MKTG 201 - Exam 1
1/275
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BYU - Scott Rackham
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
276 Terms
Market
The aggregate of individuals and organizations that have (1) needs and wants and (2) the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase products and services that satisfy their needs and wants
Marketing
The activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
Strategic Triangle
Three main stakeholders for any business - Customer, Company, Competition
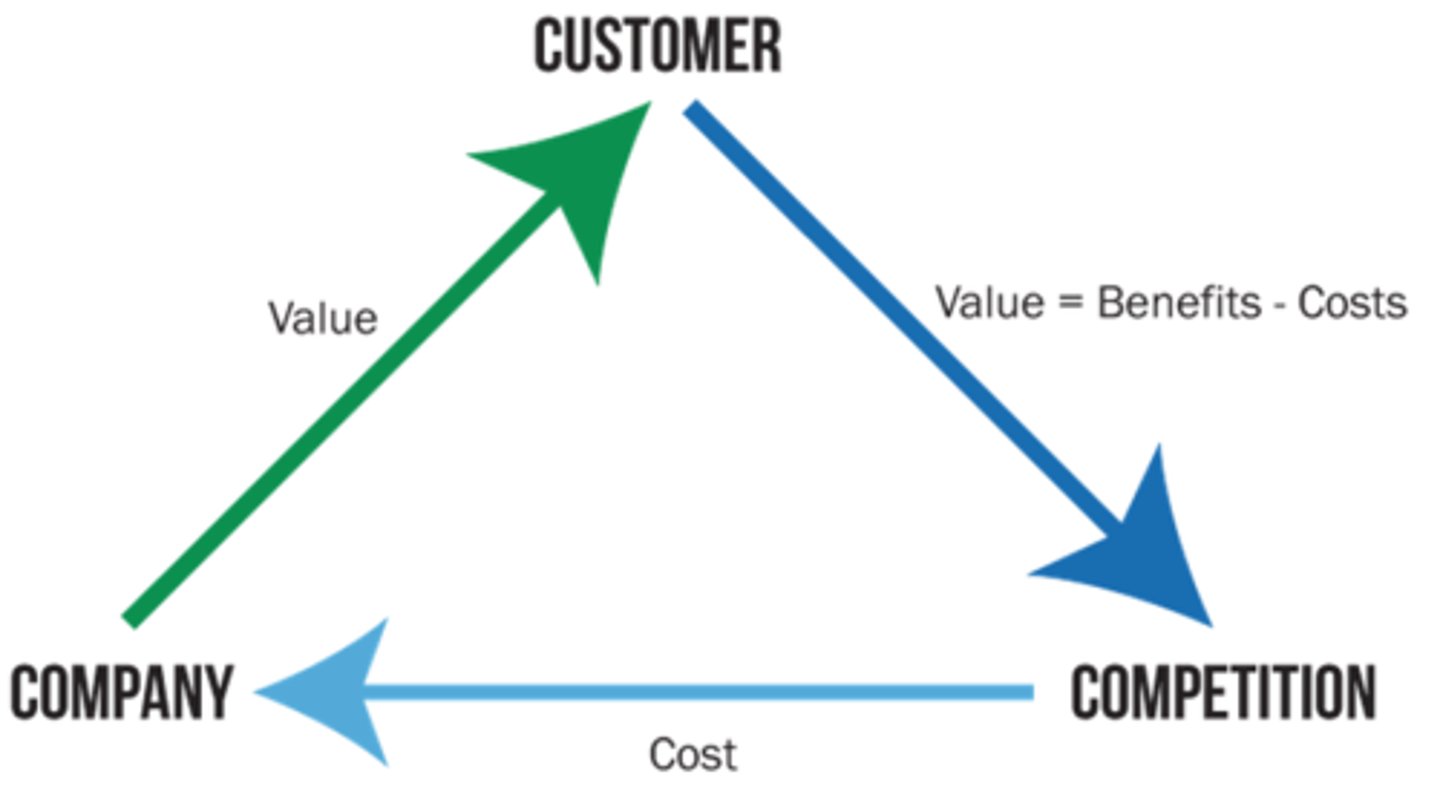
Components of marketing strategy
1. Corporate Strategy
2. Strategic Business Unit Strategy
3. Marketing Strategy
Marketing Mix - 4 Ps
1. Product
2. Price
3. Place (distribution)
4. Promotion
brand champions
customers who love the products and then champion the products to other people
4 marketing philosophies
1. Market penetration
2. Product development
3. Market development
4. Diversification
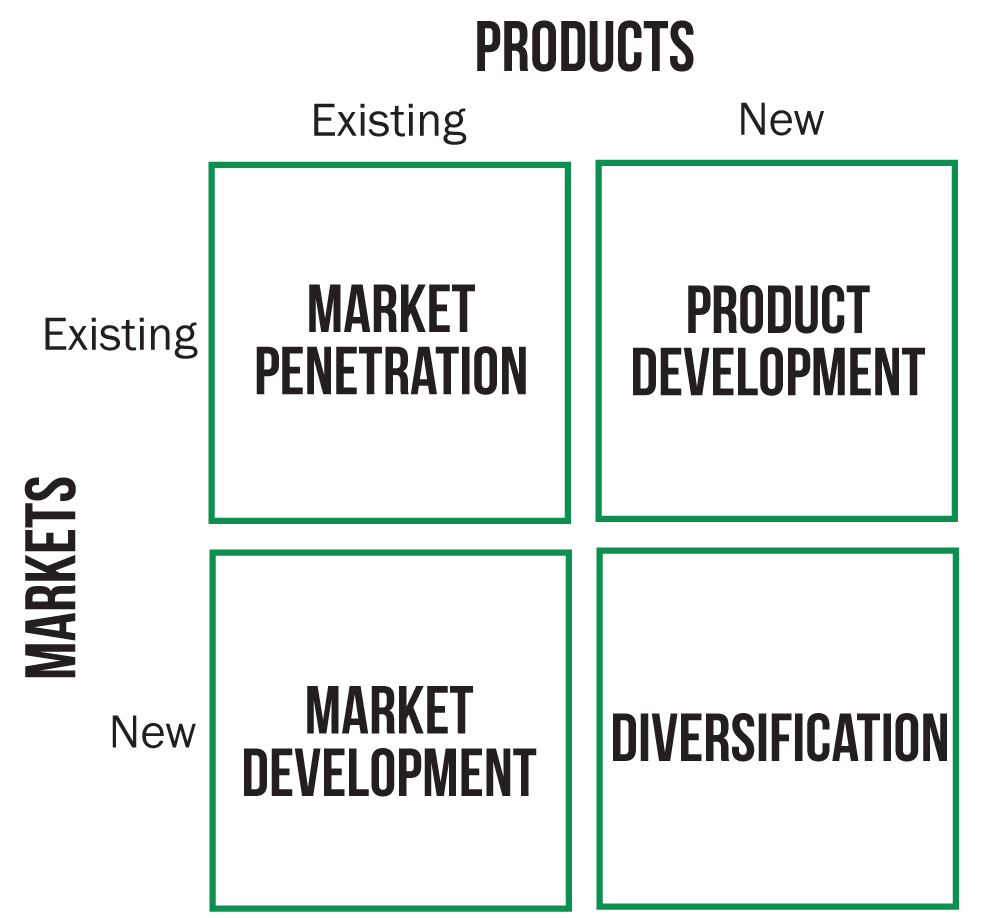
3 components of marketing concept
1. The exchange that takes place between sellers and buyers
2. Creates, communicates, and delivers value to facilitate exchanges
3. By delivering value, marketing satisfies customer needs and wants at a profit
Corporate Strategy
Answers the question "What business should we be in"? A strategy that determines the types of businesses to include in a firm’s portfolio.
Strategic Business Unit Strategy
Answers the question "How do we compete effectively in a given business"?
Marketing Strategy
A cohesive marketing mix of product, place, price, and promotion, designed for a specific target market. Answers the question "How do we orchestrate the marketing mix to deliver value to a particular market segment"?
Stars
High market growth rate, high relative market share
Question marks
High market growth rate, low relative market share
Cash cows
Low market growth rate, high relative market share
Dogs
Low market growth rate, low relative market share
Product
Products or service - a bundle of attributes that satisfies a customer’s needs or wants
Price
The amount paid for a product
Promotion
Marketing communication activities - such as advertising, public relations, sales promotions, trade promotions, personal selling, and digital marketing
Place
Where products are purchased
Market penetration
Selling more of the existing products in existing markets
Product development
The process of creating a customized product for the target market
Market development
Introducing existing products to new markets
Diversifications
Introducing new products to new markets
Profitability Drivers
1. Customer Acquisition
2. Customer Retention
3. Sales per customer
4. Margin
Customer Acquisition
Acquire and keep customers
Customer Retention
The practice of keeping customers by building long-term relationships
Sales per Customer
The amount of sales from a particular customer.
Margin
The difference between price and costs
Production Orientation
Supply generates its own demand
Sales Orientation
Marketing's only role is to sell products once they are made
Market Orientation
Every product or service should focus on satisfying customer needs and wants at a profit
Societal Orientation
Every product or service should provide value to the customer as well as to society as a whole
Social Forces
1. Culture
2. Demographics
External Forces
1. Social
2. Economic
3. Technological
4. Competitive
5. Regulatory
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
a tool for assessing how a company’s internal abilities and capacities are affected by external forces
Culture
Shared value, attitudes, and practices that shape human behaviors
Demographics
Statistical data that describe a population
Economic
Changes in the economy affect consumer spending and thus have a broad impact on marketing strategies
Technological
The application of science and research to accomplish a function more efficiently or to solve a problem more effectively
Competitors
Companies and organizations vying for the same customers
Regulatory
Marketers compete within the constraints of government regulation
Competitive rivalry
Rivalry among existing companies in a particular industry varies in intensity based on the type and number of competitors and on the basis of competition
Power of suppliers
Powerful suppliers can drive down industry profits by charging higher prices and/or reducing product and service quality
Power of suppliers
Powerful suppliers can drive down industry profits by charging higher prices and reducing product and service quality
Threat of entrants
New entrants can shake up an industry and cause increased competition as they seek to take market share from existing companies in the industry
Threat of substitutes
Substitute products have the potential to replace existing products because they perform a similar function
3 types of geographic marketing
Domestic, International, Global
4 risks of global marketing expansion
1. Competitive
2. Economic
3. Legal
4. Political
4 market entry strategies
1. Exporting
2. Licensing
3. Joint Venture
4. Foreign Direct Investment
Standardization
The same marketing mix is used in the foreign market as is used in the domestic market
Customization
Tailoring the marketing strategy to fit the needs, tastes, and preferences of the local market
Domestic Marketing
Focuses on customers in the firm's home country
International Marketing
Exporting products to one or more countries outside the domestic market while remaining invested in the domestic country
Global Marketing
Selling or licensing products for sale in countries throughout the world
Competitive Risk
risk that arises from competitors responses to the new product's entry into the local market
Economic Risk
The potential mismanagement of a country's economy as exhibited by inflation and government debt
Legal Risk
inadequate protection of contracts and intellectual property
Political Risk
Associated with regulations, demonstrations, strikes, civil strife, abrupt government changes, violence, and terrorism
Exporting
Shipping goods produced in the home country to a distributor or retailer in the foreign market
Licensing
A firm in one country agrees to allow a firm in another country to use its manufacturing, processing, trademark, know-how, patent, or some other skill or value
Joint Ventures
2 or more companies agree to create a new business, jointly owned by the participating companies
Foreign Direct Investment
Companies will decide to make direct investments in building up wholly owned operations in other countries
Myths of unethical marketing
1. Marketers push products consumers don't want to buy.
2. Consumers are no match for the power of marketing.
3. Marketing is deceptive and not truthful or honest.
4. Marketers believe in planned obsolescence.
3 ethical norms
1. Do no harm
2. Foster trust in the marketing system
3. Embrace ethical values
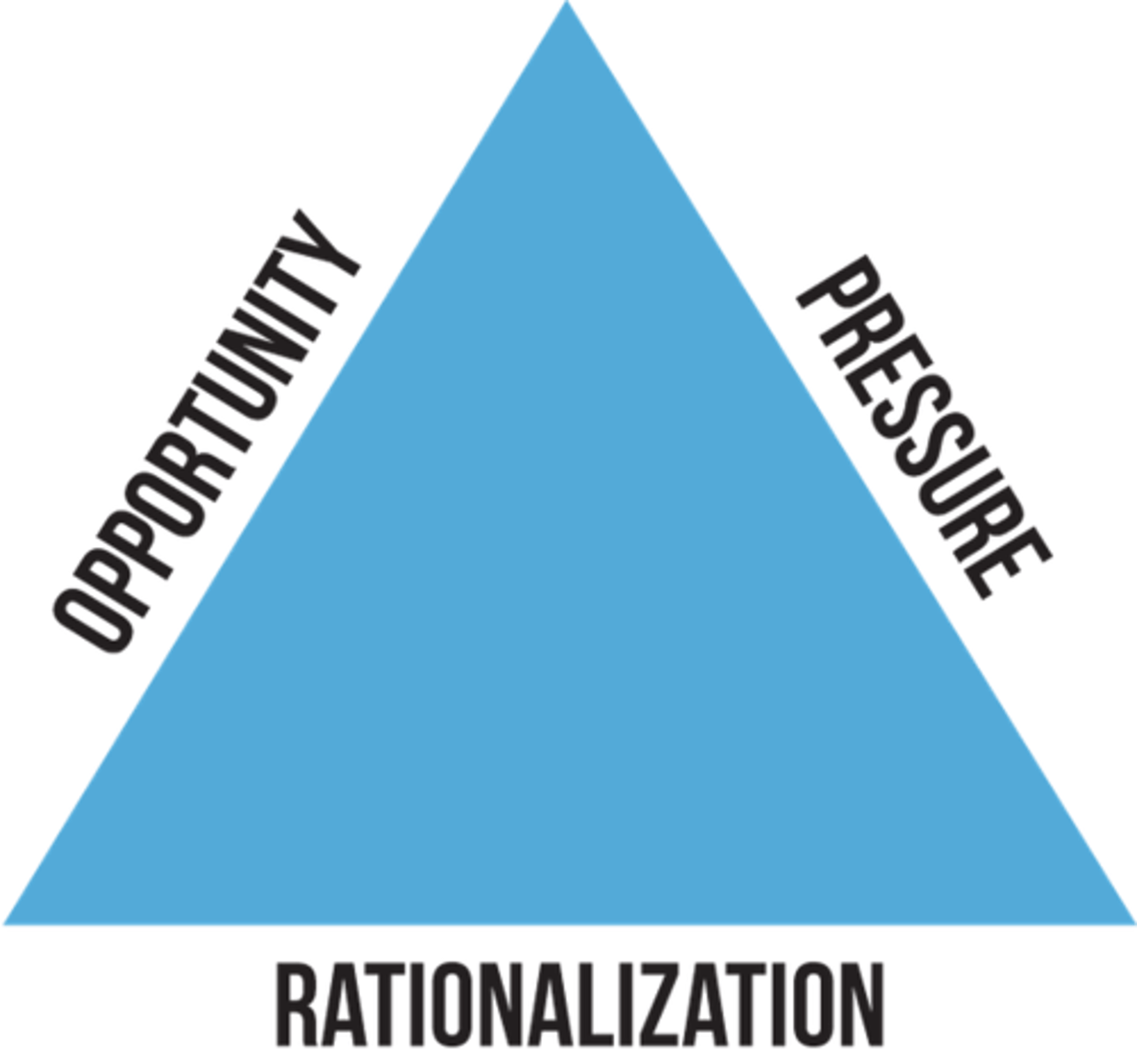
Fraud triangle
opportunity, pressure, rationalization (designed to show the reasoning behind why a person commits workplace fraud)
Ethical framework
1. Personal ethical understanding
2. Application of ethic to business
3. Ethical courage
4. Ethical leadership understanding
Social Responsibility
The businesses and organizations are part of a larger society and that they are accountable to that society for their actions
Green marketing
Marketing efforts to produce, promote, and reclaim environmentally sensitive products
5 components of the marketing research process
1. Define the marketing problem
2. Design the research project
3. Collect data
4. Analyze the data
5. Take action
3 key elements to consider when designing a marketing research study
1. The type of information to be collected
2. Possible data sources
3. A procedure for collecting data
3 key differences between big data and traditional marketing research data
1. Volume
2. Velocity
3. Variety
5 problems associated with minimizing measurement error
1. Respondent characteristics (knowledge or mood)
2. Situational factors (time of day or interview environment)
3. Data collection factors (influence of the researcher)
4. Questionnaire factors (misleading questions)
5. Data analysis factors (using the wrong data analysis method)
Hypothesis testing
Uses statistics to determine the likelihood that a given belief is true
4 factors that help marketing researchers generate insights for an organization
1. Experience of the research team
2. Quality of the data sample
3. Expertness of the data analysis
4. Nature of the survey questions
Exploratory Research
Marketing research to gather preliminary information that will help define problems and suggest hypotheses
Conclusive Research
Research designed to verify insights through objective procedures and to help marketers in making decisions
Syndicated Data
Data collected for an industry and paid for by the industry
Secondary Data
Information collected for other purposes and usually readily available
Primary Data
Information collected specifically for the purpose of the investigation at hand
Ad tracking
Determining whether an ad is being seen and remembered
Buyer decision process
Marketing manager want to manage as much of the buying decision process as possible
Concept Testing
Marketing manager must sort through multiple concepts when trying to identify promising brand extensions, line extensions, and messaging
Customer satisfaction research
Customers provide valuable feedback for improving the product, introducing complementary product, or keeping the product on strategy
Marketing effectiveness and analytics
Aim to measure the dollar-by-dollar effectiveness of marketing expenditures
Sales forecasting
Estimates future sales projections
Segmentation research
Dividing a market into segments
Test marketing
Test markets are selected to determine potential success of a new product
Nominal scale
A label like male or female
Ordinal scale
Numbers ordered into an increasing size like finishers in a foot race
Interval scale
Equal distance between numbers
Ratio scale
Equal ratios
Marketing analytics
Measures the effectiveness of marketing activities, transforming data into information that will drive marketing efforts profitably forward
Consumer insights
An accurate, deep, and intuitive understanding of a customer
4 steps in Big Data analytics process
1. Data wrangling
2. Data exploration
3. Data modeling
4. Data deployment and socialization
Data Wrangling
The process of cleaning, unifying, and preparing unorganized and scattered data sets for easy access and analysis
Data Exploration
Discovery through numerical summaries and visualizations
Data modeling
The process of transforming the data to extract insights
Deployment and Socialization
Putting the data into effect
Focus groups
Asks individuals from the target market for feedback
Depth interviews
Interview with a respondent to get detailed information about that person's perspective in relation to a product or service.