Workshop 1 - respiratory function
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Spirometry
Measures lung volumes and flows
Useful for diagnosis of respiratory diseases
Capnography
Measure CO2 concentration in airway during respiration
Volumes and capacities
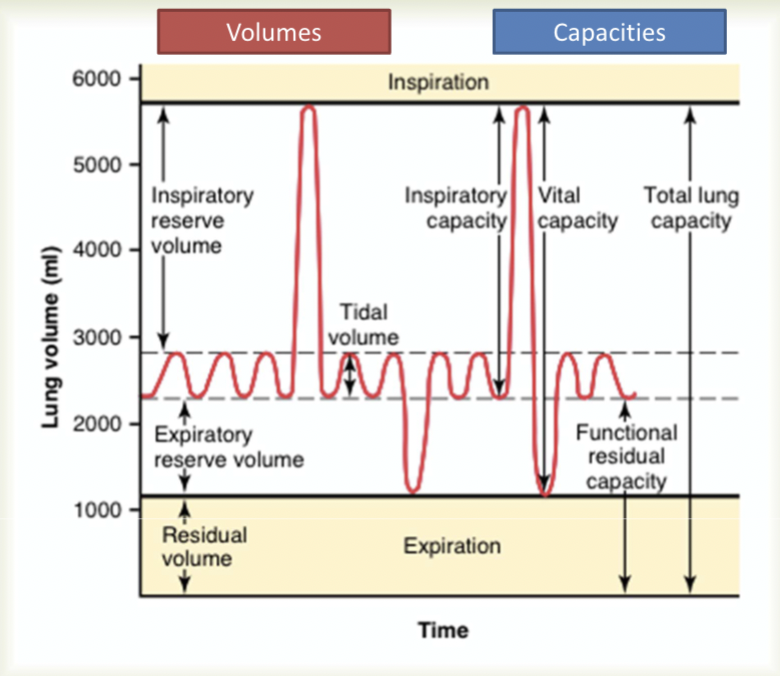
Spirometric values
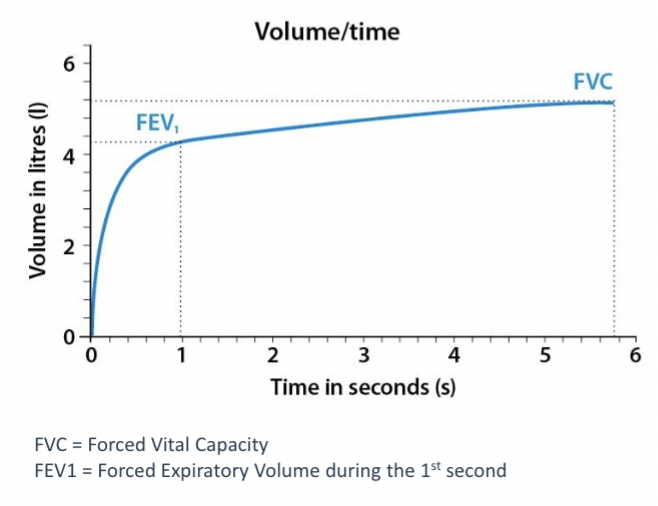
FVC - forced vital capacity - total air exhaled after maximum exhale effort
FEV1 - forces expiratory volume in 1 second - air exhaled in the first second of forced exhalation
FEV1/FVC ratio - determines airway obstruction severity
Graphical representation of spirometry - volume/time curve
Shows how quickly a person exhales
Relates volume expired with time taken for inspiration
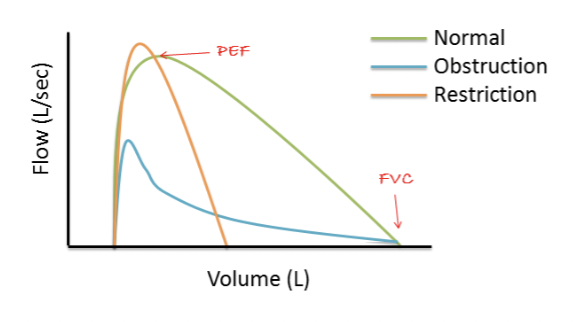
Graphical representation of spirometry - flow/volume curve
Relates flow expired at each instant with the volume expired at that instant
Harder to interpret but are more detailed
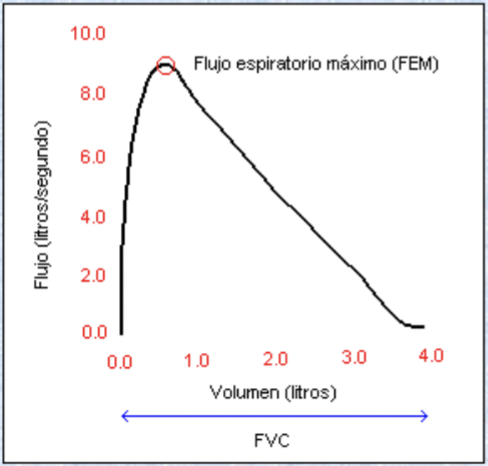
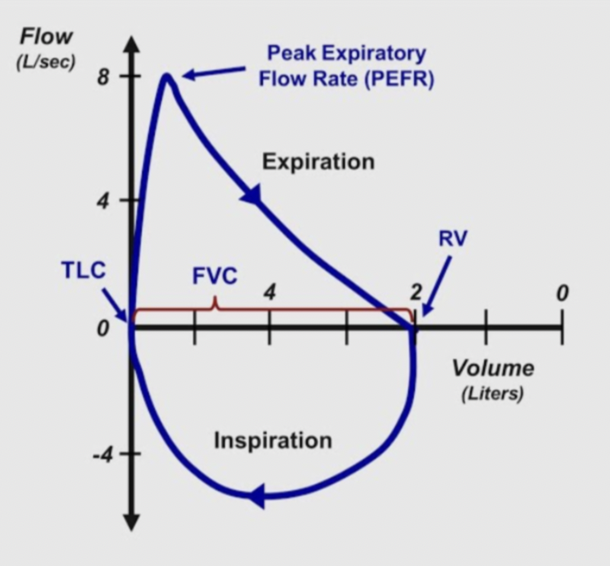
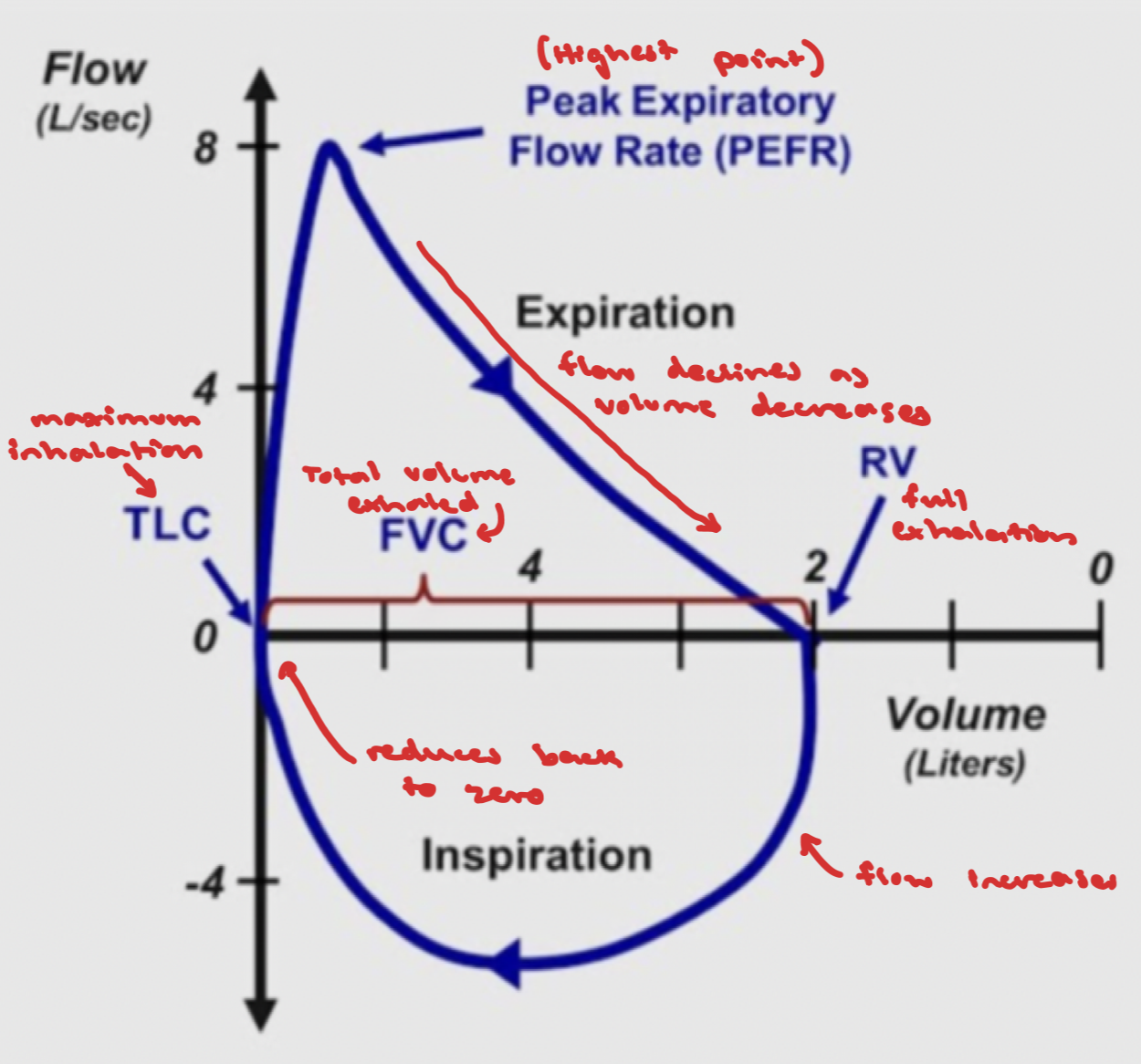
Flow volume loop
Expiration is above horizontal axis, inhalation under axis
Expiration - starts at total lung capacity → reaches peak expiratory flow → after PEF, flow declines as lung volume decreases → ends at residual volume
Inspiration - starts at RV → airflow increases until reaches TLC → flow reduces back to 0
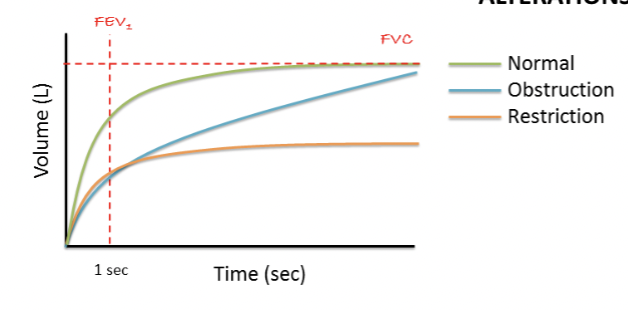
Spirometry alternations - volume/time curve
Obstructed - reduced airflow due to airway resistance
Restricted - reduced lung volume due to stiffness of deformation
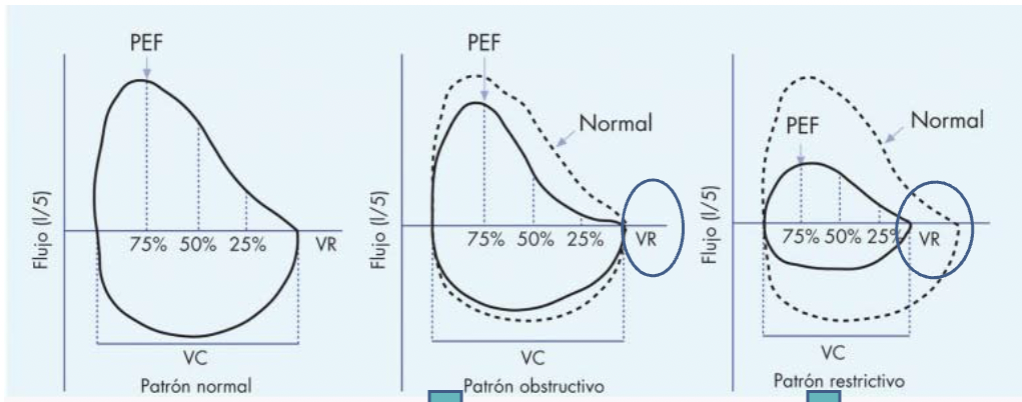
Spirometry alternations - volume/flow curve
Obstructive - difficulty exhaling, resistance in airway, reduction airflow
Restrictive - limited lung expansion
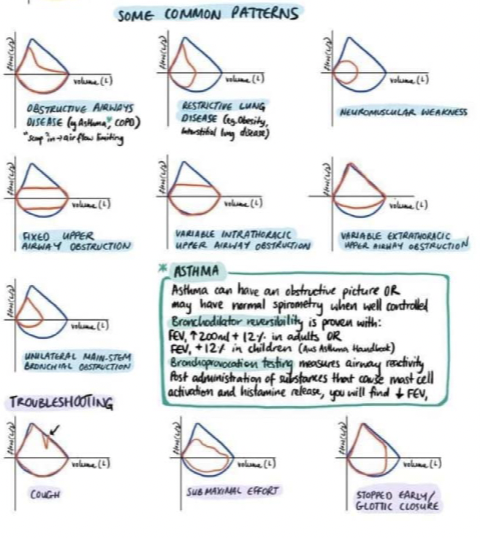
Spirometry loops
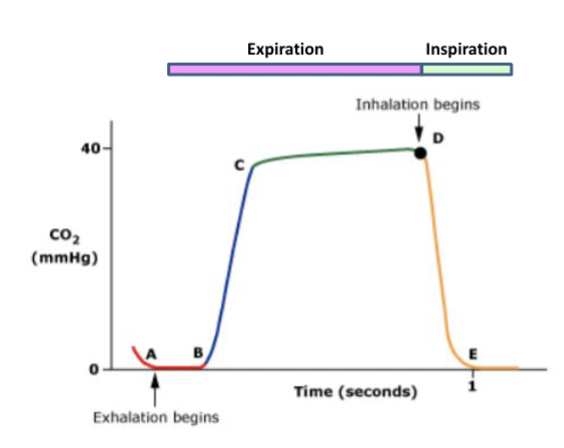
Capnography
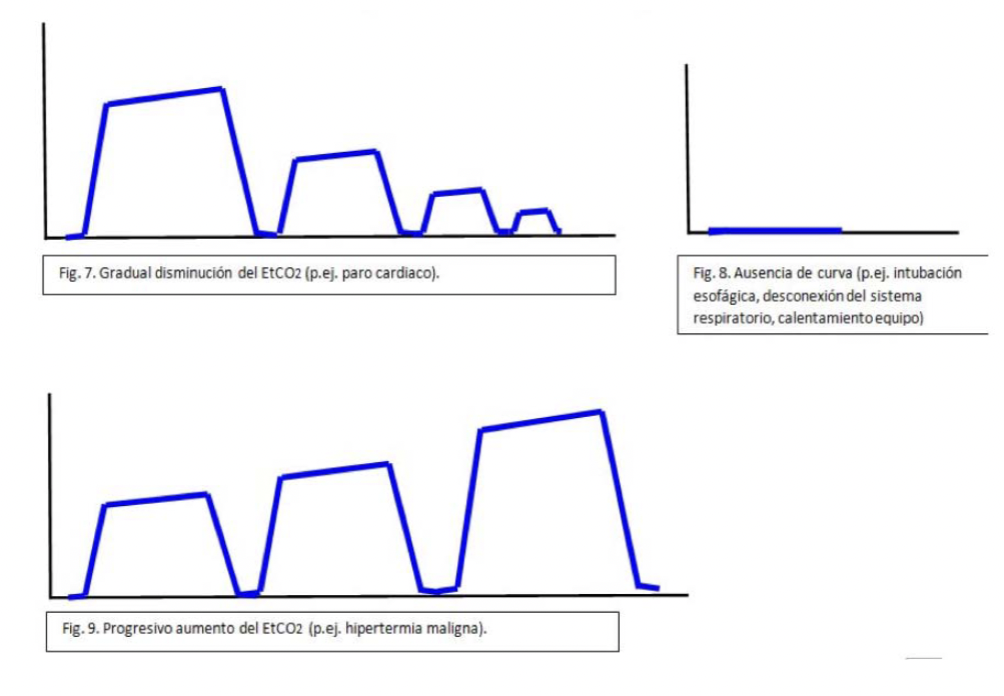
A-B : dead space ventilation, no CO2 detected
B-C : expiratory phase, CO2 starts increasing
C-D : alveolar plateau, steady CO2 levels
D-E : inspiration phase, CO2 drops as fresh air enters
Clinical importance of capnography
Shape change indicated respiratory disease
End tidal CO2 helps assess ventilation efficiency, treatment effectiveness and correct endotracheal tube placement
Capnography alternations 1
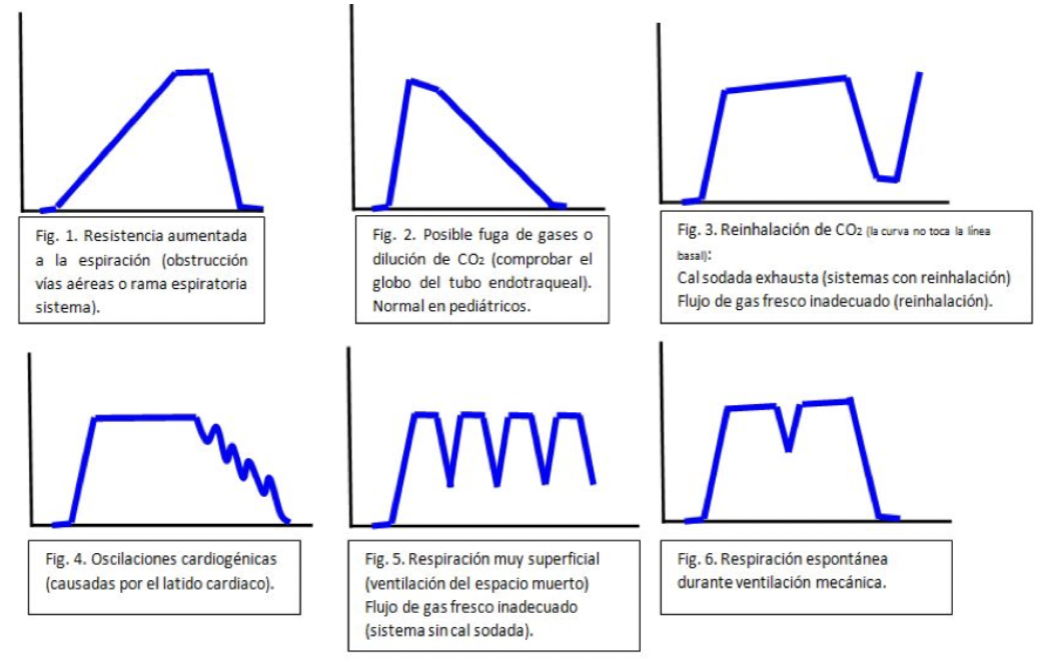
Capnography alternations 2