Exam 4 Microbiology N251 IUPUI
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Epidemiology
the study of the distribution and determinants of diseases and other health outcomes in human population.
also deals with the natural history of diseases and it can provide evidence that contributes to their prevention
health care and planning
tool for investigation of the cause of disease
(defining disease characteristics, such as prevalence, incidence and mortality)
What is the importance of Epidemiology?
identify disease origin
mode of transmission
observe and conduct clinical studies, disease reporting surveys, questionnaires, interviews
What are some of the roles of an Epidemiologist?
scientific method
What is the scientific method?

disease surveillance
Ongoing systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of specific health data for use in public health.
sporadic level
occasional cases occurring at irregular intervals
endemic level
persistent occurrence with a low to moderate level
hyper endemic level
persistently high level of occurrence
epidemic
the occurrence of more cases of a disease than expected for a given time period
a peak in an epidemic curve
pandemic
epidemic spread over several countries or continents, affecting large number of people
epidemiological triangle
used for describing the causality of infectious diseases
provides a framework for organizing the causality of other types of environmental problems
Cholera
an acute intestinal infection caused by ingestion of contaminated water or food
caused cramps, vomiting, diarrhea
blue face, feet
died in less than a day
focus on individual
uses tools for diagnosis
does not take other factors in account
does not form assumptions
does not help in policy formulation
not a qunatitative science
clinical medicine
focus on group
uses tools for community diagnosis
takes into account all factors
forms assumptions/ hypothesis
helps public health policy formulation
quantitative and qualitative science
epidemiology
common source outbreak
people are exposed intermittently or continuously to a common harmful source
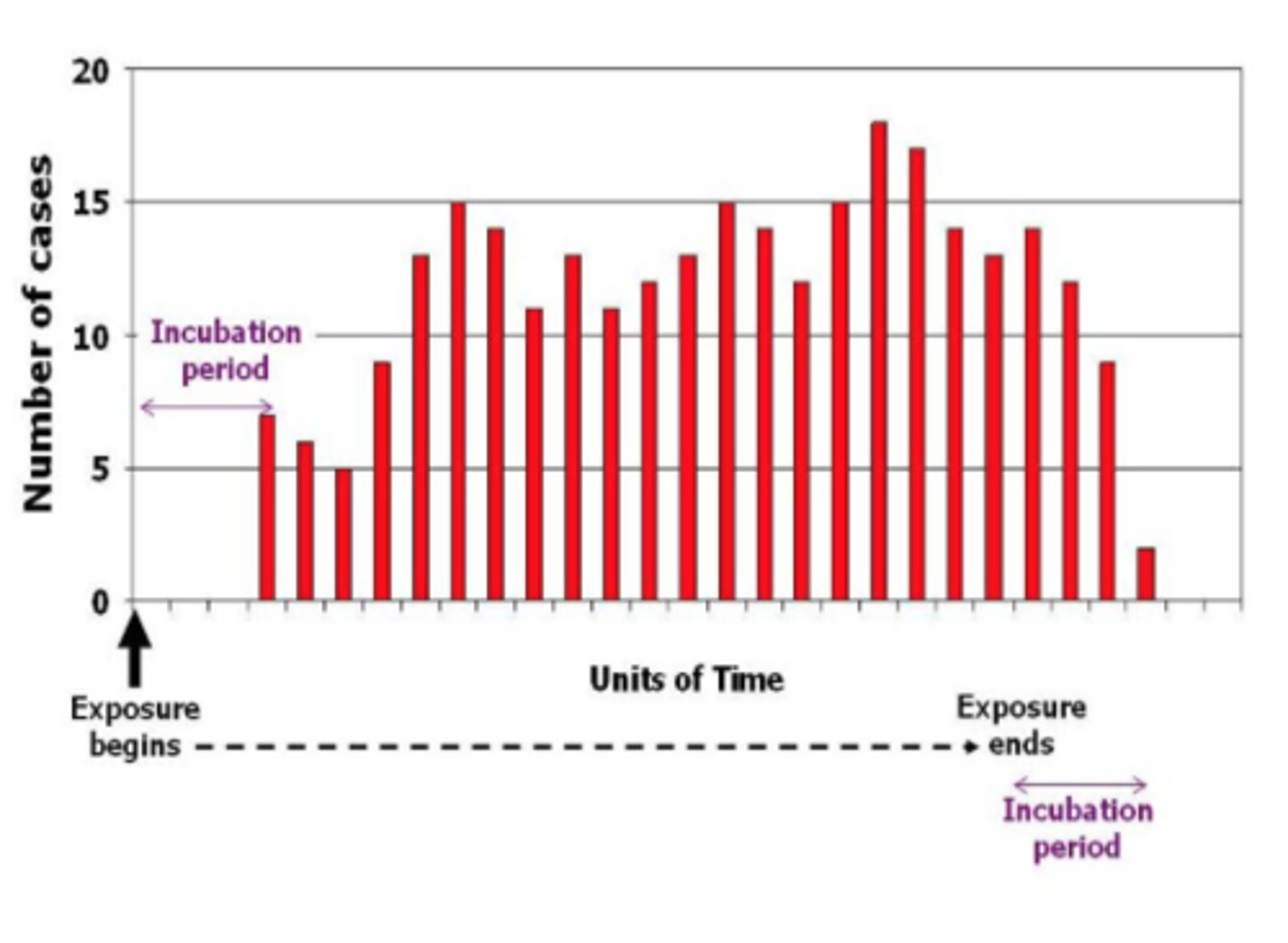
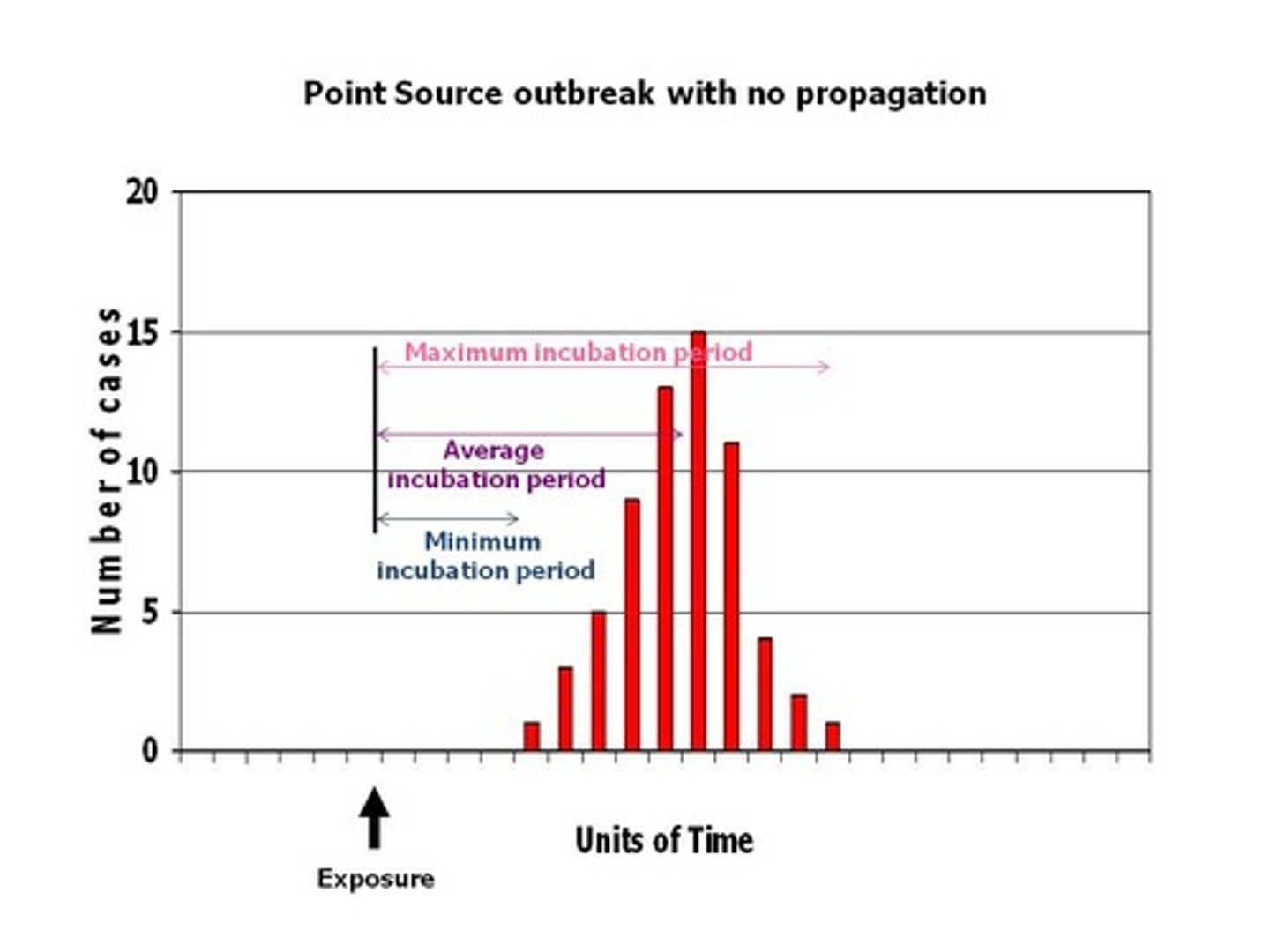
point source outbreak
an epi curve with a sharp upward slope and a gradual downward slope
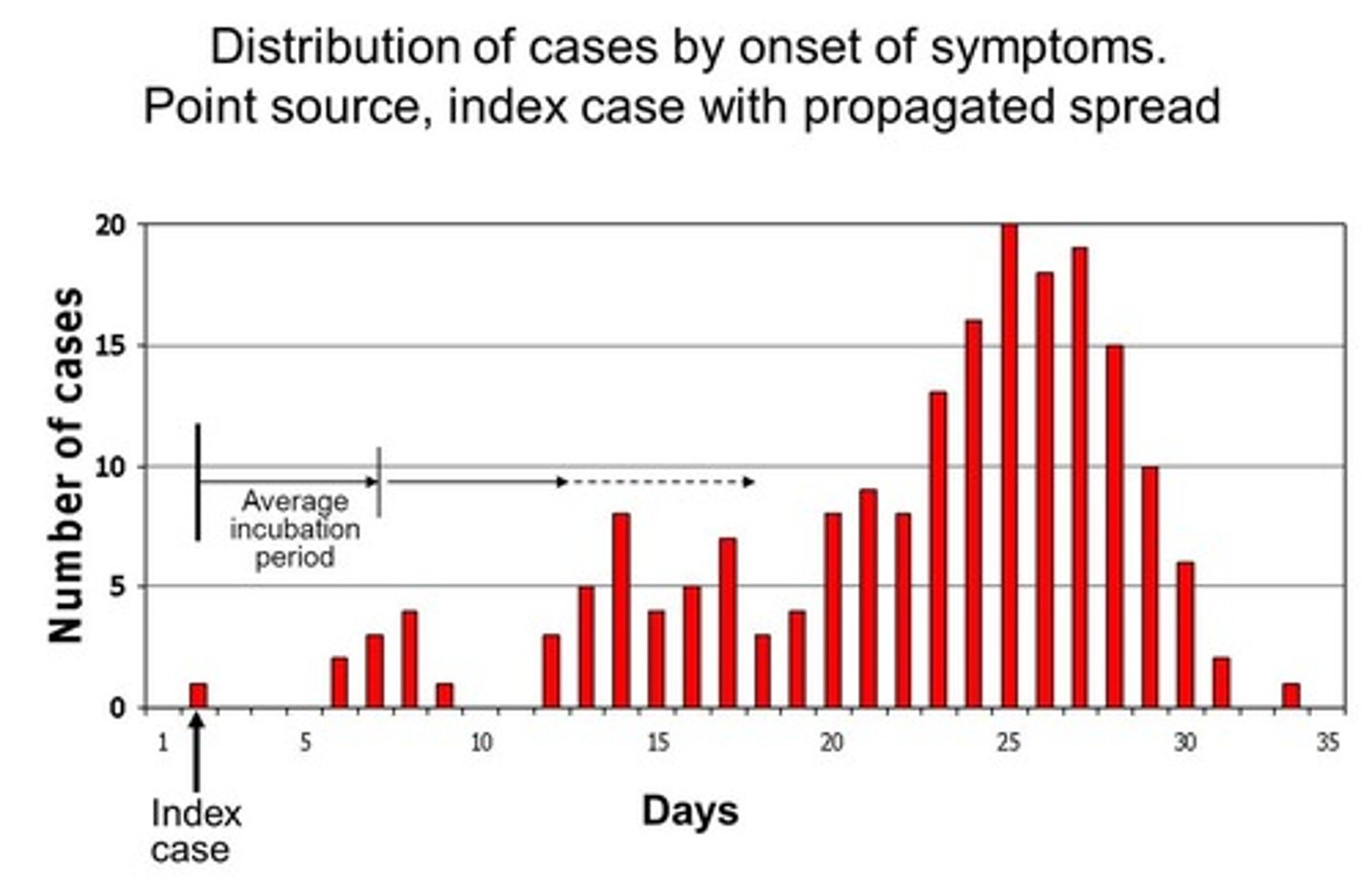
propagated outbreak
an outbreak that is spread from person to person
malaria
giardia
protozoans-single celled eukaryotic organisms
bot fly
tick
arthropods
hookworms
roundworms
pinworms
tapeworms
worms
malaria
Anopheles mosquito
fever, chills, and flu like symptoms
pregnant women are at high risk
can lead to death
giardia
cause of giardiasis
an infection in small intestines
water supply becomes contaminated with raw sewage
arthropods
human bot fly (buries its head inside human skin with butt in air)
south american parasite
adult arthropod
lays egges on
1. blood sucking vector --> larvae enters host after vector takes a blood meal
2. on human skin
then eggs become larva or can be pupa in soil
start all over again
What is the life cyle of an arthopod?
ticks
carry several types of diseases
Rocky mountain spotted fever
lyme disease
anaplasmosis
Spring: eggs
Summer: larva - first blood meal
Fall: larva
Winter: larva
Spring: nymph
Summer: second blood meal
Fall: third blood meal
What's the two year life cycle of a tick?
hookworms
small worms that enter through the skin and eventually migrate to small intestines
they enter the body body from outer environment (soil, grass)
makes its way to lungs through circulatory system, coughed up, and swallowed and ends up in intestines
eggs are passes in feces and ends outside again
Life cycle of worms in general
roundworms
large intestinal nematode
very common: may infect 25% of world pop.
12-40 cm long
transmitted via stools of infected people, dirty hands, unwashed fruits and veg
eggs can lay in soil for years
lie in small intestine but can crawl around (coming out of nose or climbing up a tear duct
large numbers can block the intestine
they absorb nutrients leading to nutrient def.
pinworms
most common nematode infection
its complete life cycle occurs in human host
the female worm lays eggs around child's anal area
child scratches area and gets eggs under fingernails (fomite) spreads eggs
Enterobiasis (Pinworms)
anail itching, esp at night, can lead to PID or vaginitis
tapeworms
the intestinal worm
parasite of dogs or farm animals, transmitted fecal-orally.
transmission can occur if a domesticated farm dog eats infected carcass and then transmits it to food crops of directly to humans
- Eukaryotes
- Heterotrophs
- Cell wall made of chitin
- multinucleated cells
- NO chloroplasts
What are the characteristics of Fungi?
- Eukaryotes
- Autotrophs
- Cell wall made of cellulose
- Single-celled nuclei
- HAS CHLOROPLASTS
What are the characteristics of plants?
Leaves, stems, roots
chlorophyll
What are things fungi do not have, but plants DO have?
An external carbon source (heterotrophic)
What do fungi require in order to live?
identification
The cell wall of fungi is made up of chitin. What does this aid in?
yeasts
Type of fungi that are singled celled fungal forms
molds
type of fungi that has multiple cells forming a filamentous mycelium
spores
type of fungi are reproduced by spores (sexually/asexually)
morphology, arrangement and mode of derivation of spores
What are good criterias for genus and species identification of spores?
spore - germ tube - hypha - mycelium
What are the different stages of molds?
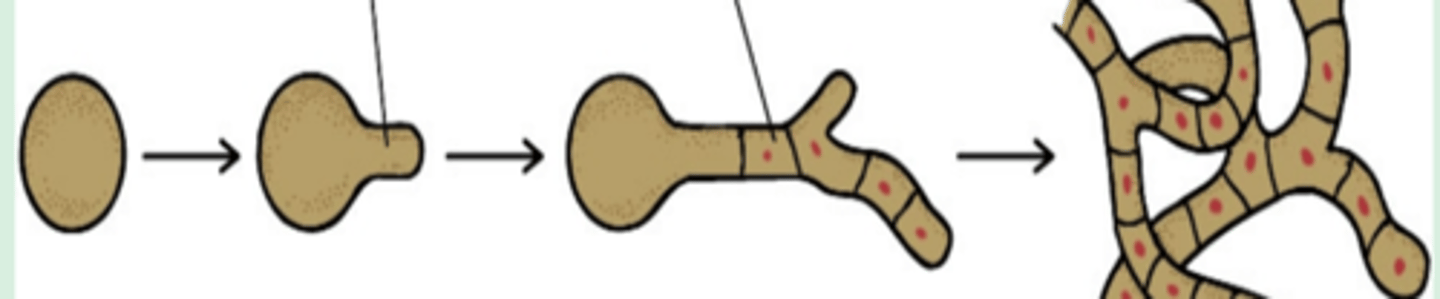
found in nearly every habitat on earth where organic materials exist
What is the habitat of fungi?
1. Allergic reaction
2. Reaction to toxin
3. Fungi that destroy human food supply
4. Colonization in human body
What are the 4 ways fungi can disease/affect humans?
allergic reaction
exposure to fungi causes person to become sensitized (immediate hypersensitivities)
reaction to toxin
exposure to fungi causes
- hallucinogenic properties of some mushrooms
- poisonous effects of ergot fungus (ryre smut)
- carcinogenic toxins of Aspergillus (aflatoxins)
Ergoitism on wheat stalk/rye
Ergot fungi causes what?
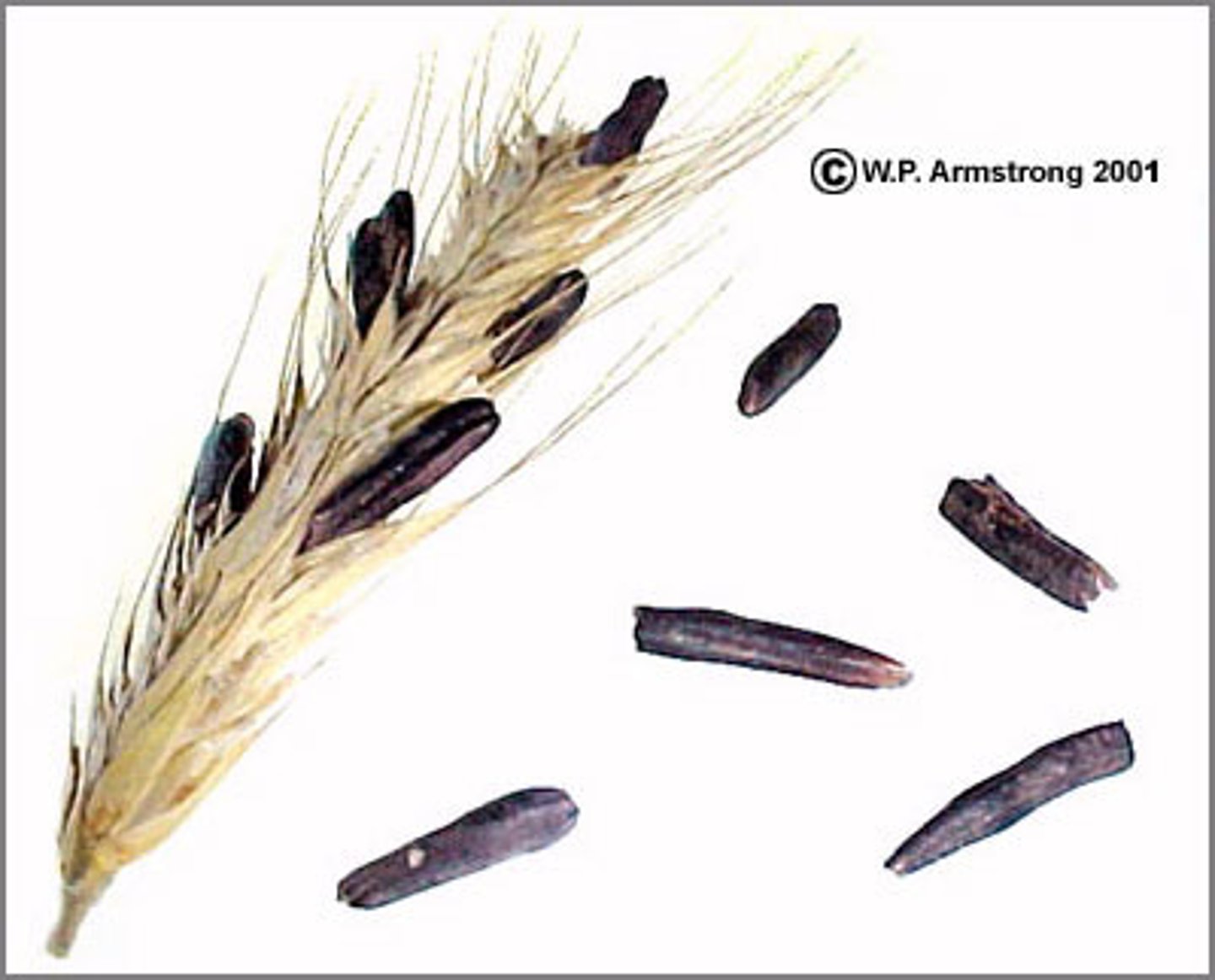

Ergotism
severe pathological syndrome affecting humans or animals that have ingested plant material containing ergot alkaloid, such as ergot-contaminated grains.
hallucinations
irrational behavoir
convulsions
death
The neurotropic activities of the ergot alkaloids may cause what?
induce uterine contractions and control bleeding after childbirth
What does Ergometrine (from Ergot) used for?
Wheat rust
puccinia graminis
Dutch elm disease
Ceratocystis ulmi
Potato blight
Phytophthora infestans
Aspergillus
Cause of Aspergillosis
superficial mycoses
intermediate mycoses
systemic mycoses
What are the different levels of fungal colonization of the human body?
nasal sinuses
lungs
blood vessels (injury/catheters)
oesophagus
stomach
intestine
skin
What are some routes of entry for fungal contamination?
brains
lungs
heart
spleen
liver kidney
What are some areas of deep mycoses for fungal contamination?
- Candidiasis (thrush, vaginal)
- Dermatophytes (athel. foot, Tinea capitis, jock itch, nails)
- Sporotrichosis (gardener's hazard)
- Blastomycosis (skin)
What are some example of superficial mycoses?
Candidiasis (caused by Candida albicans (Yeast))
What is the fungus that causes thrush or yeast infections?
Athlete's foot (tinea pedis)
common skin infection between toes and soles of feet
may spread to palms, groin, and body
causes itching, scaling and redness
may blister in severe cases
- Aspergillus
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcus
- All dimorphics
- Mucormycosis
What are some fungi that can cause intermediate mycoses?
- Mucormycosis
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcus
- All dimorphics
What are some fungi that can cause systemic mycoses?
Aspergillosis
name given to wide variety of diseases caused by infection of fungi Aspergillus
most cases occur in people with underlying illnesses (TB, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), people with deficient immune systems
Dimorphics
mycotic organisms that posses different morphological forms under different temperature conditions
- histoplasmosis
- blastomycosis
- coccidiomycosis
Murcormycosis
a serious but rare fungal infection caused by a group of MOLDS.
They live throughout the environment
Affects people with weakened immune systems and can occur in nearly any part of the body
Cryptococcus neoformans
a fungus that lives in the environment throughout the world.
people become infected after breathing in the microscopic fungus
extremely rare in people who are otherwise healthy; most occur in people with weakened immune systems
- Fungi as useful tools for genetic and biochemical studies
Neurospora crassa:
Yeasts:
human insulin
growth hormone
somatostatin
vaccine against viral hepatitis
- Fungi as food:
mushrooms
alcohol, breads
- Fungi in symbiosis:
linchens
How can fungi be good?
skin scrapings, hair and nail clippings
tissue imprints or sections
- special stains
What are direct observations in lab diagnosis of fungal infections?
handling of specimens in prep for culture
How are cultures used in fungal lab diagnosis of fungal infections?
Sabouraud's dextrose agar
Not-selective media for fungi
Mycobiotic agar
Sabouraud's with anitbiotics agar
Cyclohexamide agar
Selective media for fungi
Brain heart infusion with blood agar
Potato dextrose agar
Enriched media for fungi
Lactophenol Aniline Blue
In mount preparation slides for mold, what dye is used?
- yeast-like (creamy, pasty to mucoid)
- mold (cottony to wooly)
- rate of growth
- colony pigmentation
- growth on media containing anti fungal agents
- dimorphic growth
- mount prepations (molds)
*tease mount
* scotch tape mount
What are some preliminary isolate observations for fungal identification?
subculture
biochemical
DNA techniques to aid in identification
What are some things that can be done for fungal identification?
prion
contains only protein material
prion
a type of protein that can trigger normal proteins in the brain to fold abnormally
by infected meat products
Prion diseases can affect both humans and animals. How can prion diseases be spread to human?
Prion Hypothesis
suggests that an abnormal conformer (PrPSc) of the cellular prion protein (PrPc) is capable of inducing PrPc to undergo a change of conformation into PrPSc
Brain looks spongy because of the tissues that were destroyed
What does prion folding do?
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy
Chronic Wasting Disease
Scrapie
What are some examples of prions found in animals?
Bonvine Spongiform Encephalopathy
a chronic degenerative disease affecting the central nervous system of cattle
"Mad cow disease"
they were fed left over cow meat that had been infected
humans get the disease from eating the contaminated meat (primarily in the brain or spinal cord tissue)
How do cows get bovine spongiform encephalopathy?
How do humans get it?
Chronic Wasting Disease
prion disease in elk and deer
causes them to walk as if they are "drunk"
currently being monitored in Indiana
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
- prion in humans
- caused by abnormal prions that are not killed by standard methods of sterilizing surgical equipment
- causes those to lose ability to think and move properly and suffer memory loss. The brain SHRINKS
always fatal
1. sporadic/classical - unknown cause
2. familial/infectious - inherited mutation in genes
3. Iatrogenic - contamination in hospital
4. variant - exposure to BSE
What are the four different types of CJD?
Kuru
prion disease in New Guinea by the Fore tribe
After passings, brains were consumed by women and children. (cannibalism)
Symptoms: headache, joint pain, difficulty walking, death
viroids
Infectious particles that cause disease in plants
made up of genetic material
no protein coat
only a little larger than prions
potato spindle viroid
spread through contact between plants
virus
a submicroscopic particle made up of nucleic acid that replicate inside living cells using the cellular synthetic machinery for production of progeny virions
either RNA or DNA, NEVER BOTH!
host range
range of animal spp and tisue cells that a virus can infect (can be broad or limited)
capsomeres
morphological subunits from which the virus capsid is built
determines the shape of virus
capsid
protein shell or coat that encloses nucleic acid genome (virus)
envelope
lipid-containing membrane that surrounds some viruses
nucleocapsid
capsid together with enclosed nucleic acid
virion
complete infective virus particle (synonym)
incomplete virion
virion without nucleic acid (empty capsid)
pseudovirion
during viral replication, capsid sometimes encloses host nucleic acid rather than viral nucleic acid; looks like ordinary virus particles when observed by electron microscope, but do not replicate
provirus
viral DNA that is inserted into host cell chromosome in latent state and must be activated before it is transcribed, leading to production of progeny virions;
transmissible from parent cell to daughter cell
- made up of nucleic acid & has a capsid (protein coat)
- very small in size (smaller than even E. coli) and contains very few genes
- contain either RNA or DNA (not both)
- lack cellular components needed to generate energy & synthesize proteins (need host)
- contain few enzymes
- contain min. amount of genetic info
What are the general characteristics of a virion (bacteriophage)?