Mechanisms of toxicity
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Temporal aspects
Cellular toxicity
Organ & tissue toxicity
Pathology of Toxicity (3)
Delivery (from the site of exposure to the target )
Reaction of the Ultimate Toxicant with the Target Molecule
Cellular Dysfunction and Resultant Toxicities
Repair or Dysrepair
Steps/Mechanisms of Toxicity [4]
On-target adverse effects
Off-target adverse effects
Production of toxic metabolites
Production of harmful immune responses
Idiosyncratic responses
MECHANISMS OF TOXICITY [5]
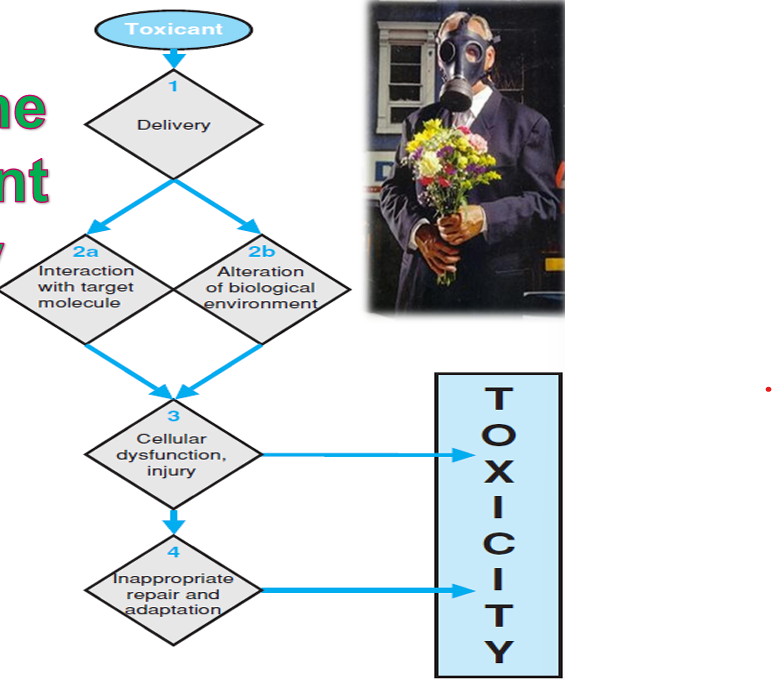
Toxicant
Delivery
Interaction with the Target
Aletration of biological environment
Cellular dysfunction injury
Inappropriate repair and adaptation
Potential Stages in the Development of Toxicity after Chemical Exposure [6]
Nerve Agents
These are potent organophosphorus agents that cause inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase and subsequent excessive muscarinic and nicotinic stimulation
Tabun
GA
Sarin
GB
Soman
GD
Cyclosarin
GF
Methylphosphonothioic Acid
VX
Organophosphorus
Carbamate Insecticides
Tabun
Sarin
Soman
Cyclosarin
Methylphosphonothioic acid
Example of Neve Agent [7]
Nerve agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
Organophosphorus
Nerve agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
Carbamate Insecticides
Blister Agents
Vesicants are also known as ____________
Nitrogen and sulfur mustards
_____________ and ______________mustards are hypothesized to act by alkylating cellular DNA and depleting glutathione, leading to lipid peroxidation by oxygen free radicals
Nitrogen mustrad
Sulfur mustard
Phosgene
Lewisite
Example of Vesicants (5)
Sulfur mustard
HD
Nitrogen Mustard
HN
Lewisite
L
Phosgene
CX
Thiol moieties
Lewisite combines with _________ moieties in many enzymes and also contains trivalent arsenic.
trivalent arsenic
Lewisite combines with thiol moieties in many enzymes and also contains _____
Phosgene
diphosgene
chlorin
chloropicrin
Example of Choking Agents [4]
Choking agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
Phosgene
Choking agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
diphosgene
Choking agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
chlorine
Choking agents
[ Identify it Toxicity Class : ]
chloropicrin
Choking Agents
These agents include chlorine and lacrimator agents
Choking agents
These gases and mists are highly irritating to mucous membranes. In addition, some may combine with the moisture in the respiratory tract to form free radicals that lead to lipid peroxidation of cell walls
pulmonary injury
Phosgene causes less acute irritation but may lead to delayed ____________
Blood agents
Cyanides is aka ____
Cyanide
Hydrogen Cyanide
Cyanogen Chloride
Cyanides include ___ (3)
Cyanides (blood agents)
These compounds have high affinity for metalloenzymes such as cytochrome, thus derailing cellular respiration and leading to the development of a metabolic acidosis.
metalloenzymes
cytochrome
Cyanides (blood agents) compounds have high affinity for ____ such as ___, thus derailing cellular respiration and leading to the development of a metabolic acidosis
metabolic acidosis.
Cyanides (blood agents) compounds have high affinity for metalloenzymes such as cytochrome, thus derailing cellular respiration and leading to the development of a____
Incapacitating agents
These are a variety of agents have been considered, including strong anticholinergic agents such as scopolamine, stimulants such as amphetamines and cocaine, hallucinogens such as LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide and Other Hallucinogens), and CNS depressants such as opioids (Opiates and Opioids).
Anticholinergics
stimulants
hallucinogens
Depressants
DRUG TYPES that are considered 'incapacitating agents' [4]
Incapacitating agents
[ Identify its Toxicity Class ]
scopolamine
Incapacitating agents
[ Identify its Toxicity Class ]
amphetamines
Incapacitating agents
[ Identify its Toxicity Class ]
cocaine
Incapacitating agents
[ Identify its Toxicity Class ]
LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide)
Incapacitating agents
[ Identify its Toxicity Class ]
opioids (Opiates and Opioids)
D. Reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) by glutathione reductase (GR)
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT AN IMPORTANT STEP IN DETOXICATION OF CHEMICALS?
A. Formation of redox-active reactants
B. Reduction of hydrogen peroxide by
glutathione peroxidase
C. Formation of hydrogen peroxide by
superoxide dismutase
D. Reduction of glutathione disulfide
(GSSG) by glutathione reductase (GR)
E. Conversion of hydrogen peroxide to
water and molecular oxygen by catalase
Endogenous compounds
___compound causes cross-linking
Antigen
This is also known as a xenobiotic that is a stranger
Superoxide Anion Radical
Superoxide Dismutase
Peroxynitrite
Hydroxyl radical
Radicals That Form with Superoxide Ion [4]
Regulatory
Functional
Functions Cell [2]
Absorption
Distribution Toward the Target
Reabsorption
Toxication
Presystemic Elimination
Distribution from Target
Excretion
Detoxication
The process of Toxicant delivery (8)
MNEMONICS : [ ADR TP DED ]
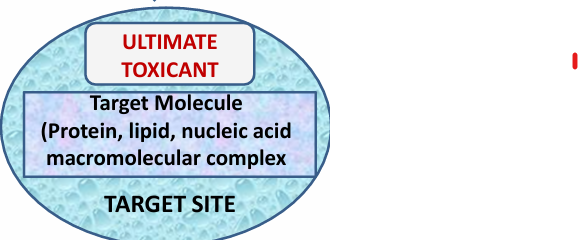
Protein
lipid
nucleic acid macromolecular complex
Target Molecules [3]
Parent Xenobiotics
Xenobiotic metabolites
Reactive Oxygen or Nitrogen Species
Endogenous compounds
Types of Ultimate Toxicants[4]
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Pbions
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Tetrodotoxin
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
TCDD
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Methylisocyanate
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
HCN
Parent xenobiotics
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
CO
Tetrodotoxin
Toxin from Pufferfish
Amygdalin ► HCN
Arsenate ►Arsenite
Fluoroacetate►Fulurocitrate
Ethylene Glycol►oxalic acid
Hexane►2,5-Hexanedione
Acetaminophen►N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI)
CCl4►CCl3OO
Benzo[a]pyrene ►BP-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide/BP- Radical cation
Example of Xenobiotic Metabolite [7]
HCN (Hydrocyanic Acid)
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Amygdalin ►___
Arsenite
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Arsenate ►___
Fluorocitrate
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Fluoroacetate ►___
Oxalic acid
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
ethylene glycol ►___
2,5-Hexanedione
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Hexane ►___
N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine ( NAPQI )
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Acetaminophen►___
CCl3OO•
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
CCl4 (Carbon Tetrachloride) ►___
BP-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide or BP-Radical Cation
Xenobiotic metabolites as ultimate toxicants:
Benzo[a]pyrene (BP) ►___
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Amygdalin
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Arsenate
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Fluoroacetate
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Ethylene glycol
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Hexane
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Acetaminophen
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
CCl4
Xenobiotic metabolites
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Benzo[a]pyrene (BP)
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Diquat
doxorubicin
nitrofurantoin
Cr(V)
Fe(II)
Mn(II)
Ni(II)
Examples of toxins that produces Hydroxyl radical (HO•) [4]
Peroxynitrite (ONOO-)
Paraquat produces what reactive nitrogen species ?
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Hydrogen peroxide
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Diquat
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
doxorubicin
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
nitrofurantoin
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Cr(V)
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Fe(II)
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Mn(II)
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Ni(II)
Reactive oxygen or nitrogen species
[Classify What Types of Ultimate Toxicants]
Paraquat
Paraquat
Identify The name of the Structure
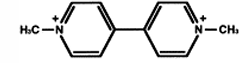
Diquat
Identify The name of the Structure
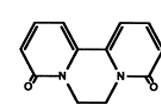
Diquat-monopyridone
Identify The name of the Structure
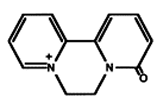
Diquat-dipyridone
Identify The name of the Structure
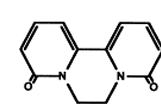
Lipid peroxyl radicals
Lipid alkoxyl radicals
4-Hydroxynon-2-enal
Products that may be produced when Carbon Tetrachloride ( CCl3OO ) reacts with unsaturated fatty acids___ (3)
Sulfonamides
This drug family may displace bilirubin in the bound-state in albumin
Sulfonamides
[Identify the Toxicity Class ]
albumin-bound bilirubin
Protein carbonyls
____ can be formed when Hydroxyl radicals (HO•) react with proteins
D. Opening of ion channels
ALL OF THE FOLLOWING ARE COMMON
EFFECTS OF TOXICANTS ON TARGET
MOLECULES EXCEPT:
A. blockage of neurotransmitter
receptors
B. Interference with DNA replication
due to adduct formation
C. Cross-linking of endogenous
molecules
D. Opening of ion channels
E. Mounting of an immune response
Superoxide dismutase
An enzyme that can convert superoxide anion radical into peroxide
Peroxynitrite and peroxide
Superoxide anion radical can be converted into ______ or _______
Hydroxyl Radical and Hydroxide
Peroxide can be further converted into _________ and ___________
Noncovalent binding
Covalent binding
Hydrogen abstraction
Electron transfer
Enzymatic reaction
Reaction Types for the Second Step in the Development of Toxicity (5)
Mitochondria
This is the powerhouse of the cell
Toxication
This refers to the biotransformation that causes harmful response ?