Unit 3: Political Culture and Participation & Party and Electoral Systems and Citizen Organization
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
citizens
individuals that belong to polity

society
large group of people that are connected by interactions/commonalities in order to form a sense of identity

state
common unit of political organization

civil society
voluntary organizations that aren’t controlled by state; strongest in democratic states. can still exist in authoritarian states, just weaker.

political ideology
a set of principles about government functions; shapes judgment of legitimacy and authority
regime
embraces political ideology to a certain degree

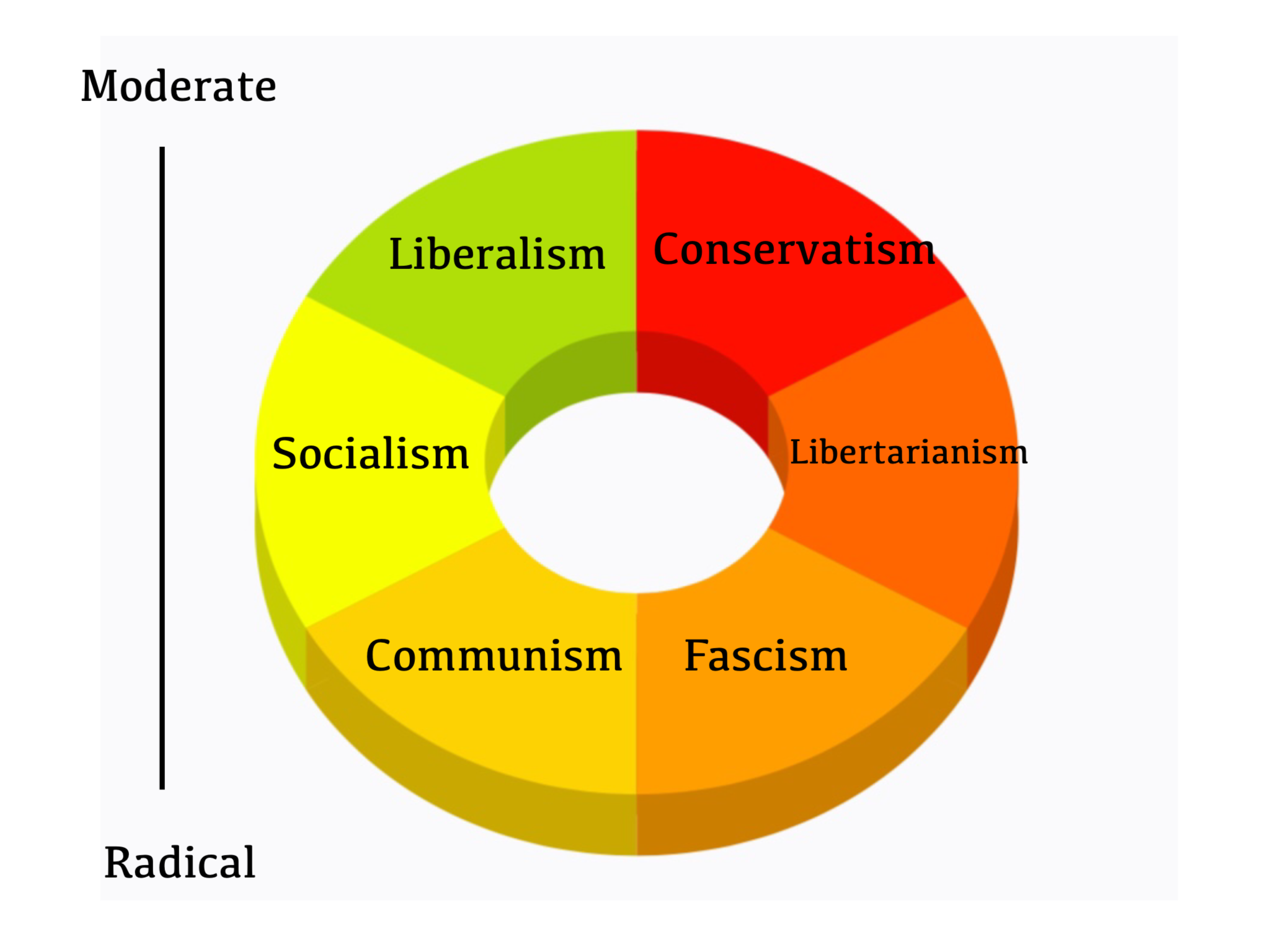
liberalism
individualist; against government intrusions (preference of minor gov intrusion in economy); maximize personal liberties + rights; economic liberalism

communism
collectivist (equality trumps individuality); government ownership of economy and government control of social systems (individual rights must give way to equality)

socialism
gov controls means of production w/ some private ownership; can be democratic or undemocratic; more concerned with maintaining welfare state than nationalizing means of production

conservative ideologies
protecting status quo; minimal economic regulation; little to no concern for equality

liberatarian ideologies
minimal government influence in everything

reactionary ideologies
more conservative than conservatives; want to “go back in time“

fascism
glorify state and military; 100% collectivist

political culture
set of values people hold regarding political system where they live:
Beliefs about authority
Group v. individual
Libery v. security
Legitimacy
Political community

political socialization
process/institutions that give us beliefs
political community
self-identity? Rarely monolithic; elite vs mass p.c. this is where legitimacy, authority, and sovereignty come from (attitudes, beliefs, symbols that influence political interactions)

where does p.c./p.s. come from?
political culture comes from…
Defining events
Repeated experiences
political socialization comes from…
Family
Friends
School
Media
Religious institutions

cross-cutting cleavages
moderate society; groups pull apart on issues

complementary cleavages
reenforcing/coinciding/polarizing; groups pull in one direction

race
group members are thought to have genetically transmitted physical differences

ethnic identity
common history/culture/descent; often lack belief in right to political control

religion
can combine with ethnicity to cause violence; strong today but weak in modernized societies

gender
differences that can help shape the identity groups of male and female; gender shows how traits, roles, behavior, and attitudes are perceived

class
harsh historically, not so much anymore

political participation
how individuals participate in politics; strong, effective political institutions thrive on mass political participation

conventional participation
accepted means of already established institutions (ex. Voting in dem states); contacting rep, donated to an i.g. or p.p.; nondemocratic - elite discouraging participation

unconventional participation
boycotts, strikes, violence, terrorism; activities that disrupt political or social stability; elite do not approve

non-participation
people feel alienated. Don’t understand or want to understand politics

citizenship
official membership in a state; comes with responsibilities and rights; one needs to go through naturalization and some states allow for dual citizenships

naturalization
the admittance of a foreigner to the citizenship of a country
