3rd Quarter Vocabulary - Earth Science - 6th Grade
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
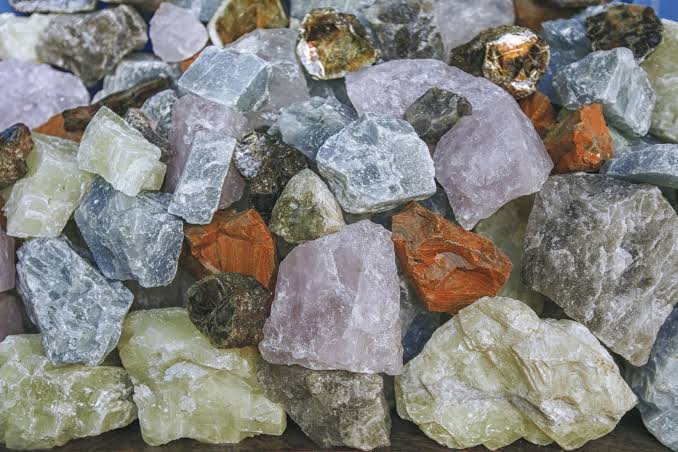

inorganic
Not made from living things.

crystal
A solid with flat sides and sharp edges that form a regular pattern.
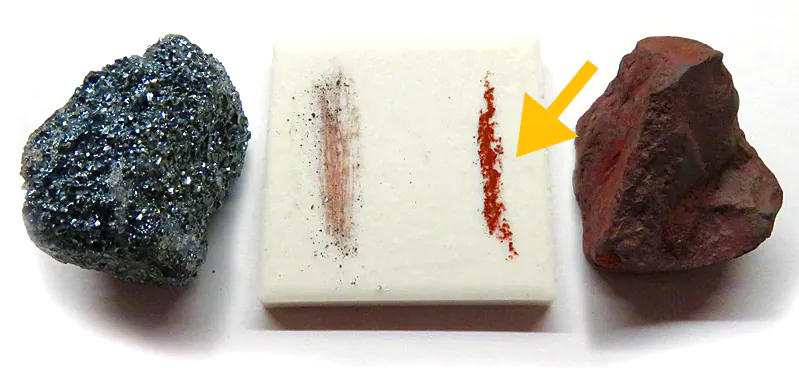
streak
The color of a mineral when it is powdered.
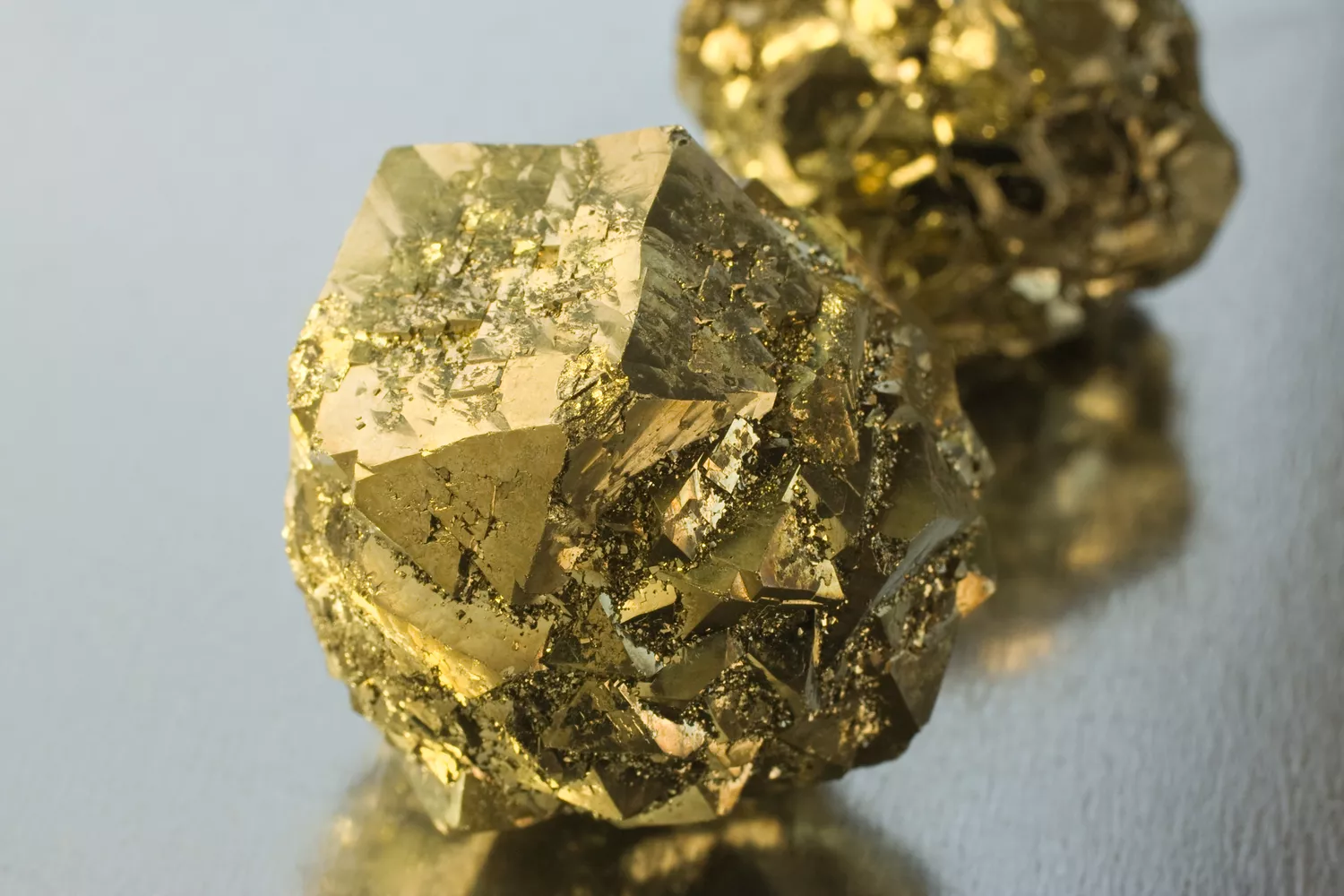

luster
How light reflects from a mineral’s surface (shiny, dull, etc.).
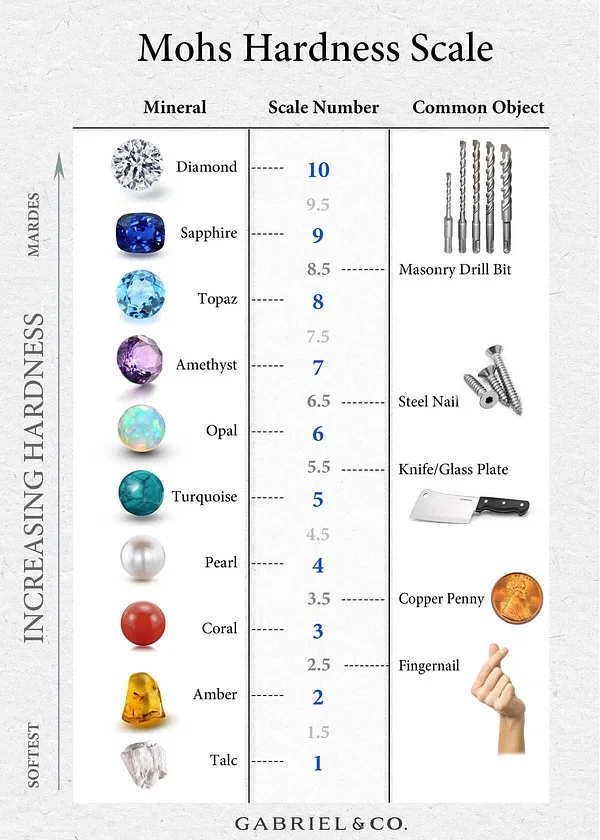
Mohs hardness scale
A list that ranks minerals from softest to hardest.
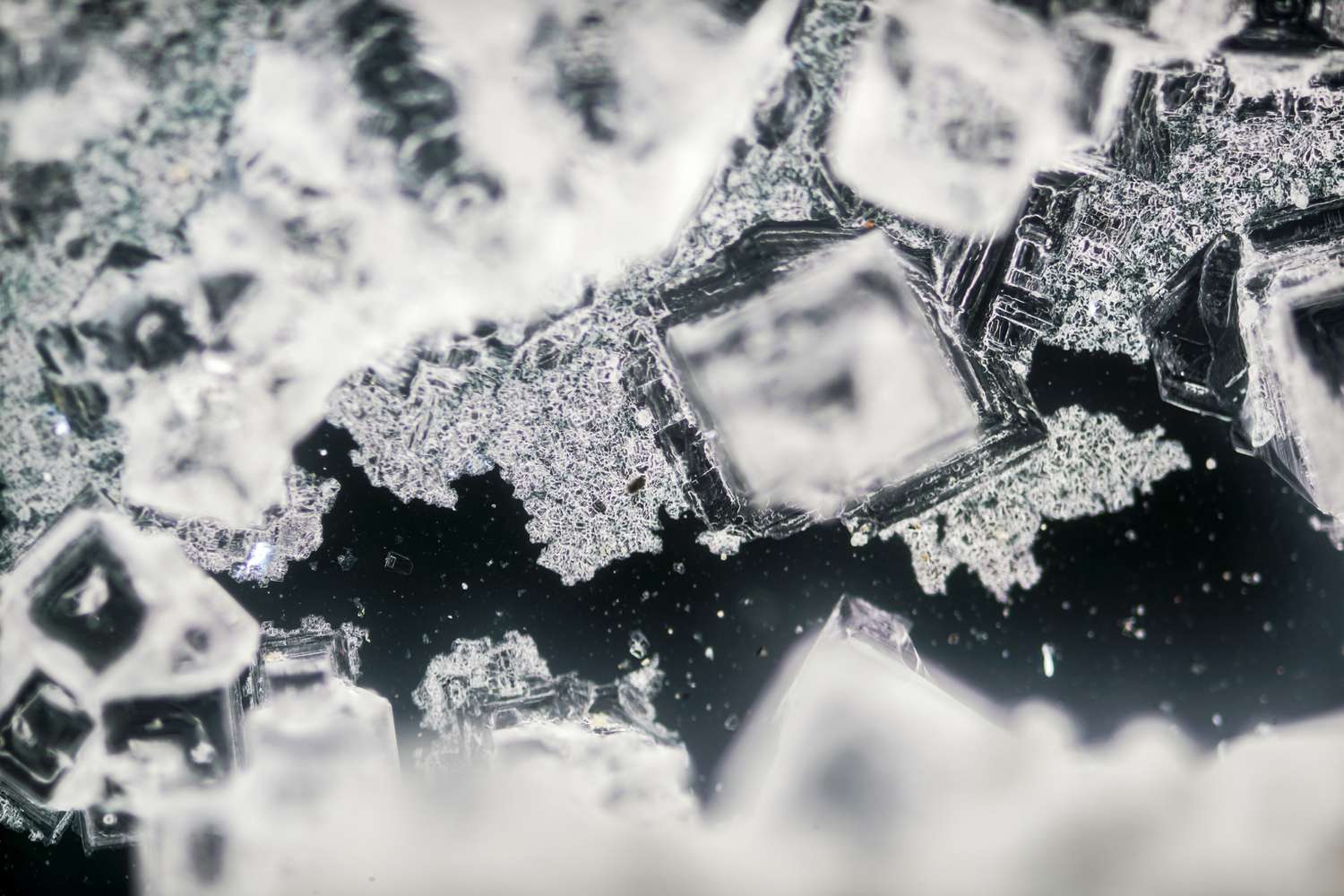

crystallization
The process by which crystals form from cooling magma or from a solution.

grains
The small pieces or particles that make up a rock.

texture
The look and feel of a rock’s surface.

extrusive igneous rock
Rock formed from lava that cools quickly on Earth’s surface.
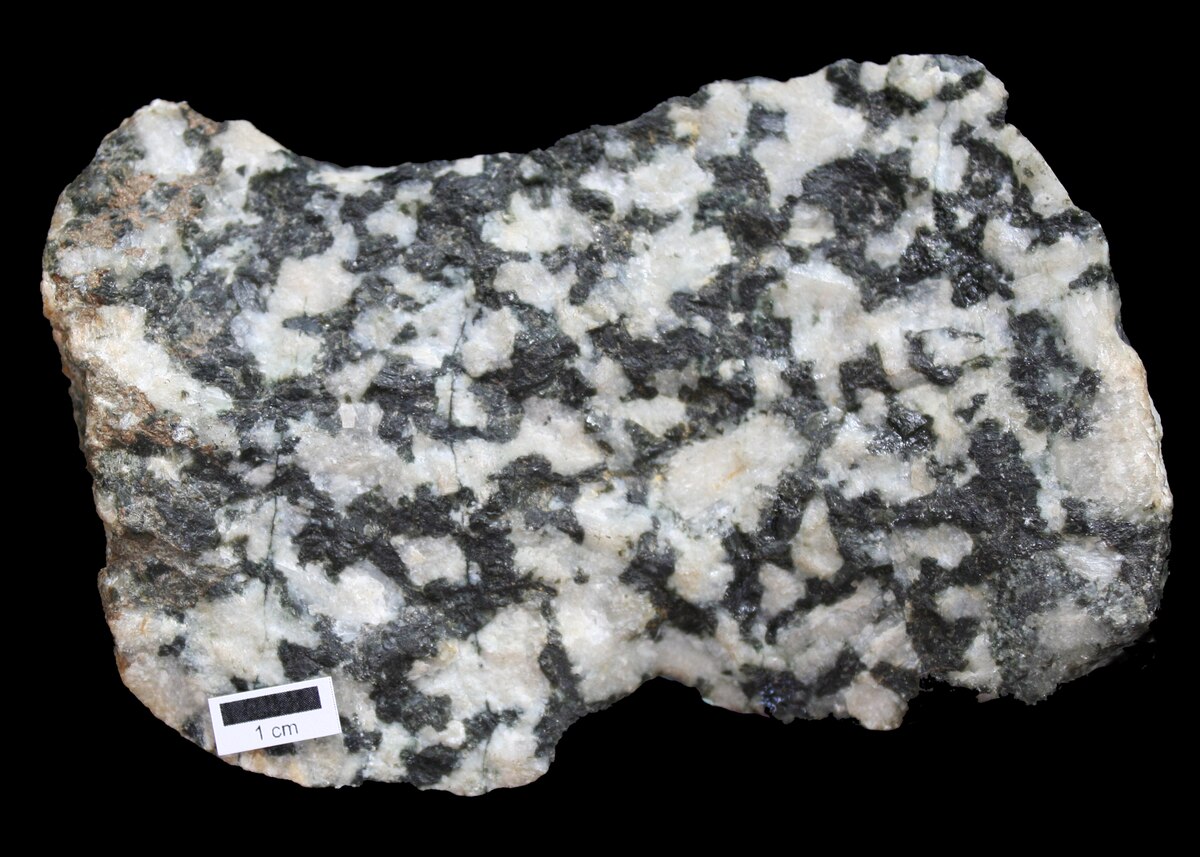

intrusive igneous rock
Rock formed from magma that cools slowly below Earth’s surface.
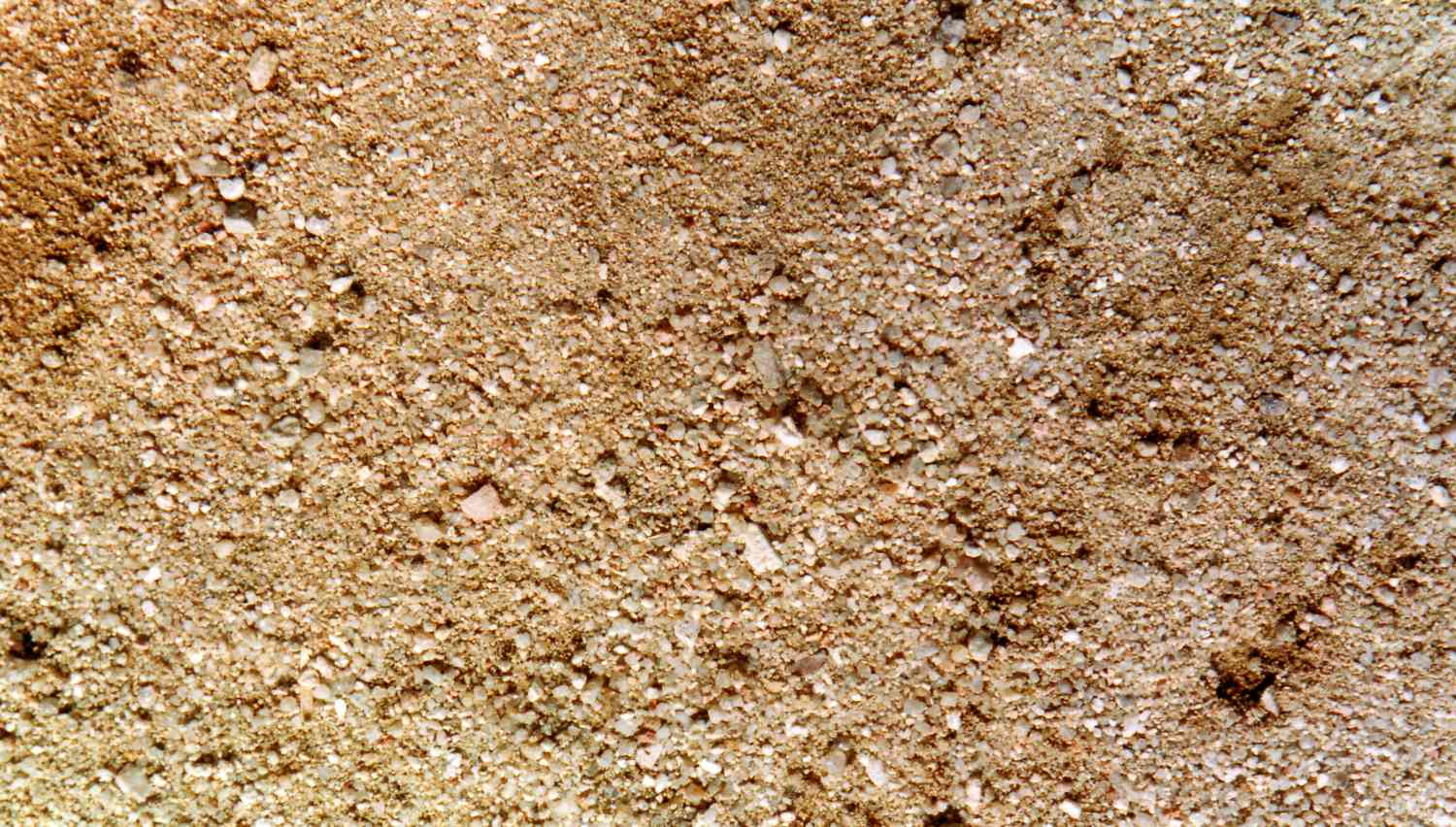

sediment
Small pieces of rock, plant, or animal material.
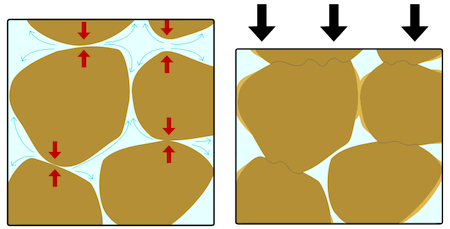
compaction
The process of pressing sediments together.

cementation
When minerals fill spaces between sediments and glue them together.

soil
The loose material on Earth’s surface that plants grow in.
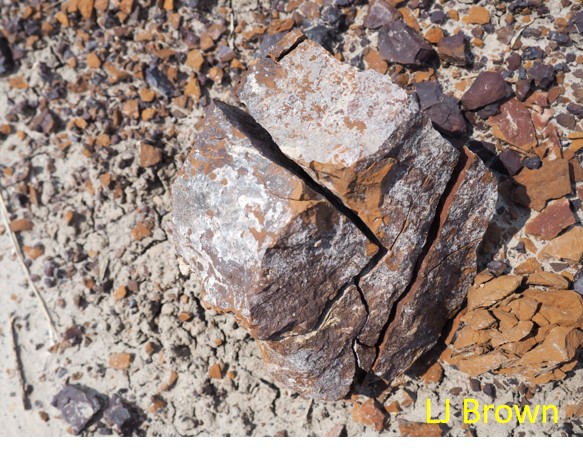

mechanical weathering
The breaking of rocks into smaller pieces without changing their composition.
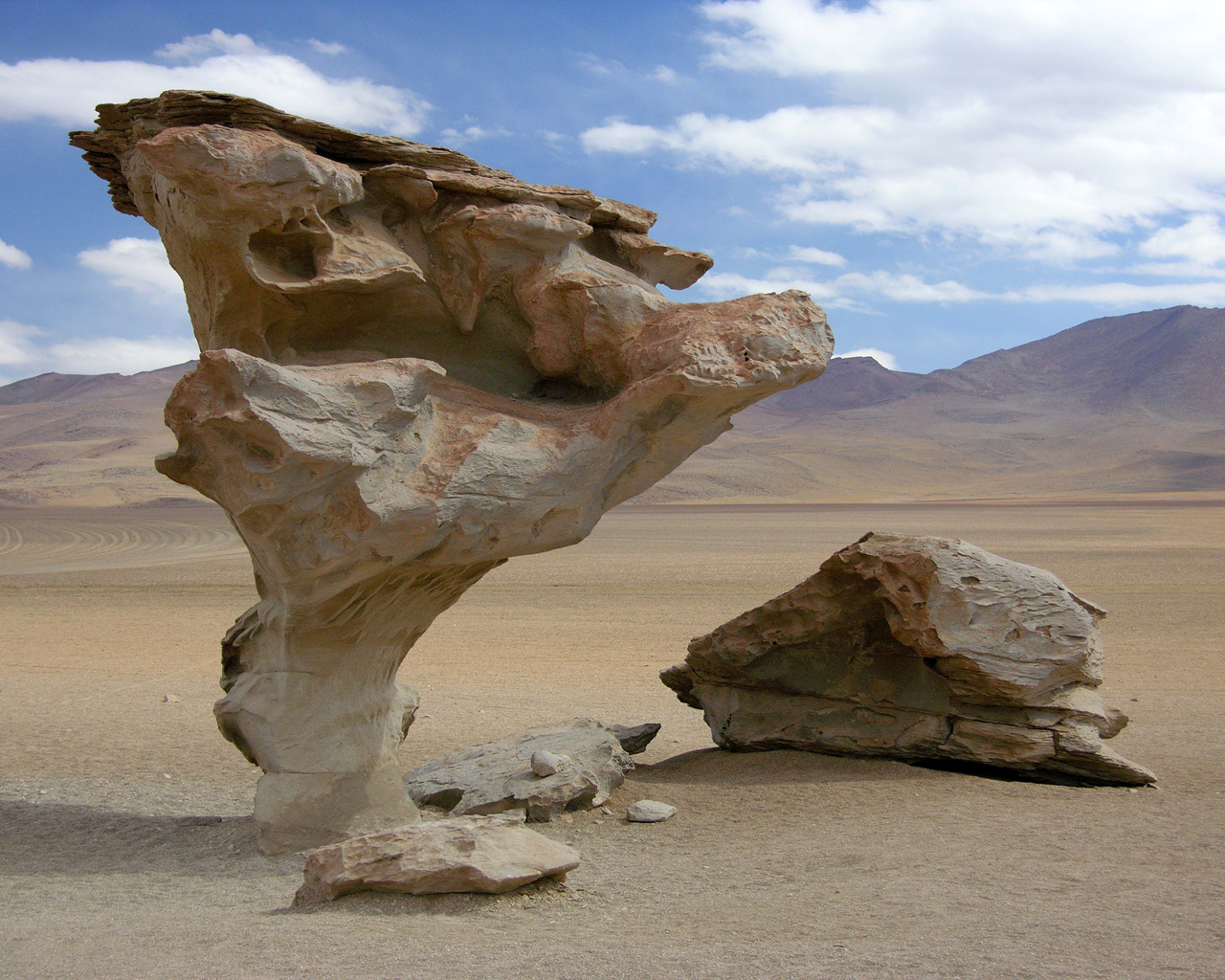

abrasion
The wearing away of rock by rubbing or scraping.
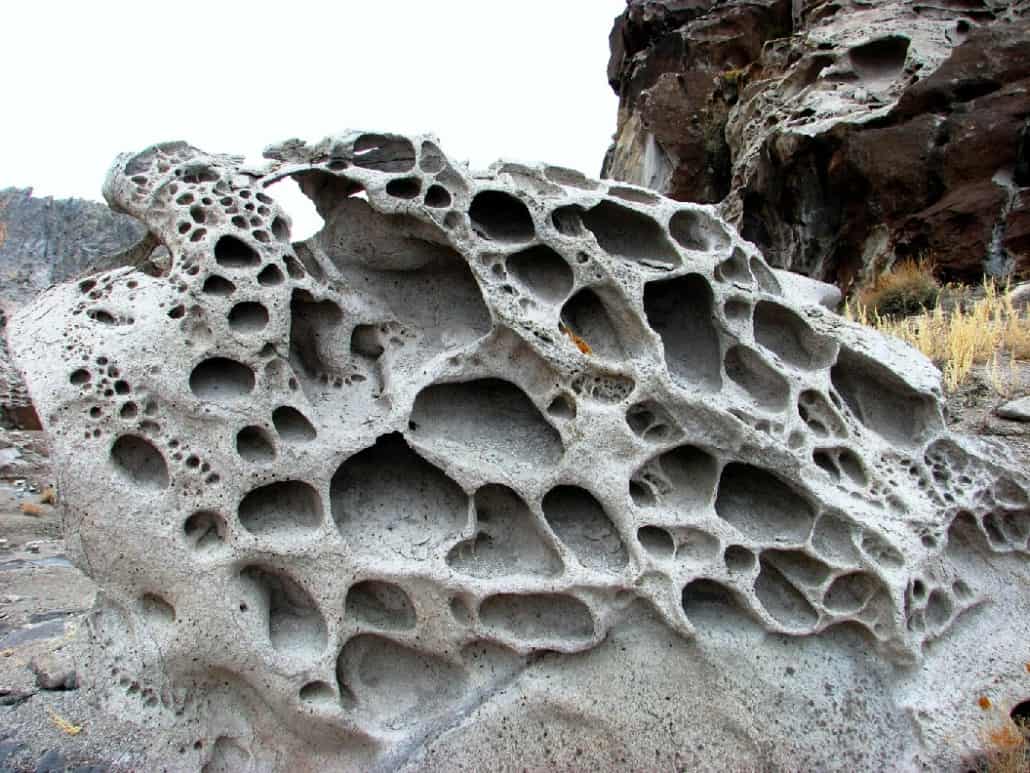

chemical weathering
The breaking down of rocks through chemical changes.
permeability
How easily water can pass through a material.
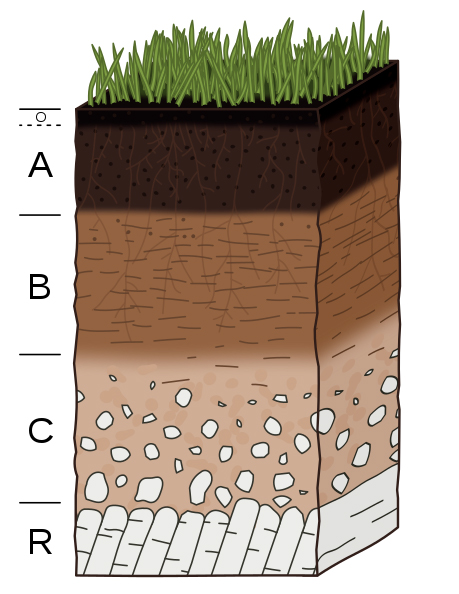
soil horizon
A layer of soil that differs in color or texture from the layers above or below it.

decomposer
An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals.

humus
The dark, rich part of soil made from decayed plants and animals.

topsoil
The top layer of soil where plants grow best.

bedrock
The solid rock layer beneath soil and loose materials.

soil conservation
Ways to protect soil from being lost or damaged.

non-renewable resource
A resource that cannot be replaced quickly after it is used.
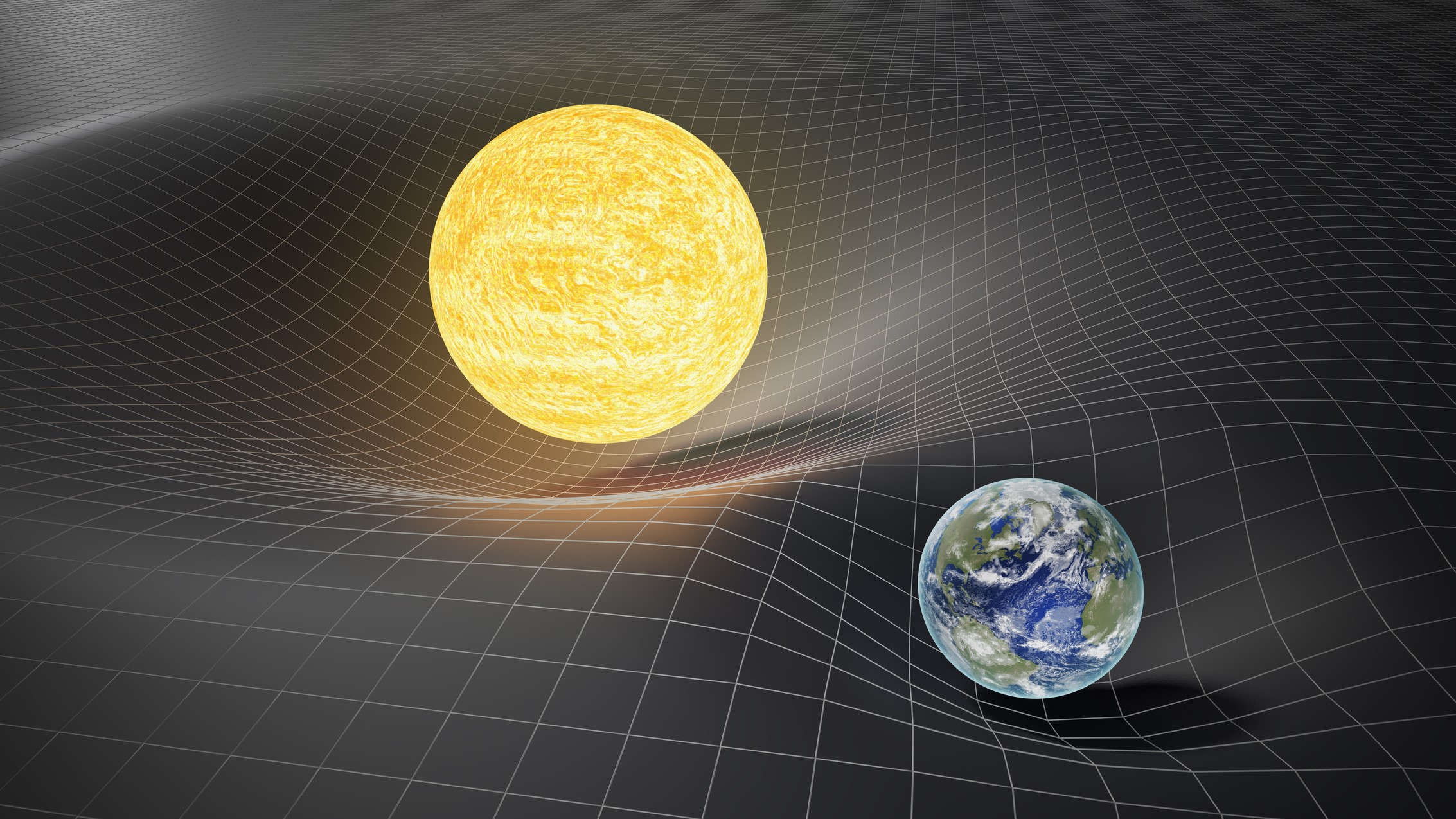
Gravity
The force that pulls things toward each other, like how Earth pulls us down.
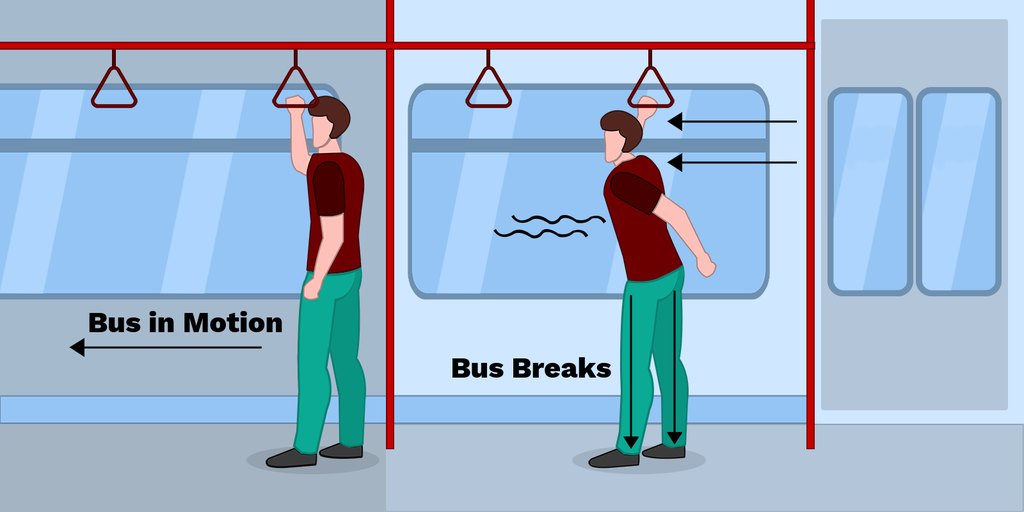
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion.

Ecosystem
A community of living and nonliving things that work together.
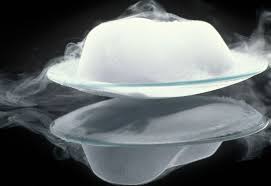
Sublimation
When ice turns straight into vapor without melting first.
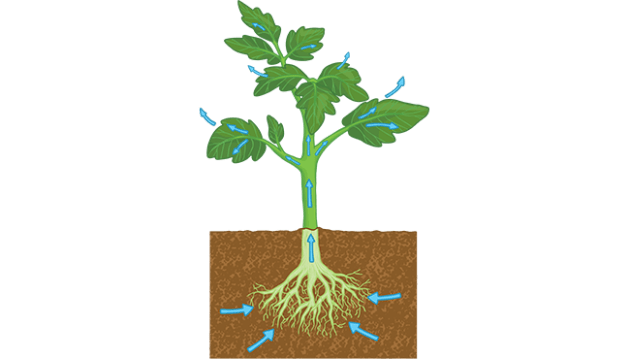
Transpiration
When plants release water vapor into the air.
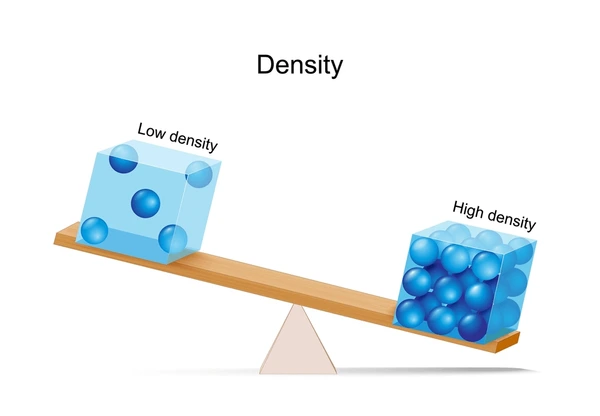
Density
How tightly packed the matter in something is.

Weather
The day-to-day conditions outside (sunny, rainy, windy, etc.).

Climate
The usual weather in a place over a long time.
Temperature
How hot or cold something is.

Energy
The ability to make things move or change.
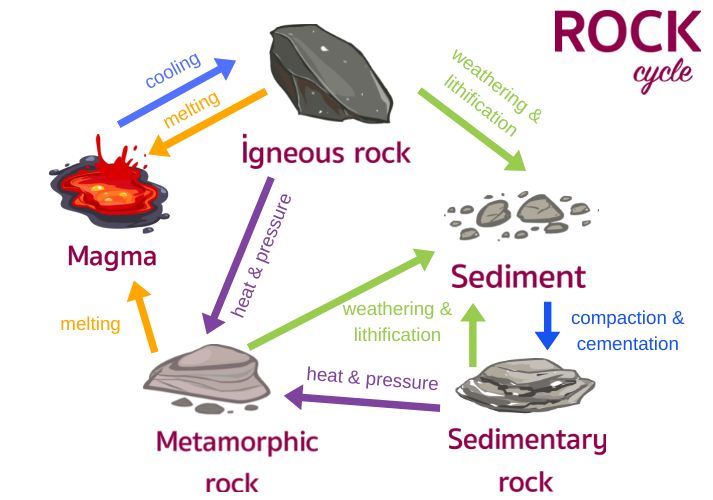
rock cycle
The process by which rocks transform from one type to another over time.
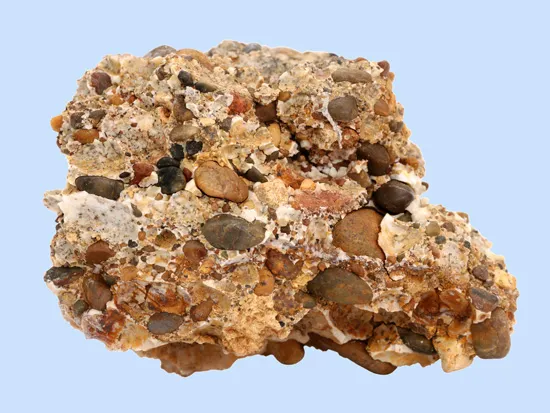

sedimentary rock
Rock formed by the accumulation and compaction of sediments.

igneous rock
Rock formed from the cooling of magma or lava.

metamorphic rock
Rock formed when existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical processes.

weathering
The breakdown of rocks and minerals at Earth’s surface.

erosion
The movement of weathered materials by wind, water, ice, or gravity.

deposition
The laying down of sediment carried by wind, water, or ice.
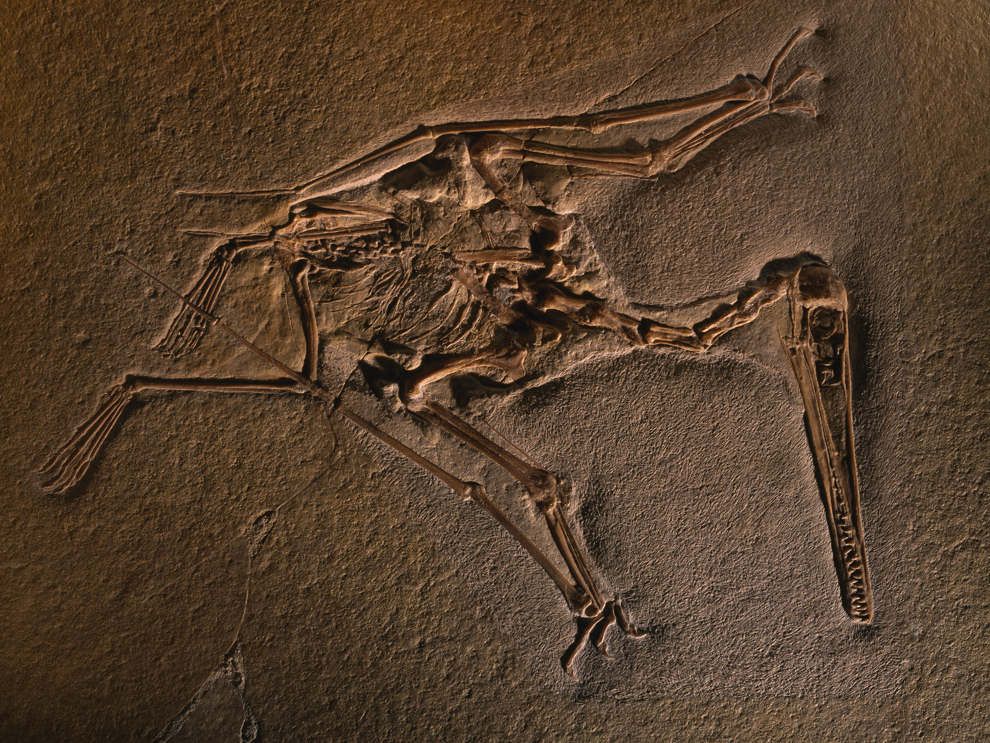

fossil
The preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms.
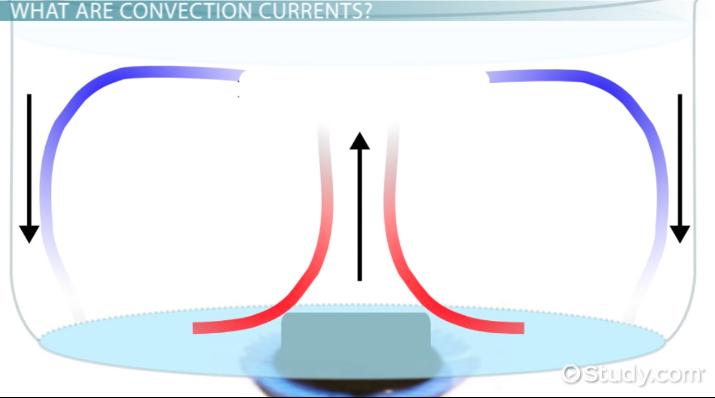
convection current
Movement within a fluid caused by differences in heat and density, driving plate motion.

mineral
A naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a definite chemical composition and crystal structure.