HGAP 2.1 - 2.5
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Population Distribution
(2.1) Description of locations on Earth’s surface where populations live.
Ecumene
(2.1) The portion of Earth’s surface occupied by permanent human settlement
Arable Land
(2.1) Land suitable for growing crops
Arithmetic Density
(2.1) Number of people per unit of land
Physiological Density
(2.1) Number of people per arable land
Agricultural Density
(2.1) The number of farmers per acre of arable land
Carrying Capacity
(2.2) The largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can support
Overpopulation
(2.2) A situation in which the number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at decent standard of living
Urban Services
(2.2) Public services and public facilities typically provided in the cities
Population Composition
(2.3) Structure of population in terms of age, sex, and other propetries such as marital status and education
Census
(2.3) A survey of the size and demographic characteristics of a population
Sex Ratio
(2.3) The number of males per 100 females in the population
Stage 1 Population Pyramid
(2.3) High Birth rates, high death rates, low or zero population growth.
Stage 2 Population Pyramid
(2.3) High birth rates, rapidly decreasing death rates, high growth rates
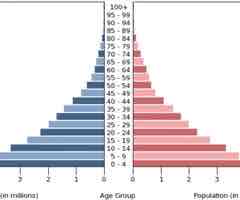
Stage 3 Population Pyramid
(2.3) Rapidly decreasing birth rates, low death rates, slow population growth rates
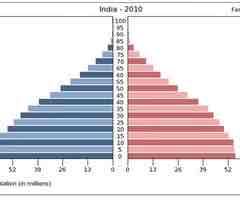
Stage 4 Population Pyramid
(2.3) Low birth and death rates, low or zero growth rates
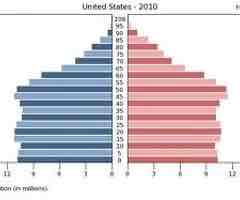
Stage 5 Population Pyramid
Low birth and death rates, birth rates are lower than death rate so negative growth rates occur.
Fertility
(2.4) The natural capability to produce offspring
Contraception
(2.4) Birth control
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
(2,4) The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society
Total Feritility Rate
(2.4) The average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years
Mortality
(2.4) The state of being subject to death
Infant Mortality Rates (IMR)
(2.4) The annual number of deaths of infants under one year old per 1,000 people in a population
Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR)
(2.4) The annual number of female deaths per 100,000 live birth from any cause related to or aggravated by pregnancy or it management (excluding accidental or incidental causes)
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
(2.4) Total number of deaths in a year of every 1,000 people alive in the society. The annual number of deaths per 1,000 population
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
(2.4) The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
Growth Rate
(2.4) Rate of increase or decrease of a population (includes births, deaths, immigration, and emigration)
Double Time (rule of 70)
(2.4) The number of years it takes a population to double. 70/r (r = growth rate)
Replacement Rate
(2.4) The total fertility rate needed for a population to replace itself. The TFR should be over 2 in order to at least meet the replacement rate (two children to replace the two parents)
Demography
(2.5) Scientific study of human populations
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
The process of change in a society’s population from condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth an death rates, low rate of natural increase, and higher total population.
Medical Revolution
(2.5) Medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to poorer countries of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. Improved medical practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death in poorer countries and enabled more people to live longer and healthier lives.
Demographic Momentum
The tendency for growing population to continue growing even after fertility rates decline. The occurs because even though TFR is low, once the large young population reaches child bearing age, there are so many people having kids that the population continues to grow for another generation.
Less Developed Country (LDC)
(2.5) Also known as developing country, a country that is relatively early stage in the process of economica development.
Newly Industrialized Country (NIC)
(2.5) A country that is undergoing or has recently undergone rapid industrialization and economic growth
More Developed Country (MDC)
(2.5) Also known as developed country, a country that has progressed relatively far along the continuem of development.
Epidemology
(2.5) Branch of medical science concerned with the incidence distribution, and control of diseases that affect large number of people.
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM)
(2.5) Distinctive causes of death rates in each stage of demographic transition. There are 5 stages, stage 1 is pestilence and famine, Stage 2 is receding pandemics, Stage 3 is degenerative diseases, Stage 4 is delayed diseases and Stage 5 is called “reemergence of Infectious Diseases.” These infection disease that were previously cured are now causing death rates to increase slightly because of increase global connections, and virus’s ability to evolve, and areas with poverty have limited access to healthcare or education.

Pandemic
(2.5) Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of population.