Cardiovascular System
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the cardiovascular system, including anatomy, physiological processes, and pathophysiology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the double-layered sac that encloses the heart called?
Pericardium
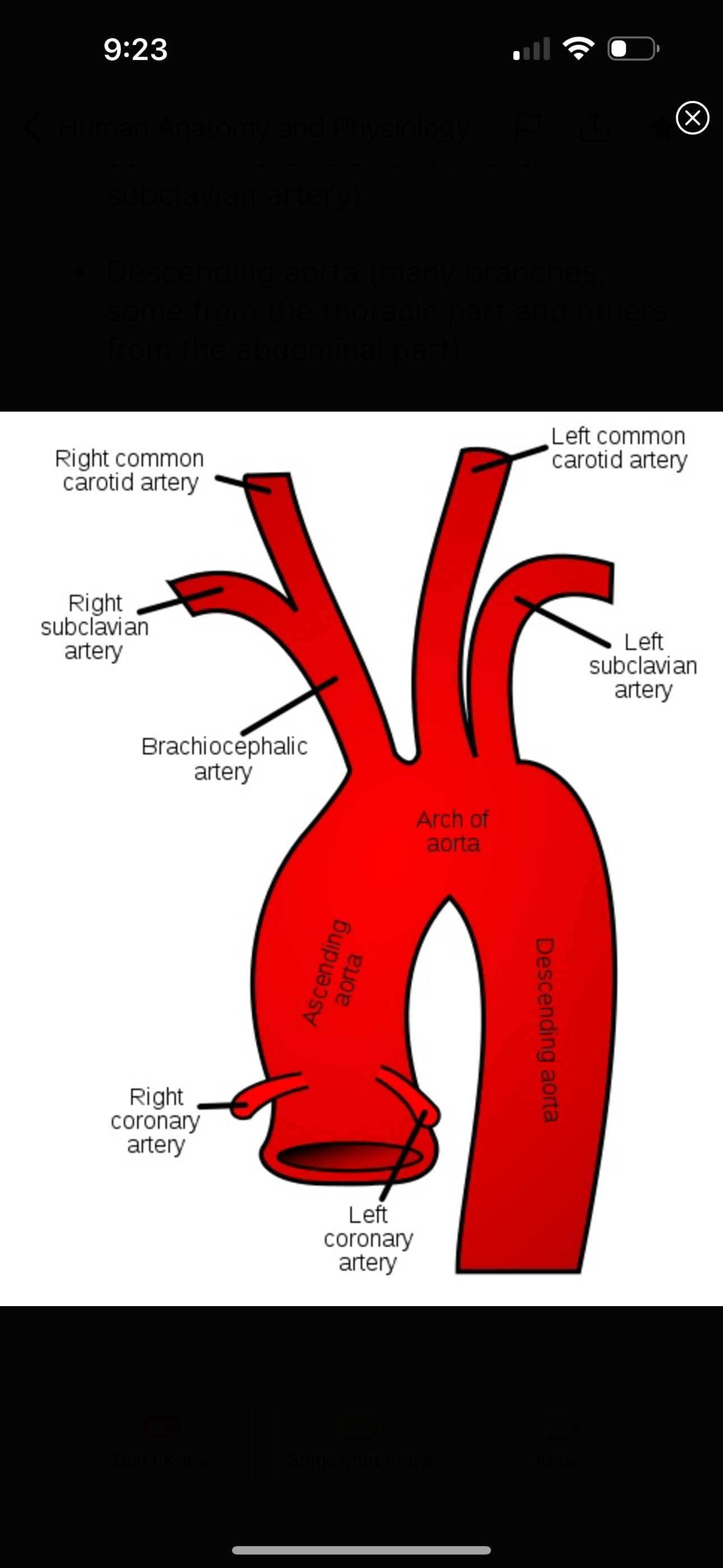
what does the ascending aorta supply?
the right and left coronary arteries of the heart
aortic arch supplies what
brachiocephalic truck
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
blood component %
Which layer of the heart is responsible for its pumping action?
Myocardium
Blood flows from the left atrium into the left ventricle through which valve?
Mitral (bicuspid) valve
Which vessels deliver oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart?
Pulmonary veins
What is the name of the valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
Which structure is responsible for initiating the heartbeat?
Sinoatrial node
What is the phase called when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood?
Systole
Which structure prevents backflow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle?
Aortic valve
What primarily produces the 'lub-dub' sound of the heart?
Opening and closing of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves
Which factor does NOT influence blood pressure?
ABO blood type
An acidic blood pH would be a value that is:
Less than 7.35
Which blood type is considered the universal recipient?
AB
The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body are called:
Arteries
In the cardiac conduction system, after the SA node fires, the impulse travels to the:
Atrioventricular node
During which phase does the heart relax and fill with blood?
Diastole
What is the largest artery in the body?
Aorta
Which valve prevents backflow of blood from the pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle?
Pulmonary valve
The 'pacemaker' cells of the heart are located in the:
Sinoatrial node
AV NODE
wait signal to allow the atriums to empty into the ventricles
delays for 0.1 seconds
Blood pressure is usually expressed as two numbers. The higher number represents:
Systolic pressure
An individual with Type O blood should NOT receive:
AB blood
Which component of the vascular system is responsible for nutrient and gas exchange?
Capillaries
The term 'cardiac output' refers to:
The amount of blood the heart pumps in one minute
A decrease in blood pH can be caused by:
Accumulation of metabolic acids
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cardiovascular system?
Production of hormones
An increase in which factor would lead to a decrease in blood pressure?
Vessel diameter
In the cardiac cycle, which complex seen in an ECG represents Ventricular depolarization?
QRS complex
P wave
atrial contraction
T wave
ventricular relaxation
purkinje fibers
specialized cardiac muscle fibers
located in ventricles
Rapidly spread the electrical signal through the ventricles
Ensure ventricles contract together and efficiently
fetal circulation
Because the lungs don’t work before birth, blood has to bypass them.
1⃣
Foramen ovale
What it is: Opening between right atrium → left atrium
Purpose: Bypasses the lungs
Closes after birth → becomes fossa ovalis
2⃣
Ductus arteriosus
⭐ (MOST TESTED)
What it is: Vessel connecting pulmonary artery → aorta
Purpose: Sends blood away from lungs
Closes after birth → becomes ligamentum arteriosum
3⃣
Ductus venosus
What it is: Vessel connecting umbilical vein → inferior vena cava
Purpose: Bypasses the liver
Closes after birth
Buffy coat of blood
made of WBCs and platelets
lymph system does what
removes excess interstitial fluid and filters it out
open system
has an immune role
failure of lymph system
EDEMA ( fluid build up in tissues )
cardiac output
heart rate x stroke volume
beats/min x amount of blood pumped per min
higher resistance in BV caused what
Vasoconstriction which narrows blood vessels making blood pressure higher
pulse pressure
systolic-diastolic
assesses atrial stiffness
stroke volume changes
viscosity
blood thickness
MAIN REASONS BLOOD GETS THICKER (TEAS LEVEL)
1⃣
More Red Blood Cells
Higher hematocrit
More cells in the same amount of plasma → thicker blood
📌 Example:
Polycythemia (too many RBCs)
Living at high altitude (body makes more RBCs)
2⃣
Dehydration
⭐ VERY HIGH-YIELD
Less plasma (fluid)
Same number of cells
Blood becomes more concentrated → thicker
📌 This is the most common TEAS answer.
3⃣
High Plasma Proteins
More proteins (like fibrinogen)
Increases resistance to flow
4⃣
Clot Formation (Localized)
Blood thickens at the clot site
Increases risk of blockage
LUB
AV closure
DUB
semilunar valve closure- start of diastole
flow of heart conduction
atrial pressure is high blood is filled in both
blood moves from high pressure to low causing the AV valves to open
blood starts slowly filling in ventricles
SA node fires to start atrial contraction
AV node says wait!= 0.1 delay
ventricles start contracting
LUB (AV valve shuts) now ventricle pressure is high
blood naturally ejects to arteries from semilunar valves
semilunar valve shuts so ventricles can’t fill back up making DUB sound
= one full heart beat
hypertension
elevated BP
increases workload of heart damaged BV bc blood tries pushing harder
since higher resistance = more blood volume and less vessel elasticity
hypotension
What it is:
Blood pressure too low (<90/60)
Effects:
Dizziness, fainting
Inadequate tissue perfusion
TEAS likes:
Blood loss, dehydration → hypotension
atherosclerosis
Buildup of fatty plaques in medium & large arteries
Why it matters:
Narrows arteries
Reduces blood flow
Raises blood pressure
TEAS phrase to recognize:
“Plaque buildup in arterial walls”
ischemia
What it is:
Reduced blood flow to tissues
Cause:
Blocked or narrowed arteries
TEAS link:
Can lead to chest pain or organ damage
myocardial infarction
Death of heart muscle tissue
Cause:
Blocked coronary artery
TEAS wording:
“Interruption of blood supply to myocardium”
arrhythmia
irregular heart beat
electrical issue
cardiac muscle cells
striated due to sarcomere (basic contractile unit of the muscle) besides smooth
Branched
→ Cells connect to each other in a networkSingle nucleus per cell (usually 1)
Short, rectangular cells
intercalted discs
Intercalated discs
Specialized connections between cardiac muscle cells
Allow:
Electrical communication
Synchronized contraction
This is why the heart contracts as a unit
bundle of HIS
also known as AV bundle
carries the delay signal from AV node to ventricles
have left and rich bundle branches that travel down the interventricular septum carrying signal to apex of heart (base) so ventricular contraction pushes blood toward arteries.
The blood vessels that return deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart are:
Veins
What is the name of the inferior tip of the heart?
Apex
The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure is known as:
Pulse pressure
Which component of the cardiac conduction system rapidly transmits impulses to the ventricular muscles?
Purkinje fibers
Which factor can lead to an increase in blood pressure?
Increased sodium intake
Which chamber of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body?
Right atrium
Which blood type lacks antigens?
O
A decrease in which factor can lead to an increase in blood pressure?
Blood volume
In a normal cardiac cycle, when are the ventricles filled with blood?
Ventricular diastole