Stage 1 - Carbon Chemistry
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Why is Carbon an important element?
It can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms and are small enough to fit in a complex structures.
2
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds consisting only of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
3
New cards
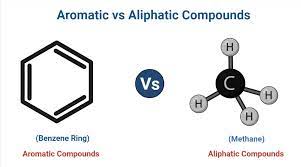
What is the difference between an aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbon?
Aliphatic has no aromatic rings and Aromatic has aromatic rings.
4
New cards
Alkane
A type of saturated hydrocarbon consisting of single bonds.
5
New cards
Alkene
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon consisting of at least one double bond.
6
New cards
Alkyne
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon consisting of at least one triple bond.
7
New cards
What are examples of common Alkyl groups (Branches)?
* Methyl
* Ethyl
* Propyl
* Butyl
* Pentyl
* Ethyl
* Propyl
* Butyl
* Pentyl
8
New cards
What are formula types will you often use?
* Molecular formula
* Structural formula
* Semi-structural formula
* Condensed semi-structured formula
* Skeletal formula
* Structural formula
* Semi-structural formula
* Condensed semi-structured formula
* Skeletal formula
9
New cards
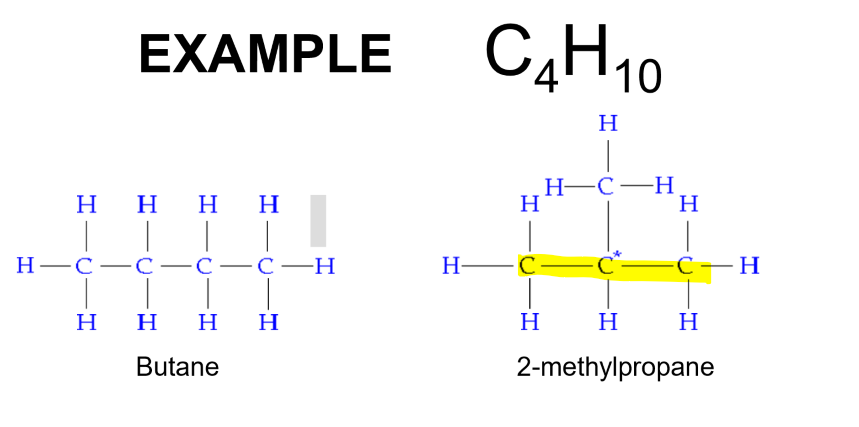
Structural Isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms.
10
New cards
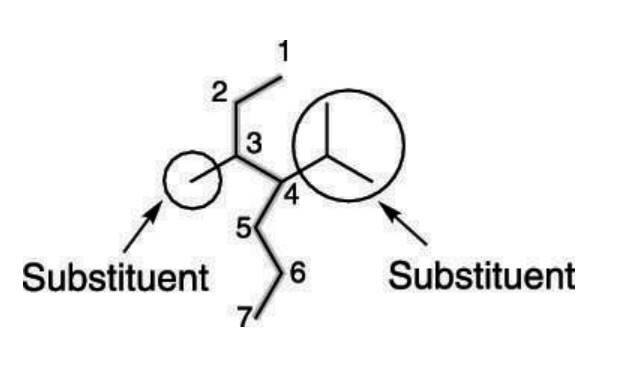
Branches
Atoms or group of atoms that replaces a hydrogen and gets attached to the carbon in the longest carbon chain.
11
New cards
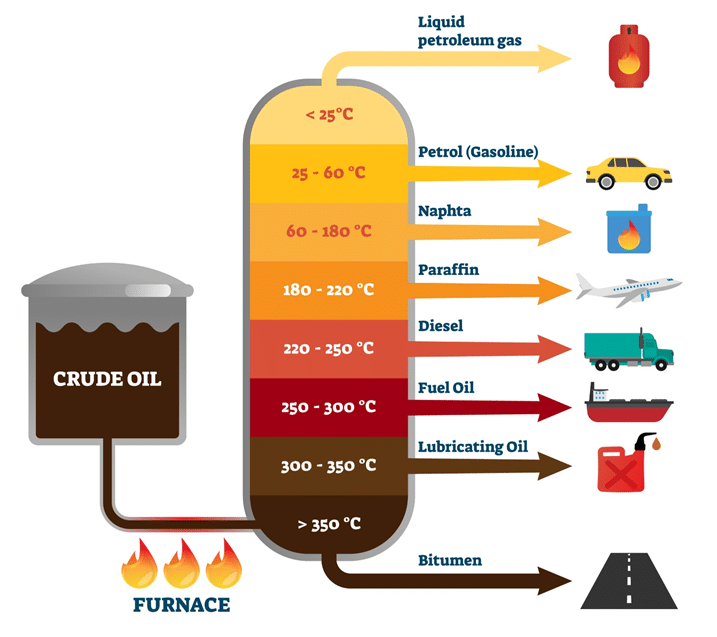
Crude Oil
Unprocessed oil from underground that is extremely valuable that provides hydrocarbons to be used in various industries.
12
New cards
Fractional Distillation
A process that separates hydrocarbons of crude oil into fractions with similar boiling points.
13
New cards
What is the general formula for Alkanes?
CxH2x+2
14
New cards
What is the general formula for Alkenes?
CxH2x
15
New cards
What is the general formula for Alkynes?
CxH2x-2
16
New cards
The prefix for 1 carbon atom is…
Meth-
17
New cards
The prefix for 2 carbon atoms is…
Eth-
18
New cards
The prefix for 3 carbon atoms is…
Prop-
19
New cards
The prefix for 4 carbon atoms is…
But-
20
New cards
The prefix for 5 carbon atoms is…
Pent-
21
New cards
The prefix for 6 carbon atoms is…
Hex-
22
New cards
The prefix for 7 carbon atoms is…
Hept-
23
New cards
The prefix for 8 carbon atoms is…
Oct-
24
New cards
The prefix for 9 carbon atoms is…
Non-
25
New cards
The prefix for 10 carbon atoms is…
Dec-
26
New cards
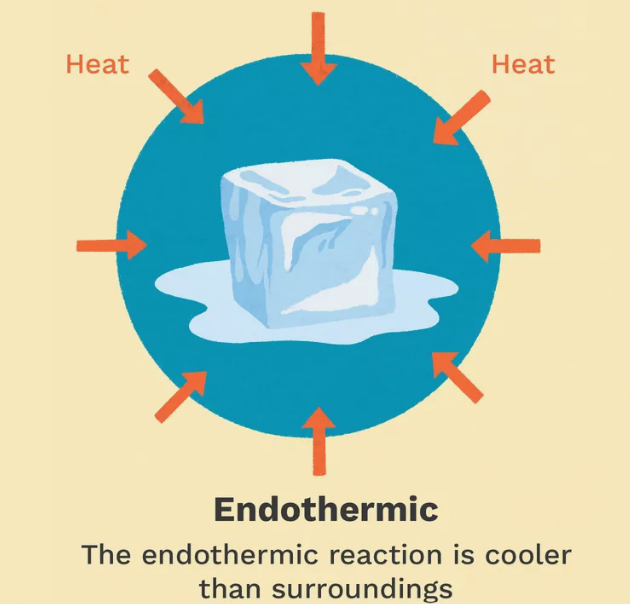
Endothermic Reactions
Reactions that absorb heat from the surroundings.
27
New cards
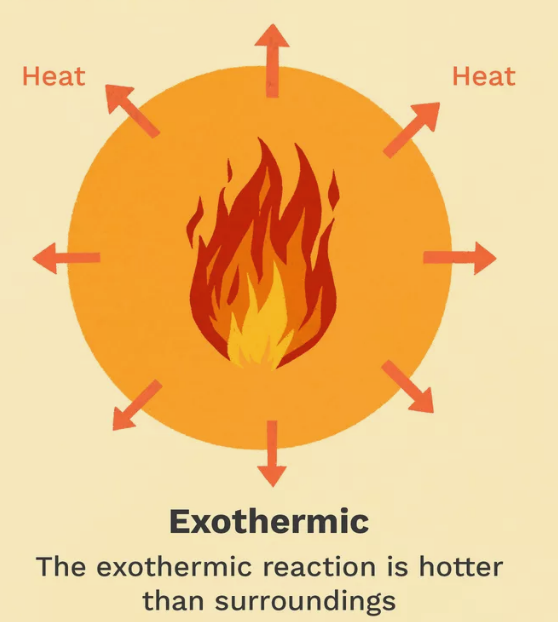
Exothermic Reactions
Reactions that release heat to the surroundings.
28
New cards
Enthalpy
Thermodynamic property that represents the total heat content of a system at constant pressure.
29
New cards
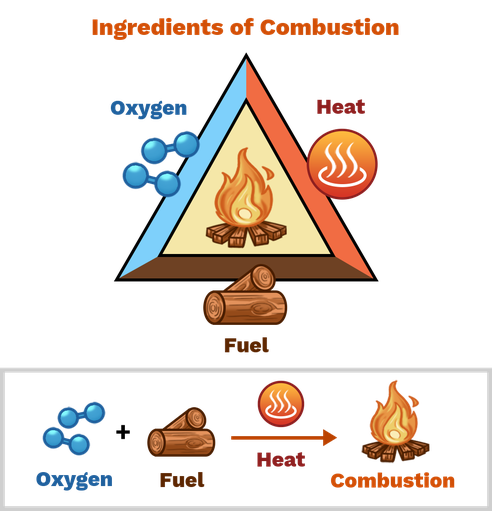
Complete Combustion
An exothermic reaction where a fuel reacts rapidly with Oxygen, releasing heat and light.
30
New cards
Functional Groups
Branches within a molecule that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of that molecule.
31
New cards
Alcohols (Hydroxyl)
A functional group consisting of one oxygen and hydrogen atom.
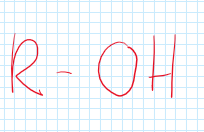
32
New cards
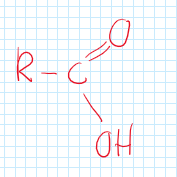
Carboxylic Acids (Carbonyl)
A functional group consisting of a carbon, double bonded oxygen, and a hydroxyl.
33
New cards
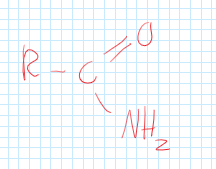
Amides
A functional group consisting of carbon, double bonded oxygen, and an amine.
34
New cards
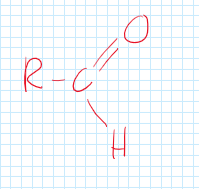
Aldehyde
A functional group consisting of carbon, double bonded oxygen, and a hydrogen.
35
New cards
Keytone
A functional group with carbon branches attached to a carbon and double bonded oxygen.
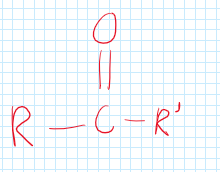
36
New cards
Incomplete Combustion
A combustion reaction where these is lack of oxygen, releasing carbon monoxide and carbon.
37
New cards
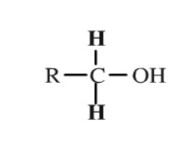
Primary Group
A functional group containing 1 hydrocarbon chain.
38
New cards
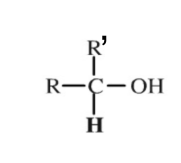
Secondary Group
A functional group containing 2 hydrocarbon chains.
39
New cards
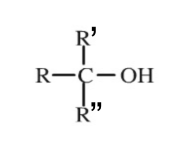
Tertiary Group
A functional group containing 3 hydrocarbon chains.
40
New cards
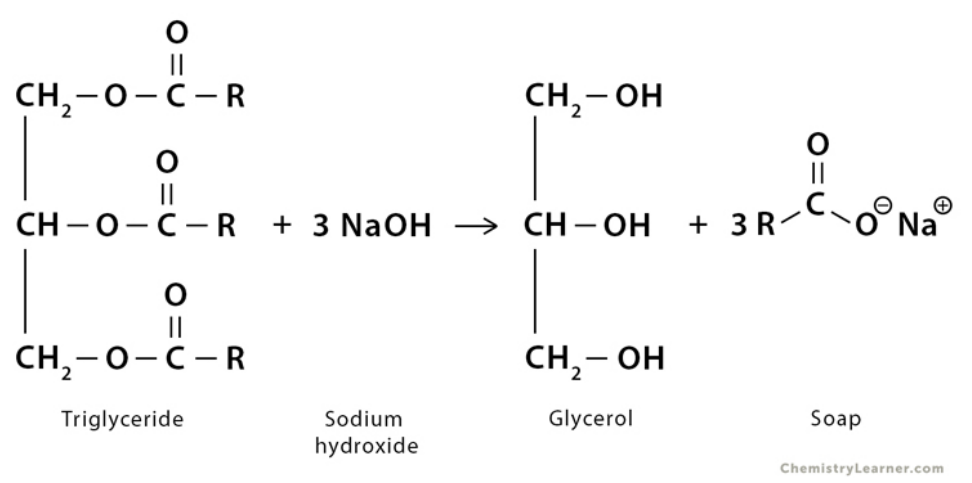
Saponification
The process of converting triglycerides into soaps and alcohols, with an aqueous alkali
41
New cards
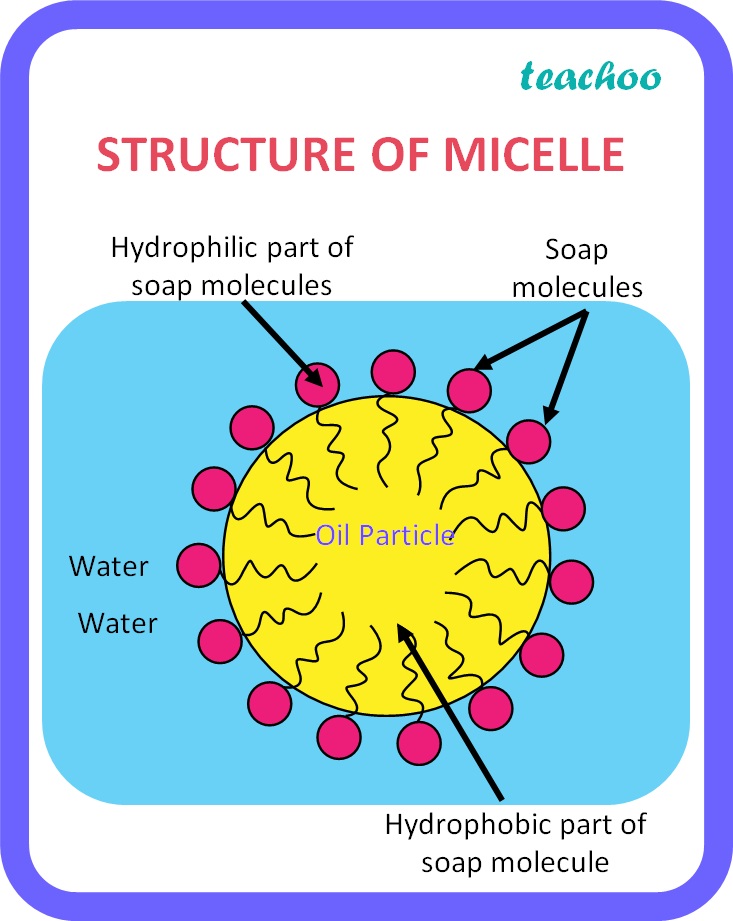
Micelle
Spherical structures containing soap anions.
42
New cards
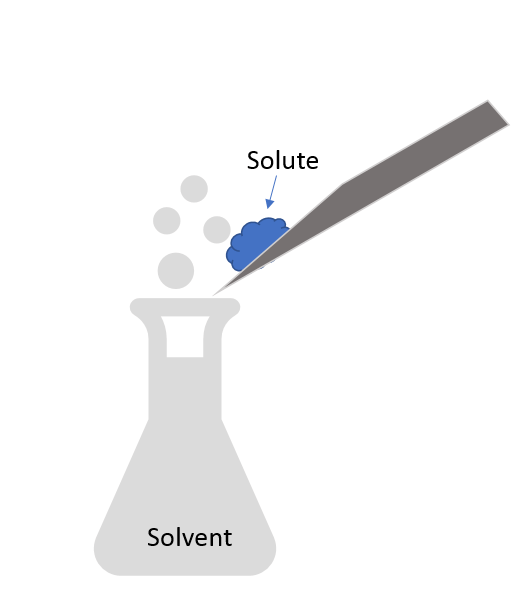
Solute
Substance that gets dissolved and is present in lesser amounts.
43
New cards
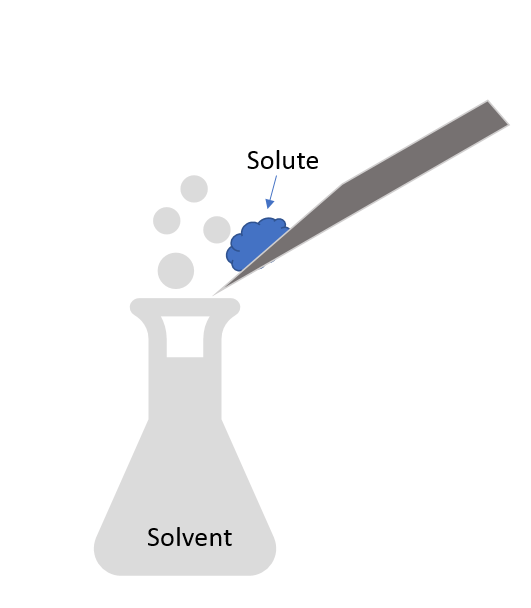
Solvent
Substance that dissolves the solute and is present in greater amounts.
44
New cards
Solubility
The ability of a solute to dissolve (become solute) in a solvent.
45
New cards
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a compound.
46
New cards
The prefix for alcohols (hydroxl) is…
\-ol
47
New cards
The prefix for carboxylic acids (carbonyl) is…
\-anoic acid
48
New cards
The prefix for amides is…
\-amide
49
New cards
The prefix for aldehydes is…
\-anal
50
New cards
The prefix for keytones is…
\-anone
51
New cards
Addition Reactions
A reaction where two or more molecules combines with another to form a larger molecule, typically of alkenes and alkynes.
52
New cards
What are the four types of addition reactions?
* Hydrogenation (with Hydrogens)
* Halogenation (with Halogens)
* Hydrogenation (with Hydroxide)
* Halohydrogenation (with both Halogens and Hydrogens)
* Halogenation (with Halogens)
* Hydrogenation (with Hydroxide)
* Halohydrogenation (with both Halogens and Hydrogens)
53
New cards
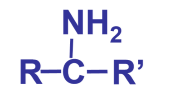
The prefix for amines is…
\-amine
54
New cards
What is the complete combustion reaction equation?
Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O
55
New cards
What is the incomplete combustion reaction equation?
Fuel + O2 → C + H2O or Fuel + O2 → CO + H2O