Lab - Tissues
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
4 basic types of tissue
Muscle, connective, epithelial, nervous
?
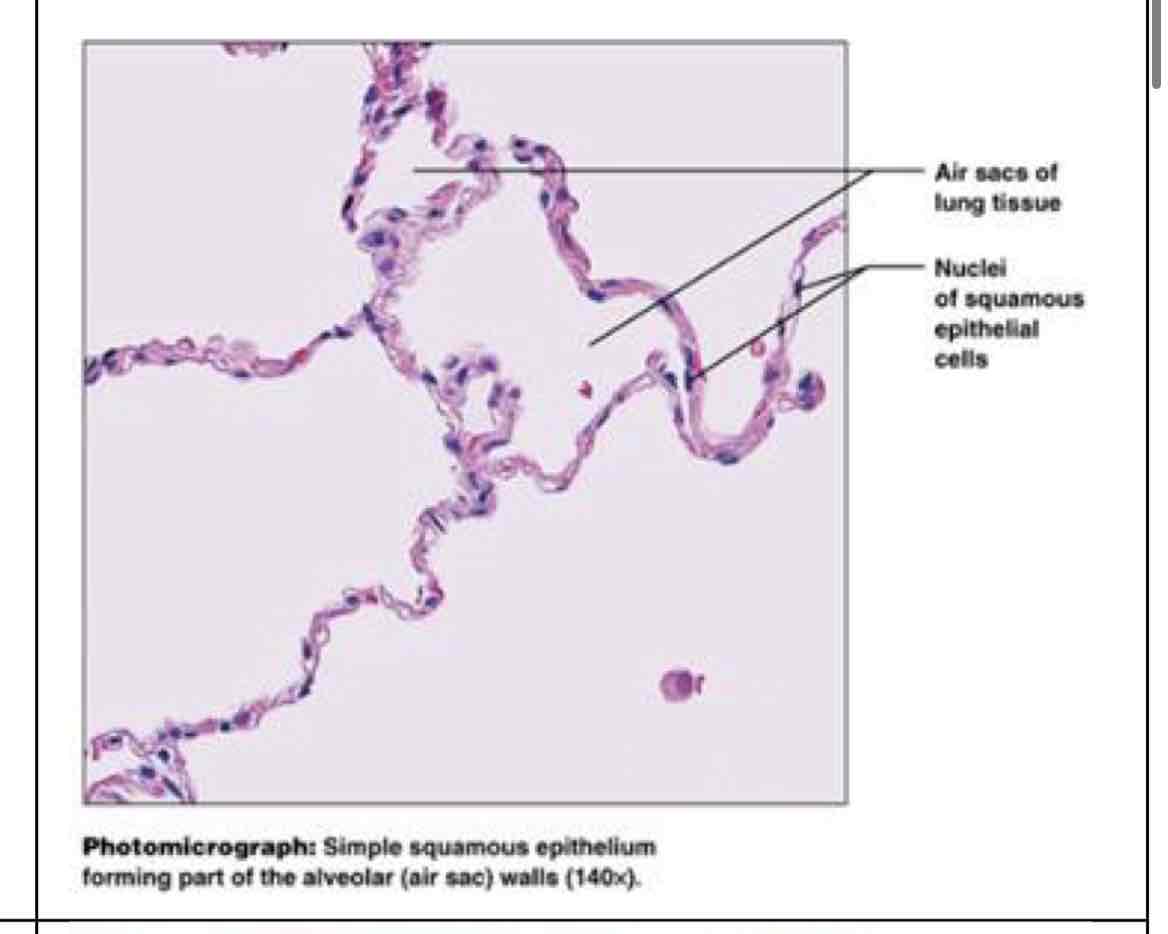
single squamous epithelial
?
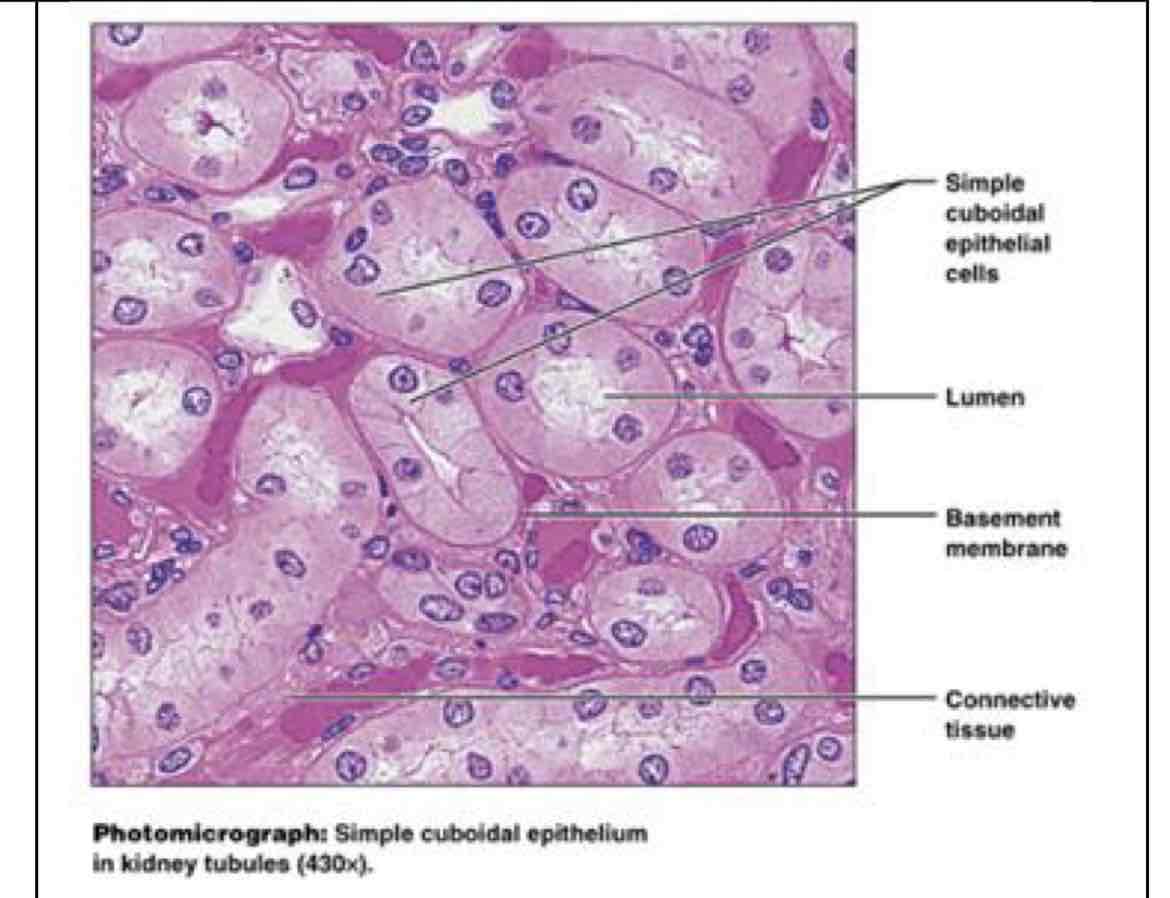
single cuboidal epithelial
?
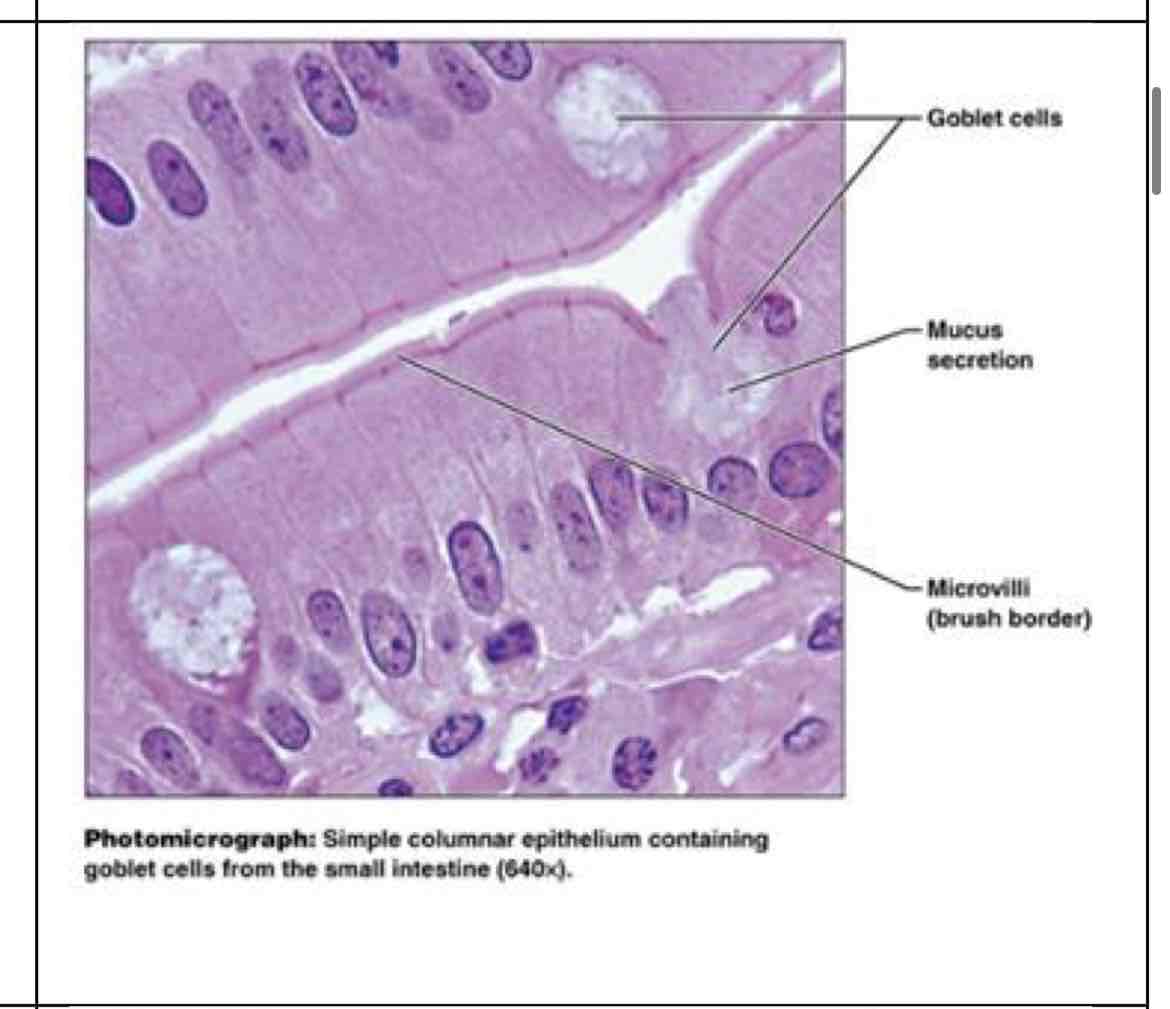
simple columnar epithelial
?
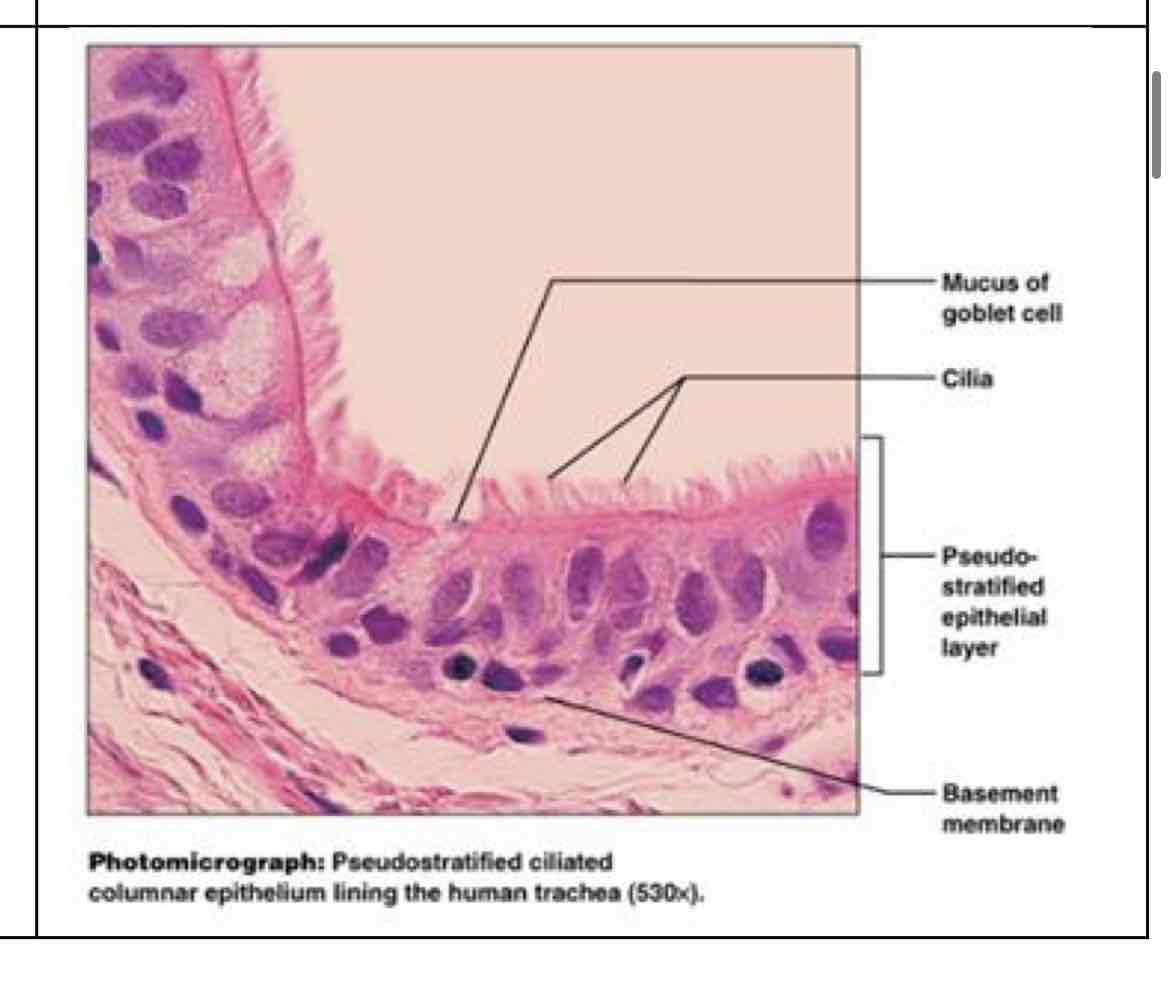
pseudostratified columnar epithelial
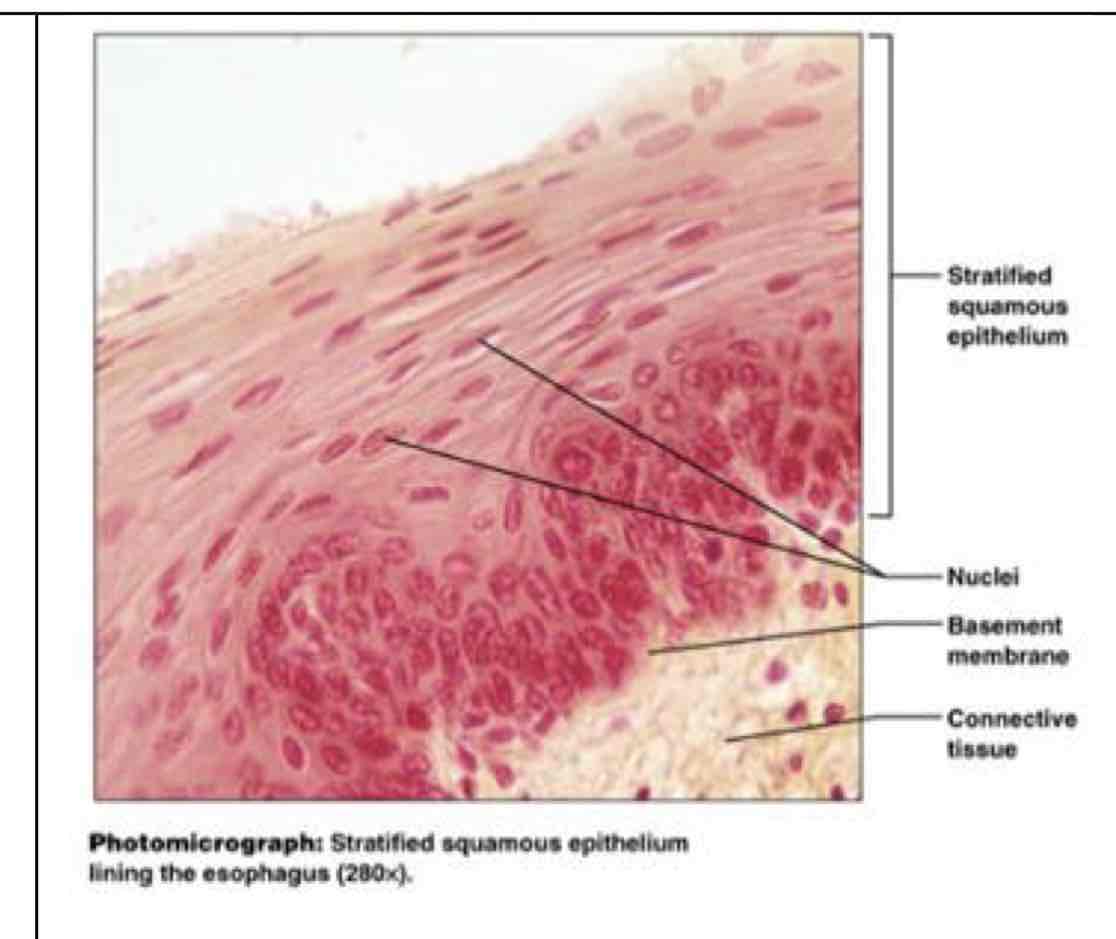
?
stratified squamous epithelial
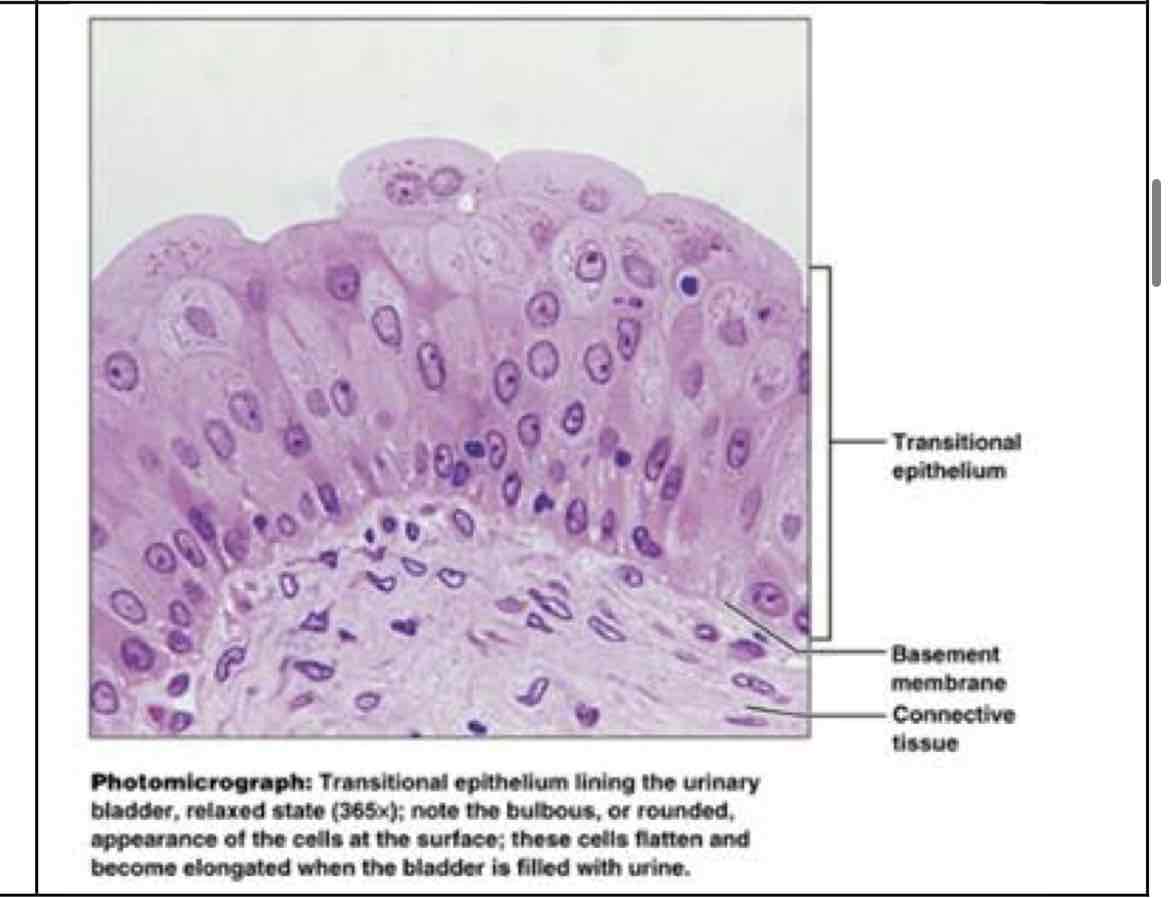
?
transitional epithelial
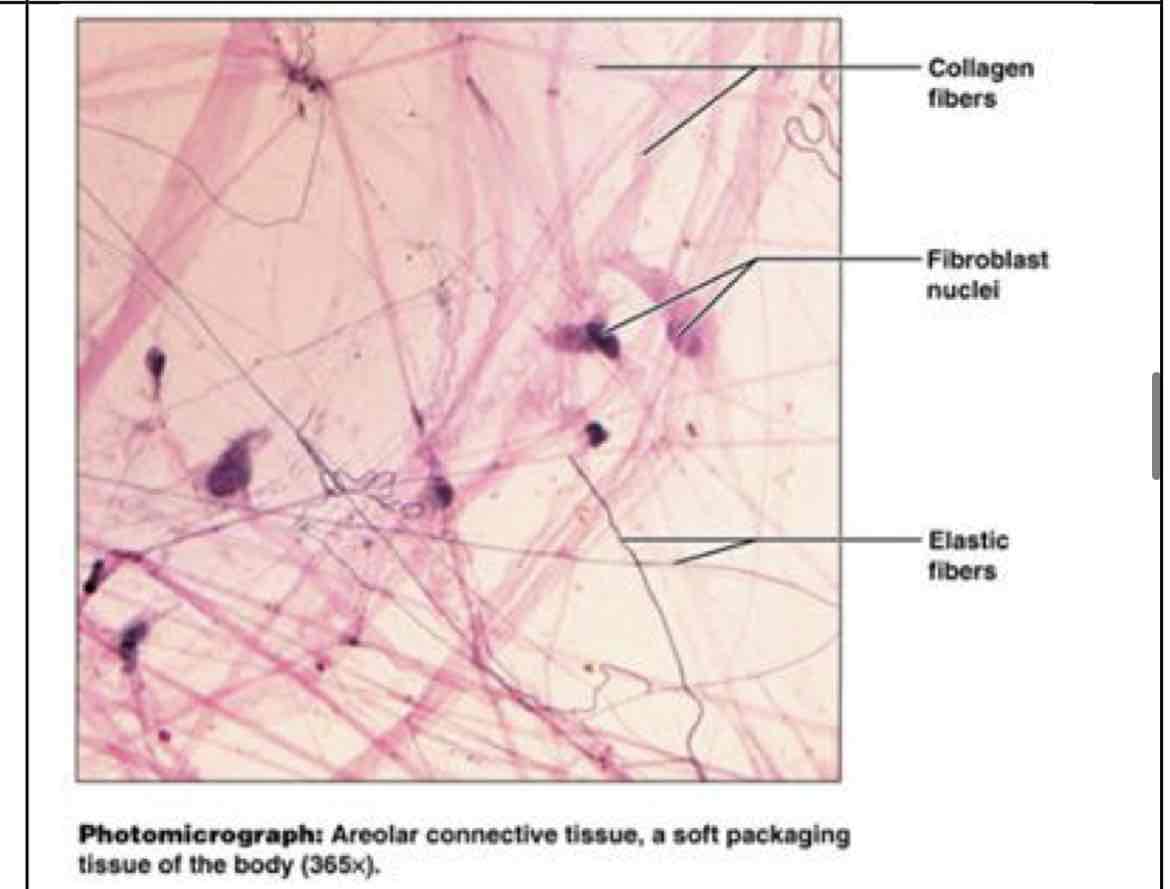
?
areolar connective
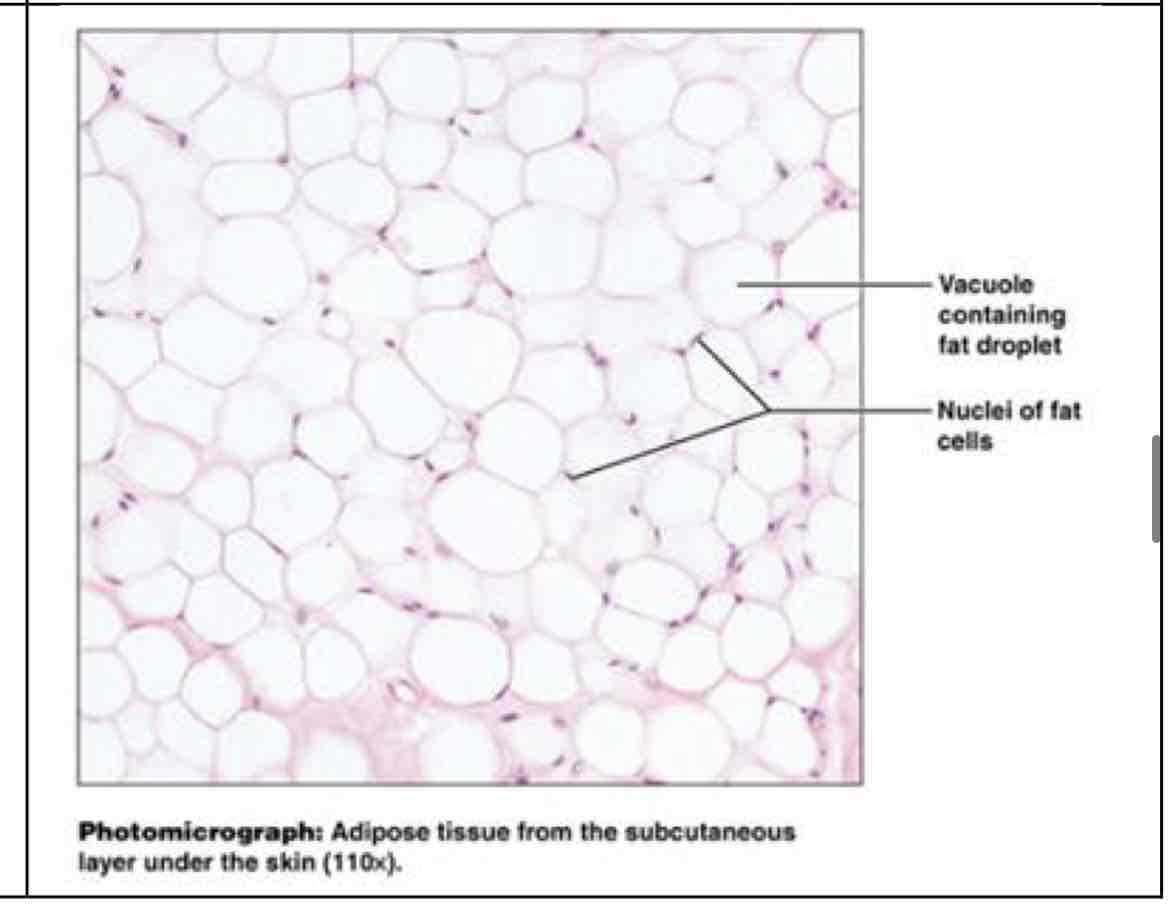
?
adipose connective
?
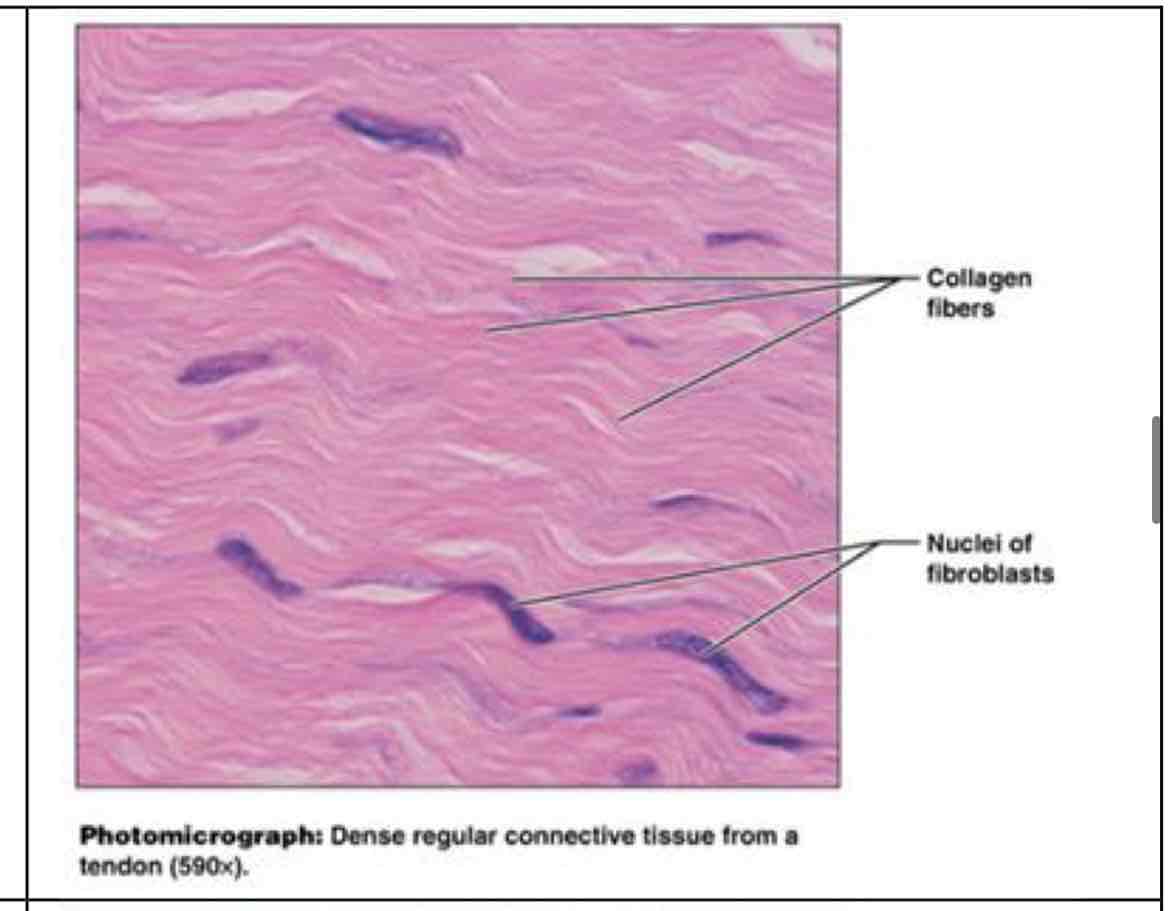
dense regular connective
?
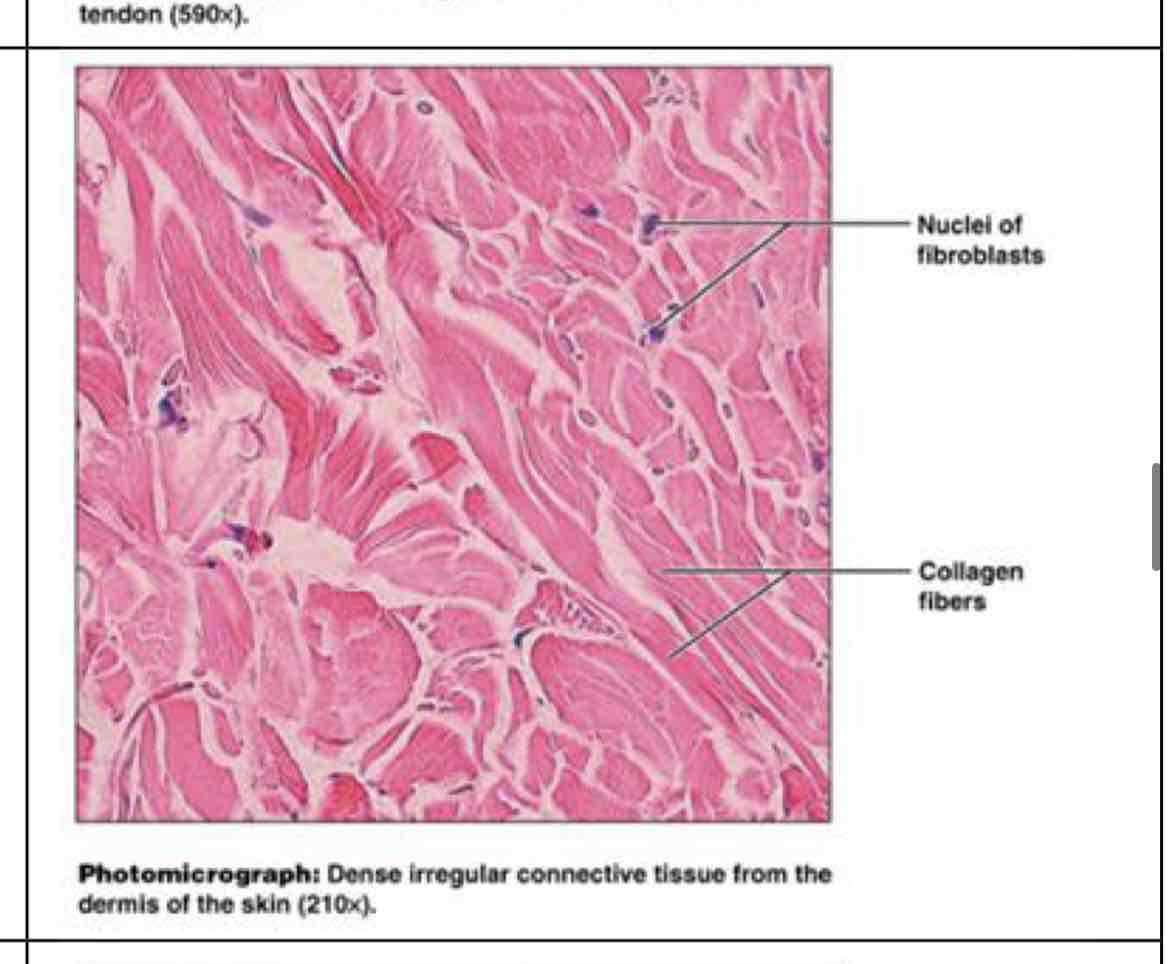
dense irregular connective
?
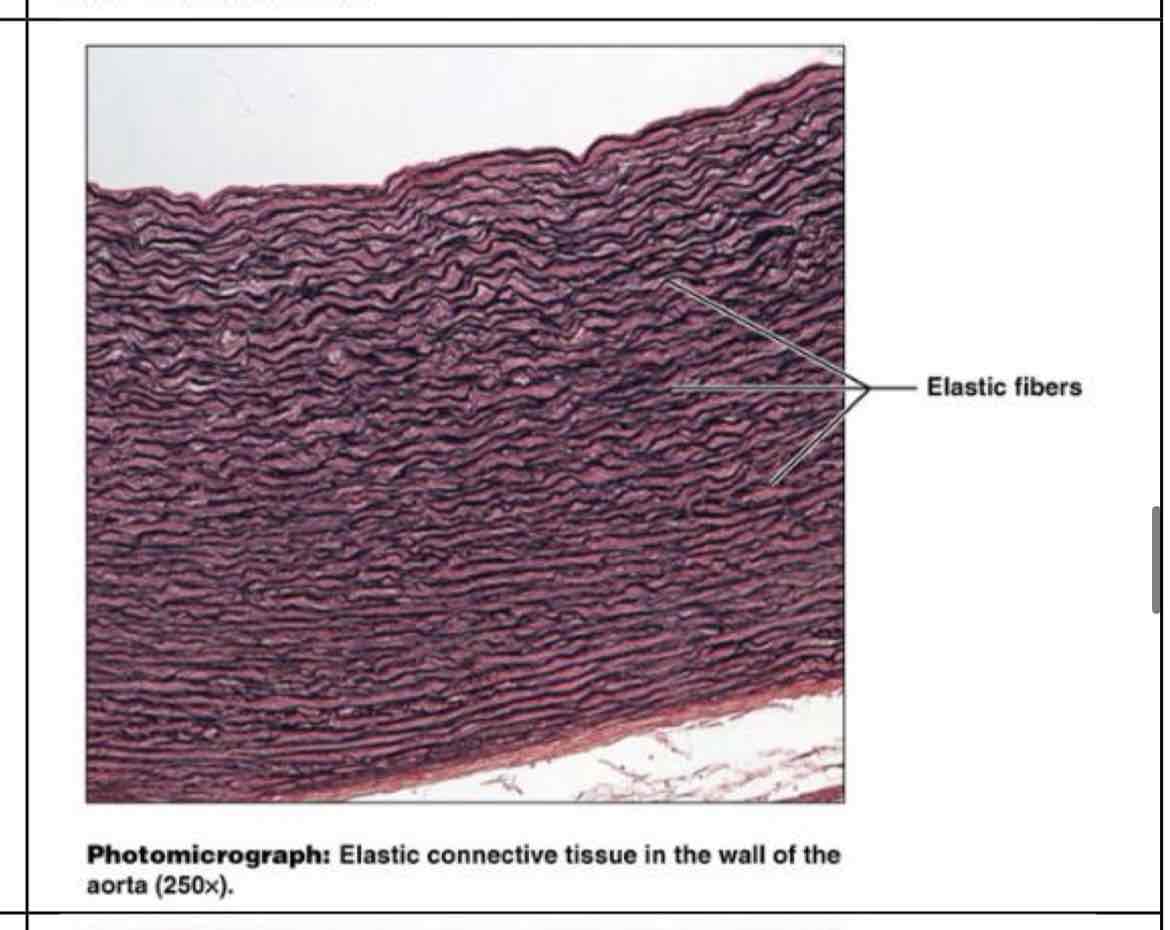
elastic connective
?
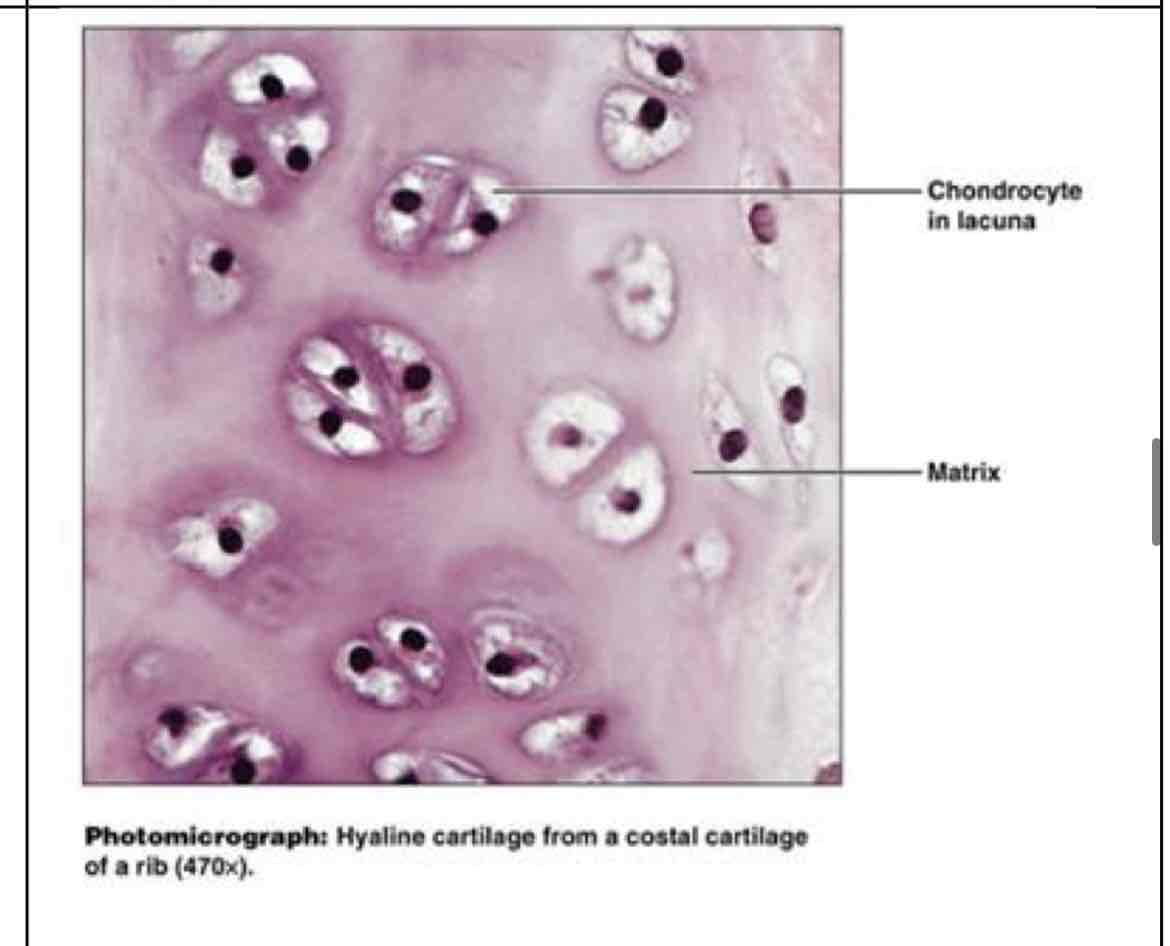
hyaline cartilage
?
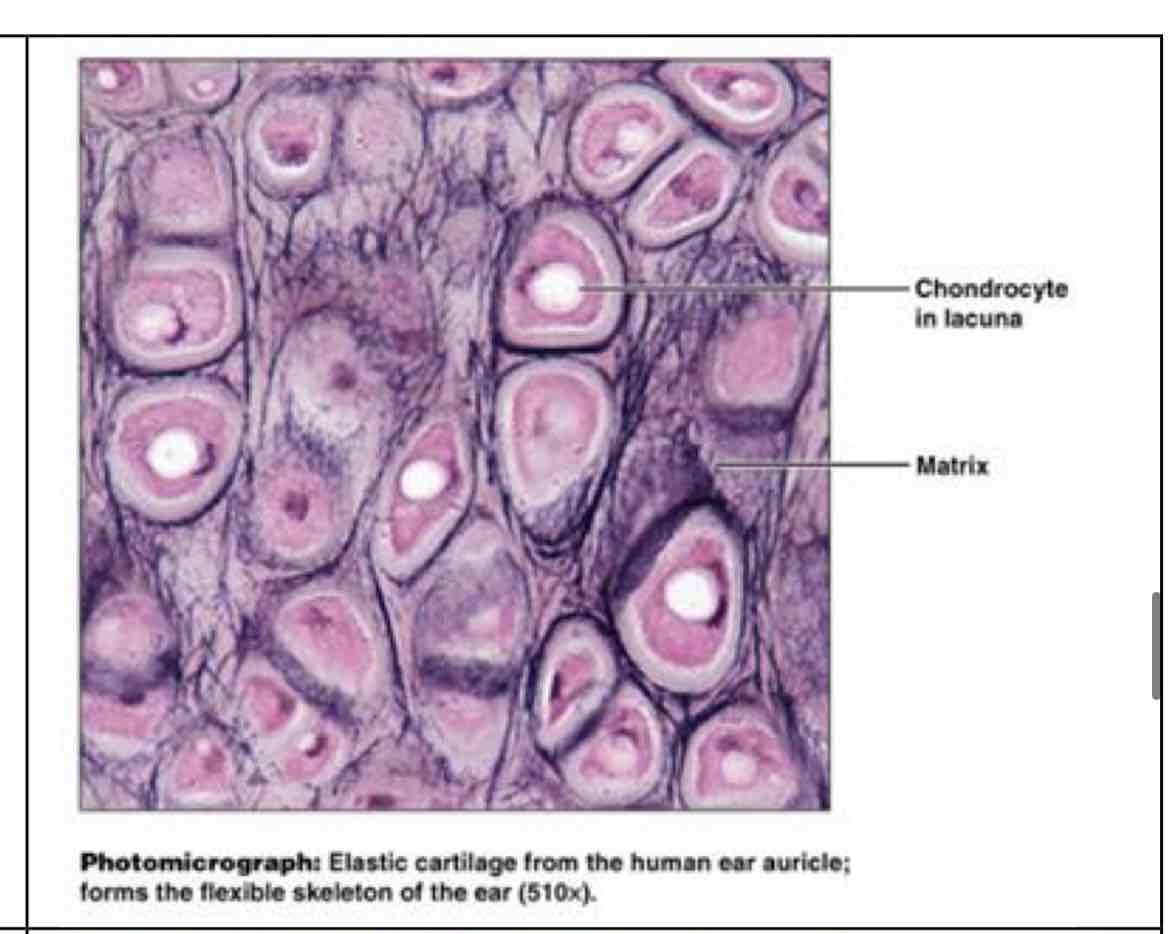
elastic cartilage
?
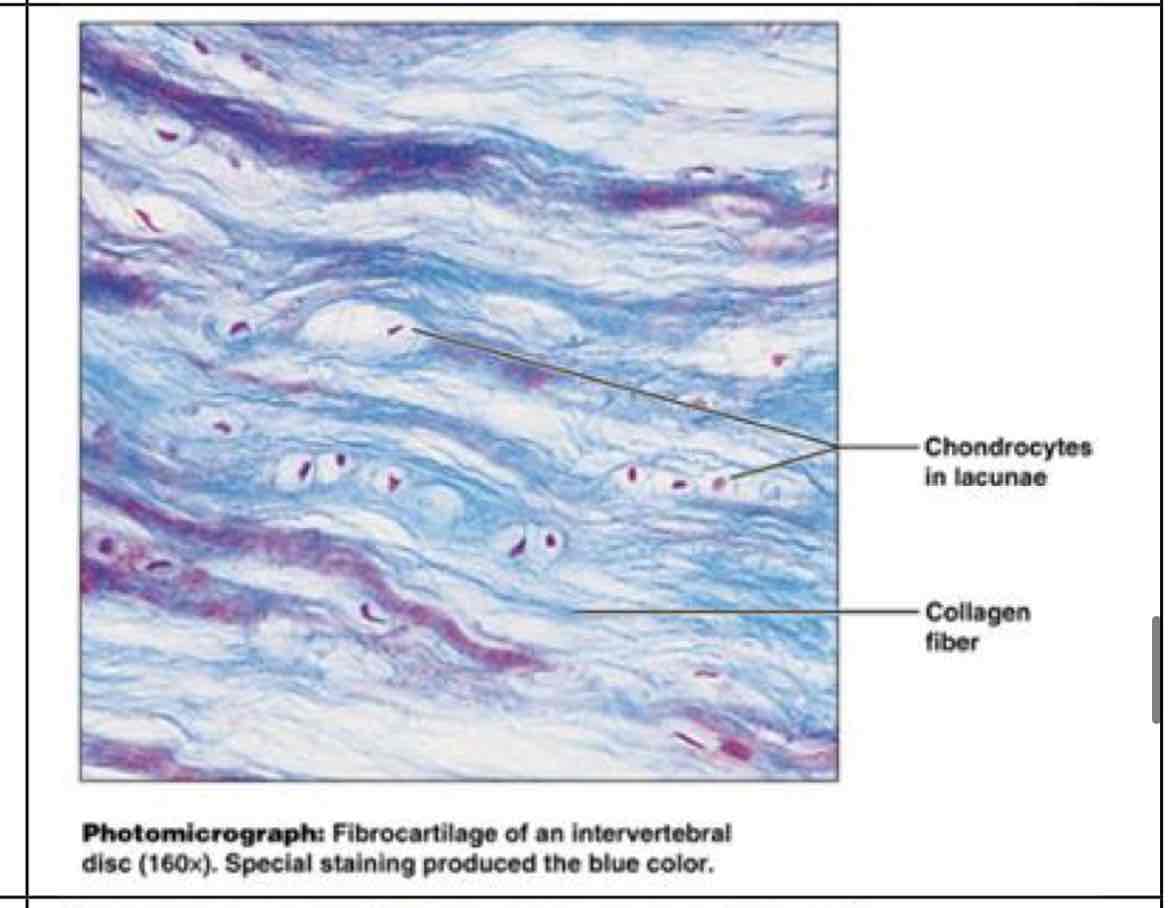
fibrocartilage
?
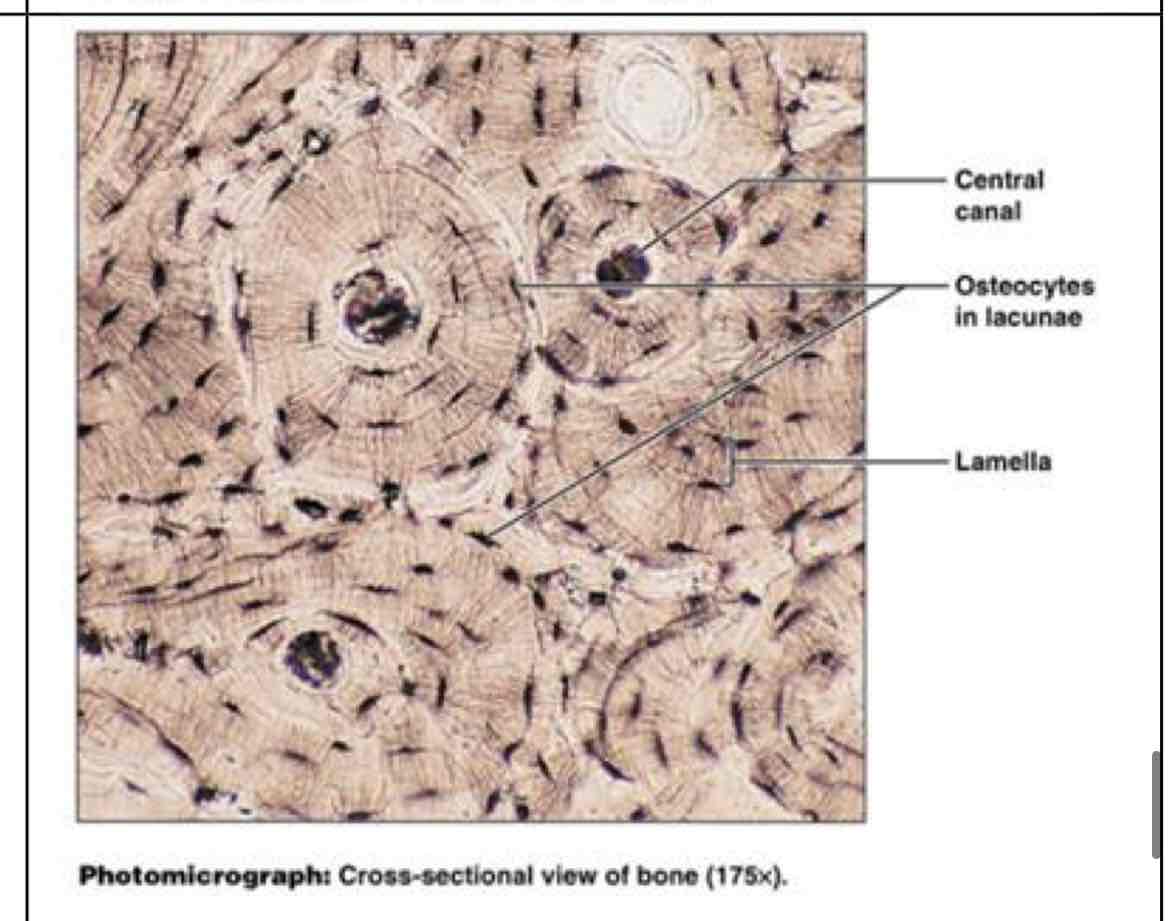
bone
?
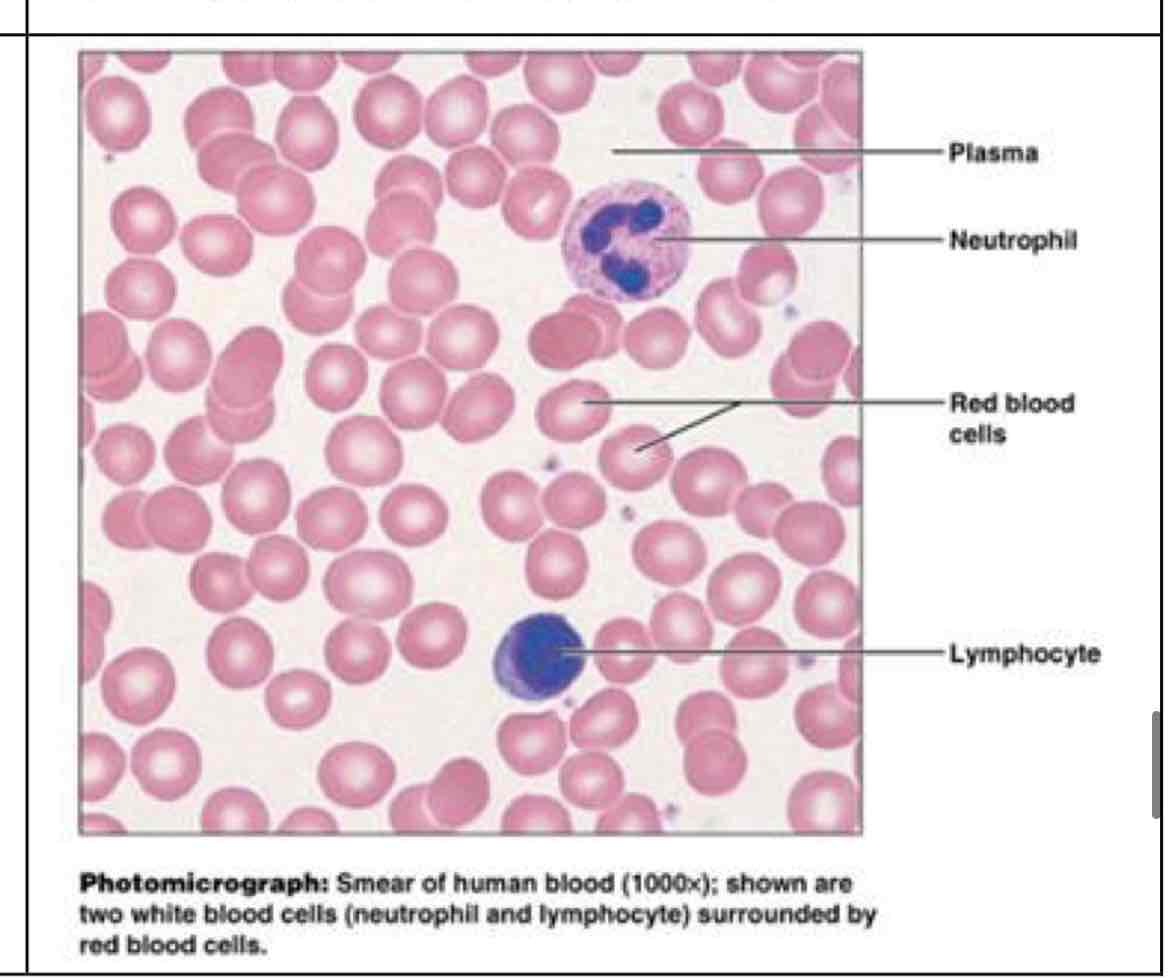
blood
?
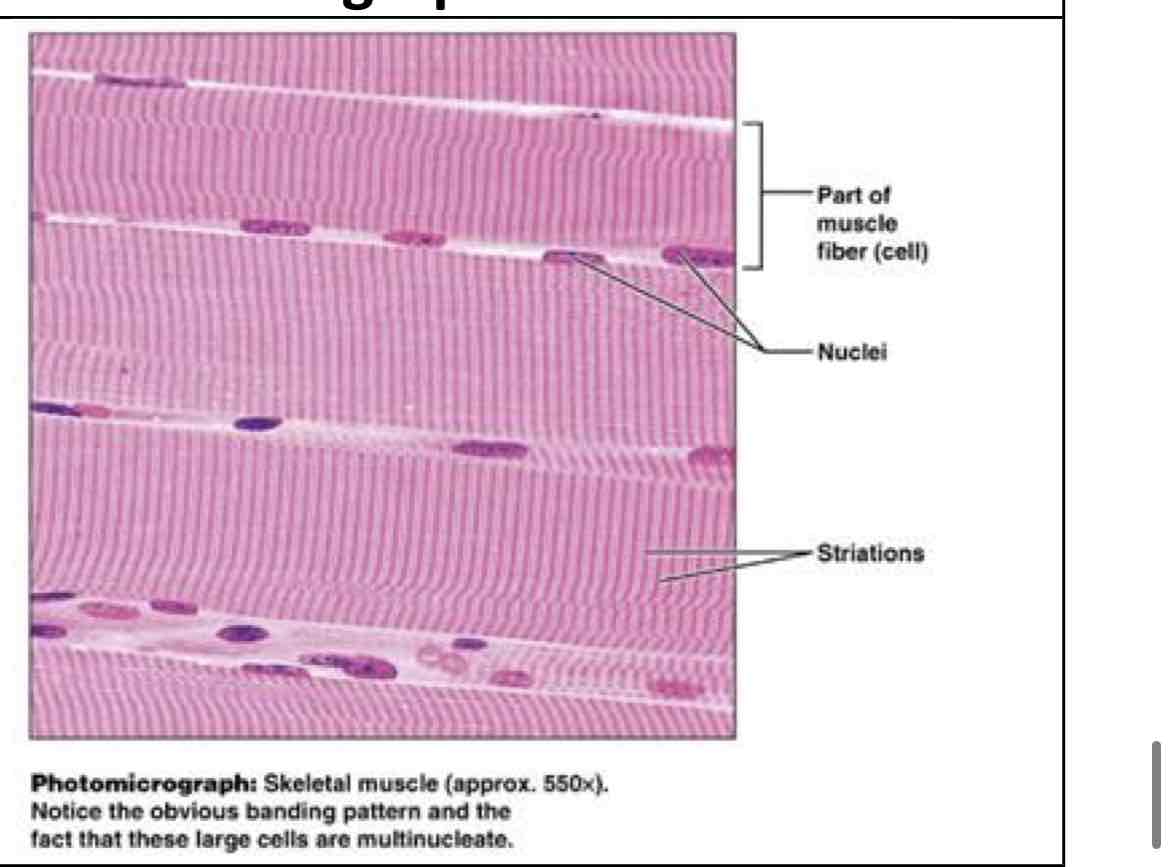
skeletal muscle
?
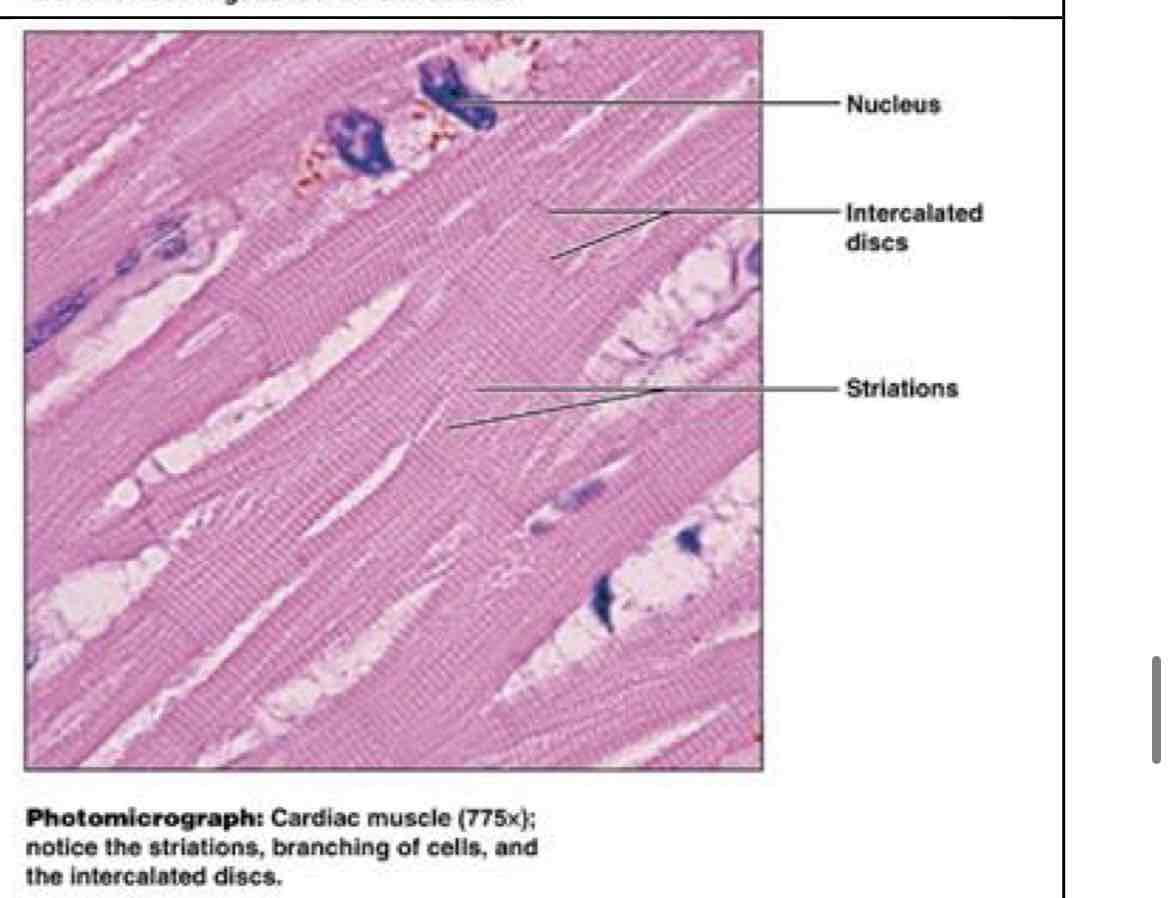
cardiac muscle
?
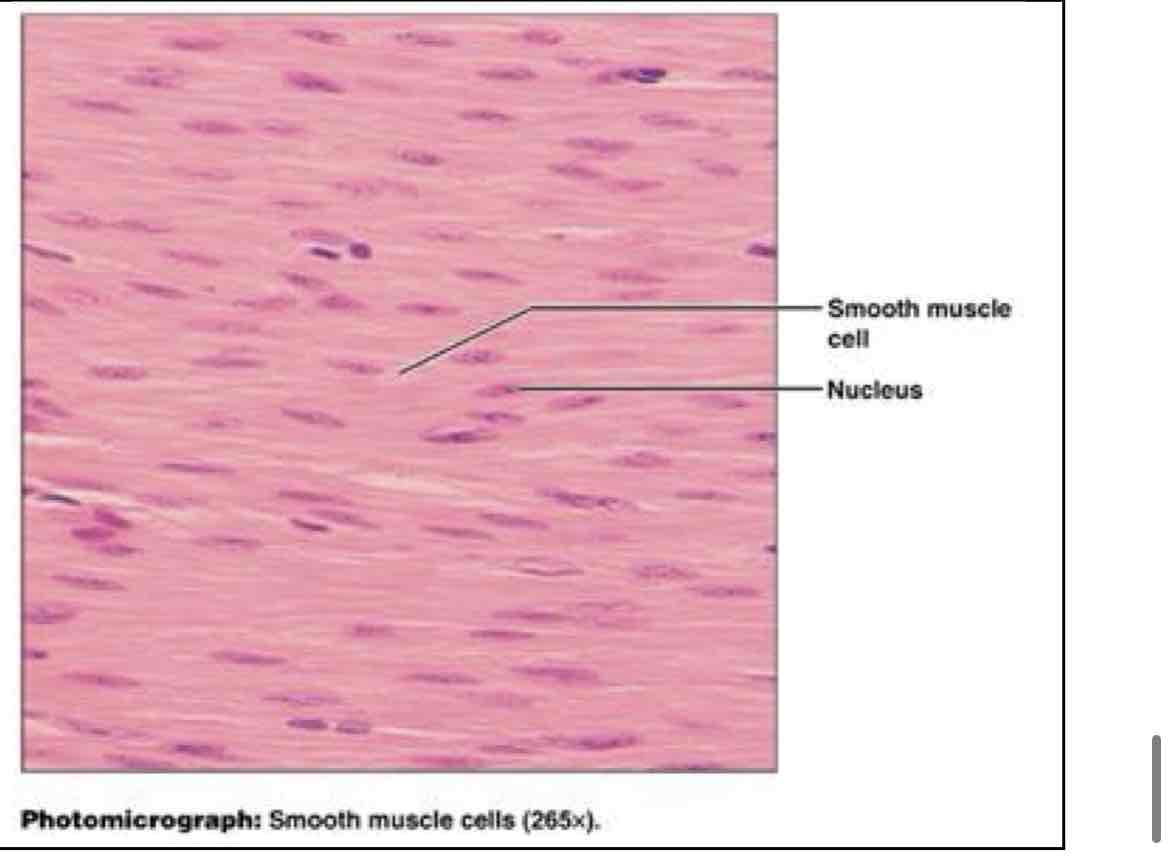
smooth muscle
?
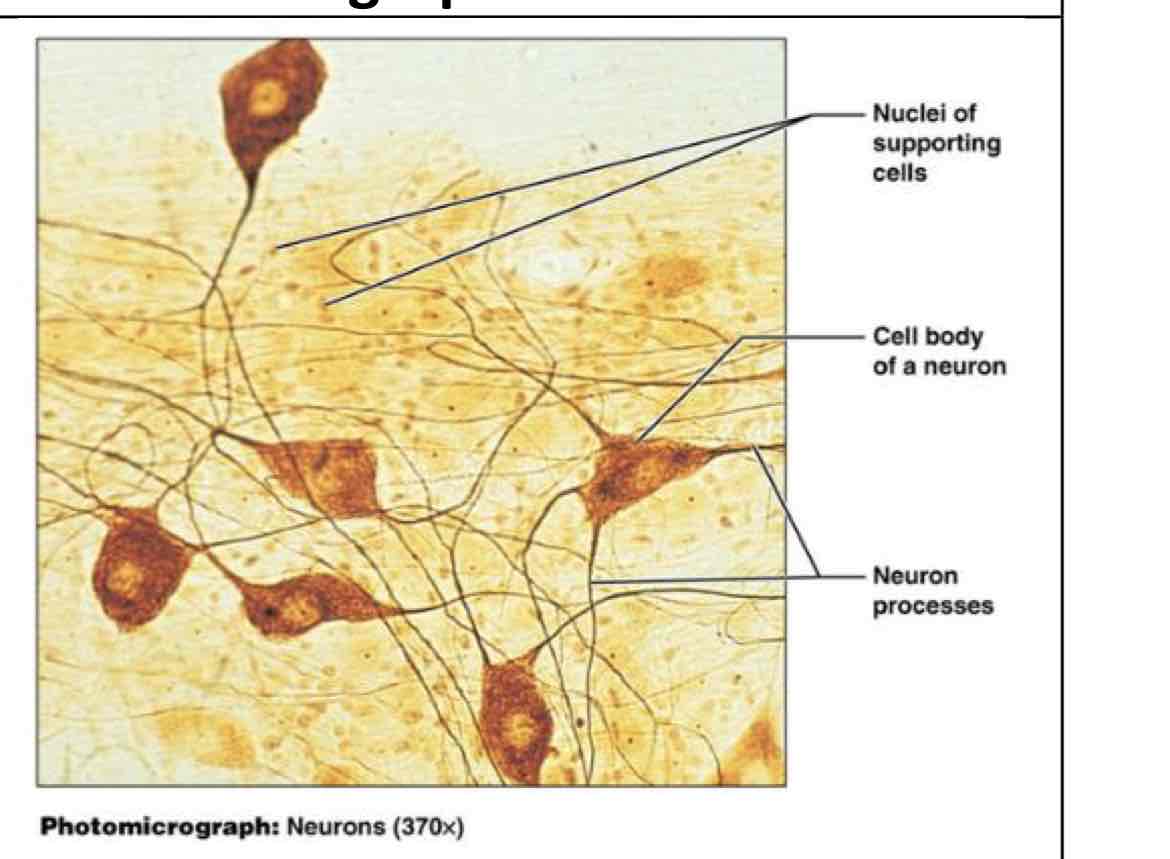
nervous
simple squamous
diffusion, osmosis, filtration where no protection needed - kidney, alveoli lungs, heart/blood vessel lining
simple cuboidal
absorption/secretion - kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands
simple columnar
absorption and secretion (mucus) - lines digestive tract (stomach/intestines - takes in nutrients) small bronchi, uterine tubes/uterus
pseudostratified columnar
secretion; can propel mucus - sperm carrying ducts, line trachea and upper respiratory tract; not stiff for movement
stratified squamous
protects underlying tissues in abrasive areas - lining of esophagus, mouth, vagina, epidermis
transitional (cuboidal/squamous)
stretches to allow digestion of urinary organ (expands and reverts) - lines ureters, bladder, and urethra
areolar
wraps/cushions other organs, inflammation, holds tissue fluid - under epithelia, packaging organs and surrounding capillaries
adipose
provides fuel for energy, insulates heat loss, cushions and protects - under skin around kidneys, in abdomen and breasts
dense regular (more fibers, dense, uniform)
attaches muscle to bone and bone to bone, withstands stress - tendons, ligaments
dense irregular (more going on)
withstands stress and tension from many directions - surrounds organs and joints, dermis of skin, digestive tract
elastic connective
allows recoil of tissue following stretching (heart beats, lungs) - walls of large arteries, within walls of bronchiole tubes
hyaline cartilage (not one shape)
supports and reinforces, serves as resilient cushion, resists compressive stress - embryonic skeleton, long end of bones, nose/trachea/larynx
elastic cartilage (more stretchy than hyaline) SOUND
maintains shape of structure while flexibility - supports external ear; epiglottis
fibrocartilage (not as flexible)
ability to absorb compressive shock - intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee
bone
supports/protects, cell formation, Ca+ mineral storage - bones
blood
transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes - contained within blood vessels
skeletal muscle (stripes)
voluntary movement, locomotion - skeletal muscles, attached to bones
cardiac muscle
involuntary movement, contraction propels circulation - walls of heart
smooth muscle (like squamous)
involuntary, propels substances (food) along internal passageways - walls of hollow organs (digestive)
nervous
electrical signals for communication/control - brain, spinal cord, nerves