BIOL 103 Unit 1 Midterm
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
1
New cards
5 themes of life
1. structure fits function
2. information, storage, and flow
3. transformation of matter and energy
4. interactions between and within systems
5. evolution
\
SUMMARIZED:
1. Organization
2. Information
3. Energy and Matter
4. Interactions
5. Evolution
2
New cards
independent variable
variable that is manipulated
\
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
\
typically plotted on x axis
\
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
\
typically plotted on x axis
3
New cards
dependent variable
the factor being measured that is predicted to be affected by the independent variable
\
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.
\
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
\
typically plotted on y axis
\
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.
\
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
\
typically plotted on y axis
4
New cards
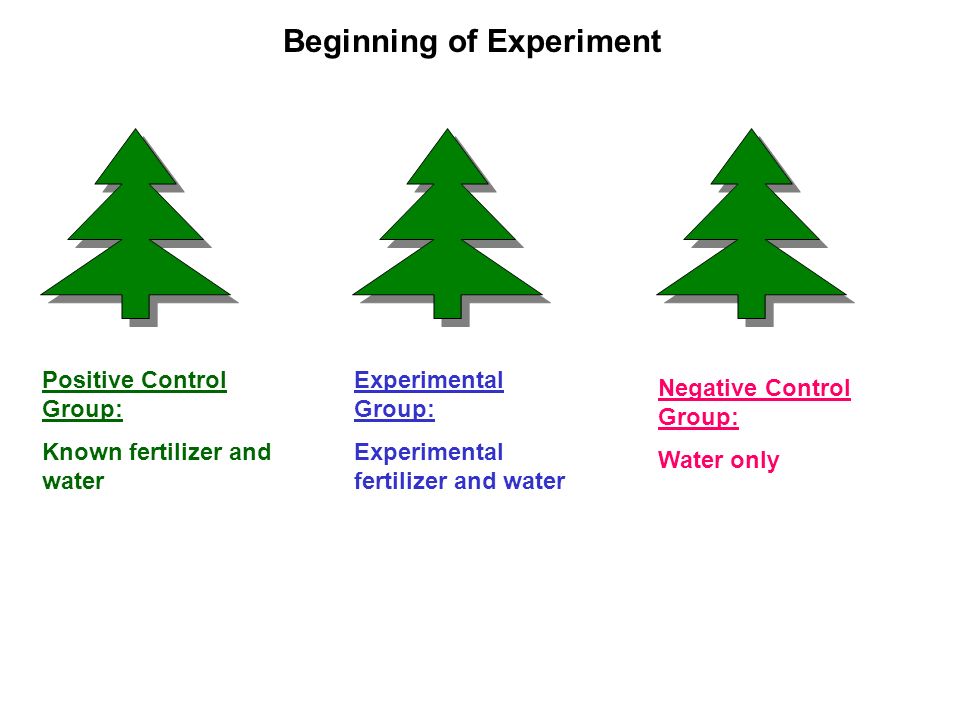
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment - BOTH positive and negative ctrls do NOT receive the independent variable
\
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
\
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
5
New cards
negative control group
a group of data lacking what is being tested so as to give expected negative results
\
Control group where conditions produce a negative outcome. Negative control groups help identify outside influences which may be present that were not accounted for when the procedure was created.
\
Control group where conditions produce a negative outcome. Negative control groups help identify outside influences which may be present that were not accounted for when the procedure was created.
6
New cards
positive control group
group where an effect is expected
\
expected to have a positive result, allowing the researcher to show that the experimental set up was capable of producing results.
\
expected to have a positive result, allowing the researcher to show that the experimental set up was capable of producing results.
7
New cards
control variables
the variables you keep the same in an experiment
\
variables held constant in an experiment so that the only variable changing is the independent variable
ex: temperature, pressure, etc
\
variables held constant in an experiment so that the only variable changing is the independent variable
ex: temperature, pressure, etc

8
New cards
experimental group
the group in an experiment that receives the variable being tested
\
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
\
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
9
New cards
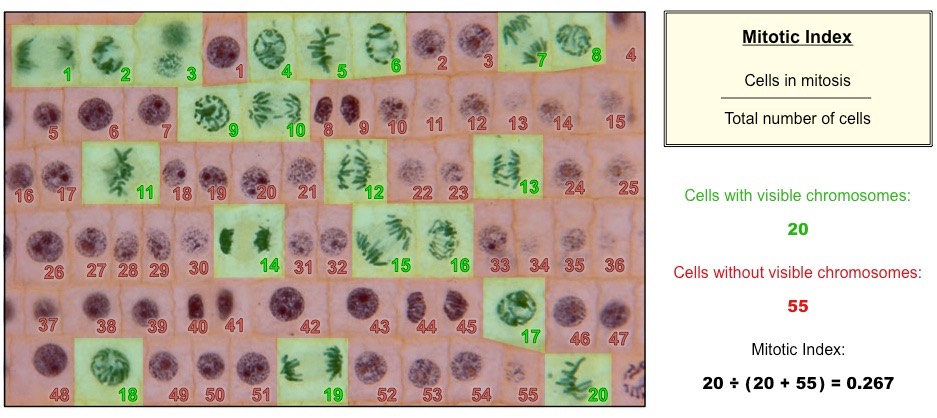
mitotic index
the ratio between the number of cells in mitosis to the total number of cells.
10
New cards
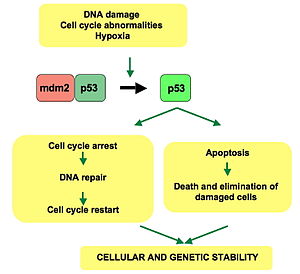
role of p53
p53 keeps cells from entering mitosis after DNA is damaged by the radiation for at least 96 hrs. When it is completely absent, cells with DNA damage begin replicating again at about 48 hrs
\
p53 activates in response to DNA damage and "assesses" whether they can be repaired. If DNA damage is limited, p53 activates DNA repair proteins. If DNA damage is so severe that it cannot be repaired, p53 activates the cascade of events leading to apoptosis, and the cell dies
\
p53 activates in response to DNA damage and "assesses" whether they can be repaired. If DNA damage is limited, p53 activates DNA repair proteins. If DNA damage is so severe that it cannot be repaired, p53 activates the cascade of events leading to apoptosis, and the cell dies
11
New cards
predict what might happen at a cellular and an individual level if a person has 1 normal and 1 mutated allele of the p53 gene
REMINDER: having a mutant (nonfunctional) p53 allele is a RECESSIVE trait → it takes BOTH alleles being mutated for p53 protein to stop functioning
\
*1 mutated allele:*
— cellular level: cells behave normal
— individual level: normal but this person does have a higher risk of developing cancer over their lifetime as only 1 allele needs to become mutated in a tissue to begin the process
*2 mutated alleles:*
— cellular level: cells divide rapidly, even when DNA is damaged
— individual level: likely means a phenotype of cancer
\
*1 mutated allele:*
— cellular level: cells behave normal
— individual level: normal but this person does have a higher risk of developing cancer over their lifetime as only 1 allele needs to become mutated in a tissue to begin the process
*2 mutated alleles:*
— cellular level: cells divide rapidly, even when DNA is damaged
— individual level: likely means a phenotype of cancer
12
New cards
is having a mutant p53 allele dominant or recessive
recessive (L1 part 1 graph \#1) - it takes 2 mutant alleles of p53 to show a mutant p53 phenotype
13
New cards
p53 protein
"guardian of the genome"
\
— encoded by the ***tumor suppressor gene***
— plays an important role in halting the division of cells (mitosis) that have sustained DNA damage
— arrests the cell cycle at 2 diff times: before DNA replication (G1→S) and before cell division begins (G2→M) - arresting the cel cycle at these points helps prevent the division of cells containing damaged DNA, which could become cancerous
— p53 is often mutated in cancers (this gene is mutated more often than any of the other 20,000 human genes) - a deeper understanding of the role of p53 in the cell cycle can therefore improve our understanding of cancers and perhaps lead to new forms of heat
\
— encoded by the ***tumor suppressor gene***
— plays an important role in halting the division of cells (mitosis) that have sustained DNA damage
— arrests the cell cycle at 2 diff times: before DNA replication (G1→S) and before cell division begins (G2→M) - arresting the cel cycle at these points helps prevent the division of cells containing damaged DNA, which could become cancerous
— p53 is often mutated in cancers (this gene is mutated more often than any of the other 20,000 human genes) - a deeper understanding of the role of p53 in the cell cycle can therefore improve our understanding of cancers and perhaps lead to new forms of heat
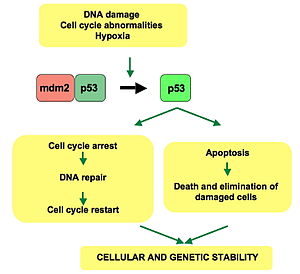
14
New cards
lateral flow assays
rapid lab test technique involve immunomigration (immunoassay) technology - used for at home COVID tests, pregnancy tests, etc
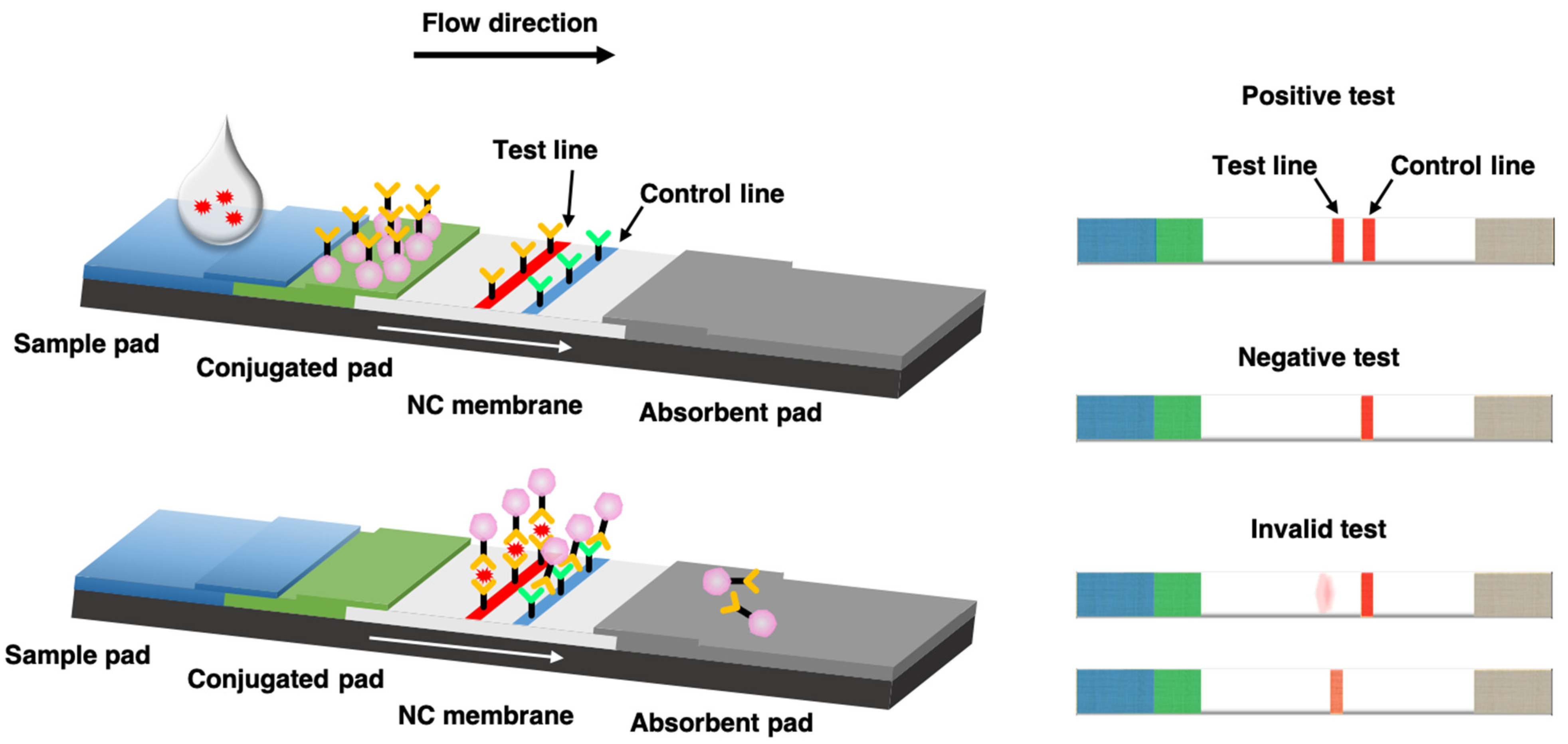
15
New cards
how do lateral flow tests work
1. add a sample to the test sample pad (ex: liquid you swirled your nasal swab in for COVID; urine for a pregnancy test) → that sample either has or does not have the analyte (the thing you're looking for - a protein from SARS-CoV2 for COVID test; hCG protein for pregnancy test)
\
2. the liquid moves soluble (unbound) antibody-nanoparticle complexes up the test strip
\
3. *IF analyte is present* the antibodies bind to the analyte proteins (ex: COVID proteins) through SPECIFIC binding bwn the soluble antibodies, nanoparticles, and analyte molecules
\
4. antibodies bind to the incubation and detection pad within the detection window where there is a test line and control line
a. REGARDLESS of if analyte is present, some antibodies are specific to ONLY the nanoparticles and antibodies on the ctrl line → antibodies that are soluble bind to the ctrl line antibodies and the nanoparticles → produces a line that shows the CTRL LINE recognized soluble antibodies and thus THE TEST IS WORKING
b. IF analyte IS present, you would ALSO see a line where the soluble antibodies have bound to the nanoparticles on one end and the analyte proteins on another end AND the test line's bound antibodies → the binding of both sets of antibodies to the nanoparticles AND the ANALYTE material ALSO produce a line, indicating that THE SAMPLE HAS THE ANALYTE IN IT (ex with COVID tests: this is the T line that shows up when you HAVE COVID)
16
New cards
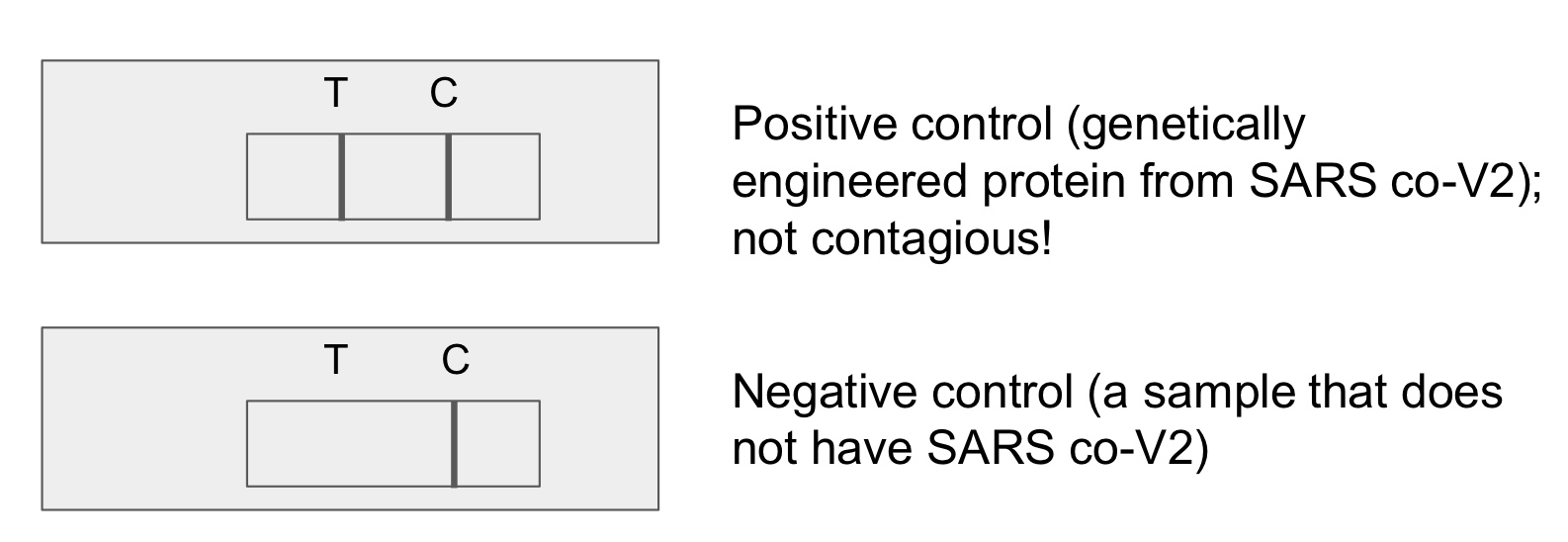
results of negative controls in lateral flow tests
control line: appears (proves that the test is working no matter if the analyte molecule is present or not)
\
test line: does not appear (proves that the test cannot detect the correct analyte molecule bc it is absent in a negative ctrl)
\
test line: does not appear (proves that the test cannot detect the correct analyte molecule bc it is absent in a negative ctrl)
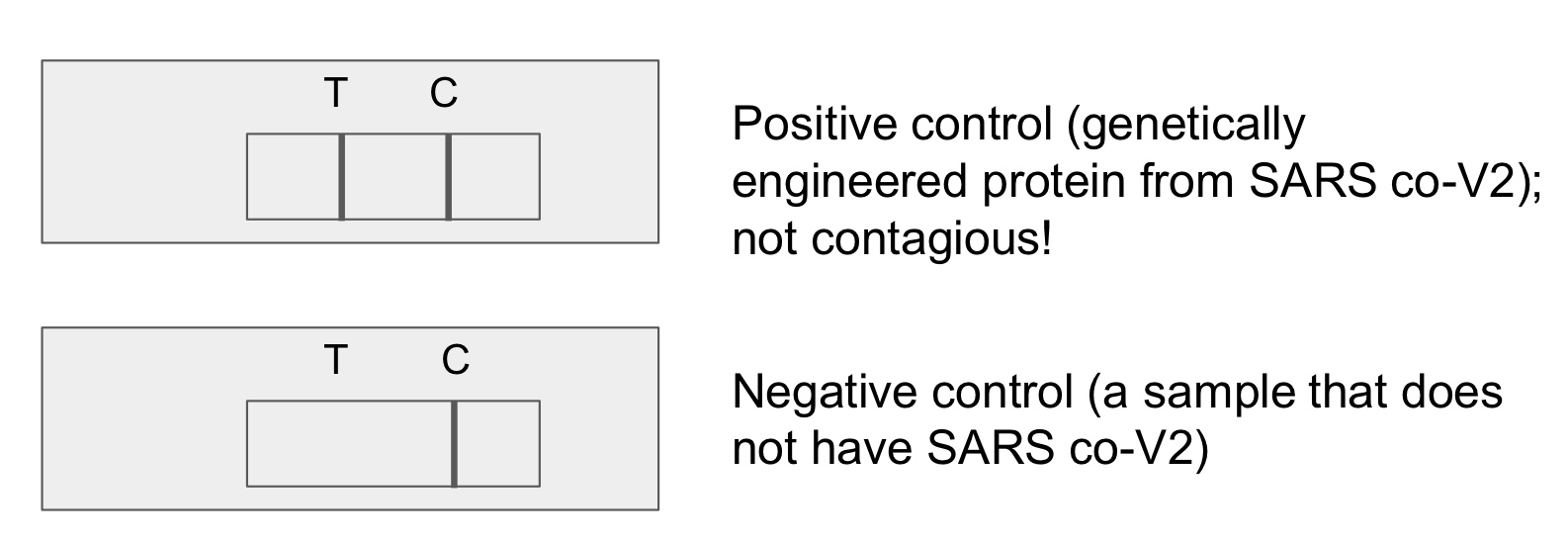
17
New cards
results of positive controls in lateral flow tests
control line: appears (proves that the test is working no matter if the analyte molecule is present or not)
\
test line: does appear (proves that the test can detect the correct analyte molecule bc it is present in a positive ctrl)
\
test line: does appear (proves that the test can detect the correct analyte molecule bc it is present in a positive ctrl)
18
New cards
correlation coefficient
a statistical measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other
\
a statistical measure of how closely data fit a linear relationship
\
(coefficient *r* ranges from from -1 to +1)
\
a statistical measure of how closely data fit a linear relationship
\
(coefficient *r* ranges from from -1 to +1)
19
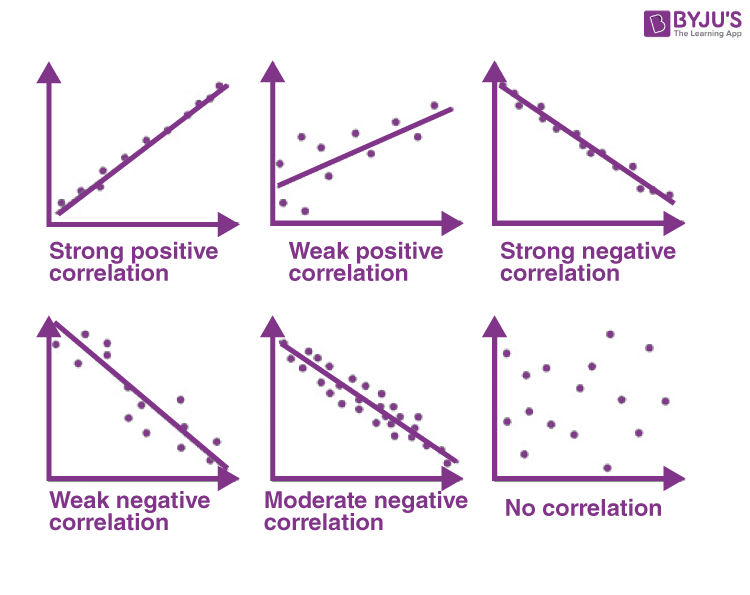
New cards
correlation coefficient values and meaning
r ranges from -1 to +1
\
|r| tells the strength of correlation:
* the closer |r| gets to 1, the stronger the correlation
* the closer |r| gets to 0, the weaker the correlation
\
sign of r (negative or positive) tells the direction of correlation:
* when r>0, x and y are *positively* correlated (y becomes larger as x becomes larger)
* when r
\
|r| tells the strength of correlation:
* the closer |r| gets to 1, the stronger the correlation
* the closer |r| gets to 0, the weaker the correlation
\
sign of r (negative or positive) tells the direction of correlation:
* when r>0, x and y are *positively* correlated (y becomes larger as x becomes larger)
* when r
20
New cards
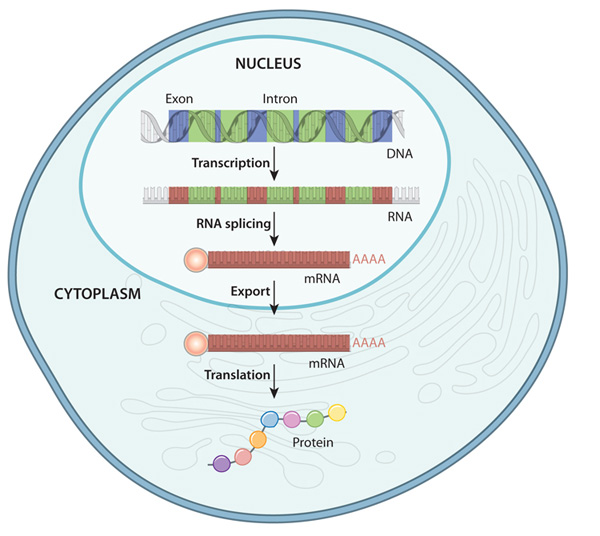
gene expression order
1. transcription (DNA → pre-mRNA)
2. mRNA processing (pre-mRNA → mature mRNA)
3. mRNA transport (nucleus → cytoplasm)
4. translation (mature mRNA → polypeptide sequence)
5. protein processing (polypeptide sequence → folded/modified protein)
6. protein transport (cytoplasm → various locations)
21
New cards
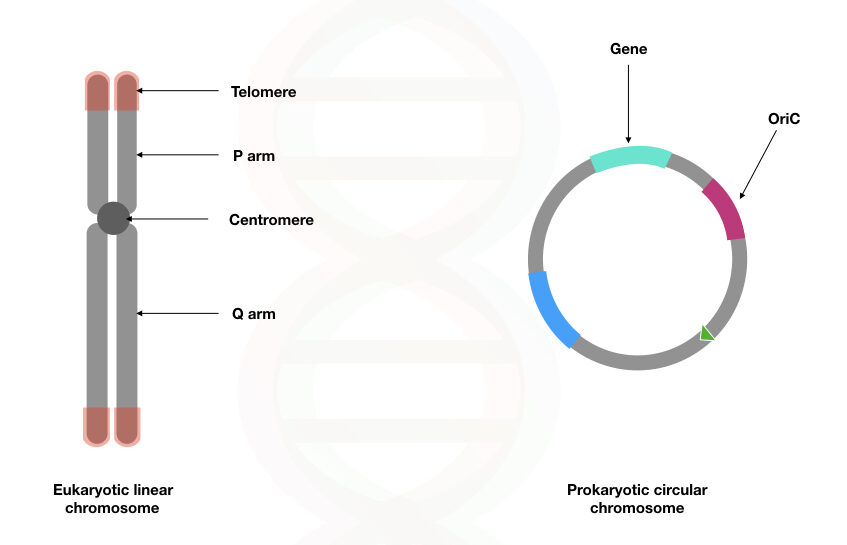
1. structure of DNA
2. where is DNA found in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes
3. how is DNA packaged in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes
1. double-helix structure: sugar-phosphate backbone, nitrogenous base (A, C, T, or G)
\
2. location of DNA:
1. eukaryotes: found in nucleus
2. b. prokaryotes: found in nucleoid region (cytoplasm)
\
3. DNA packaging:
1. eukaryotes: DNA unwound is packaged as chromatin wrapped around histones; packaged DNA is linear chromosomes
2. prokaryotes: DNA unwound is NOT packaged around histones; packaged DNA is circular chromosomes
22
New cards
transcription:
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
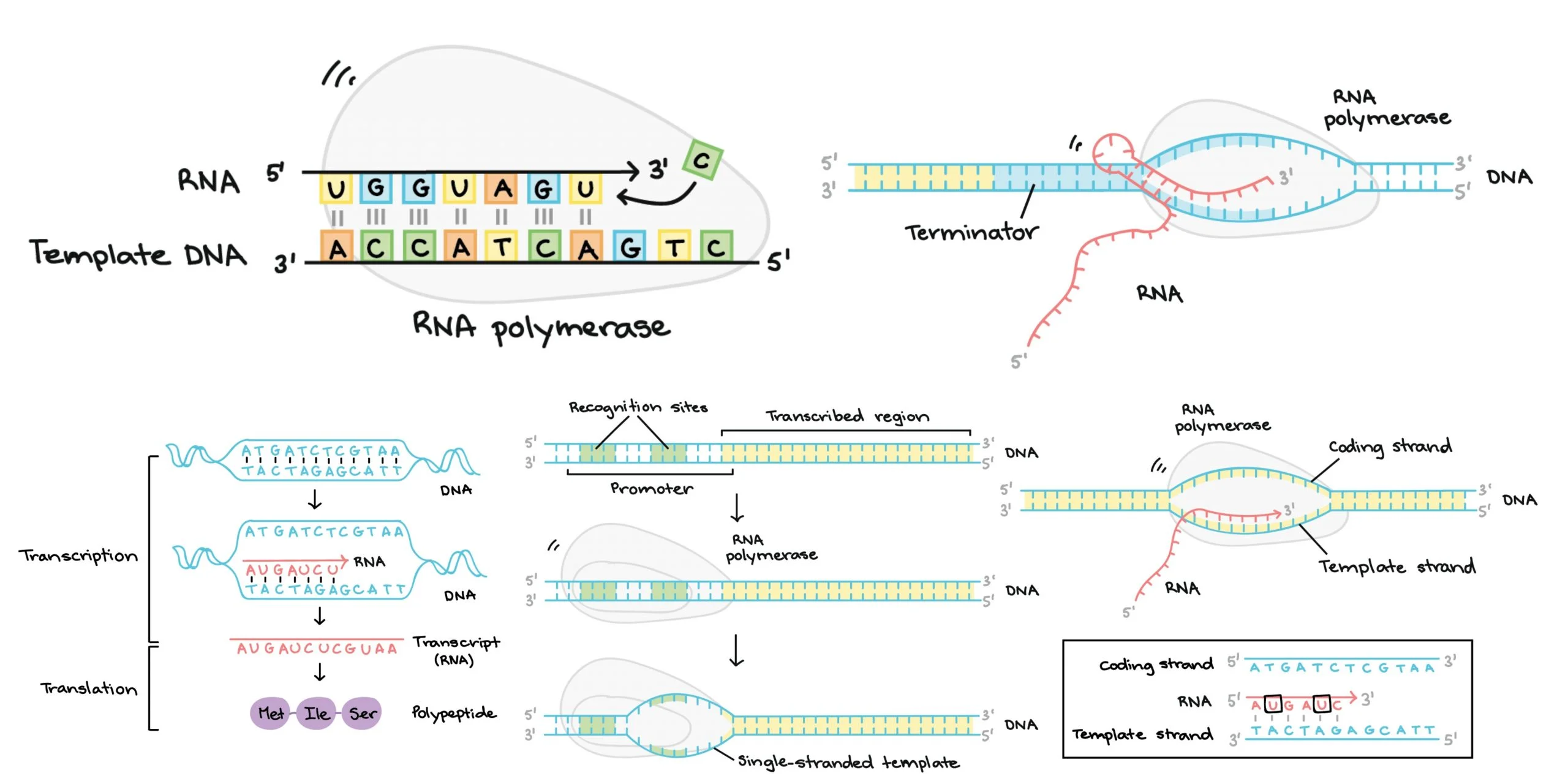
1. synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
2. takes place in nucleus
3. involves:
1. DNA template strand (3’→5’)
2. RNA polymerase (binds to template strand and reads DNA 3’→5’ while building mRNA 5’→3’)
4. unmodified RNA molecule containing exons and introns
23
New cards
transcription steps
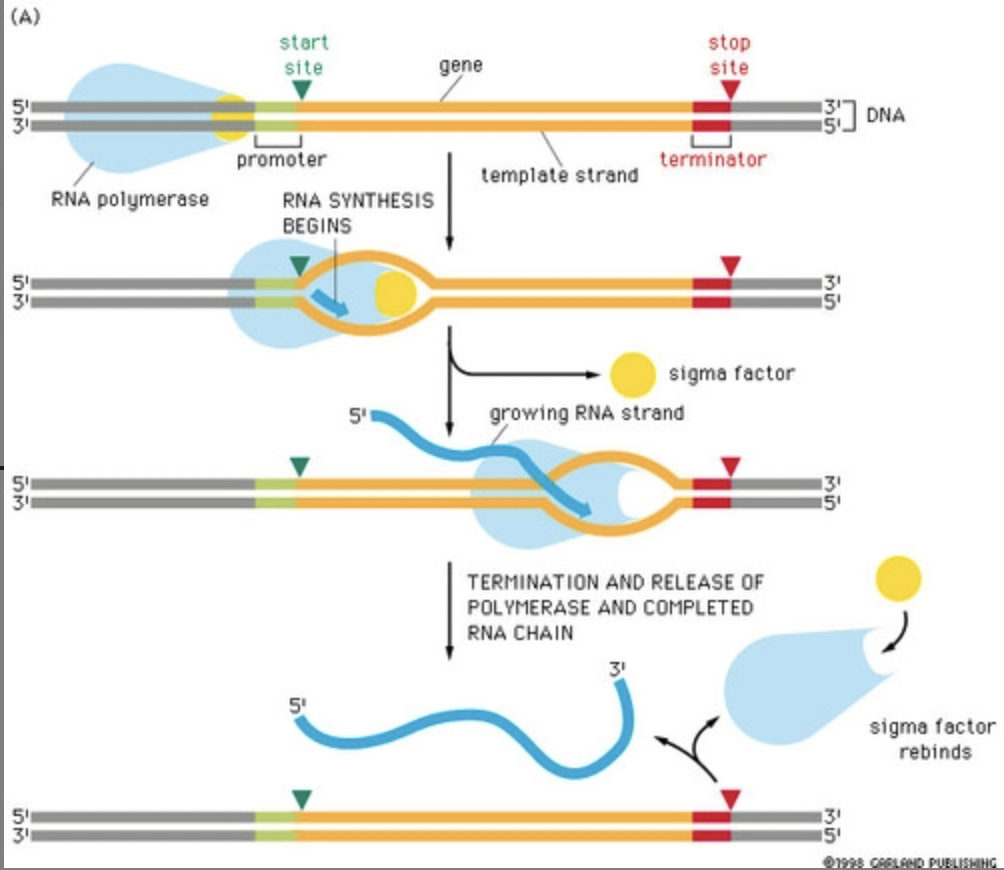
***1. Initiation:*** RNA polymerase binds to the promoter (TATA) at the beginning of the gene to be transcribed
\
***2. Elongation:*** RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA molecules in 5' → 3' direction by reading DNA in 3' → 5' direction
\
***3. Termination:*** ends when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence → DNA "re-zips" and is unchanged by the process
\
***2. Elongation:*** RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA molecules in 5' → 3' direction by reading DNA in 3' → 5' direction
\
***3. Termination:*** ends when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence → DNA "re-zips" and is unchanged by the process
24
New cards
RNA modifications
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
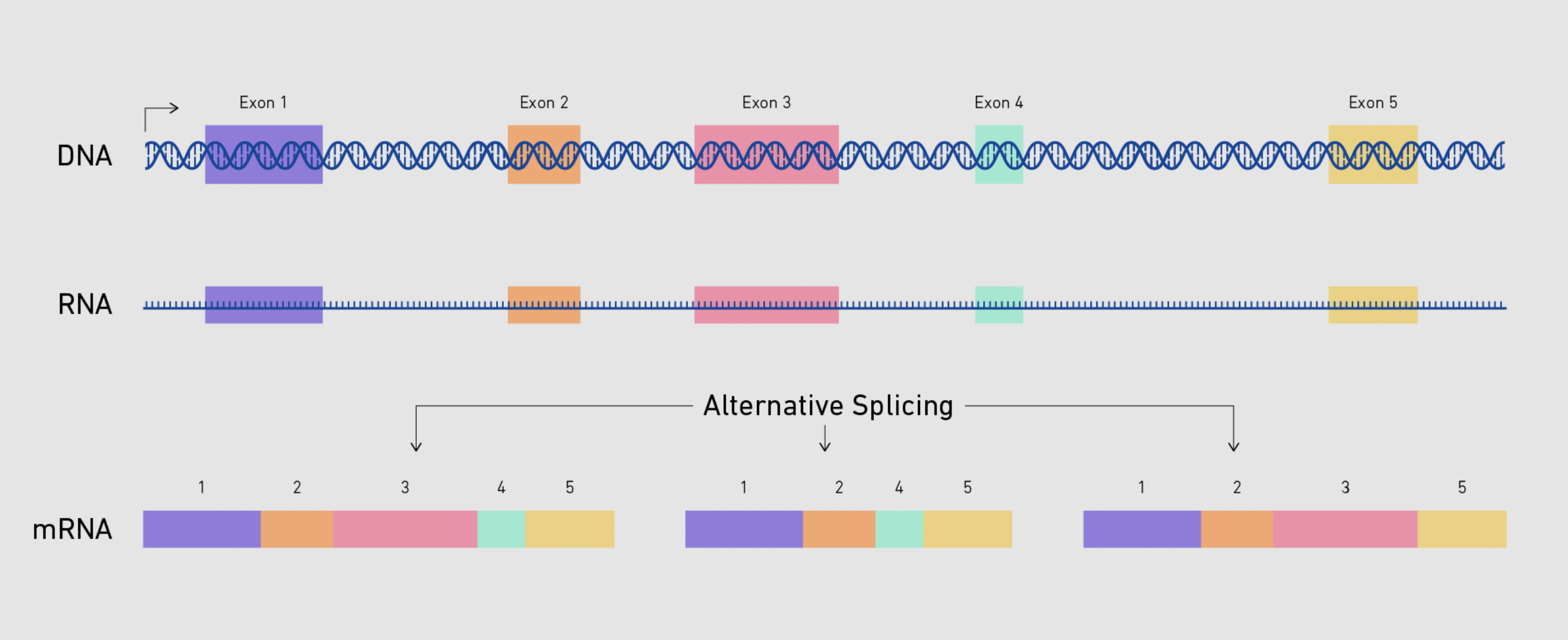
1. modifying the RNA molecule produced from transcription to prepare it for RNA export
2. takes place in nucleus
3. involves:
1. spliceosome (protein that removes introns and joins exons together)
2. GTP (methyl) - added to 5’ end of RNA
3. Adenine - added to 3’ end of RNA
4. result: mature mRNA produced
1. introns removed from pre-mRNA and exons rejoined
2. GTP cap (5’) and poly-Adenine tail (3’) added (protects ends from degredation by exonucleases in cytoplasm and assists with translation initiation)
\
*important regulatory process with splicing: ALTERNATIVE splicing*
25
New cards
translation:
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
1. overview of process
2. location
3. what is involved
4. result
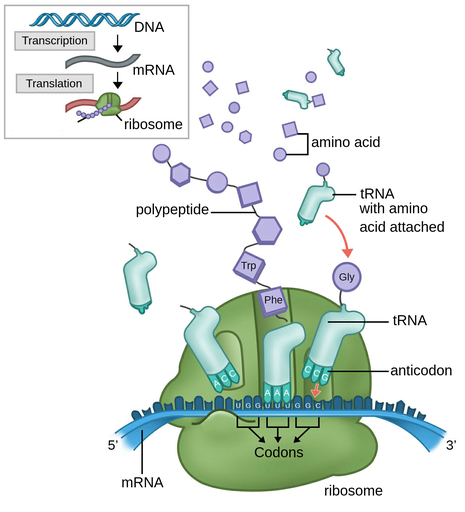
1. polypeptide synthesized from mRNA molecule
2. location in the cytoplasm
3. involves:
1. ribosome (both small and large subunits)
2. tRNA (transfer RNA) to carry amino acids to correct codon on the ribosome
3. mature mRNA
4. result: 1º (primary) sequence of polypeptide joined together
26
New cards
3 sites of ribosome
A site: "acceptor site" (actually aminoacyl-tRNA binding site) - where new tRNAs get accepted; when AUG (start codon) enters A site → translation begins
\
P site: "peptide site" (actually peptidyl-tRNA binding site) - the peptide (covalent) bond forms bwn amino acid @ P site and amino acid @ A site
\
E site: "exit site" - empty tRNA exits the ribosome to pick up another amino acid from cytoplasm
\
P site: "peptide site" (actually peptidyl-tRNA binding site) - the peptide (covalent) bond forms bwn amino acid @ P site and amino acid @ A site
\
E site: "exit site" - empty tRNA exits the ribosome to pick up another amino acid from cytoplasm
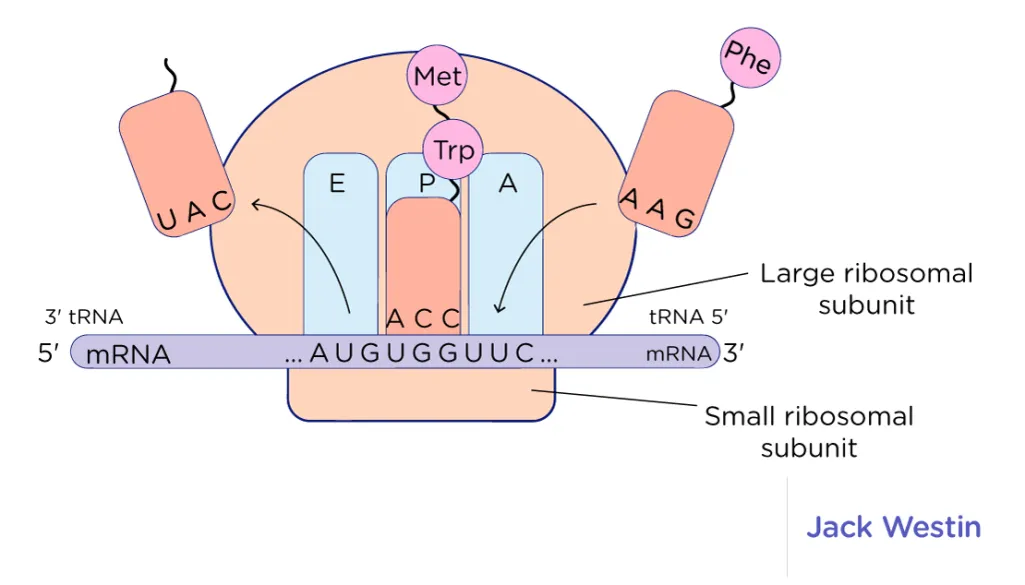
27
New cards
translation steps
***1. Initiation:*** mRNA in cytoplasm binds to a ribosome (rRNA) → translational complex forms (E, P, A are already together on SMALL subunit of ribosome BUT when AUG of mRNA gets in the P site, the LARGE subunit combines with small subunit + tRNA comes in → forms transitional complex) and tRNA carrying Methionine brings first amino acid in polypeptide chain to bind to start codon on mRNA
→ in prokaryotes, small ribosome can bind to EITHER the mRNA OR methionine tRNA in EITHER order
→ in eukaryotes, small ribosome binds to mRNA 5' cap FIRST and and THEN moves/scans downstream along mRNA until it reaches AUG codon; THEN tRNA binds to ribosome/AUG codon
\
***2. Elongation:*** tRNAs bring amino acids by one to add to polypeptide chain (tRNAs anticodons bind to the codons on the mRNA sequence) - mRNA loaded into A site of ribosome and the tRNA comes to A site with the proper amino acid → amino acid binds to codon and is now in close proximity with P site amino acid → PEPTIDE BOND is formed bwn amino acid @ P and @ A site and tRNA bond with amino acid is broken (one bond formed leads to breaking the other - energy coupling) → amino acid and mRNA (now broken from each other) shift to E site and leave ribosome, allowing new codon to enter A site
\
***3. Termination:*** release factor recognizes stop codon (UAA/UAG/UGA) and binds to A site where stop codon is → release factor causes the addition of a WATER molecule instead of amino acid to polypeptide chain → this rxn HYDROLYZES (BREAKS) the bond bwn completed polypeptide and the tRNA in the P site → translational complex dissociates and completed polypeptide is released through the exit tunnel of the ribosome's large subunit
→ in prokaryotes, small ribosome can bind to EITHER the mRNA OR methionine tRNA in EITHER order
→ in eukaryotes, small ribosome binds to mRNA 5' cap FIRST and and THEN moves/scans downstream along mRNA until it reaches AUG codon; THEN tRNA binds to ribosome/AUG codon
\
***2. Elongation:*** tRNAs bring amino acids by one to add to polypeptide chain (tRNAs anticodons bind to the codons on the mRNA sequence) - mRNA loaded into A site of ribosome and the tRNA comes to A site with the proper amino acid → amino acid binds to codon and is now in close proximity with P site amino acid → PEPTIDE BOND is formed bwn amino acid @ P and @ A site and tRNA bond with amino acid is broken (one bond formed leads to breaking the other - energy coupling) → amino acid and mRNA (now broken from each other) shift to E site and leave ribosome, allowing new codon to enter A site
\
***3. Termination:*** release factor recognizes stop codon (UAA/UAG/UGA) and binds to A site where stop codon is → release factor causes the addition of a WATER molecule instead of amino acid to polypeptide chain → this rxn HYDROLYZES (BREAKS) the bond bwn completed polypeptide and the tRNA in the P site → translational complex dissociates and completed polypeptide is released through the exit tunnel of the ribosome's large subunit
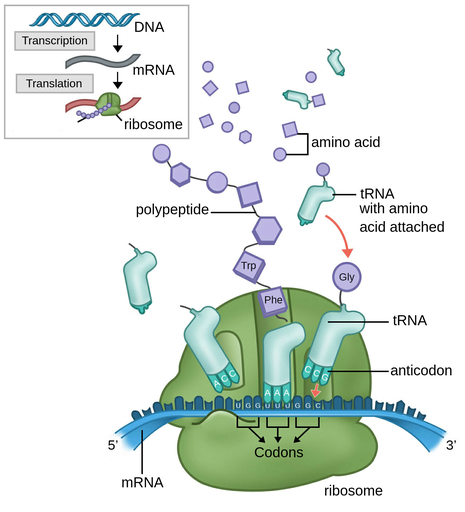
28
New cards
what makes a protein mature
* folded properly (dictated by primary sequence of amino acids interacting with each other and the environment)
* some amino acids may be added/removed
* sugars or other chemical groups may be added
* other polypeptides may be joined
* some amino acids may be added/removed
* sugars or other chemical groups may be added
* other polypeptides may be joined
29
New cards
polarity of polypeptides
N-terminus: *positively-charged*
* the end first made by the ribosome
* corresponds with 5’ end of mRNA (3’ end of template strand DNA)
* contains the amine group for protein backbone (NH3+)
\
C-terminus: *negatively-charged*
* the end made last by the ribosome
* corresponds with 3’ end of mRNA (5’ end of template strand DNA)
* contains the carboxyl group for protein backbone (COO-)
* the end first made by the ribosome
* corresponds with 5’ end of mRNA (3’ end of template strand DNA)
* contains the amine group for protein backbone (NH3+)
\
C-terminus: *negatively-charged*
* the end made last by the ribosome
* corresponds with 3’ end of mRNA (5’ end of template strand DNA)
* contains the carboxyl group for protein backbone (COO-)
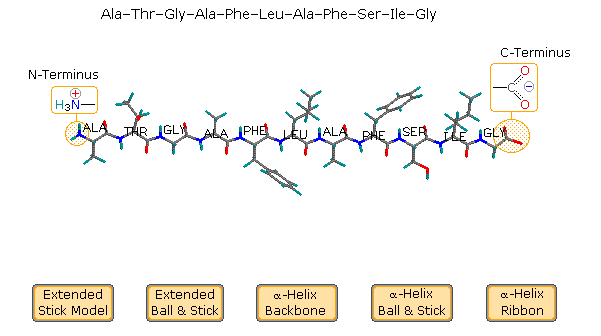
30
New cards
how do proteins fold?
hydrophilic R groups fold together and fold facing hydrophilic molecules in the environment
\
hydrophobic R groups fold together and fold facing hydrophobic molecules in the environment
\
hydrophobic R groups fold together and fold facing hydrophobic molecules in the environment
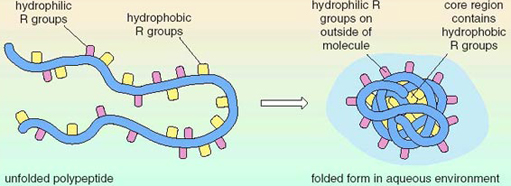
31
New cards
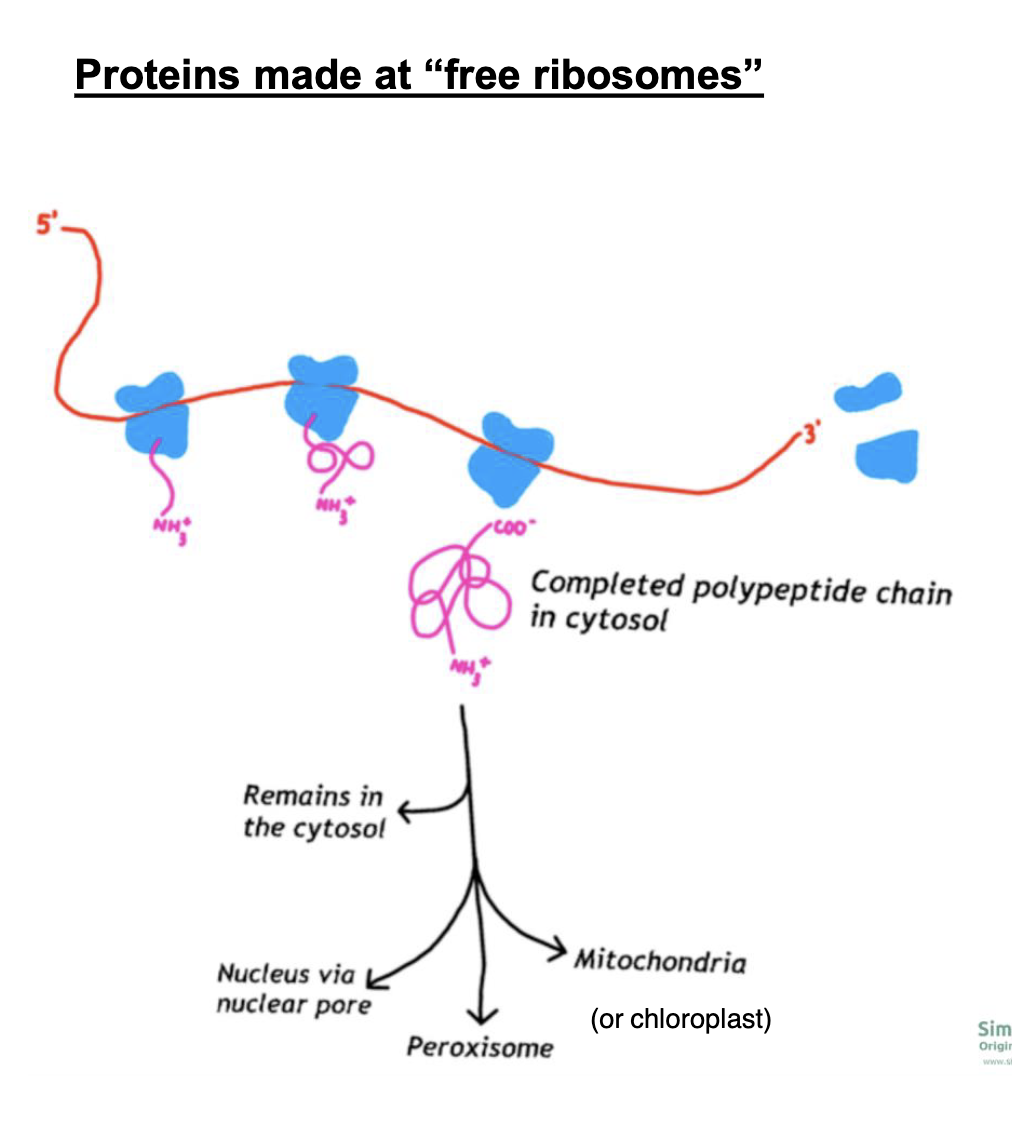
where can proteins made in the cytosol by free-floating ribosomes end up?
* remain in the cytosol
* enter nucleus via nuclear pore
* go to mitochondria (or chloroplast)
* go to peroxisome
* *go to ROUGH ER - signaled to go to other places OUT of the cell*
* enter nucleus via nuclear pore
* go to mitochondria (or chloroplast)
* go to peroxisome
* *go to ROUGH ER - signaled to go to other places OUT of the cell*
32
New cards
where can proteins made by the rough ER end up?
*enter endomembrane system*
\
* remain in the rough ER
* go to golgi apparatus to get modified/packaged and go to:
* secretory vesicle (exits cell)
* lysosome
* plasma membrane (remain attached to cell)
\
* remain in the rough ER
* go to golgi apparatus to get modified/packaged and go to:
* secretory vesicle (exits cell)
* lysosome
* plasma membrane (remain attached to cell)
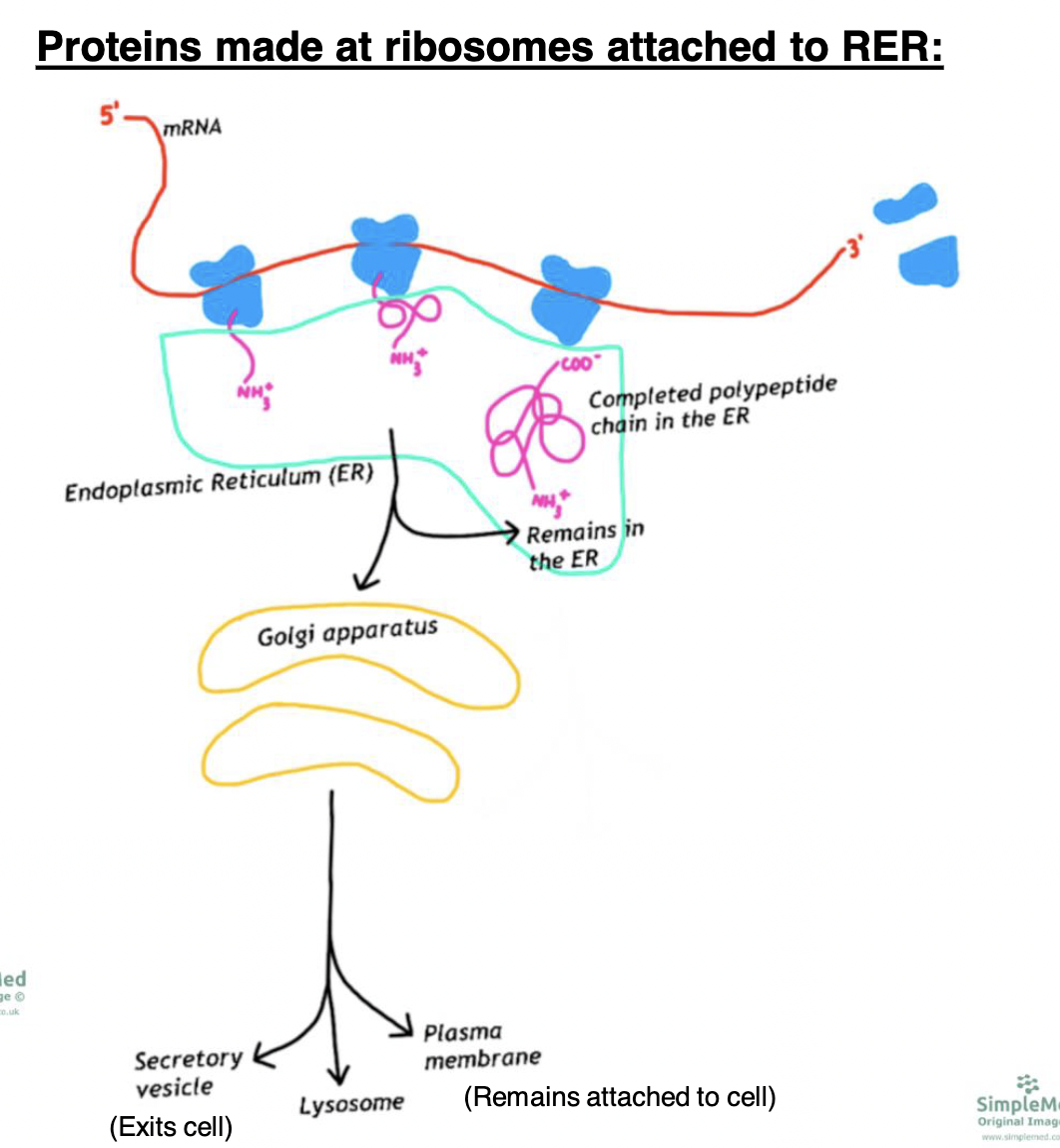
33
New cards
how did scientists find the sequence for proteins that acts like a zip code for the rough ER?
scientists used gene cutting/pasting techniques to cut specific sequences of amino acids from a polypeptide chain KNOWN to go to rough ER and attached these sequences to a known cytoplasmic protein (NOT destined for RER) → produced a bunch of hybrid proteins in the cell that were cytoplasmic proteins + diff short sequences from RER-destined proteins to find which specific sequence of amino acids served as the ***signal sequence*** for a RER-destined protein
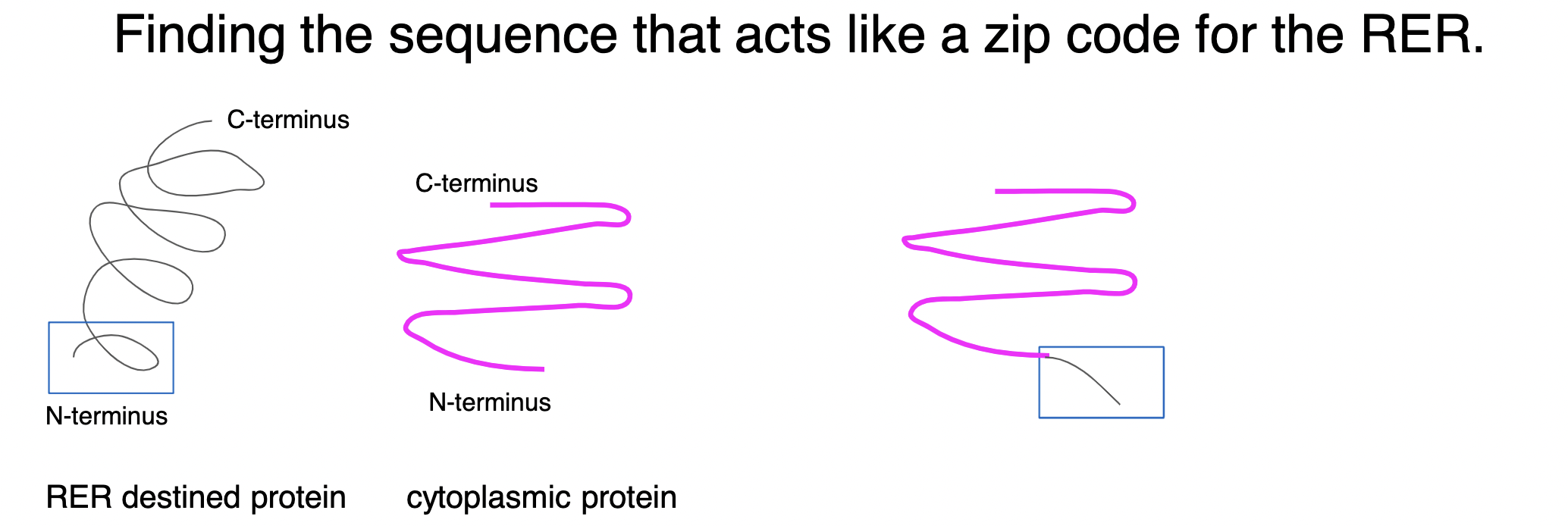
34
New cards
signal sequence
short tail of amino acids that directs a protein to a specific cellular compartment/organelle
\
a short sequence of amino acids (approx. 15 amino acids), usually found at the N-terminus of a protein being translated, that directs the ribosome and its associated mRNA to the membranes of the rough ER where translation will be completed
\
*signal sequences are found on membrane-bound proteins, secreted proteins, and proteins destined for other organelles*
\
a short sequence of amino acids (approx. 15 amino acids), usually found at the N-terminus of a protein being translated, that directs the ribosome and its associated mRNA to the membranes of the rough ER where translation will be completed
\
*signal sequences are found on membrane-bound proteins, secreted proteins, and proteins destined for other organelles*
35
New cards
do signal sequences exist only for RER-destined proteins?
NO - there are other sequences that locate proteins to specific locations such as a nuclear localization sequence or a mitochondrial localization sequence
36
New cards
what happens to signal sequences after a protein is directed to the appropriate location?
sometimes, they’re cleaved (cut) off, and sometimes they stay as a part of the protein
37
New cards
hemoglobin
a protein in the cytoplasm of red blood cells that functions to deliver oxygen to all of our cells
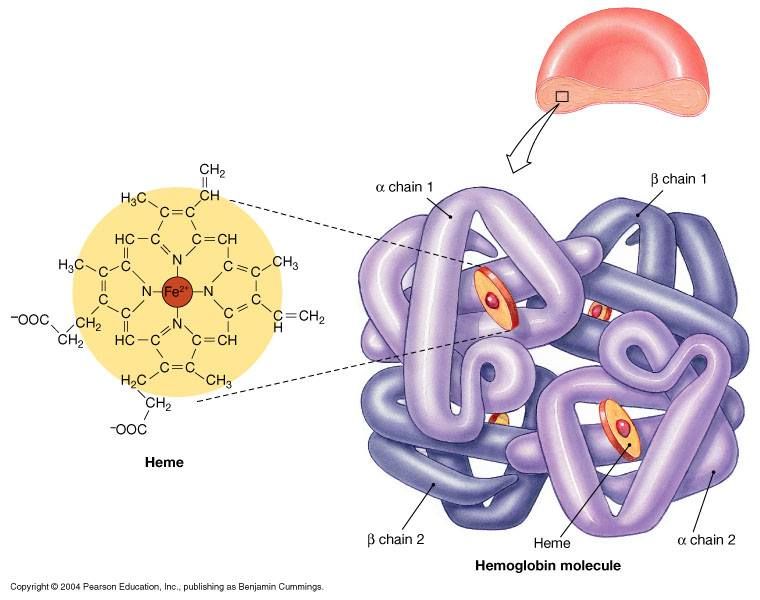
38
New cards
what structure allows hemoglobin to hold oxygen?
hemoglobin is a protein with ***quaternary structure*** (more than 2 polypeptides that make up its structure) made up of ***4*** polypeptide subunits → each subunit holds a ***heme group*** that has a high affinity for binding oxygen
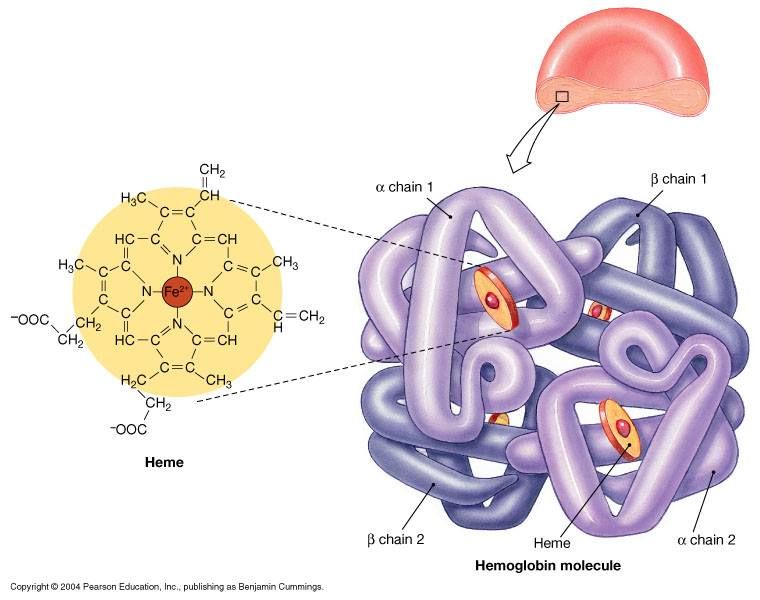
39
New cards
1. is the DNA of every cell in the body the same?
2. are all genes expressed in every cell?
1. YES - so every cell has the same GENES
2. NO - NOT all pieces of DNA gets transcribed/translated/expressed in every cell → how cells can have the same DNA but perform different functions
40
New cards
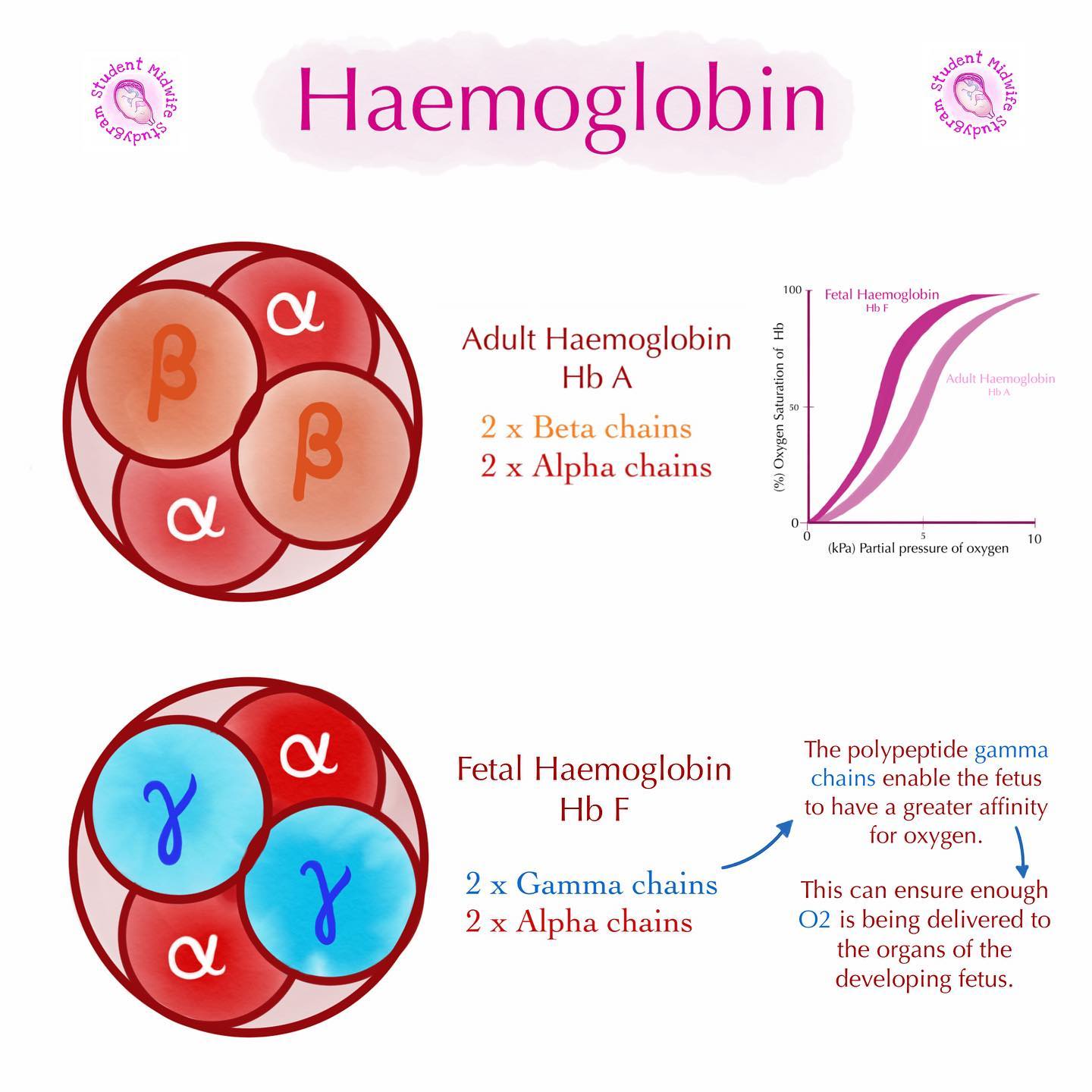
fetal vs adult hemoglobin
fetal: made from 2 α subunits (transcribed/translated from α gene) and 2 γ subunits (transcribed/translated from γ gene)
\
adult: made from 2 α subunits (transcribed/translated from α gene) and 2 β subunits (transcribed/translated from β gene)
\
adult: made from 2 α subunits (transcribed/translated from α gene) and 2 β subunits (transcribed/translated from β gene)
41
New cards
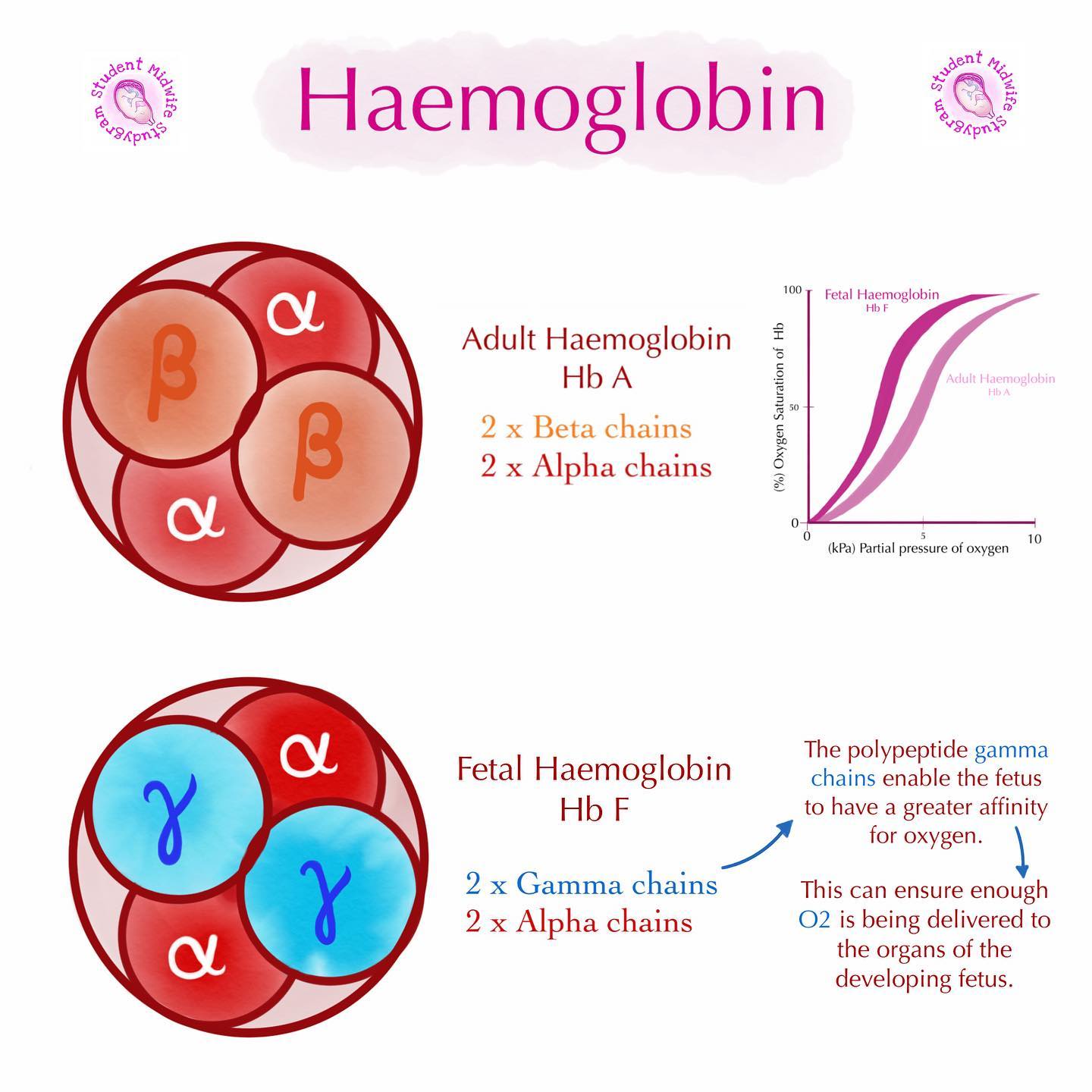
why is fetal hemoglobin different from adult hemoglobin?
REMINDER: fetal hemoglobin made from 2 α subunits + *2 γ subunits* VS. adult hemoglobin made from 2 α subunits + *2 β subunits*
\
fetus gets O2 from mother - blood of mom does NOT circulate to fetus directly: blood from mom gets stopped from transferring to baby by placenta → placenta then transfers the O2 from mom’s blood to fetal blood → fetal hemoglobin has to have a HIGHER O2 affinity → makes O2 transfer easier
\
fetus gets O2 from mother - blood of mom does NOT circulate to fetus directly: blood from mom gets stopped from transferring to baby by placenta → placenta then transfers the O2 from mom’s blood to fetal blood → fetal hemoglobin has to have a HIGHER O2 affinity → makes O2 transfer easier
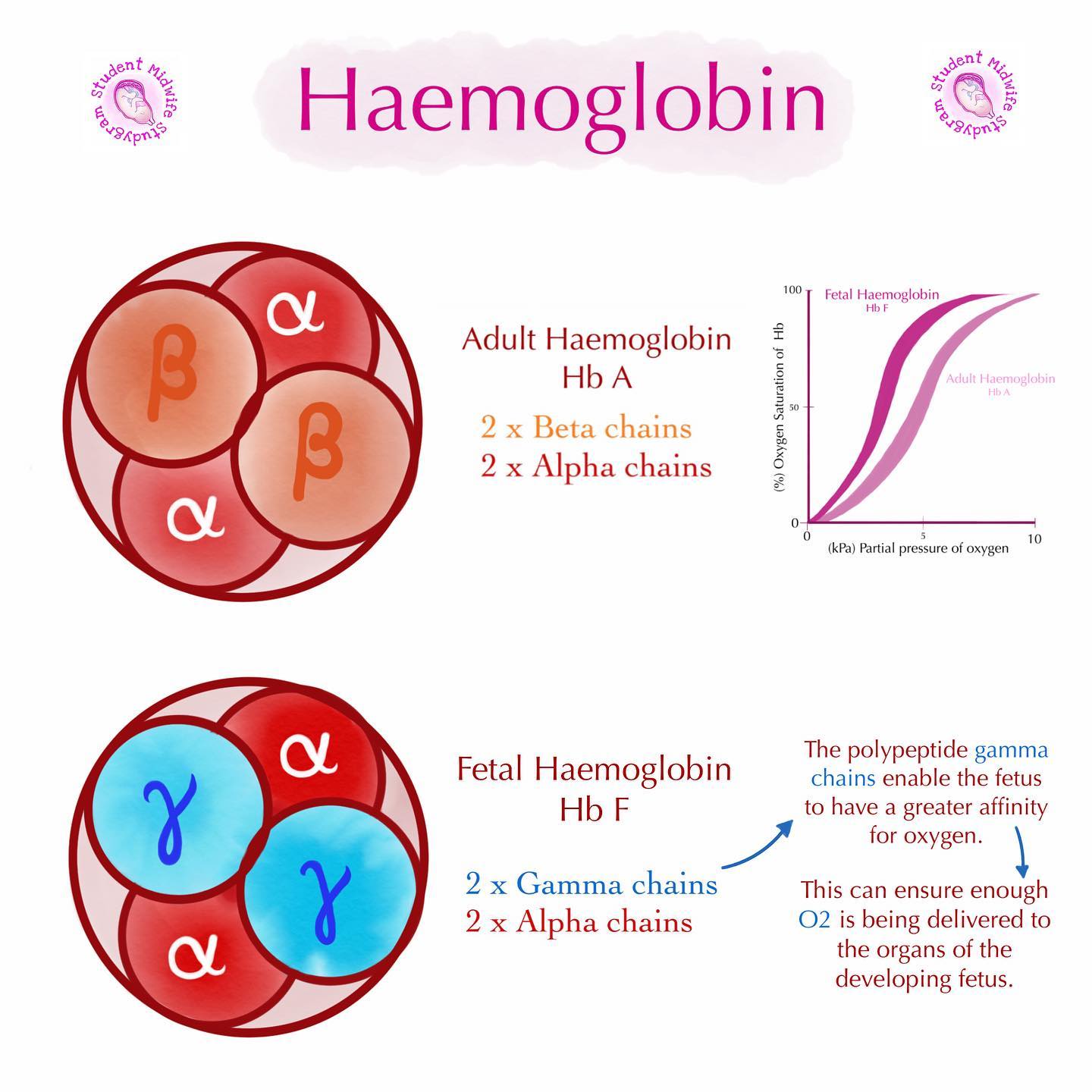
42
New cards
how does the body switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin
REMINDER: fetal hemoglobin made from 2 α subunits + *2 γ subunits* VS. adult hemoglobin made from 2 α subunits + *2 β subunits*
\
after birth, BCL11A protein BLOCKS transcription of γ gene (gene still exists BUT transcription of gene is inhibited) → γ subunits NOT transcribed/translated into γ gene → α subunits still being made but now β subunits ALSO being made
\
after birth, BCL11A protein BLOCKS transcription of γ gene (gene still exists BUT transcription of gene is inhibited) → γ subunits NOT transcribed/translated into γ gene → α subunits still being made but now β subunits ALSO being made
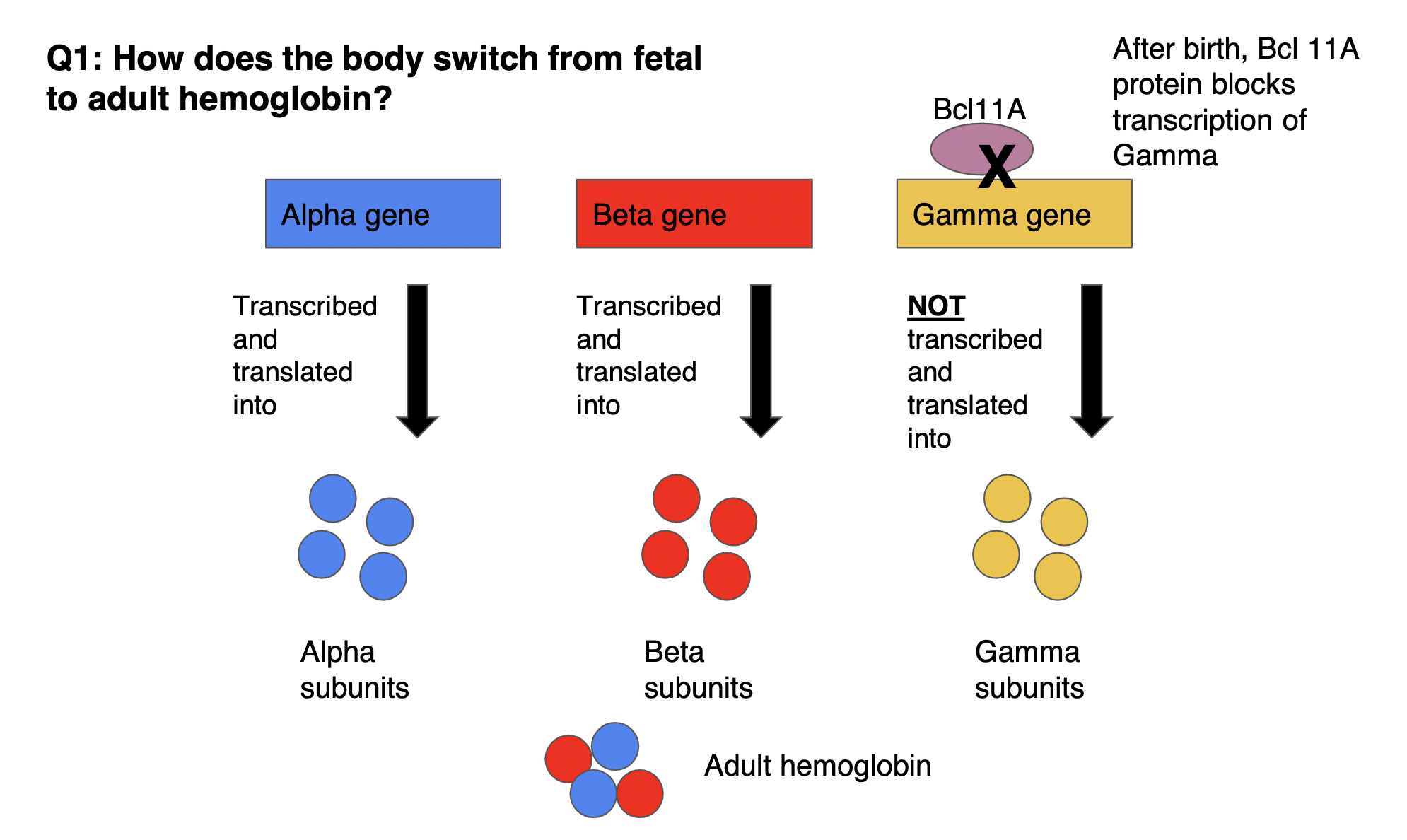
43
New cards
what is sickle-cell hemoglobin?
a mutation (DNA change) to the β gene, resulting in mutated β subunits being produced in adult hemoglobin (*reminder:* *BCL11A still represses γ gene transcription like normal adult hemoglobin)* → forms misshapen blood cell that has lower O2 binding affinity AND bc of the shape can easily also get stuck in/clog capillaries
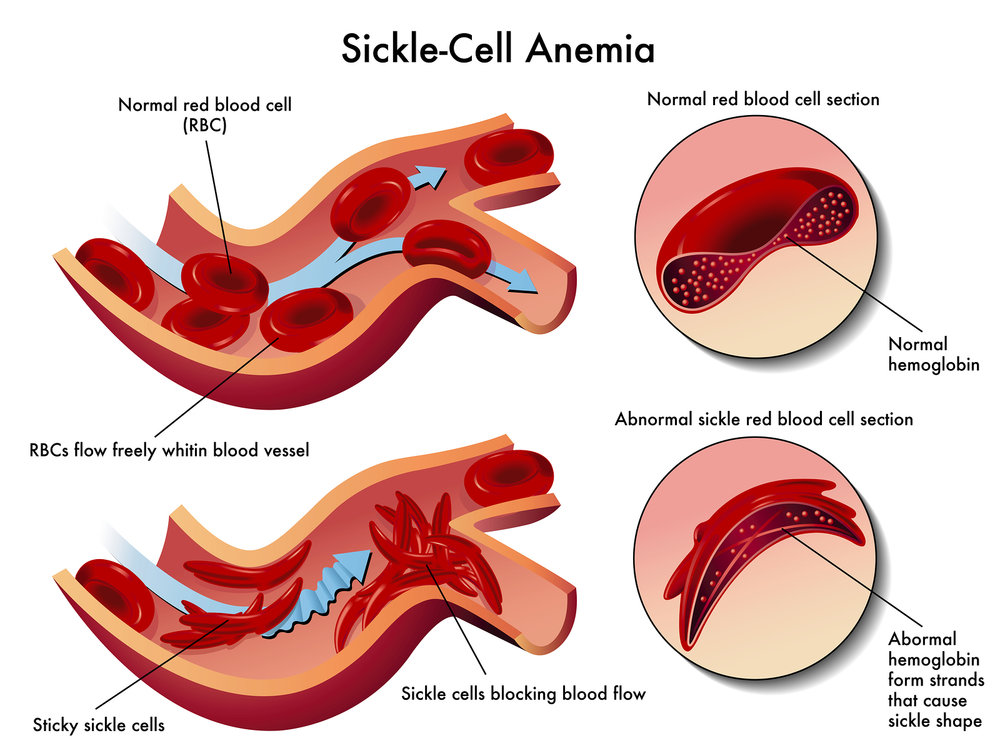
44
New cards
genetic medicine techniques
1. CRISPR
2. gene therapy
3. gene switches
4. RNA interference
5. small molecule drug
45
New cards
RNA interference
(genetic medicine technique)
\
(also regulatory mechanism within cells to destroy RNA so that it doesn't get repeatedly translated)
\
Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA/siRNA silencing complex
\
technique to silence the expression of selected genes in organisms; uses synthetic double-stranded RNA molecules matching the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene's messenger RNA
\
(also regulatory mechanism within cells to destroy RNA so that it doesn't get repeatedly translated)
\
Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA/siRNA silencing complex
\
technique to silence the expression of selected genes in organisms; uses synthetic double-stranded RNA molecules matching the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene's messenger RNA
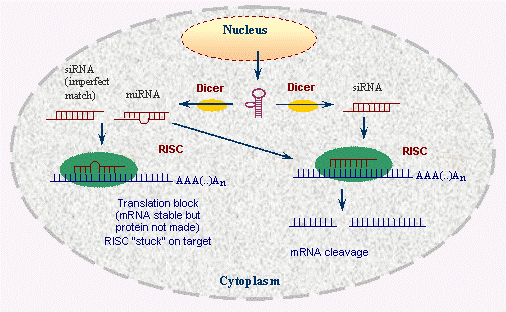
46
New cards
how does RNA interference work?
(RNA interference = RNAi)
\
process is called GENE SILENCING: regulates mRNA lifespan - breaks down mRNA or stops it from functioning so no more protein can be made
\
RNAi involves either small interfering RNAs (siRNA) OR microRNA (miRNA)
\
OVERALL PROCESS:
1. introduction of dsRNA (double-stranded RNA) (sequence generated in lab)
2. dsRNA is cut into 21 nucleotide frags by an enzyme "DICER" *(fragments consist of 19 base pairs with 2 nucleotide of unpaired base at each 5' end)*
3. the 2 strands of the fragments are separated and incorporated into the RISC complex
4. single stranded 21 nt RNA guides RISC to a complementary mRNA
5. finally degradation occurs
\
siRNA binds to complimentary RNA strand, binding activates RISC complex, siRNA-RISC has catalytic activity that can degrade the complimentary mRNA
\
process is called GENE SILENCING: regulates mRNA lifespan - breaks down mRNA or stops it from functioning so no more protein can be made
\
RNAi involves either small interfering RNAs (siRNA) OR microRNA (miRNA)
\
OVERALL PROCESS:
1. introduction of dsRNA (double-stranded RNA) (sequence generated in lab)
2. dsRNA is cut into 21 nucleotide frags by an enzyme "DICER" *(fragments consist of 19 base pairs with 2 nucleotide of unpaired base at each 5' end)*
3. the 2 strands of the fragments are separated and incorporated into the RISC complex
4. single stranded 21 nt RNA guides RISC to a complementary mRNA
5. finally degradation occurs
\
siRNA binds to complimentary RNA strand, binding activates RISC complex, siRNA-RISC has catalytic activity that can degrade the complimentary mRNA
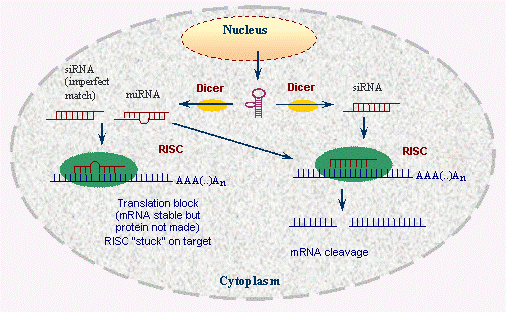
47
New cards
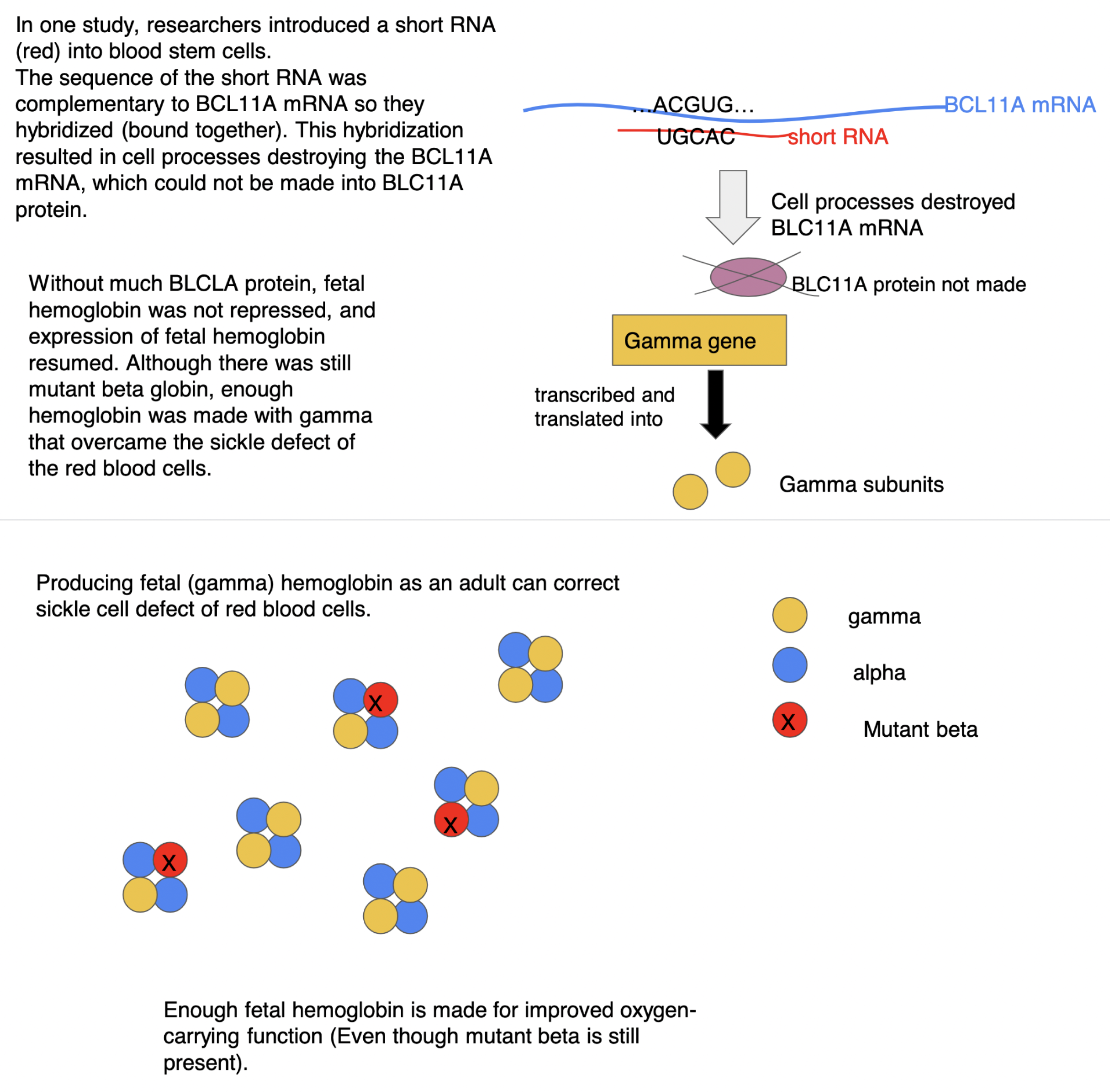
RNA interference as a means of treating sickle-cell
1. in 1 study, researchers introduced a short RNA into blood stem cells
2. this sequence of the short RNA was COMPLEMENTARY to BCL11A mRNA → BCL11A mRNA + short RNA ***hybridized*** (bound together)
3. hybridization resulted in cell processes destroying the BCL11A mRNA, which could not be made into BCL11A protein
4. if no BCL11A protein being made → no γ gene transcription repressed → fetal hemoglobin expressed (bc both α and γ subunits made) → sickle cell defect treated
\
\*NOTE: there is still SOME mutant β globin BUT *ENOUGH* hemoglobin can be made with γ subunit through RNA interference technology to overcome the sickle defect of red blood cells
48
New cards
small molecule drug
(genetic medicine technology)
\
chemical compounds with low molecular weight that are synthesized in the lab
\
ex: aspirin, gleevec, ivacator
\
small molecule drugs make up over 90% of the drugs on the market today
\
chemical compounds with low molecular weight that are synthesized in the lab
\
ex: aspirin, gleevec, ivacator
\
small molecule drugs make up over 90% of the drugs on the market today
49
New cards
how can small molecule drugs serve as a genetic medicine technology?
bc of their small sizes, these molecules can easily be taken up by cells AND may be administered to patients as pills OR by injections → small molecule drugs may interact DIRECTLY with disease-causing proteins OR through other molecules (cell signaling pathways) → *some small molecule drugs block the negative effects of disease-causing proteins (by mutated DNA), whereas others restore proper functioning (also from mutated DNA)*
50
New cards
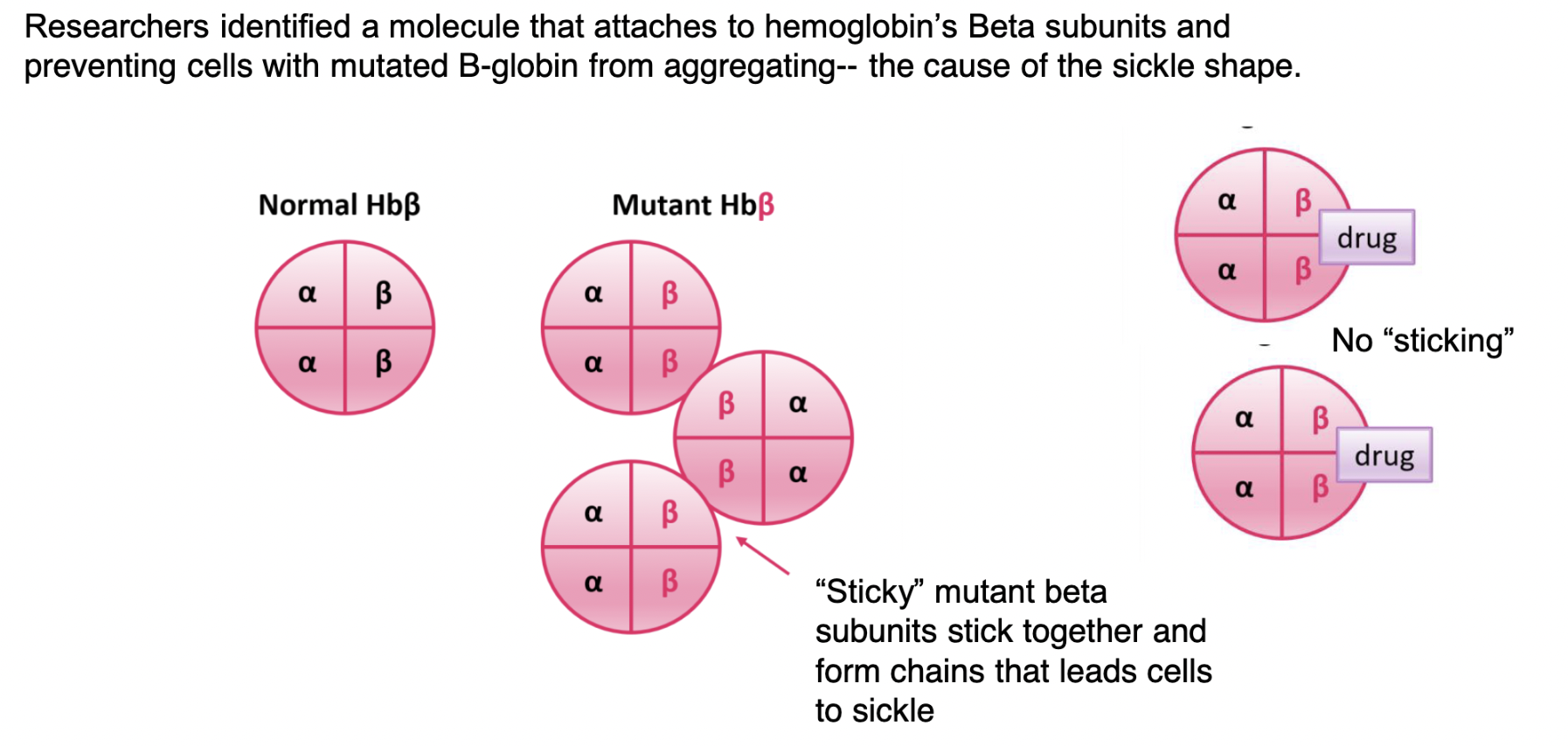
small molecule drugs as a means of treating sickle-cell
researchers identified a molecule that attaches to hemoglobin’s β subunits and prevents cells with mutated β-globin from collecting (the cause of the sickle shape) → introducing this molecule results in BLOCKING the “sticky” portions of cells → no sticking means sickle cells won’t clog arteries
51
New cards
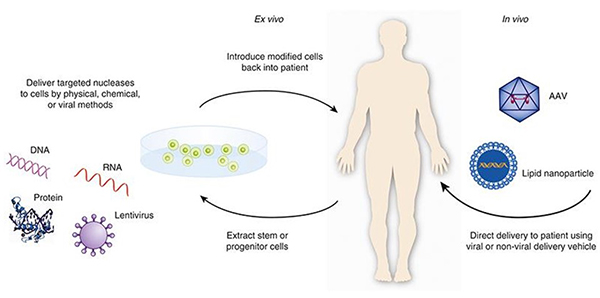
gene therapy
(genetic medicine technique)
\
the insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder in an attempt to correct the disorder
\
the insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder in an attempt to correct the disorder
52
New cards
how does gene therapy work in GENERAL?
viral vectors
\
a virus with a normal copy of a defective gene is used to infect diseased cells to give them the normal gene
\
2 common viral vectors: adeno-associated viral vectors, retroviral vectors
\
a virus with a normal copy of a defective gene is used to infect diseased cells to give them the normal gene
\
2 common viral vectors: adeno-associated viral vectors, retroviral vectors
53
New cards
Adeno-associated virus (AAV)
non-enveloped virus (travels across cellular membranes through pores in membrane) that can be engineered to deliver DNA to target cells,
\
Originally thought that it could only replicate in cells infected with the adenovirus
\
Can also infect cells that are infected with other viruses or that have had their DNA disrupted through other means
\
Originally thought that it could only replicate in cells infected with the adenovirus
\
Can also infect cells that are infected with other viruses or that have had their DNA disrupted through other means
54
New cards
why are AAVs good for gene therapy?
\- small simple virus
\- elicits only a weak immune response
\- has never been shown to cause disease in humans
\
the ability to generate recombinant AAV particles lacking any viral genes and containing DNA sequences of interest for various therapeutic applications has thus far proven to be one of the safest strategies for gene therapies
\- elicits only a weak immune response
\- has never been shown to cause disease in humans
\
the ability to generate recombinant AAV particles lacking any viral genes and containing DNA sequences of interest for various therapeutic applications has thus far proven to be one of the safest strategies for gene therapies
55
New cards
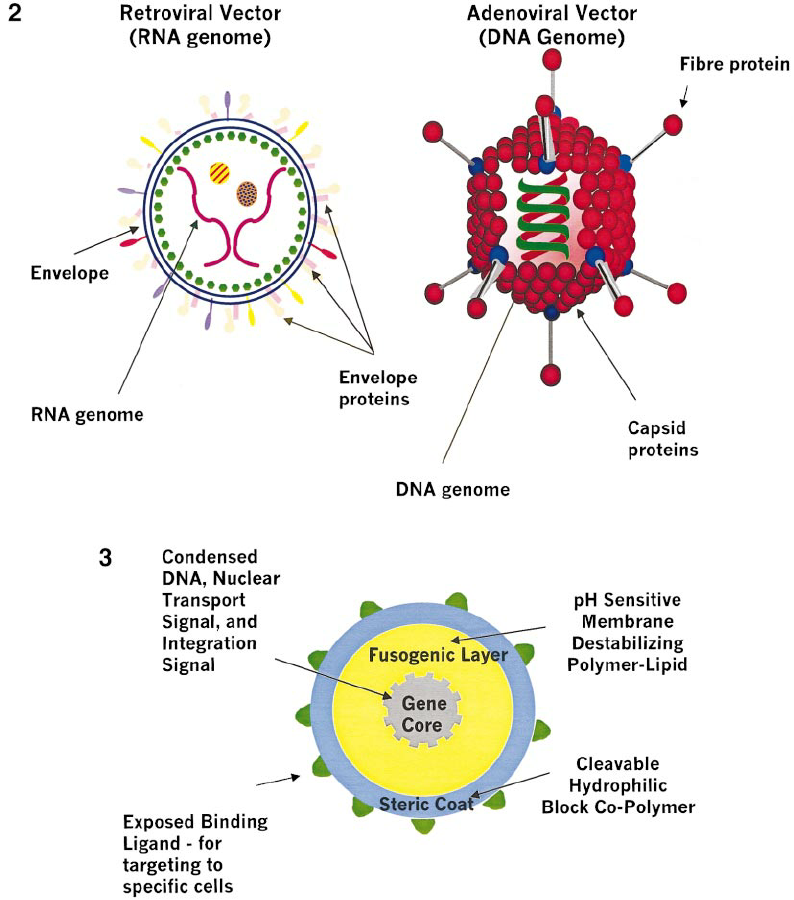
How does gene therapy work with adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) as viral vectors?
1\. 2 native AAV genes are removed → replaced with DNA that contains:
* functional gene with instructions to produce a normal protein
* a promoter (drives production of functional protein)
* promoter. + functional gene are flanked by signals called "inverted terminal repeats" that allow the DNA to be packaged inside the protein shell of the AAV vector
\
2\. AAV vectors are delivered into human cells → they deliver a copy of the functional gene directly into the nucleus
\
3\. once AAV DNA is inside the nucleus, the functional gene can support the production of normal protein and correct the underlying cause of the disease (malfunctioned/mutated DNA)
* functional gene with instructions to produce a normal protein
* a promoter (drives production of functional protein)
* promoter. + functional gene are flanked by signals called "inverted terminal repeats" that allow the DNA to be packaged inside the protein shell of the AAV vector
\
2\. AAV vectors are delivered into human cells → they deliver a copy of the functional gene directly into the nucleus
\
3\. once AAV DNA is inside the nucleus, the functional gene can support the production of normal protein and correct the underlying cause of the disease (malfunctioned/mutated DNA)
56
New cards
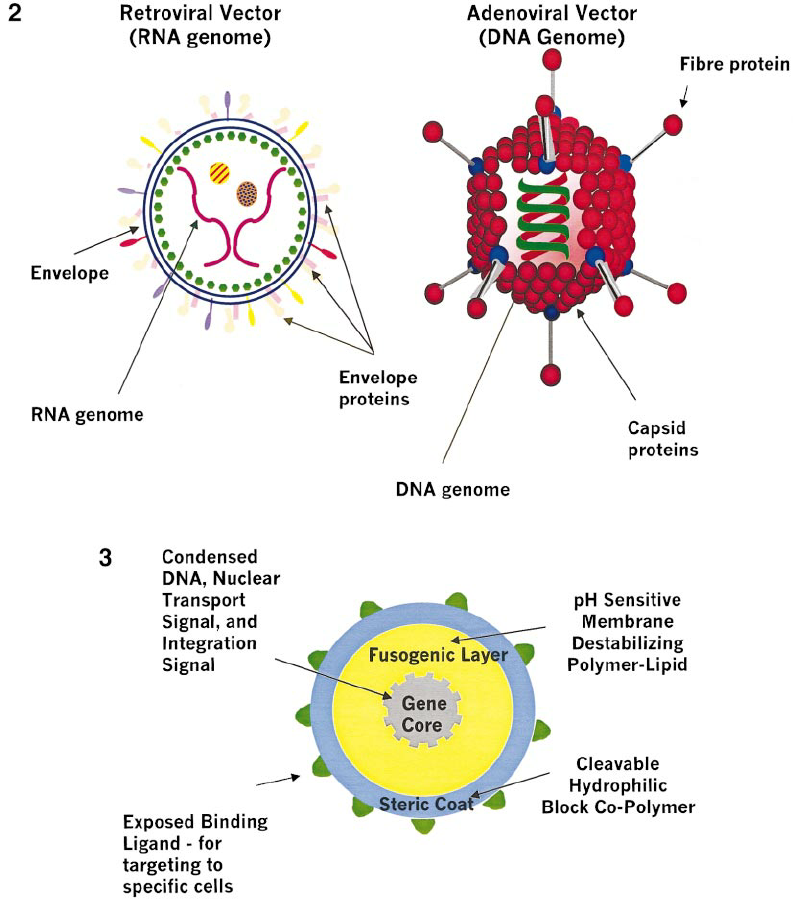
How does gene therapy work with retroviruses as viral vectors?
gene therapy is the addition of new genes to a patient's cells to replace missing or malfunctioning genes (it can involve inserting a normal allele into a genome to compensate for a mutated gene OR involve introducing a completely novel gene into an organism OR inactivate/knock out a mutated gene so that it will not be expressed)
\
1\. an RNA version of the normal ("therapeutic") allele for the gene is synthesized
\
2\. this normal RNA is then inserted into a RETROVIRUS (ex: LENTIVIRUS) while the VIRAL DNA in the retrovirus (the harmful gene) is CUT OUT → cutting out the virus gene and replacing it with a normal allele makes the retrovirus a host for a HEALTHY gene
\
3\. the retrovirus is injected into the host cell (the cell with the virus) and carries out reverse transcription to make a DNA transcript out of its RNA genome
\
4\. the retrovirus containing the cloned gene is then able to infect bone marrow cells that have been removed from the patient (a lab culture of cells)
\
5\. the virus is taken into these cells → the "viral" DNA (which contains the NORMAL gene of interest) is inserted into the cellular genome
\
6\. these recombinant cells are then injected BACK into the bone marrow of the patient → as these now HEALTHY cells continue to divide over an extended period of time, more and more cells gain the capacity to produce the vital enzyme → → → the disorder is alleviated
\
1\. an RNA version of the normal ("therapeutic") allele for the gene is synthesized
\
2\. this normal RNA is then inserted into a RETROVIRUS (ex: LENTIVIRUS) while the VIRAL DNA in the retrovirus (the harmful gene) is CUT OUT → cutting out the virus gene and replacing it with a normal allele makes the retrovirus a host for a HEALTHY gene
\
3\. the retrovirus is injected into the host cell (the cell with the virus) and carries out reverse transcription to make a DNA transcript out of its RNA genome
\
4\. the retrovirus containing the cloned gene is then able to infect bone marrow cells that have been removed from the patient (a lab culture of cells)
\
5\. the virus is taken into these cells → the "viral" DNA (which contains the NORMAL gene of interest) is inserted into the cellular genome
\
6\. these recombinant cells are then injected BACK into the bone marrow of the patient → as these now HEALTHY cells continue to divide over an extended period of time, more and more cells gain the capacity to produce the vital enzyme → → → the disorder is alleviated
57
New cards
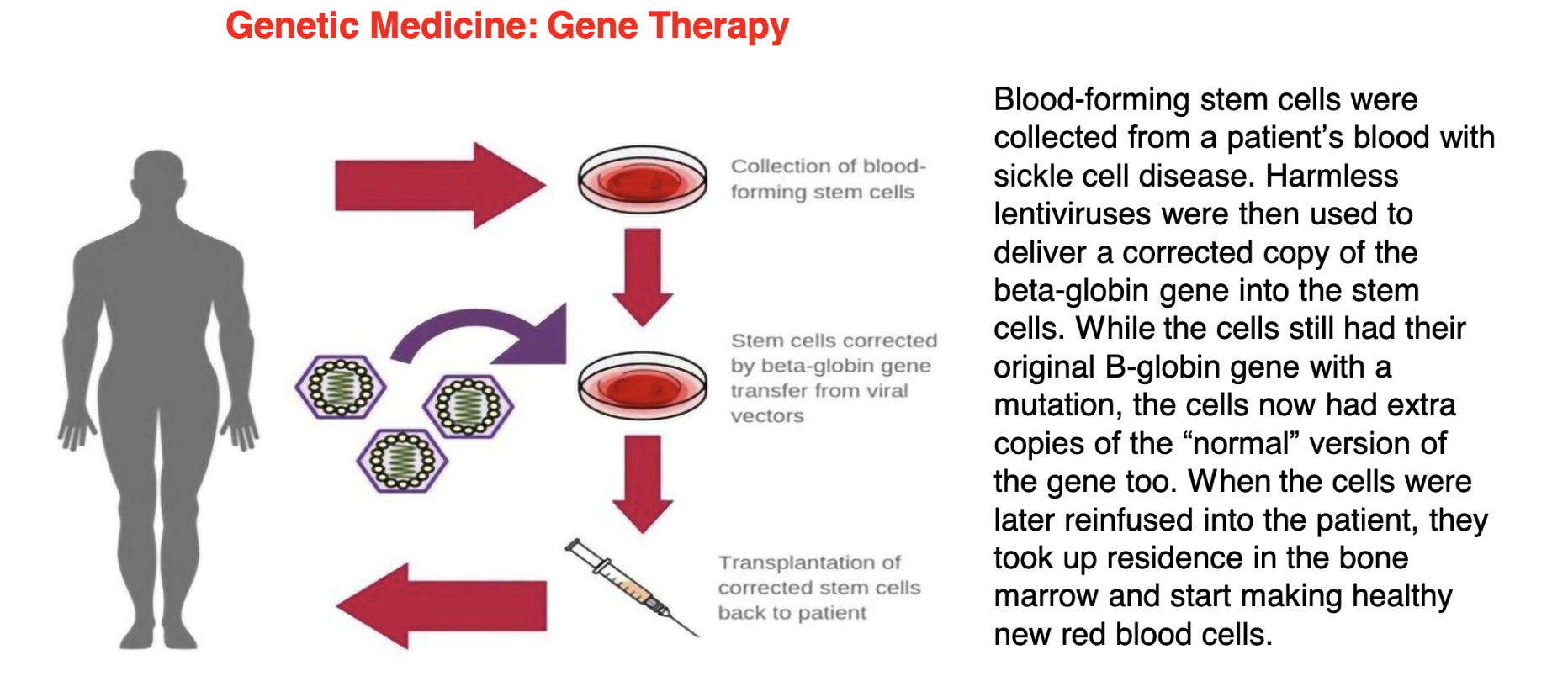
gene therapy as a means of treating sickle-cell
1. blood-forming stem cells collected from a patient’s blood with sickle cell disease
2. harmless lentiviruses (type of retrovirus) used to deliver a corrected copy of β-globin gene into the stem cells
3. ALTHOUGH the cells still have their original β-globin gene with a mutation, they now ALSO have EXTRA copies of the “normal” version of this gene too
4. when these cells are later reinfused into the patient, the cells take up residence in the bone marrow and start making healthy new red blood cells
\
\*NOTE: still use patient’s ORIGINAL cells to prevent an immune reaction from happening (bc the body doesn’t recognize foreign cells bc they’re not the body’s own cells)
58
New cards
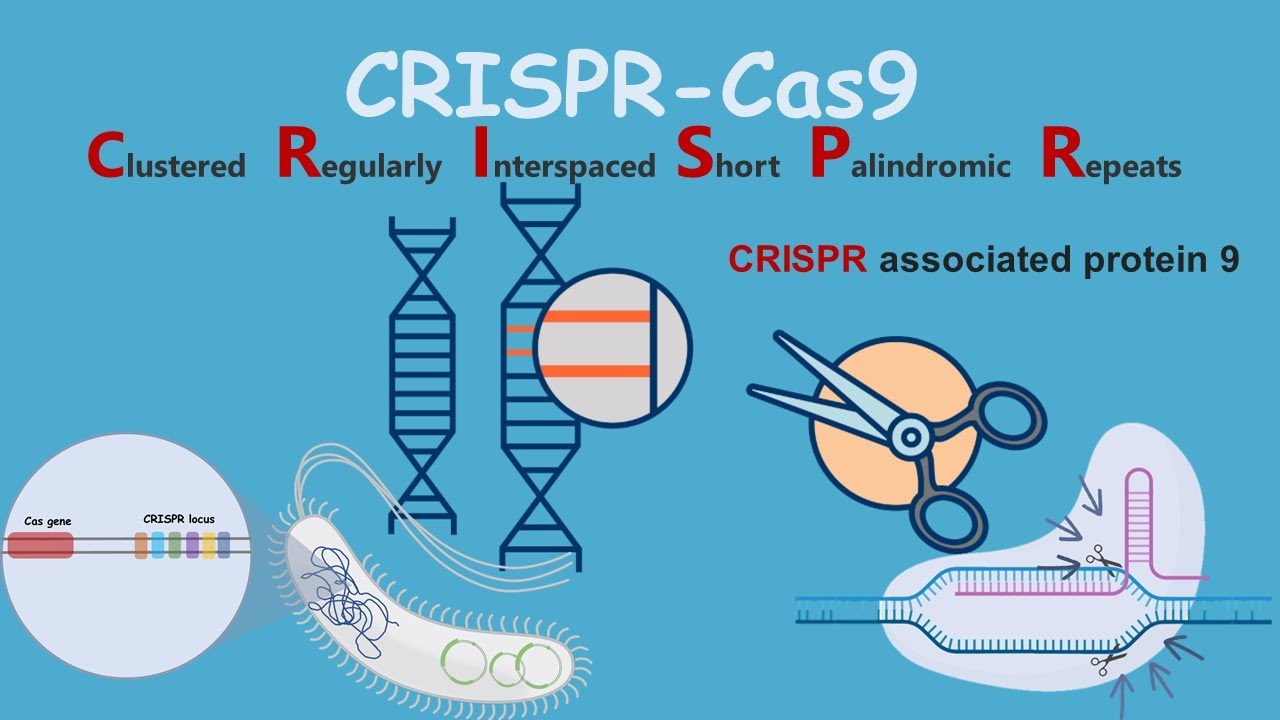
CRISPR
(genetic medicine technique)
\
(extremely precise gene editing technology)
\
CRISPR = __C__lustered __R__egularly __I__nterspaced __S__hort __P__alindromic __R__epeats
\
a technique for editing genes in living cells, involving a bacterial protein called Cas9 associated with a guide RNA complementary to a gene sequence of interest
\
(extremely precise gene editing technology)
\
CRISPR = __C__lustered __R__egularly __I__nterspaced __S__hort __P__alindromic __R__epeats
\
a technique for editing genes in living cells, involving a bacterial protein called Cas9 associated with a guide RNA complementary to a gene sequence of interest
59
New cards
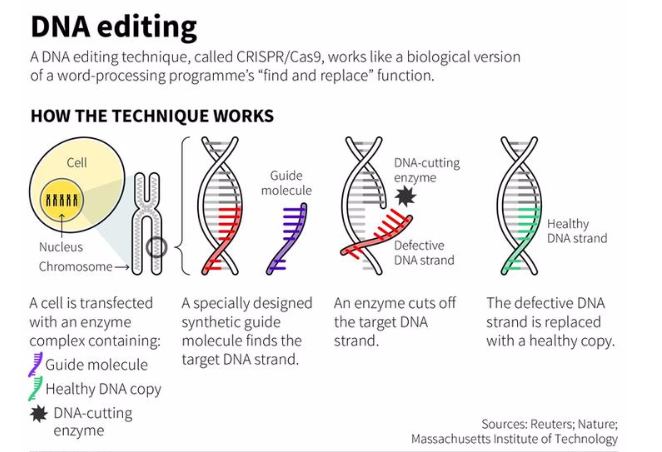
how does CRISPR technology work?
1. Scientists make guide RNA (gRNA has an unpaired end that is complementary to the gene/bases of interest) and attach it to Cas9 enzyme (protein) → forms a protein-RNA complex
\
2. Cas9-gRNA roam the DNA in search of the DNA that matches the gRNA
\
3. Once it finds it, it cuts open the double-stranded (ds) DNA to make sure it's a match by breaking the H-bonds bwn the dsDNA paired bases
\
4. Then it cuts out the target DNA sequence
\
5. Two possible results occur: nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR)
1. NHEJ results in short deletion disrupting the open reading frame
2. HDR involves adding a specific change through a template and homologous recombination
60
New cards
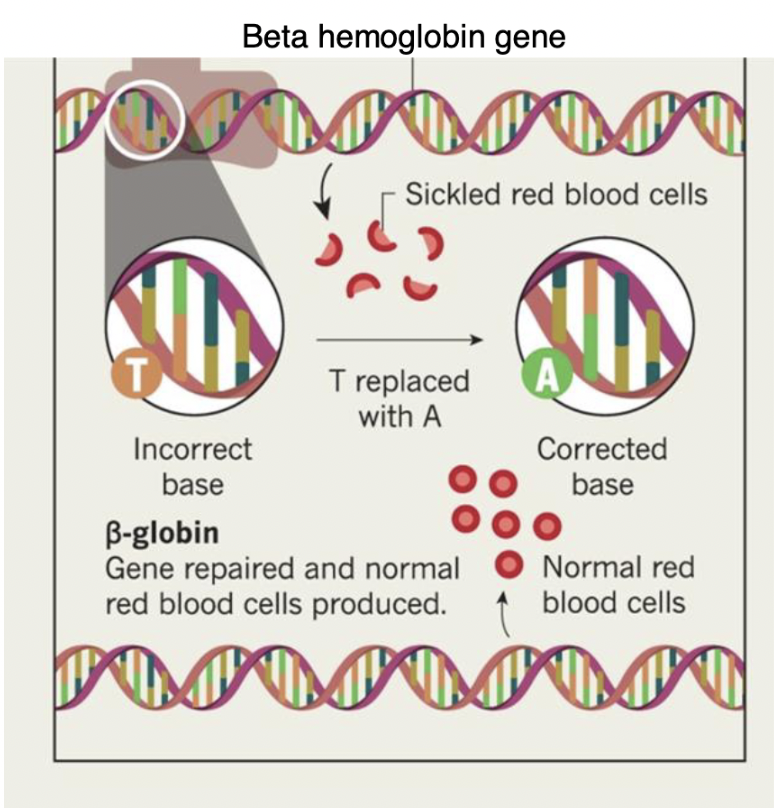
CRISPR as a means of treating sickle-cell
1. remove blood stem cells from the body
2. use CRISPR to correct the DNA mutation for sickle cell in the nucleus
1. the incorrect DNA code has a “T” at a specific location in the β globin gene
2. CRISPR can precisely edit the gene to correct this DNA nucleotide to an “A”
3. return the stem cells to the bone marrow where these cells produce normal β globin subunits
\
\*NOTE: this can CURE sickle cell disease
61
New cards
gene switches
(genetic medicine technique)
\
proteins called transcription factors bind to specific short sequences of DNA that flank the gene and by doing so, switch genes on and off
\
parts of DNA slightly UPSTREAM the gene that regulate gene expression by binding to different proteins that affect the activity of RNA polymerase (gene switches affect TRANSCRIPTION) → gene switches are the repressor/activator proteins (SPECIFIC transcription factors aka proteins that bind to the regulatory region) that bind to the pre-initiation complex (bind to RNA polymerase when DNA folds over to initiate or inhibit transcription from occurring
\
proteins called transcription factors bind to specific short sequences of DNA that flank the gene and by doing so, switch genes on and off
\
parts of DNA slightly UPSTREAM the gene that regulate gene expression by binding to different proteins that affect the activity of RNA polymerase (gene switches affect TRANSCRIPTION) → gene switches are the repressor/activator proteins (SPECIFIC transcription factors aka proteins that bind to the regulatory region) that bind to the pre-initiation complex (bind to RNA polymerase when DNA folds over to initiate or inhibit transcription from occurring
62
New cards
How does technology use gene switches to alter gene expression?
*REMINDER: ALL cells have the same DNA → all cells have the same enhancer/represser regions BUT regulatory regions do not always fold over to meet the same genes BC not all cells have the same regulatory PROTEINS to bind to regions →* ***RNA polymerase does NOT transcribe all genes***
\
if you move switches closer to a DIFFERENT gene, now the different gene can be expressed
\
New genetic technologies can target the *noncoding* regulatory DNA sequences in the genome (the "gene switches" aka where regulatory proteins bind to affect RNA polymerase activity) → these swtiches bind regulatory proteins present that turn transcription of genes off or on → depending on the regulatory proteins present in a cell, genes can be expressed in different tissues, at different stages of development, or in response to certain stimuli → → → THUS this technology can be used either to PREVENT genes linked to diseases from being turned on OR to KEEP beneficial genes from being turned off
\
if you move switches closer to a DIFFERENT gene, now the different gene can be expressed
\
New genetic technologies can target the *noncoding* regulatory DNA sequences in the genome (the "gene switches" aka where regulatory proteins bind to affect RNA polymerase activity) → these swtiches bind regulatory proteins present that turn transcription of genes off or on → depending on the regulatory proteins present in a cell, genes can be expressed in different tissues, at different stages of development, or in response to certain stimuli → → → THUS this technology can be used either to PREVENT genes linked to diseases from being turned on OR to KEEP beneficial genes from being turned off
63
New cards
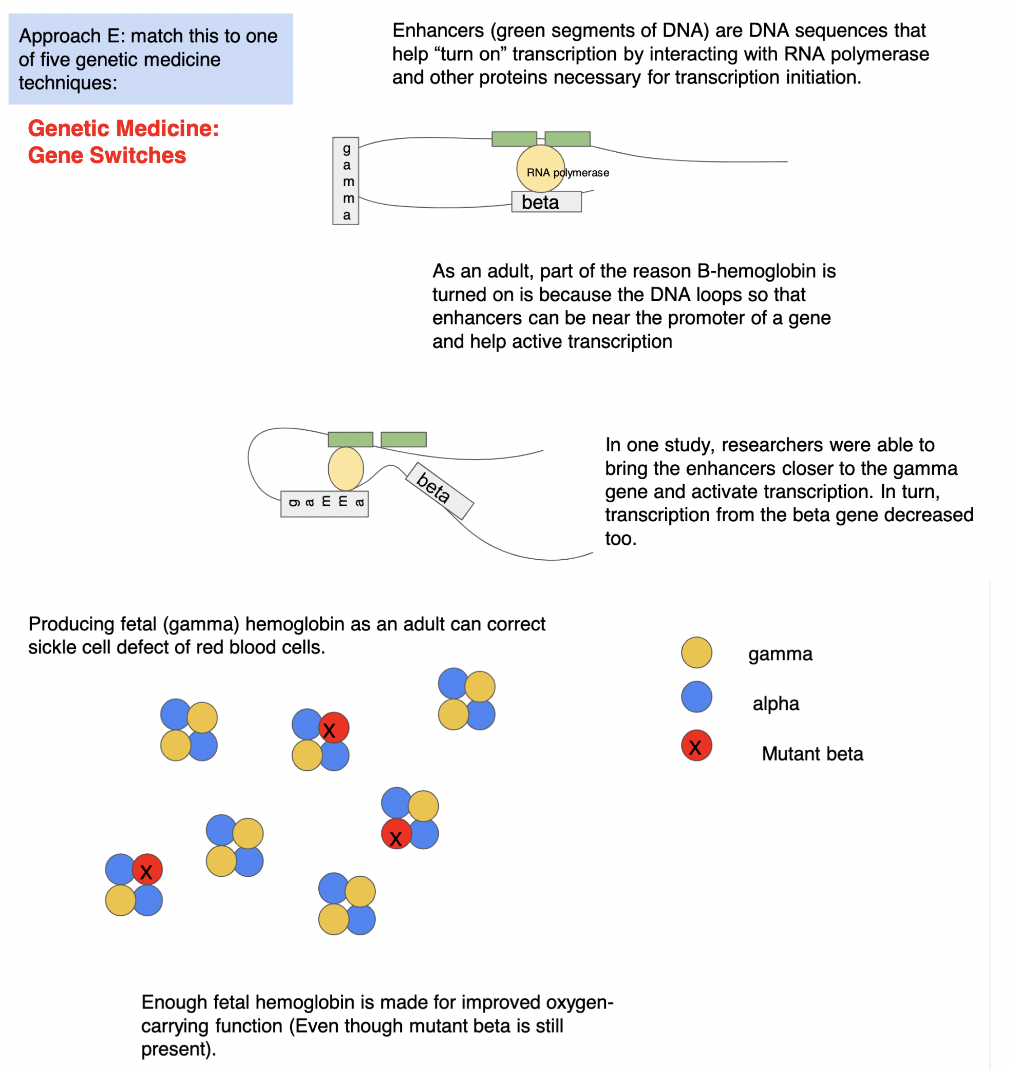
gene switches as a means of treating sickle-cell
part of the reason β hemoglobin is turned on is bc the DNA loops so that enhancers can be near the promoter of the β gene and help activate transcription of the β gene BUT in 1 study, researchers were able to bring enhancers closer to the γ gene and activate γ gene transcription → in turn, transcription from the β gene decreased TOO → producing fetal (γ) hemoglobin as an adult can correct for sickle cell defect of red blood cells bc *ENOUGH* fetal hemoglobin is made for improved oxygen-carrying function (EVEN THOUGH mutant β is still present)
\
*REMINDER: ALL cells have the same DNA → all cells have the same enhancer/represser regions BUT regulatory regions do not always fold over to meet the same genes BC not all cells have the same regulatory PROTEINS to bind to regions →* ***RNA polymerase does NOT transcribe all genes***
\
if you move switches closer to a DIFFERENT gene, now the different gene can be expressed → in __sickle-cell__, move enhancer near γ subunit so now γ expression can be turned on → this moves switches away from β subunit so β transcription turned off
\
*REMINDER: ALL cells have the same DNA → all cells have the same enhancer/represser regions BUT regulatory regions do not always fold over to meet the same genes BC not all cells have the same regulatory PROTEINS to bind to regions →* ***RNA polymerase does NOT transcribe all genes***
\
if you move switches closer to a DIFFERENT gene, now the different gene can be expressed → in __sickle-cell__, move enhancer near γ subunit so now γ expression can be turned on → this moves switches away from β subunit so β transcription turned off
64
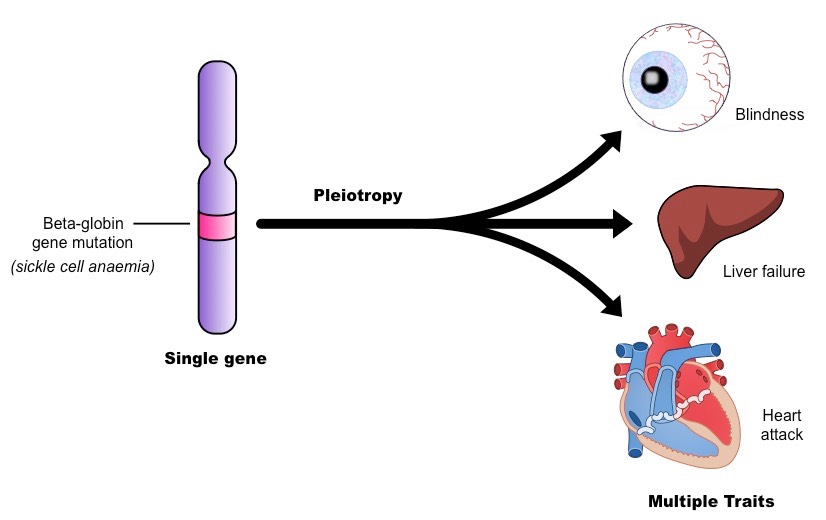
New cards
pleiotropy
when one gene influences multiple (unrelated) traits
65
New cards
polygenic inheritance
when one trait is influenced by multiple (independent) genes
66
New cards
autosomal dominant inheritance
* rare (often unusual to see homozygous dominant individuals if severe phenotype)
* *NOTE: for autosomal dominant diseases, assume anyone affected with the disease is a heterozygote unless otherwise stated*
* males and females (usually) equally affected (autosomal)
* affected individuals have an affected parent (dominant)
* doesn’t skip generations (dominant)
* *NOTE: for autosomal dominant diseases, assume anyone affected with the disease is a heterozygote unless otherwise stated*
* males and females (usually) equally affected (autosomal)
* affected individuals have an affected parent (dominant)
* doesn’t skip generations (dominant)
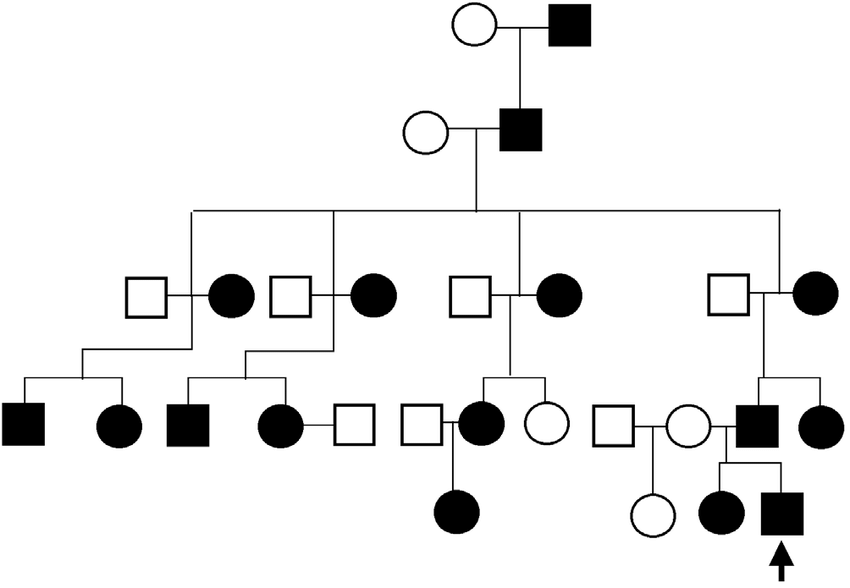
67
New cards
myotonic dystrophy
* example of *pleiotropic* inheritance
* characteristics:
* Difficulty with thinking and problem solving
* Emotional and behavior problems
* Excessive daytime sleepiness
* Nerve damage in feet and hands
* Muscle weakness (myopathy)
* Muscle stiffness and trouble relaxing a muscle \n (myotonia)
* Muscle wasting that gets worse over time (atrophy)
* Severe muscle weakness and delayed development \n in newborns and infants
* Heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias)
* Enlarged heart muscle
* Low blood pressure
* Sudden death
* CTG trinucleotide DNA repeat
* DMPK is the protein that is mutated in myotonic dystropy
* **autosomal dominant inheritance**
* characteristics:
* Difficulty with thinking and problem solving
* Emotional and behavior problems
* Excessive daytime sleepiness
* Nerve damage in feet and hands
* Muscle weakness (myopathy)
* Muscle stiffness and trouble relaxing a muscle \n (myotonia)
* Muscle wasting that gets worse over time (atrophy)
* Severe muscle weakness and delayed development \n in newborns and infants
* Heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias)
* Enlarged heart muscle
* Low blood pressure
* Sudden death
* CTG trinucleotide DNA repeat
* DMPK is the protein that is mutated in myotonic dystropy
* **autosomal dominant inheritance**
68
New cards
Huntington’s disease
* mutation in Huntingtin gene
* phenotype: huntingtin collects in neurons; shaking; personality changes → death within approx. 15 years
* **example of autosomal dominant inheritance**
* phenotype: huntingtin collects in neurons; shaking; personality changes → death within approx. 15 years
* **example of autosomal dominant inheritance**
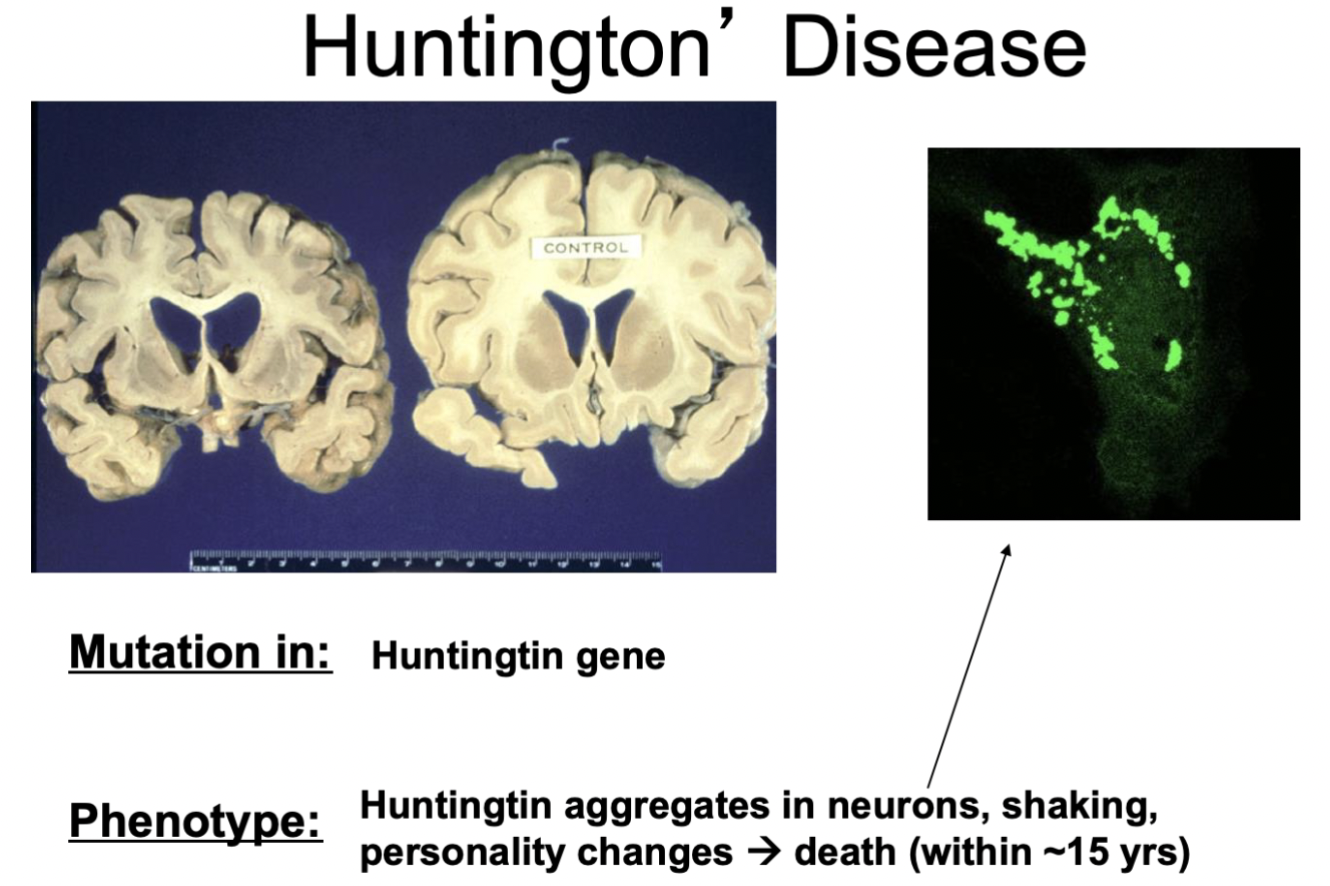
69
New cards
X-linked recessive inheritance
* rare *(NOTE: assume females entering into family are NOT carriers (homozygous dominant for trait) UNLESS otherwise stated in question)*
* males affected more frequently (X-linked)
* skips generations (recessive)
* unaffected individuals have affected children (recessive)
* NEVER have father→son transmission (X-linked) (bc son gets __Y__-chromosome from father and condition is RECESSIVE)
* males affected more frequently (X-linked)
* skips generations (recessive)
* unaffected individuals have affected children (recessive)
* NEVER have father→son transmission (X-linked) (bc son gets __Y__-chromosome from father and condition is RECESSIVE)
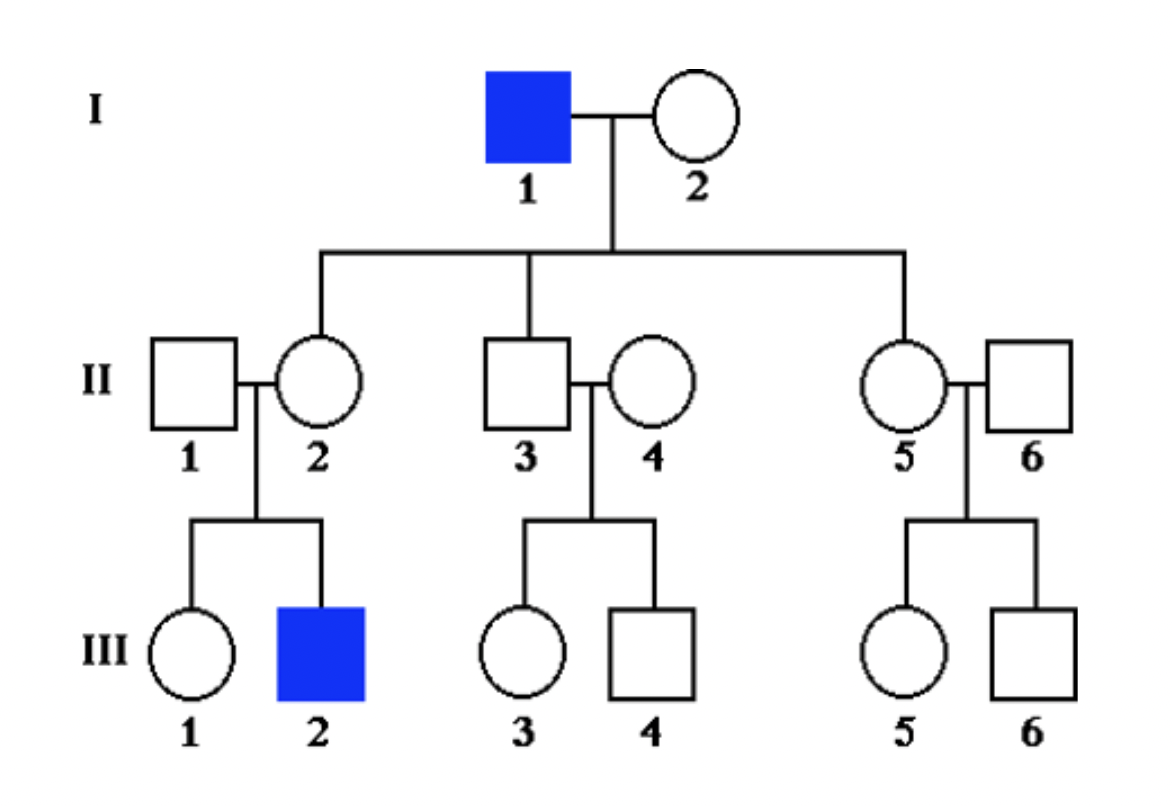
70
New cards
autosomal recessive inheritance
* rare *(NOTE: assume people entering into these families are NOT carriers (must be homozygous dominant for trait) UNLESS otherwise stated in question)*
* males and females equally affected (autosomal)
* unaffected individuals have affected children (recessive)
* skips generations (recessive)
* becomes more common with inbreeding (recessive)
* males and females equally affected (autosomal)
* unaffected individuals have affected children (recessive)
* skips generations (recessive)
* becomes more common with inbreeding (recessive)
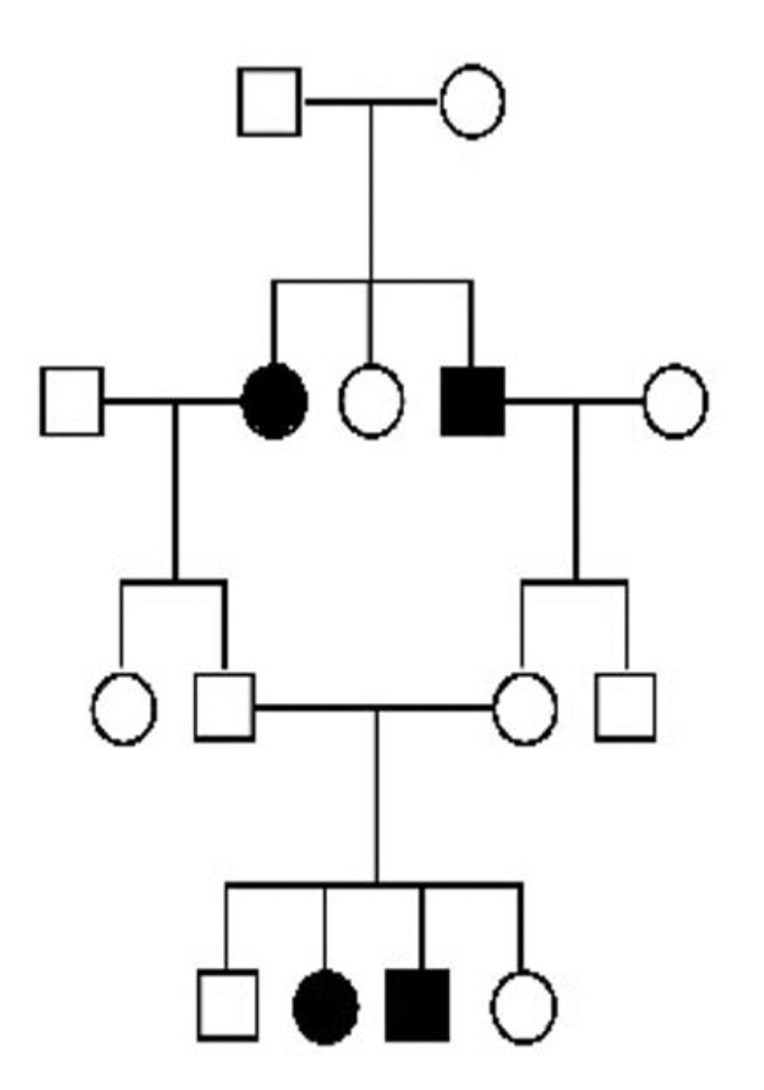
71
New cards
Werner’s syndrome
* condition that causes premature aging
* people with Werners typically develop and grow normally until puberty → at puberty, growth stops and adults with Werner syndrome are typically shorter than average → by early 20s-30s, ppl with this syndrome develop conditions usually associated with more advanced ages + ppl with Werners have an increased risk of developing cancer, especially thyroid and skin cancers
* heart attacks and cancer are the most common causes of death (most ppl with this condition die in late 40s to mid 50s depending on how well symptoms are managed + presence of other health conditions
* Werner syndrome caused by mutations in the WRN gene - condition diagnosed based on symptoms and genetic testing
* **application of autosomal recessive inheritance**
* people with Werners typically develop and grow normally until puberty → at puberty, growth stops and adults with Werner syndrome are typically shorter than average → by early 20s-30s, ppl with this syndrome develop conditions usually associated with more advanced ages + ppl with Werners have an increased risk of developing cancer, especially thyroid and skin cancers
* heart attacks and cancer are the most common causes of death (most ppl with this condition die in late 40s to mid 50s depending on how well symptoms are managed + presence of other health conditions
* Werner syndrome caused by mutations in the WRN gene - condition diagnosed based on symptoms and genetic testing
* **application of autosomal recessive inheritance**
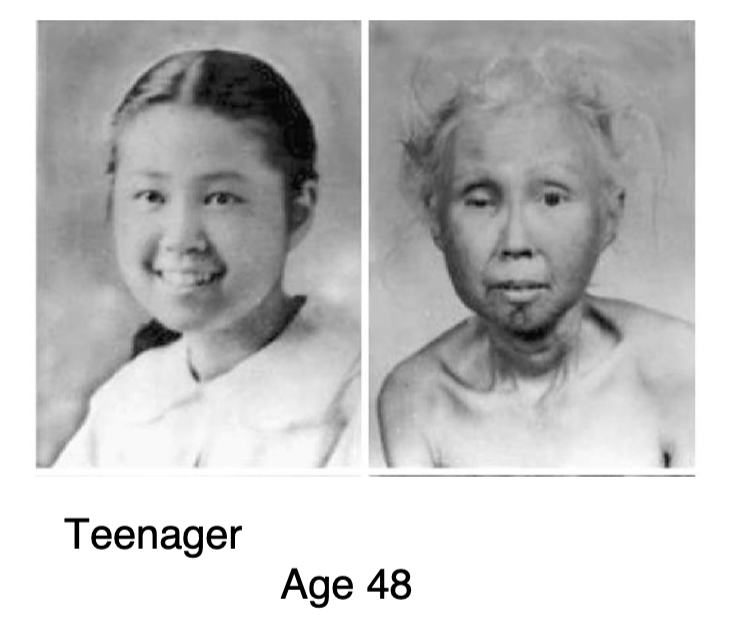

72
New cards
law of segregation
the 2 alleles for each character separate fro each other during gamete formation
\
first law of heredity stating that pairs of alleles for a trait separate when gametes are formed
\
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
\
first law of heredity stating that pairs of alleles for a trait separate when gametes are formed
\
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
73
New cards
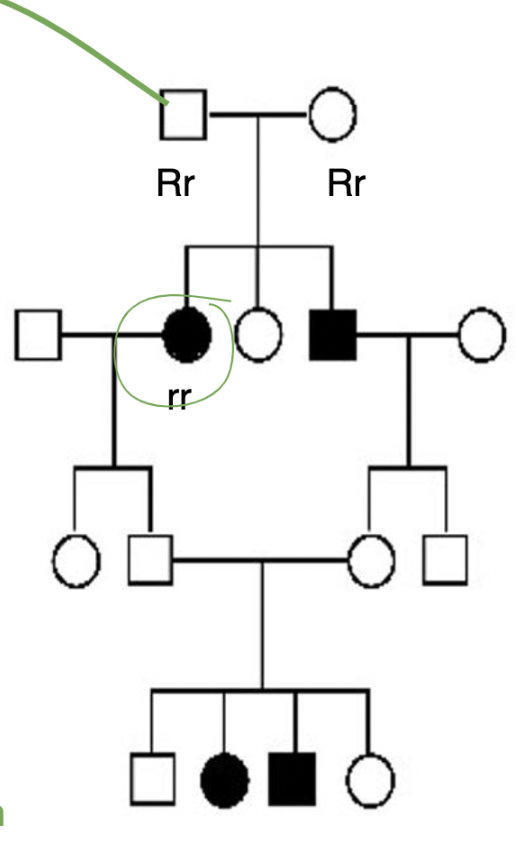
how does this image apply to law of segregation?
*mode of inheritance is autosomal recessive*
\
unaffected individuals can have affected children bc **alleles for a trait separate independently in gamete formation** → THUS people can be CARRIERS for a disease but pass on the trait to their children who EXPRESS the disease
\
(in pic: individuals with genotypes Rr and Rr have a child with genotype rr → both Rr genotypes don’t express Werner syndrome phenotype BUT their CHILD does express this phenotype)
\
unaffected individuals can have affected children bc **alleles for a trait separate independently in gamete formation** → THUS people can be CARRIERS for a disease but pass on the trait to their children who EXPRESS the disease
\
(in pic: individuals with genotypes Rr and Rr have a child with genotype rr → both Rr genotypes don’t express Werner syndrome phenotype BUT their CHILD does express this phenotype)
74
New cards
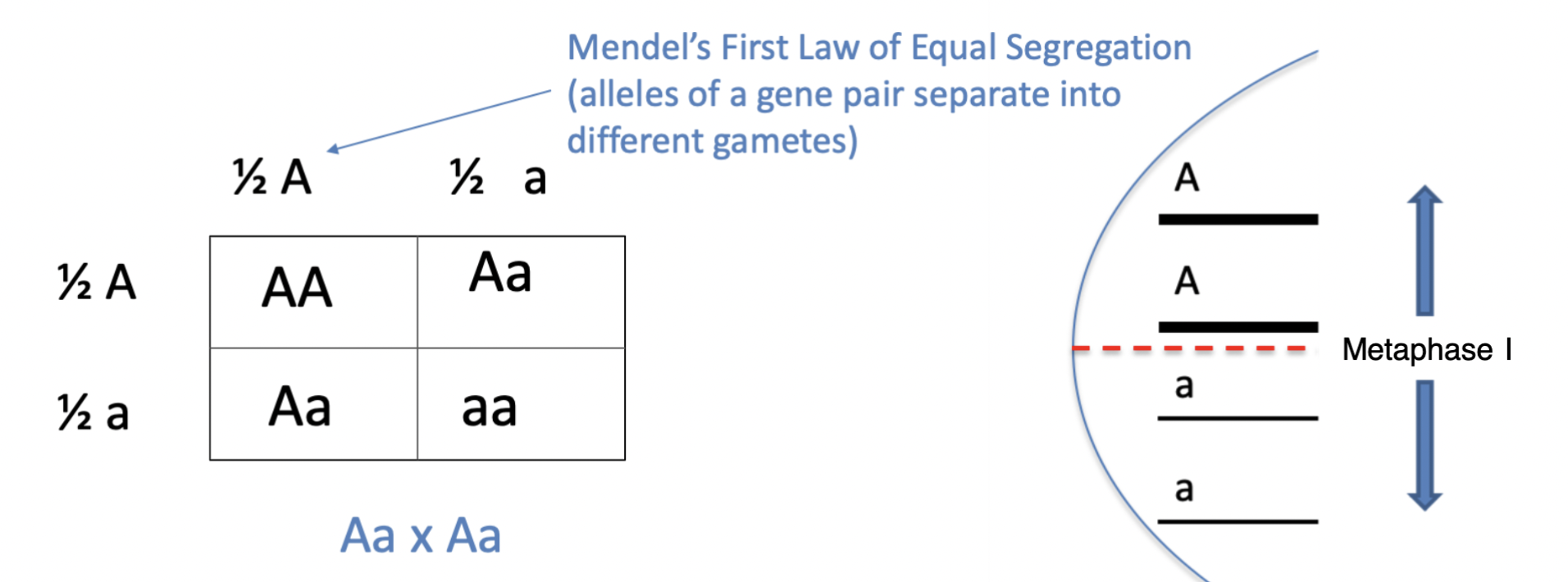
Punnett Squares
a chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
75
New cards
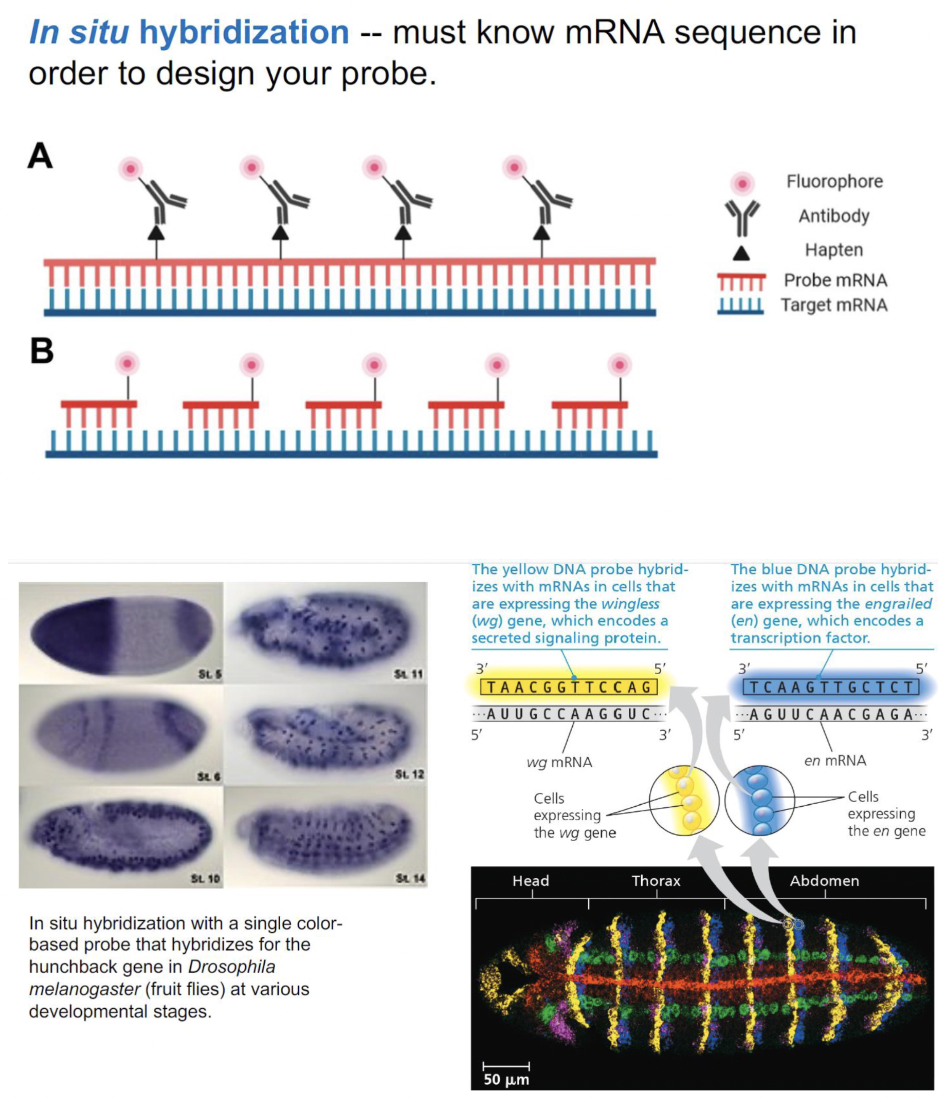
in situ hybridization
a technique using nucleic acid hybridization with a labeled probe to detect the location of a specific mRNA in an intact organism
\
STEPS:
* design a DNA probe that is complementary to the specific mRNA and has a fluorescence molecule attached
* fluorescence molecule allows you to see where the DNA probe is binding
* when cells express the specific mRNA, it means probe has binded so you see fluorescence
* when cells don’t express mRNA: probe did NOT have anything to bind to → don’t see fluorescence
* hybridize (bind) the probe to various tissue sections
* visualize tissues under a microscope to see if mRNA is present in any of these tissues
\
STEPS:
* design a DNA probe that is complementary to the specific mRNA and has a fluorescence molecule attached
* fluorescence molecule allows you to see where the DNA probe is binding
* when cells express the specific mRNA, it means probe has binded so you see fluorescence
* when cells don’t express mRNA: probe did NOT have anything to bind to → don’t see fluorescence
* hybridize (bind) the probe to various tissue sections
* visualize tissues under a microscope to see if mRNA is present in any of these tissues
76
New cards
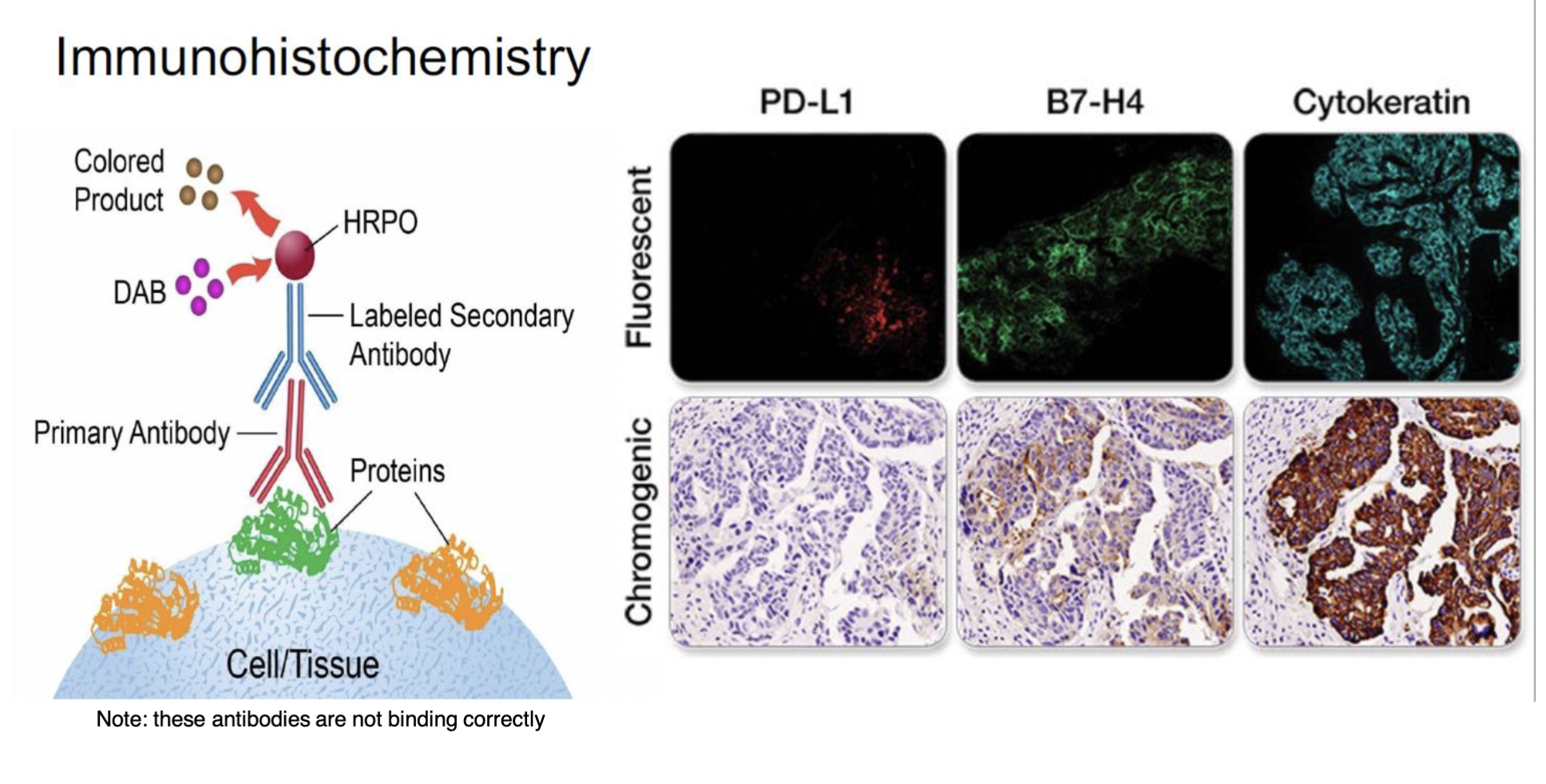
immunohistochemistry
(IHC)
\
immuno = antibodies
histo = tissue
chemistry = binding that occurs bwn the two
\
a technique used to locate where certain proteins are expressed (and in what cells they’re expressed in)
\
SUMMARY of steps:
1. add primary antibody that recognizes the specific protein
2. add secondary antibody that recognizes the primary antibody and is bound to a fluorescence molecule
3. visualize with microscope where protein is/is not expressed within cells in different tissues
\
DETAILED steps:
1. PREP: tissue has to be collected + placed on a microtome that functions as a knife to cut the tissues into 3-5 µm sections → a section is placed on a slide
2. ON THE SLIDE: tissue section is made of cells; on a cell are diff shaped receptors called antigens → these antigens bind to y-shaped molecules called antibodies (made by injecting proteins from tissue sample into an animal)
3. bc the proteins are foreign + bad to the animals, the animals' immune response kicks in and creates antibodies
4. the antibodies that attach first are called primary antibodies → once the primary antibodies are bound to the cell, secondary antibodies are introduced + those bind to the primary antibody
5. the secondary antibodies are typically bound to a fluorescent tag (made of a FLUOROPHORE molecule) - the specimen is illuminated with a light of a specific wavelength, absorbed by the fluorophores causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths → scientists can visualize the light being emitted by the fluorophores
6. RESULT: can take colorful photos of the protein being expressed
\
immuno = antibodies
histo = tissue
chemistry = binding that occurs bwn the two
\
a technique used to locate where certain proteins are expressed (and in what cells they’re expressed in)
\
SUMMARY of steps:
1. add primary antibody that recognizes the specific protein
2. add secondary antibody that recognizes the primary antibody and is bound to a fluorescence molecule
3. visualize with microscope where protein is/is not expressed within cells in different tissues
\
DETAILED steps:
1. PREP: tissue has to be collected + placed on a microtome that functions as a knife to cut the tissues into 3-5 µm sections → a section is placed on a slide
2. ON THE SLIDE: tissue section is made of cells; on a cell are diff shaped receptors called antigens → these antigens bind to y-shaped molecules called antibodies (made by injecting proteins from tissue sample into an animal)
3. bc the proteins are foreign + bad to the animals, the animals' immune response kicks in and creates antibodies
4. the antibodies that attach first are called primary antibodies → once the primary antibodies are bound to the cell, secondary antibodies are introduced + those bind to the primary antibody
5. the secondary antibodies are typically bound to a fluorescent tag (made of a FLUOROPHORE molecule) - the specimen is illuminated with a light of a specific wavelength, absorbed by the fluorophores causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths → scientists can visualize the light being emitted by the fluorophores
6. RESULT: can take colorful photos of the protein being expressed
77
New cards
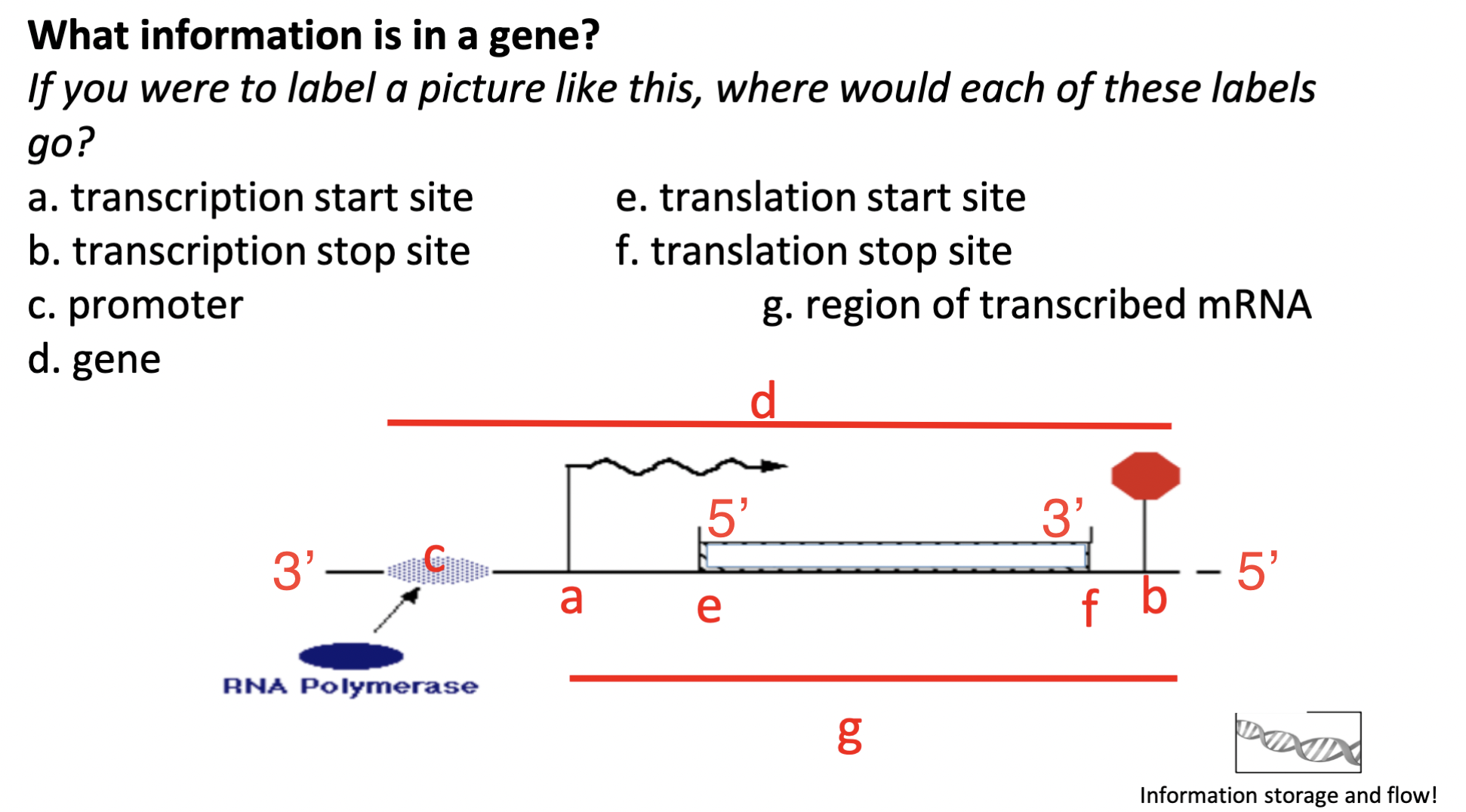
label the image
78
New cards
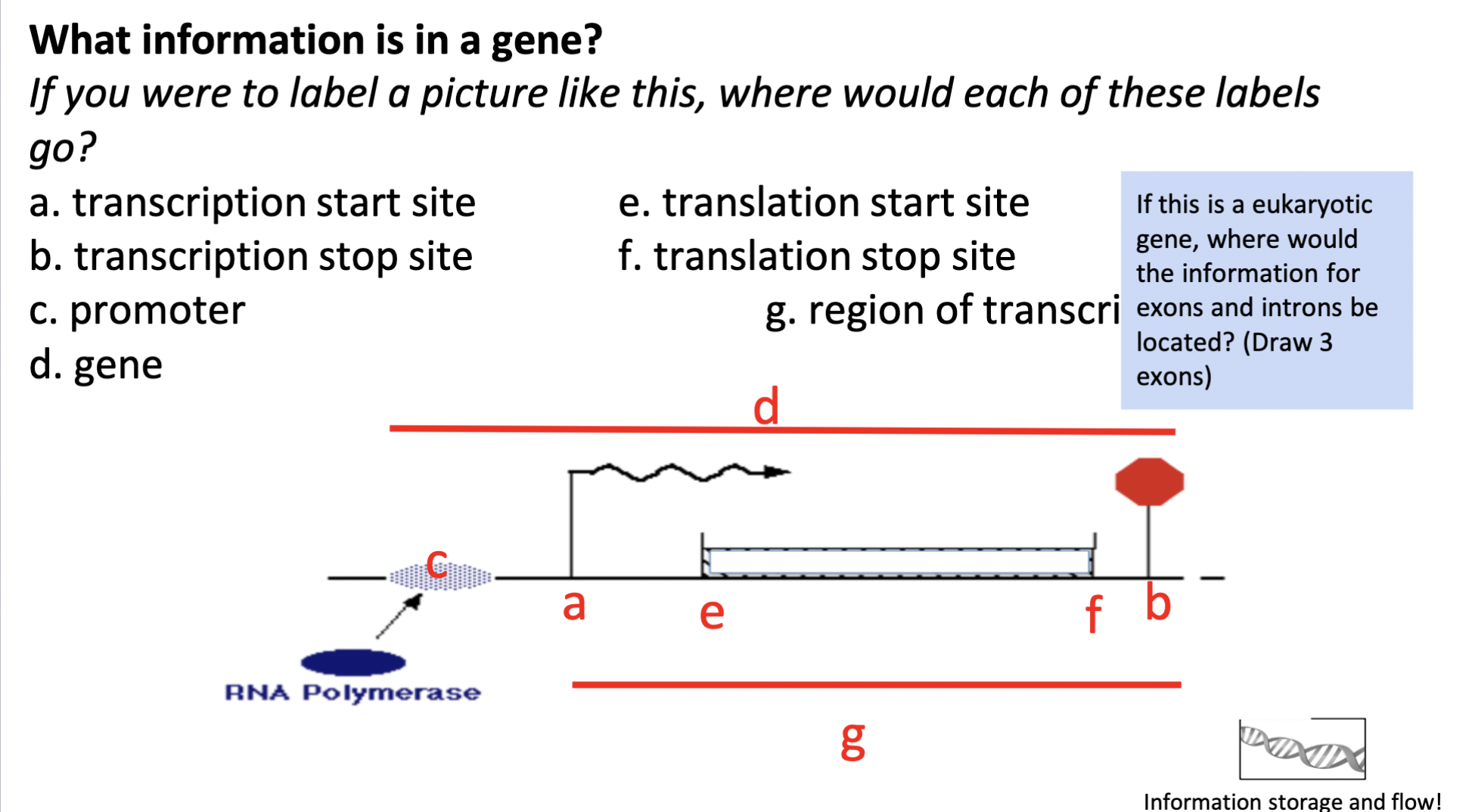
label the image but instead with:
* exons
* introns
* enhancer region
* exons
* introns
* enhancer region
(green region = exons; white region bwn green = introns; red = enhancer)
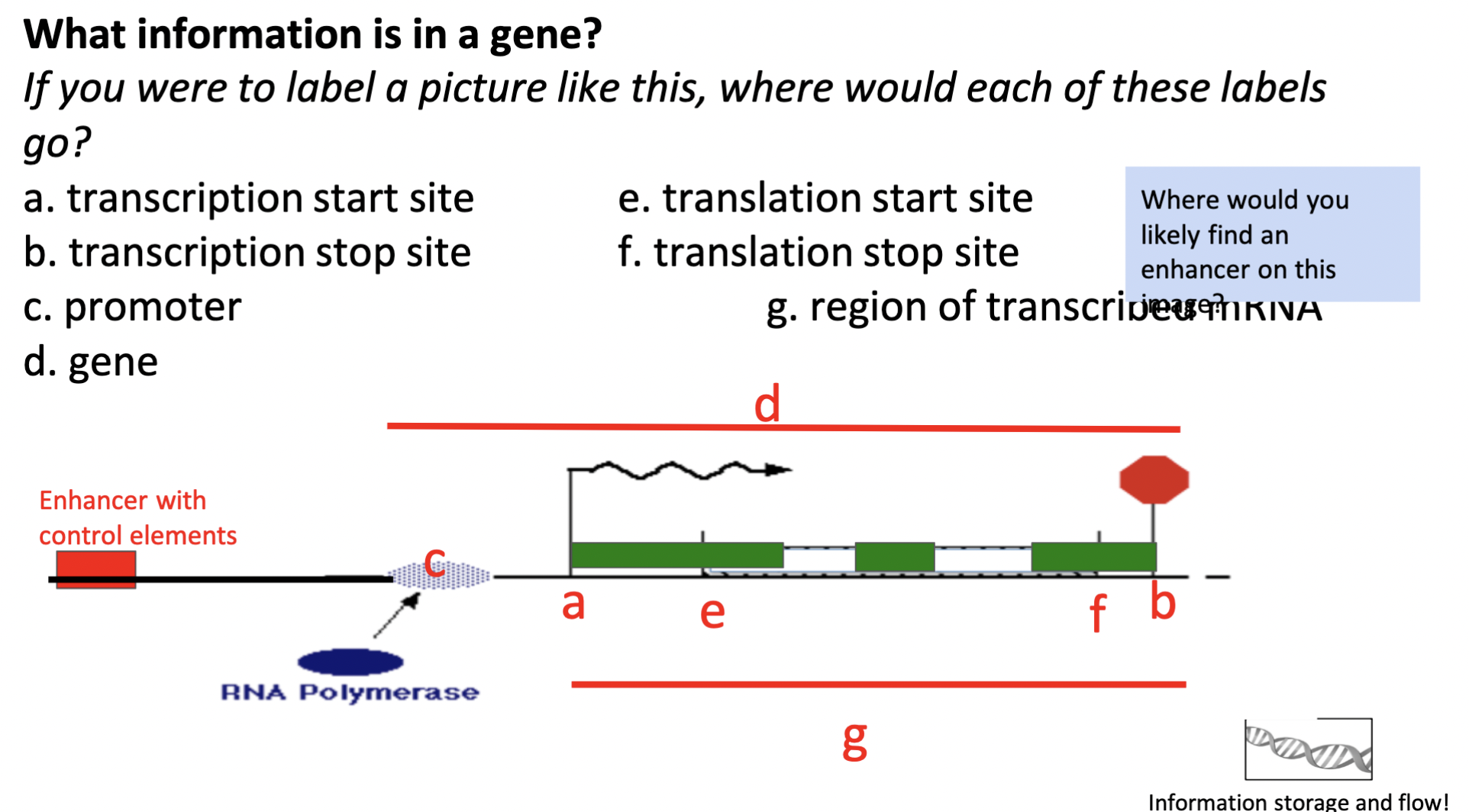
79
New cards
how does initial mRNA differ from mature mRNA
1. introns spliced out, exons put together
2. UTR modified - 5’ cap, 3’ poly-A tail
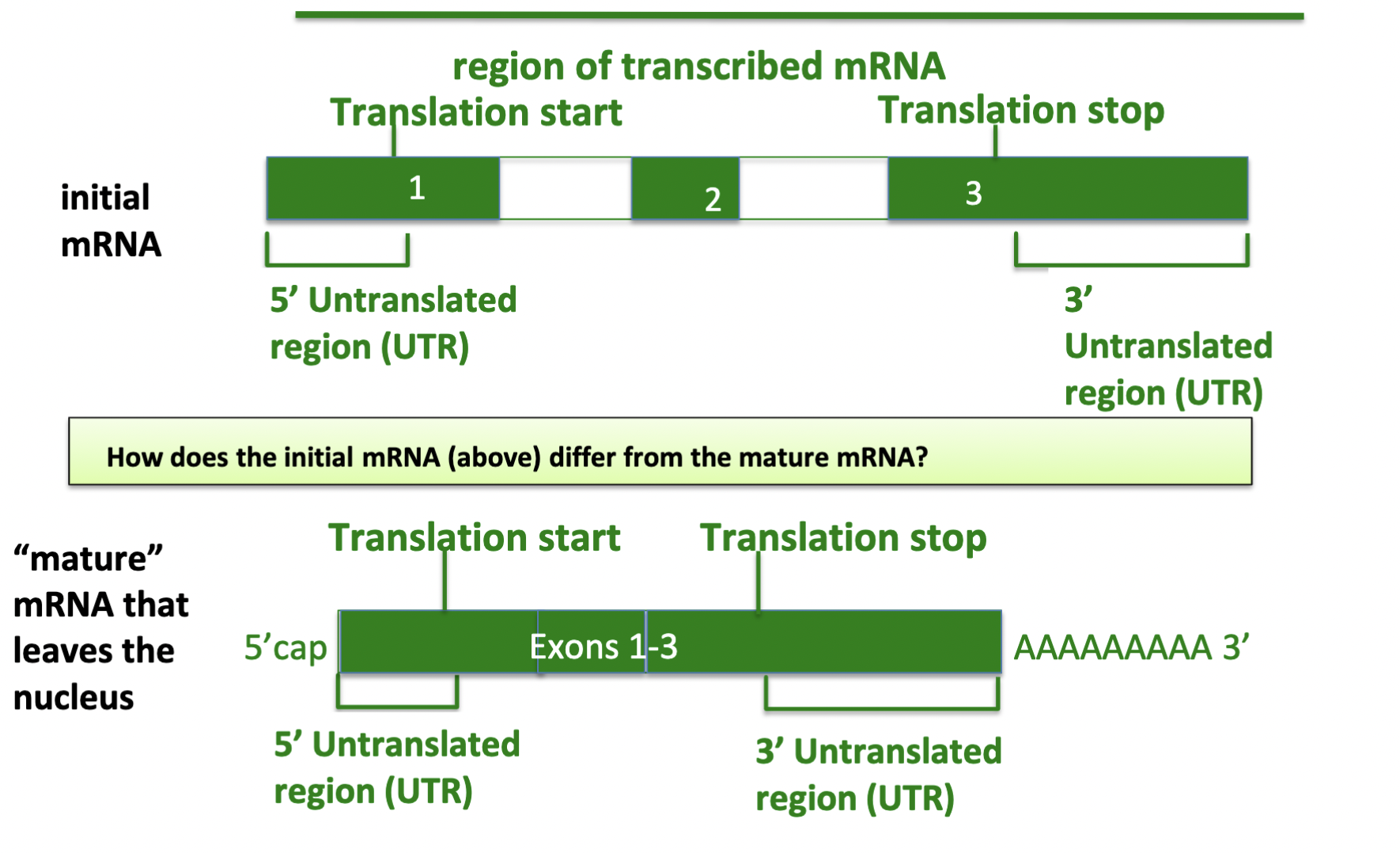
80
New cards
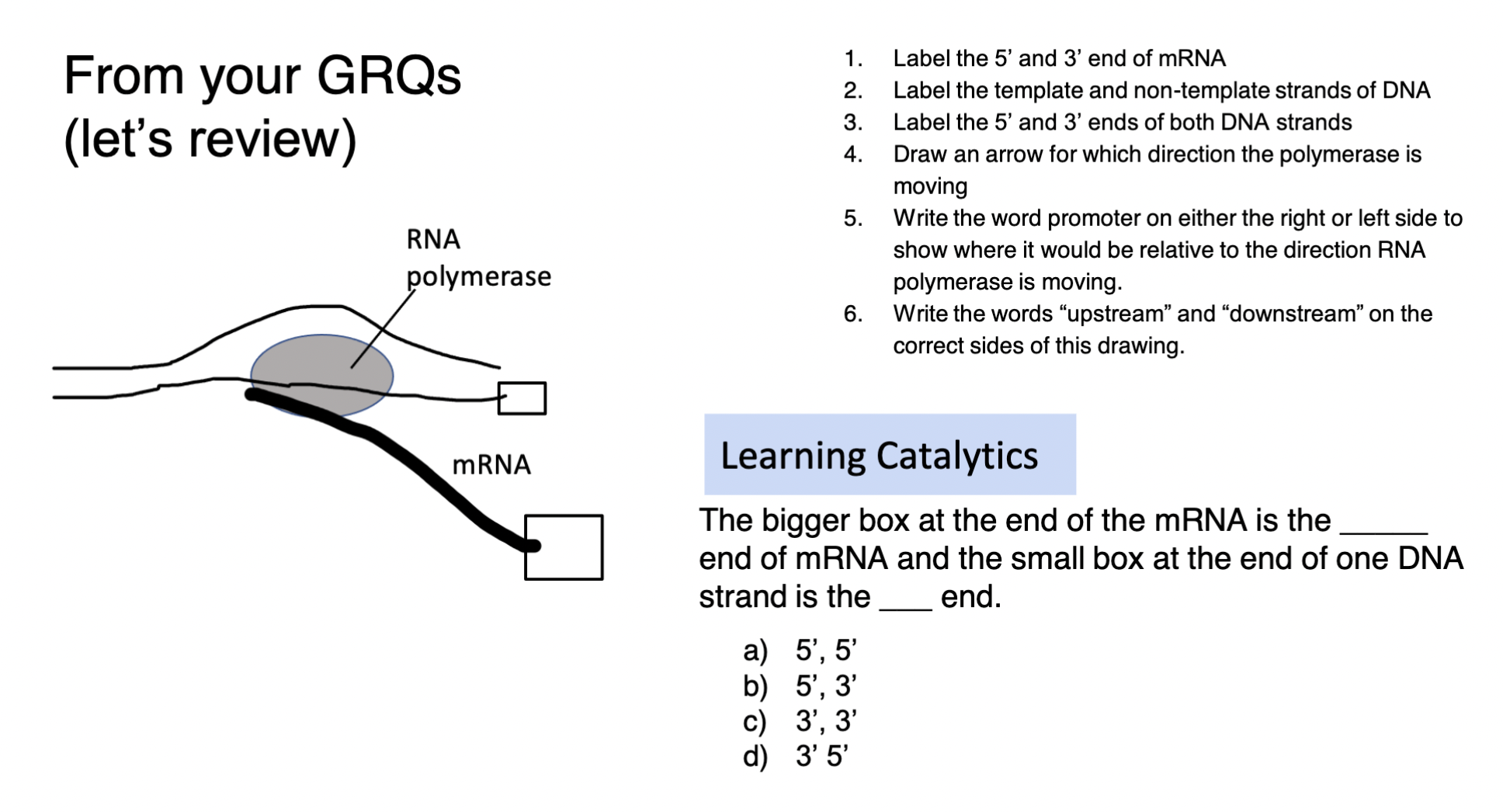
label the image
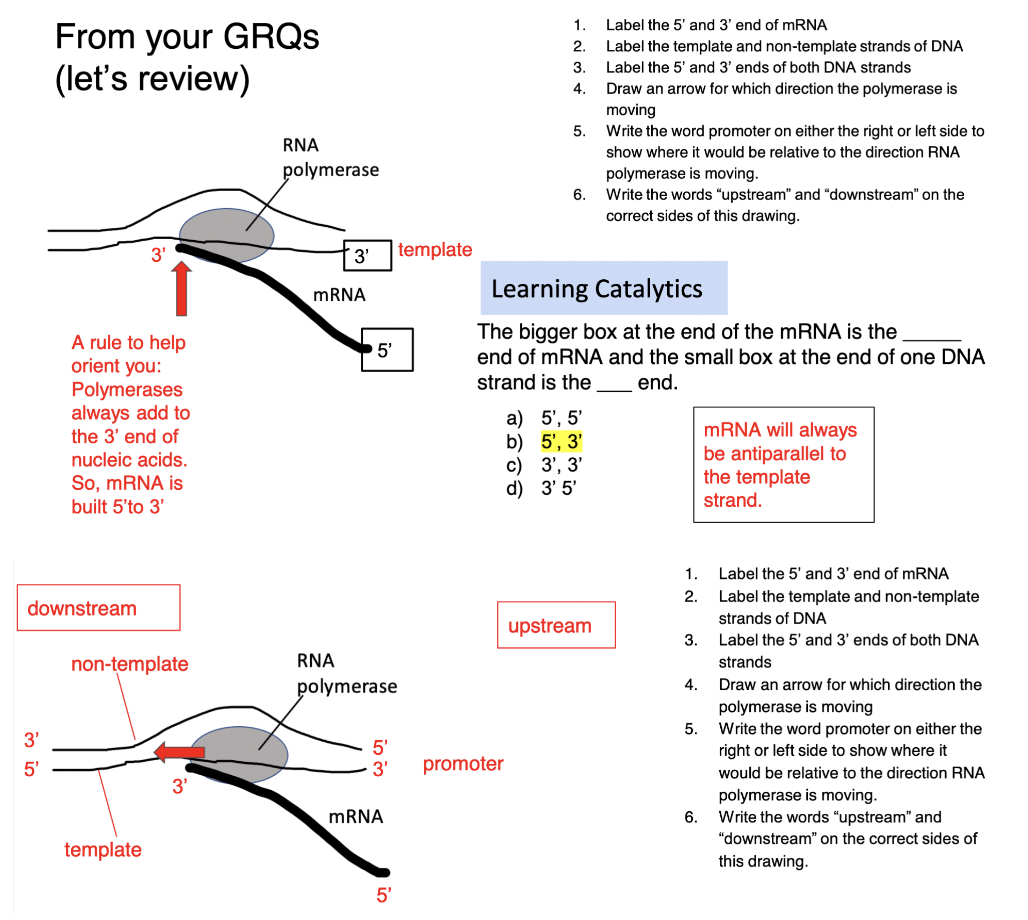
81
New cards
which way do polymerases build vs. read nucleic acids?
read 3’ → 5’
\
build 5’ → 3’ *(always add to the 3’ end of nucleic acids)*
\
build 5’ → 3’ *(always add to the 3’ end of nucleic acids)*
82
New cards
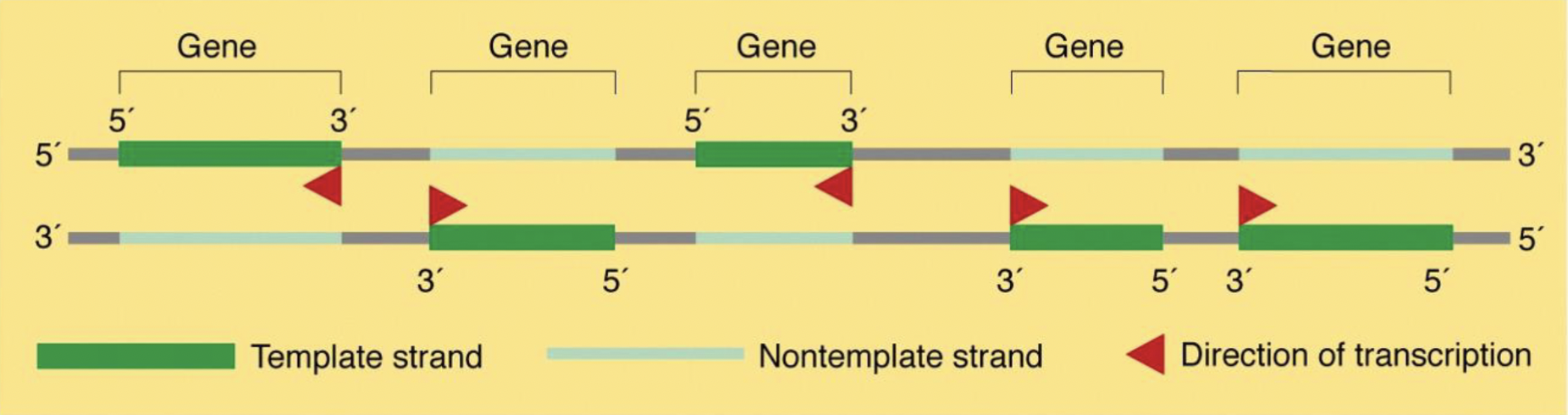
what can you conclude from the image?
transcription always moves in the direction of 3’→5’ along the *template* strand BUT the template strand for one gene might be the *coding* strand of a different gene → **different strands of the DNA double helix are used as the template for different genes**
83
New cards
for a given gene, what will determine which strand is used as a template?
the location of the PROMOTER sequence
\
specific 3’ TATA 5’ sequence on *template* strand ← RNA polymerase binds to HERE on the template strand to transcribe gene
\
specific 3’ TATA 5’ sequence on *template* strand ← RNA polymerase binds to HERE on the template strand to transcribe gene
84
New cards
1. in all cells, are the same regulatory regions (enhancers/repressors) of genes present?
2. what about the transcription factors (activator/silencer) proteins that bind to the regulatory DNA?
1. ALL cells have the same regulatory regions (bc all cells have the same DNA)
2. BUT NOT all cells have the same specific transcription factors bc not all proteins in each cell are expressed
85
New cards
how/why do cells have different sets of (specific) transcription factors?
TF = transcription factor
\
1. certain TFs are localized to 1 part of the cell
2. when the cell undergoes mitosis, because the TFs are on ONE side of the cell, the cell splits where only 1 of the daughter cells has the TFs in it (whereas the other daughter cell doesn’t get the TFs)
3. this results in cells producing different sets of proteins due to different TFs (ex: diff activator proteins)
\
1. certain TFs are localized to 1 part of the cell
2. when the cell undergoes mitosis, because the TFs are on ONE side of the cell, the cell splits where only 1 of the daughter cells has the TFs in it (whereas the other daughter cell doesn’t get the TFs)
3. this results in cells producing different sets of proteins due to different TFs (ex: diff activator proteins)
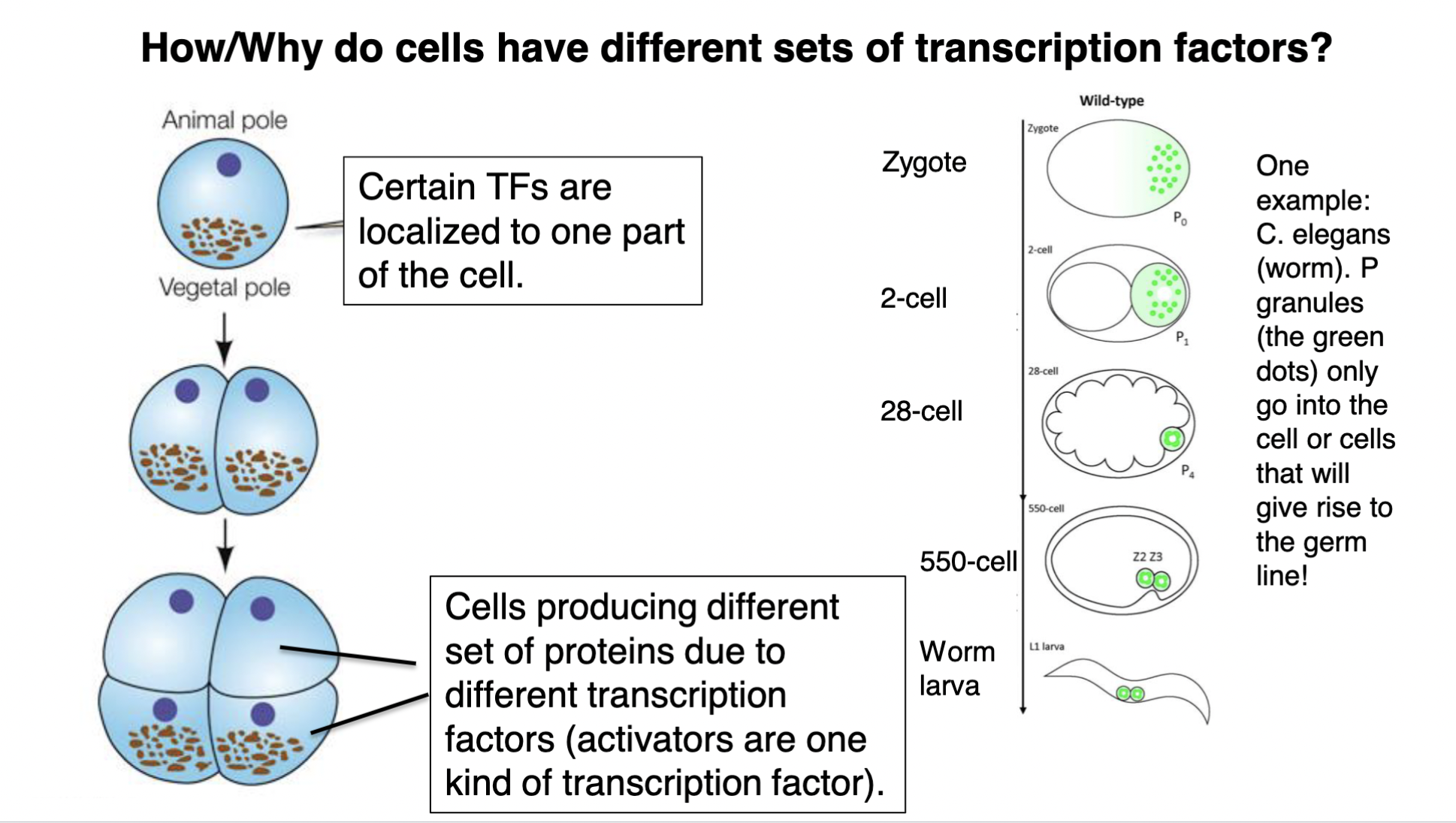
86
New cards
All DNA instructions (the genes AND their control elements) are the _____ in every cell. What differs between cells are the _____ that turn different genes on and off.
(1) SAME
(2) transcription factors (proteins)
(2) transcription factors (proteins)
87
New cards
how might a mutation *outside* the coding region of a gene cause disease or dysfunction?
changes in regulatory region → change expression of gene (cause over/under-expression)
88
New cards
how does a nonsense mutation affect the length of the gene? what about length of the protein?
does NOT affect length of the GENE BUT would likely SHORTEN the length of a protein (usually significantly)
89
New cards
what is a key mutation in Werner’s syndrome?
impaired nuclear *localization* of defective DNA helicases - DNA helicase proteins function to unwind DNA before DNA replicates BUT needs to be *inside* the nucleus to function and help cells replicate → there is an ***early stop codon*** that causes helicase to lose its signal sequence (its “zip code” signal) for the nucleus, leaving it in the cytoplasm before it is degraded by the cell
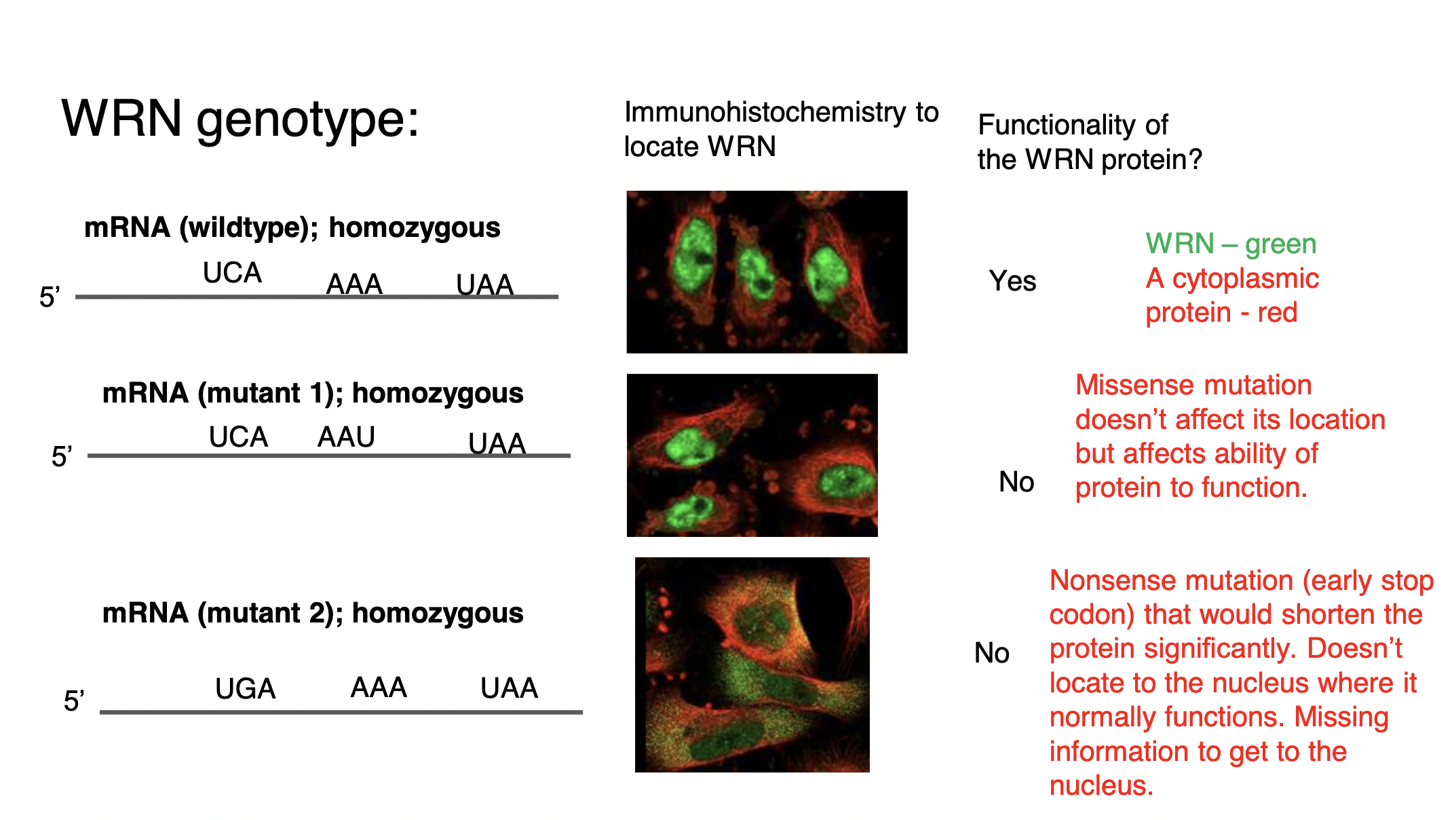
90
New cards
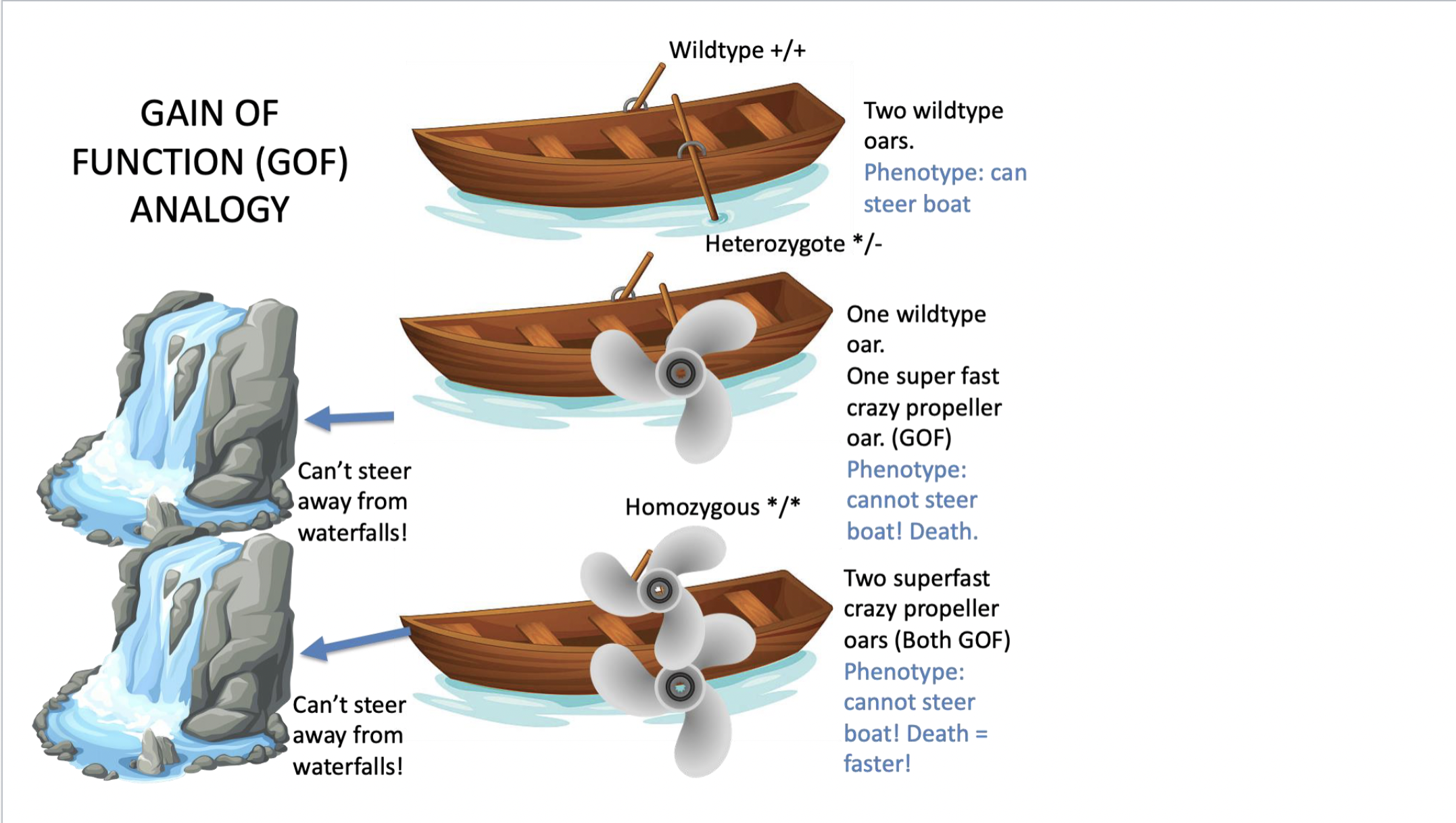
gain of function mutation
results in getting a new function not present in normal allele (doing something it didn’t do before) - need to know what the normal function did NOT do BEFORE concluding whether a mutation is a gain of function
\
a mutation that confers new or enhanced activity on a protein
\
produces a new trait or causes a trait to appear in inappropriate tissues or at inappropriate times in development
\
causes the appearance of a new trait or function or causes the appearance of a trait in inappropriate tissue or at an inappropriate time
\
a mutation that confers new or enhanced activity on a protein
\
produces a new trait or causes a trait to appear in inappropriate tissues or at inappropriate times in development
\
causes the appearance of a new trait or function or causes the appearance of a trait in inappropriate tissue or at an inappropriate time
91
New cards
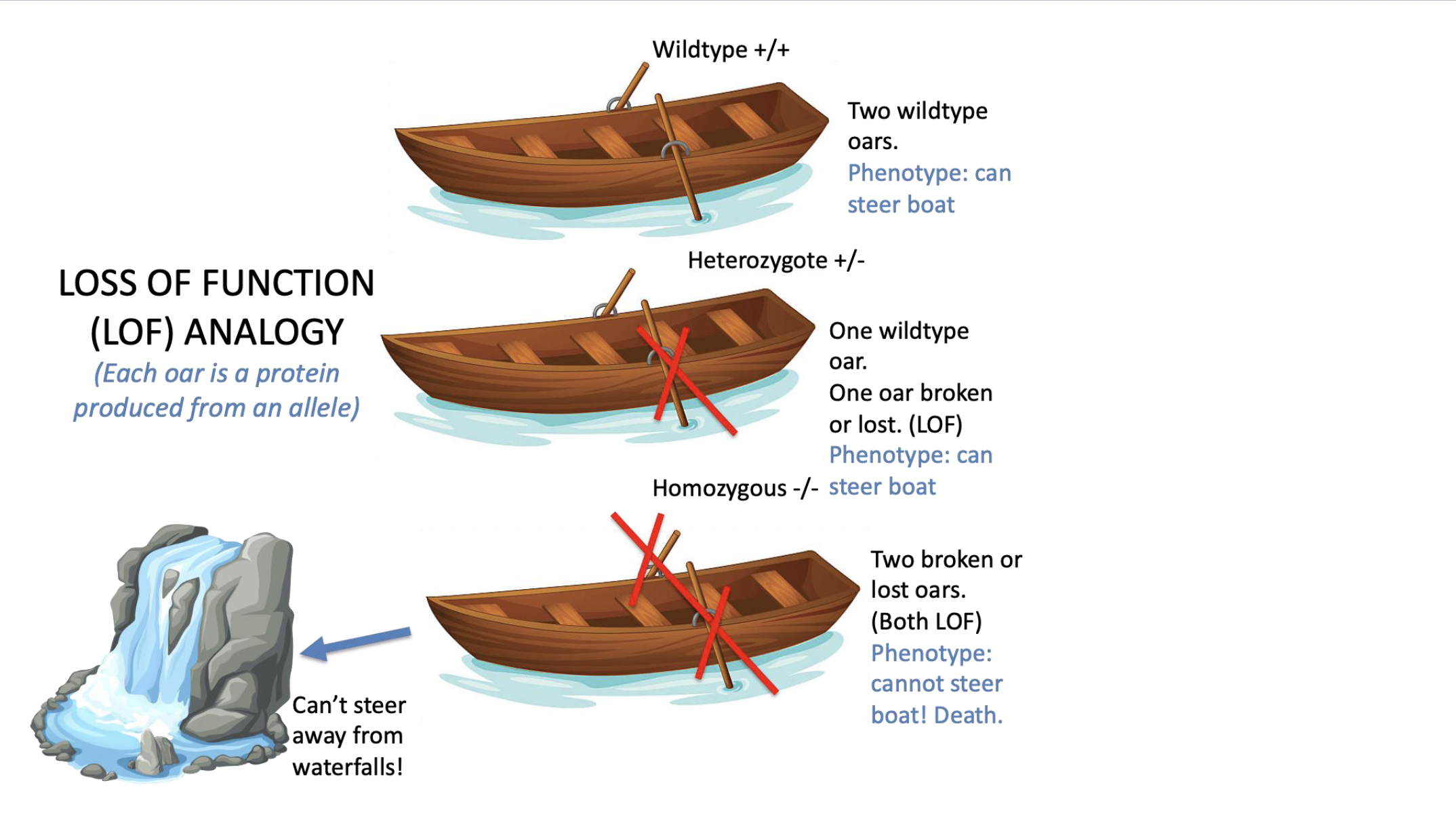
loss of function mutation
causes a complete or partial loss of function
\
causes a loss of NORMAL function (need to know what the normal function was BEFORE concluding whether a mutation is a loss of function)
\
causes a loss of NORMAL function (need to know what the normal function was BEFORE concluding whether a mutation is a loss of function)
92
New cards
null mutation
COMPLETE loss of function mutation
93
New cards
dominant allele
an allele that expresses its phenotypic trait in a heterozygote (requires only 1 copy)
94
New cards
recessive allele
an allele that produces its characteristic phenotype only when its paired allele is identical (requires 2 copies)
95
New cards
which mutations change the size of a gene?
FRAMESHIFT mutations - big *insertions* (many extra nucleotides in the gene) or big *deletions* (many nucleotides deleted - or maybe entire gene not present)
96
New cards
what technique would you use to look to see if a gene was present or if the size of a gene was much bigger or smaller?
PCR + electrophoresis
\
**NOTE: electrophoresis is only good for when we are looking for BIG insertions/deletion mutations (NOT point mutations, NOT small insertions/deletions)*
\
**NOTE: electrophoresis is only good for when we are looking for BIG insertions/deletion mutations (NOT point mutations, NOT small insertions/deletions)*
97
New cards
what technique would you use to look to see if there is a small mutation to the sequence of a gene?
PCR + DNA sequencing
\
**NOTE: electrophoresis is only good for when we are looking for BIG insertions/deletion mutations (NOT point mutations, NOT small insertions/deletions)* → canNOT use electrophoresis when looking for small changes to DNA bases
\
**NOTE: electrophoresis is only good for when we are looking for BIG insertions/deletion mutations (NOT point mutations, NOT small insertions/deletions)* → canNOT use electrophoresis when looking for small changes to DNA bases
98
New cards
what causes Huntington’s Disease?
\
how does this affect the size of the gene? what about size of the protein?
\
how does this affect the size of the gene? what about size of the protein?
a replication slippage and expansion of a CAG repeat → lots of CAG triplets added to wildtype allele to produce HG (mutated) allele
\
gene is now MUCH bigger and protein is also much bigger in mutated version
\
gene is now MUCH bigger and protein is also much bigger in mutated version
99
New cards
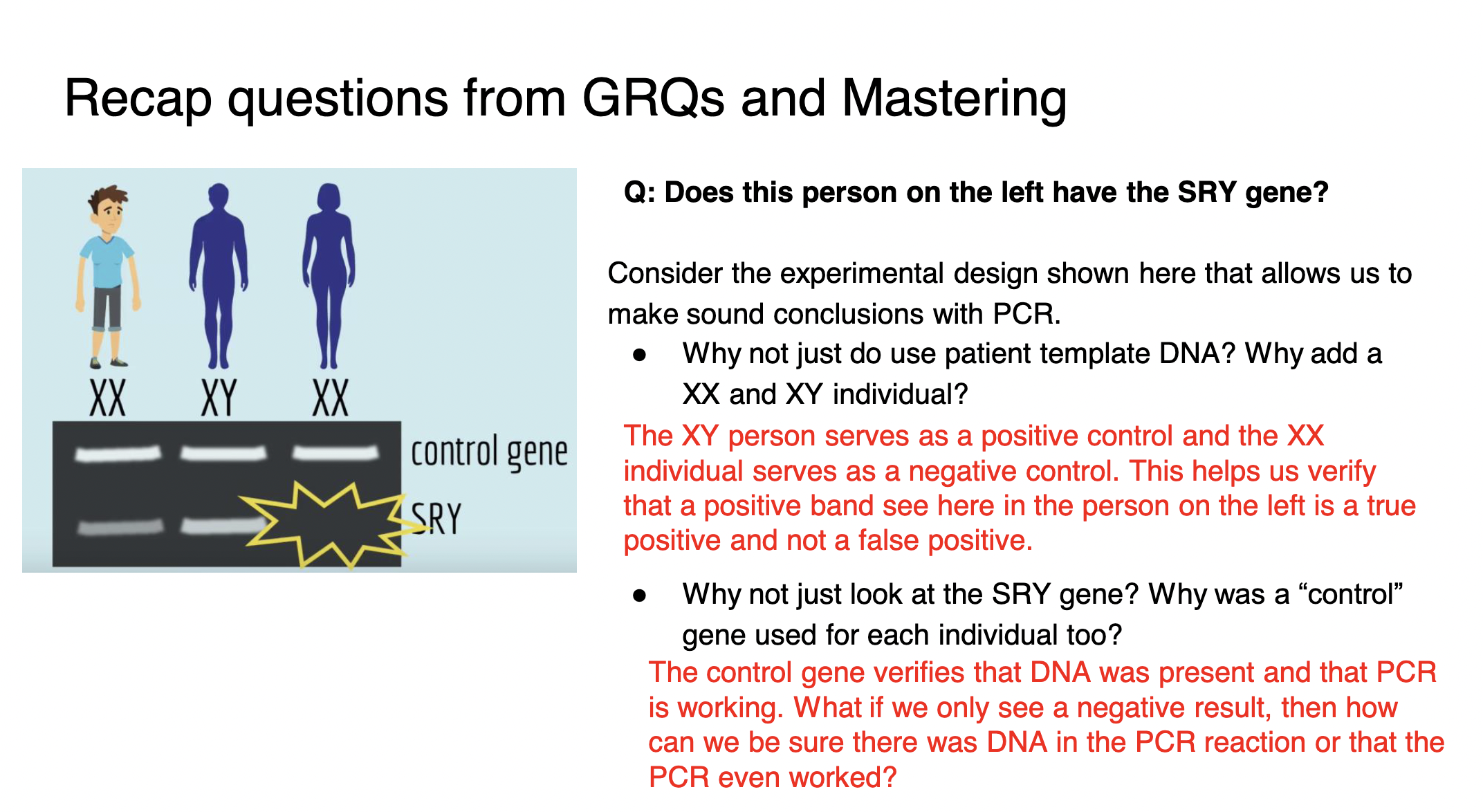
controls in gel electrophoresis
*NEGATIVE controls:*
* DNA UNCUT by restriction enzymes - shows how long the DNA polymer is in TOTAL (how many base pairs total we should get when we sum up the base pairs of our fragments)
* **when looking to determine if an individual has a certain gene:** need DNA from a known individual without the gene to serve as a negative control (see image)
\
*POSITIVE controls:*
* **when looking to determine if an individual has a certain gene:** need DNA from a known individual WITH the gene to serve as a positive control (see image)
* DNA UNCUT by restriction enzymes - shows how long the DNA polymer is in TOTAL (how many base pairs total we should get when we sum up the base pairs of our fragments)
* **when looking to determine if an individual has a certain gene:** need DNA from a known individual without the gene to serve as a negative control (see image)
\
*POSITIVE controls:*
* **when looking to determine if an individual has a certain gene:** need DNA from a known individual WITH the gene to serve as a positive control (see image)
100
New cards
mutations that change the size of gene
(looking for mutations that change the size of the DNA)
\
* Big insertions (ex: trinucleotide expansions like HD)
* Big deletions (part of all of a gene may be missing)
\
* Big insertions (ex: trinucleotide expansions like HD)
* Big deletions (part of all of a gene may be missing)