Inhalation Product Design and Testing
what are the considerations for inhaler design?
• Must ensure the right dose is delivered at the right time.
• The emitted dose should be of suitable aerodynamic particle size to be delivered to the peripheral airways.
• Patient and clinician acceptability.
• Cost of manufacturing.
• Easy of use
what are the aims of device design?
Compact - Convenient - Economical
– Consistent drug delivery
– High lung penetration
– Multiple dosing design
– Minimise device size
– Maximise patient convenience
– Optimise drug actuation
– Minimal side effects
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are the considerations for inhaler design?
• Must ensure the right dose is delivered at the right time.
• The emitted dose should be of suitable aerodynamic particle size to be delivered to the peripheral airways.
• Patient and clinician acceptability.
• Cost of manufacturing.
• Easy of use
what are the aims of device design?
Compact - Convenient - Economical
– Consistent drug delivery
– High lung penetration
– Multiple dosing design
– Minimise device size
– Maximise patient convenience
– Optimise drug actuation
– Minimal side effects
what are the scientific challenges to inhalation device design?
- Poor site-specific targeting
- Poor intracellular delivery - getting into cells
- Toxicology & immunogenicity
- Poor in vitro-in vivo correlation
- Formulation Instability - how it is stability enhanced
what are the industrial and regulatory challenges to inhalation device design?
- £££ - device design required
- Lack of licensed excipients
- Inadequate screening tools
- Inefficient delivery
- Multi-drug regimens
- Patient acceptability
how are most pulmonary products tested and why?
- tested in vitro
- In vitro study determines performance in a controlled environment outside of a living organism.
- Allows prediction of the effects of the formulations in vivo (within body)
- Simpler, more convenient, often cheaper and more detailed
analysis is possible compared to in vivo
• 3Rs: reduction, refinement and replacement
- in vitro easier and more controlled than in vivo
what is the process in designing a new inhaler?
- fully characterised drug formulation
- device selection
- dose retrieval
- characterisation post aerosolization
- bioactivity pre/post aerosoliation
- breathing simulator studies
- in vitro bioactive inhaled therapeutic
- in vivo studies
what are the BP tests for inhaled devices?
1. Uniformity of delivered dose
2. Fine particle dose
3. Aerodynamic particle size distribution
4. Number of deliveries per inhaler
5. Effectiveness of antimicrobial preservative
6. Leakage (pMDIs)
what is uniformity of delivered dose?
- Ensure consistency of the dose emitted and the fine particle
mass throughout the life of the container (from the first dose
until the last labelled dose).
- To ascertain that the inter- and intra-device variability of the
dose is acceptable.
- A dose collection apparatus containing a filter is used.
- Generally >10 doses from the
combination of the beginning,
middle, and end of the container
be tested, and >3 containers from
two different batches.
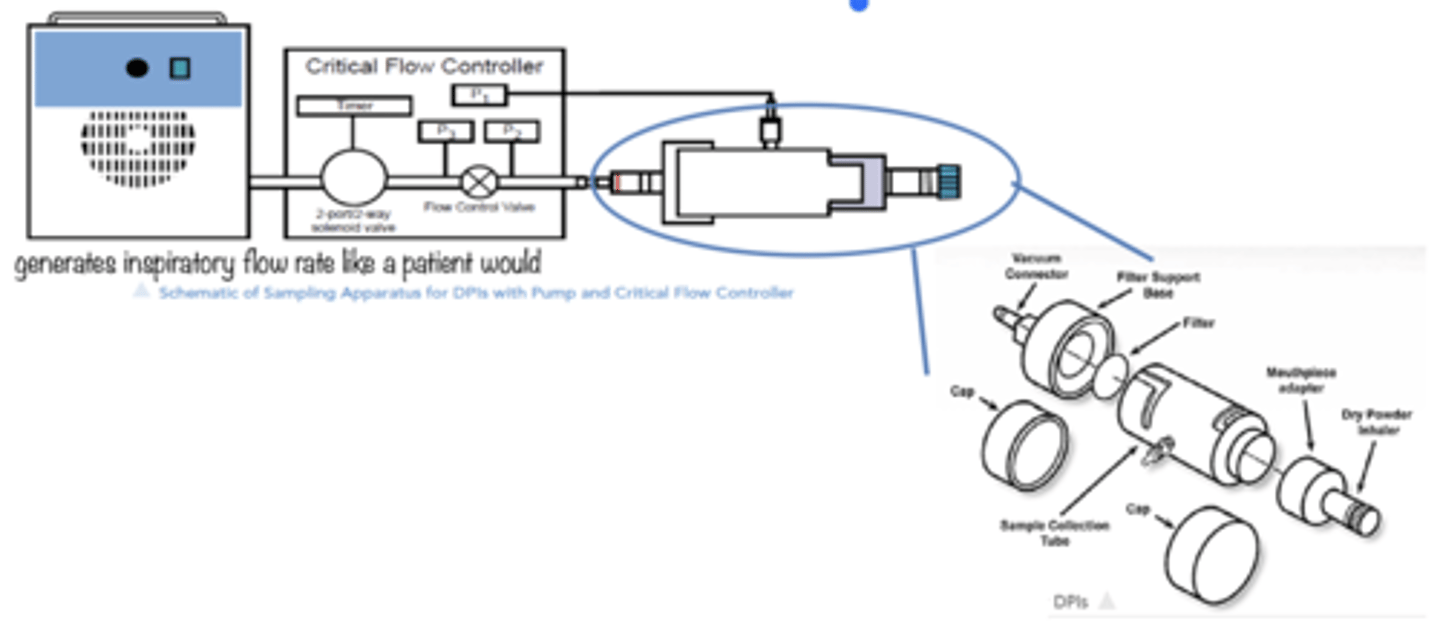
what is the dose collection apparatus for DPIs?
- DPIs reply on patient's inspiratory flow rate rather than a
propellant for dose emission.
• A critical flow controller is used to allow adjustable flow and
inhaled volume of a typical patient
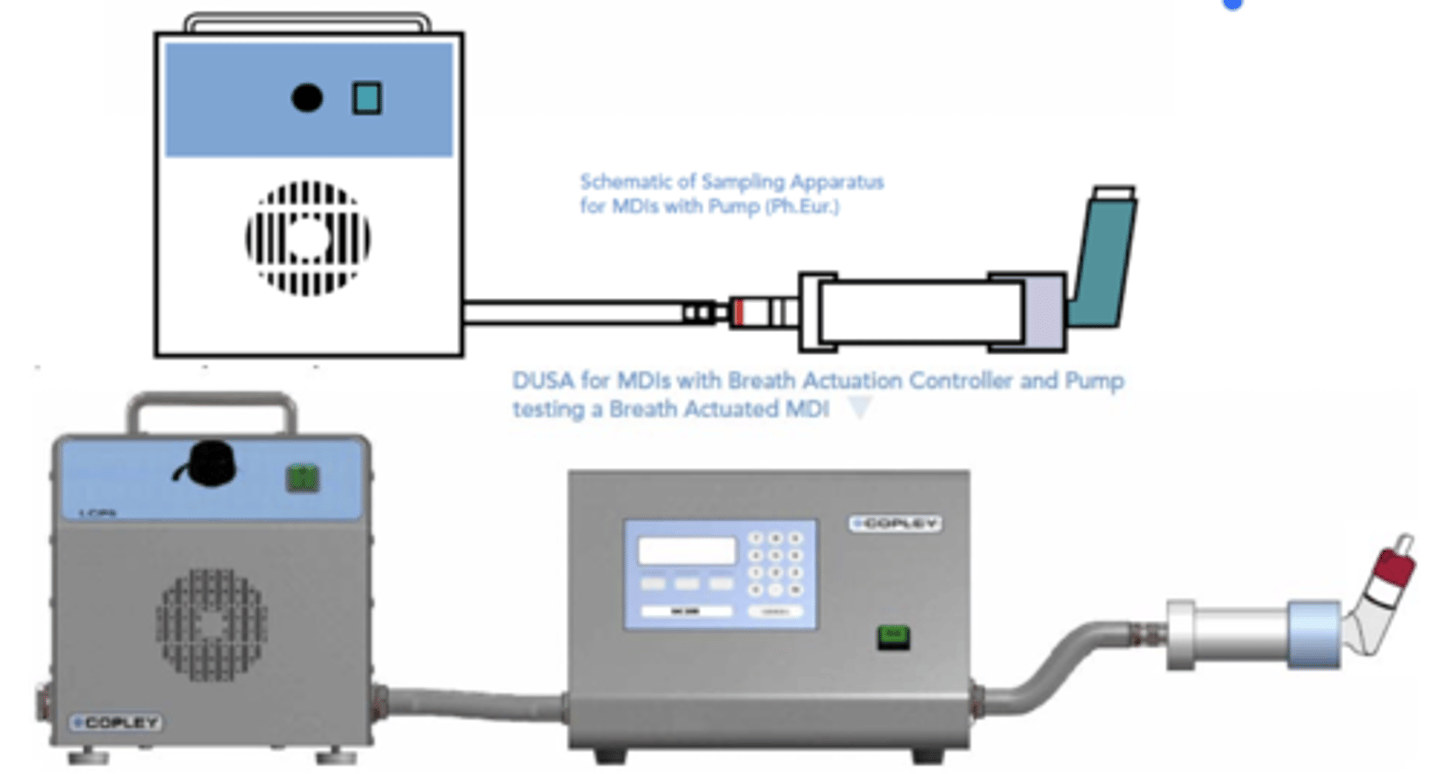
what is the dose collection apparatus for pMDIs?
• The vacuum source is adjusted to draw air through at 28.3
L/min (± 5%) continuously through the apparatus to avoid
loss of the active substance into the atmosphere
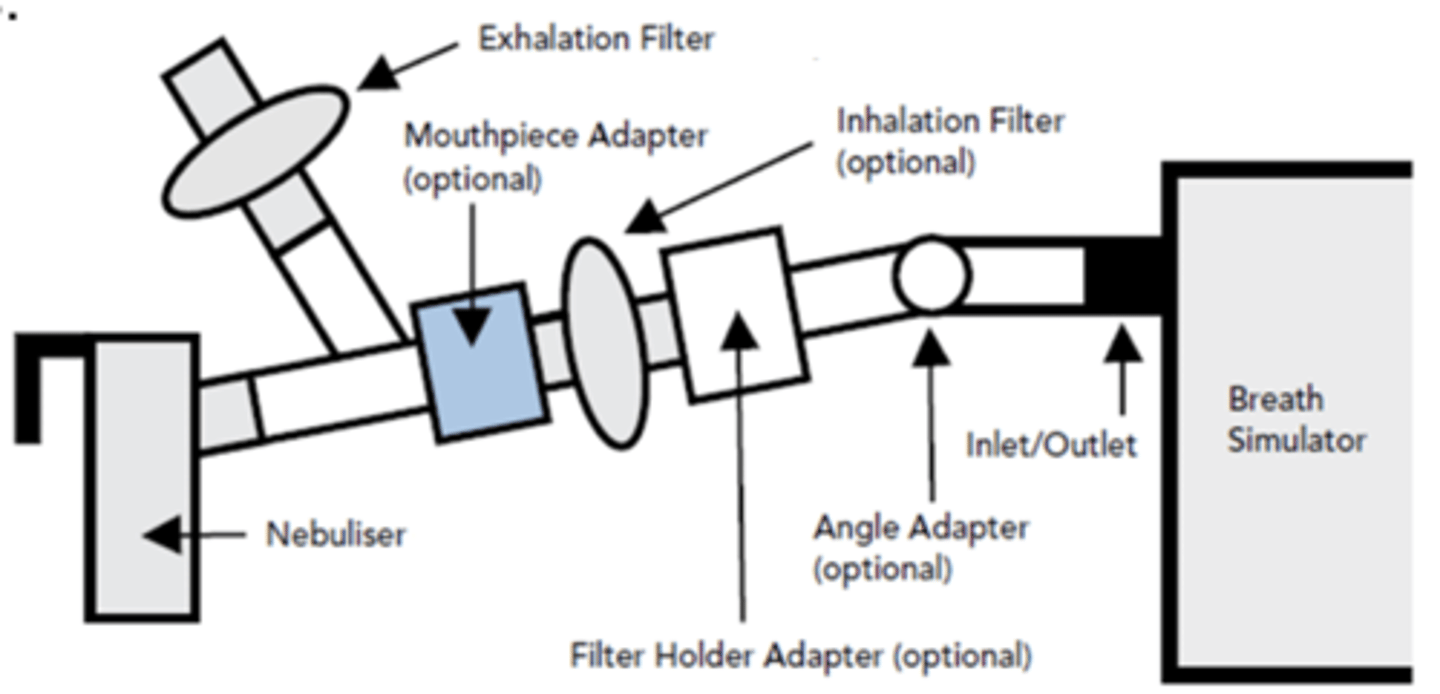
what is the dose collection apparatus for nebulisers?
• The breathing pattern is particularly important as it
determines the amount of API available to the patients.
• So the tests are based on standardised tidal flow conditions
generated by a breath simulator, as opposed to fixed flow
rates.
what is fine particle dose/fraction?
• The amount or fraction of delivered dose that lies below the 5μm cut-off.
• Determined in parallel to aerodynamic particle size distribution.
• Cascade impaction techniques.
what is aerodynamic particle size distribution?
• Aerodynamic size distribution determines where the API is deposited.
• The fraction that will deposit in the lung is often referred to as the fine particle fraction (FPF).
- The optimal size for peripheral airway deposition upper limit is 5μm.
- Generally no lower limit is defined, but under 1μm likely to be exhaled.
how is particle deposition determined?
• In vitro techniques can determine aerodynamic size hence predict deposition in vivo.
• BP approved technique is the cascade impactor to:
- Determine aerodynamic size of the aerosol generated.
- Ascertain the particle size is suitable for deposition in the lungs.
- Differentiate between API and other formulation components.
• Other methods only provide overall particle size distribution.
how do cascade impactors work?
• Cascade impactors comprise a series of progressively finer jets and collection plates.
• Separate particles on the basis of particle inertia (which is a function of velocity and aerodynamic particle size) without the need to know either particle density or shape.
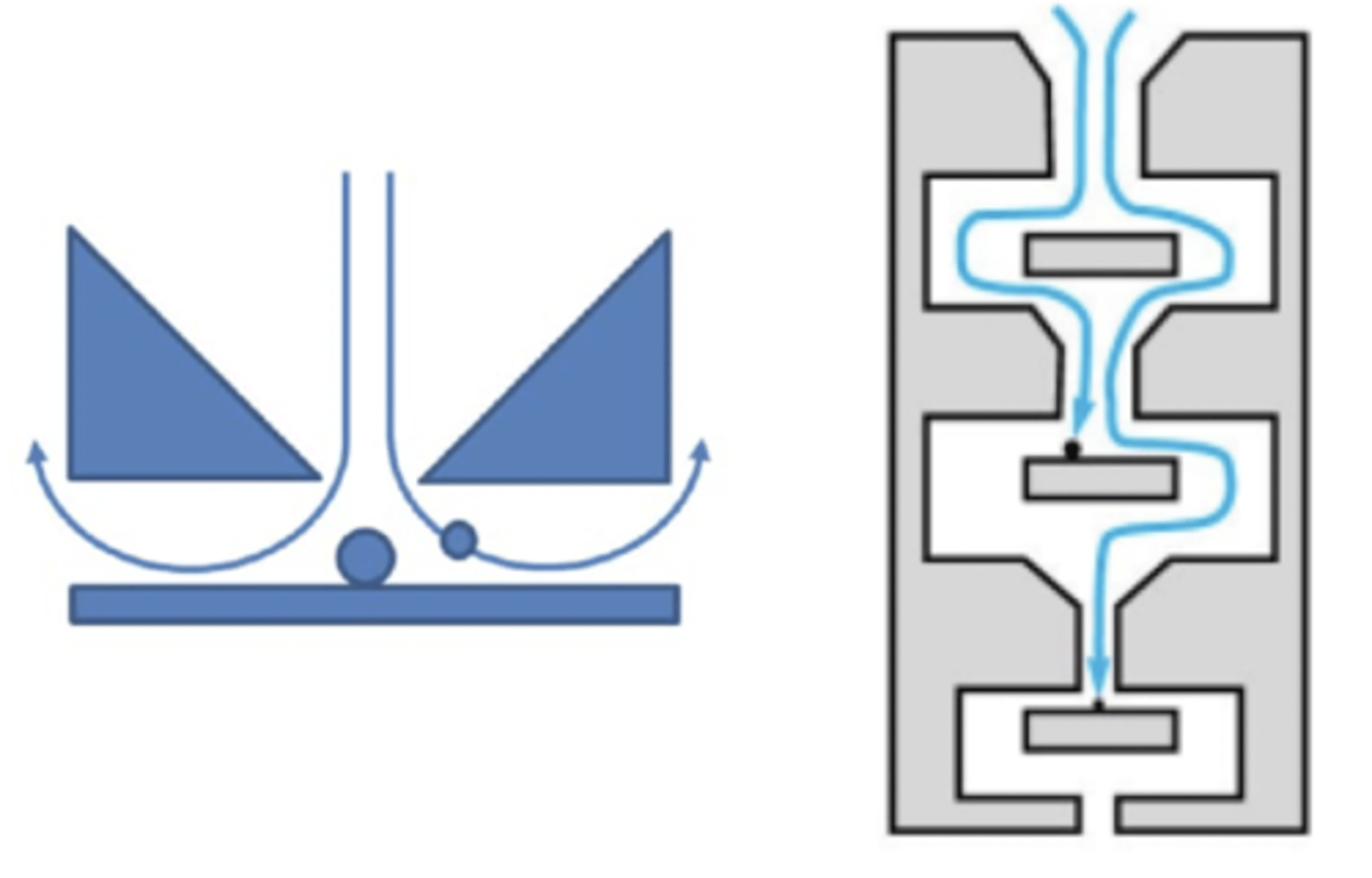
what is the process of operation of a cascade impactor?
• consists of a series of stages, each made up of a plate,
with specific nozzle arrangement and collection surface.
• Samples drawn into the impactor flowing sequentially through the stages.
• Nozzle size and total nozzle area decrease with stage number.
• Particles either remain in the air stream or break through the lines of flow impacting on the collection surface.
• Particles with sufficient inertia are collected, the rest pass onto the next stage.
• Each stage is associated with a cut-off diameter
- as nozzle size decreases, velocity increases, allowing collection of increasingly small particles
- any residual materials are captured in final stage
what are the types of cascade impactor designs?
- Apparatus A - Glass impinger
- Apparatus C - Multi-stage liquid impinger (MSLI)
- Apparatus D - Andersen cascade impactor (ACI)
- Apparatus E - Next generation impactor (NGI)

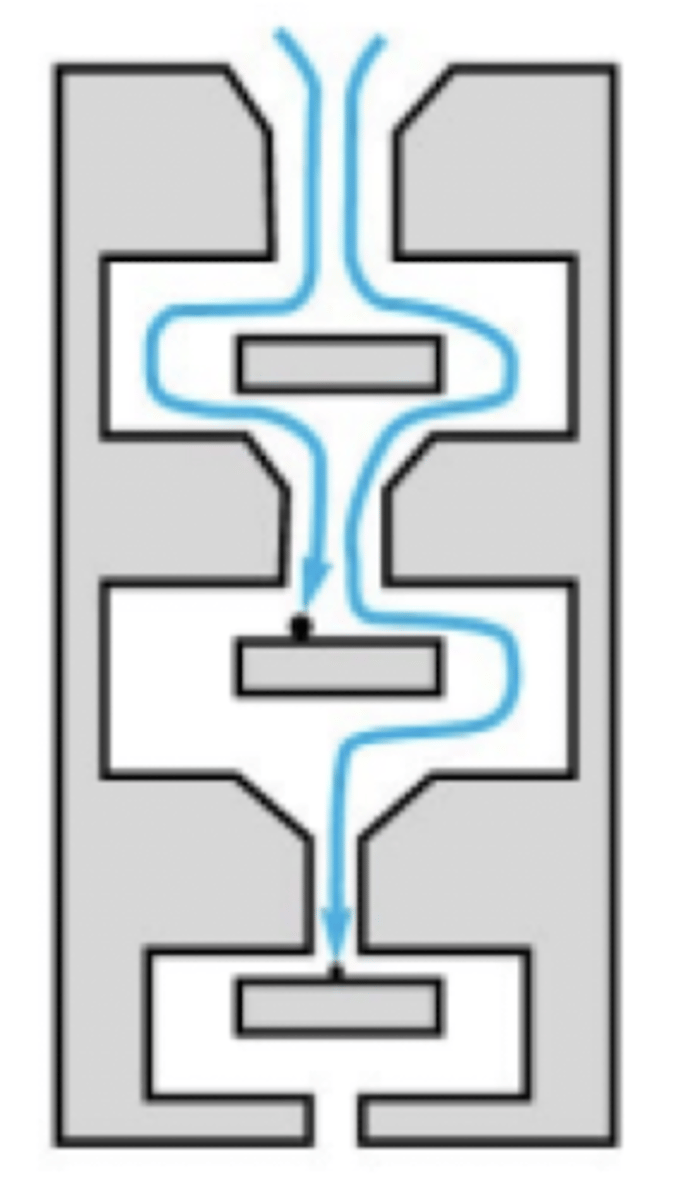
what are glass impingers? how do they work?
• Used in routine analysis to test pMDIs, DPIs, and nebulisers.
• Simple quick method but with limited information regarding particle size distribution.
• Particles collected in the throat and the upper impinger (stage 1) is considered 'non-respirable'.
• Particles collected in lower impinge (stage 2) is 'respirable'.
- The cut-off diameter is 6.4μm.
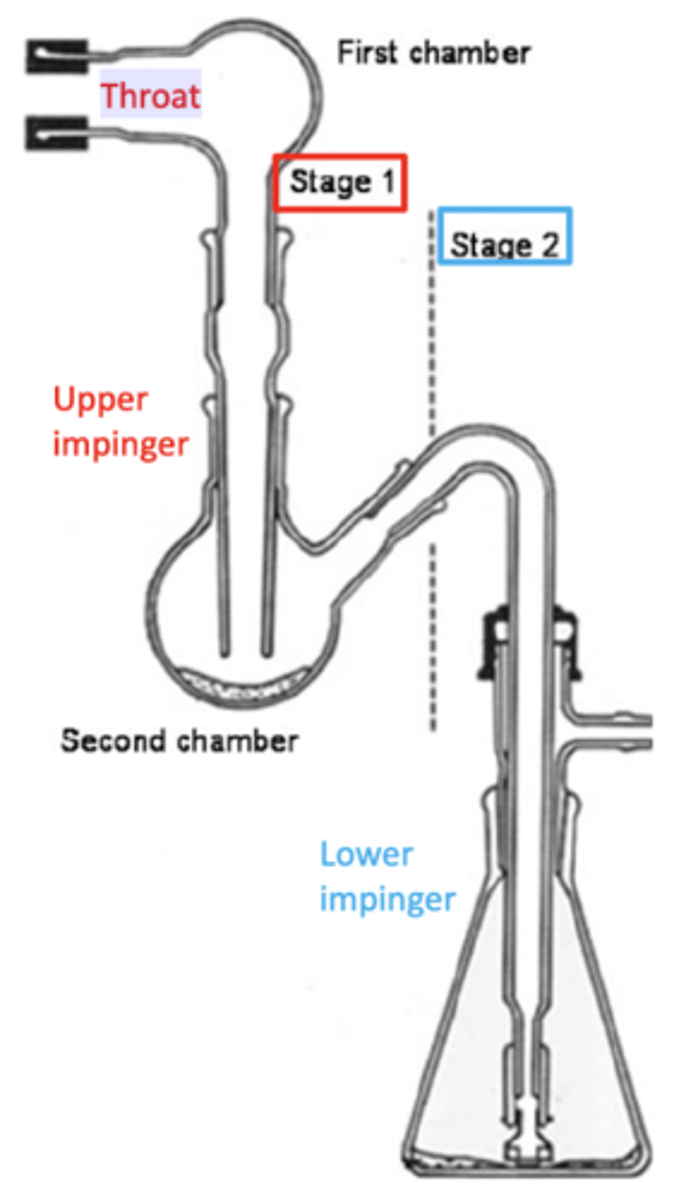
what are multi-stage liquid impinger (MSLI)? how do they work?
• For DPIs and pMDIs.
• The 4-stage with a filter terminal is most commonly used MSLI.
• It has no inter-stage losses.
• The collection stages are kept moist eliminates particle bouncing off the collection plates.
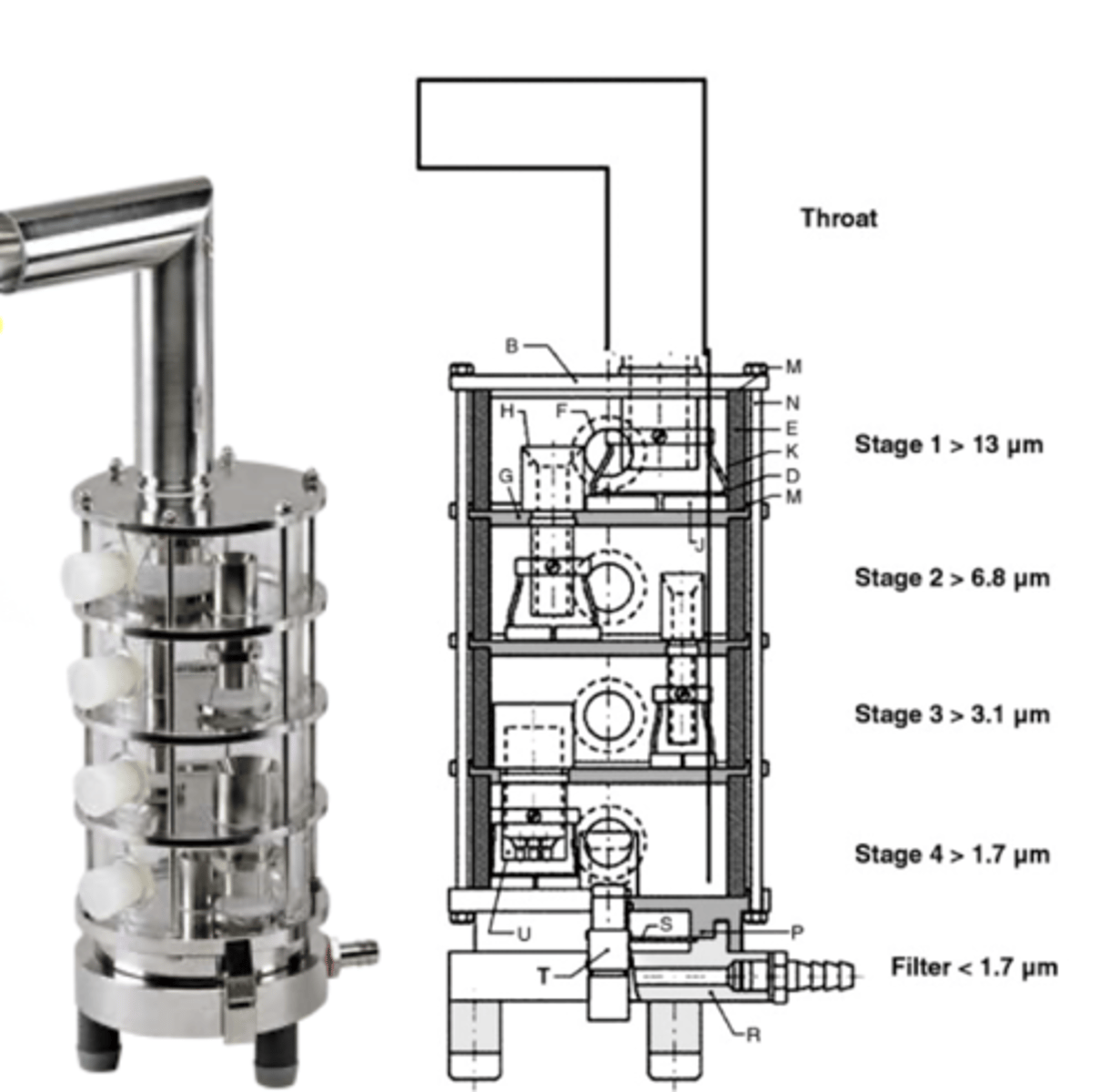
what are andersen cascade impactors (ACI)?
- 8-stage cascade impactor
• Suitable for MDIs and DPIs.
• Advantages of ACI:
- Easy to handle stack-up design.
- Damaged stages can be replaced.

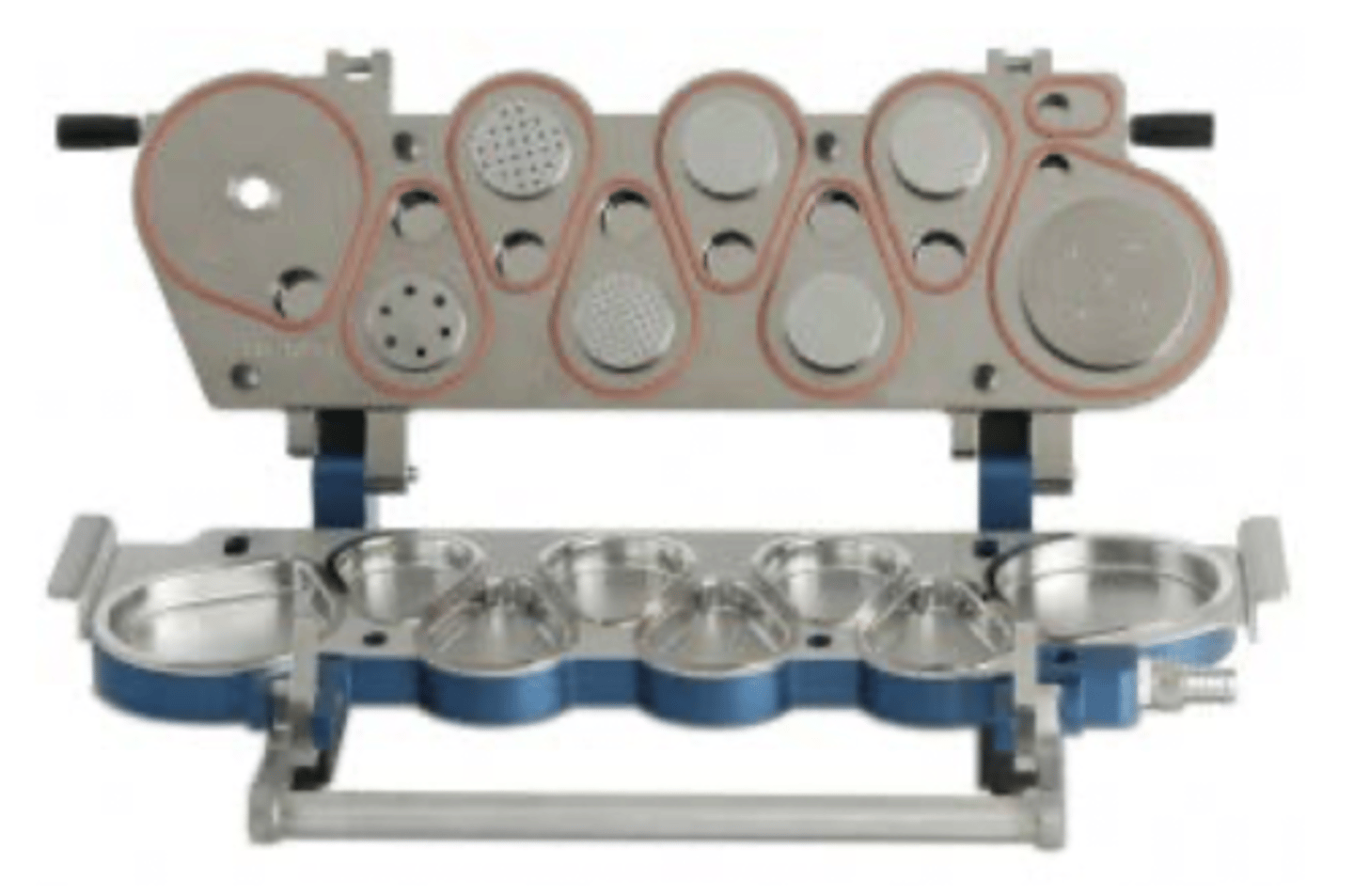
what are next generation impactors (NGI)?
- NGI uses collection cups rather than plates.
• Each stage has a cut-off diameter determined by flow rate
• Operates between 15-100 L/min flow rates.
• Test pMDIs, DPIs and nebulisers.
• High performance and precision with 7 stages plus a micro-
orifice collector.
what is the number of deliveries per inhaler test?
• Take an inhaler and discharge the contents to waste until
empty.
• Actuating the valve at intervals of not less than 5 sec.
• To meet the requirements: the total number of deliveries discharged from the inhaler must not less than the number stated on the product label
what is the efficacy of antimicrobial preservative test?
• Taking samples from its final container and inoculate with the appropriate micro-organisms, storing the inoculated preparation at a given temperature and given period.
• The preservative properties are adequate if there is a significant fall or no increase, as appropriate, in the number of micro-organisms in the inoculated preparation after the times and at the temperatures specified
what is the leakage pMDIs test?
• Formulation is a solution/suspension.
• The preparation passes the test if the total loss of mass over the entire shelf life (D) is not more than 10% of the nominal fill mass of the container - extrapolate date
• 12 containers selected and weighted (M1)
• Stood upright at 25 oC for not less than 3 days (T) and weighed again (M2)
• Leakage rate calculated in mg per year:
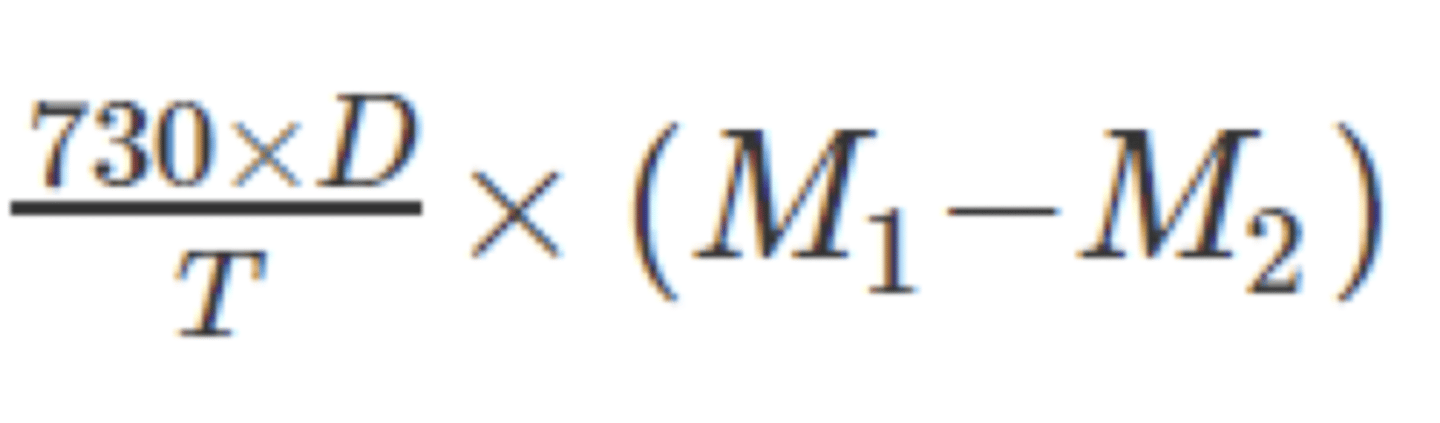
what are the two most critical tests for inhaled products outlined in the BP?
- delivered dose uniformity
- aedrodynamic particle size