Exam 1: Coverings of CNS and CSF
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Ghosh - Fall 2023
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
meninges
membraneous tissue that covered the brain and spinal cord; 3 components and all are continuous
meningeal layers
dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater
dura mater location
outer, thick layer of the meninge
arachnoid location
the thin, middle layer of the meninge
pia mater location
the thinnest, and innermost layer of the meninge
components of the dura mater
periosteal and meningeal layers
periosteum
consists of collagenous connective tissue and arteries that cover the inner side of the skull
what are the periosteum and cranial bones supplied by?
meningeal arteries
middle meningeal artery
largest vessel supplying the cranium
what does the middle meningeal artery split into? when?
anterior and posterior branches
after entering the cranial cavity
what does the anterior and posterior branches of the middle meningeal artery supply?
lateral surface of the cranium
how many fossae does the cranial fault (floor) have? names?
3 fossae: anterior, middle, and posterior
what is the anterior fossa formed by?
frontal + ethmoid and sphenoid bones
what is the middle fossa formed by?
temporal and sphenoid bones
what is the posterior fossa formed by?
occipital and petrous part of the temporal bone
calvarium
roof of the cranial cavity
structures in the anterior cranial fossa
frontal lobes of the brain, crista galli, and cribriform plates
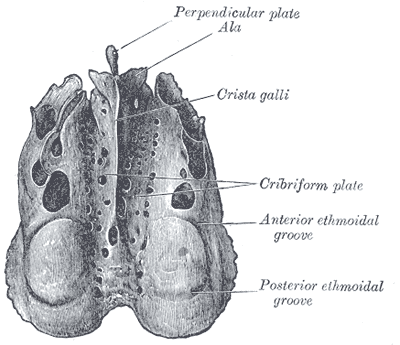
crista galli
sharp ridge in the midline of the anterior fossa and is the attachment site for the falx cerebri (a portion of the dura)
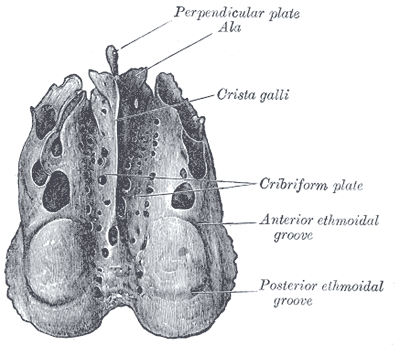
cribriform plates
depression on both sides of the crista galli and is the location for the olfactory bulb
structures in the middle cranial fossa
temporal lobe, hypophyseal fossa, optic foramen, superior orbital fissure, foramen rotundum, foramen ovale, foramen spinosum, and foramen lacerum
hypophyseal fossa
pituitary gland sits on top of this fossa
optic foramen
optic nerve (CN II) and the ophthalmic artery pass through
superior orbital fissure
oculomotor, trochlear, ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, and abducens nerve pass through
(CN III, IV, V, and VI)
foramen rotundem
maxillary division of CN V (Vagus) pass through
foramen ovale
mandibular division of CN V (Vagus) passes through
foramen spinosum
middle meningeal artery passes through
foramen lacerum
internal carotid artery passes through
structures in the posterior cranial fossa
occipital lobe, cerebellum, brain stem, foramen magnum, hypoglossal canal, and jugular foramen
what part of the brain stem is included in the posterior cranial fossa?
mainly the pons and medulla
foramen magnum
vertebral arteries pass through here
hypoglossal canal
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) passes through here
jugular foramen
internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, and accessory nerve pass through (CN IX, X, and XI)
what protects the brain?
the skull, cranial meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood-brain barrier
purpose of the cranial meninges
protects the brain from cranial trauma
dura mater composition
opaque and is a single layer around the spinal cord and a double layer inside the skull
what is located between the two dura mater layers?
venous sinuses
what is occupied in the dura mater epidural space?
simple squamous epithelium and some fluid
arachnoid mater composition
spider web-like, transparent appearance and contacts the epithelial layer of dura mater
pia mater composition
follows all the tissues of the brain and spinal cord and cannot be distinguished from nervous tissue
how is the pia mater attached?
to the brain surface by astrocytes
epidural space
potential space superior to the dura
subdural space
potential space between dura and arachnoid mater
subarachnoid space
consists of connective tissue strands from pia to arachnoid
filled with CSF and contains the blood vessels supplying the brain
arachnoid granulations
projections of the arachnoid membrane into the dural sinuses to allow CSF to pass through to the venous system
dural folds
folded inner layer of the dura mater that extends into the cranial cavity to stabilize and support the brain
what do the dural folds contain?
collecting veins for dural sinuses
dural fold names
falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, and falx cerebelli
falx cerebri
where: attached to the front of the crista galli and goes back to tentorium cerebelli and hangs above corpus callosum
what: vertical divide in the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres
tentorium cerebelli
lies between the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum
runs transversely
falx cerebelli
located in the posterior cranial fossa and extends vertically for a short distance between the cerebellar hemispheres
what ventricles are located in the brain
lateral, third, and fourth
location of lateral ventricle
deep within the cerebrum
location of the third ventricle
connected by interventricular foramen
location of the fourth ventricle
connected by cerebral aqueduct and connects to the subarachnoid space so it can return to the bloodstream
venous draining in dural sinuses
veins draining the brain empty into the sinuses of the dura mater then goes into the internal jugular veins
superior sagital sinus
space between the layers of the meninges and communicates with nasal vein in the front
what drains into the superior sagital sinus
the superior cerebral vein and it is continuous with the right transverse sinus
inferior sagital sinus
lies alone the free border of falx cerebri and drains into the straight sinus
straight sinus (rectus)
located where the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli meet
transverse sinus
lies in a groove on the occipital bone alone the margin of the tentorium cerebelli
when does the transverse sinus become the sigmoid sinus?
when it reaches the petrous part of the temporal bone and is continuous with the internal jugular vein
cavernous sinuses
located on the side of the sphenoid bone and drains into the transverse sinus via the superior petrosal sinus
internal jugular vein
direct continuation of sigmoid sinus and receives all blood from inside the skull
what is the 3rd major fluid of the body? what is the adult and newborn volume?
CSF
adult: 90-150 mL
neonate: 10-60 mL
where is CSF produced? what is the rate?
choroid plexus of the 4 ventricles by modified ependymal cells
20mL/hour
where does CSF flow through? what is the volume here?
through the subarachnoid space at a volume of 90-150 mL for adults
where is CSF reabsorbed?
arachnoid granulation to eventually be reabsorbed into the blood
CSF circulation
lateral ventricles → third ventricle → interventricular foramen → third ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → fourth ventricle → medial OR lateral aperture → cerebello medullary cistern (medial) OR pontine cistern (lateral) →subarachnoid space and central canal → arachnoid villi → superior sagittal sinus → sinuses → internal jugular vein
how is the movement of CSF assisted?
pulsation of arteries in the subarachnoid space
roles of CSF
1: cushions and insulates delicate nervous tissue
2: gives buoyancy to the brain
3: exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
4: transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products
properties of CSF
volume: 80-150 mL
pressure: 80-180 cm H2O
glucose: 40-60 mg / dL
protein: very low
hydrocephalus
enlarged ventricles with excess CSF
blood brain barrier
restrictive barrier around blood vessels in the brain and is created by astrocytes
blood brain barrier purpose
prevents most blood-borne toxins from entering the brain but not ABSOLUTE
what can pass through the BBB?
O2, glucose, CO2, alcohol, nicotine, and anesthetics