ochem reactants
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
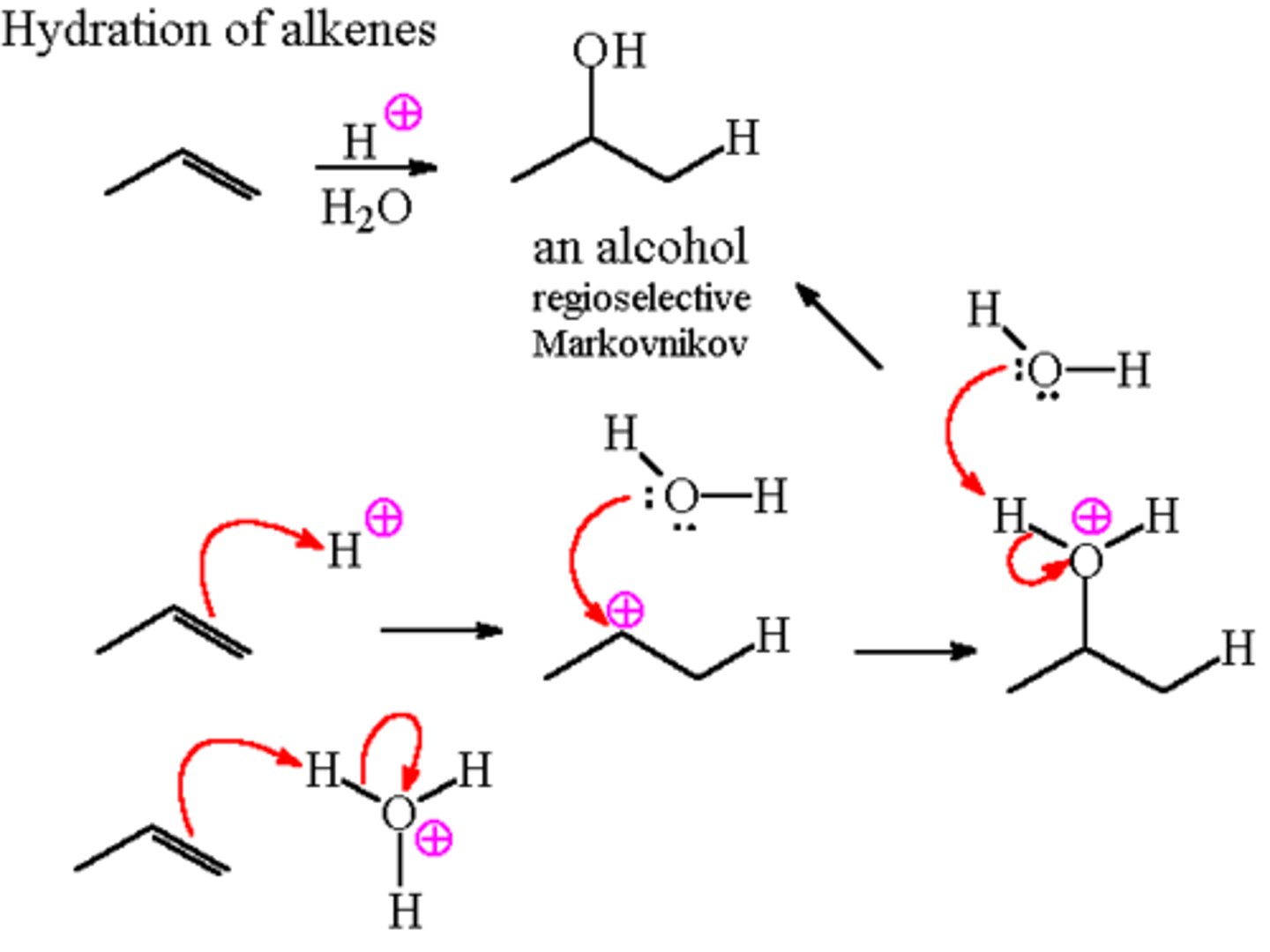
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
H3O+
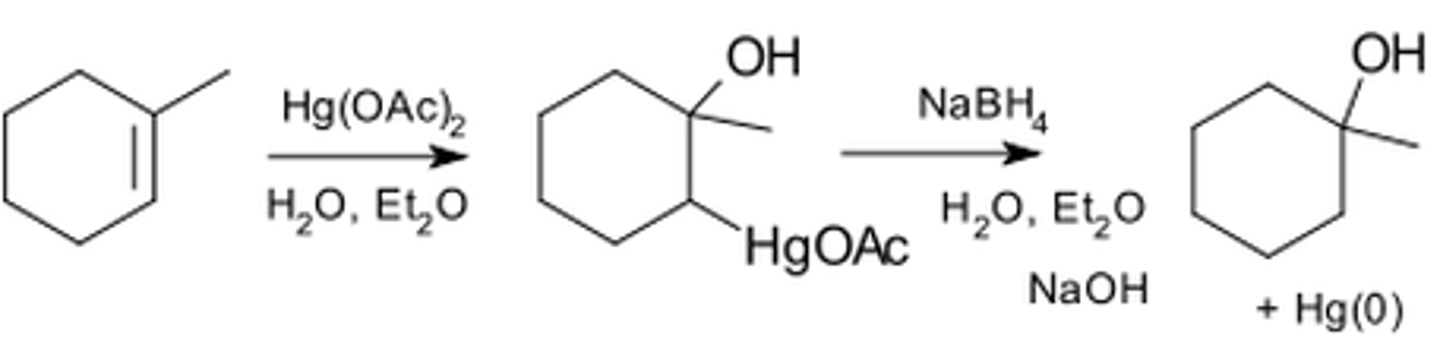
Oxymercration
1. Hg(OAc)2
2. H2O
3. NaBH4
Dihydroxylation
1. KMnO4
2. H2O2, NaOH
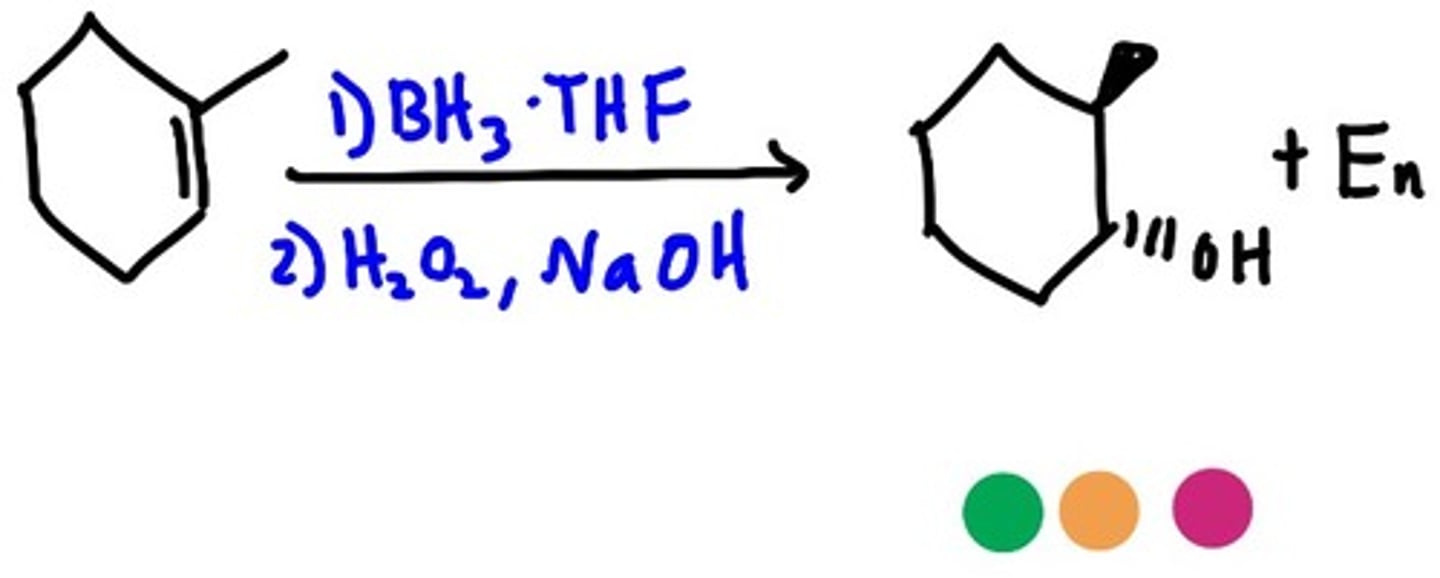
Hydroboration-Oxidation
1. BH3, THF
2. H2O2, NaOH, H2O
Anti-Dihydroxylation
1. MCPBA
2. H3O+
Oxidative Cleavage (Alkene)
1. O3
2. DMS
Halogen Addition
Br2
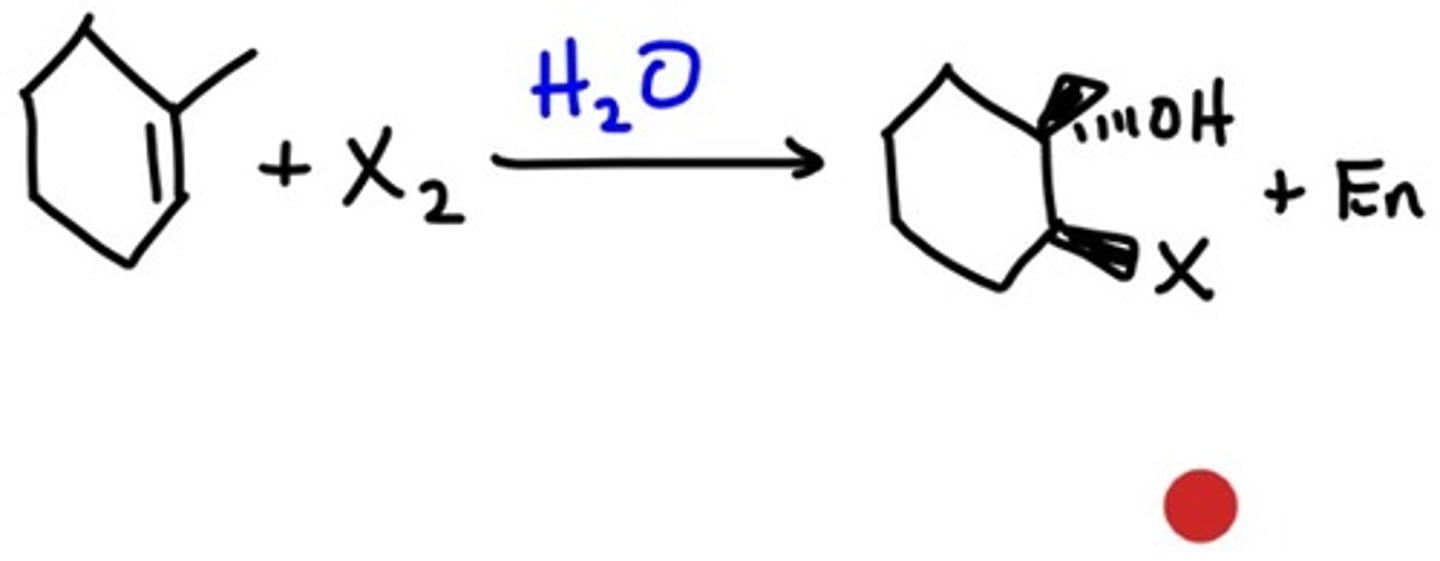
Halohydrin Formation
1. Br2
2. H2O
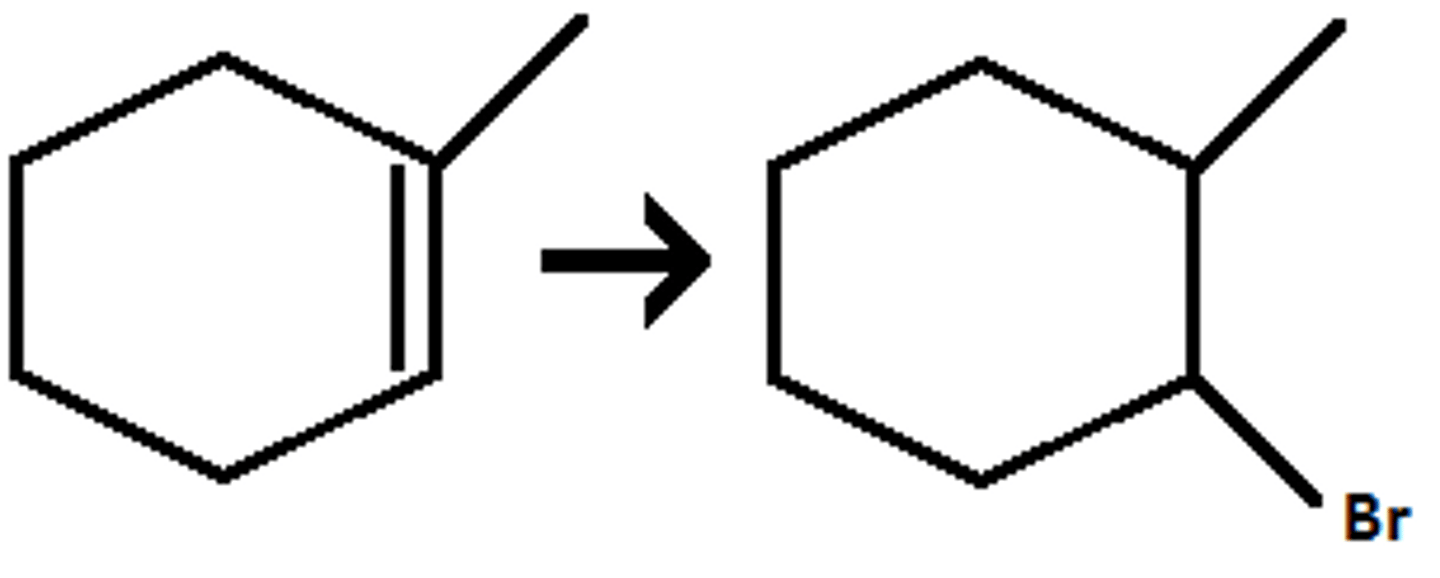
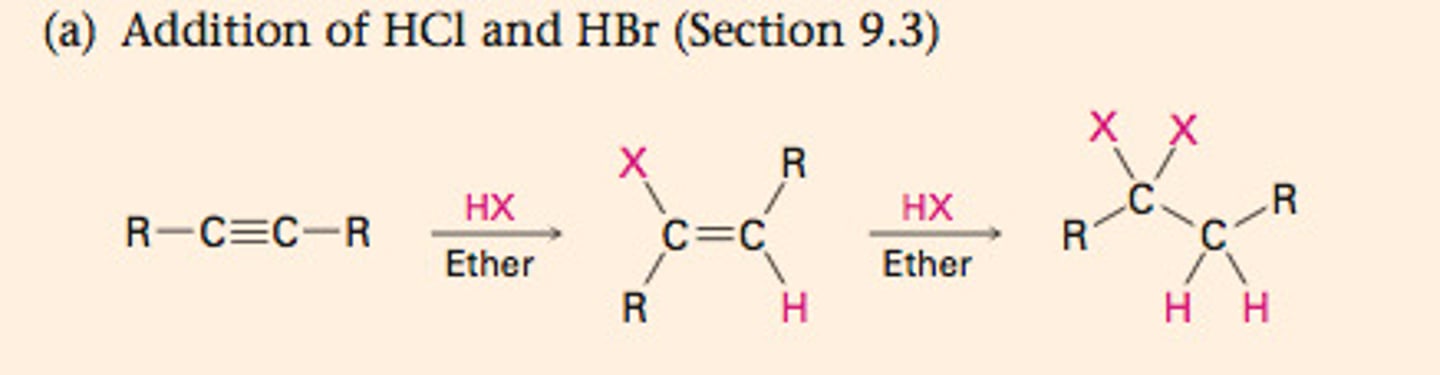
Hydrohalogenation
H-X
Anti-Hydrohalogenation
1. H-X
2. H2O2
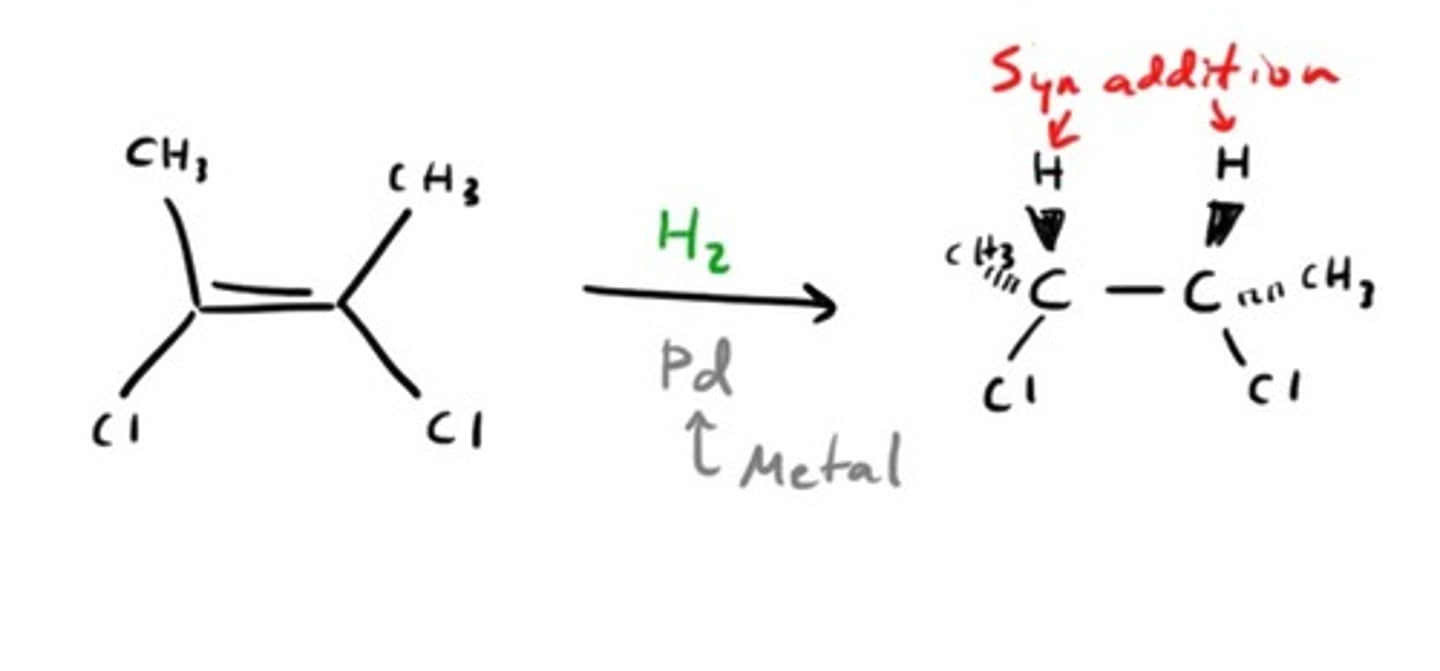
Catalytic Hydrogenation
1. H2
2. Pt
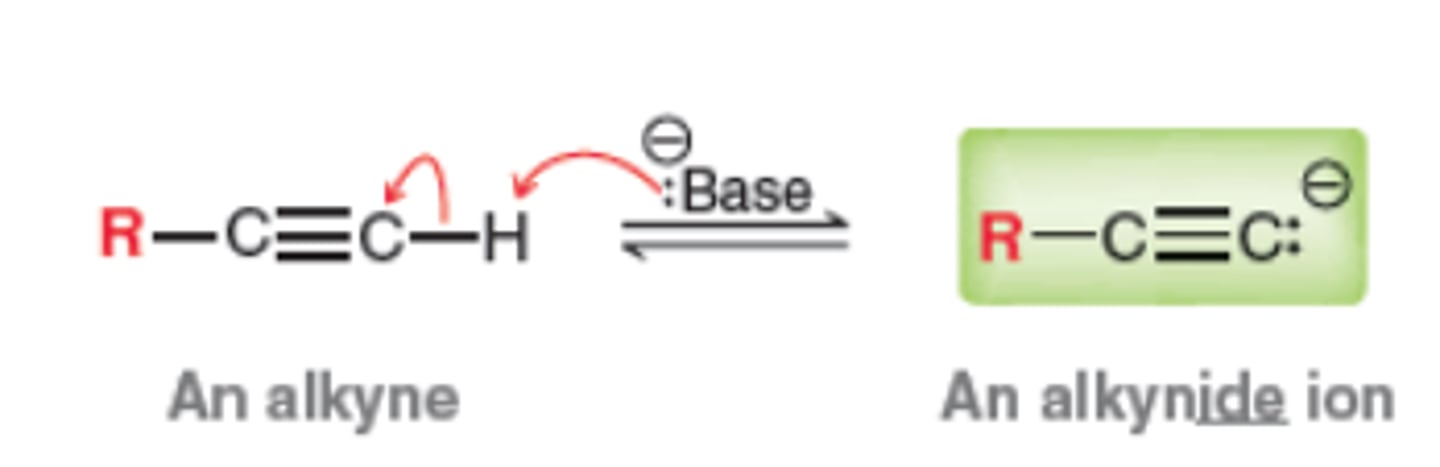
Deprotonation
NaNH2
Preperation of Alkyne
1. HX
2. NaNH2, NH3
3. H2O
Reduction to Alkane
1. (xs) H2
2. Pt
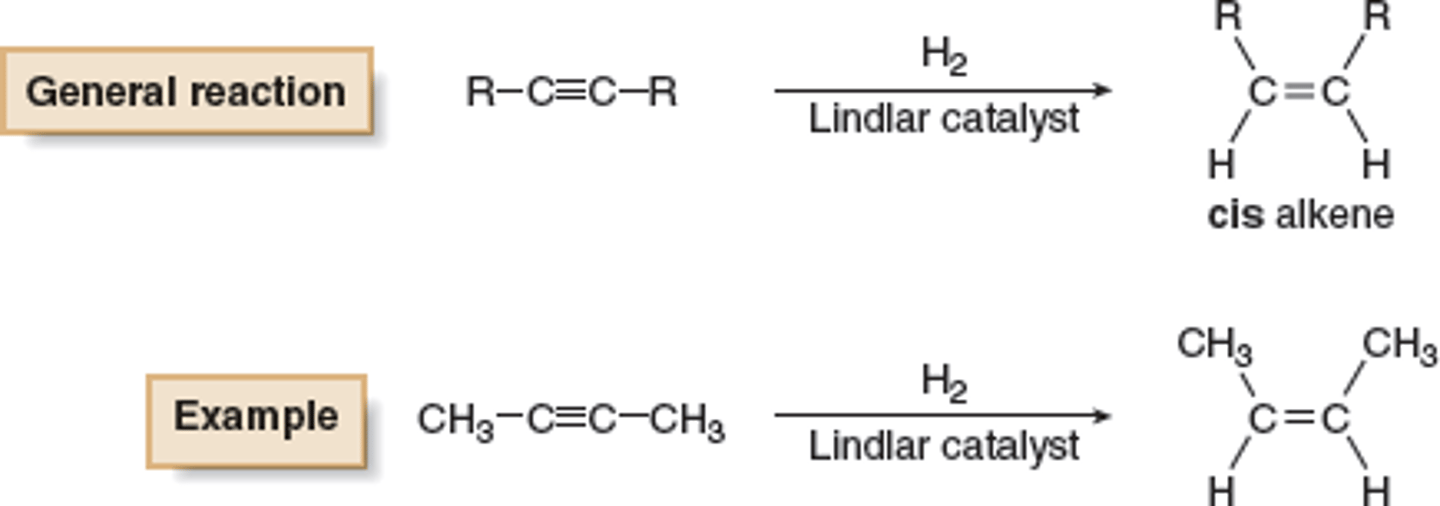
Reduction to Cis Alkene
1. H2
2. Lindlar's Catalyst
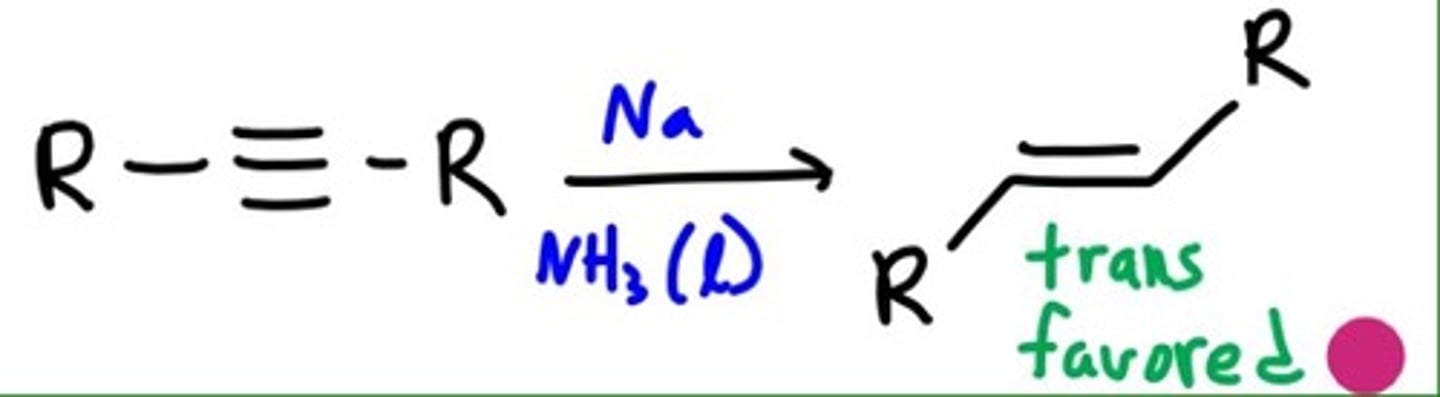
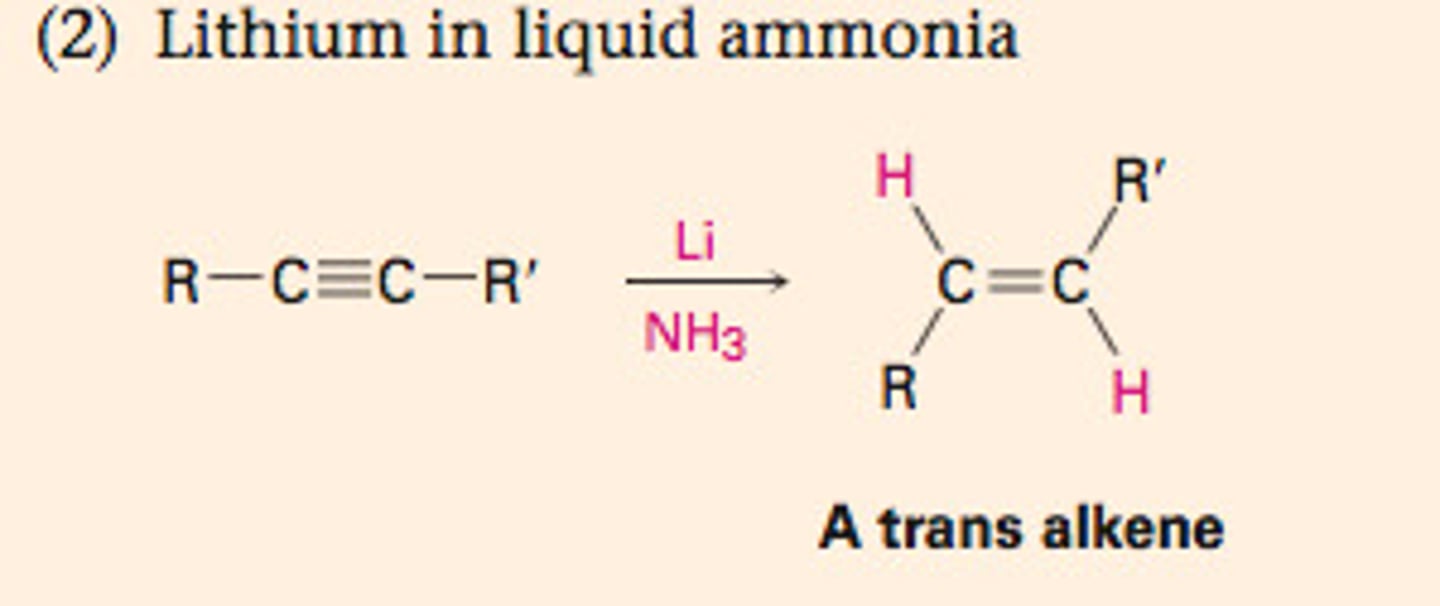
Reduction to Trans Alkene
1. Na
2. NH3
Addition of Halogen
HX
Anti-Addition of Halogen
1. HBr
2. H2O2
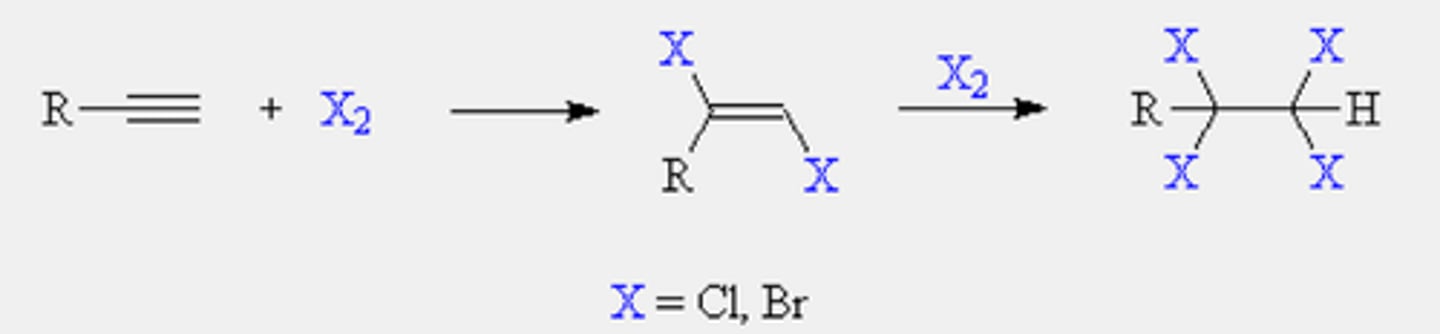
Halogenation
1. X2
2. CCl4
Hydration
1. H2O, H2SO4
2. HgSO4
Hydroboration
1. BH3, THF
2. H202, NaOH
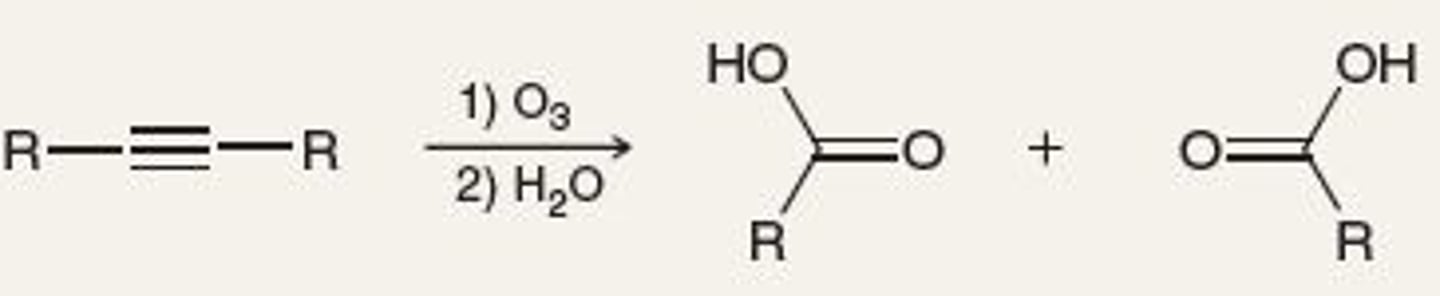
Oxidative Cleavage (Alkyne)
1. O3
2. H2O
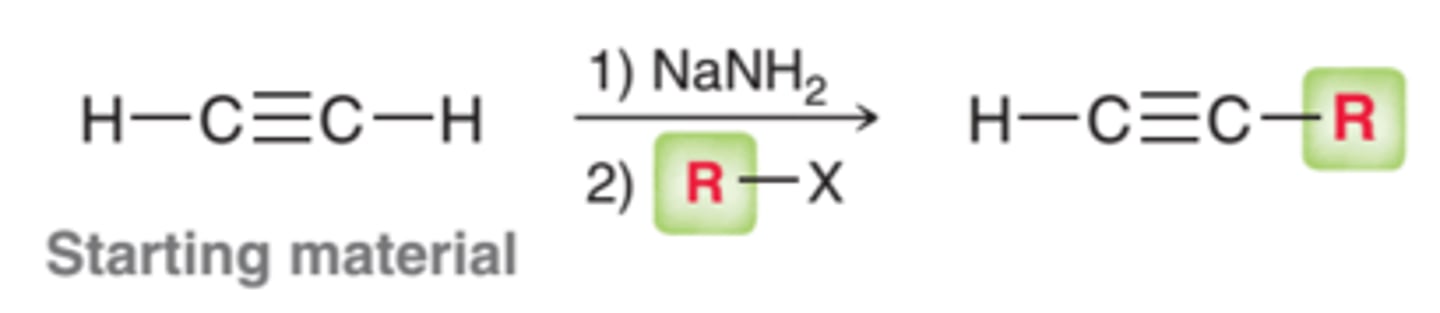
Alkynation
1. NaNH2
2. Me/Et-LG
What yields anti-Markovnikov's products for Alkynes?
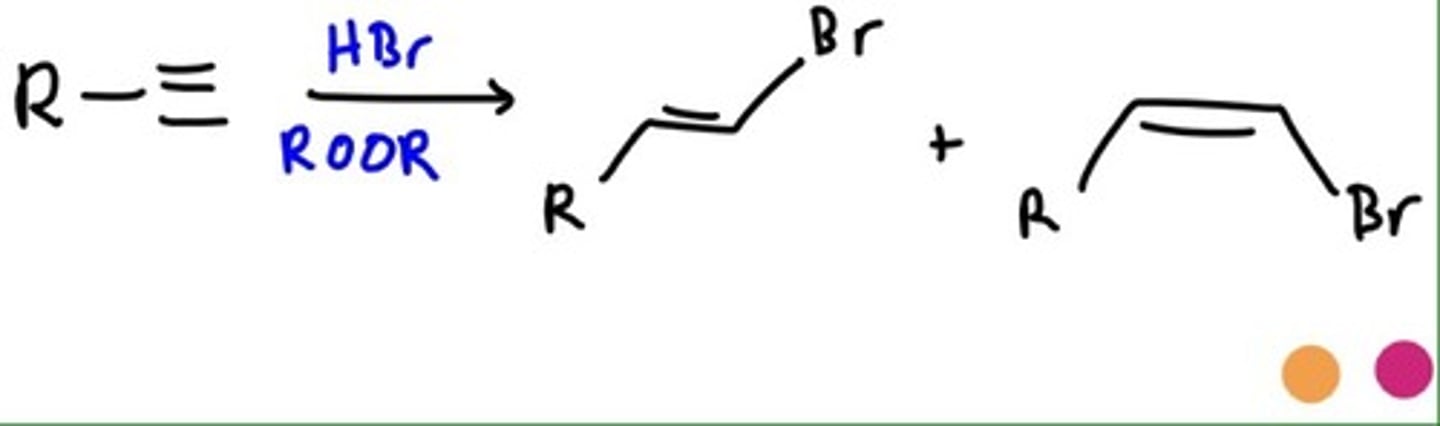
Radical Addition of HBr and Hydroboration
What yields trans major products for Alkynes?
Reduction using 1. Na and 2. NH3 and Halogenation
What causes Keto-Enol Tautomerization?
Hydration of Alkynes
What yields anti-Markovniko products for Alkenes?
Hydroboration-Oxidation and Anti-Hydrohalogenation
What has syn stereospecificty for Alkenes?
Hydroboration-Oxidation, Dihydroxylation, and Catalytic Hydrogenation
What has anti stereospecificty for Alkenes?
Anti-Dihydroxylation and Br2 Addition
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
Markovnikov
Racemic R/S
Oxymercuration
Hydroboration-Oxidation
Dihydroxylation
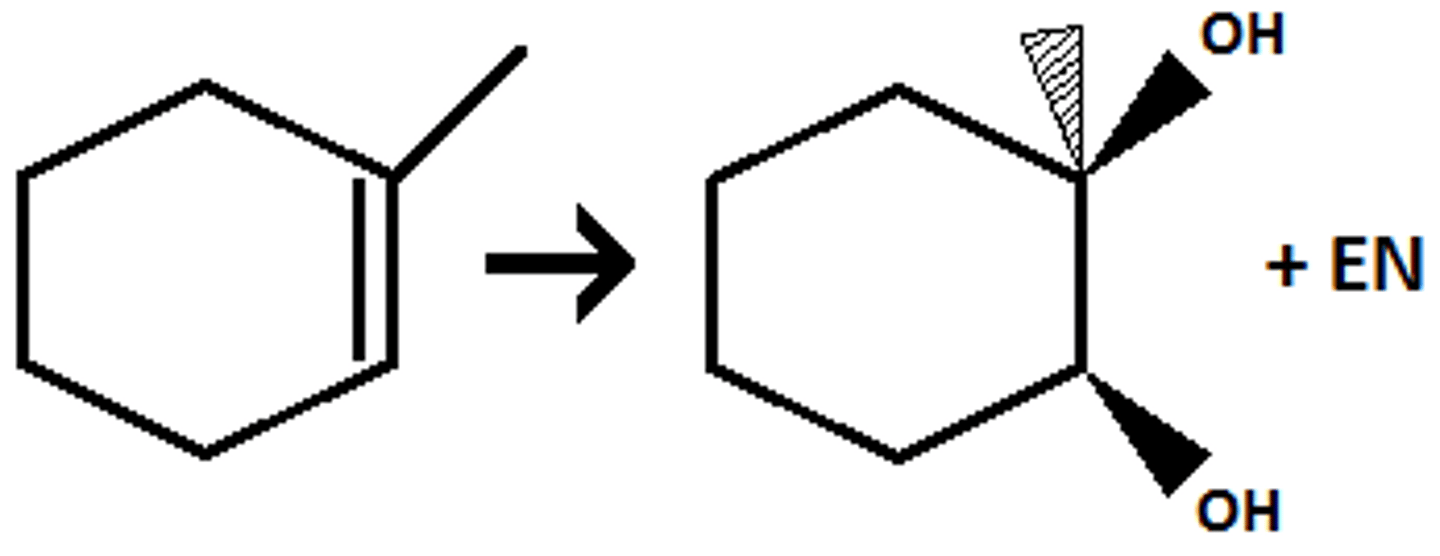
Anti-Dihydroxylation
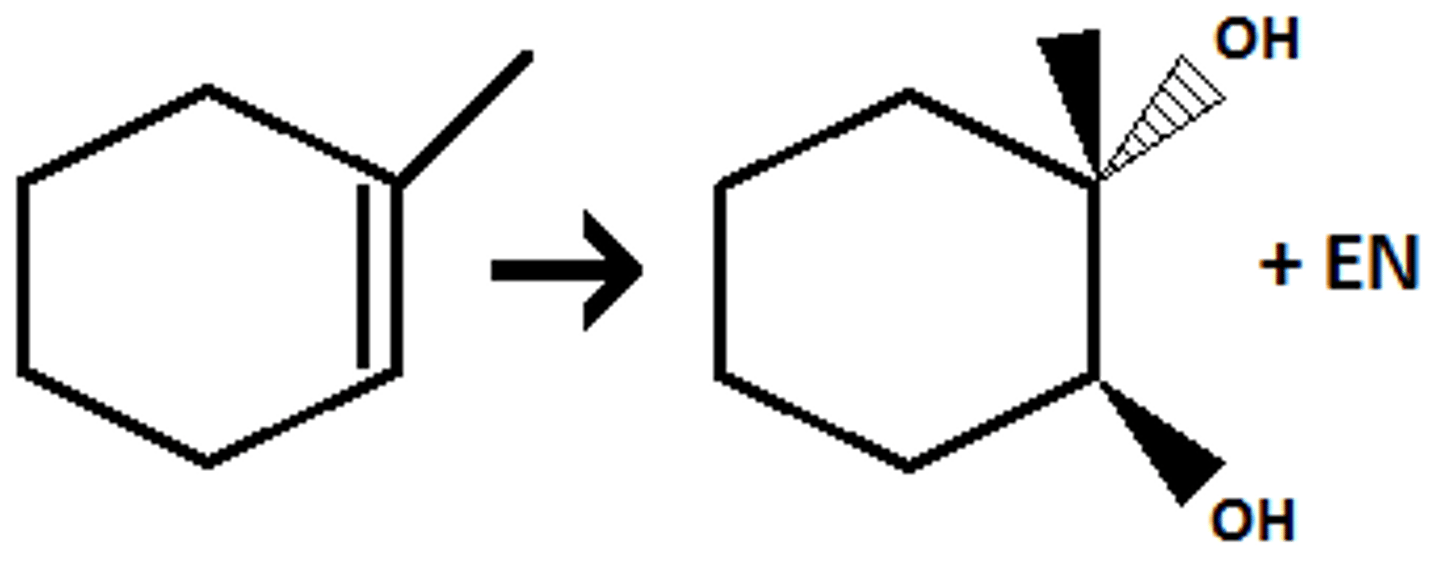
Oxidative Cleavage
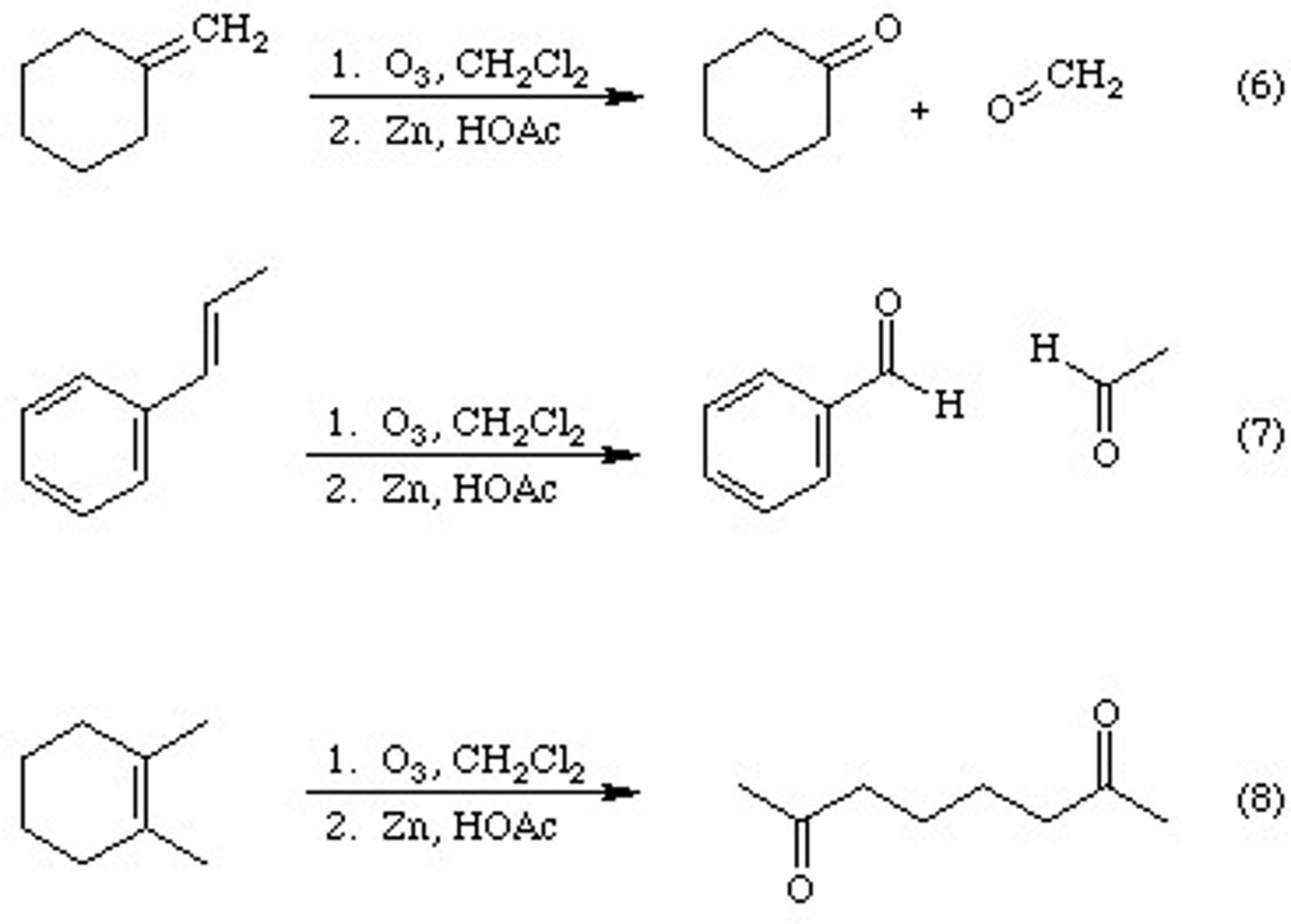
Radical Bromination
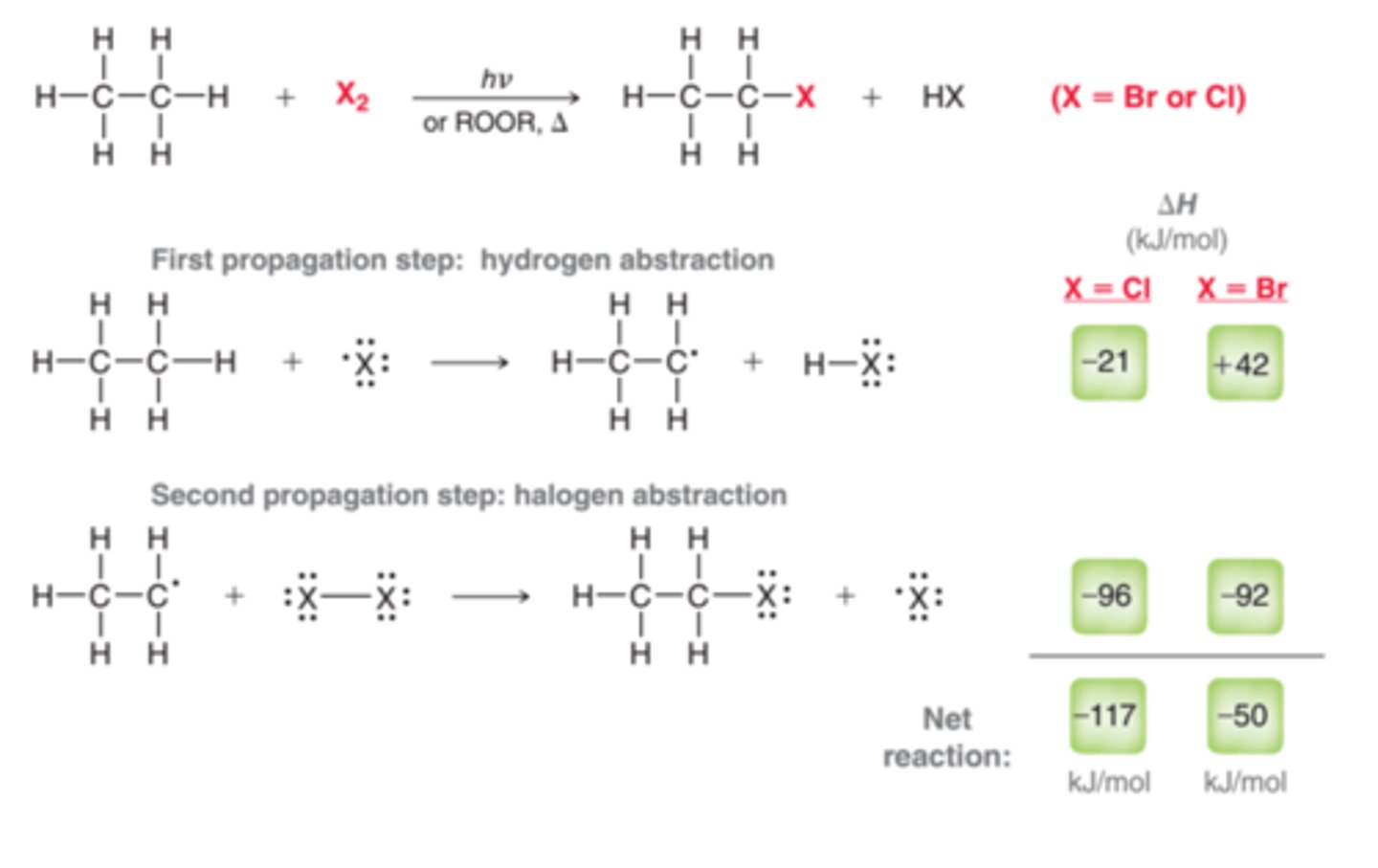
Halohydrin Formation
Hydrohalogenation
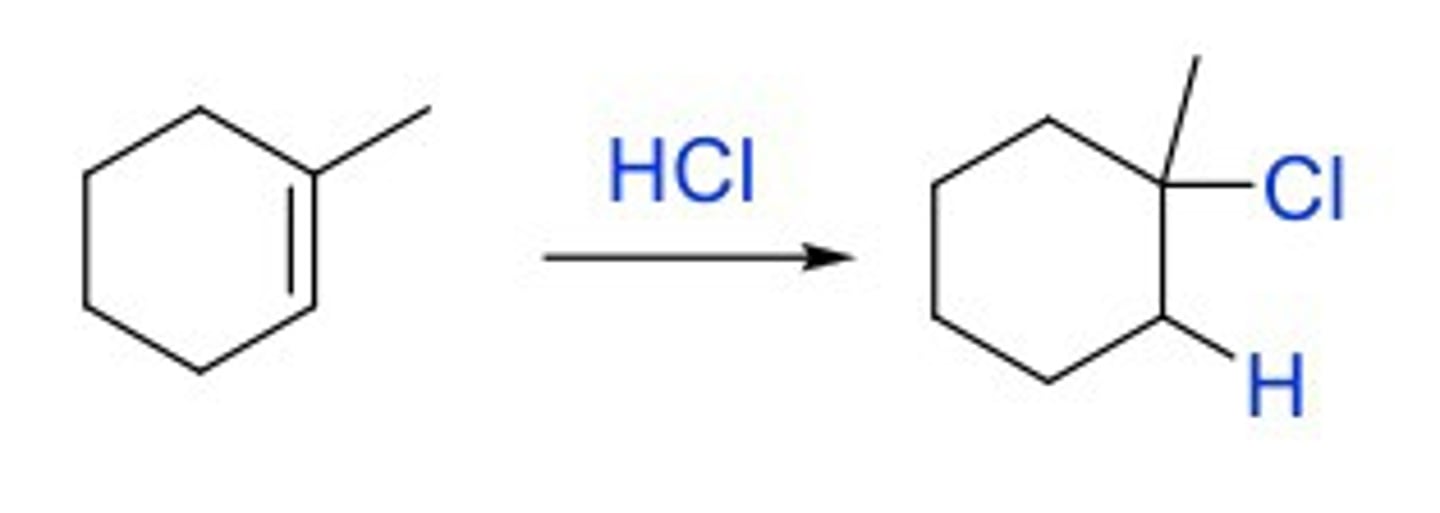
Hydrohalogenation
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Deprotonation
Preparation of Alkyne
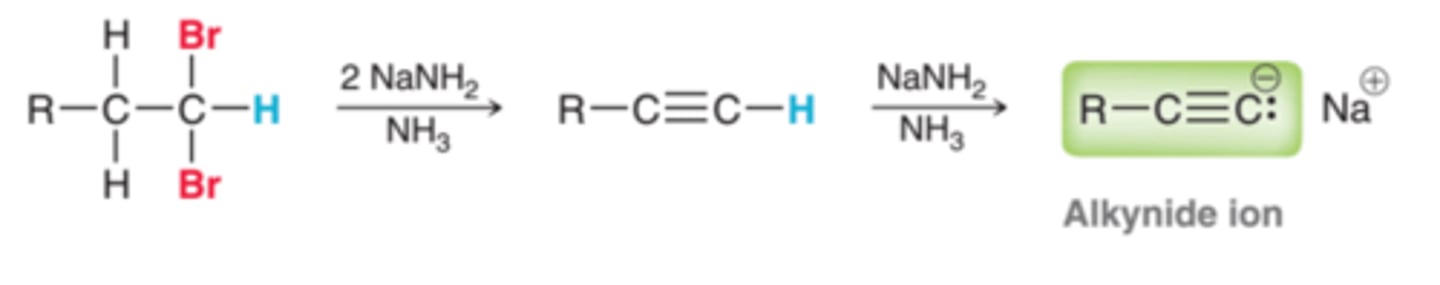
Reduction to Alkane
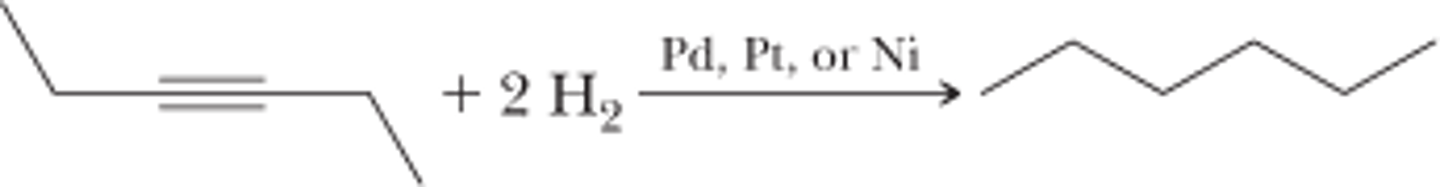
Reduction to Cis Alkene
Reduction to Trans Alkene
Addition of HX
Radical Addition of HBr
Halogenation
Hydration
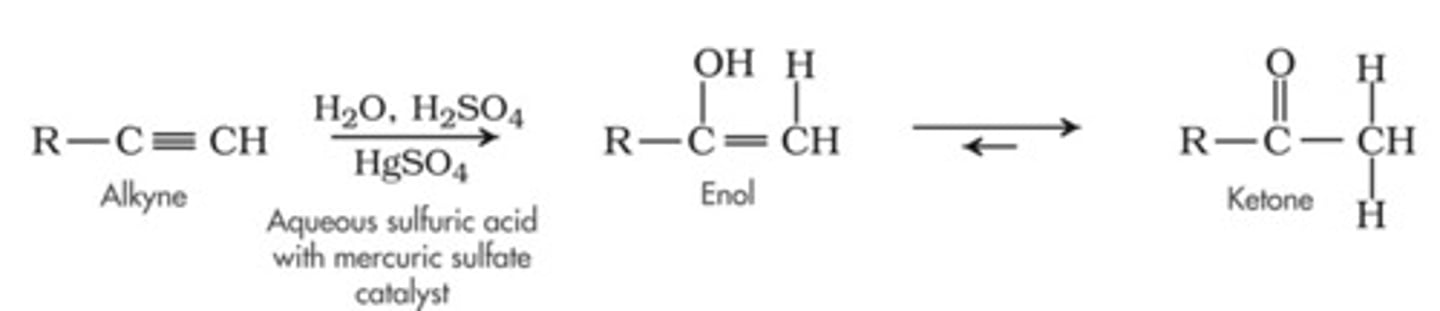
Hydroboration
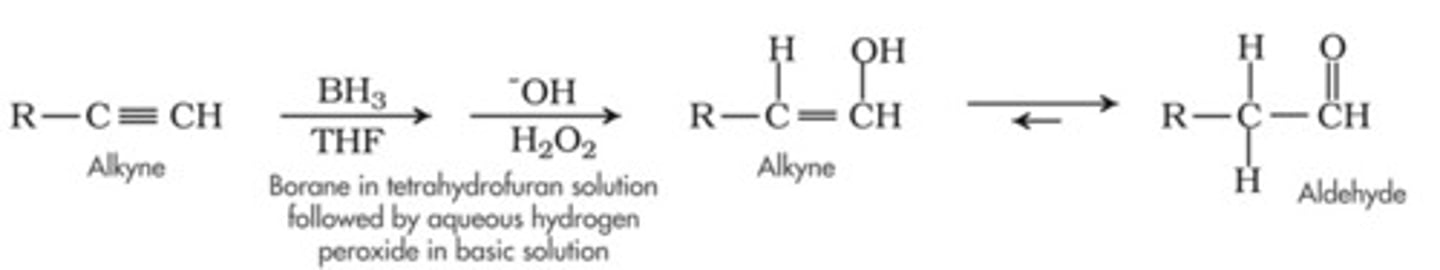
Oxidative Cleavage (Alkyne)
Alkylation
TERM
Reagent 6
DEFINITION
1. Br2
TERM
Reagent 7
DEFINITION
1. Br2, H2O
TERM
Reagent 8
DEFINITION
1. RCO3H 2. H3O+
TERM
Reagent 9
DEFINITION
KMnO4, NaOH (Cold)
TERM
Reagent 9
DEFINITION
1. OsO4 2. NaHSO3, H2O
TERM
Reagent 10
DEFINITION
1. O3 2. DMS
TERM
Reagent 1
DEFINITION
HX
TERM
Reagent 2
DEFINITION
1. HBr 2. H2O2
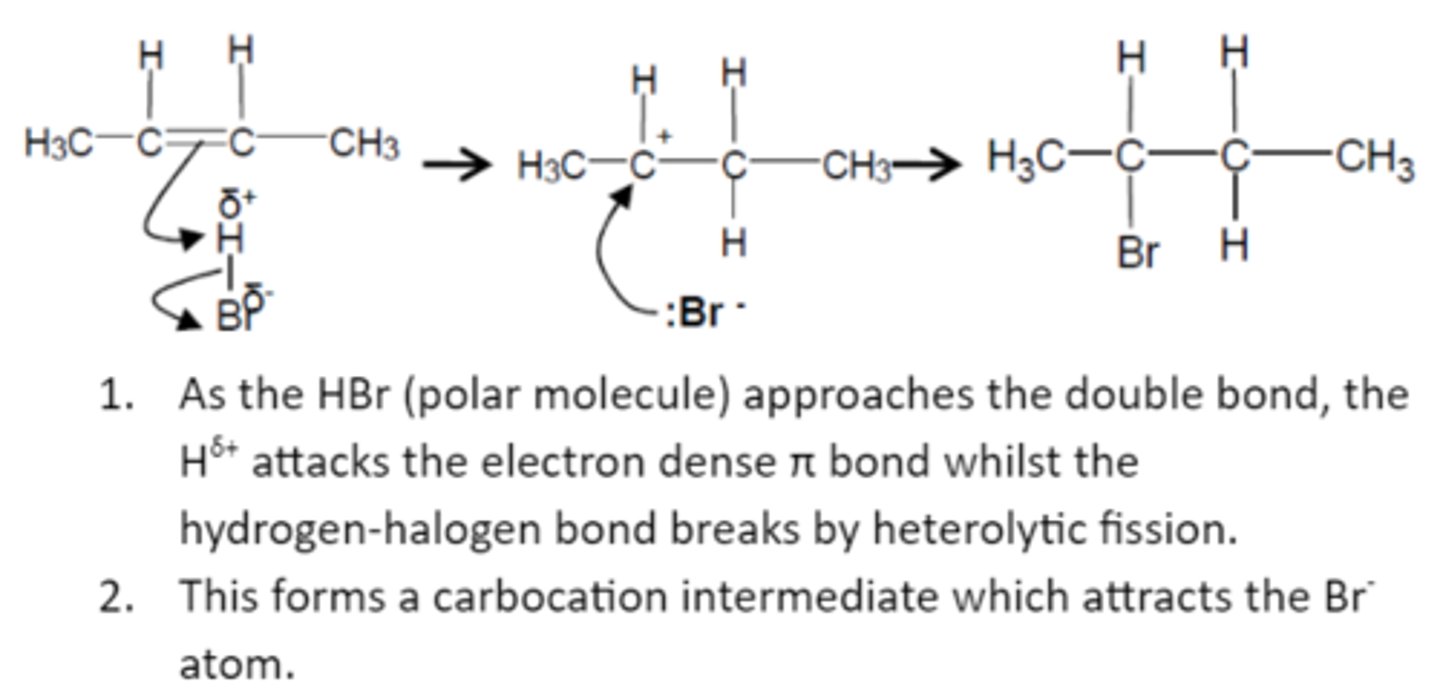
Electrophilic Addition
CH3CH=CHCH3 + HBr
Follows Markovnikov's rule
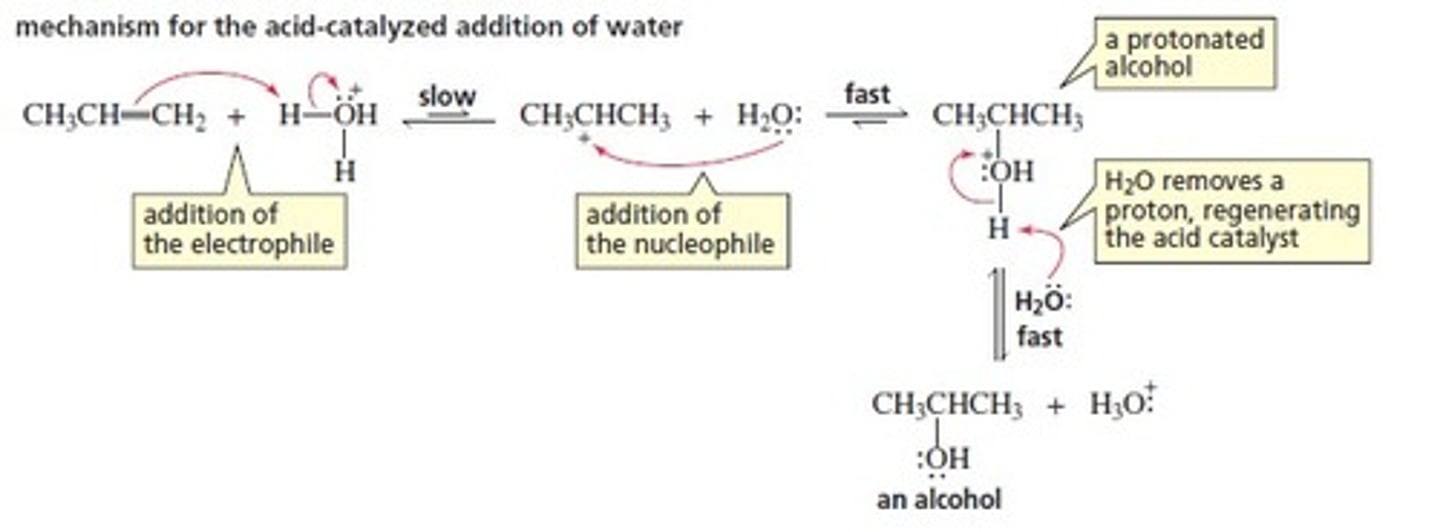
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration Reaction
CH3CH=CH2 + H2O
Follows Markovnikov's rule
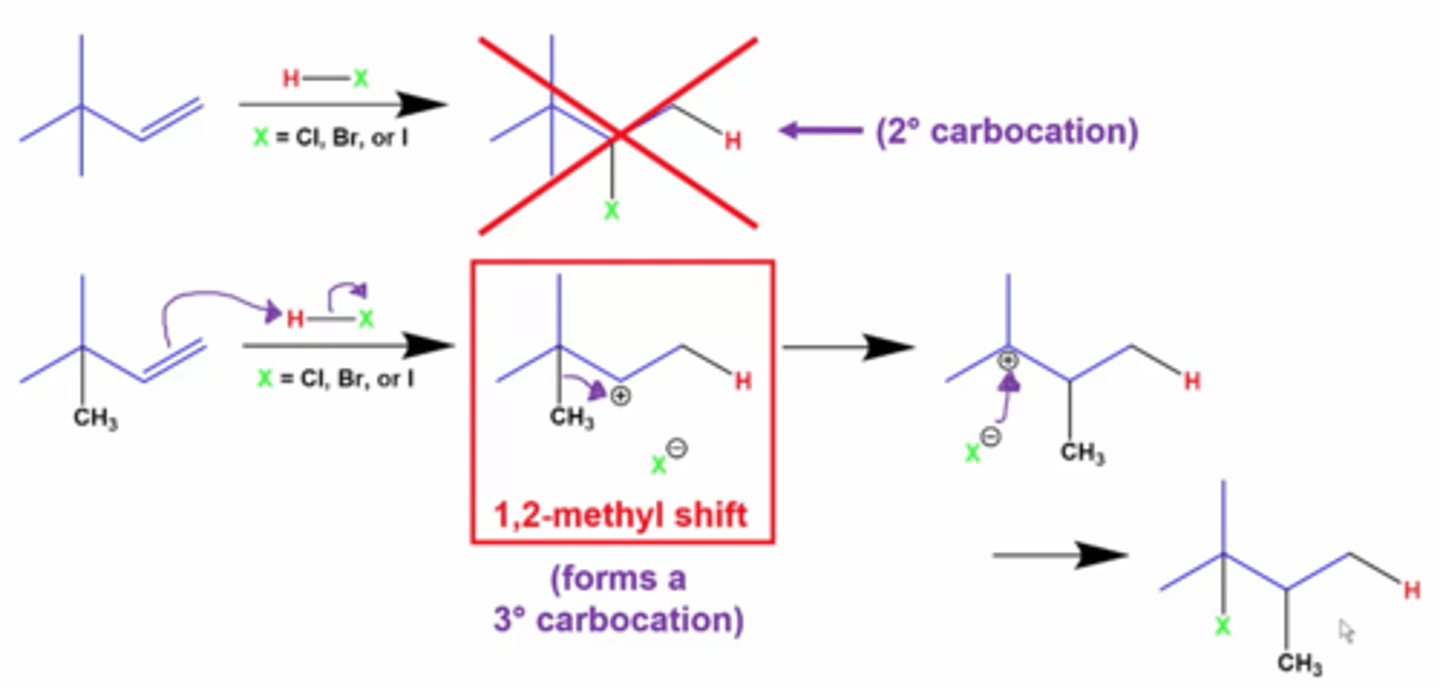
1,2 Shift
3-Dimethylbut-1-ene + HCl
Occurs to produce a more stable carbocation
Can occur in any reaction (electrophilic addition, hydration, etc)
Generation of a Halohydrin
1-methylcyclopentene + H2O + Br2
Both regioselective and antistereoselective (i.e., the two groups have to be trans of each other)
Halogen binds to the less substituted carbon
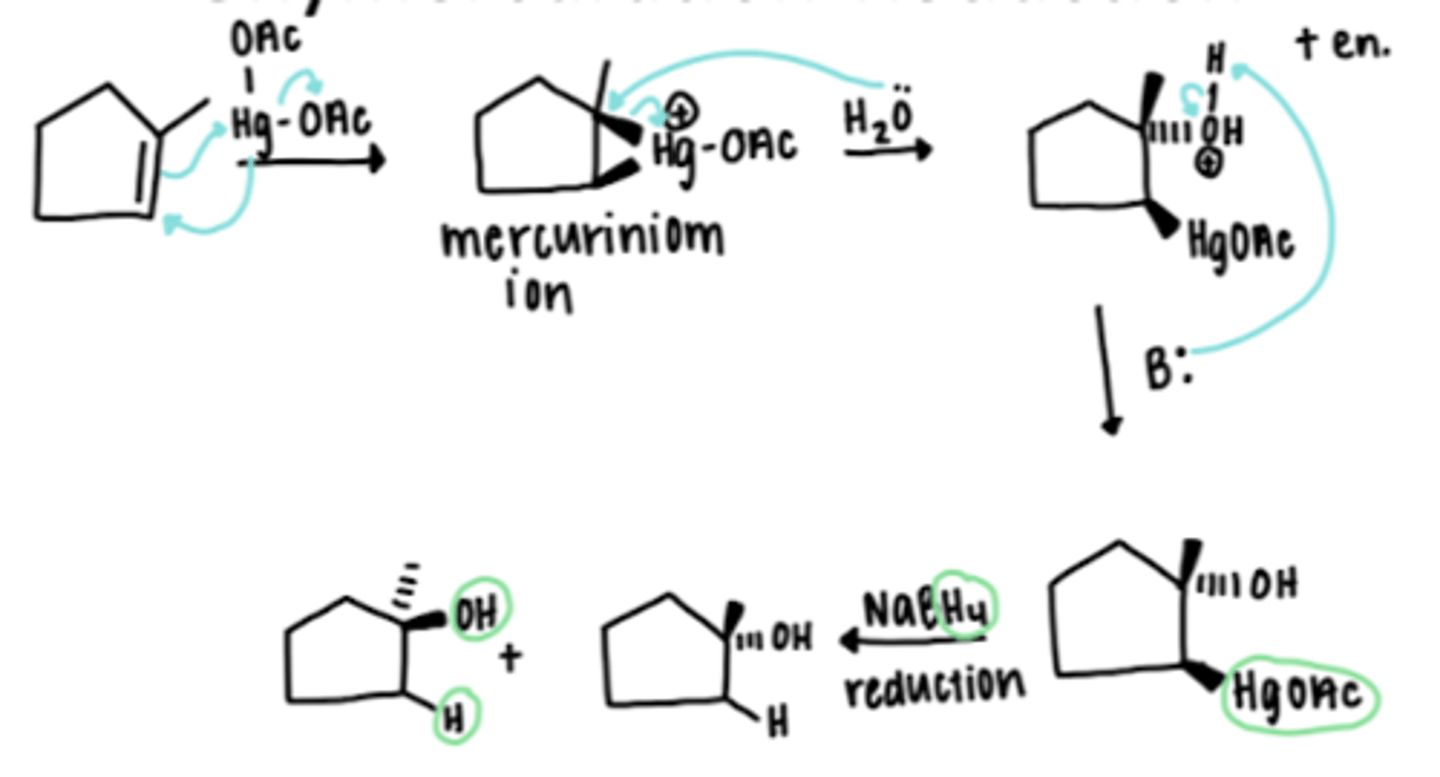
Oxymercuration reduction of an alkene
1-methylcyclopentene + (1) HgOAc (2) NaBH4
Essentially the same as the Markovnikov addition of H2O to an alkene
OH bonds to the more substituted carbon and HgOAc to the less substituted carbon; reduction by NaBH4 replaces the HgOAc with an H
Occurs without rearrangement, indicating that a carbocation isn't formed
Hydroboration-oxidation reaction of an alkene
1-methylcyclohexene + (1) BH3 (2) H2O2, NaOH
Non-Markovnikov hydration of an alkene; i.e., the OH group is added to the less substituted carbon
Occurs without rearrangement
Involves the cis-addition of H-OH
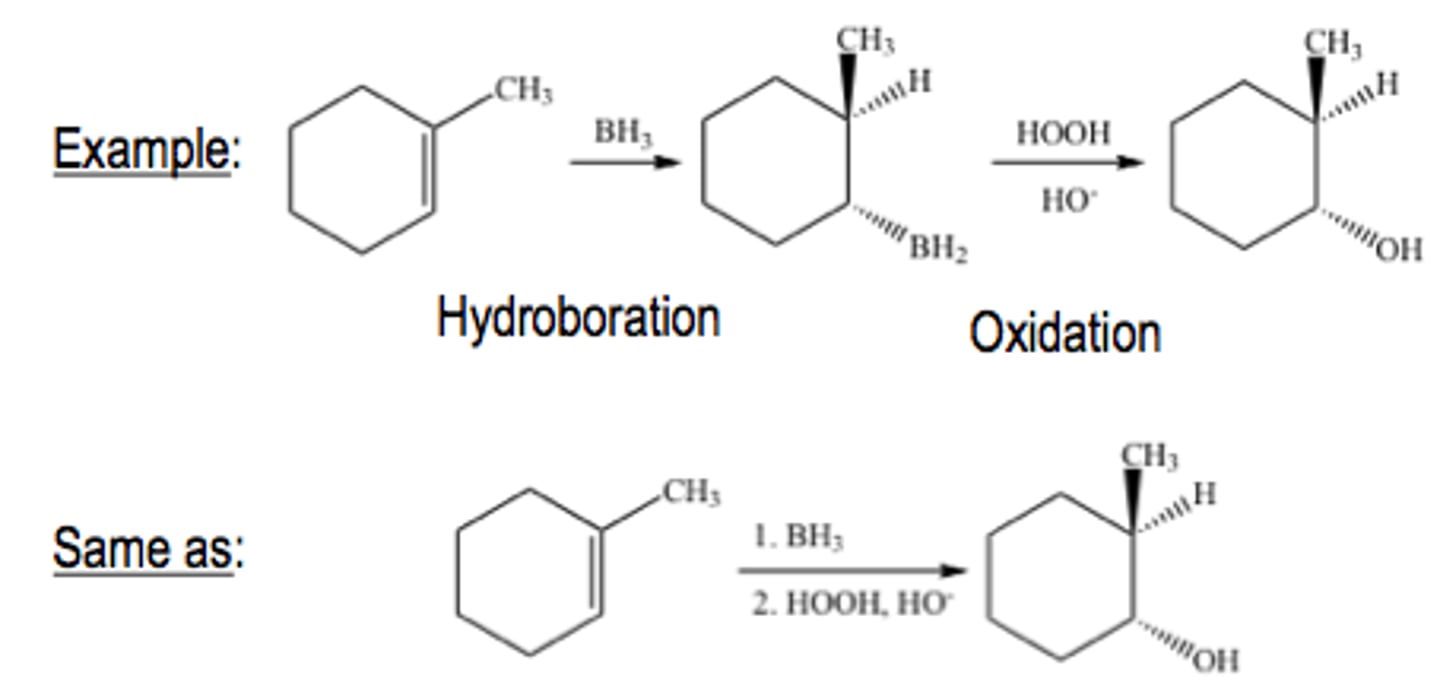
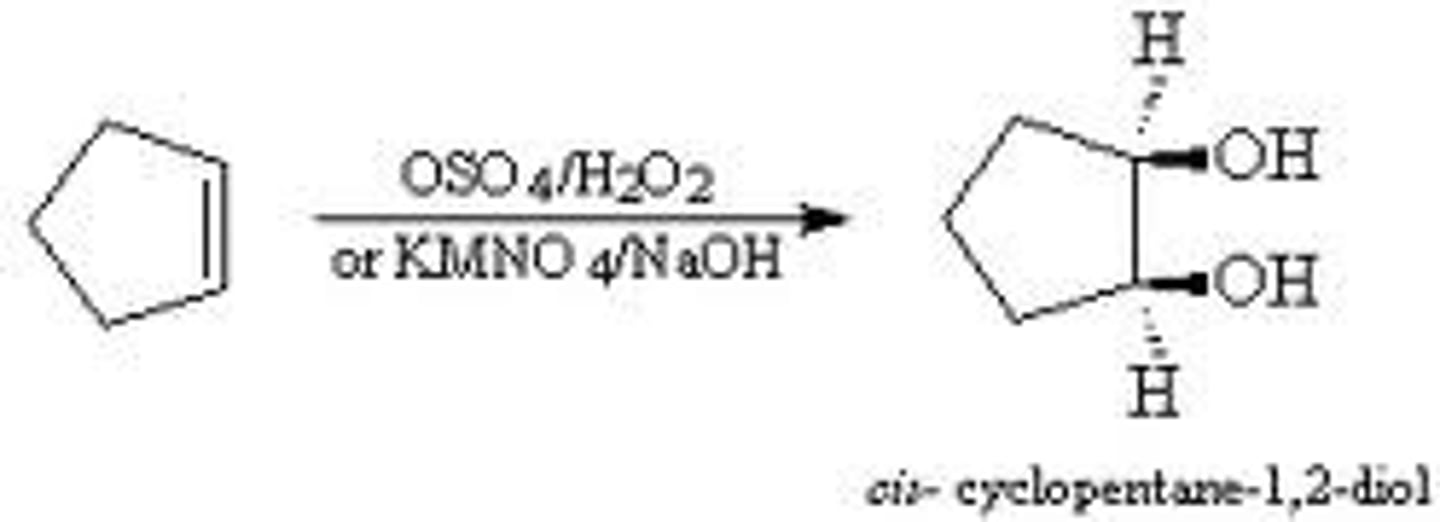
Oxidation of an alkene with OsO4 or MnO4
Cyclopentene + OsO4
Converts an alkene to a 1,2 diol
Involves the cis-addition of an OH group to each carbon of a double bond
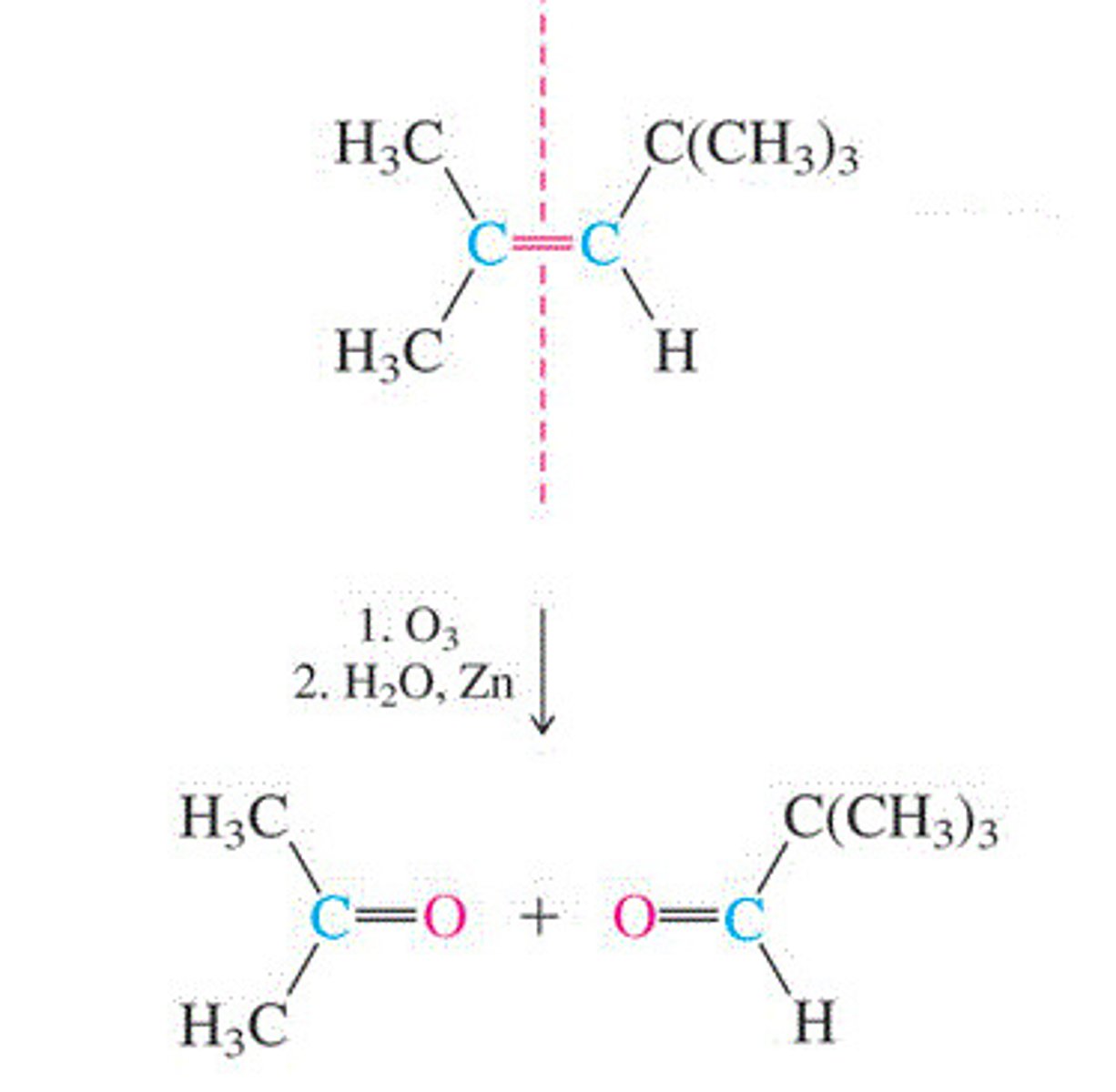
Ozonolysis of an alkene
2-methyl-2-pentene + O3
Cleaves the carbon-carbon double bond and leaves two C=O groups in its place
Forms a ketone and an aldehyde (the aldehyde is only stable if there are no oxidizing agents present)
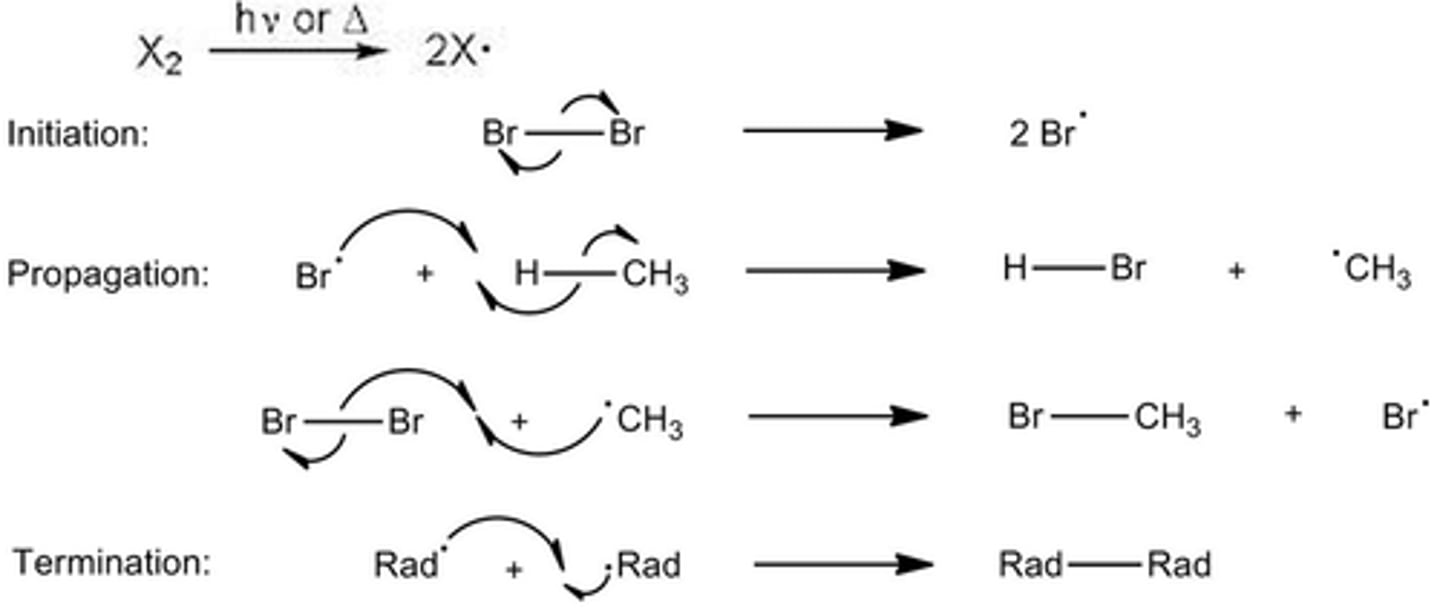
Halogenation of Alkanes
CH3CH2CH3 + Cl2
is a radical substitution reaction; regioselective for the more substituted carbon
Radical chain reaction
Products are a racemic mixture
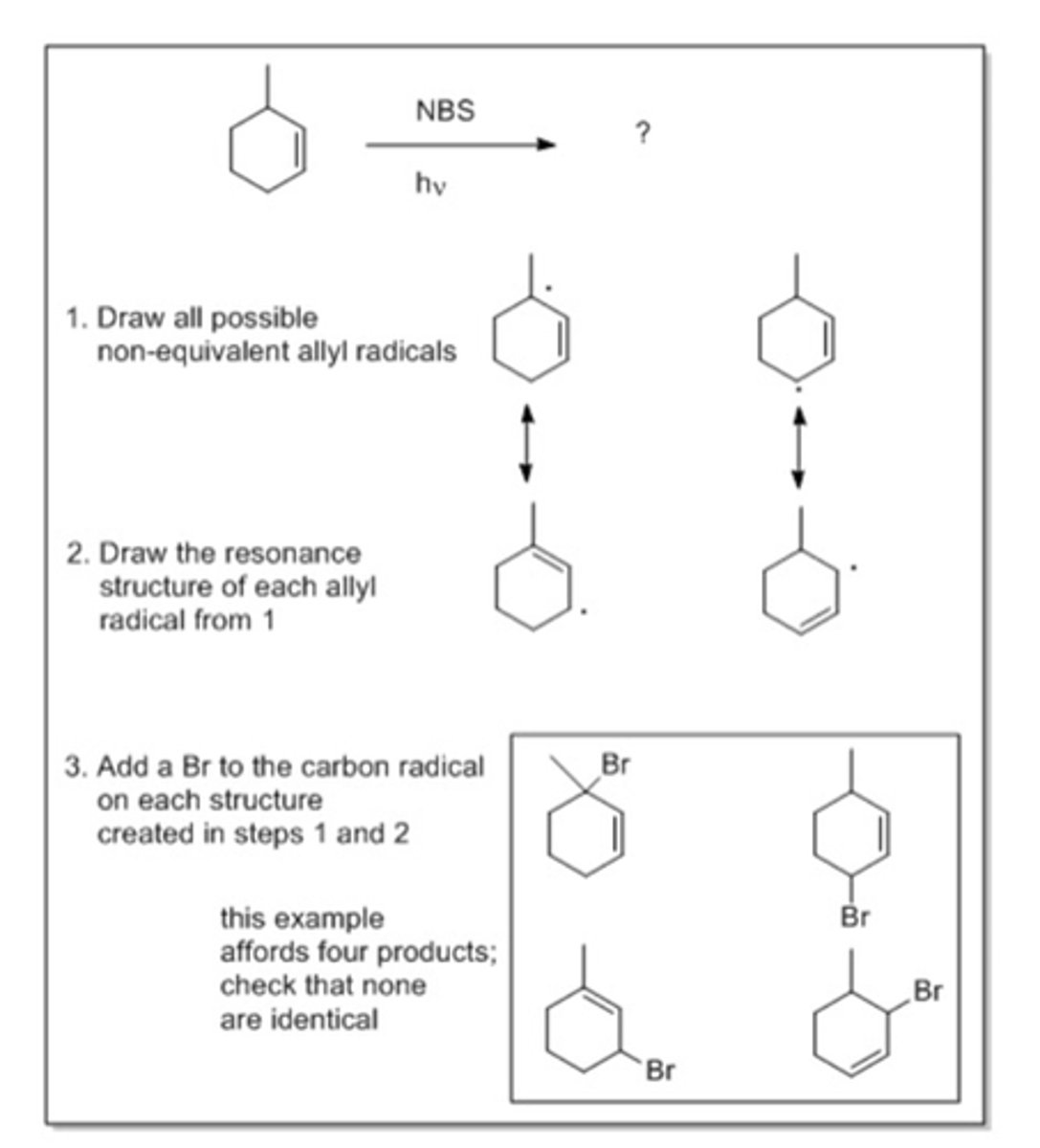
NBS Reaction
Cyclohexene + NBS
Useful method for carrying out allylic bromination (the allylic carbon is the carbon next to the double bond)
Radical chain reaction initiated by light
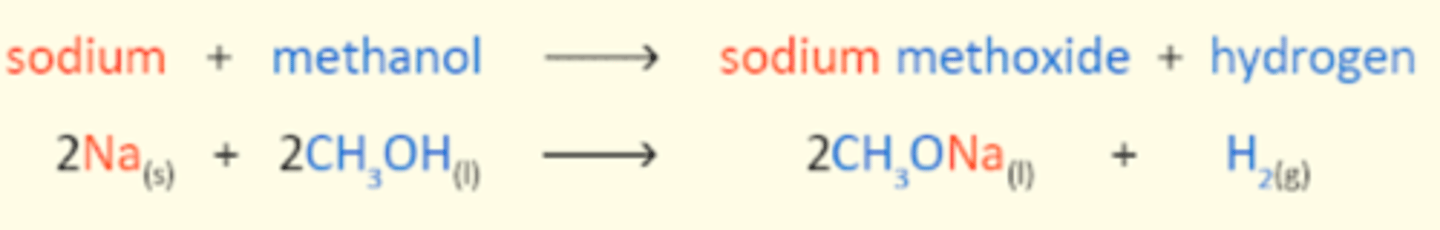
Reaction of alcohols with reactive metals
CH3OH + Na
Gives metal alkoxide ions and hydrogen gas
alkoxide ions are very basic
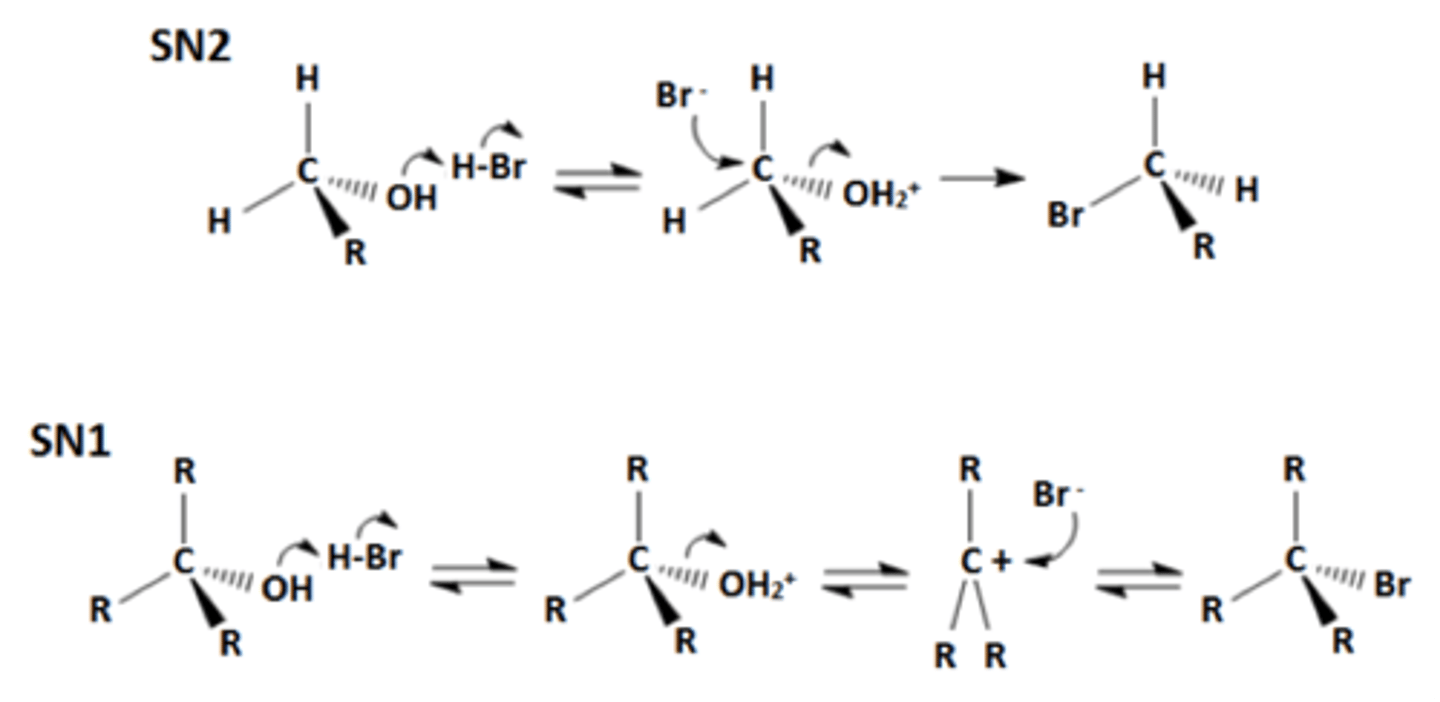
Reaction of alcohols with hydrogen halides
2-Methyl-2-Propanol + HCl
2,2-Dimethyl-1-propanol + HBr
1-Butanol + HBr
forms haloalkanes
2º and 3º occurs through SN1 mechanism
branched 1º occur with rearrangements via SN2
unbranched 1º occur through SN2 mechanism
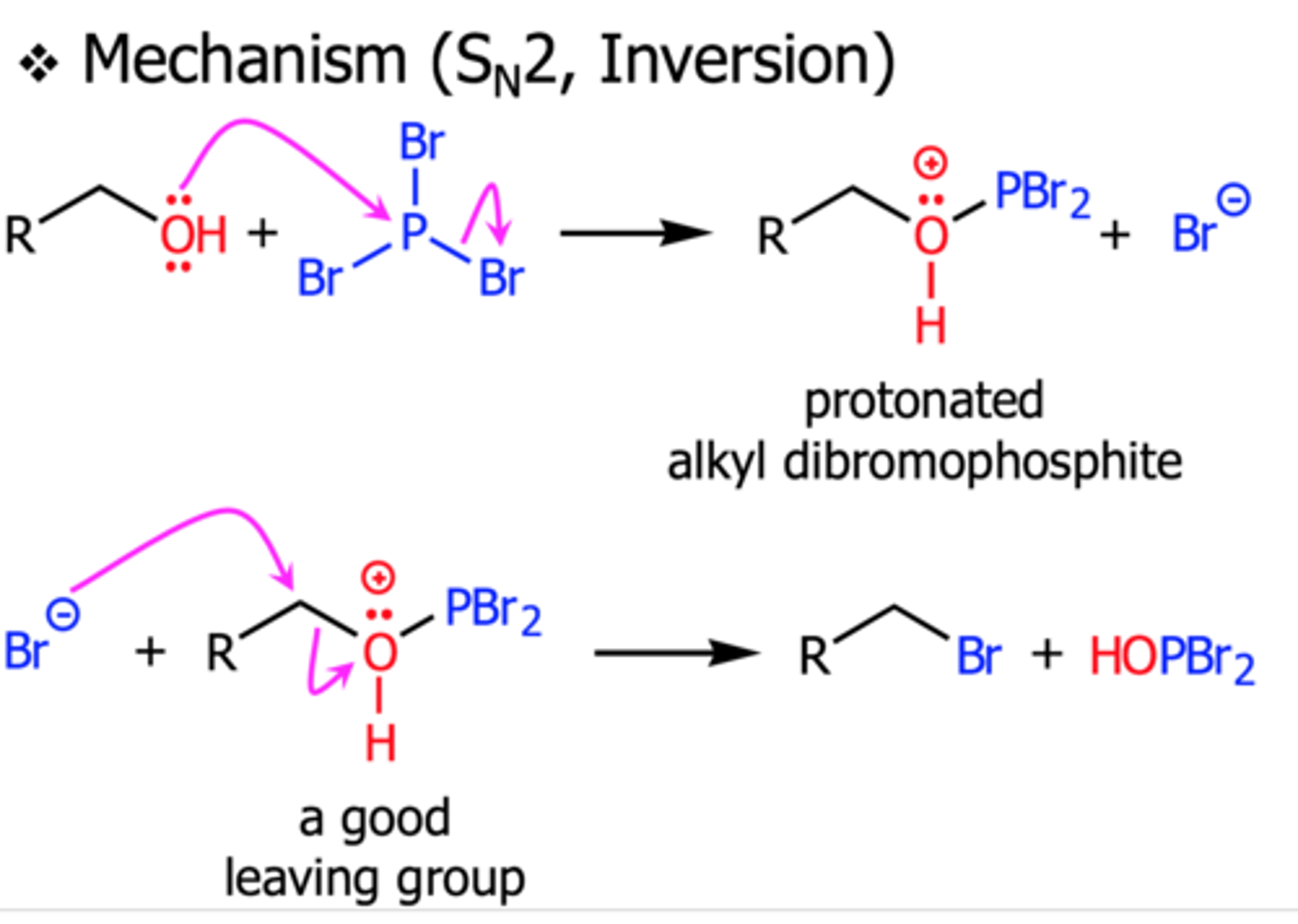
Reaction of alcohols with PBr3
CH3CH2OH + PBr3
Forms bromoalkanes
only works with primary and secondary alcohols
occurs via SN2 mechanism, so no rearrangements
Reaction of alcohols with SOCl2
1-Heptanol + SOCl2
Forms chloroalkanes
only works with primary and secondary alcohols
occurs via SN2 mechanism, so no rearrangements
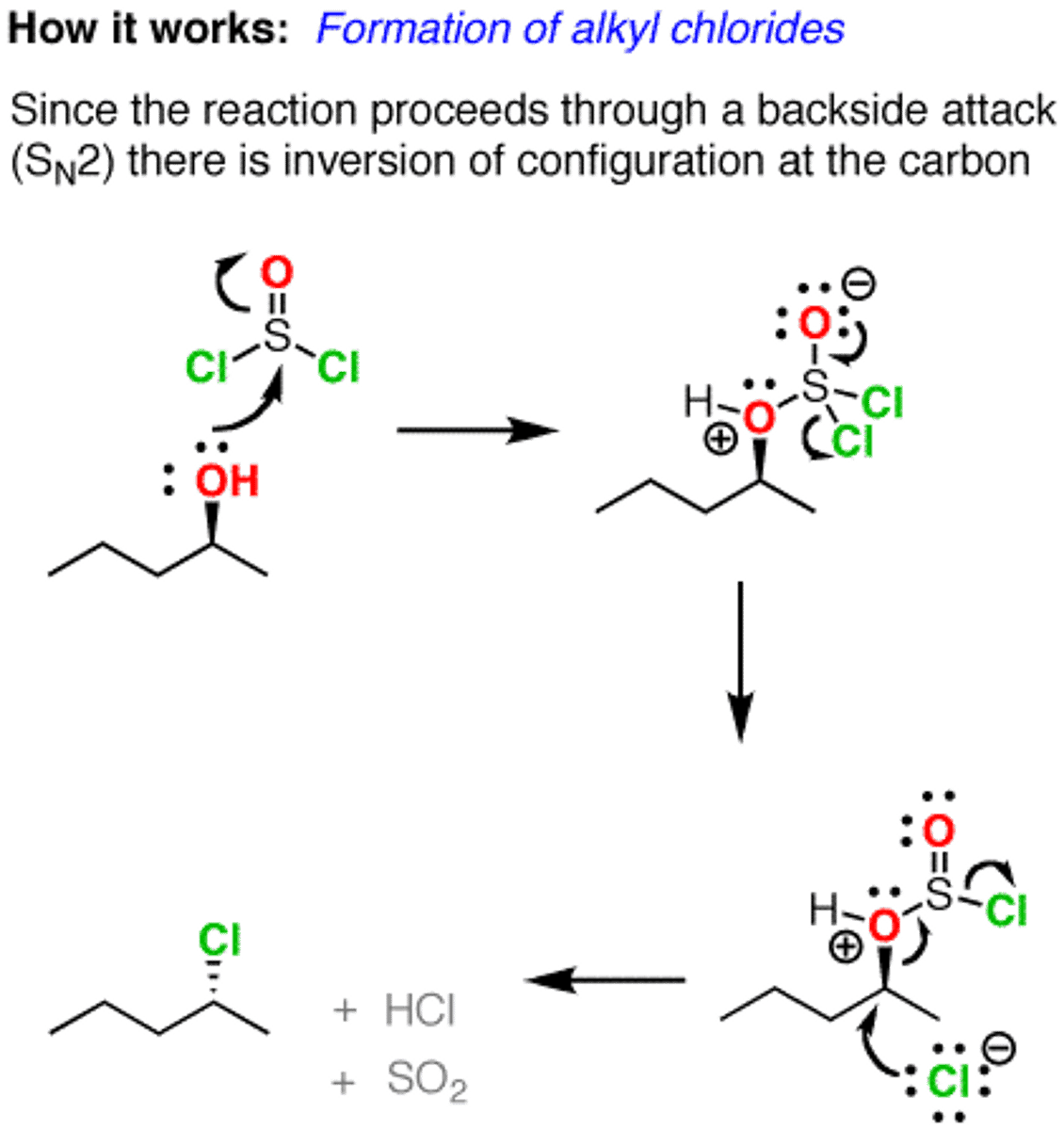
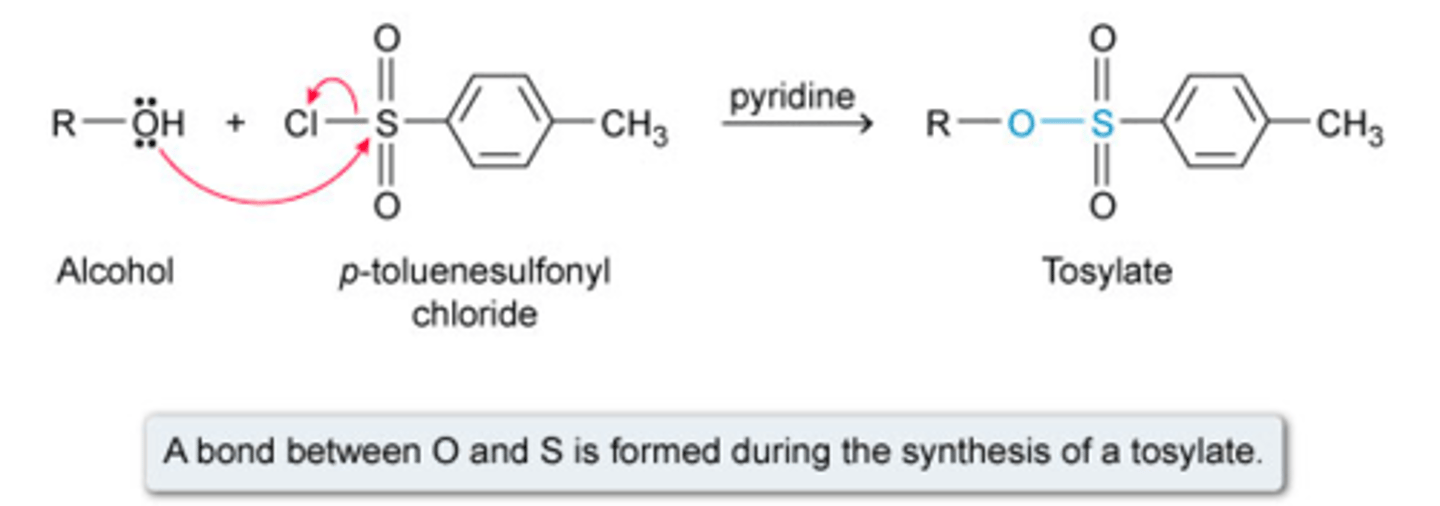
Reaction of alcohols with MsCl or TsCl
Cyclohexanol + TsCl
Forms haloalkanes
only works with primary and secondary alcohols
occurs via SN2 mechanism, so no rearrangements
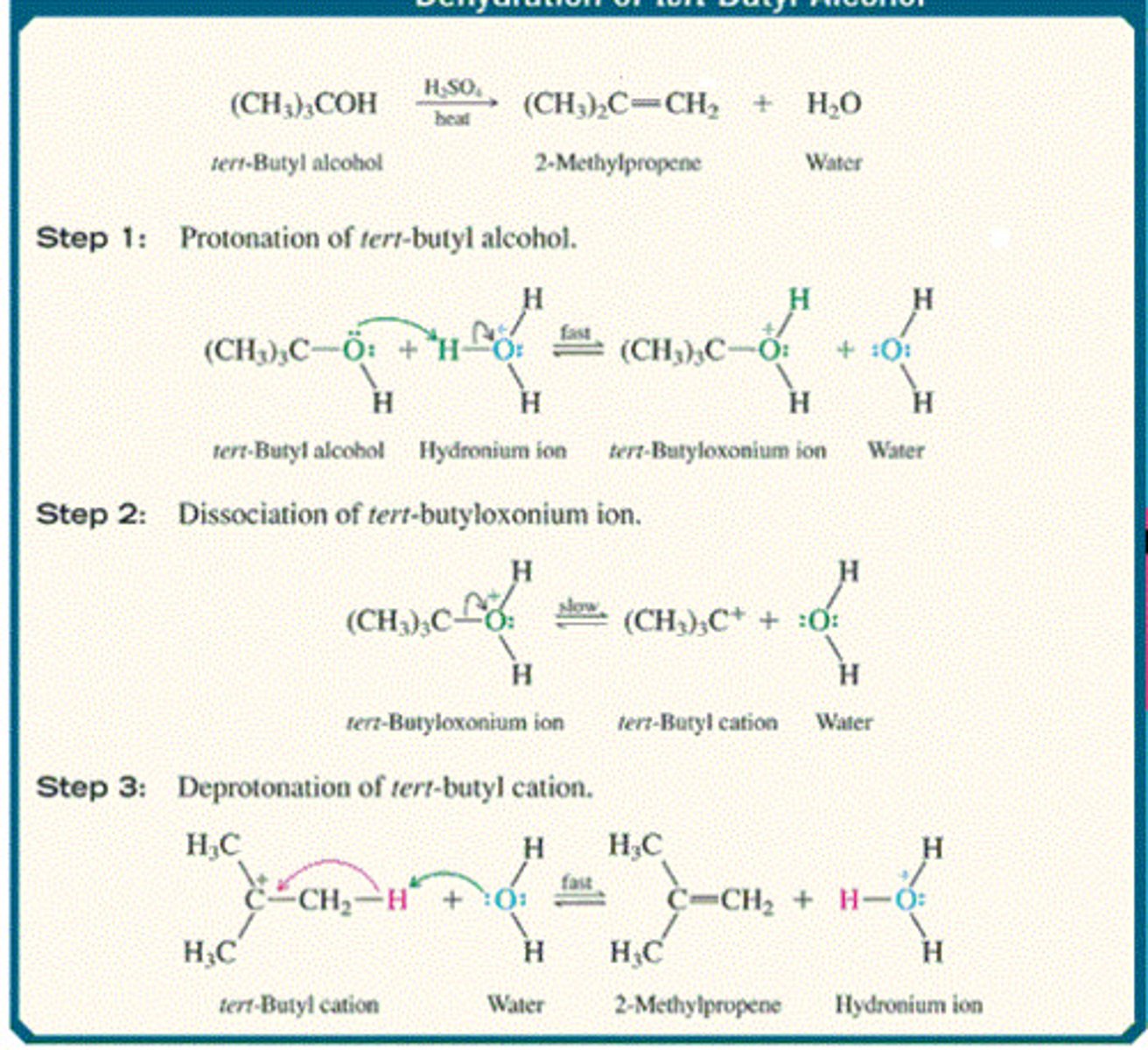
Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol
tert-Butyl alcohol + H2SO4
2-Butanol + H2SO4
1-Butanol + H2SO4
Forms alkenes
the more substituted the alchol, the easier it is to dehydrate
dehydration of 1º and 2º alcohols is often accompanied by rearrangement
occurs via an E1 mechanism (i.e., carbocations are formed)
the most stable product predominates
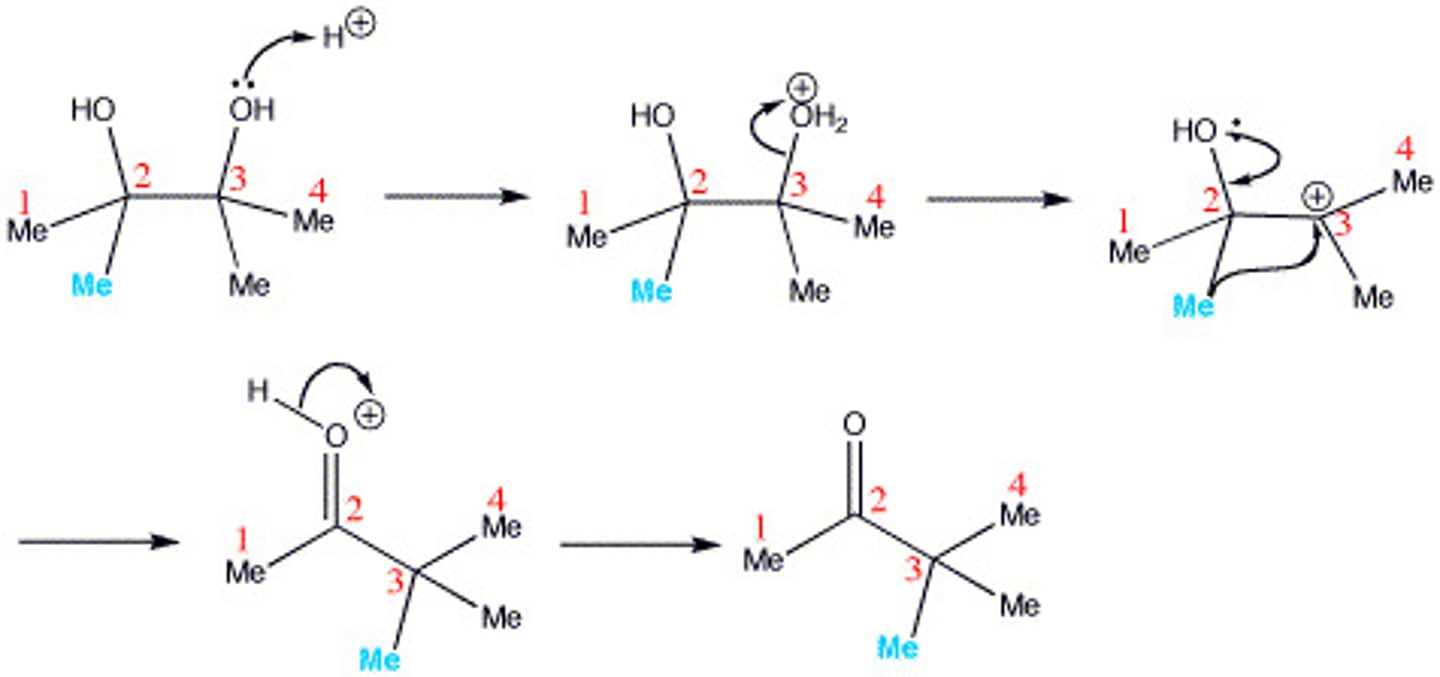
Pinacol rearrangement of diols
2-Methyl-1,2-Propanediol + H2SO4
the more substituted OH group is the one that leaves first
results in a ketone/aldehyde
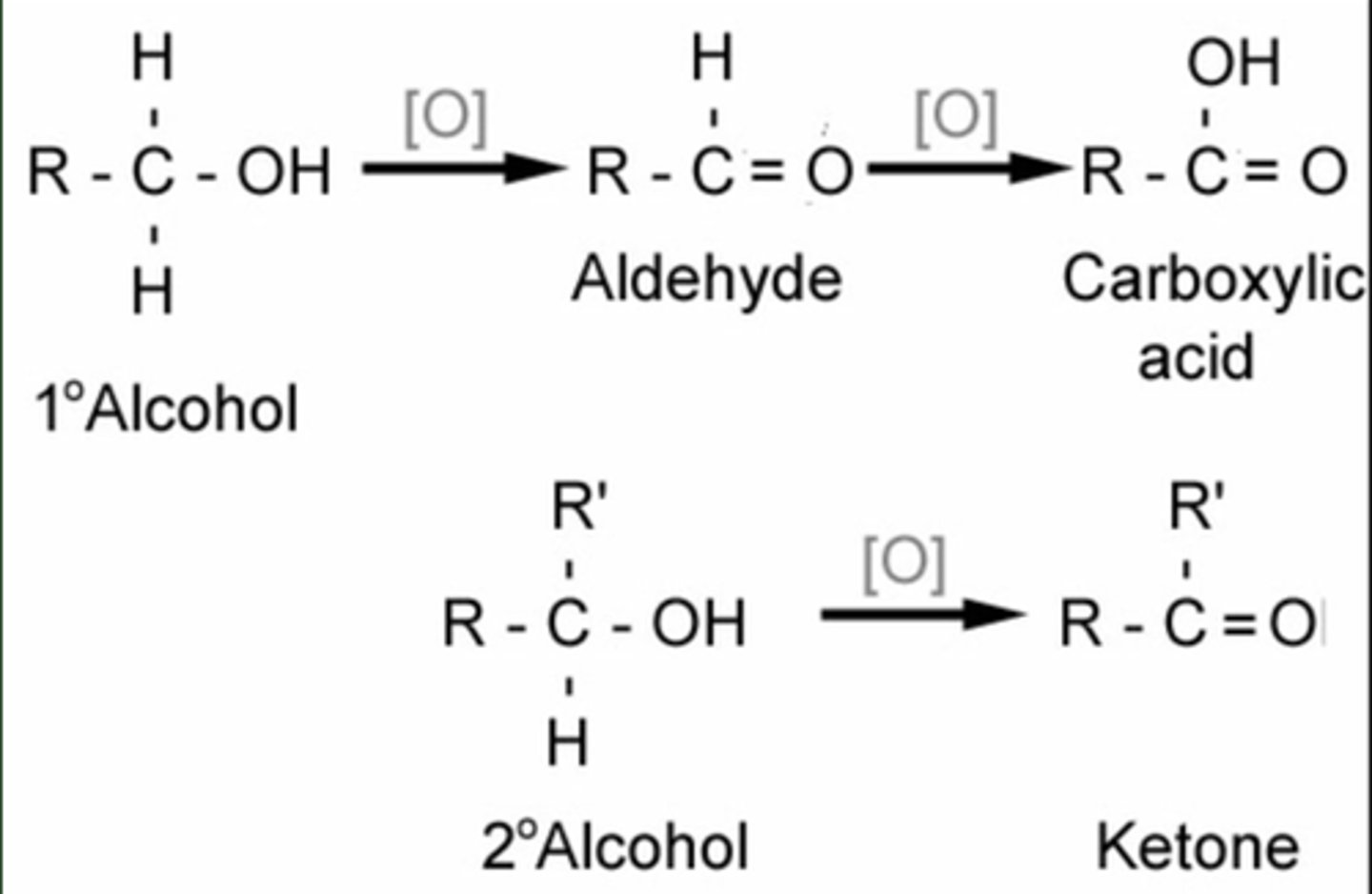
Oxidation of alcohols with Jones Reagent
1-Hexanol + H2CrO4
Cyclohexanol + H2CrO4
1º are oxidized to aldehydes/carboxylic acids
2º are oxidized to ketones
3º are not oxidized
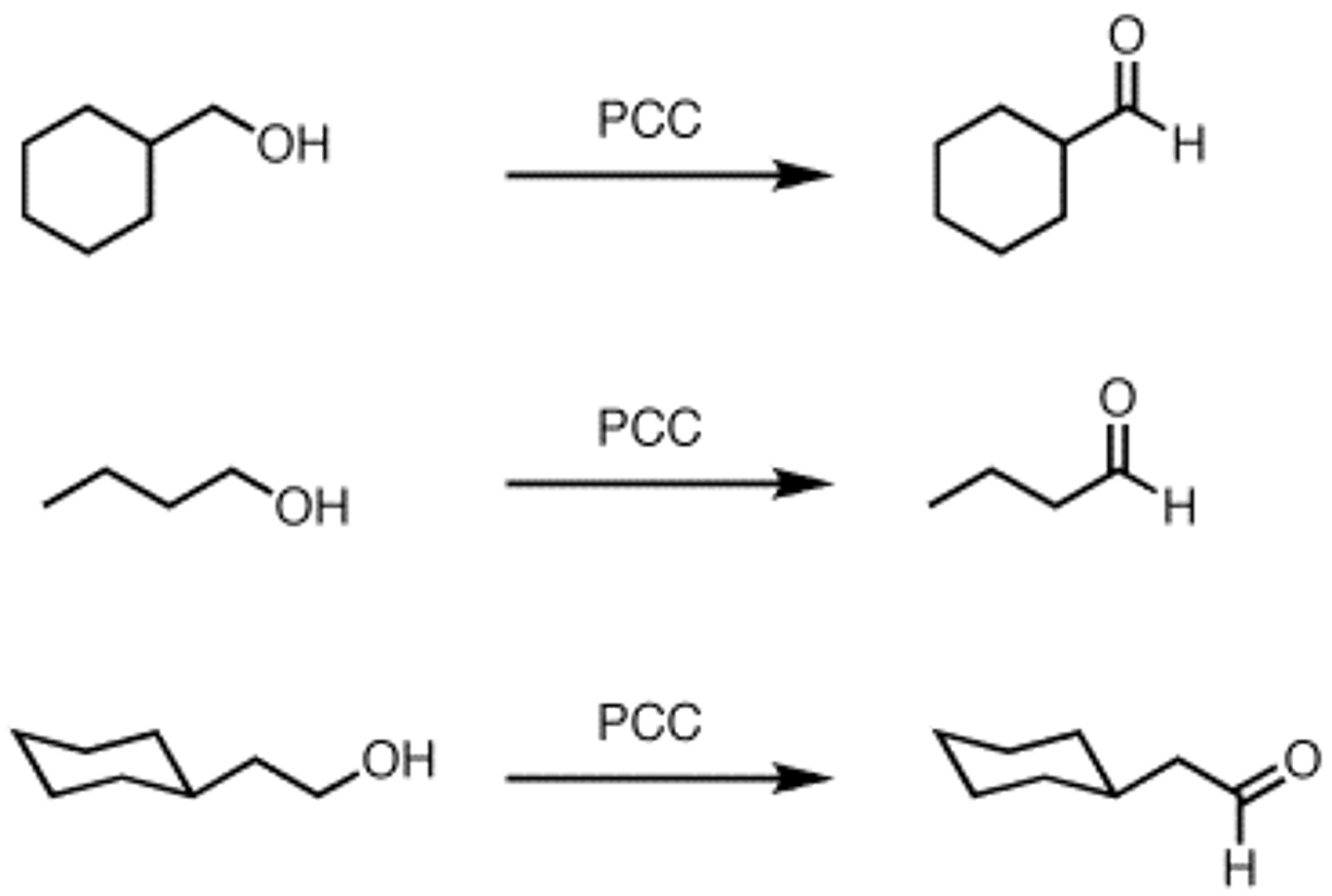
Oxidation of alcohols with PCC
1-Butanol + H2CrO4
1º are oxidized to aldehydes
2º are oxidized to ketones
3º are not oxidized
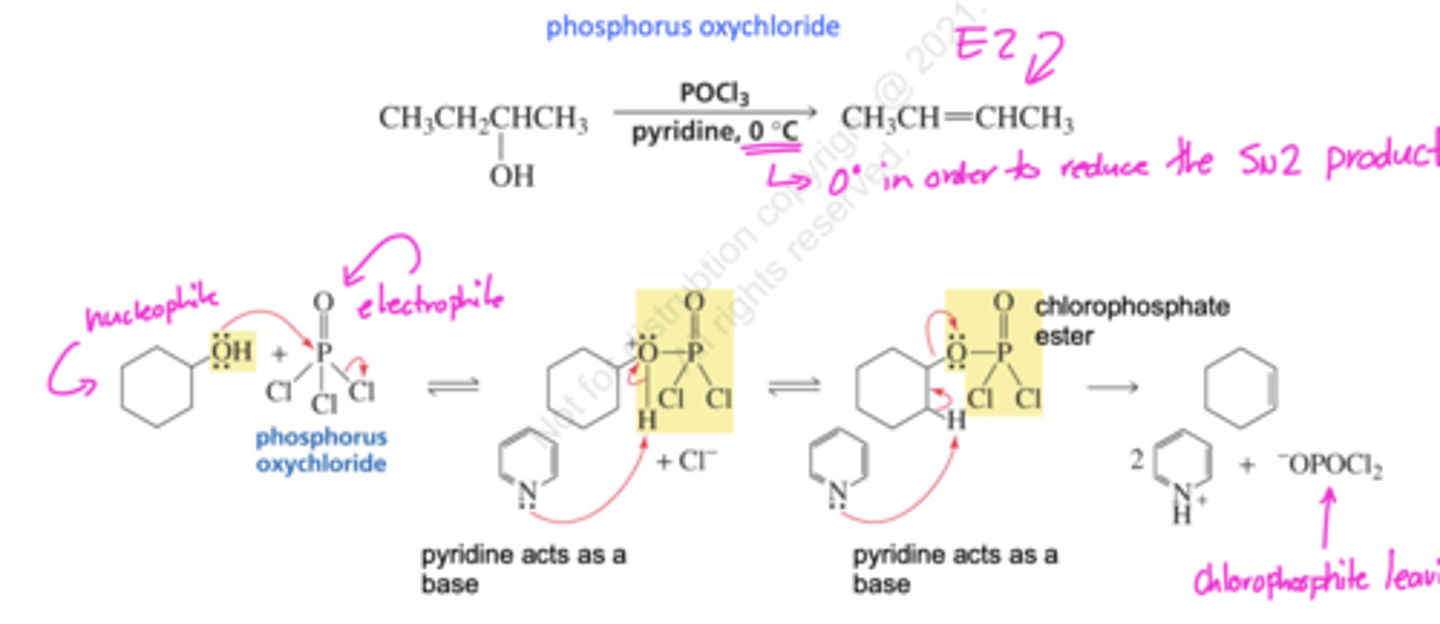
Reaction of alcohols with POCl3
1-Butanol + POCl3
forms an alkene via a E2 mechanism
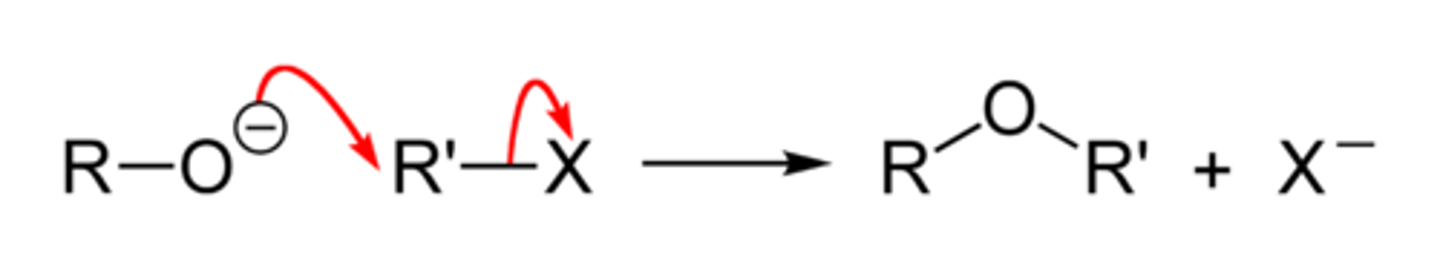
Williamson Ether Synthesis
CH3CH2CH2ONa + CH3CH2Br
Involves the nucleophilic displacement of a halide by an alkoxide ion via an SN2 mechanism
works best on 1º halides, less well on 2º halides, and fails completely on 3º halides due to competition with E2 mechanism
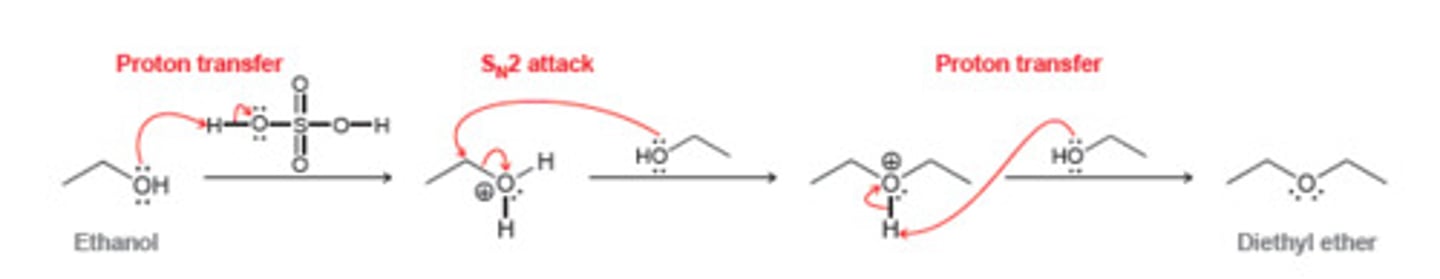
Ether Formation by Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of Primary Alcohols
CH3CH2OH + H2SO4
Works best with 1º alcohols, less well with 2º alcohols, and fails completely with 3º alcohols due to competition with dehydration to an alkene
Occurs via an SN2 mechanism
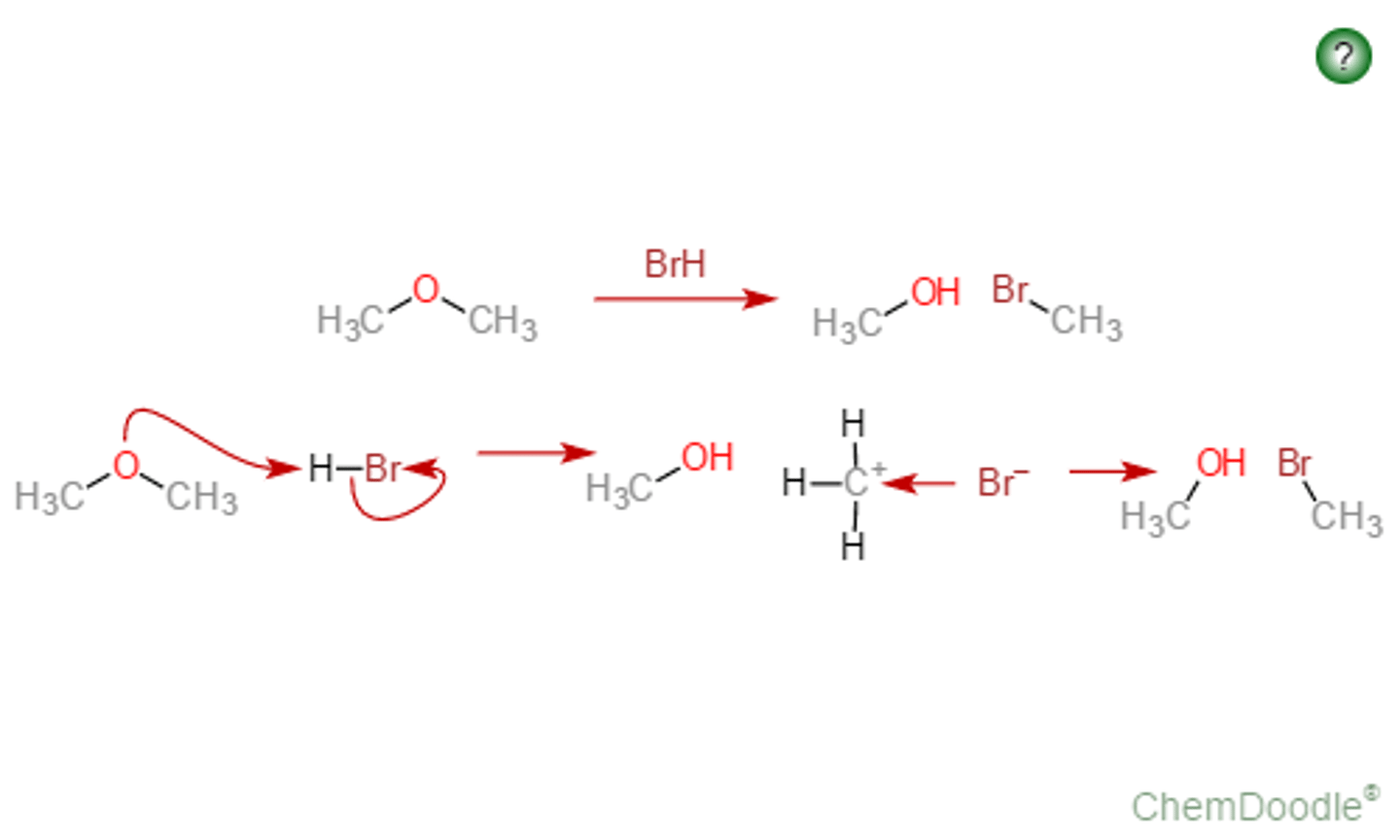
Cleavage of Ethers by HX
CH3OCH3 + HBr
Produces an alcohol and an alkyl halide
1º reacts via SN2 mechanism
2º and 3º react via SN2 mechanisms
the alcohol reacts further with the HX to form another molecule of alkyl halide
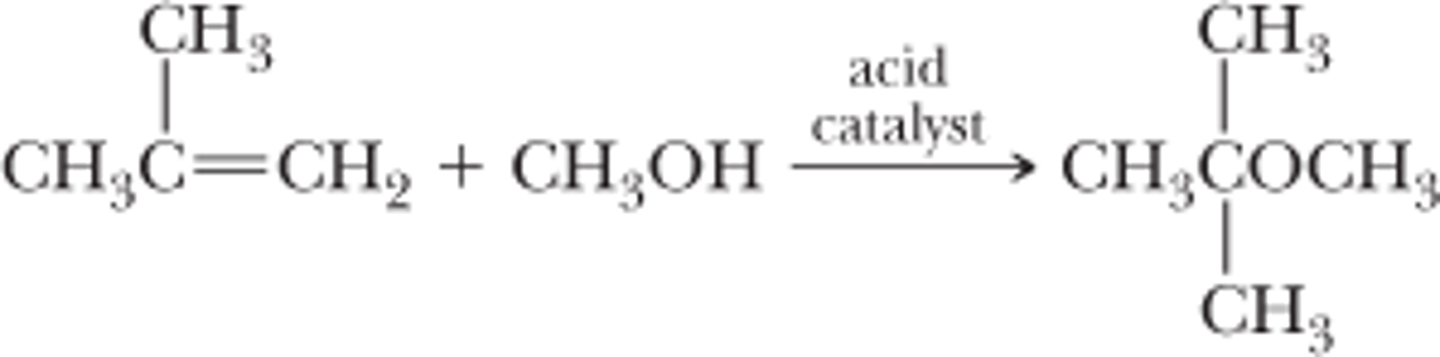
Synthesis of an Ether from an Alkene
2-methylpropene + methanol
can only be done with alkenes that form stable carbocations and primary alcohols
alcohol acts as a weak nucleophile to attack the carbonation formed by the alkene via an SN1 mechanism
requires an acid catalyst
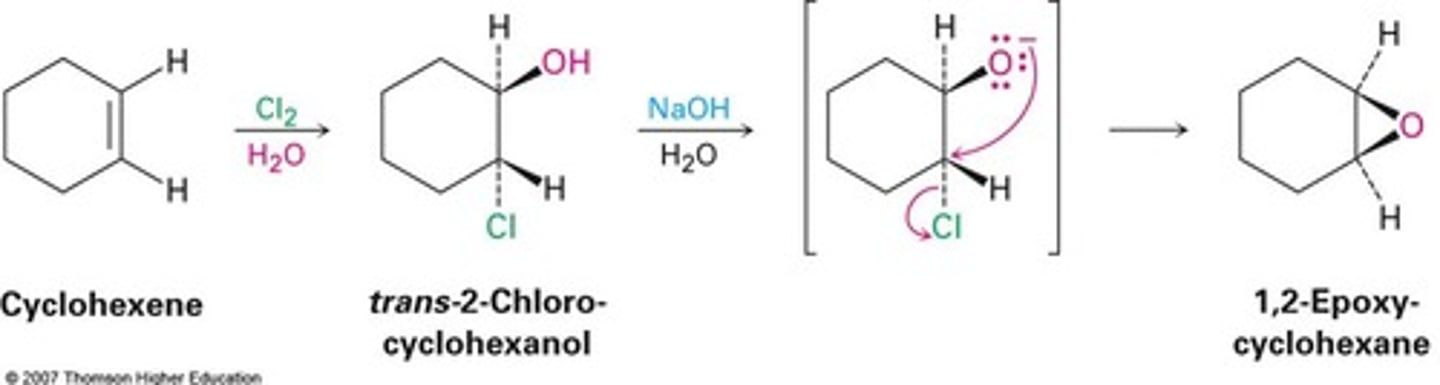
Synthesis of Epoxides from Halohydrins
cyclohexene + (1) Cl2 (2) NaOH
occurs via an internal SN2 mechanism
configuration is conserved
can only occur in basic conditions
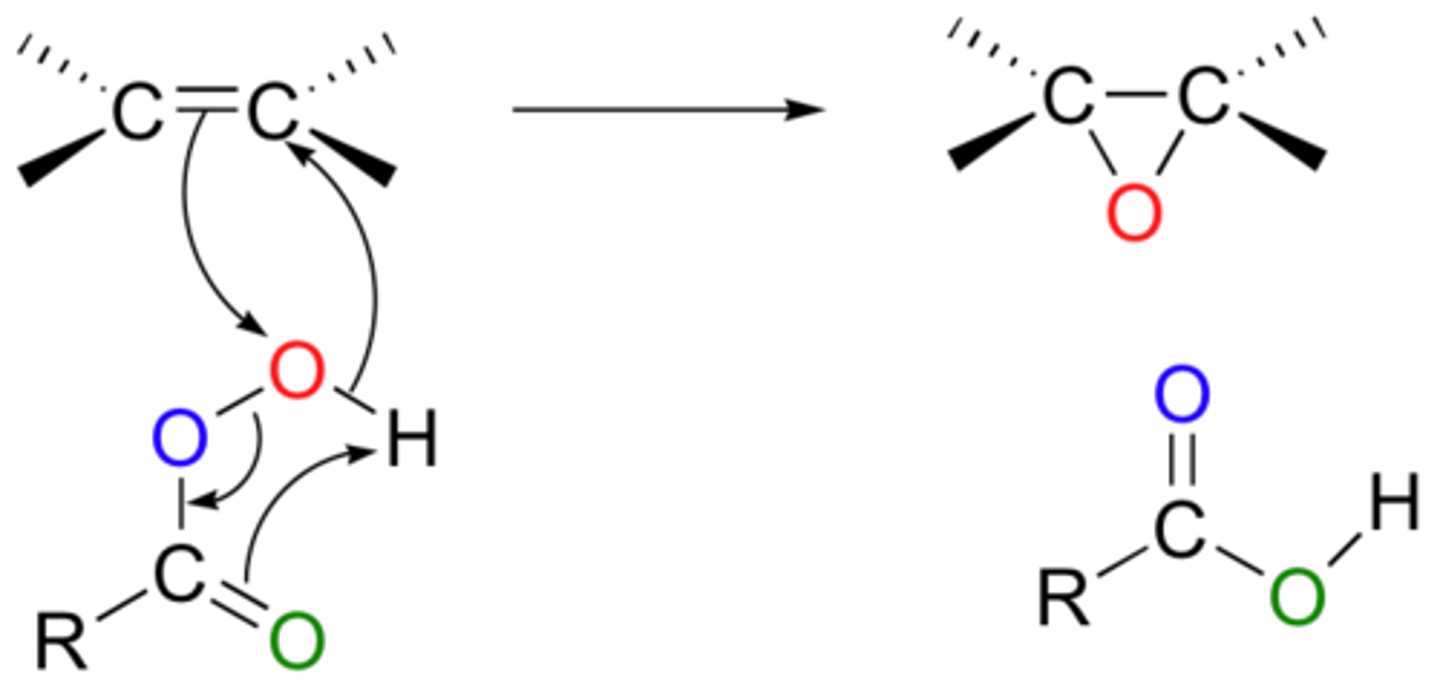
Oxidation of alkenes with peroxyacids (MCPBA)
cyclohexene + RCOOOH
forms epoxides
configuration is conserved
the steps of this reaction are concerted
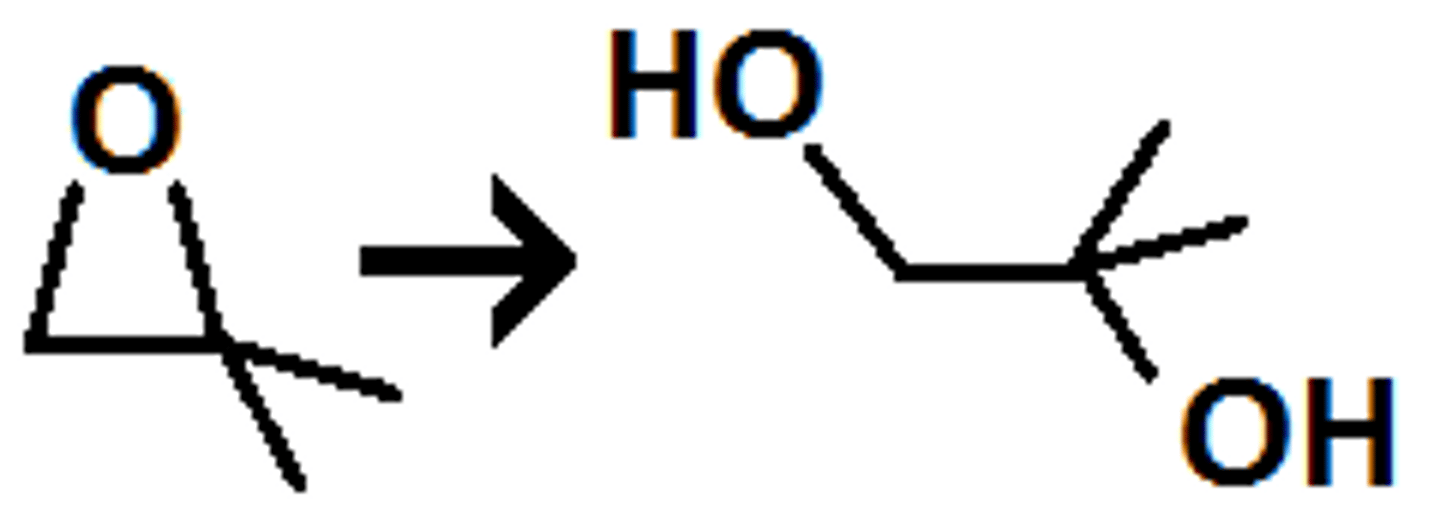
Acid Catalyzed Ring Opening of Epoxides
Ethylene Oxide + H2O
produces trans glycols
nucleophile attacks more substituted carbon
Nucleophilic Ring Opening of Epoxides
Propylene Oxide + CH3ONa
nucleophile attacks less substituted carbon
occurs via an SN2 mechanism
attack of the nucleophile is anti to the leaving group, resulting in an inverse in configuration
Reaction of Alkynes with NaNH2
CH3CCH + NaNH2
forms an alkyne; if terminal, it forms an alkyne carbocation
the carbocation can then act as a strong nucleophile and react with other molecules (e.g., alkyl halides, acids, etc)
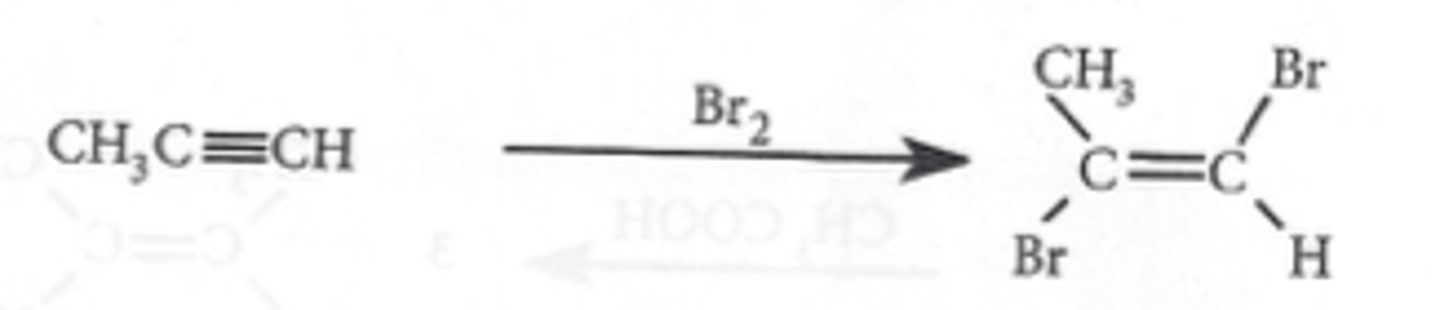
Electrophilic addition of alkynes
CH3CCCH3 + Br2
CH3CCH + HBr
addition of a halogen gives a dihaloalkene; the halogen atoms are added anti to one another
same mechanism as addition to alkenes
follows Markovnikov's rule
Hydroboration-Oxidation of an Alkyne
follows anti-Markovnikov addition; the OH group adds to the less substituted carbon
forms an enol, which immediately rearranges to form a more stable ketone/aldehyde
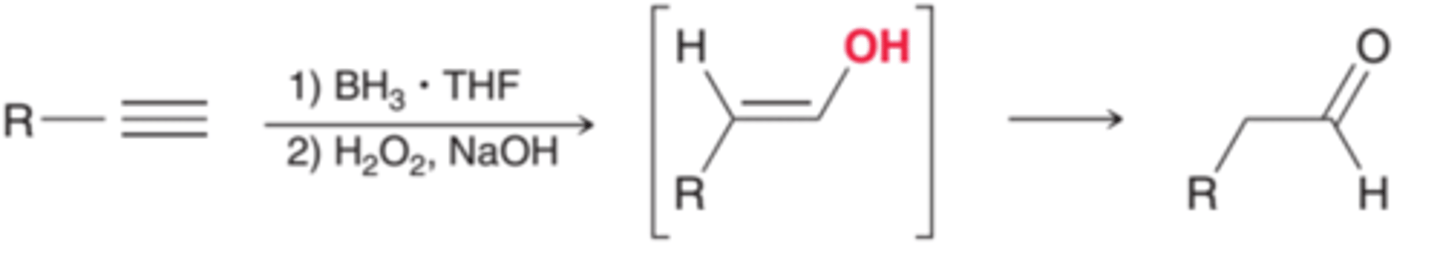
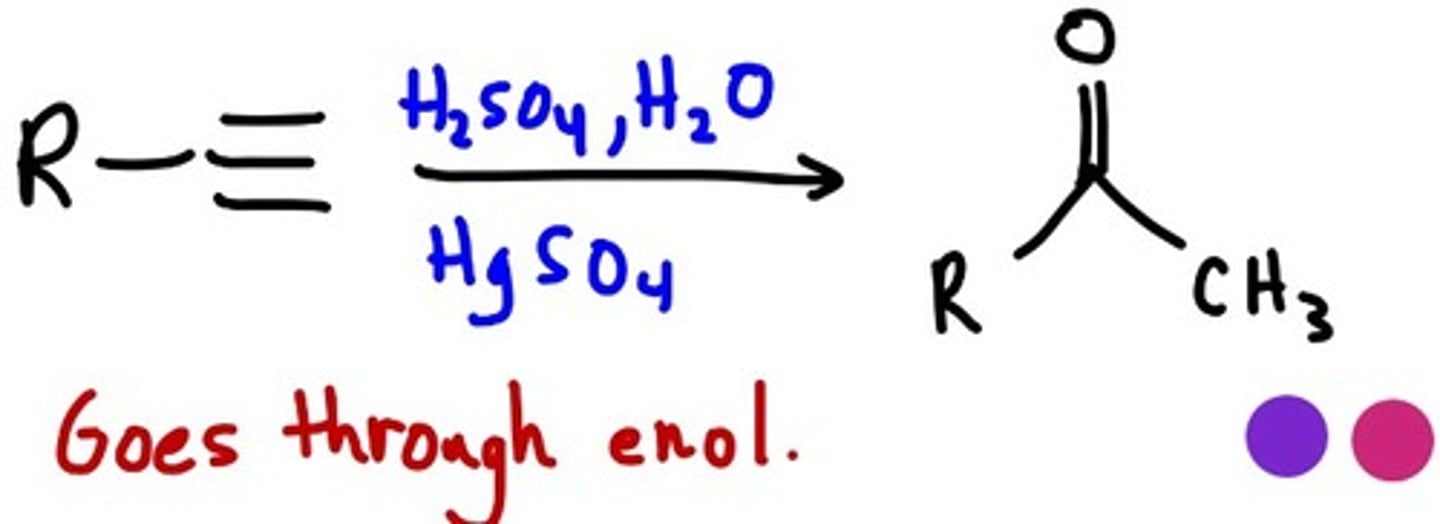
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of an Alkyne
CH3CCH + H2O
Follows Markovnikov's rule; the OH group adds to the more substituted carbon
forms an enol, which immediately rearranges to form a more stable ketone/aldehyde
Catalytic Reduction of Alkynes
CH3CCCH3 + H2 (Lindlar)
CH3CCCH3 + 2H2 (Ni)
Forms cis alkene with Lindlar catalyst
Forms alkane with other transition metal catalyst
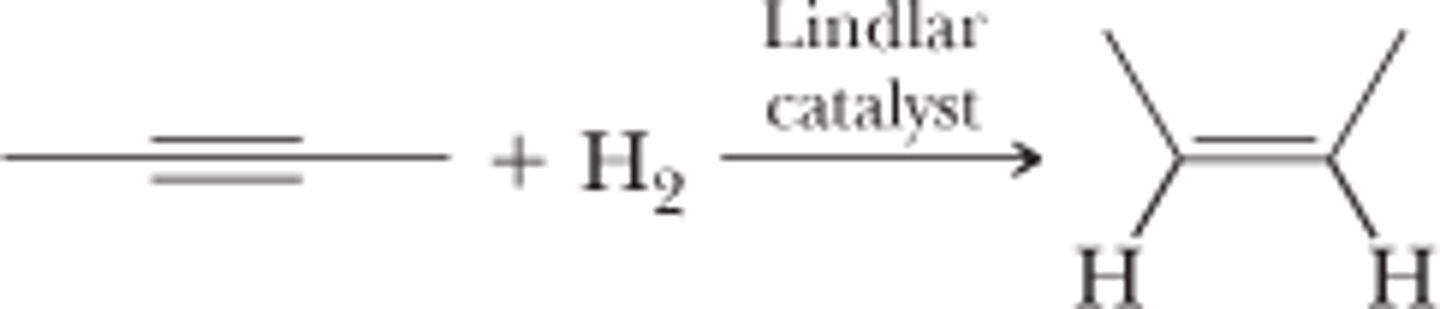
Dissolving Metal Reduction of Alkynes
CH3CCCH3 + 2Na (NH3)
forms trans alkenes
involves the anti addition of two hydrogen atoms to the triple bond