L19 Parasitic diseases
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Medical parasitology

Protozoa
kingdom of life
characteristic
structure
kingdoms of life: animals, plants, fungi, Protista (algae and protozoa)
singled celled, animal-like
ex. amoebae, ciliates, flagellates, sporozoans
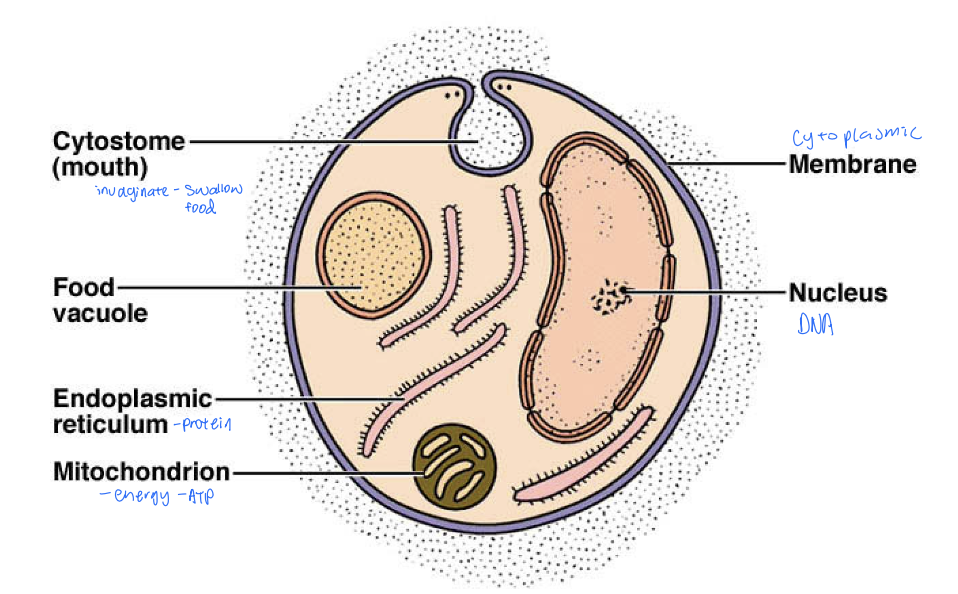
structure:
cytoplasmic membrane
cytoplasm
cytostome (mouth)
vacuole
nucleus w/ DNA
ER
mitochonrion
usually with flagellum
Protozoa Life processes

Protozoa life cycle
reproduction
encystment

Infective amoebas general properties

amoebiasis epidemiology
typical places
spreading mechanism
a tropoical and subtropical diseases
spread in tropical more than US cuz sewage used as fertilizers in tropical
Spread: refer to pic

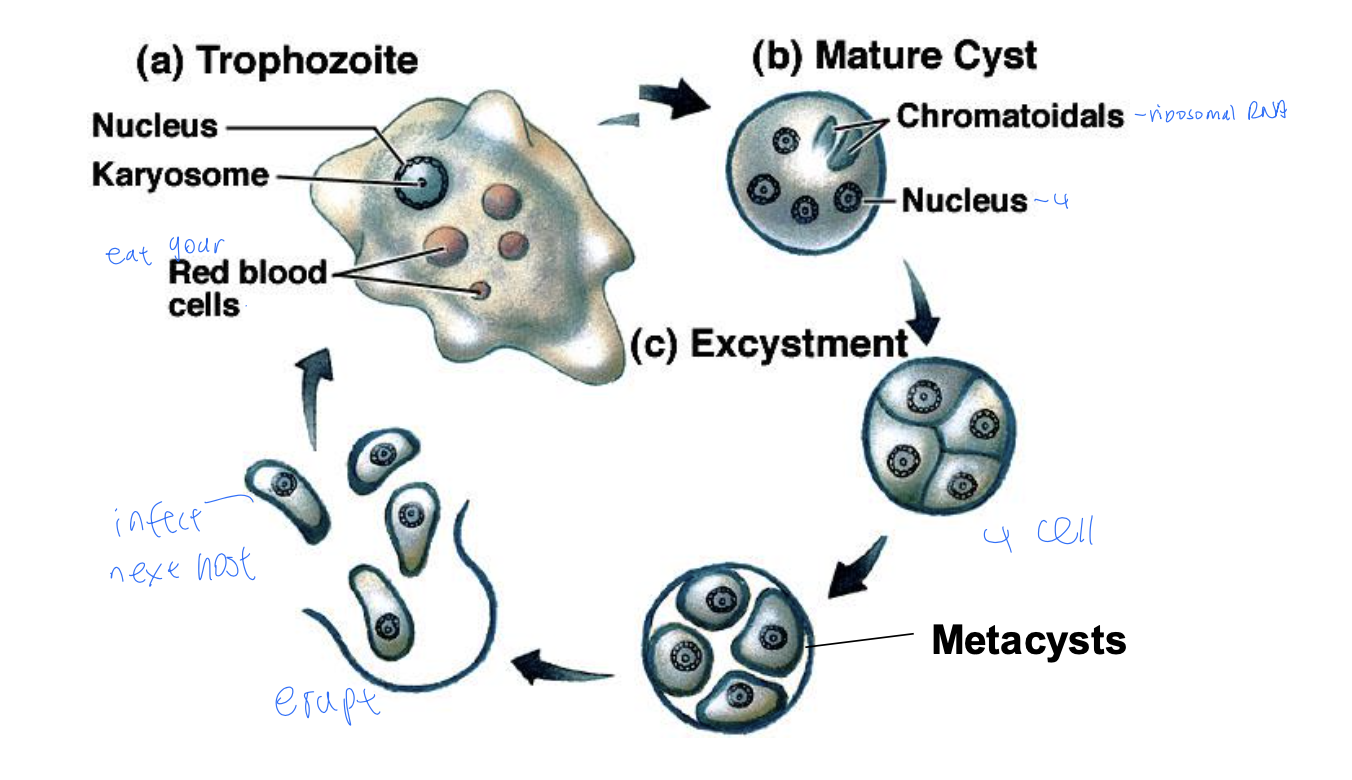
Amoebiasis life cycle
Amoebiasis
diagnosis
treatment
diagnosis
Trophozoite that has ingested RBC
4 nuclei in cysts
symptom
treatment
drugs targeting parasites in both feces and the tissue
Naegleria fowleri and acanthamoeba characteristics

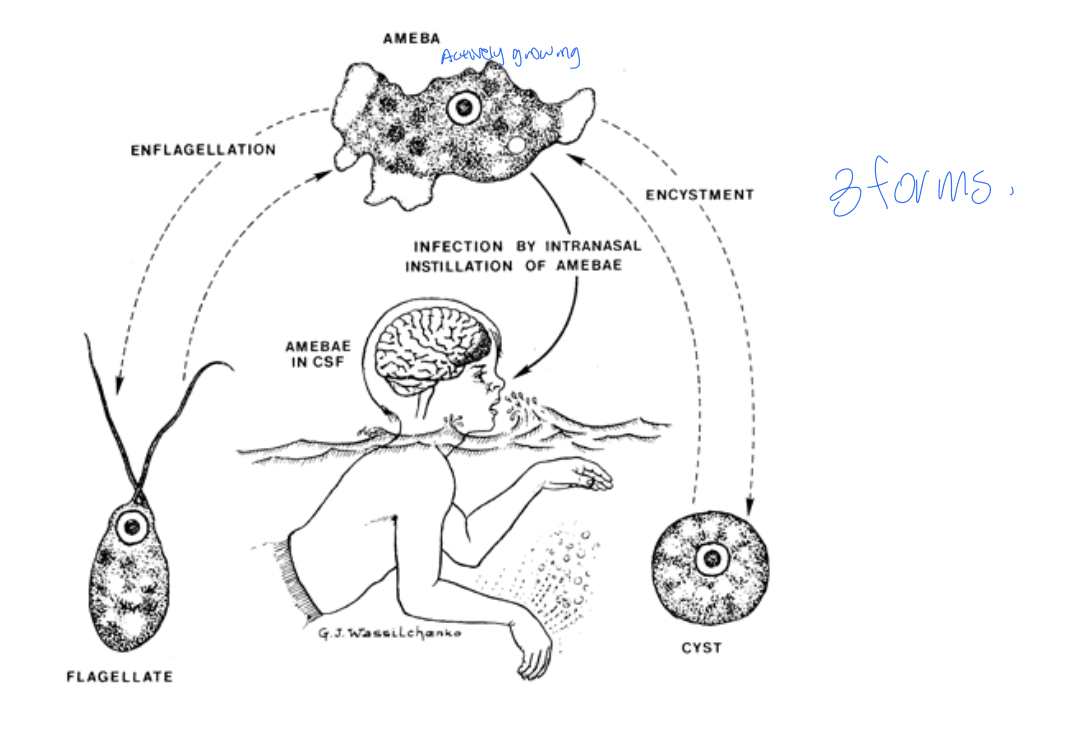
Naegleria fowleri life cycle
Naegleria fowleri pathogenesis
Naegleria infection starts at the nasal mucosa
The amoeba burrows in, multiplies, and migrate into the brain → primary acute meningoencephalitis: rapid, massive destruction of the brain and spinal tissue.
Symptoms: hemorrhage and coma, death in a week
ciliate characteristics

Balantidium Coli Reservoir (Natural habitat)
large intestines of pigs, and other domestic animals, primates
cysts are in the feces
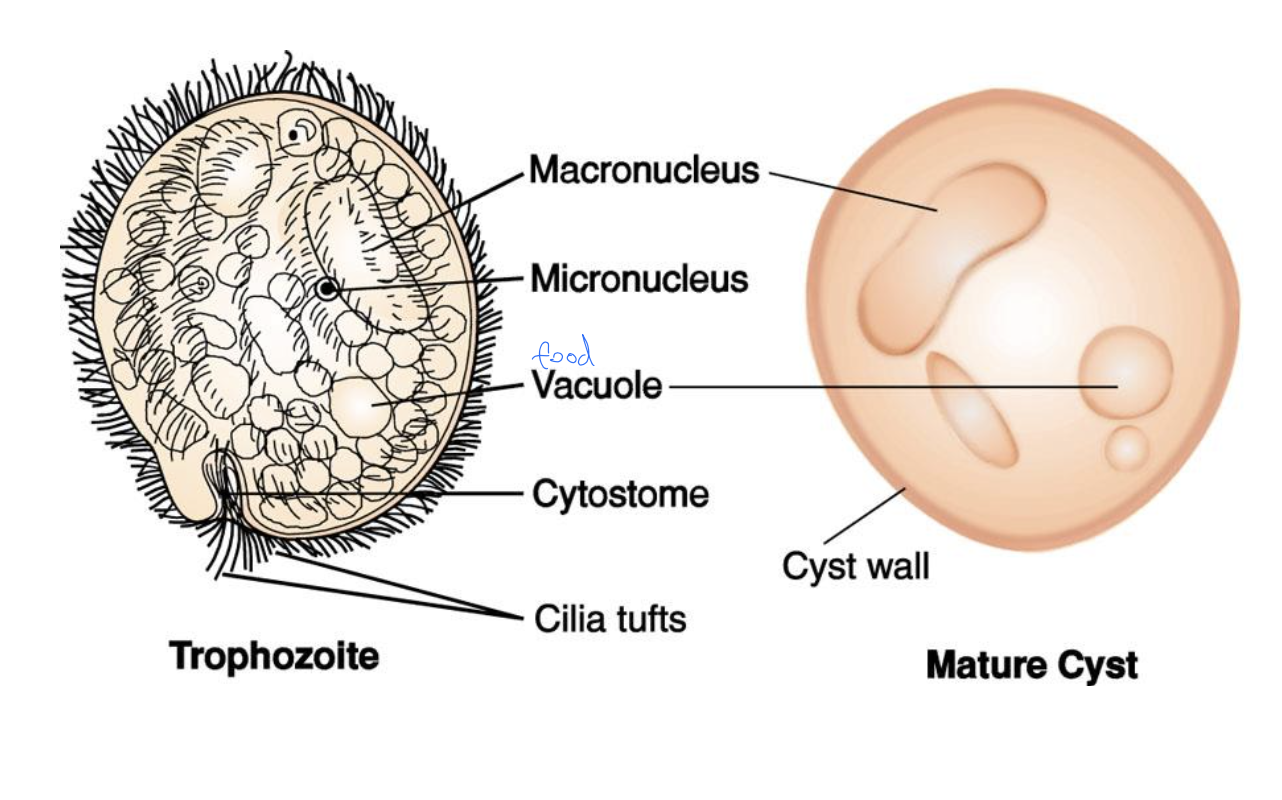
anatomy of balantidium coli
* trophozoite vs mature cyst
Mature cyst only consist of macronucleus
trphozoite has macro and micronucleus
Balantidium coli prevention
prevent food or drink contamination with pig manure
Flagellates (mastigophorans) common features
long filamentous flagella
flagellate morphology
Undulating membrane = wavy fin-like structure for movement
Axostyle = internal supporting rod
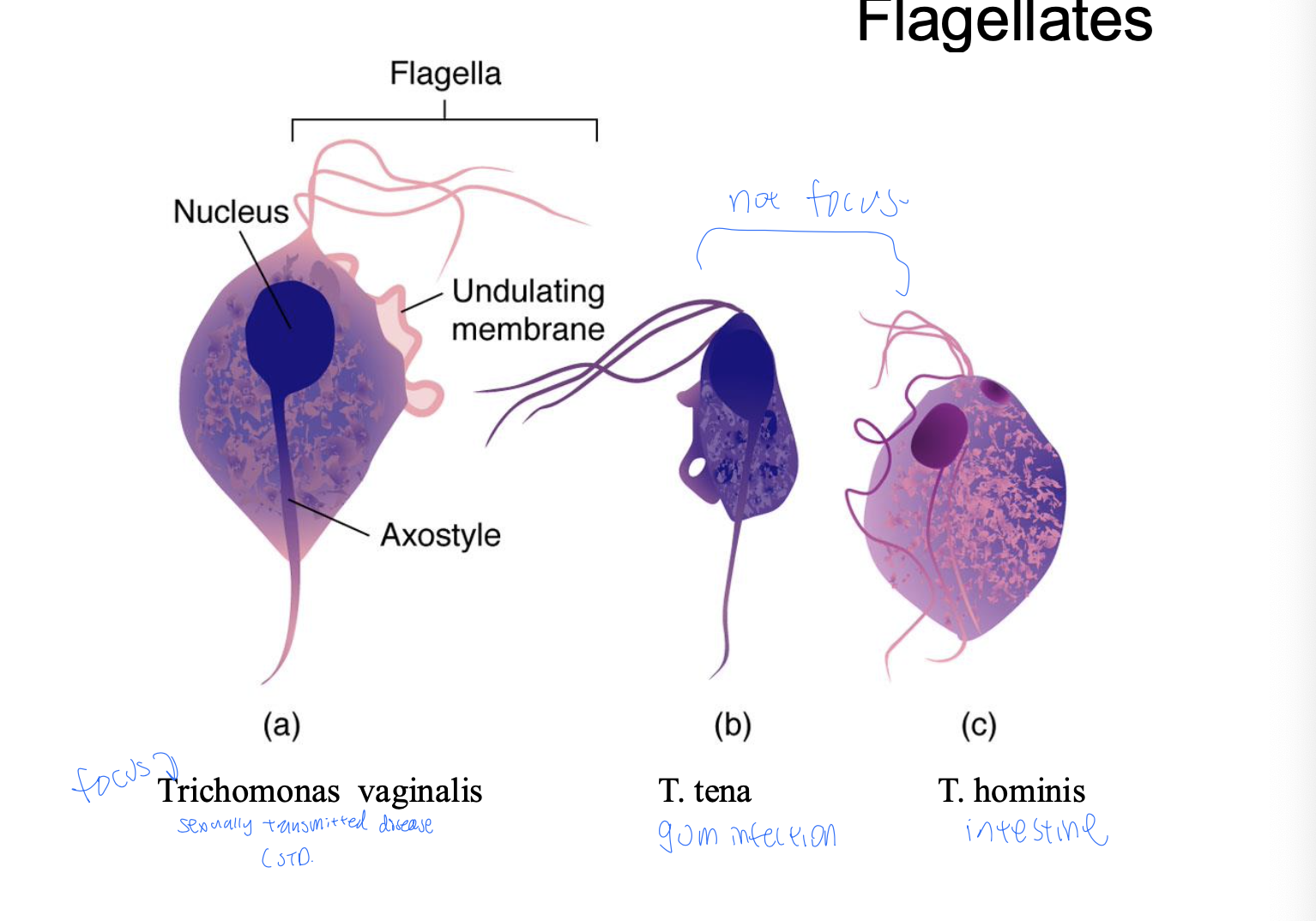
Trichomonads reservoir
human urogenital tract: 50% asymptomatic
Trichomoniasis symptoms and treatment
Female
foul smell, green to yellow vaginal discharge
vulvitis, cervicitis
urinary frequency and pain
male
milky discharge
urethritis
prostate infection
Treatment
antibiotic and both sexual partners have to be treated
Giardiasis life cycle

Giardiasis outbreaks example

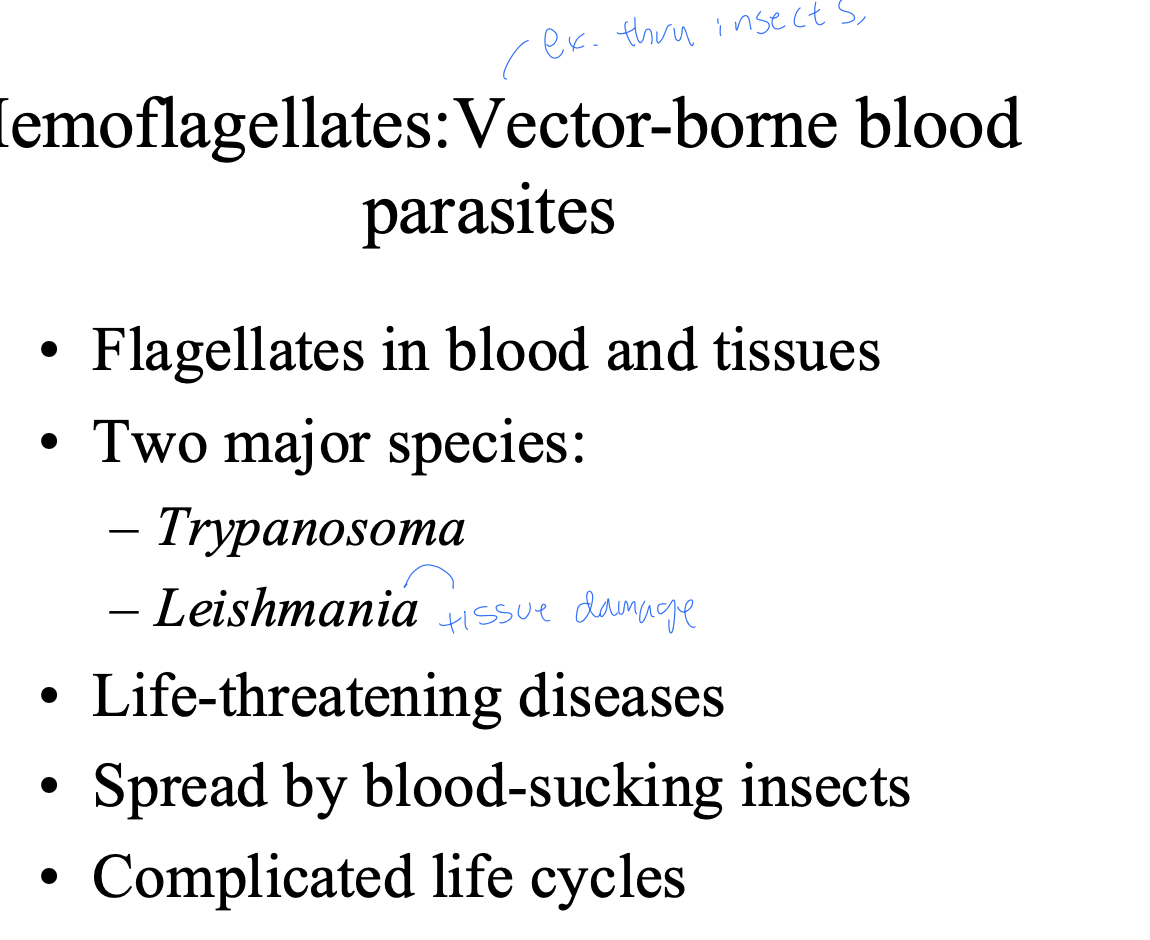
Hemoflagellates characteristic
vector-borne blood parasites
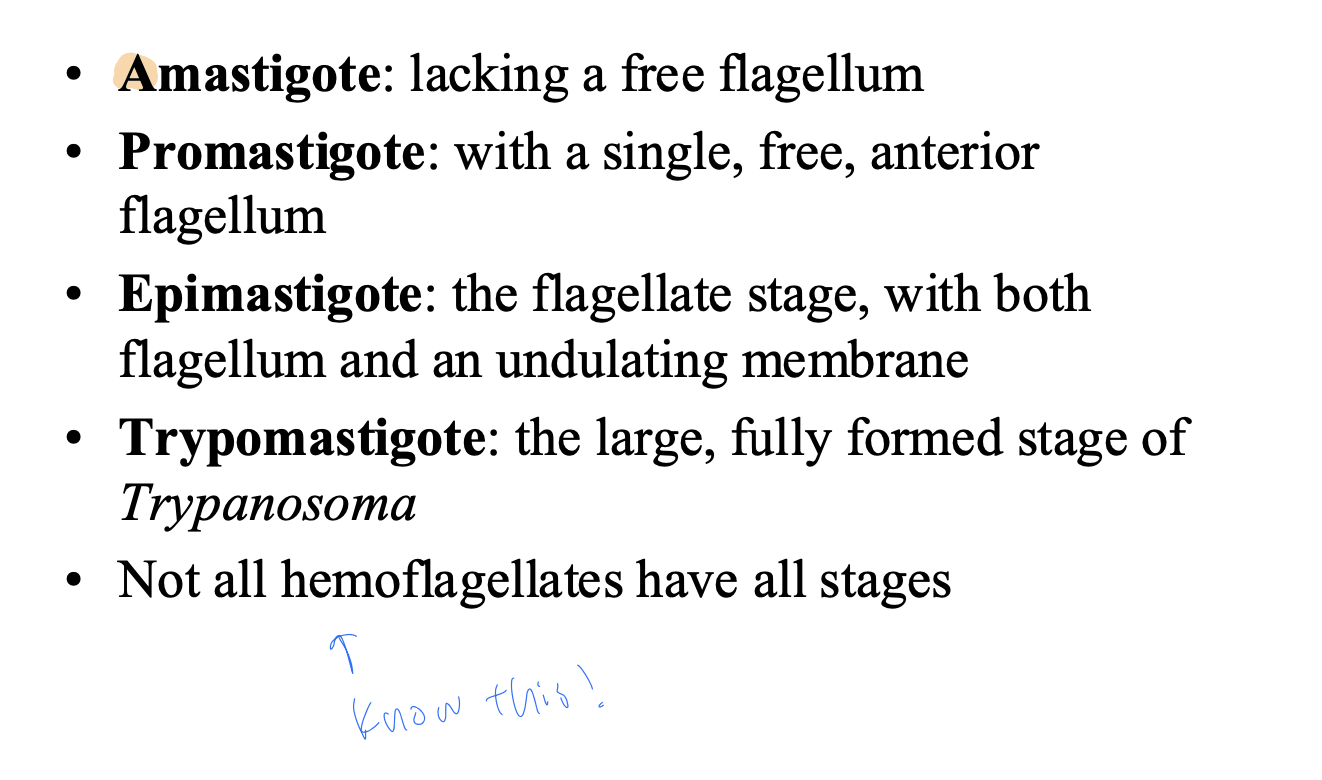
Developmental stages of hemoflagellates
amastigote
promastigote
epimastigote
trypomastigote
amastigote
promastigote
epimastigote
trypomastigote
Infection by T. brucei
rhodesian form
gambian form

Pathology of sleeping sickness
Intermittent fever, enlarged spleen, swollen lymph nodes, joint pain
Personality change, sleep disturbances
Sleepiness during the day
Sleeplessness at night
Advanced neurological disorders:
– Muscular tremors, shuffling gait, slurred speech, epileptic seizures, paralysis
– Death: coma, secondary infections, heart damage
Treatment and prevension of sleeping sickness

Why the immune system can not defeat the trypanosome

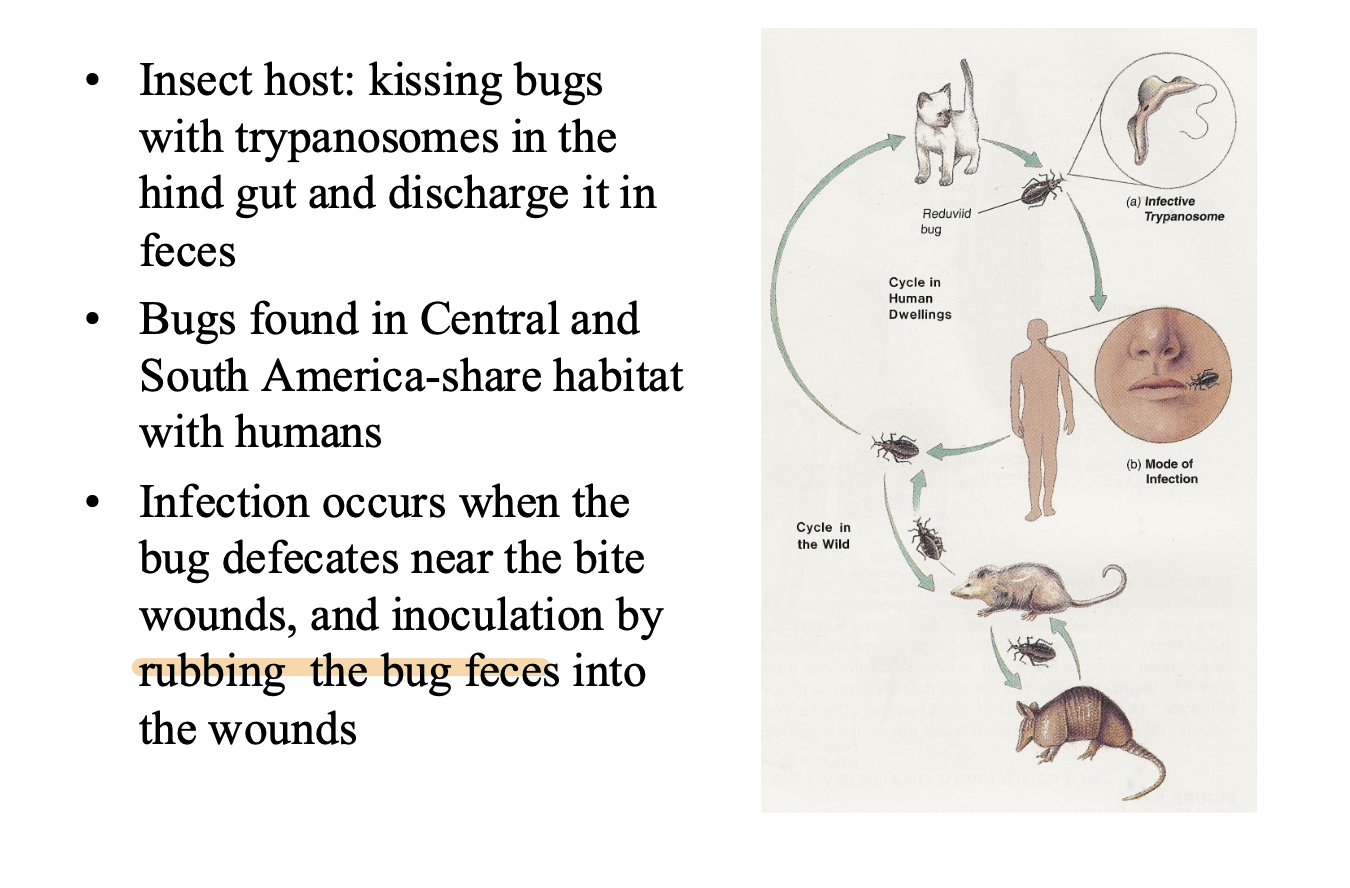
T. cruzi infection
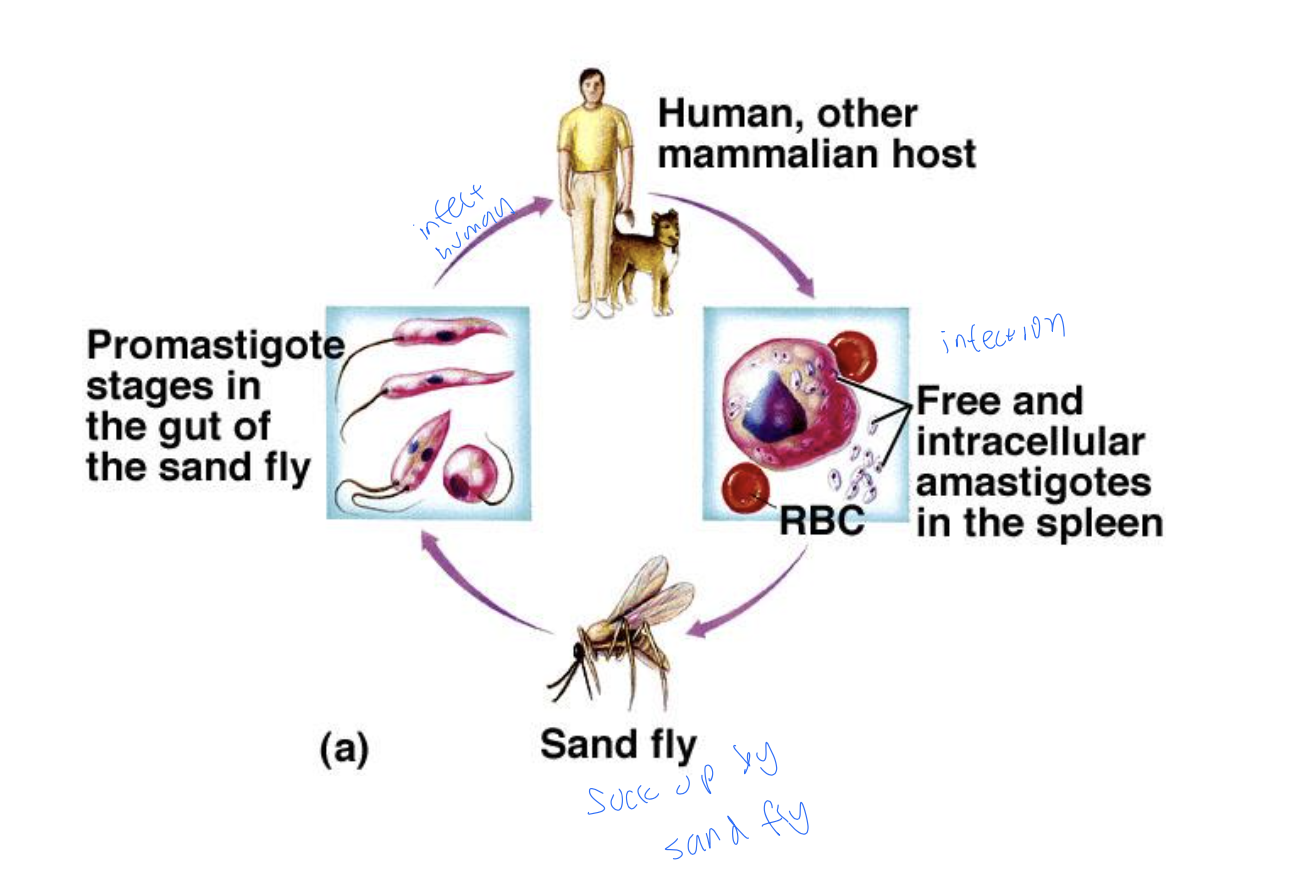
Leishmaniasis characteristics

Leishmania life cycle
Apicomplexan parasite characteristic

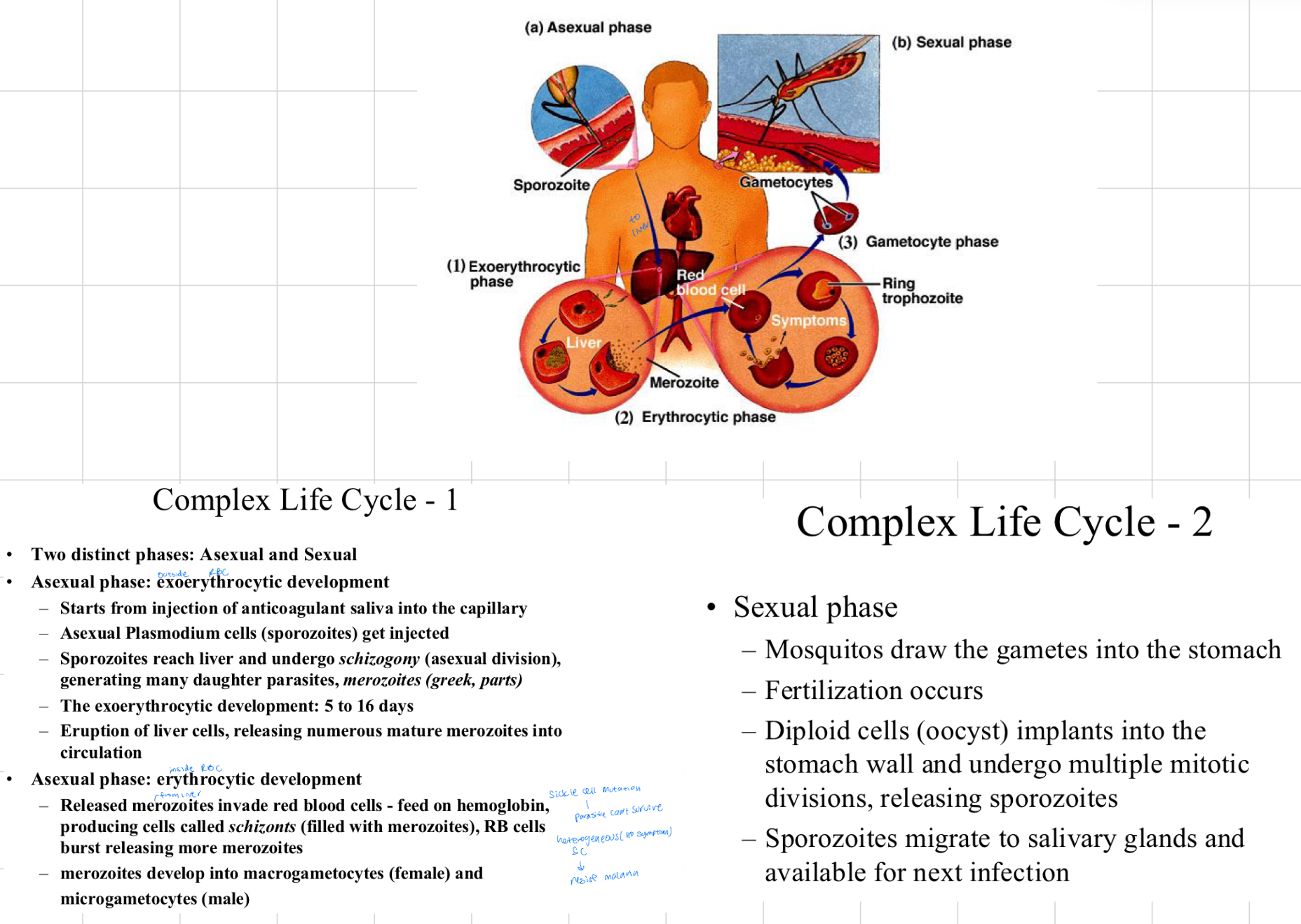
Malaria symptoms
chills and fever at regular intervals, followed by sweating: 48 to 72 hours, due to synchronous rupturing of RBCs.
Anemia in young children; organ rupture from accumulated cell debris (spleen, liver and kidneys)
Long recovery: up to 5 years
Malaria plasmodium species
P. falciparum - – Most severe malaria
Persistent fever, rapid pulse, cough, weakness for weeks without relief, high death rate in acute phase
P. malariae;
P. vivax;
P. ovale
Malaria transmission

Malaria life cycle
Genetic change that wards off malaria

Malaria
treatment
diagnosis
control
treat with antimalaria drugs
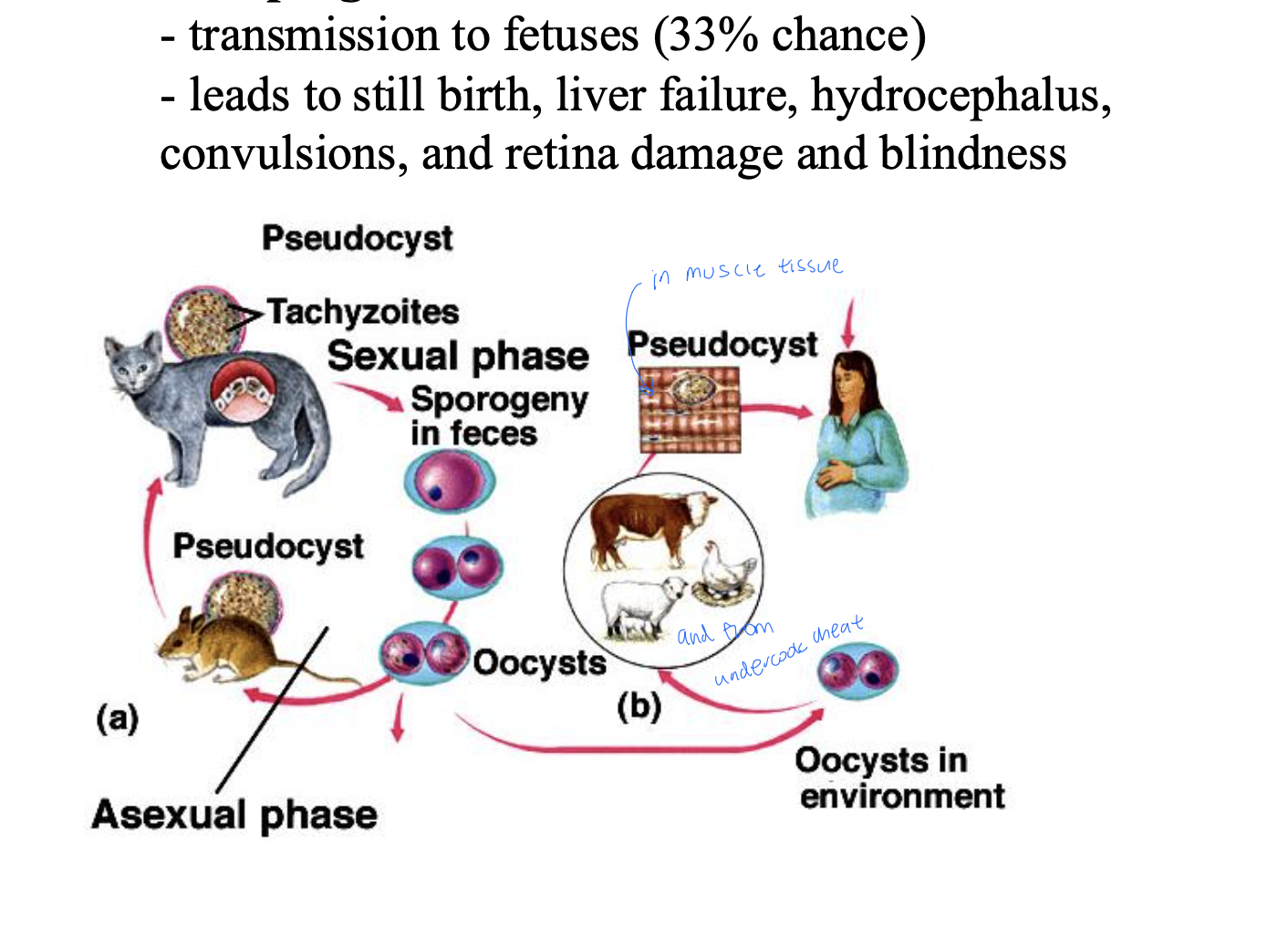
Toxoplasmosis characterstic
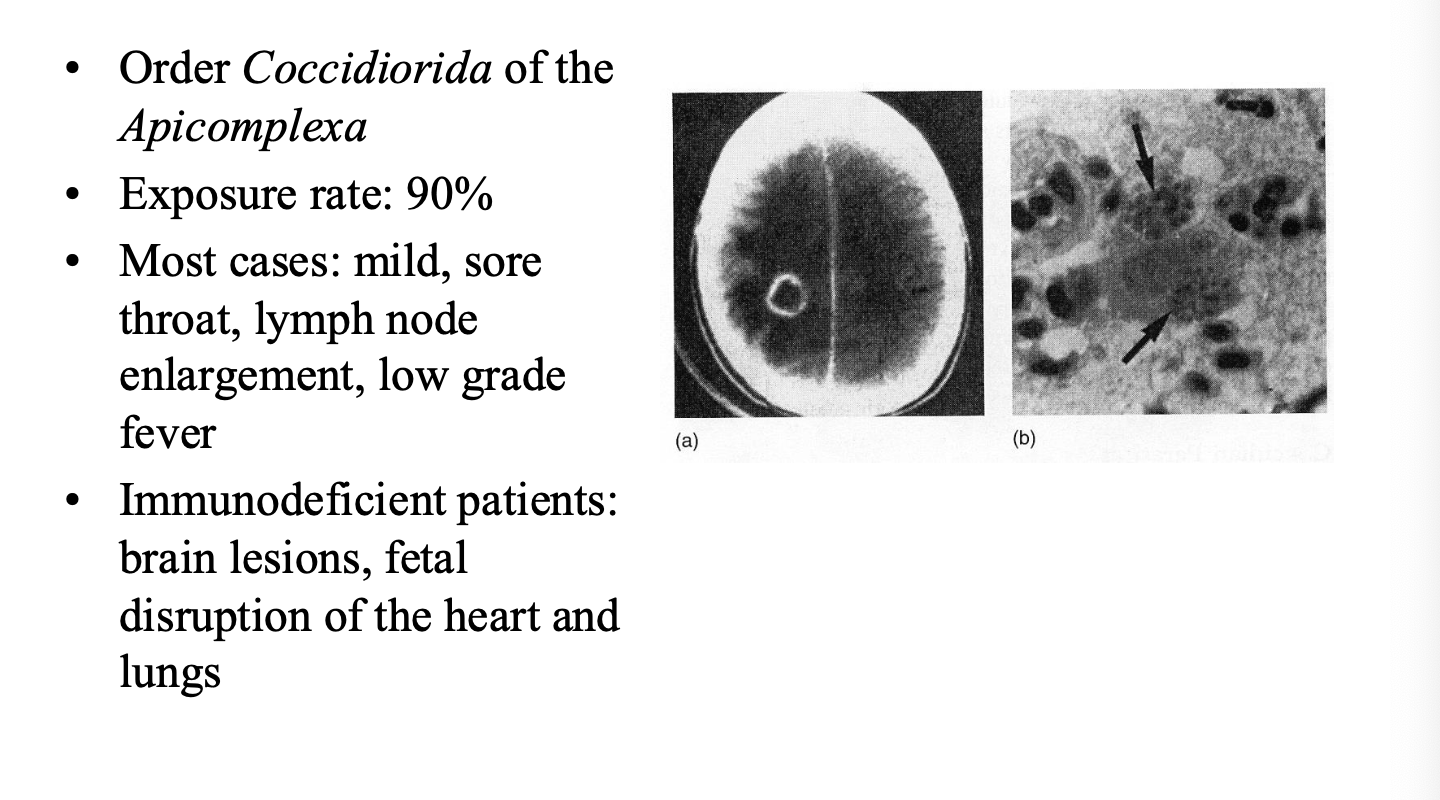
Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women