Weeks 1-7/Midterm
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
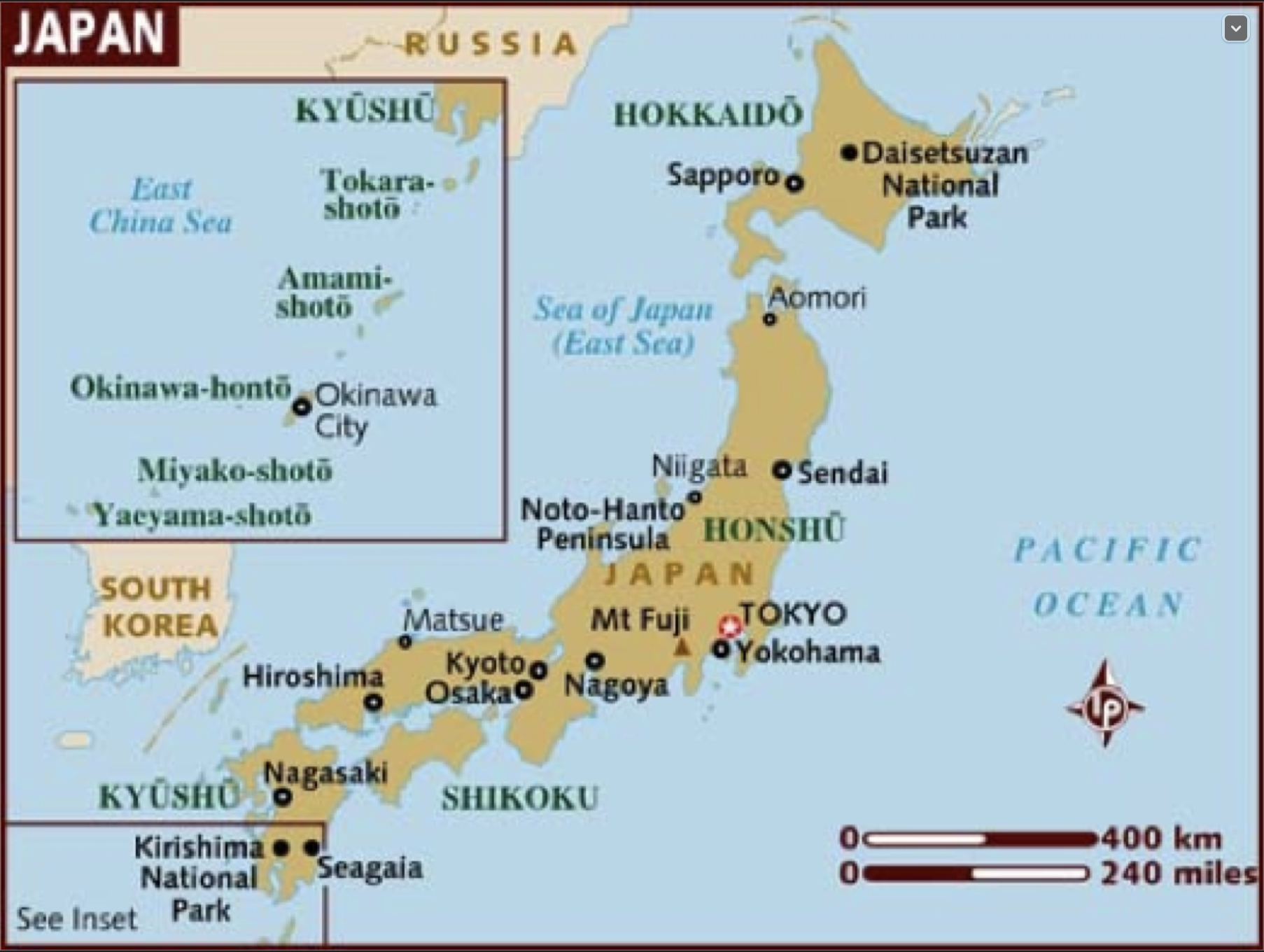
Japan in an archipelago made up of more than 6,800 islands.
Japan is an ___ made up of more than ___ ___.
2
New cards
Twin gods Izanami & Izanagi
Two gods who created Japan in myths:
3
New cards
Izanami and Izanagi were tasked with procreating to fill empty space, they did not know how to procreate until they saw the wagtail bird's back and forth tail movements; they began to pile sand and eventually created islands
What is the myth of how Japan was created?
4
New cards
Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, Shikoku
Four largest islands that take up 97% of Japan's land area and are called "home islands":
5
New cards
Leaning towards nature, asymmetrical, imperfection
What are the 3 main aspects of Japanese aesthetics in art?

6
New cards
Leaving the material as it is and how it forms
What is the layering technique?
7
New cards
Japanization = combining Chinese and Korean influence to make something fit with Japanese principles and aesthetics; often called "Yamato-é"
What is Japanization and what is the umbrella term for it?
8
New cards
Minimalism, imperfection, asymmetry
What are 3 main aspects of Japanization aesthetics?

9
New cards
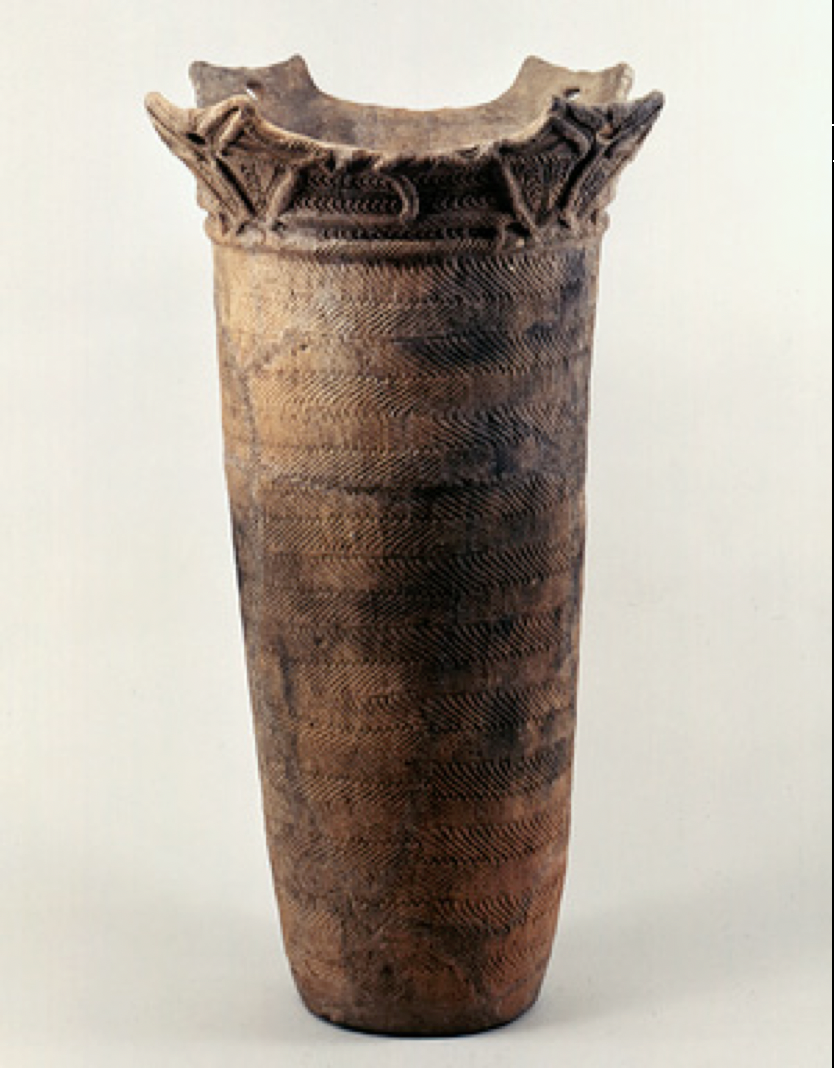
Jomon Culture = "cord impressed" clay pots
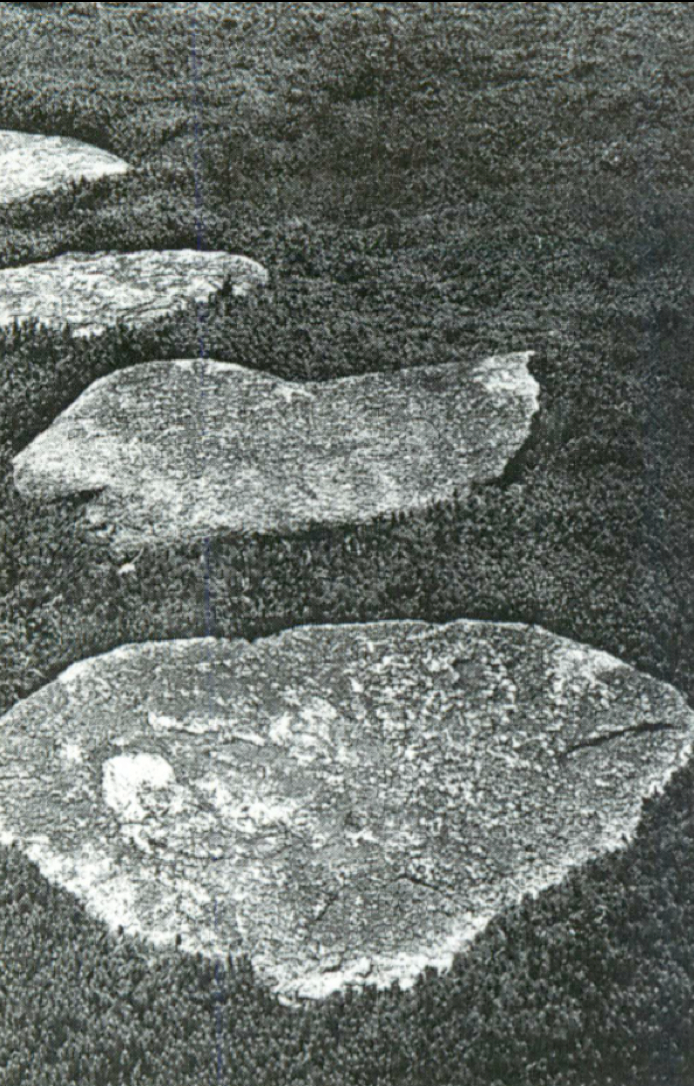
Way of life: mesolithic = hunting/fishing
Nomadic Culture; built stone circles/sundial burial pits
Way of life: mesolithic = hunting/fishing
Nomadic Culture; built stone circles/sundial burial pits
What is the first time period (11,000 BCE to 400 BCE) and describe:
- what name means/what they were known for
- way of life
- what kind of culture
- what name means/what they were known for
- way of life
- what kind of culture

10
New cards
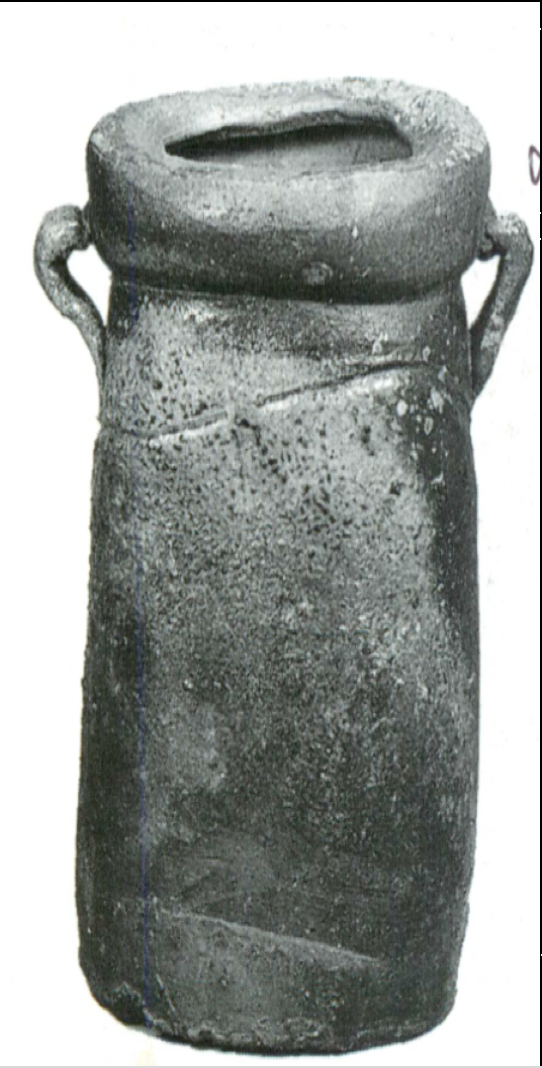
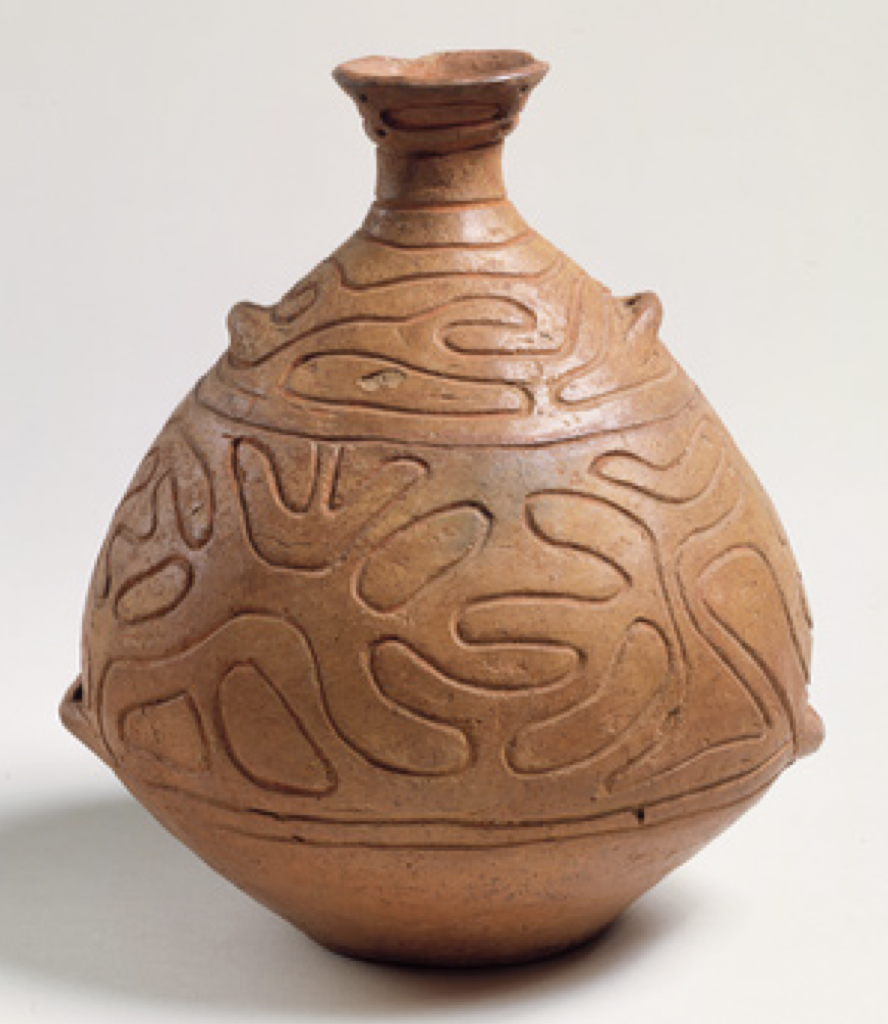
Yayoi Culture
Known for: wheel-thrown pottery, haniwas, knew baking, metallurgy to protect against conflict ex. helmets, arrows, armour
Culture: advancing to beginnings of settlement and agrarian culture
Known for: wheel-thrown pottery, haniwas, knew baking, metallurgy to protect against conflict ex. helmets, arrows, armour
Culture: advancing to beginnings of settlement and agrarian culture
What is the second time period (400 BCE to 300 CE) and describe:
- what name means/what they were known for
- what type of culture
- what name means/what they were known for
- what type of culture

11
New cards
Marine inspired design, flowing water design
What is Ryusui?
12
New cards
Essence, "spirit" found everywhere in nature; ex. trees have "treeness", because nature is seen as pure
What is Kami at the end of Yayoi?
13
New cards
yaoyorozu no kami = 8 million kami
How many kami are there believed to be and what is this called?
14
New cards
Bronze ritualistic bell; best excavated examples of sophisticated metal work
What is the Dotaku Bell?
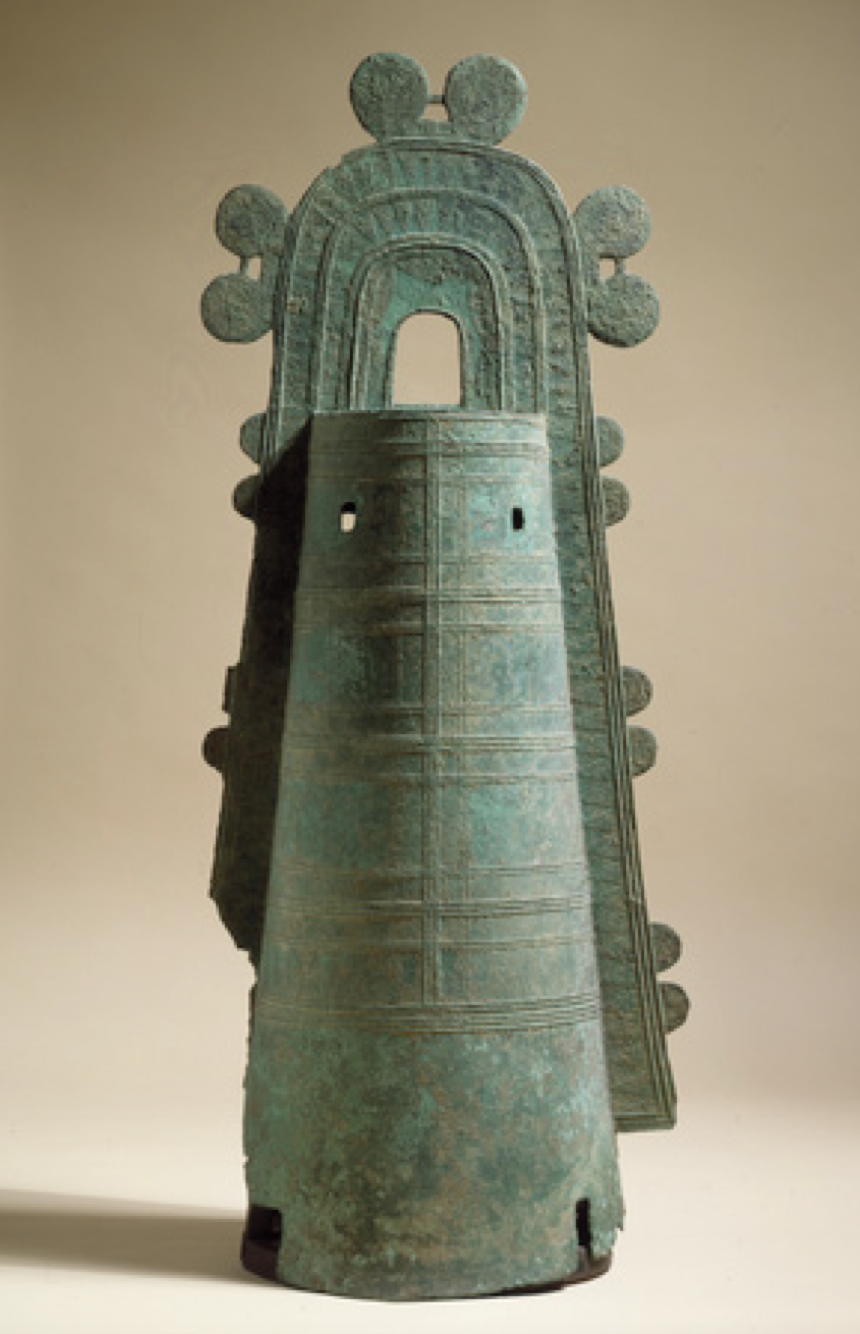

15
New cards
Specially crafted statues & figurines placed around burial ground
What are Haniwas during Yayoi period?
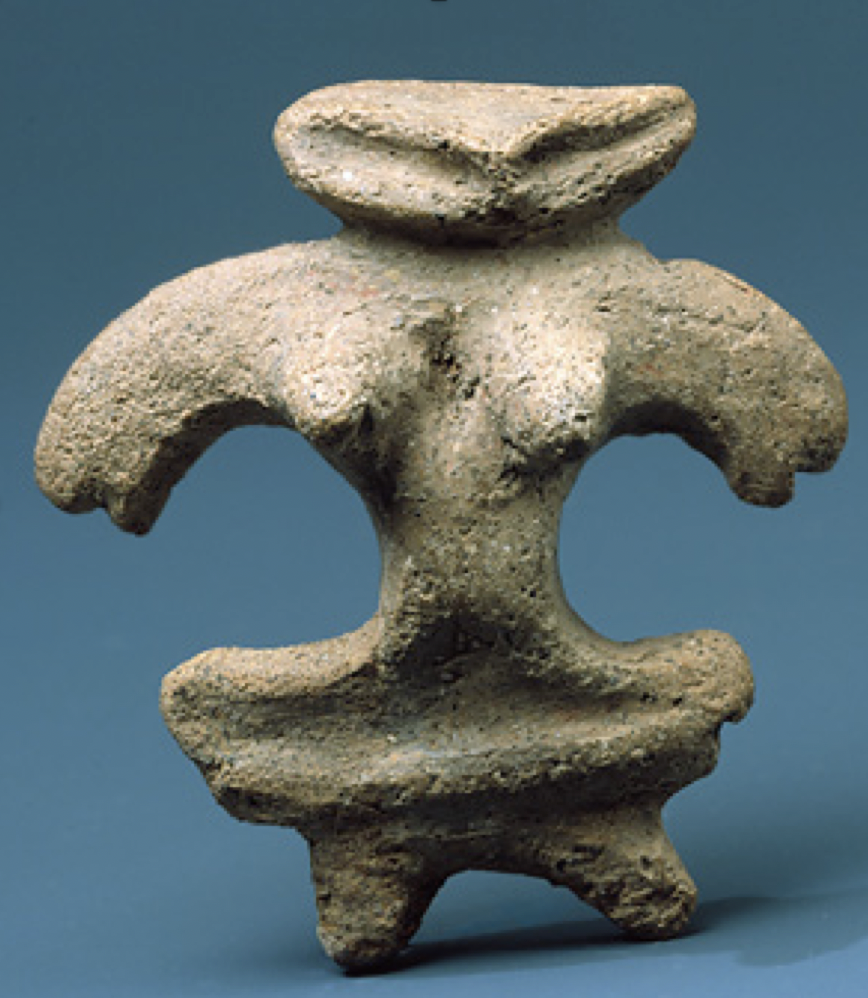

16
New cards
Kofun Culture = huge mounded tombs, first round then "keyhole" shaped
- Developed culture & society with kingdoms emerging through conflict
- Advanced metallurgy; armour, shields, helmets
- Developed culture & society with kingdoms emerging through conflict
- Advanced metallurgy; armour, shields, helmets
What is the third time period (300 CE to 710 CE) and describe:
- what name means/what they were known for
- what kind of culture
- what name means/what they were known for
- what kind of culture
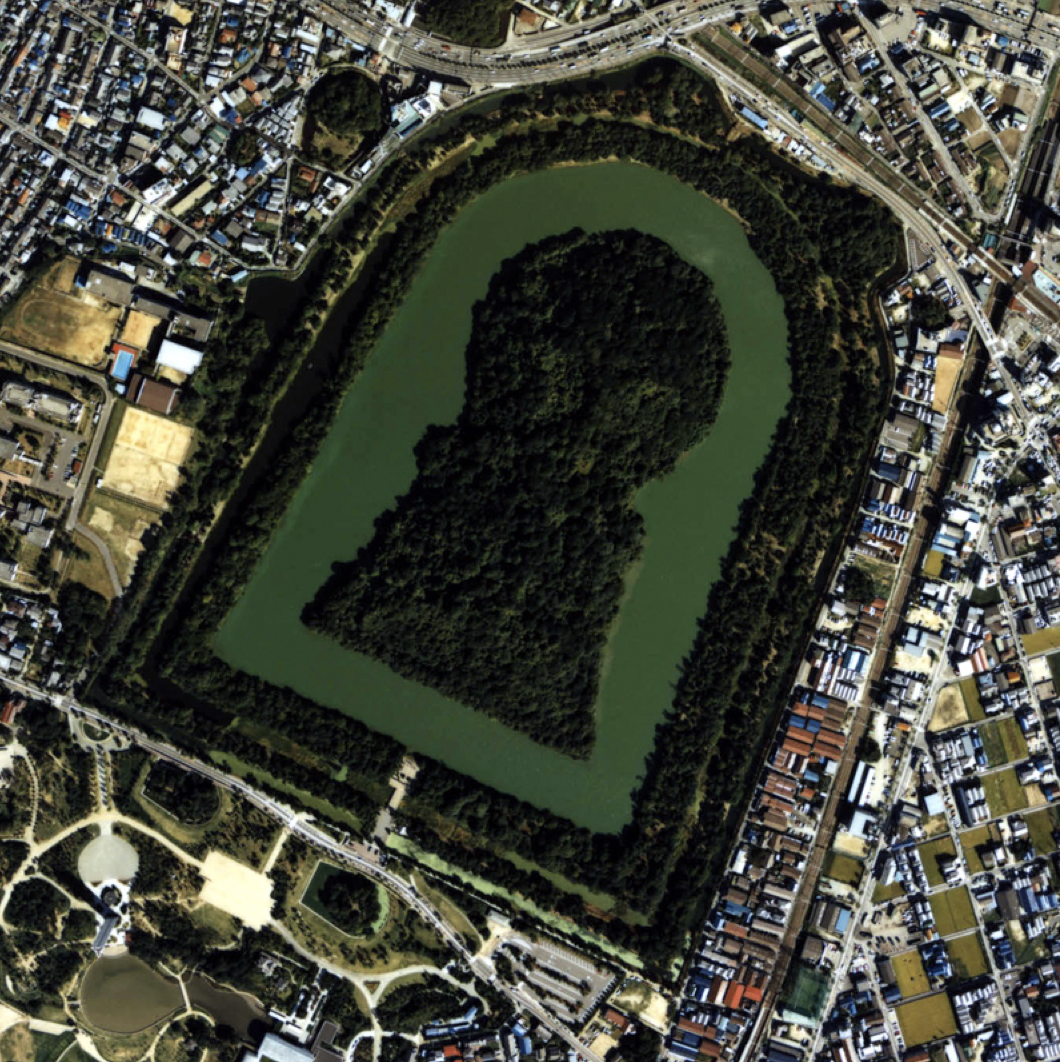

17
New cards
Daisen Kofun/Tomb in Osaka built for Emperor Nintoku; surrounded by haniwas and 3 moats and is not allowed to be excavated/disturbed at all, completely private to visitors
What is the largest Kofun, and who is it for?
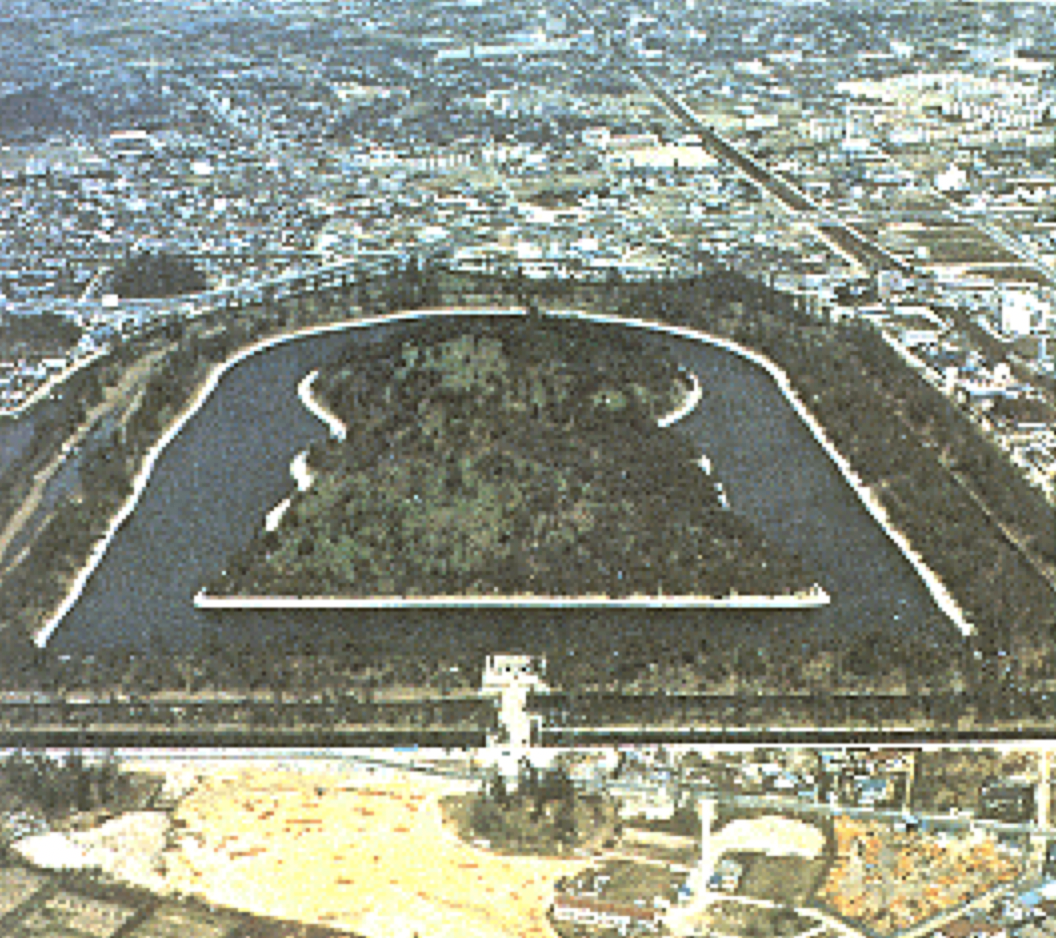

18
New cards
Design with straight lines and arcs
Define Chokkomon style
19
New cards
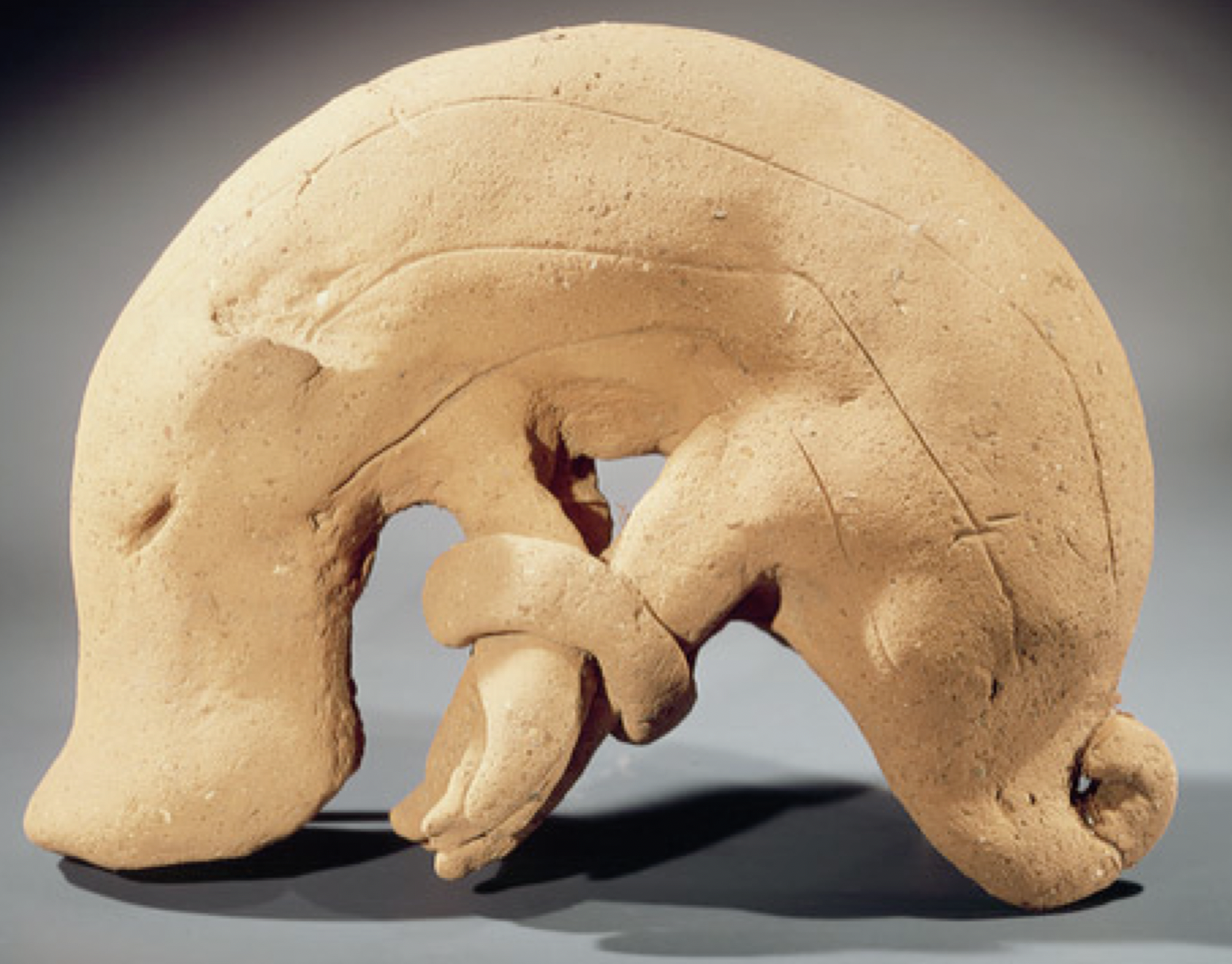
Changed to anthropomorphic figures and later human figures for rituals
What are Haniwas during Kofun period?

20
New cards
- "way of the gods" or "path of the spirits" "way of the kami"
- begins at end of Yayoi into beginning of Kofun (660 BCE)
- comes from Chinese word "Shendao"; shin = spirit/kami, dao = philosophical path/study
- kami and nature are important principles
- begins at end of Yayoi into beginning of Kofun (660 BCE)
- comes from Chinese word "Shendao"; shin = spirit/kami, dao = philosophical path/study
- kami and nature are important principles
What is Shintoism and when did it start?
21
New cards
Codified in the Kojiki (Record of Ancient Matters, 712 CE) and Nihon Shoki/Nihon-gi (Chronicles of Japan, 720 CE) in 8th century BCE
When and in what text was Shinto codified?
22
New cards
Harae = purification, cleanse yourself of sins, rebirth, appease Kami; done by priest = kannushi
What is the most important Shinto ritual/idea and what is it called?

23
New cards
Kannagara or kami-no-michi = knowing/reaching the gods
1. Sincerity (makoto)
2. honesty (tadashii)
3. purity (kiyome)
- aside: sins are called impurity or kegare
1. Sincerity (makoto)
2. honesty (tadashii)
3. purity (kiyome)
- aside: sins are called impurity or kegare
What is the term that refers way of the kami and what are the 3 principles?
24
New cards
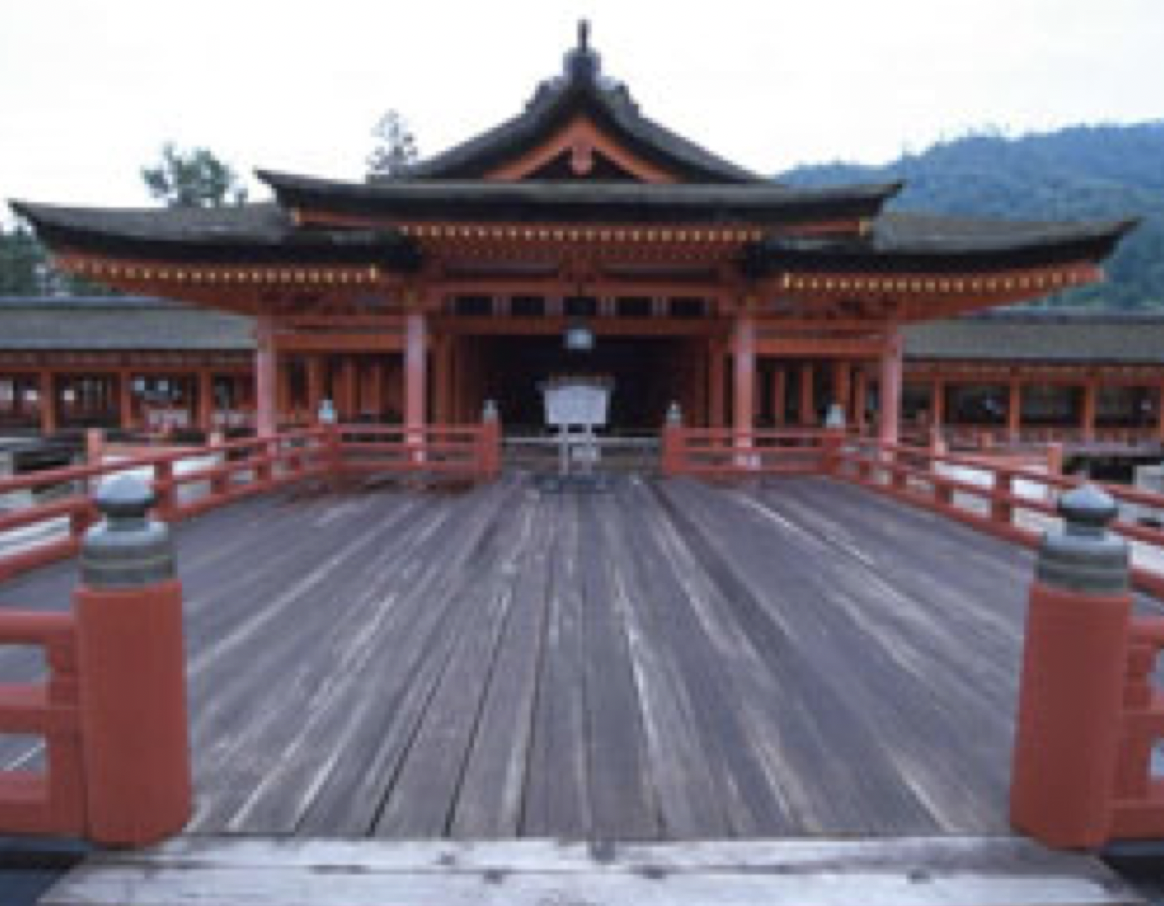
Built shrines as a house for the kami to dwell in
- Kamidana: shelf inside to house greatest kami
- Kamidana: shelf inside to house greatest kami
Why did they build Shinto shrines and what is a kamidana?

25
New cards
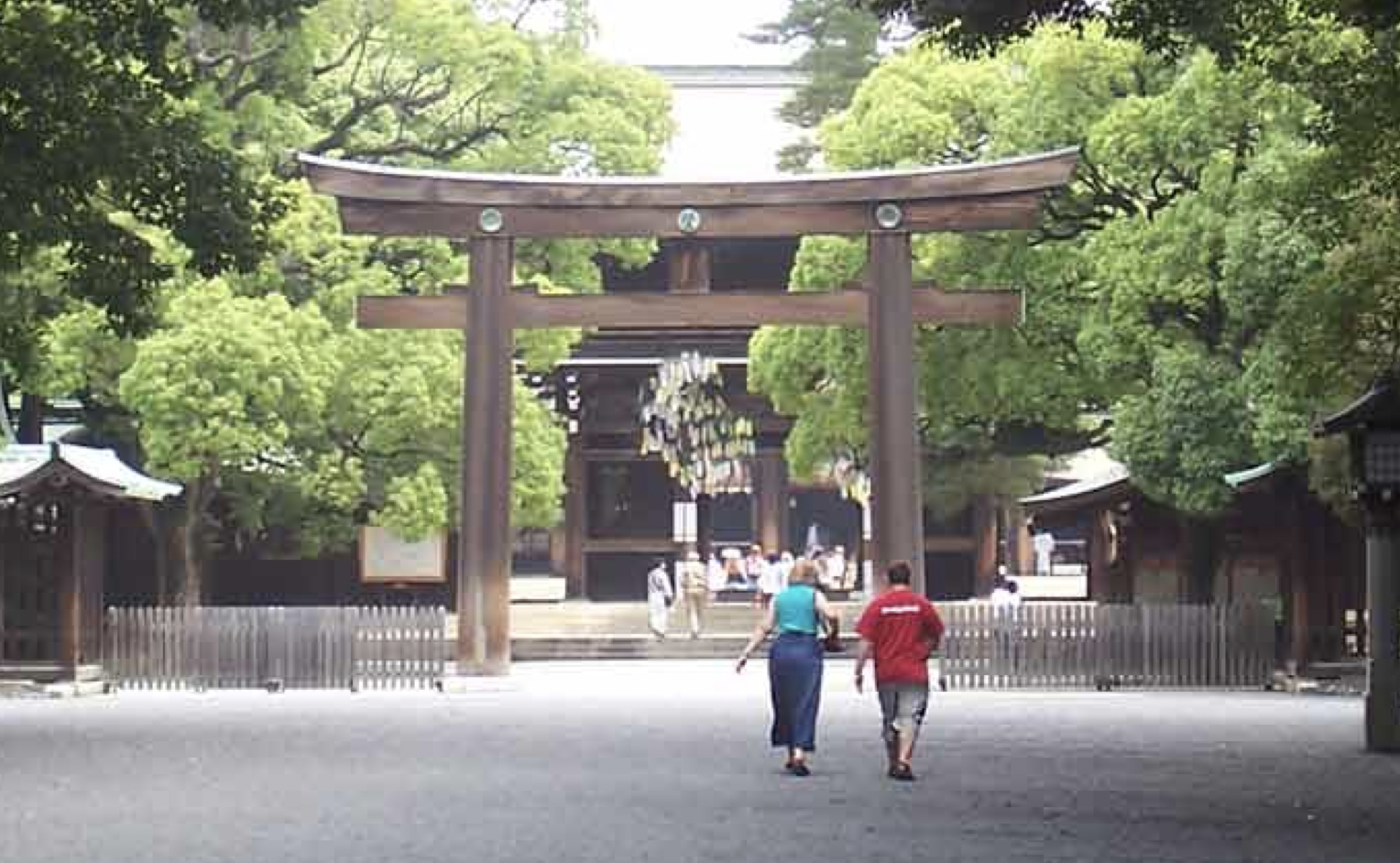
Torii gates: symbolizes leaving behind the worldly world and all its distractions to reach jinja and reach the sacred space (walk a long way to leave behind worldly aspects)
What is the first thing you will see upon approach of a Shinto shrine and its symbolism?

26
New cards
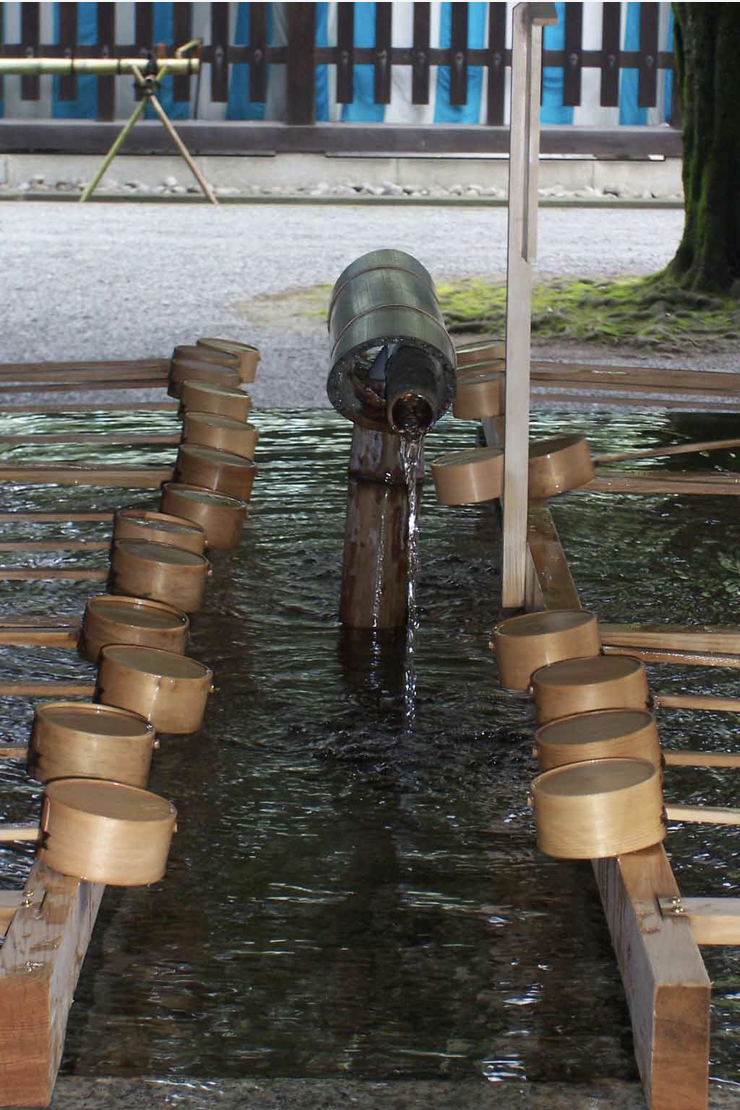
Water, used in large basin to wash mouth and hands to purify yourself before entrance
What is temizu in the shrine?
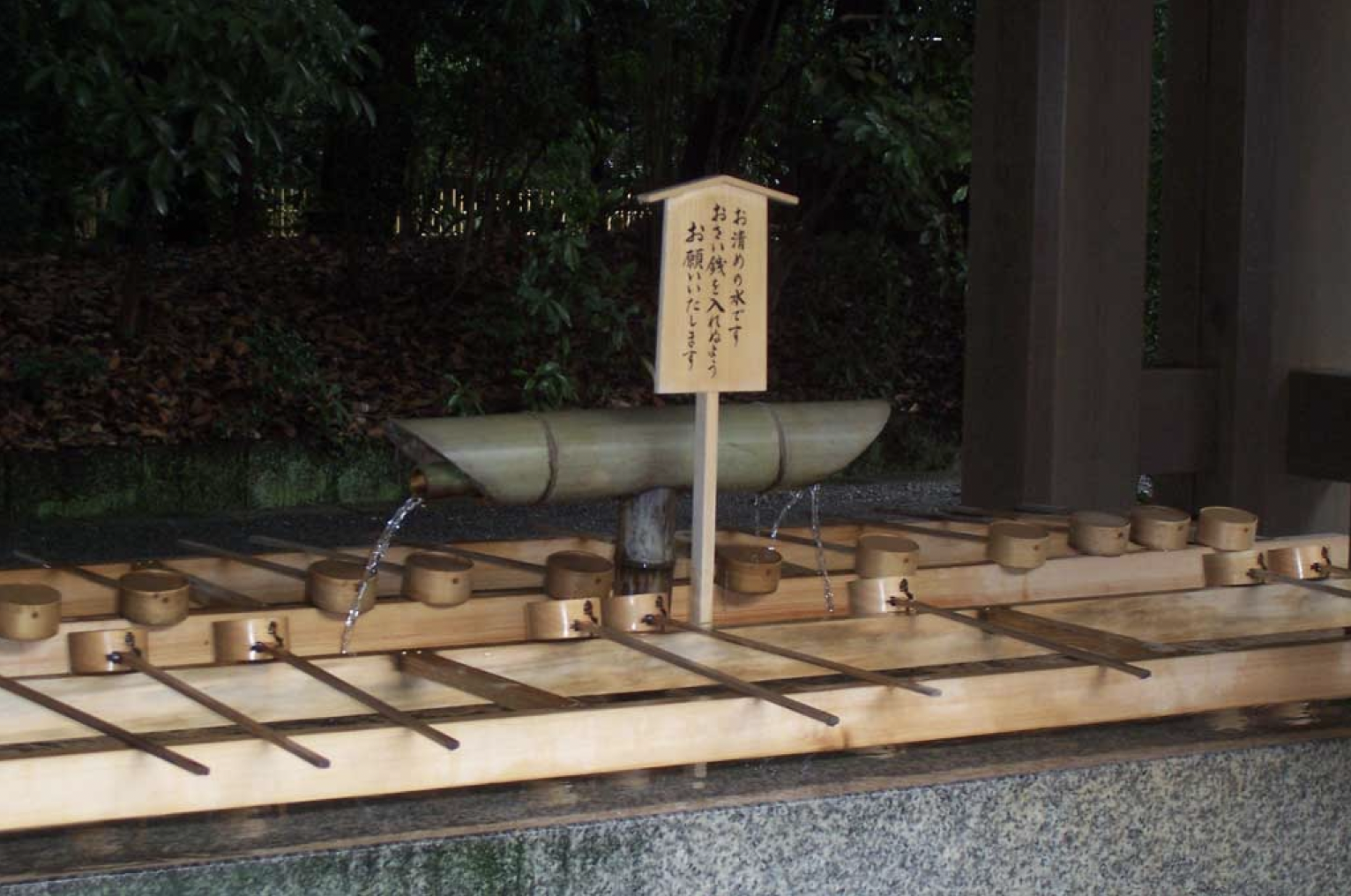

27
New cards
Stand in front and clap/ring bell to awaken kami and begin to pray
What is the first thing you do when you enter the shrine?
28
New cards
Amaterasu = Sun Goddess, ancestor of Imperial family
Brother: Susanoo = Storm god, causes and protects from disaster
Brother: Susanoo = Storm god, causes and protects from disaster
Who is the greatest of the kami and her brother?
29
New cards
- Ujigami = ancestors of clans who are ancestors and protectors
- natural objects and creatures, forces of nature
- souls of dead humans with outstanding achievement
- natural objects and creatures, forces of nature
- souls of dead humans with outstanding achievement
Three types of kami:
30
New cards
Prince Siddartha, Indian prince born around 4th-5th century BCE who leaves kingdom and has 3 encounters which change his life forever
Who was Buddha originally and when was he born?
31
New cards
1. Old person in pain, wants to be able to walk; encounters desire and pain and suffering
2. Diseased person, wishes for health; encounters desire and pain and suffering
3. Dead person; encounters death, mourning, attachment, pain and suffering
2. Diseased person, wishes for health; encounters desire and pain and suffering
3. Dead person; encounters death, mourning, attachment, pain and suffering
What are Siddartha's three encounters on his journey?
32
New cards
1. All life is sorrowful.
2. The cause for the suffering is desire, attachments, cravings (trsna), ignorance (avidya), and never being satisfied, etc.
3. One must cease the suffering.
4. One must follow the Middle/8-Fold Path (avoiding extremes, doing everything the right way, right duties, right knowledge and behavior)
2. The cause for the suffering is desire, attachments, cravings (trsna), ignorance (avidya), and never being satisfied, etc.
3. One must cease the suffering.
4. One must follow the Middle/8-Fold Path (avoiding extremes, doing everything the right way, right duties, right knowledge and behavior)
What are the 4 Noble Truths?
Remember: No matter the school of thought, these NEVER change.
Remember: No matter the school of thought, these NEVER change.
33
New cards
Yana = boat
Samsara = cycle of life
- to achieve nirvana, you must ferry across the rushing river of samsara, and never look back to detach from the worldly world
Samsara = cycle of life
- to achieve nirvana, you must ferry across the rushing river of samsara, and never look back to detach from the worldly world
What is the idea behind "Yana" and the "rushing river of Samsara"?
34
New cards
someone on the cusp/threshold of achieving Nirvana, either cannot fully achieve or holds self back in order to teach Buddha's teachings to others
Define Bodhisattva:
35
New cards
candles flicker constantly, you must blow out the flame to rid yourself of distraction and not look back
What is the symbolism of a candle in Buddhism?
36
New cards
- around 6th century CE
- Prince Shotoku brings it from China via the Silk Road and scholars he sent to China and it was then Japanized
- Mahayana: great ferryboat, Buddha has become divine and iconic shown in human form
- Prince Shotoku brings it from China via the Silk Road and scholars he sent to China and it was then Japanized
- Mahayana: great ferryboat, Buddha has become divine and iconic shown in human form
When and how does Buddhism become popular in Japan and what is this phase called?
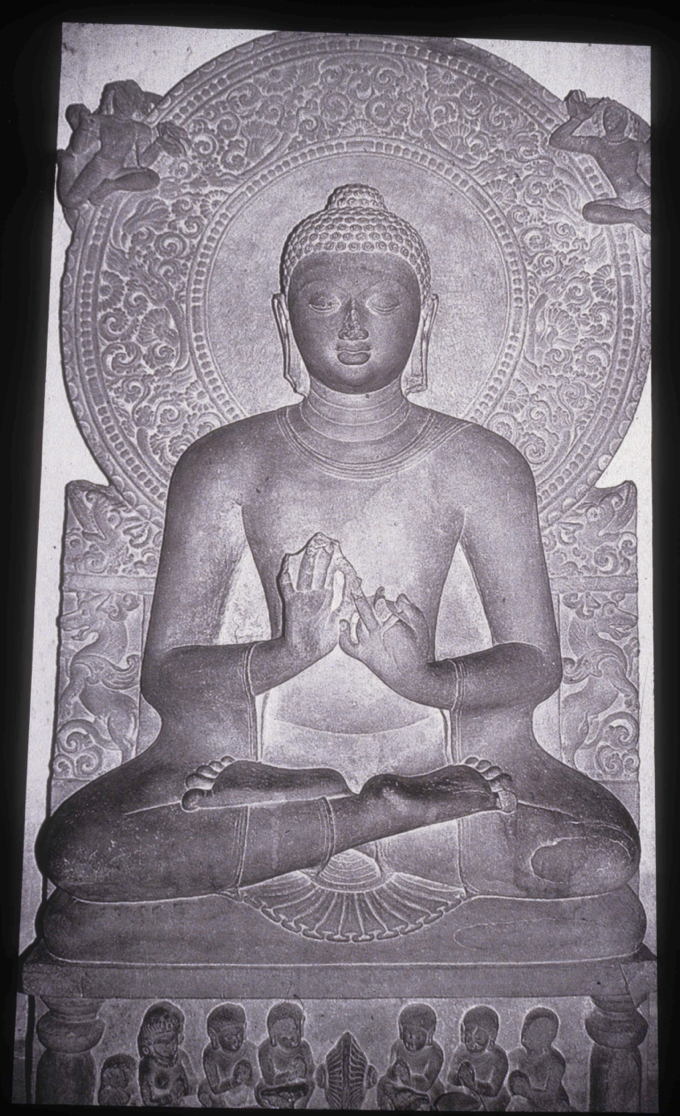

37
New cards
mounds built originally by Prince Ashoka in India said to contain Buddha's ashes; represents PariNirvana (death of Buddha) in hinayana phase of Buddhism
Define stupa:
38
New cards
Asuka-Nara phase: capitol moves
- Kami becomes humanized
- Focus on Gods instead of natural essence
- Prince Shotoku brings Buddhism to Japan
- Begin building Buddhist temples
- Kami becomes humanized
- Focus on Gods instead of natural essence
- Prince Shotoku brings Buddhism to Japan
- Begin building Buddhist temples
What is the fourth time period (552 to 645 BCE) and its characteristics?
39
New cards
Horyu-ji
- built in 607 CE by Prince Shotoku
- completely wooden
- Japanized setup = horizontal instead of vertical, simplistic, asymmetrical, rustic
- built in 607 CE by Prince Shotoku
- completely wooden
- Japanized setup = horizontal instead of vertical, simplistic, asymmetrical, rustic
What is the first/oldest Buddhist temple built in Japan and its characteristics?
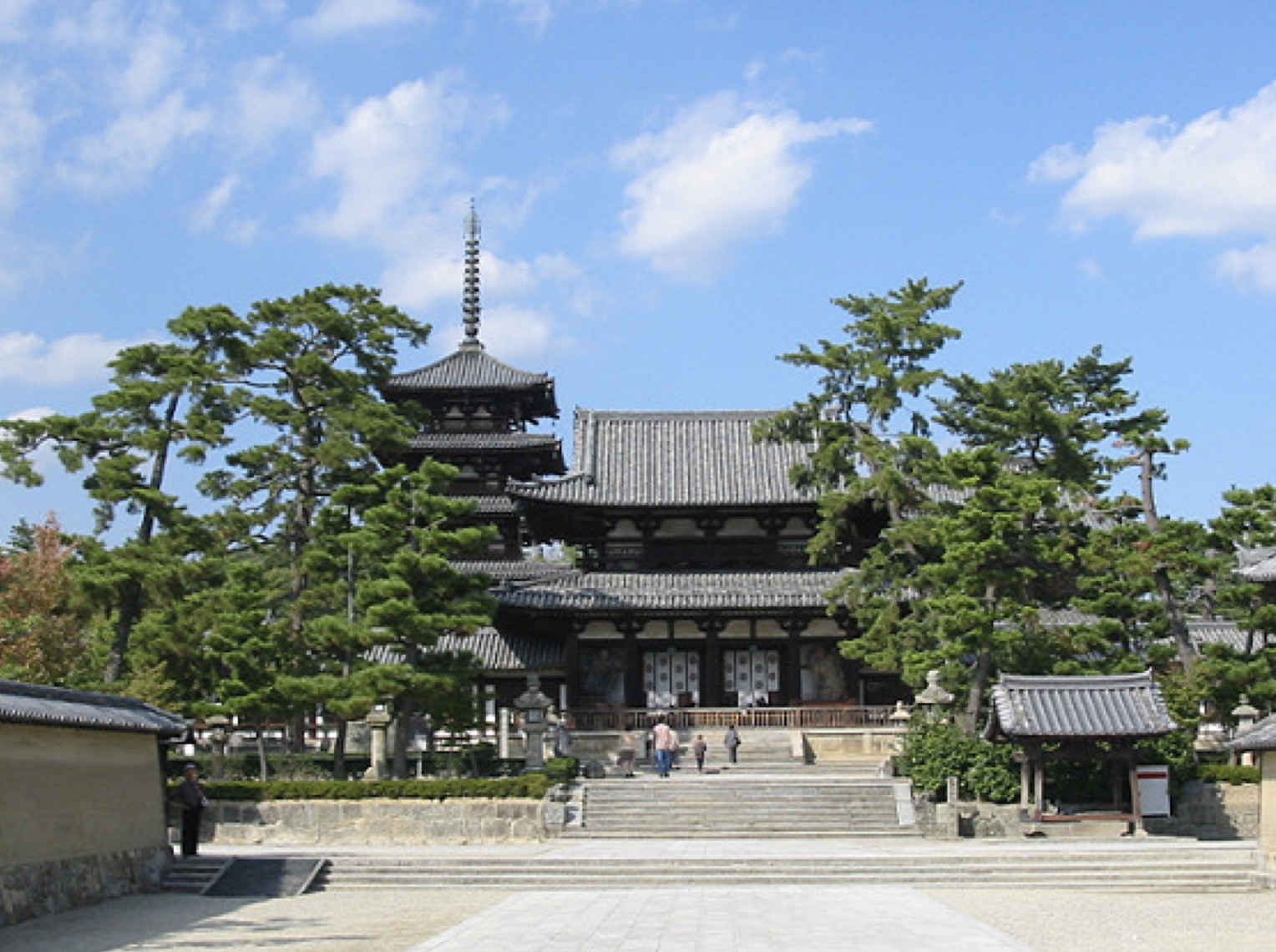

40
New cards
- Pagoda: influenced by stupas
- Yumedono: private prayer hall
- Kondo: main hall/golden hall, where the Buddha is housed
- Yumedono: private prayer hall
- Kondo: main hall/golden hall, where the Buddha is housed
What are the 3 main buildings at Horyu-ji?
41
New cards
Yakushi Nyorai, the healer Buddha
Who is the Buddha in Horyu-ji?
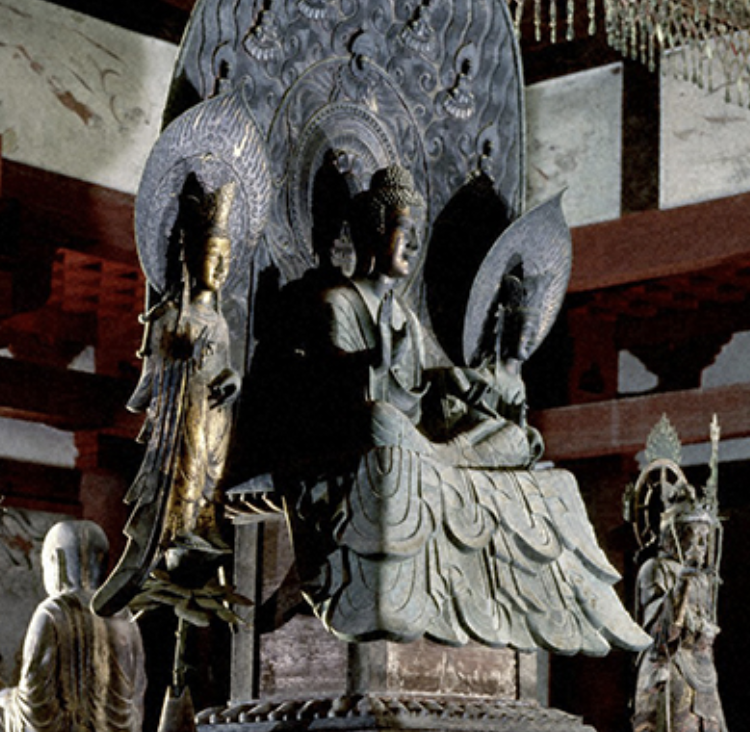

42
New cards
The bell, there was a fire in the 9th century and everything had to be rebuilt. Relics are now housed in the museum with copies in the temples
What is the only original piece left in Horyu-ji and why?
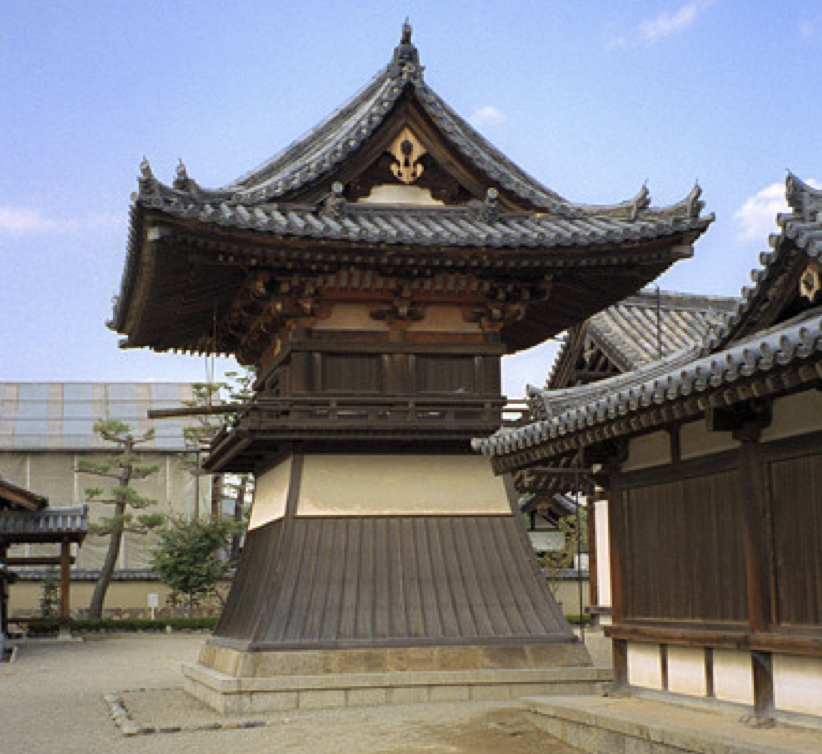

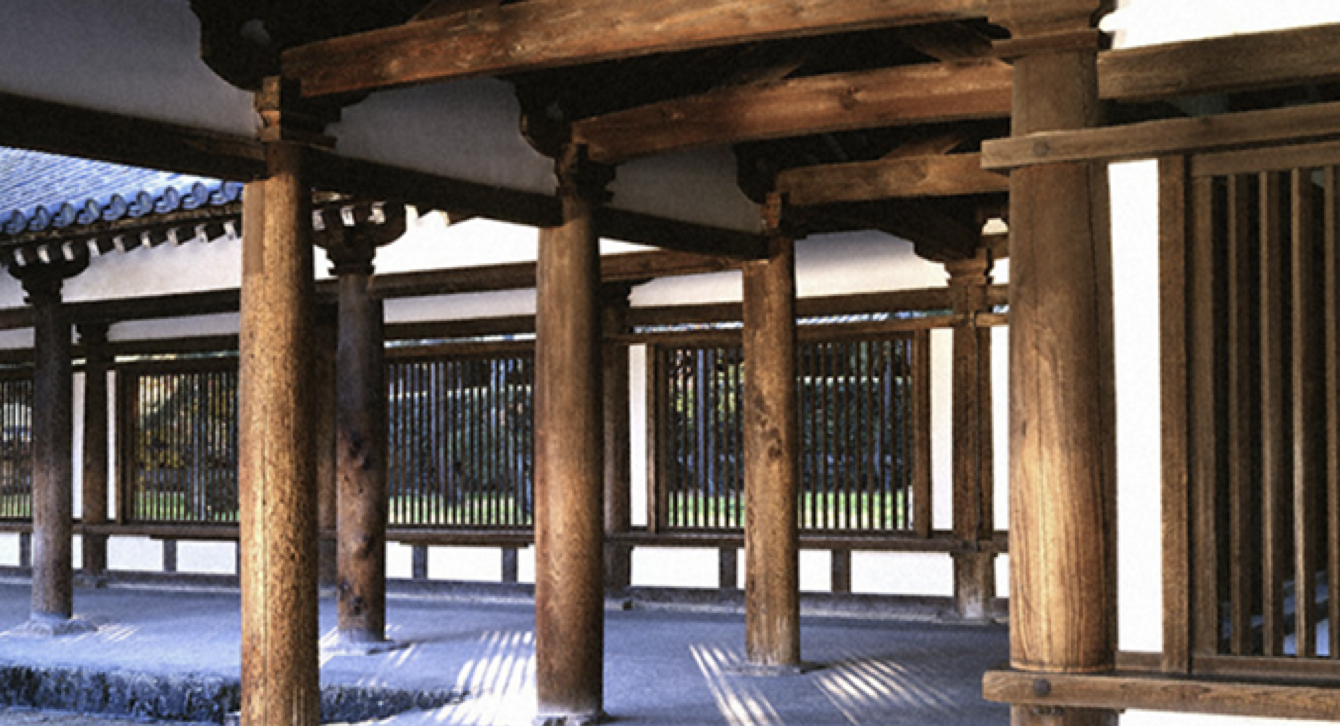
43
New cards
Columns built narrow at the top and bottom and wider in the middle, all made of cypress trees, 80 plus columns supporting kondo
What is the entasis style in Horyu-ji?

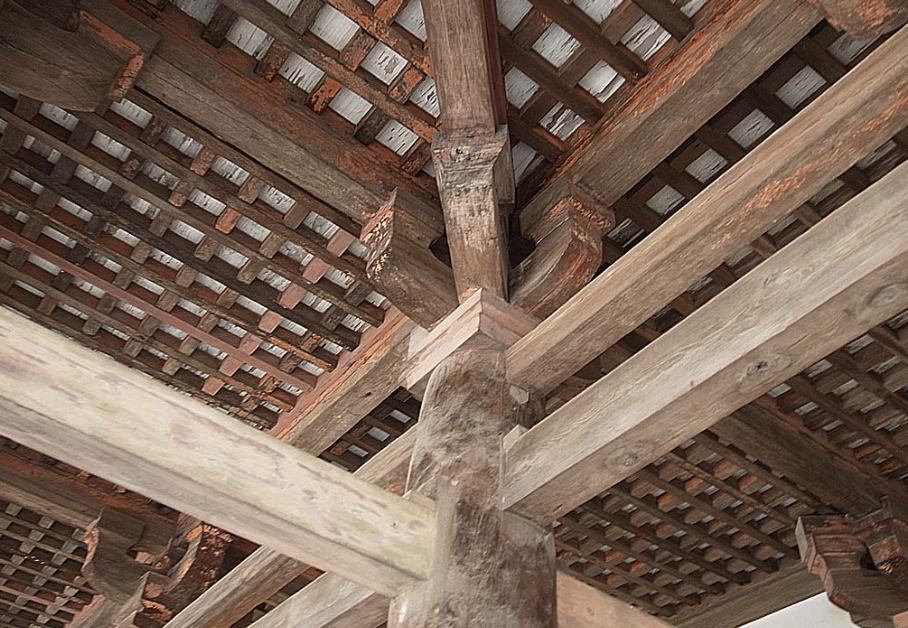
44
New cards
Checkerboard style design on ceilings
What is coffering?

45
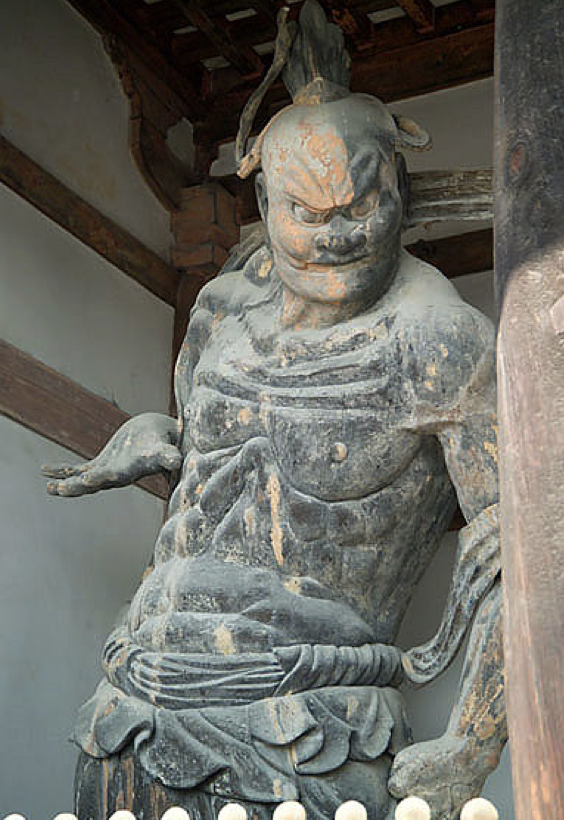
New cards
- Shown garish and ferocious
- Trample ignorance & the unfaithful
- Guard both sides of entrance to temple
- Carry lassos, spears, and stupa
- Called 4 Kings
- Sometimes one with mouth open, one with mouth closed to show beginnings and end aka samsara
- Trample ignorance & the unfaithful
- Guard both sides of entrance to temple
- Carry lassos, spears, and stupa
- Called 4 Kings
- Sometimes one with mouth open, one with mouth closed to show beginnings and end aka samsara
Describe the guardian figures at Horyu-ji and Todai-ji:

46
New cards
4 color laquer painting; used for paintings that depict previous lives of Buddha called Jataka tales (animal fables with moralistic purpose) ex. Mahashewatajataka, or tigress tale
What is Mitsuda-é technique and how is it used in the Horyu-ji temple?

47
New cards
Chinese
- Harsher, cleaner lines, more majestic, symmetrical
Korean
- Rustic, imperfect, natural
- Harsher, cleaner lines, more majestic, symmetrical
Korean
- Rustic, imperfect, natural
What is the difference between Chinese influence and Korean influence?
48
New cards
- Todai-ji Temple aka Great Eastern Temple
- Commissioned by Emperor Shomu in the 740s CE
- Commissioned by Emperor Shomu in the 740s CE
What is the second temple that at the time was the largest project ever built in Japan, who was it commissioned by, and when?
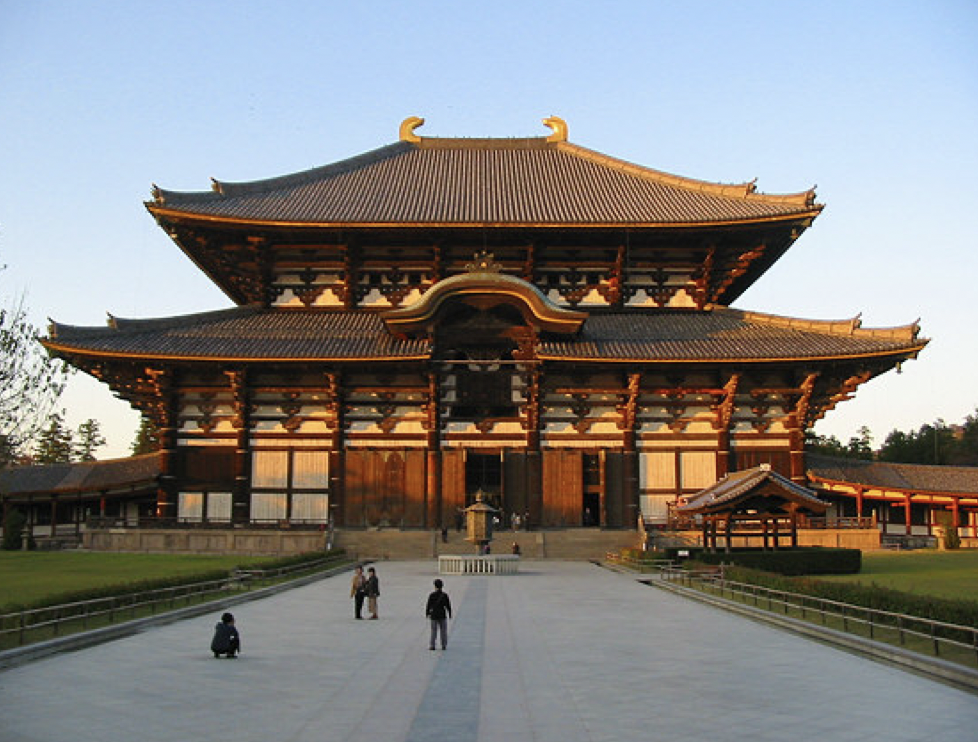

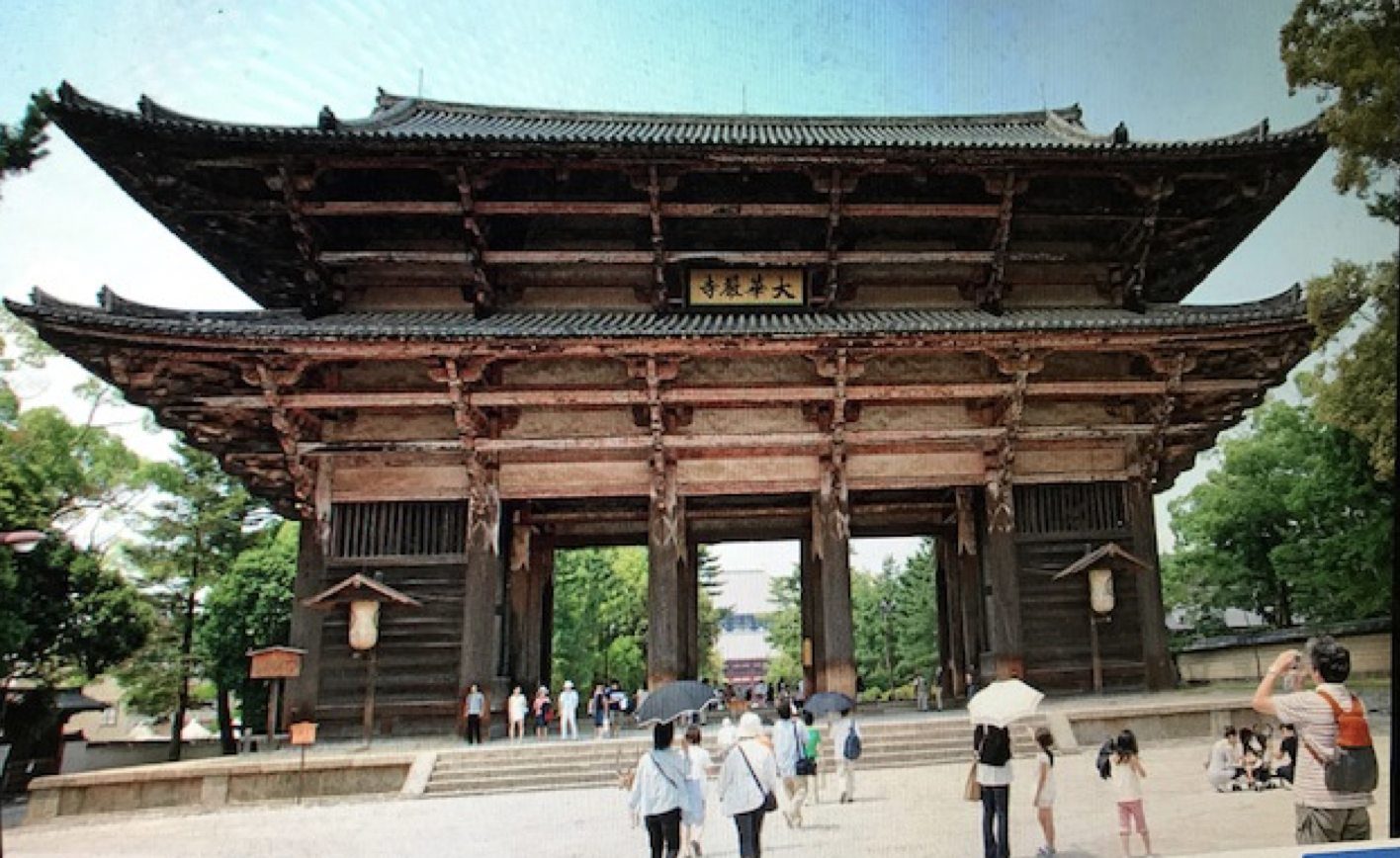
49
New cards
1. Twin pagodas
2. Main hall = Hondo/Daibutsuden (Great Buddha Hall)
3. Great South Gate (Nandaimon)
2. Main hall = Hondo/Daibutsuden (Great Buddha Hall)
3. Great South Gate (Nandaimon)
What are the 3 main buildings in Todai-ji?

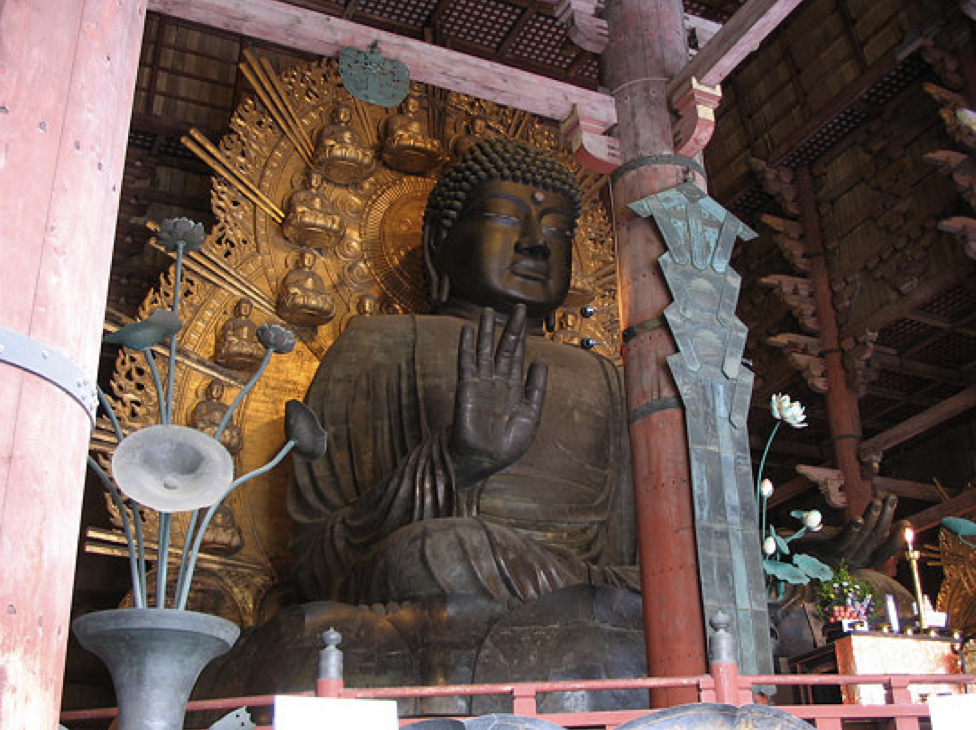
50
New cards
- Rushana Buddha (universal light) / Daibutsuden / Vairocana (enlightened)
- Hand gesture: Abhayamudra = do not fear, blessings not to fear
- Was HUGE, Emp. Shomu completely depleted all available copper in Japan to build; was built in several stages
- Hand gesture: Abhayamudra = do not fear, blessings not to fear
- Was HUGE, Emp. Shomu completely depleted all available copper in Japan to build; was built in several stages
Who is the Buddha in Todai-ji, what hand gesture does it have, and what is special about it?

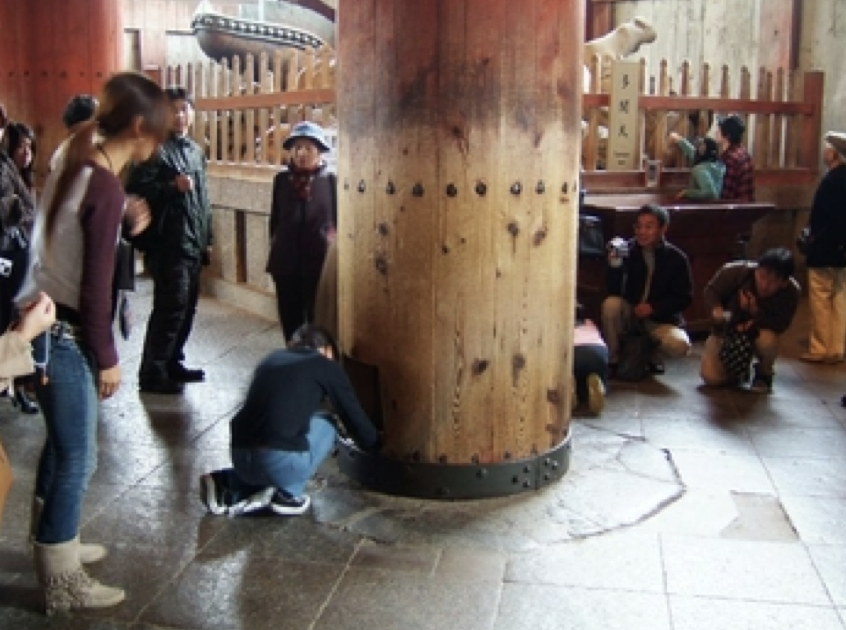
51
New cards
It has a hole cut out the size of the Buddha's nostril, and if you can fit through it, you are said to leave all your sins and impurities behind
What is special about one particular column in Todai-ji?

52
New cards
Warihagi technique: uses positive and negative side molds/templates
What is the technique that emerges called to "mass-produce" Buddha statues and how?
53
New cards
- schools of Buddhism emerging (Shingon and Tendai Lotus)
- sculptures in Jogen Warihagi style
- classical period of Japanese art, secular and religious paintings
- Gods and Goddesses influencing art
- sculptures in Jogen Warihagi style
- classical period of Japanese art, secular and religious paintings
- Gods and Goddesses influencing art
How is the Early Heian (794-1185 CE) defined and what stands out about it?
54
New cards
- Tendai Lotus School
- "salvation for ALL"
- reading the sutras (Lotus Sutras), meditation, religious practice
- "salvation for ALL"
- reading the sutras (Lotus Sutras), meditation, religious practice
What school of Buddhism was founded by the scholar Saicho, what was the main message of the school, and what did they believe in doing to achieve salvation? (Early Heian)
55
New cards
- Shingon School; Shingon = MANTRA
- Very exclusive school, believed in mantras and "true word"
- Could only achieve salvation through chanting mantras which were oral traditions passed down from teacher to pupil; used womb mandala paintings
- Very exclusive school, believed in mantras and "true word"
- Could only achieve salvation through chanting mantras which were oral traditions passed down from teacher to pupil; used womb mandala paintings
What school of Buddhism was founded by Kukai, what was the main message of the school, and what did they believe in doing to achieve salvation? (Early Heian)
56
New cards
- Supreme Buddha in center of lotus surrounded by other Buddha's
- Mandala represents the universe, always a circle within a square, womb is from where everything starts
- Used by Shingon school to look at and chant mantras
- Mandala represents the universe, always a circle within a square, womb is from where everything starts
- Used by Shingon school to look at and chant mantras
What were womb mandala paintings, what did they represent, and what were they used for at the _____ School? (Early Heian)

57
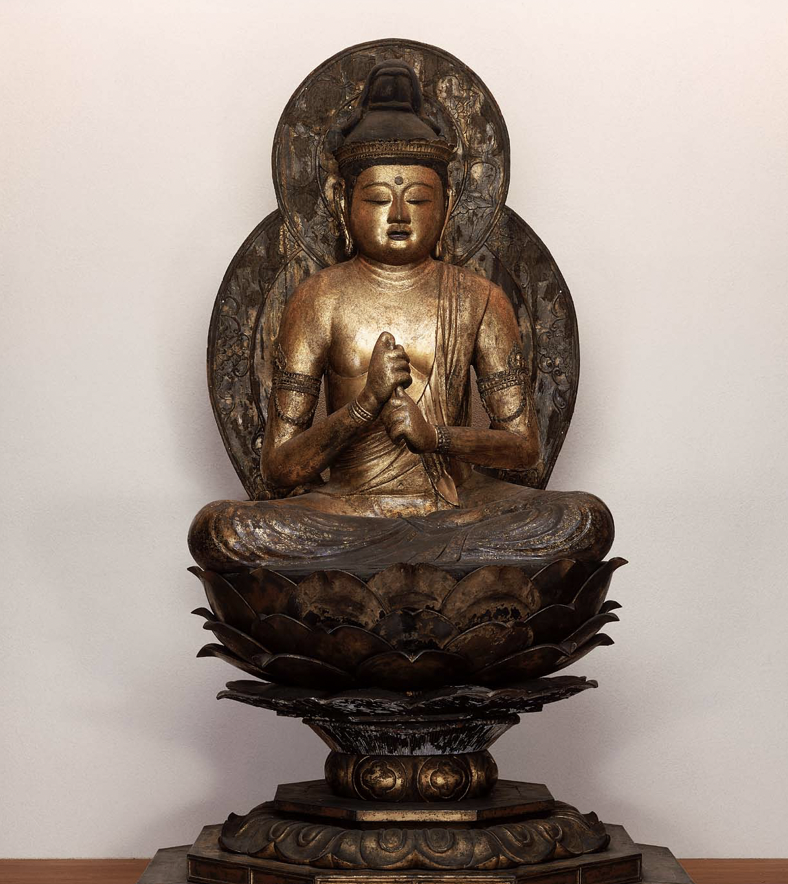
New cards
Dainichi Buddha, always shown with wisdom fist and a crown to differentiate between other Buddha
Who is the "Supreme Buddha" of the Shingon School and what hand gesture? (Early Heian)

58
New cards
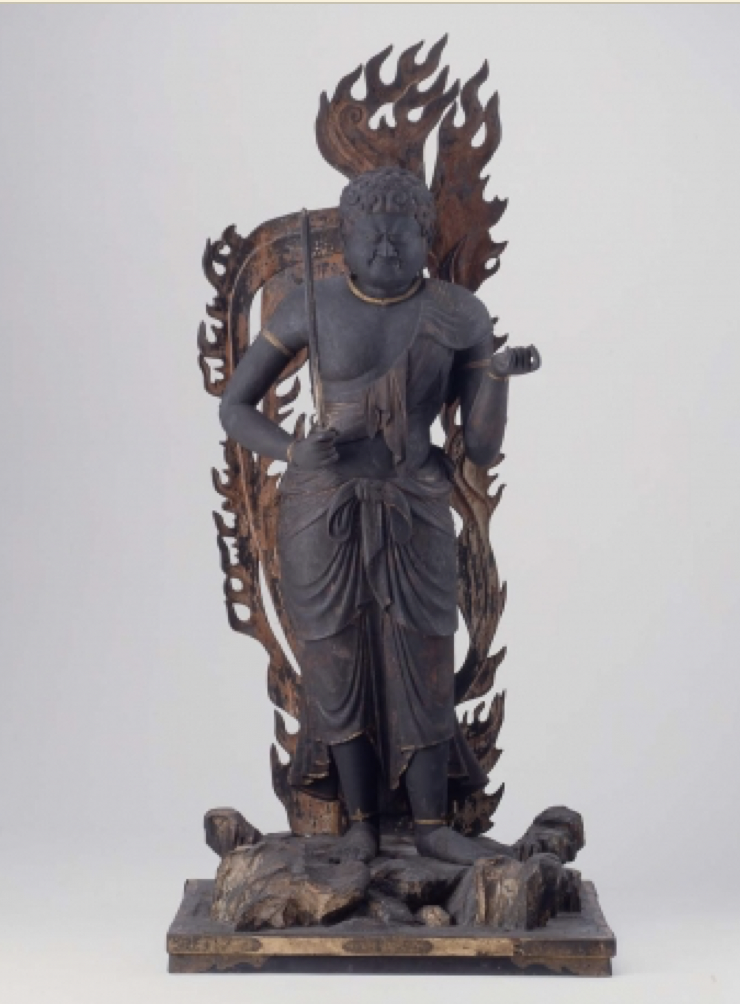
- Bringer of light and wisdom, always shown blue, sword, lasso, ferocious face, protects Buddhism
- Shingon School
- Shingon School
What is the Fudo Myoo/Blue Fudo and what school was he popular with? (Early Heian)

59
New cards
Fujiwara clan
Who is the most powerful clan during the Middle Heian period?
60
New cards
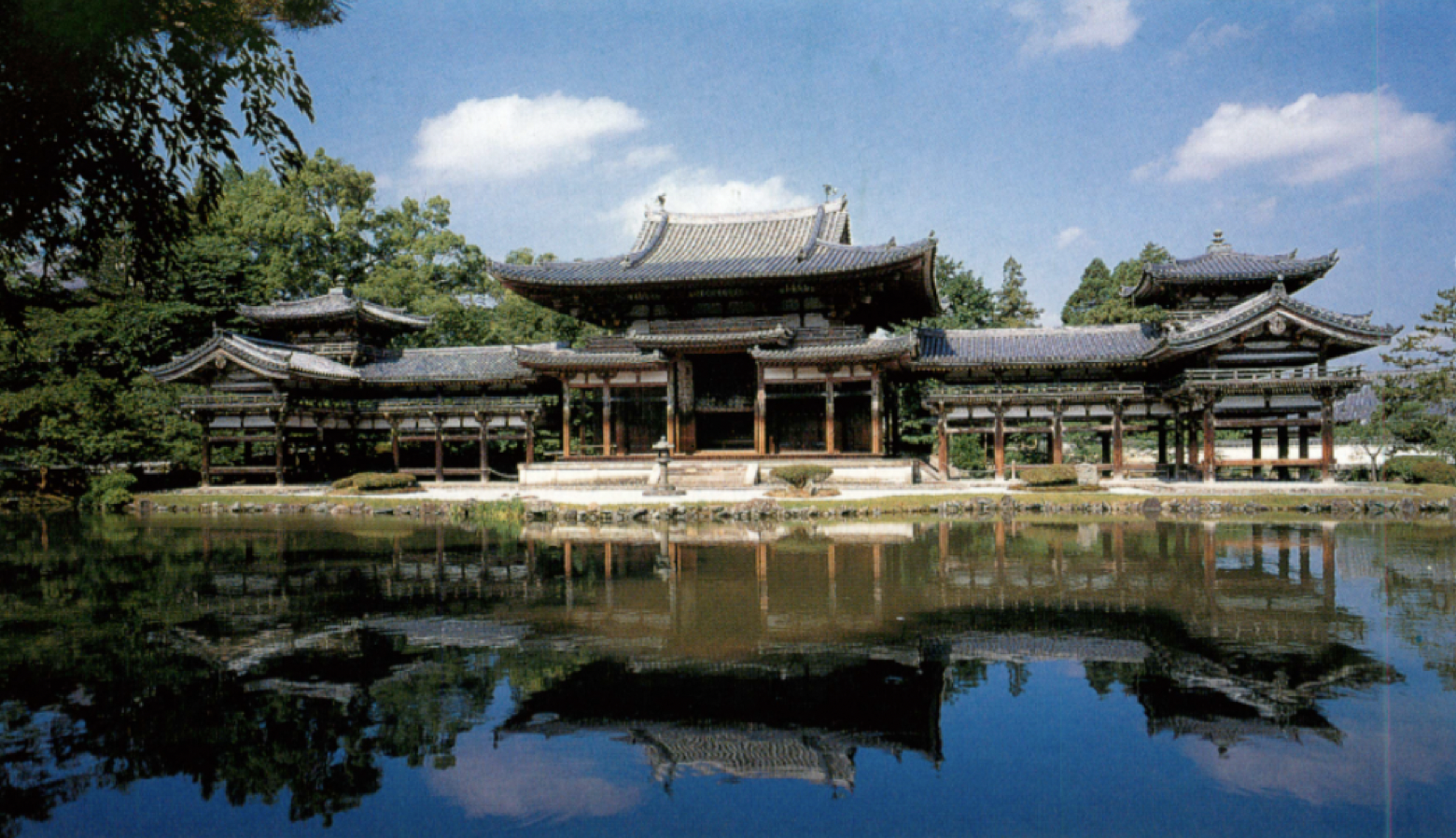
Fujiwara castle/resting place converted into a shrine
What is the Great Phoenix Hall? (Middle Heian)

61
New cards
- Raigo-Zu paintings: depict Amida Buddha coming down from the Heavens to get his disciples' souls
- Used for Nembutsu practice = ceaseless recitation
- Used for Nembutsu practice = ceaseless recitation
What are the religious paintings of the Middle Heian period and what are they used for?

62
New cards
- Amida Buddha = welcoming Buddha
- One hand welcoming, one hand imparting knowledge
- Made of wood painted in actual gold
- Downcast eyes
- Has night & day bodhisetvas on either side
- One hand welcoming, one hand imparting knowledge
- Made of wood painted in actual gold
- Downcast eyes
- Has night & day bodhisetvas on either side
Who is the Buddha depicted in Raigo-Zu and what are his characteristics? (Middle Heian)

63
New cards
Painting depicting the 9 gredations Amida Buddha comes down from and through the Samsara / cloud formations
What is Haya-Raigo? (Middle Heian)

64
New cards
Tales of Genji by Murasaki; unscroll and read part by part
What is the best example of secular paintings from the Fujiwara clan? (Middle Heian)
65
New cards
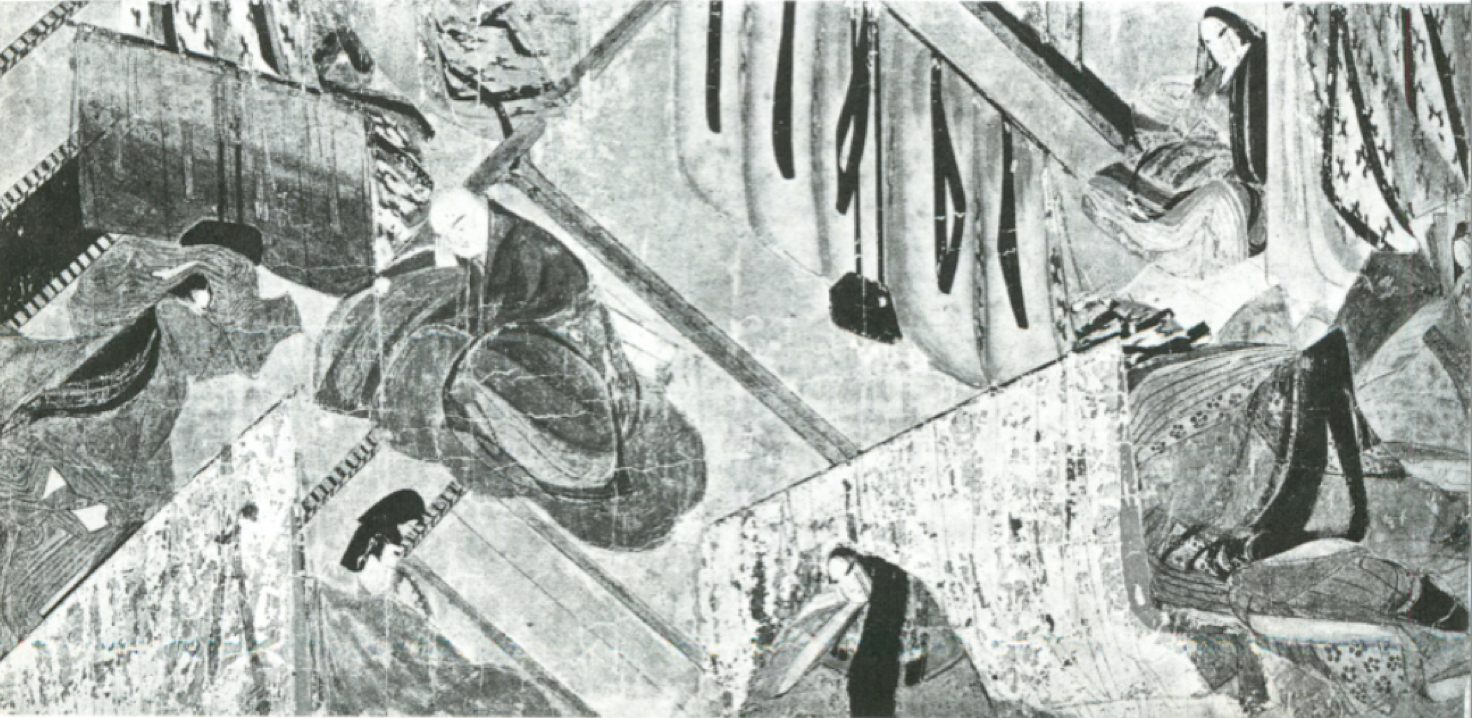
Feminine, intimate and privately displayed
What is the onna-é style under yamato-é? (Middle Heian)

66
New cards
1. Mono-no-aware/emaki-mono: pregnant moment before storm, controlled tension, no drama or spectacle, pathos, emotional shorthand
2. Fuki-Nuki-Yatai: No ceiling, bird's eye view, perspective
3. Hikime-Kagihana: Line-hook nose features, show very subtle emotional nuances
2. Fuki-Nuki-Yatai: No ceiling, bird's eye view, perspective
3. Hikime-Kagihana: Line-hook nose features, show very subtle emotional nuances
What are the 3 main characteristics of onna-é? (Middle Heian)
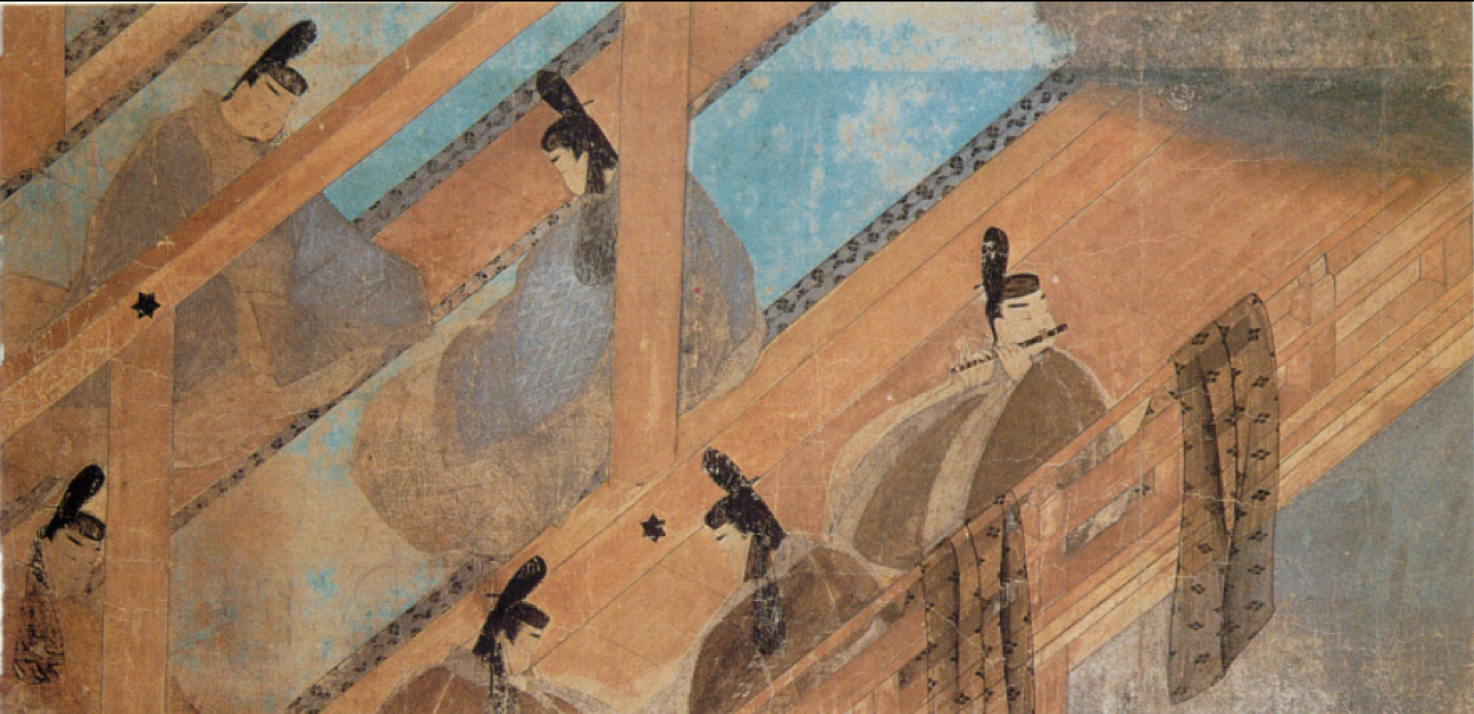

67
New cards
- Masculine style, chaotic/agitative, displayed in public, has moralistic message
- Chaos shown through movement of broken lines, hand gestures, and facial expressions
- Chaos shown through movement of broken lines, hand gestures, and facial expressions
What is otoko-é style under yamato-é and its characteristics and how are they shown? (Late Heian)
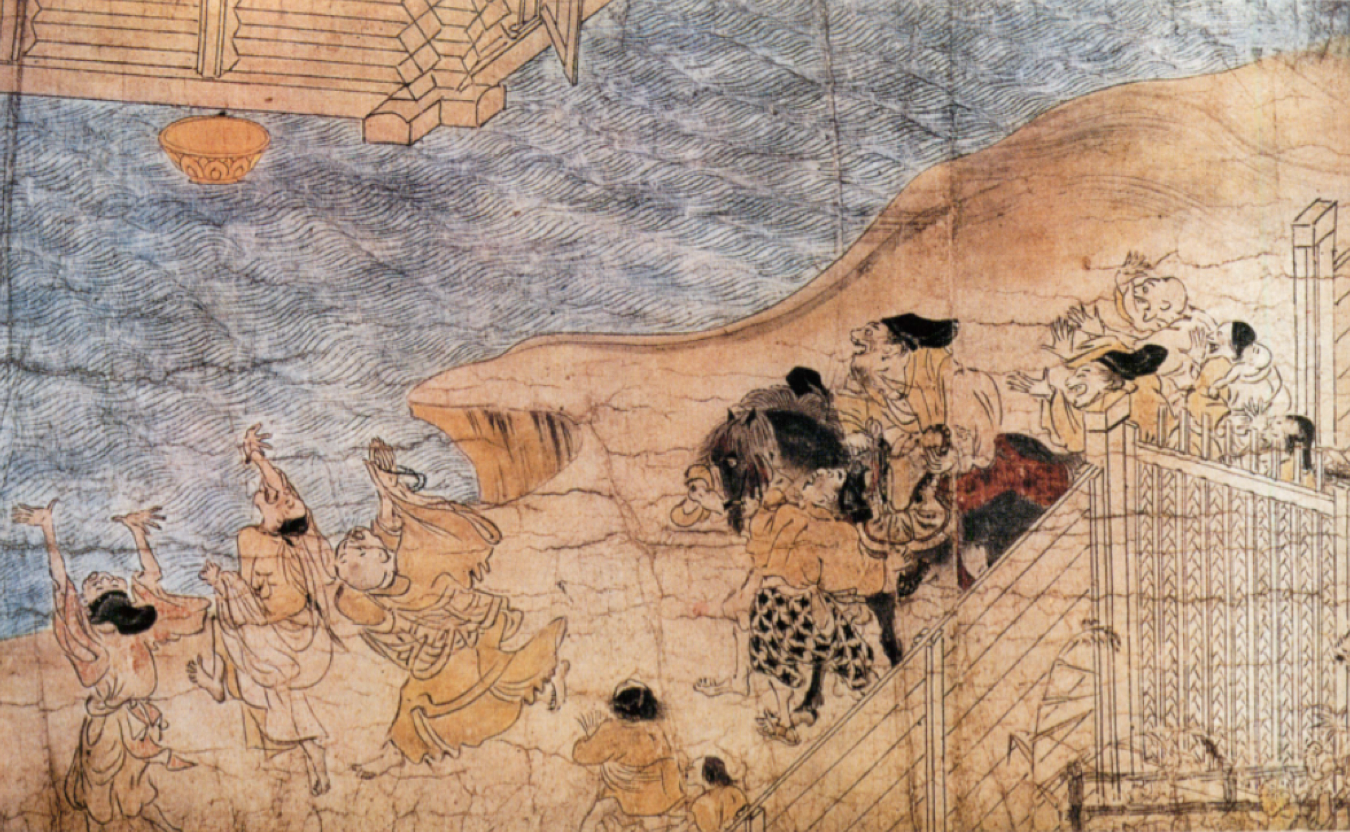

68
New cards
Didactic (educational) Buddhist with moralistic message
What is rokudo-é under otoko-é? (Late Heian)
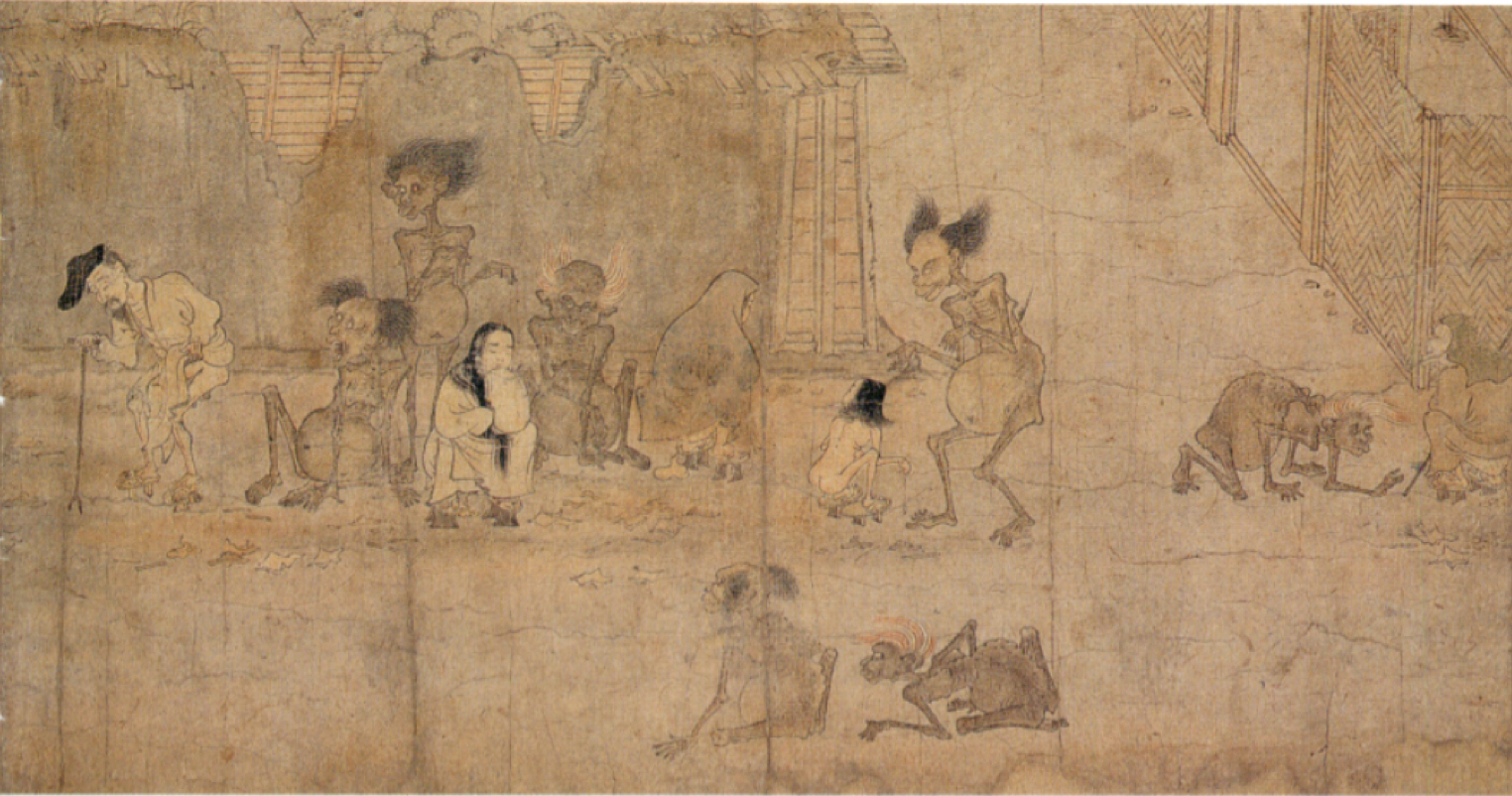

69
New cards
Monochrome art depicting frolicking animals in humorous and cynical way that teaches lesson
What is hakubyo tradition under otoko-é? (Late Heian)
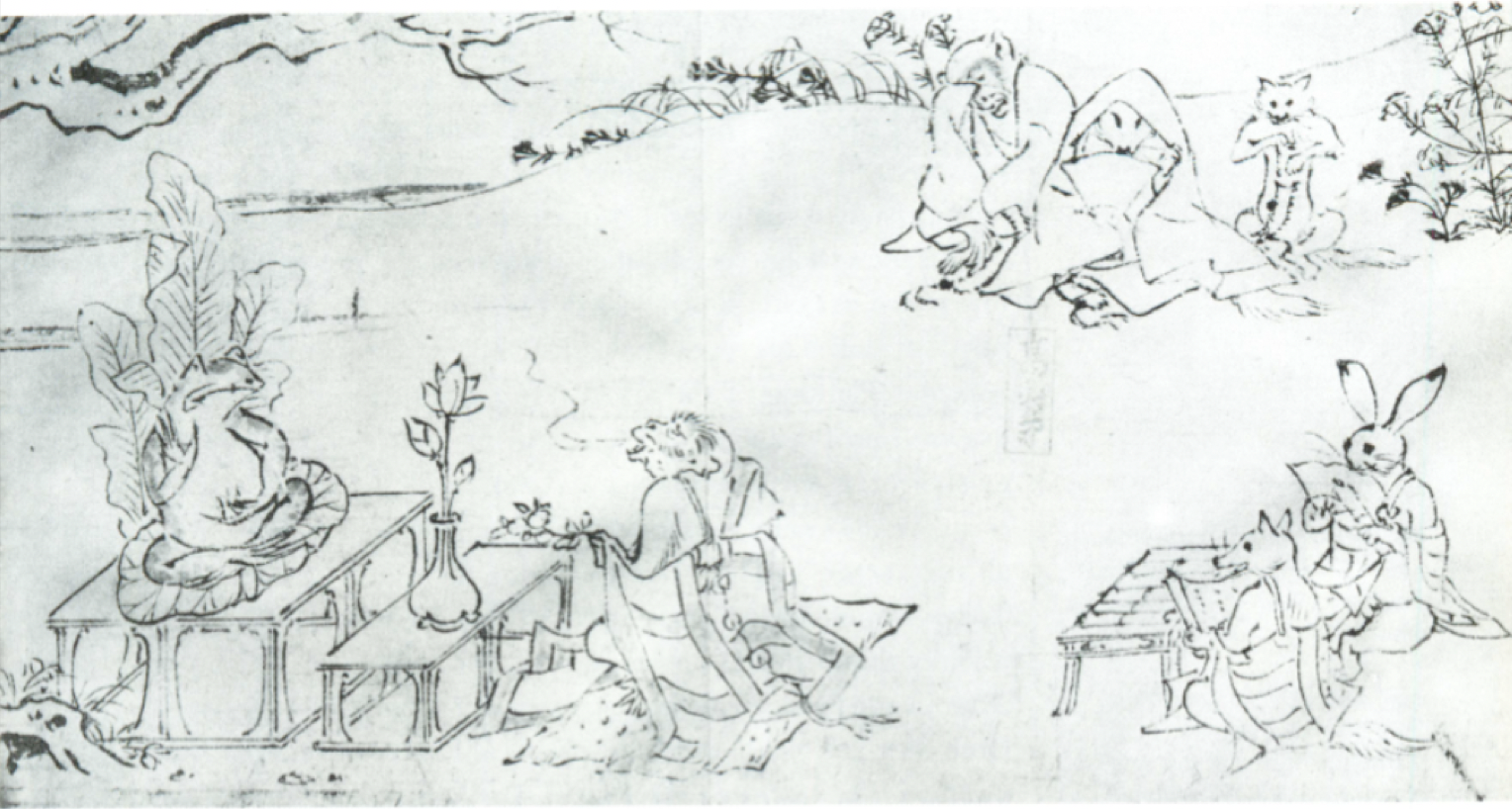

70
New cards
Religious Amida Buddha painting with hidden text
What is Ashide? (Late Heian)

71
New cards
Layers of gold foil, paper dyed in many shades; used in RELIGIOUS paintings
What is Kirigane? (Late Heian)
72
New cards
Mythological and historical scrolls, layers of color gradation, laborious coloring, very narrative
What is Tsukuri-é? (Late Heian)

73
New cards
- Yuritomo Minamoto declares himself 1st Shogun, creates a Bakufu (dictatorship)
- Samurai begin to become powerful
- Zen Buddhism becomes popular
- Samurai begin to become powerful
- Zen Buddhism becomes popular
How is the Kamakura & Muromachi period (1185-1573 CE) defined and what stands out about it?

74
New cards
- Influences from China (Song dynasty) = heightened realism
- Portraits & Realism
- Portraits & Realism
How does the art style begin to change in Kamakura & Muromachi time?

75
New cards
feminine hand painting; calligraphy, flowing and loose
What is Kana-onnade? (Kamakura & Muromachi)

76
New cards
Japanese poetry written in kana-onnade style
What is waka? (Kamakura & Muromachi)
77
New cards
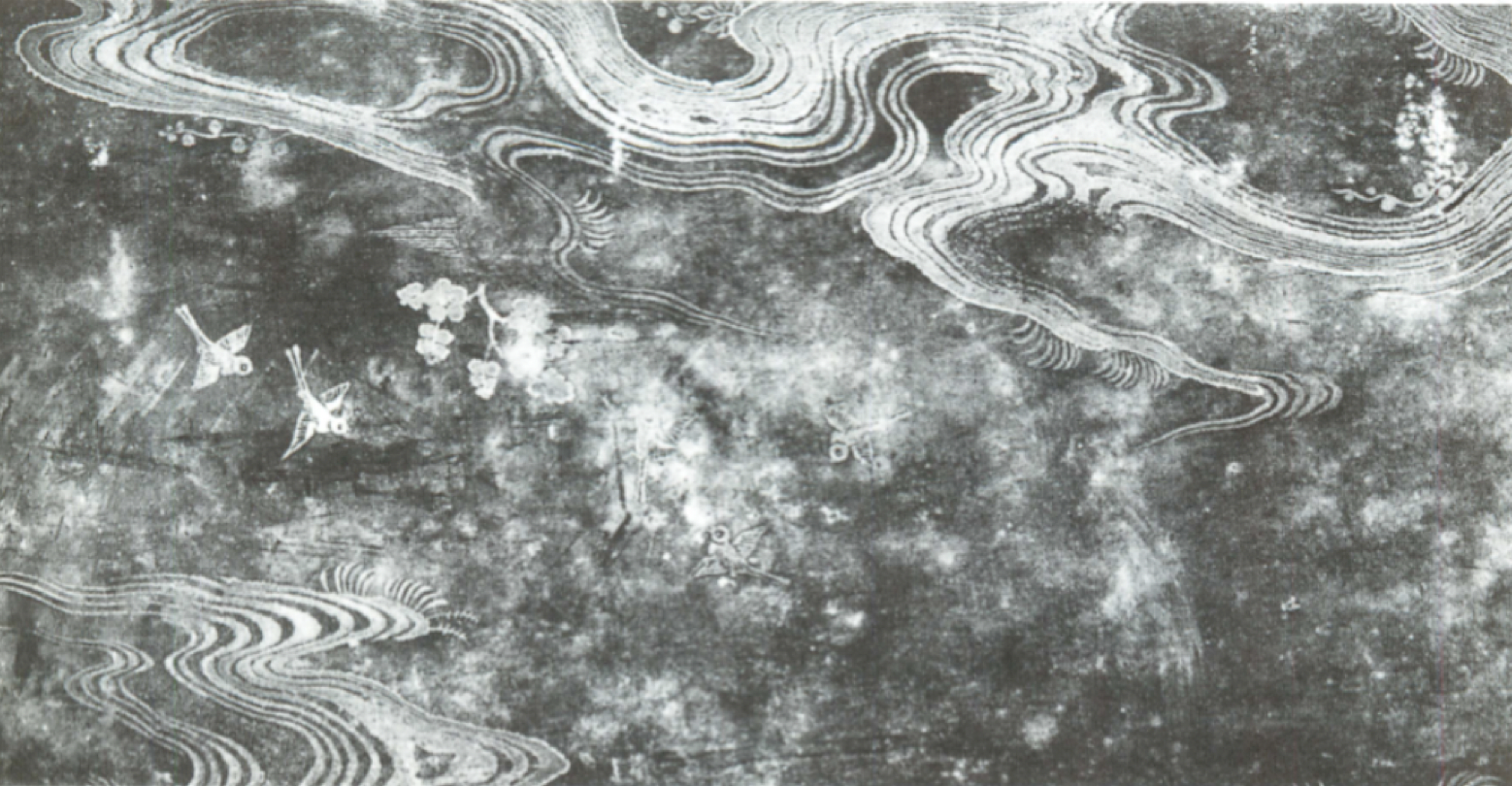
laquer paintings, colored gold, silver dusting
What is Maki-é? (Kamakura & Muromachi)
78
New cards
- Comes from Chan Buddhism from China
- Zen = Dhyana = meditation
- Becomes popular with samurai clan
- Complete meditation, devotion, to be totally within yourself, self-realization
- Zen = Dhyana = meditation
- Becomes popular with samurai clan
- Complete meditation, devotion, to be totally within yourself, self-realization
Define Zen Buddhism:
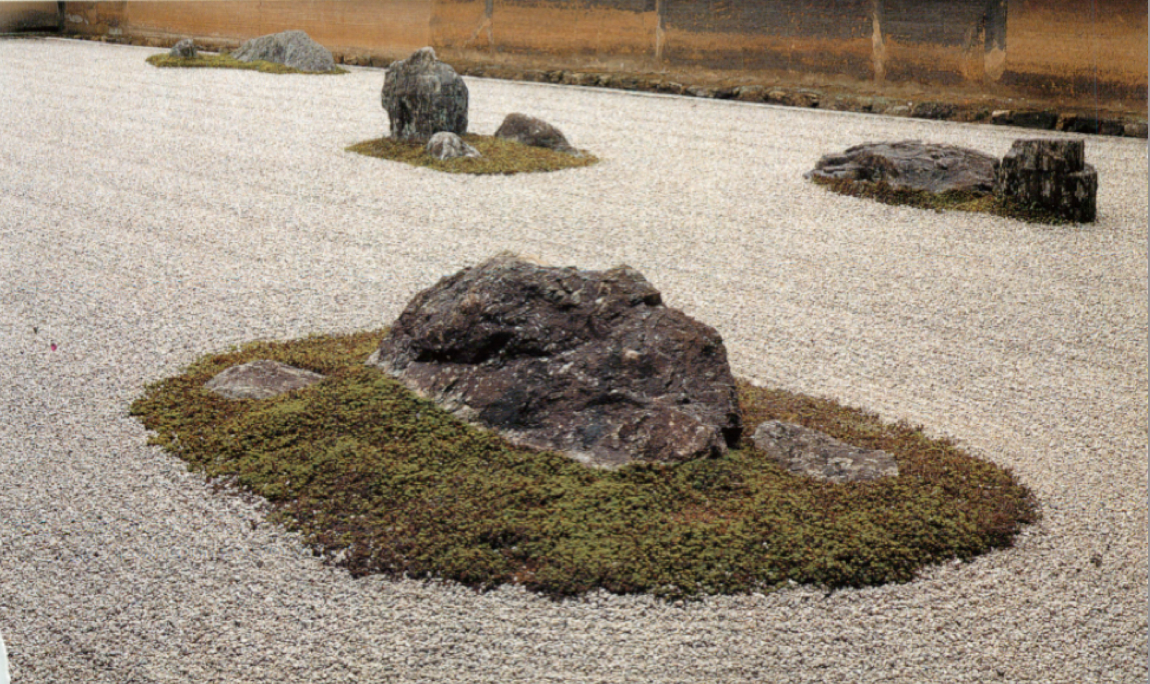
79
New cards
- Zen dry garden
- No water involved
- Used for peaceful meditation
- Pebbles represent water while rocks represent islands and usually present in odd #s
- No water involved
- Used for peaceful meditation
- Pebbles represent water while rocks represent islands and usually present in odd #s
What is a Karesansui?

80
New cards
- Shizen: natural
- Fukinsei: asymmetrical
- Kanso: simplicity, less is more
- Yugen: subtly profound
- Datsuzoku: unworldliness
- Seijaku: quiet
- Koko: bare essentials
- Contrast
- Lines
- Layers of Time
- Meigakure: viewing angles
- Ma: empty space
- Fukinsei: asymmetrical
- Kanso: simplicity, less is more
- Yugen: subtly profound
- Datsuzoku: unworldliness
- Seijaku: quiet
- Koko: bare essentials
- Contrast
- Lines
- Layers of Time
- Meigakure: viewing angles
- Ma: empty space
What are the 12 aesthetics of a Zen Dry Garden?
81
New cards
Natural, not pretentious, not manmade
What is Shizen?
82
New cards
Asymmetrical, odd numbers, achieves naturalness
What is Fukinsei?
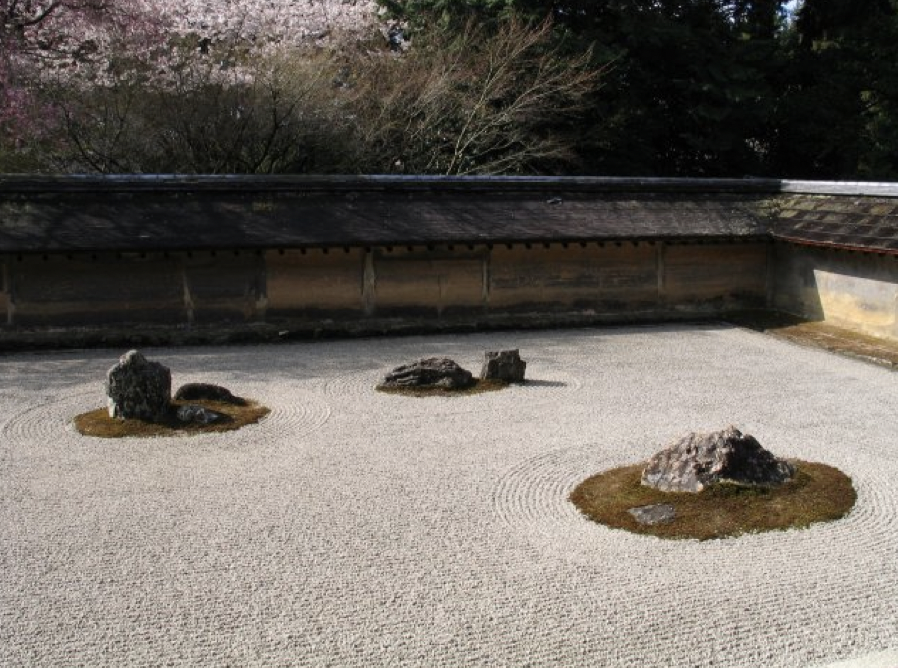

83
New cards
- Simplicity, "less is more"
What is Kanso?
84
New cards
- The ability to draw an imaginary triangle between any three elements in the garden
What is "The Triangle" in a Dry Garden?
85
New cards
- Subtly profound, suggestion, graceful
- Yu = grace, Gen = profound
- Felt with the heart not seen with the eyes
- Yu = grace, Gen = profound
- Felt with the heart not seen with the eyes
What is Yugen?
86
New cards
- Unworldliness, no worldly aspects
What is Datsuzoku?
87
New cards
- Quiet, calm, silent
What is Seijaku?
88
New cards
- Bare essentials, maturity, ex. water is important in the garden but raked pebbles can create the impression of this
What is Koko?
89
New cards
- Contrast creates tension, tension gives way to energy and harmony
Why is contrast important in the Dry Garden?
90
New cards
- Perpendicular lines = tranquility
- Diagonal lines = tension
- Curves = softening
- Diagonal lines = tension
- Curves = softening
Why are lines important in the Dry Garden?
91
New cards
- Leaving garden to natural passing of time, climate, weathering
What are layers of time in the Dry Garden?
92
New cards
- Remaining hidden from ordinary view
- There is a best viewing angle, and if you find this you control your viewers
approach
- "Rounding the corner" to fill in what may come next
- There is a best viewing angle, and if you find this you control your viewers
approach
- "Rounding the corner" to fill in what may come next
What is Meigakure?
93
New cards
- Concept of artistic interpretation of empty space
- "Music happens between the notes"
- Negative space between, without this negative space there is no art
- "Music happens between the notes"
- Negative space between, without this negative space there is no art
What is the concept of Ma?
94
New cards
- Subdued taste, simplicity
- Finding beauty in asymmetry and uneven/unbalanced things
- Finding beauty in asymmetry and uneven/unbalanced things
What is the concept of Wabi?
95
New cards
- Rustic simplicity, mellow
- Beauty of aged things ex. patina, speaks of impermanence of life through passing of time
- Beauty of aged things ex. patina, speaks of impermanence of life through passing of time
What is the concept of Sabi?
96
New cards
- controlled or shaped by man
What is the concept of Shin?
97
New cards
- things in natural state
What is the concept of So?
98
New cards
- blending of shin (manmade) and so (natural) to compliment each other
What is the concept of Gyo?
99
New cards
- Children are free from thought of judgement or consequence, so they act on instinct without thinking
What does it mean to be "childlike" in Zen Buddhism?
100
New cards
- You are so conscious of your actions that you simply do them, you have become one so you are at your core unconscious of what you are doing
What does it mean to be so conscious that you are unconscious in Zen Buddhism?