In an attempt to keep river channels open, engineers build ____ that extend the river mouth into deeper water
Jetties
(Q18) Disturbance of the natural sand balance on a barrier island will lead to ___
Beach erosion
(Q18)Concrete or stone walls protruding perpendicular to the shore are called
Groins
(Q18) The death of algae that live in coral polyps is called ____ and may be the result of global increases in seawater temperature
Reef bleaching
(Q18) Sewage and agricultural runoff into coastal waters creates ___ along coasts
Dead zones