RMIN 4000 - Exam 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Exposures
Things of value (assets) that could be lost
Perils
Things that could happen to these assets
The cause of loss (fire, tornado, burglary)
Risk Management
What do you do to protect these assets and reduce losses
Risk
A calculated possibility of a negative outcome
Calculated Possiblity
A probabilistic outcome that is known or estimated
Ranges from 0 to 1 (0% to 100%)
Negative Outcome
A loss & must be quantifiable ($)
Frequency
How often does a loss occur
Probability of a loss
Frequency Equation
Number of Losses / Number of Exposures
Severity
How much does it cost when a loss does occur
Severity Equation
Incurred Losses($) / Number of Losses
Frequency & Severity Example:
Lannister Insurance Company insures 100,000 homes. In 2024, they incurred a total of $30,000,000 in wind damage
losses to the owners of 5,000 of those homes.
- What was Lannister’s wind loss frequency in 2024?
- What was Lannister’s average wind loss severity in 2024?
Frequency = 0.05
Severity = 6,000
Hazard
Condition that creates or increases the frequency and/or severity of a loss
Does not cause a loss
The Four Types of Hazards
Physical
Moral
Morale (Attitudinal)
Legal
Physical Hazard
A physical condition that increases the frequency and/or severity of a loss
Moral Hazard
The presence of insurance changes the behavior of the insured
Ex: Using a hammer to create “hail“ damage to roof, exaggerating the value of insured property
Morale (Attitudinal) Hazard
Carelessness or indifference to a loss, which increases the frequency and/or severity of a loss
Ex: Leaving car keys in an unlocked car, neglecting a tree limb growing over your roof
Legal Hazard
Characteristics of legal system or regulatory environment that increases the frequency and/or severity of a loss
Ex: Juries in some areas are more sympathetic that other areas, GA requires Diminution in Value to be paid on real property losses (increased severity in GA)
Risk Classifications
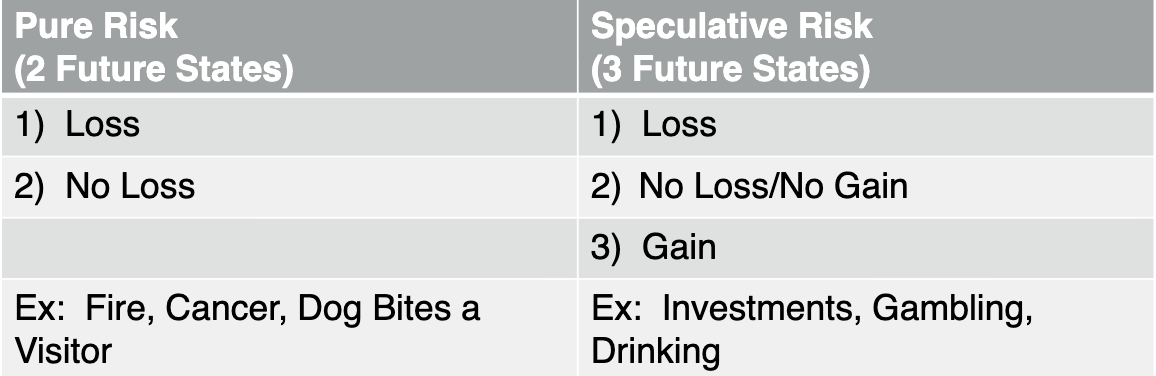
Pure v. Speculative Risk
Diversifiable Risk
Nondiversifiable Risk
Systemic Risk
Pure v. Speculative Risk
You can buy insurance for pure risks but not speculative risks
Diversifiable Risk
Affects only individuals or small groups, not entire economy
Can be reduced/eliminated through diversification
Risks aren’t correlated (fire, theft)
Nondiversifiable Risk
Affects the entire economy or large number of groups within the economy
Cannot be reduced through diversification
Government assistance may be needed to insure
Risks are correlated (inflation, unemployment)
Systemic Risk
Risk of collapse of an entire system or entire market due to the failure of a single entity or group of entities that can result in the breakdown of the entire financial system
Instability in the financial system due to the interdependency between players in the market
Millennium Bridge in London Ex.
Started swaying from a large gust of wind that made everyone react to it and start walking the same way
"Individually you do what's right for you, but when everyone does it collectively that's what creates systemic risk"
Major Types of Pure Risks
Personal Risk
Property Risk
Liability Risk
Loss of Business Income
Cyber-Security
All are relevant to individuals & families and businesses
Personal Risk
Directly affects and individual or family; involves the possibility of loss of incomes, extra expenses, depletion of financial assets
What perils might be involved
Death, unemployment, disability, inadequate retirement income
Rule of 72: 72 / % = years it will take to double
Property Risk
The possibility of losses associated with the destruction or theft of property
Direct Loss: Cost or repair to replace property damaged by a peril
Indirect Loss
Financial loss resulting as a consequence of a direct loss
Ex: After fire damages your home, you have to pay to live elsewhere while it's repaired
Liability Risk
Legal Liability (financial consequences) resulting from injuries or damages you caused to someone else
No upper limit
Liens can be placed on income, assets seized
Defense Costs - lawyers are expensive
Loss of Business Income
If a business has to shutdown for a period of time due to a physical damage loss, it is unable to generate an income
Indirect loss
Techniques for Managing Risks
Risk Control & Risk Financing
Risk Control
Techniques to reduce the frequency or severity of losses
Loss Prevention
Reduces frequency
Airport security, safety training programs
Loss Reduction
Reduces severity (fire sprinklers)
Can occur pre-loss or post-loss
Duplication, Separation, & Diversification
Avoidance
A certain loss exposure is never acquired (proactive)
An existing loss exposure is abandoned (reactive)
Risk Financing
Techniques for funding losses
Retention (if occurs, pay for out of pocket)
Retaining part or all of losses that can occur from a given risk
Active: Deliberately retaining risk (choosing a high deductible)
Passive: Unknowingly retaining risk (not purchasing disability risk)
Noninsurance Transfer
By contract
Incorporation
Insurance
Textbook Definition of Risk Management
Process that identifies loss exposures faced by an organization and selects the most appropriate techniques for treating such exposures
Loss Exposure
Any situation or circumstance in which a loss is possible, regardless of whether a loss actually occurs
Steps in the Risk Management Process
Identify loss exposures
Measure and analyze the loss exposures
Consider and select the appropriate risk management techniques
Implement and monitor the chosen techniques
Step 1: Identify Loss Exposures
What assets need to be protected?
What perils are those assets exposed to?
Most important step
If you haven't identified the loss exposure, then you're stuck paying for it
(passive retention)
Sources for Identifying Loss Exposures: Loss history, financial statements, other firms/competitors, risk managers consultants, surveys, inspections, contract analysis
Step 2: Measure and Analyze the Loss Exposures
Measure
Estimate the frequency and severity of loss exposures
Frequency (probability) - how often does it occur
Severity (outcome) - how much does it cost when a loss does occur
Analyze
Rank loss exposures according to relative importance
Severity is more important
Maximum Possible Loss - the worst loss that could happen to the firm during its lifetime
Probable Maximum Loss (PML) - the worst loss that is likely to happen
Step 3: Consider and Select the Appropriate Risk Management Techniques
Risk Control
Avoidance, Loss Prevention, Loss Reduction, Duplication, Separation, Diversification
Risk Financing
Avoidance
A certain loss exposure is never acquired (proactive), or an existing loss exposure is abandoned (reactive)
Advantage - Frequency is reduced to 0
Disadvantages - May not be possible, usually has an opportunity cost, avoiding one loss exposure may create another
Loss Prevention
Measures that reduce the frequency of a particular loss
Does not completely eliminate risk
Loss Reduction
Measures that reduce the severity of a loss
No effect on the frequency of a loss
Duplication
Having back-ups or copies of important documents or property available in case a loss occurs
Separation
Physically separating something, dividing the assets exposed to loss to minimize the harm from a single event
Ex: Firewalls in buildings, companies with multiple warehouses, president and VP can't fly on the same plane
Diversification
Spreading the risk across multiple parties, securities, or transactions
Ex: Nike branching out from just shoes
Retention
Deductible means retention
A firm or individual retains part or all of losses that can occur from a given risk
Retention level - the dollar amount of losses that the individual/firm will retain
Active - Deliberately retaining risk
Passive - Unknowingly retaining risk
When should risk be retained?
It is difficult to insure
Worst possible losses are not serious (low severity)
Losses are predictable (high frequency)
*Risk Manager needs to evaluate all potential costs before choosing retention as a risk management technique
Unfunded Retention
Don’t have money aside
Funded Reserve
Actively putting money to the side
Deductible
The amount that you are responsible for in the event of a loss when you have insurance
Captive Insurer
A business creates its own insurance company
A single-parent captive is owned by only one parent
Association/Group captive is an insurer owned by several parents
Advantages of Captive Insurer
When insurance is expensive or difficult to obtain
Lower Costs
No agent or broker commissions
Interest earned on invested premium
Easier access to reinsurance market
Possibility of lower tax rate
Possibility of favorable regulatory environment
Self-Insurance
A special form of planned retention by which part or all of a given loss exposure is retained by the firm
Risk Retention Group
Form of a group captive that can write any type of liability coverage except employers' liability, workers compensation, and personal lines
Exempt from many state insurance laws
Many physicians form a risk retention group
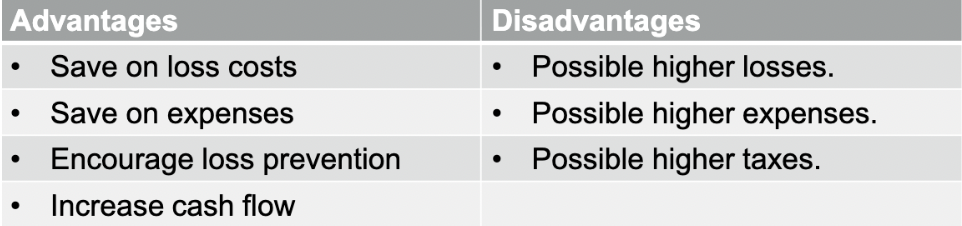
Noninsurance Transfer
Methods other than insurance by which a pure risk and its potential financial consequences are transferred to another party
Ex. Contracts, leases, hold-harmless agreements (if a 3rd party files a suit against the tenant and the landlord, the tenant assumes the risk)
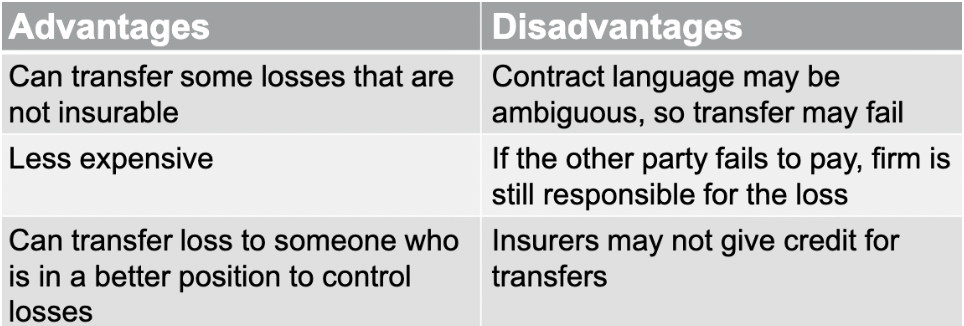
Insurance
Appropriate for low-frequency, high-severity loss exposures
These areas must be emphasized
Selection of insurance coverages
Selection of an insurer
Negotiation of terms
Dissemination of information concerning insurance coverages
Periodic review of the insurance program

Excess Insurance
A plan in which the insurer pays only if the actual loss exceeds the amount a firm has decided to retain
Have a general liability (primary) limit & can have an umbrella liability (excess)
Manuscript Policy
A policy specifically tailored for the firm
Technique Graph for What Should be Used
Separation, duplication, and diversification may appear in various quadrants depending upon how they are used
Underwriting Cycles
Hard Market - Insurer profitability is declining, underwriting standards are tightened, premiums increase, and insurance is hard to obtain
Soft Market - Profitability is improving, standards are loosened, premiums decline, and insurance become easier to obtain
Step 4: Implement and Monitor the Chosen Techniques
Often requires cooperation among multiple departments
Periodically review to ensure that technique is achieving expected results
If needed, adjust to accommodate changes in loss exposures or the availability of cost-effective risk management techniques
Benefits of Risk Management
Enables a firm to attain its pre-loss and post-loss objectives more easily
Society benefits because both direct and indirect losses are reduced
Can reduce a firm's cost of risk
Textbook Definition of Insurance
The pooling of fortuitous(accidental) losses by transfer of such risks to insurers, who agree to indemnify(compensate) insureds for such losses, to provide other pecuniary(monetary) benefits on their occurrence, or to render services connected with the risk
Law of Large Numbers
The greater the number of exposures, the more closely will actual results approach the probable results expected from an infinite number of exposures
Ex. Consider a coin flip (50/50) - the more you flip it, the closer the percentage gets to 50%
Pooling of Losses
The spreading of losses incurred by a few over the entire group
Purpose is to reduce variation (as measured by standard deviation) which reduces uncertainty (risk)
Think of standard deviation as the average distance from the mean
Payment of Fortuitous Losses
Fortuitous - unforeseen and unexpected by the insured and occurs a result of chance
Hurricane Ex. If you attempt to buy homeowners insurance when a hurricane is approaching, a wind loss is not fortuitous. Insurance company will deny you
An intentional act can result in a fortuitous loss
Risk Transfer
A pure risk is transferred from the insured to the insurer, who typically is in a stronger financial position
Indemnification
The insured is restored to its approximate financial position prior to the occurrence of the loss
Characteristics of an IDEALLY Insurable Risk
Large number of exposure units
Loss must be accidental and unintentional
Loss must be determinable and measurable
Loss should not be catastrophic
Chance of loss must be calculable
Premium must be economically feasible
Large Number of Exposure Units
Enables the insurer to predict average loss based on the Law of Large Numbers
Large numbers of similar exposure units needed
Can an insurance company insure things that they don't insure a large number of?
Yes, but there will probably be a high premium
Loss Must be Accidental and Unintentional
Loss should be outside of insured's control
Why?
Law of Large Numbers is based on randomness
If the insured can deliberately cause a loss that insurer covers, what is increased? Moral Hazard
Loss Must be Determinable and Measurable
Determinable
Can you determine if a loss occurred?
When might this be easy? Hard?
Measurable
Can you determine the amount of the loss?
When might this be easy? Hard?
Loss Should Not be Catastrophic (to the Insurer)
Allows pooling technique to work
Examples of catastrophes - terrorism, flood, earthquake
Why is a catastrophic loss problematic?
Solutions for insurers
Reinsurance
Diversification
Chance of Loss Must be Calculable
Must be able to calculate average frequency and average severity
You multiply them together to calculate expected loss
Premium Must be Economically Feasible
Insured must be able to afford it
Life Insurance Ex. The premium would be more economically feasible for a younger person than a 90 year old
Adverse Selection
Consumers with the greatest possibility of loss, are those that are most likely to purchase insurance
If not controlled by underwriting, results in higher than expected loss levels
Typically results from asymmetric information
Asymmetric Information
Occurs when one party has information that is relevant to a transaction that the other party does not have
Ex. Selling a car when you know there are some issues with it, but the buyer does not
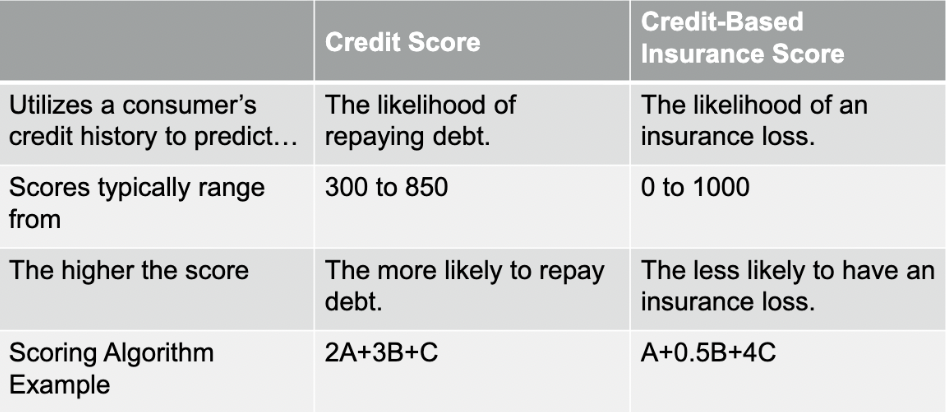
Credit-Based Insurance Score
Utilizes a consumer's credit history to predict the likelihood of future insurance losses
Introduced in the early 1990s
Not the same as credit score
Credit Score v. Credit-Based Insurance Score
Adverse Selection Pricing Example
AIC is experiencing Adverse Selection
AIC charged an average rate for all risks
High risk individuals had an incentive to buy from AIC because the premium was too low relative to their risk
Because they were high risk, AIC insureds tended to have more accidents and higher claims
AIC's underwriting results deteriorated (low premium and high losses)
Types of Private Insurance
Life & Health
Property & Liability
Life Insurance
Pays death benefits to beneficiaries when the insured dies
Health Insurance
Covers medical expenses because of sickness or injury
Property Insurance
Indemnifies property owners against the loss or damage of real or personal property
Liability Insurance
Covers the insured's legal liability arising out of property damage or bodily injury to others
Casualty Insurance
Refers to insurance that covers whatever is not covered by fire, marine, and life insurance
Government Insurance
Social Insurance Programs
Financed entirely or in large part by contributions from employers and/or employees
Benefits are heavily weighted in favor of low-income groups
Eligibility and benefits are prescribed by statute
Government Insurance Examples
Old-Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance (Social Security) - any government system that provides monetary assistance to people with an inadequate or no income
Unemployment
Medicare
Found at both federal and state level
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) - Insures banks deposit up to $250,000 per depositor
National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) - live on coast/ near body of water; provides insurance to help reduce the socio-economic impact of floods
Fair Access to Insurance Requirements Plans (FAIR) - State-mandated, last-resort insurance programs providing essential property coverage to homeowners and businesses unable to secure insurance through the voluntary market
Beach and Windstorm Plans - Designed to provide coverage for wind and hail damage in high-risk coastal areas where private insurers refuse to provide it