2. Peri-natal losses in piglets (classifying, characteristics)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the period during which perinatal losses of piglets occur?
From farrowing to the 5th day
What percentage of piglet losses can perinatal deaths account for?
Up to 50%
What are examples of causes of peri-natal losses in piglets?
Factors related to the sow
Pale pig syndrome (navel bleeding)
Hypoglycaemia
Hypothermia
Developmental defects
Infectious causes
What is the most common cause of death for suckling piglets?
Trauma or crushing by the mother
What are examples of factors related to the sow causing peri-natal losses in piglets?
Trauma/crushing by the mother
Diseases of the mammary gland
Complicated/prolonged parturition
Insufficient nutrition
Cannibalism
What can cause trauma or crushing of piglets by the mother?
Musculoskeletal disorders of the mother or overweight
What diseases of the mammary gland can affect piglets?
Agalactia, MMA/PPDS, and mammary hypoplasia
What is the name of complicated or prolonged parturition in sows?
Dystocia
What is the potential result of insufficient nutrition in sows?
Poor milk production leading to piglet issues
What is a risk associated with first-time mother sows?
Cannibalism, where they may eat their piglets
What is pale pig syndrome?
A condition where piglets are born pale and anaemic due to:
Anoxia during farrowing → blood pools into the placenta → blood not recalled before birth. Usually from old sows with large litters
Continual bleeding from the umbilicus resulting in anaemia
What happens if a piglet is born and the umbilical cord is separated too soon?
The piglet will be born pale and anaemic due to blood pooling in the placenta
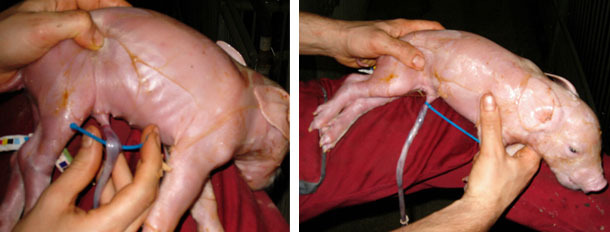
What is the treatment for navel bleeding in piglets?
Clamping the umbilicus 2-3 cm from the skin with a ligature or umbilical clip, followed by disinfection
What is hypoglycaemia in piglets?
A condition of low blood glucose levels, occurring usually within the first 12-24 hours after birth
What causes hypoglycaemia in piglets?
Limited glycogen reserves in the liver and decreased milk intake due to poor milk yield or environmental factors
What are the clinical signs of hypoglycaemia in piglets?
Sternal recumbency, shivering, hypothermia, paddling, convulsions, coma, and potentially death within 36-48 hours
What is the normal blood glucose range for healthy piglets?
5-6.6 mmol/l
How is hypoglycaemia in piglets diagnosed?
Clinical signs, Blood glucose levels: 1.5-2 mmol/l
What is the treatment for hypoglycaemia in piglets?
Milk, glucose (10 ml of 5-10% glucose intraperitoneally every 4-6 hours), and warmth (30-35 °C)
Very small piglets do better getting 2.5 % glucose
What is the ideal environmental temperature to prevent hypoglycaemia in piglets?
30-35 °C
What is the prevention for hypoglycaemia in piglets?
Optimal temperature of housing environment (30-35 °C)
Ensure sows are producing milk
Encourage milk drinking for smaller piglets (colostrum ingestion is important)
Supplementary feeding
What is hypothermia in piglets?
A condition where the body temperature drops below 37 °C
Why are piglets at risk for hypothermia?
They have insufficient thermoregulation and lack brown fat, requiring glucose to maintain body temperature → hypoglycaemia
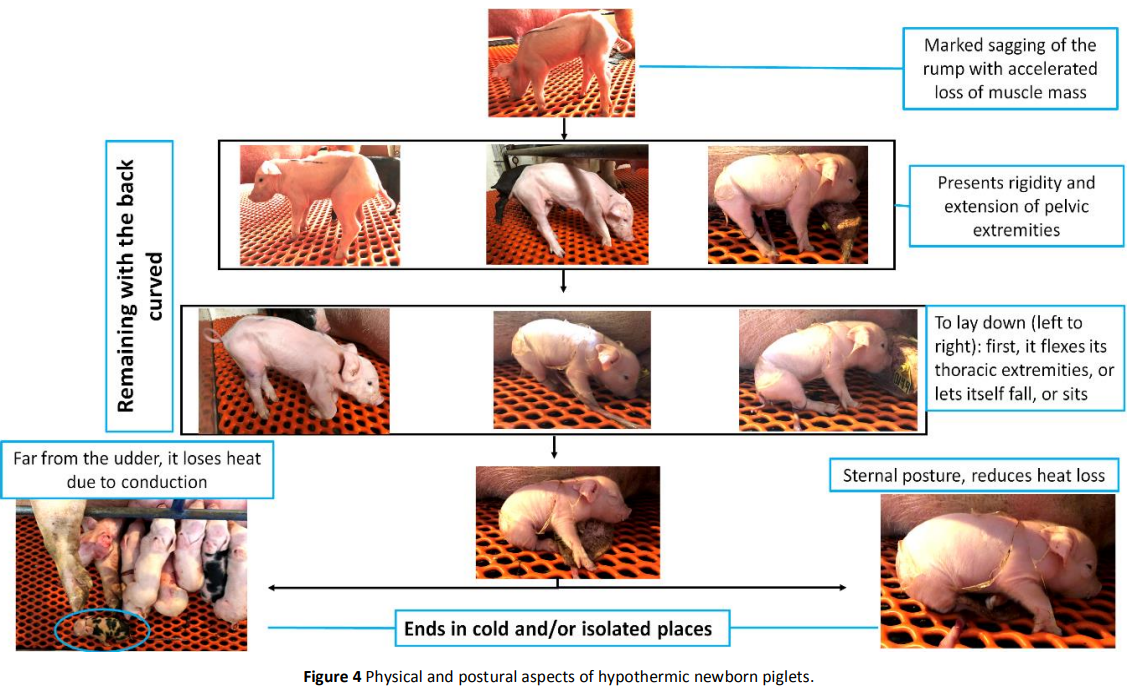
What are the signs of hypothermia in piglets?
Shivering, huddling, erect hair coat, cold skin, followed by lethargy, reduced mobility, tremors, and convulsions
How is hypothermia in piglets diagnosed?
Clinical signs, rectal temperature
What is the treatment for hypothermia in piglets?
Providing milk, glucose, and local heating
What is the ideal local environment temperature for piglets?
30-35 °C, decreasing after 1 week
What are examples of developmental/congenital defects of piglets?
Splay leg (congenital myopathy)
Congenital tremor
Hydrocephalus
Meningoencephalocele
Arthrogryposis
Cleft palate
Atresia ani et recti
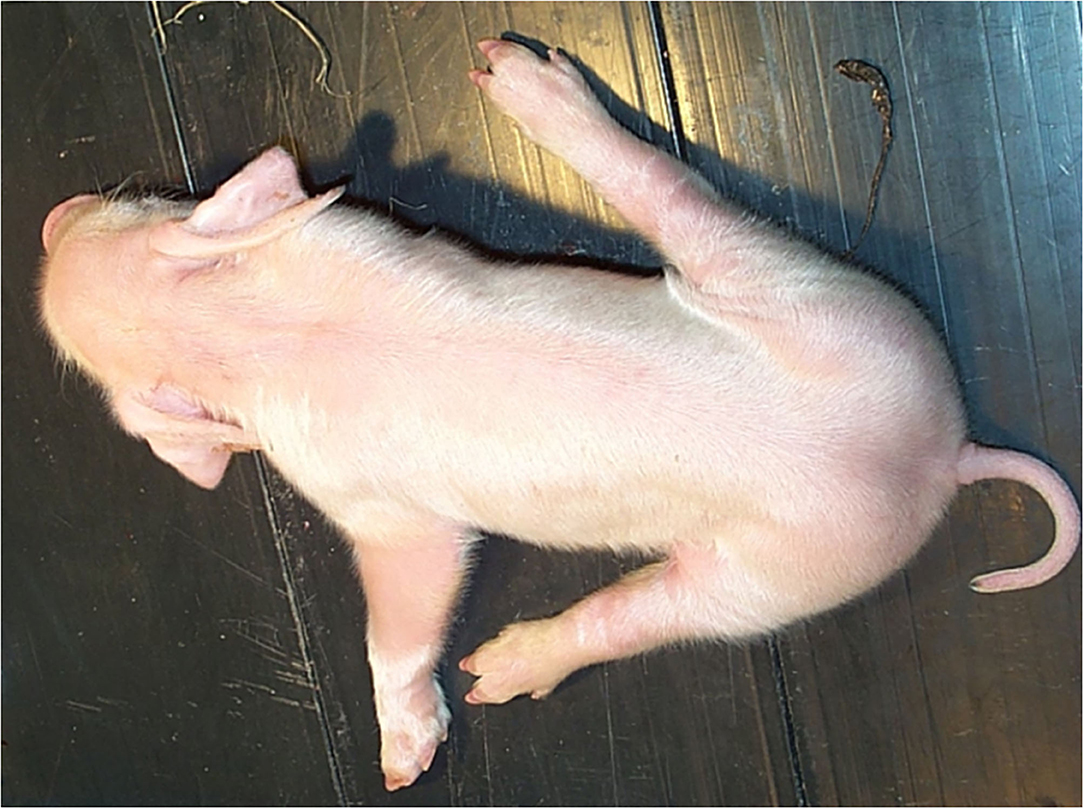
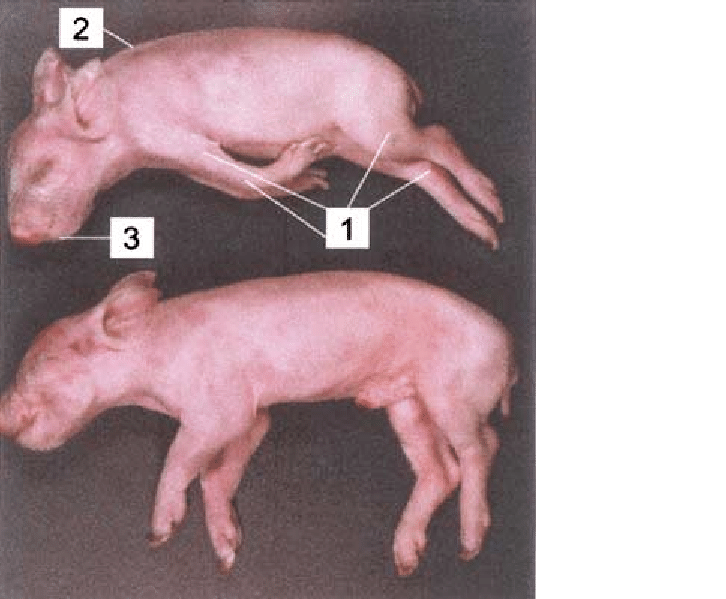
What is splay leg in piglets?
A genetic disorder causing immaturity of muscle fibres in the hind legs, leading to an inability to keep the legs together
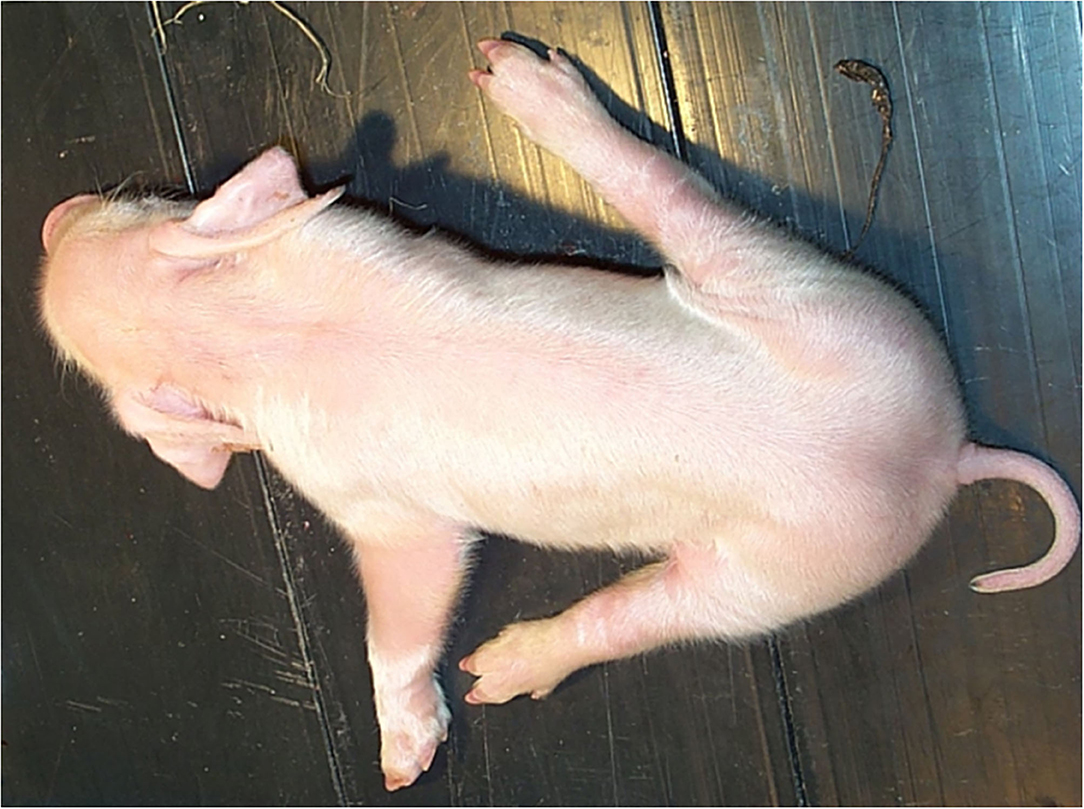

What can worsen the condition of splay leg in piglets?
Slippery or smooth floors
What is the cause of splay leg?
Genetic (meat breeds like landrace)
Inadequate nutrition of pregnant sow → choline, selenium, vitamin E
Mycotoxin.
What are the clinical signs of splay leg?
Seen 1-3 days pp.
Weak, “Dog sitting” position of legs
Hind legs (or front legs → less frequent) held out laterally. Unable to stand

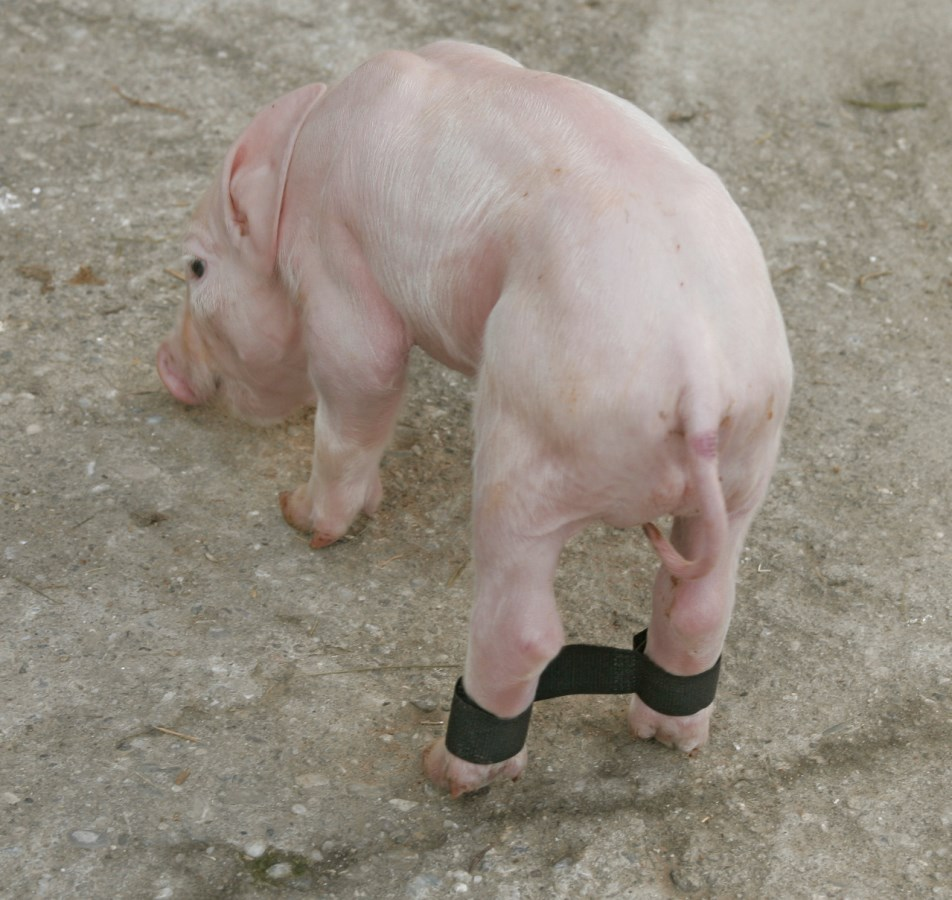
What is the treatment for splay leg in piglets?
Loosely binding the hind legs together with a 5-8 cm gap for 7-10 days and supportive care to help them suckle

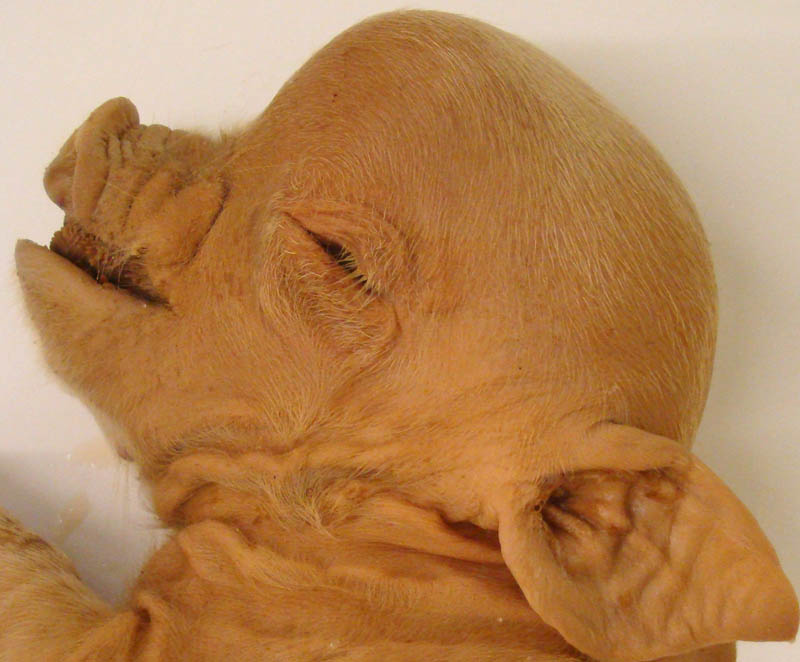
What is congenital tremor in piglets?
Shaking and tremor of the muscles of the head and body, affecting more than one piglet in a litter but not all piglets
What are common causes of congenital tremor in piglets?
Genetic (Landrace and Saddleback breeds)
Teratogens
Infectious (CSF, PCV-2 (porcine circovirus), and Aujeszky’s disease)
What is the treatment for congenital tremors?
No specific treatment. Confine, warm, put to suckle
What is hydrocephalus in piglets?
Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain

What is meningoencephalocele in piglets?
Protrusion of the brain and meninges

What is arthrogryposis in piglets?
A lethal disorder where the joints of the legs are fixed or curved, often caused by prenatal viral infection, plant or chemical poison, hyperthermia, or dietary (Mg) deficiency
What is cleft palate in piglets?
A congenital defect where the roof of the mouth is not properly formed
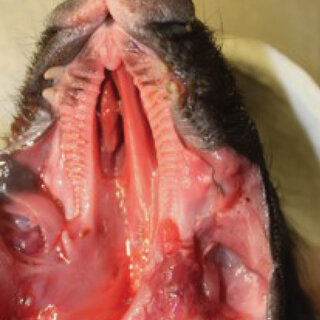
What is atresia ani et recti in piglets?
A condition where the rectum ends blindly and does not connect to the anus, 100% lethal in males and may communicate with the vagina in females

What are common pathogens causing neonatal diarrhoea in piglets?
Cystoisospora, coronavirus, rotavirus, Clostridium perfringens, and E. coli
What digestive tract congenital abnormality is fatal?
Atresia ani et recti
How is cystoisospora treated?
Toltrazuril