Reproduction in Humans and Plants Revision
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is asexual reproduction?
a process resulting in the production of genetically
identical offspring from one parent
Examples of asexual reproduction in plants are
Runners, bulbs, corms, tubers
An advantage of asexual reproduction is......
- produce many individuals rapidly
A disadvantage of asexual reproduction is ....
- offspring lack genetic variation to defend against diseases and environmental changes
An artificial example of asexual reproduction in plants is ....
Cuttings or grafting
What is sexual reproduction?
A process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes (sex cells) to form a zygote and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
What is fertilisation?
the fusion of gamete nuclei
What are gametes?
Haploid cells such as an egg or sperm. Gametes fuse during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote.
What is a zygote?
The diploid cell formed when a sperm fertilises an egg.
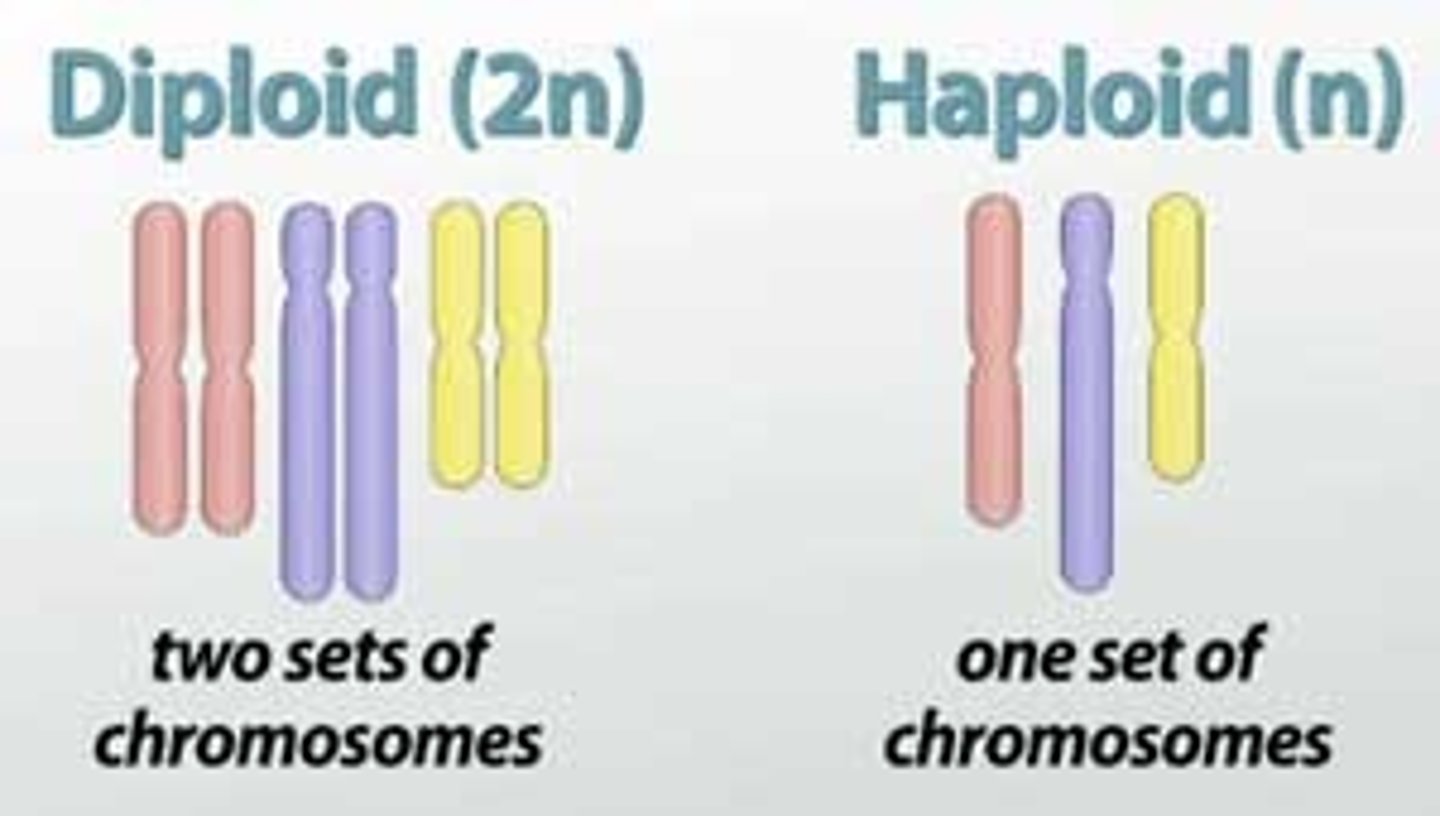
What do we mean by haploid?
Haploid contains half the number of chromosomes of a normal body cell. eg a sperm is haploid because it only contains 23 chromosomes.
An advantage of sexual reproduction
more genetic variation in the next generation
A disadvantage of sexual reproduction
Slower process, need two parents
The correct order of baby development (smallest to biggest)
zygote embryo foetus baby
Where does fertilisation take place in humans?
Oviduct
Where does fertilisation take place in flowers
Ovule
What are the male gametes in humans
Sperm cells
What are the male gametes in flowers
Pollen nucleus
Why are so many sperms released in one ejaculation
Many sperm will die on the way to the egg
Why is an egg so much bigger than a sperm cell?
The egg cell contains food to supply the developing embryo until it is embedded in the uterus wall where it can then form a placenta
What is ovulation?
When an egg is released from the ovary
When in the menstrual cycle is an egg released
Around day 14/15 (middle of the cycle)
What is menstruation and when does it happen in the menstrual cycle?
Another word for having a period-The flow of blood from the vagina as the uterus lining disintegrates. it happens on Day 1 of the menstrual cycle.
What is oestrogen?
A hormone secreted by the ovaries. it help to repair the uterus lining after a period
What is the role of the amniotic fluid?
it cushions the baby in the uterus and prevents it from being knocked and hurt
What is the role of the placenta?
it provides the baby with oxygen and food. It is connected to the baby via the umbilical cord. The baby's blood and the mother's blood do not mix. The process relies on diffusion.
Some features of insect-pollinated flowers are...
Brightly-coloured petals, nectar, scent
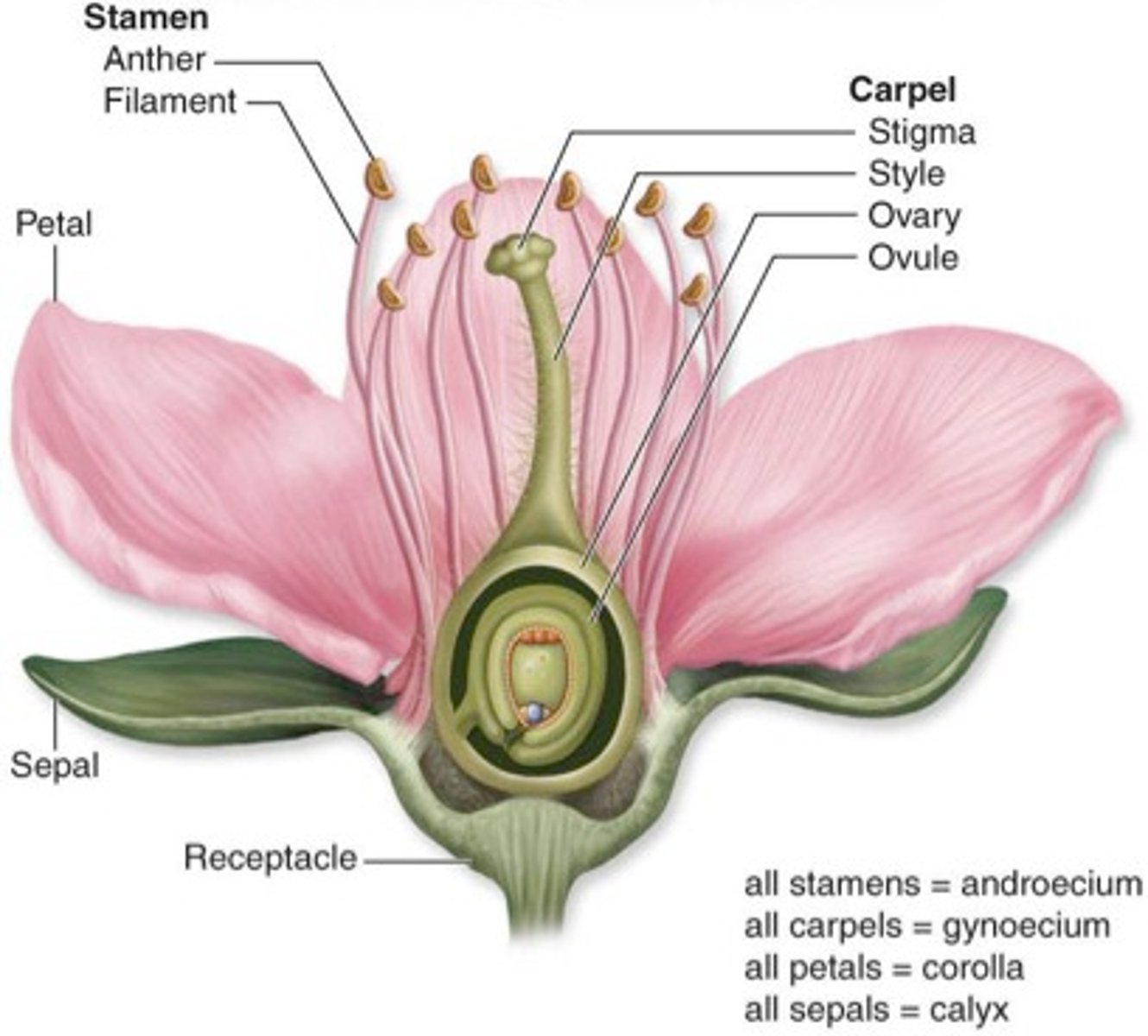
What are sepals?
Leaflike parts that cover and protect the flower bud

What is the role of anthers
Produces the male sex cells (pollen)
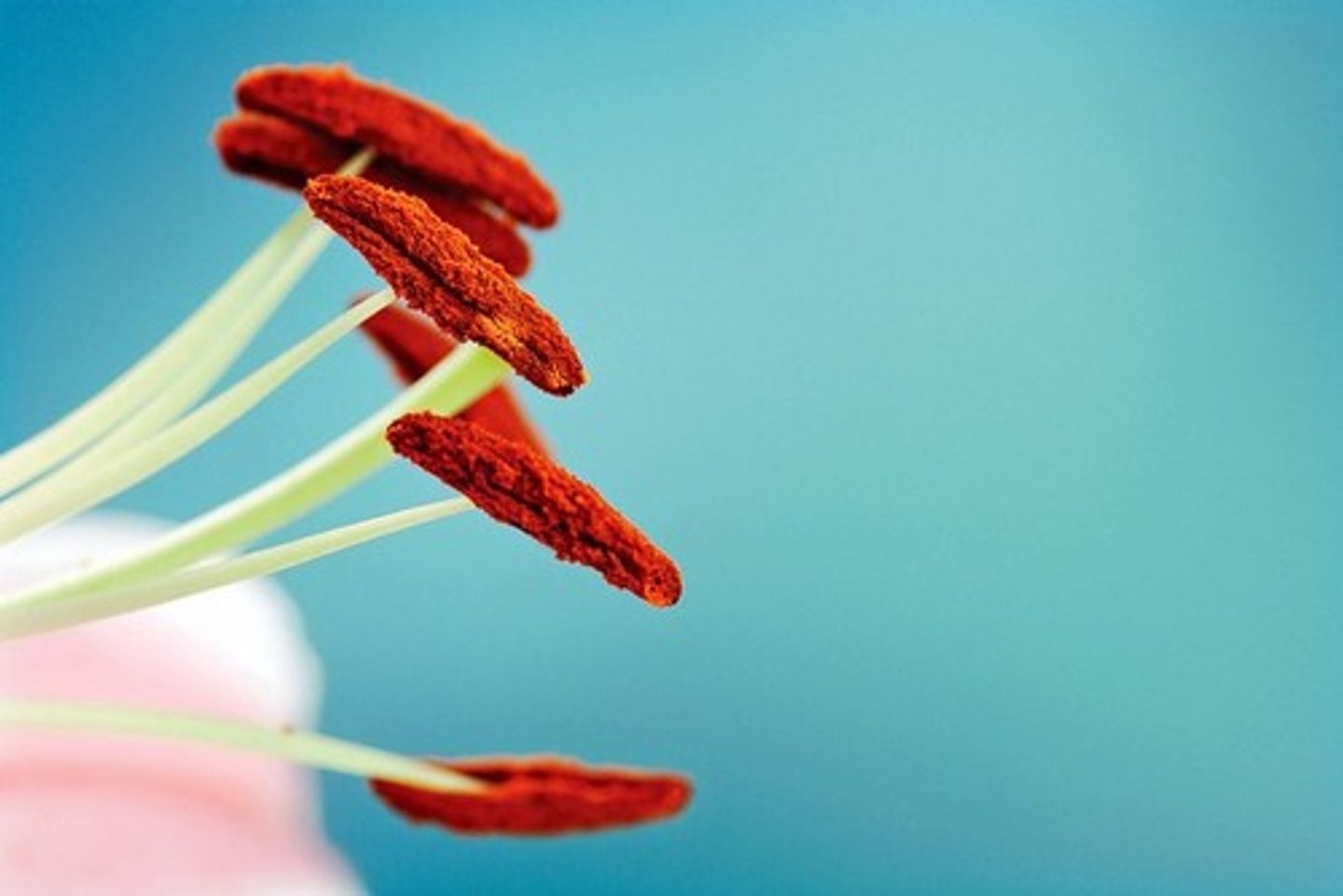

What is the stigma's function?
The top of the female part of the flower, which collects pollen grains (sticky or feathery)
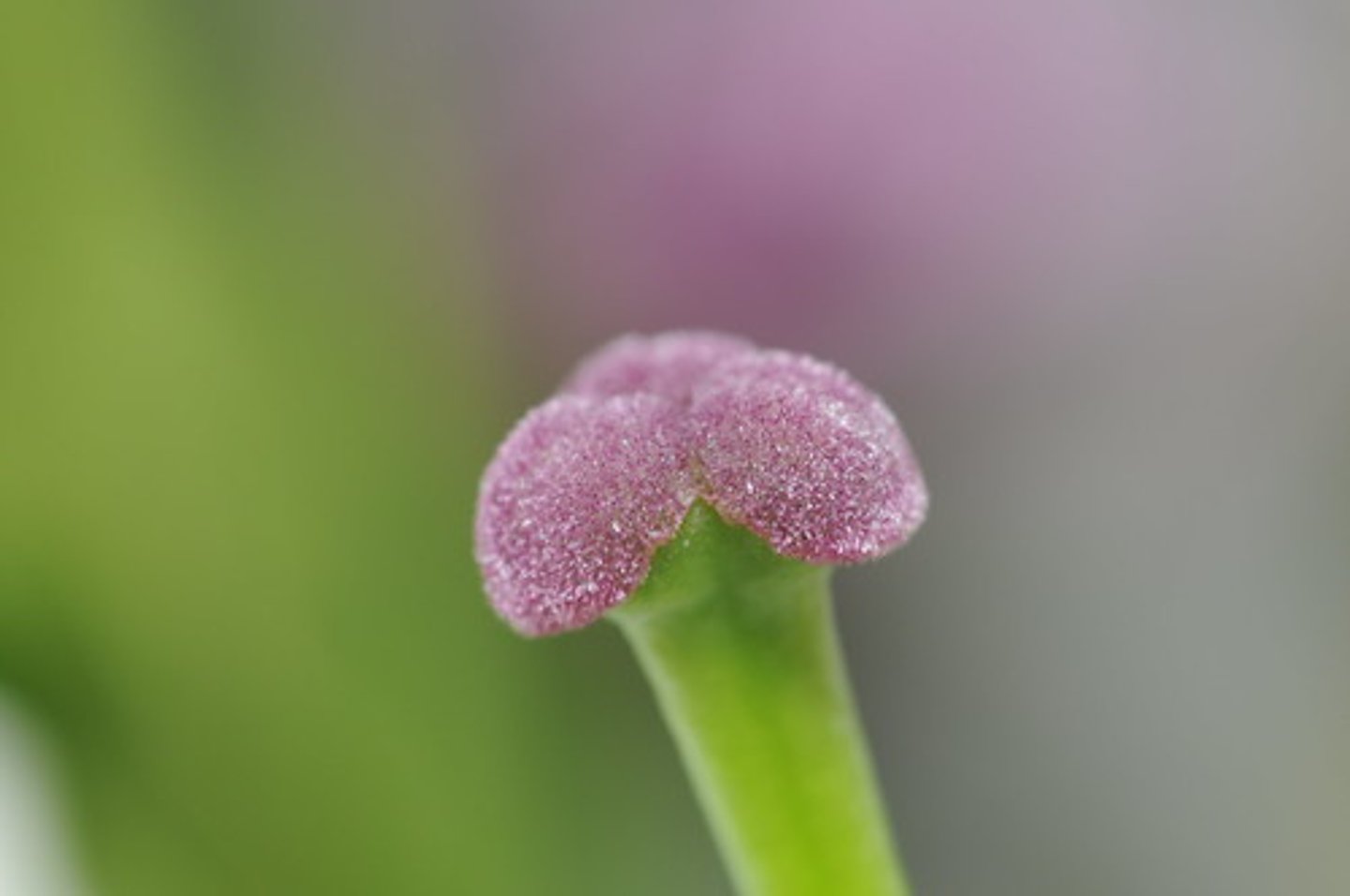

What is the role of ovaries (plant)
Produces the female sex cells (contained in the ovules)

Features of wind-pollinated flower are..,
Small petals, and their stamens and stigmas hang outside the flower.
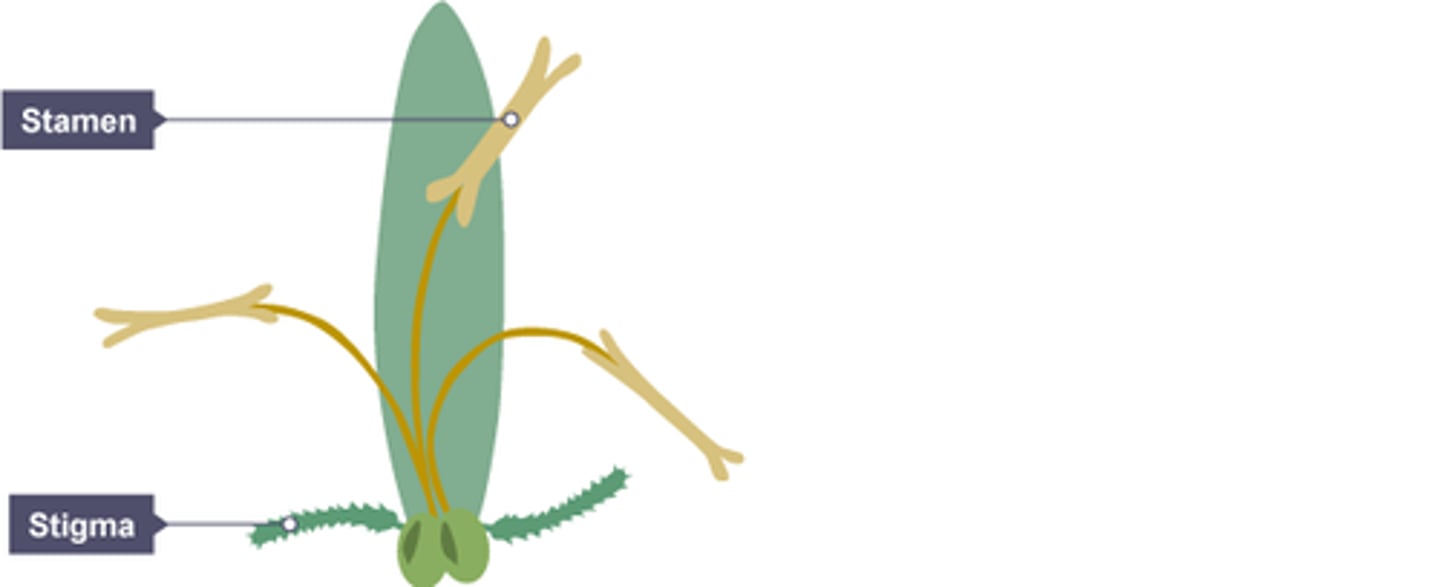
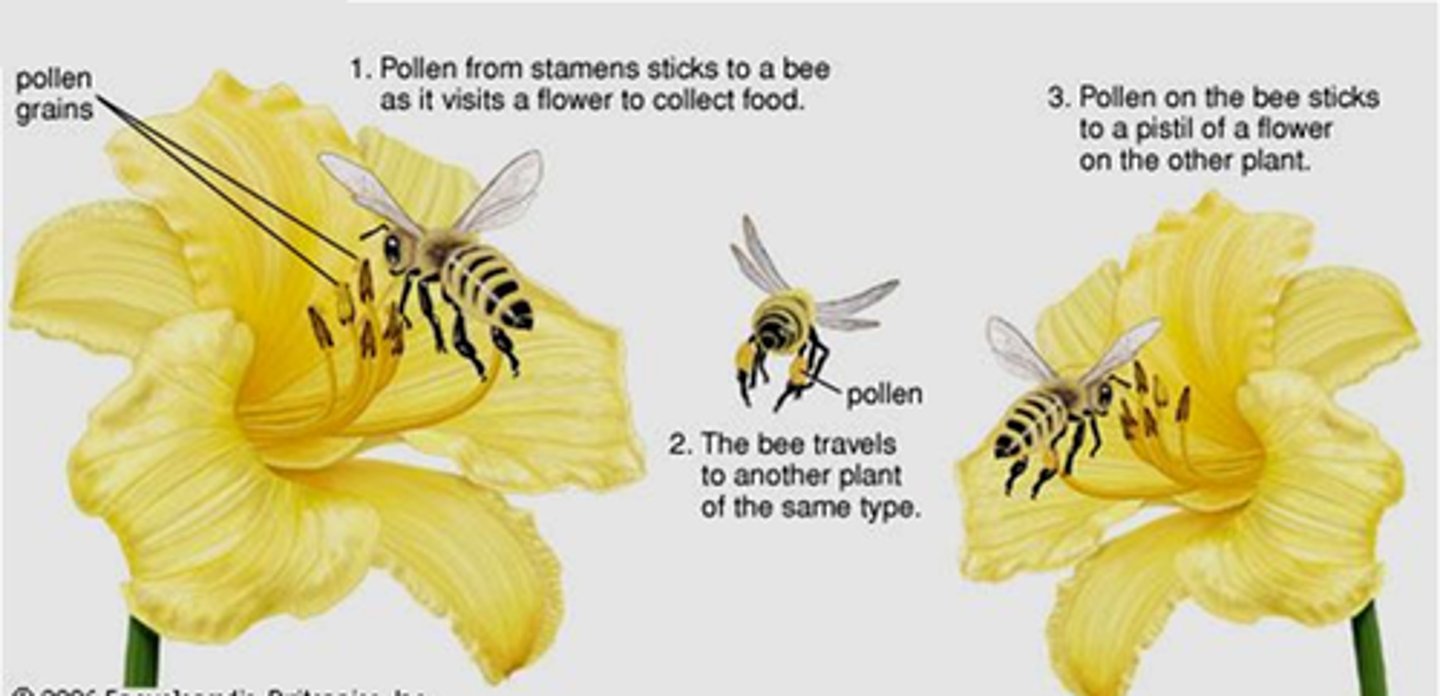
What is pollination?
transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma

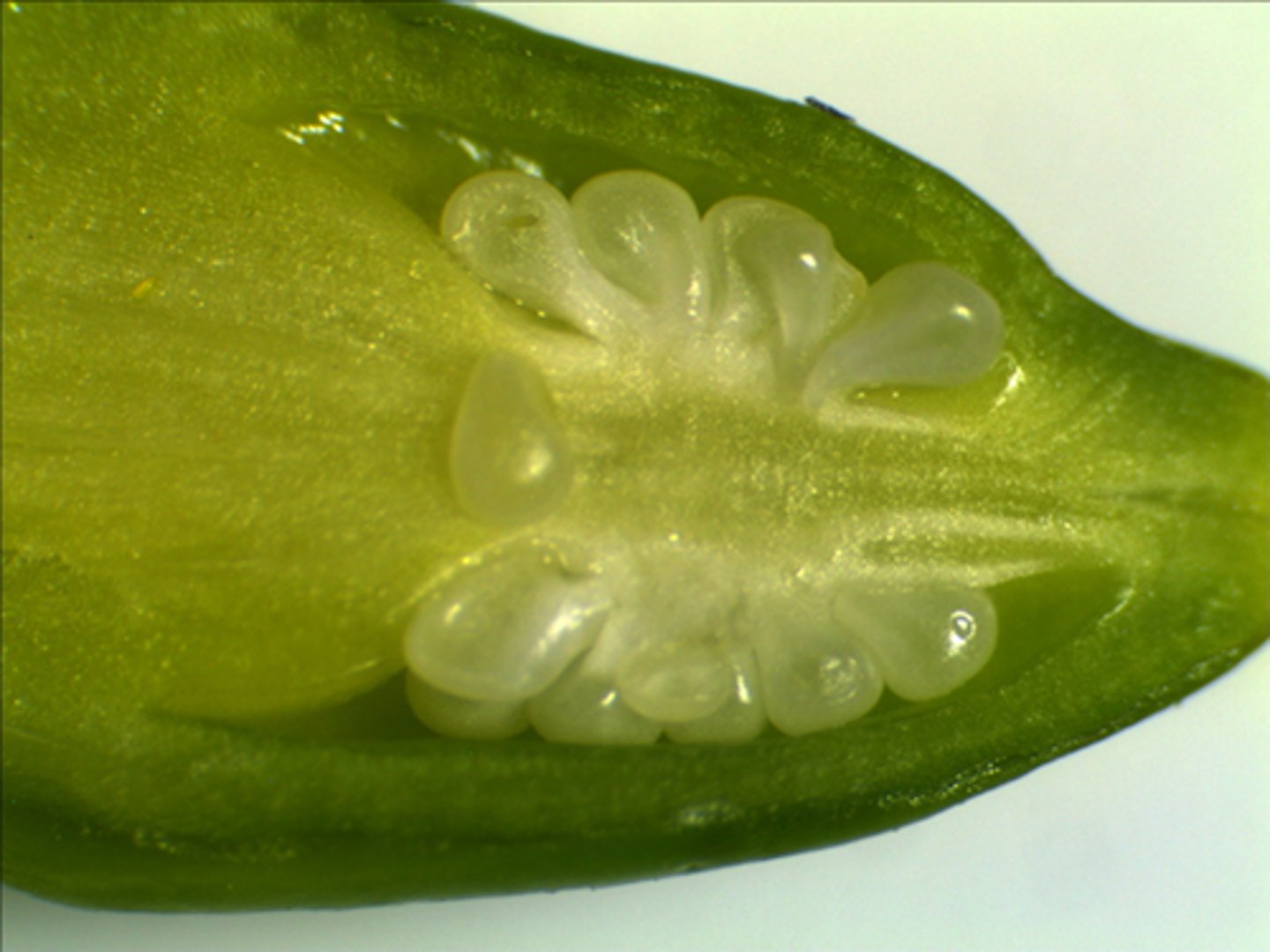
What is a pollen tube?
A tube that forms after the pollen grain lands on the stigma. Its role is to deliver the pollen nucleus to the ovule.
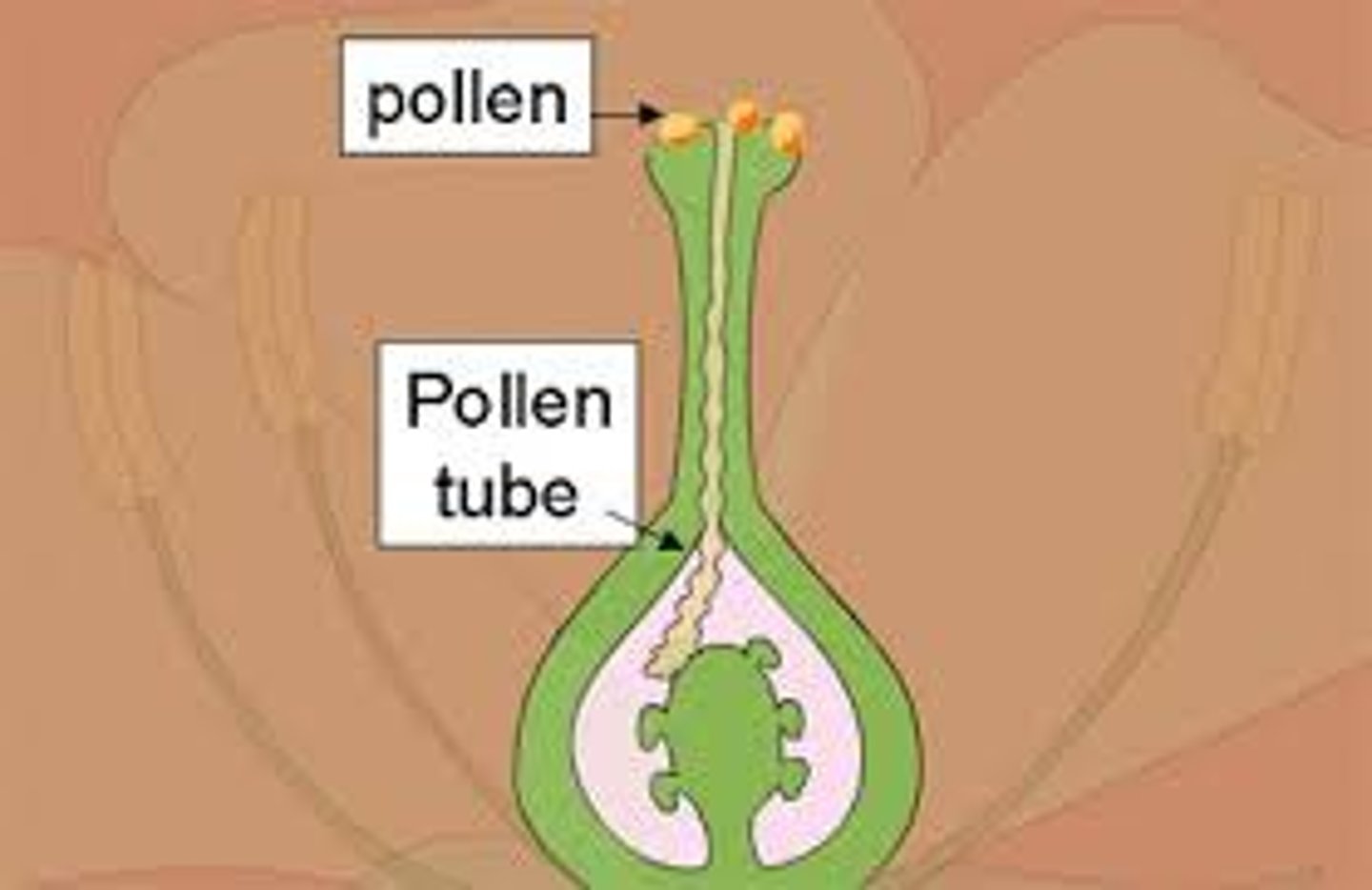
Describe fertilisation in flowering plants
- Pollen grain land on ripe stigma
- pollen grain form pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary
- pollen tube gains nutrients from style
- pollen tube carries male gamete nucleus.
- Gamete enters ovule through micropyle (tiny hole in ovule)
- Male gamete fuses with the female to form a zygote
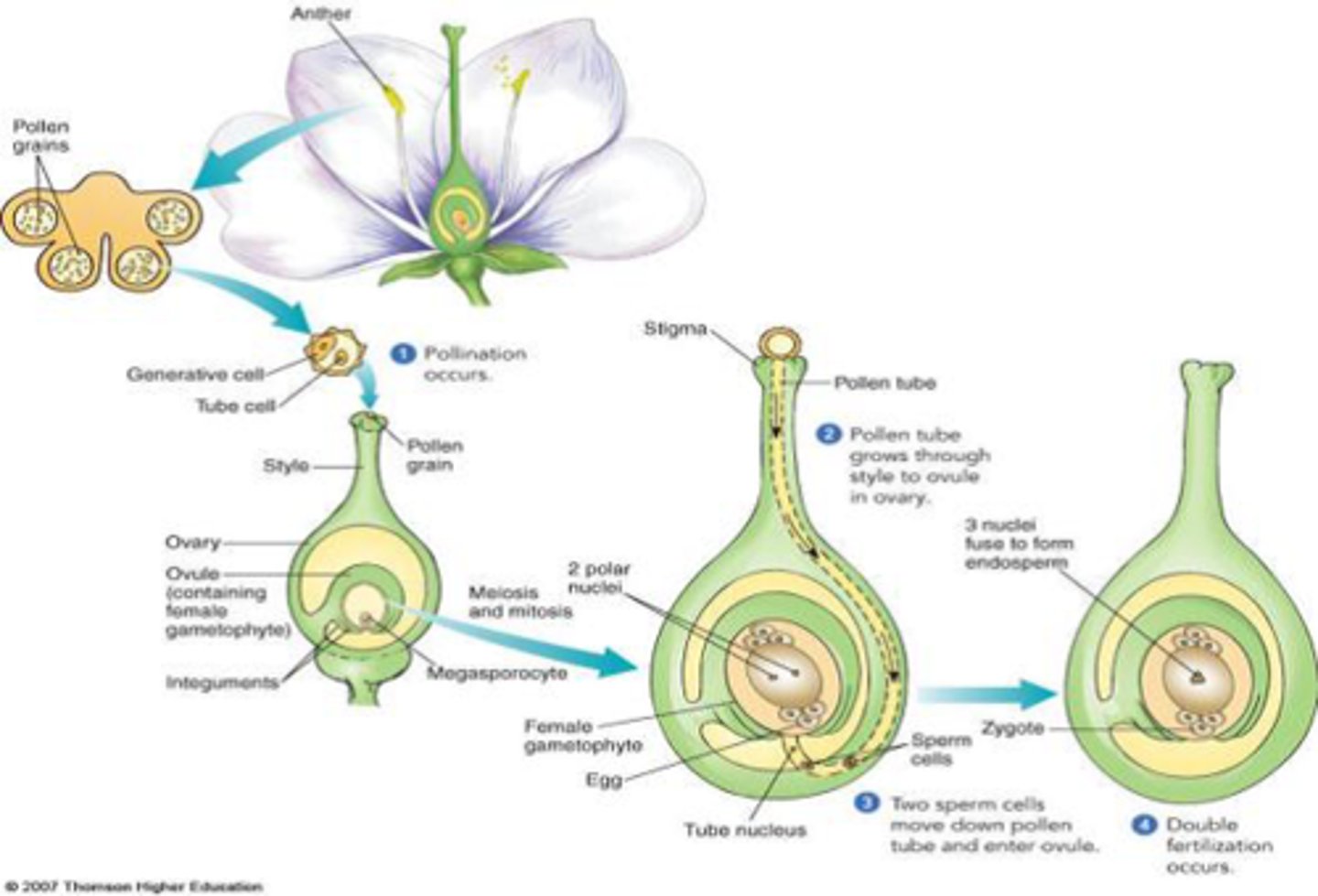
What happens to the ovule after fertilisation?
It forms the seed
Where is the embryo found in flowering plants
In the seed.
Three environmental conditions that affect germination of seeds
- requirement for water
- oxygen
- suitable temperature (warmth)
WOW
The role of the testes is to........
Produce male gametes (sperm) and hormone testosterone
The role of the scrotum is .....
Allows testes to be kept in cool environment. This maximises sperm production.
The function of sperm ducts is ....
Connects to urethra to allow semen to move out of penis to vagina during sexual intercourse
The role of the urethra
Allows urine to move out of body
The function of ovaries?
Contains undeveloped (immature) egg cells
-produce oestrogen and progesterone
Place where fertilised egg cell is implanted?
uterus
Adaptive features of sperm for its job are.....
tail - helps it move fast
enzymes in the acrosome - help it penetrate the egg cell membrane
middle section - packed with mitochondria to release energy
Adaptive features of egg cells
energy stores - large amount in cytoplasm
jelly coat - changes at fertilisation
What is copulation?
The process of mating or sexual intercourse.
The functions of the umbilical cord?
Connects foetus to placenta. Contains umbilical artery an umbilical vein.
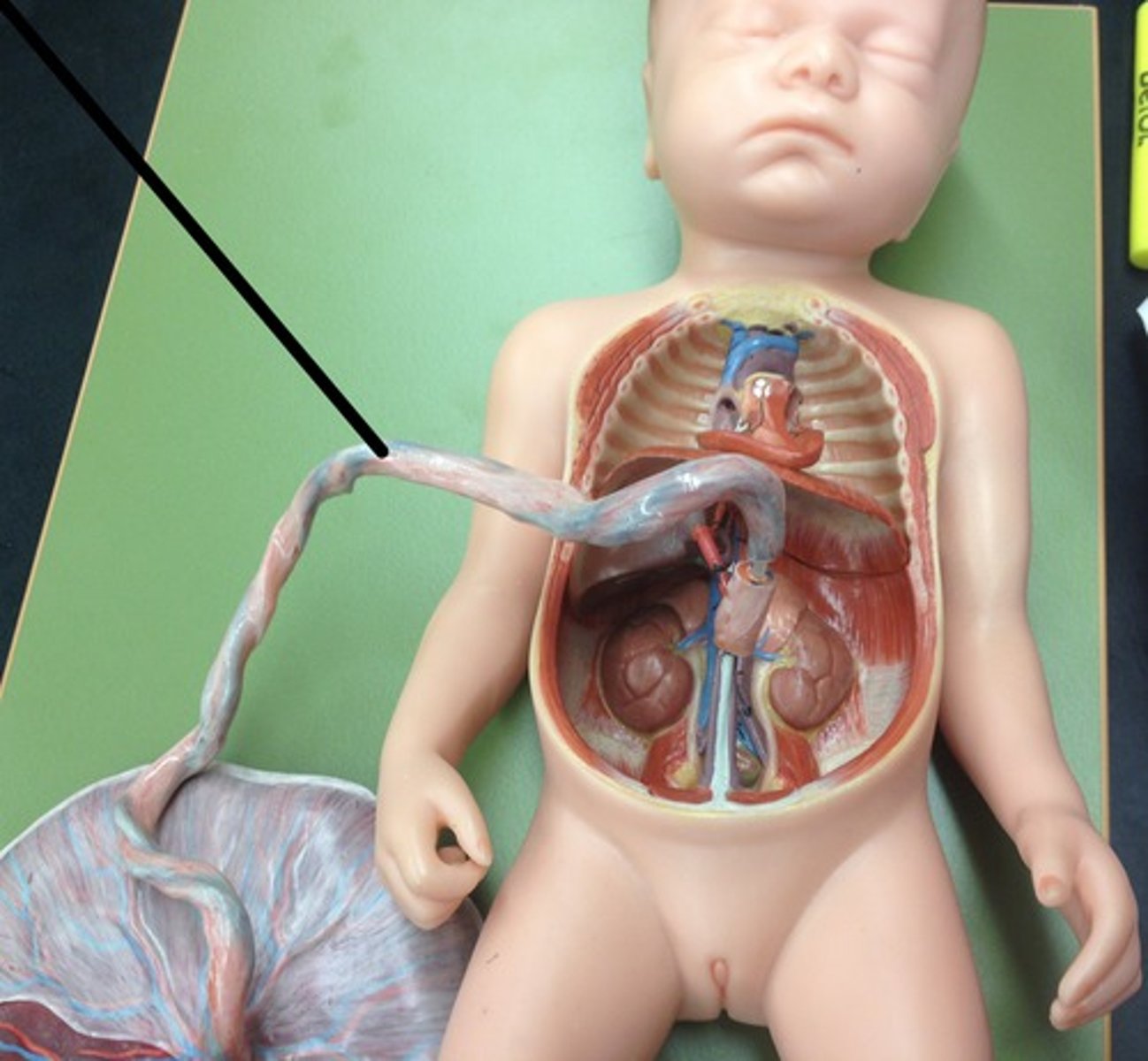
The functions of placenta
-Separates mother's blood from fetus as both may have different blood types
-Prevents mother's blood with high pressure from damaging delicate blood vessels of fetus
-Allows for diffusion of oxygen and food molecules
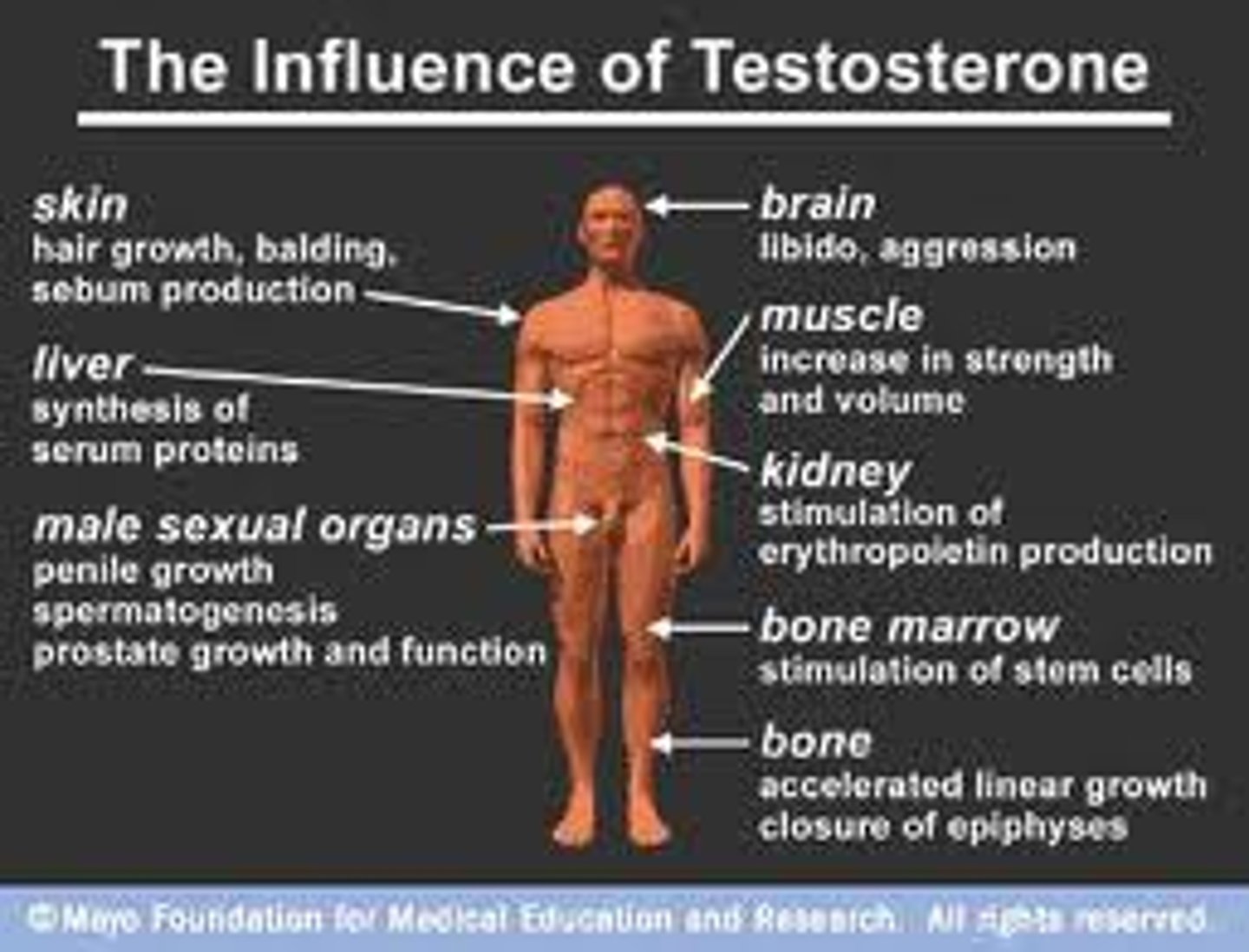
Roles of testosterone in males?
Stimulates change in male body during puberty ie secondary sexual characteristics
-Muscle growth
-Facial hair
-sperm production
Role of oestrogen in females?
Stimulate development of sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics
-Increase in hip size
-Breast develop
-Menstrual cycle starts
What is the role of two hormones in controlling the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
oestrogen - Causes thickening of the uterus lining
progesterone -Maintains the thickness of uterus lining for implantation
What is FSH and what does it do?
It is a hormone released by the pituitary gland Stimulates development of follicle cell in the ovary
What is LH and what does it do?
It is a hormone released by the pituitary gland. It stimulates the ovary to release matured egg cell