YEAR 1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT PART 1
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT PART 1
What is marketing?
The activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
What’s one of the key roles of marketing?
To bring customers viewpoint into the organisation
What 2 things underline marketing strategies the most?
Customer acquisition and/or customer retention
What are the 3 marketing environments?
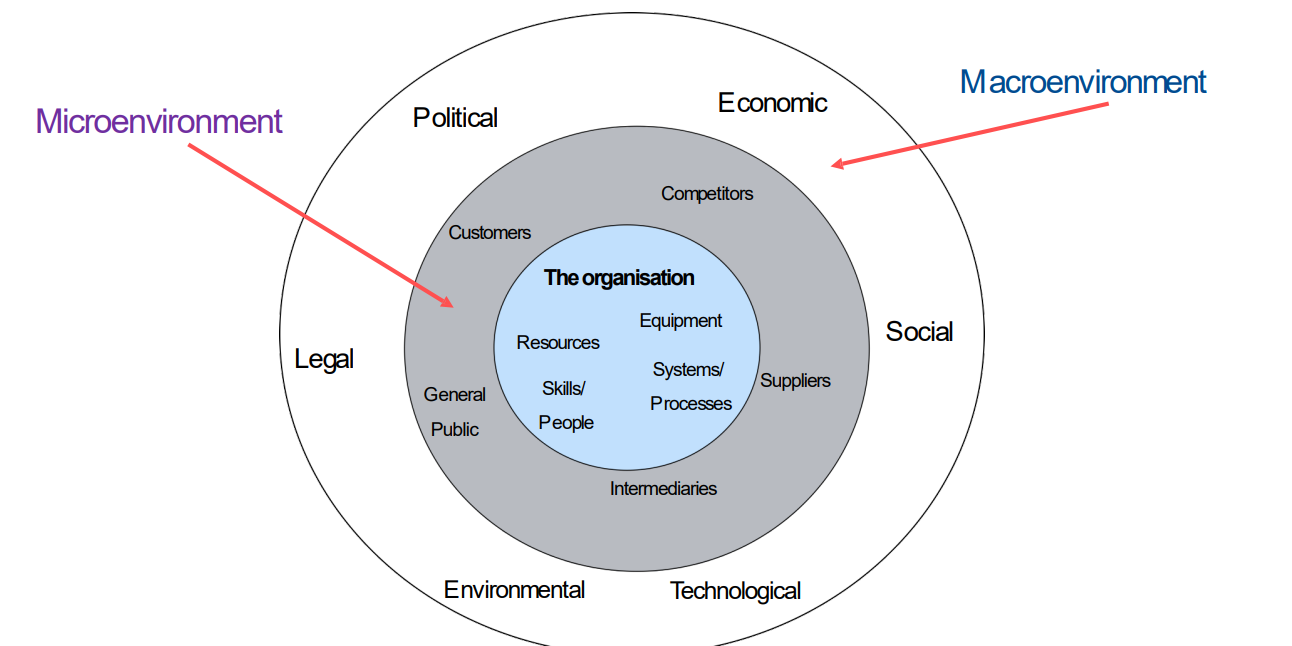
3 marketing environments - which ones have
Uncontrollable variables
Controllable variables
Uncontrollable variables = macro + micro
Controllable variables = internal organisation
What are 4 examples of macroeconomic influences?
Taxation
Government spending
Interest rates
International trading blocs/tarriffs?
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Political
Government policies
Gov contracts/finances
Regulations/deregulations
Factors that impact trade, e.g. sanctions, state relationships
Also politicians have power > can affect business activities > some try to get close (e.g. for lobbying)
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Economic
Effect through demand and supply
> Economic cycle - boom (expansion in demand) but recession (decline in sales as less discretionary expenditure spending)
> Factors - monitor unemployment levels, interest rates, gov spending, taxation, economic cycles, etc.
> Consumers - income, spending patterns, saving/investment patterns
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Social
Religion & beliefs
Lifestyle levels of education
Change in population
Social attitudes
Changing cultural norms of society
Age structure (baby boomers, gen x, millennials (gen y), gen z, etc.
Demographic - study of human population in terms of size, location, age, race, occupation, etc.
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Technological
Internet developments - affected communications, digital marketing
Mobile tech - phones, AI
Online marketing - social networks, change in consumer tech use so marketers have to adapt as well (IF DONT KEEP UP RISK FAILURE)
RFID - track products & consumers
Role of tech - administration, communications, development, distribution, customer research/support
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Environmental
Natural environment (earthquakes) & ecological factors (climate change, scarce resources)
Trends in sustainability
'Green consumerism’ - regulations, organic farming, etc.
Describe the different stages in PESTLE analysis (macro variables):
Legal
Local & regional - laws from court
Industry level - regulations specific to an industry, e.g. banking, financial services, or general (employment law)
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT PART 2
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT PART 2
Microeconomic environment:
The company
Different departments taken into account:
Accounting
R&D
Finance
operations
Microeconomic environment:
Suppliers - what is supplier relationship management?
Process of planning & managing relationships with vendors that supply any products/services to the business (e.g. raw materials, etc.)
Microeconomic environment:
Intermediaries
Firms that help the company promote & distribute product, e.g:
Real estate agents
Investment bankers
Grocery stores
Microeconomic environment:
Competitors
Important because:
Competition drives improvement
Stimulates firms to lower their own costs & run business as efficient as possible
Also remember other 2
General public & customers
What is the marketing mix (marketing activities)?
Tactics that are used to satisfy customer needs & position offerings clearly in mind of consumer
What are the 7p’s of the marketing mix?
Price
Place
Promotion
Product
(helps meet the challenges of marketing services)
People
Process
Physical evidence (shows quality of experience)
BUYER BEHAVIOUR - CONSUMER
BUYER BEHAVIOUR - CONSUMER
What is the model of buyer behaviour?

What are the 5 characteristics that affect consumer behaviour?
CSPSP
Cultural
Social
Personal
Situational
Psychological
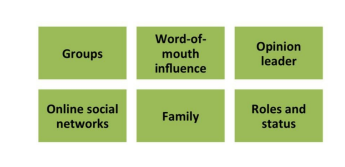
Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour - SOCIAL:
What are 6 social factors?
What are different groups that can affect behaviour?
Membership groups (groups with direct influence) - family/friends
Aspirational groups (group individual wishes to belong to)
Reference group (groups that form a comparison)
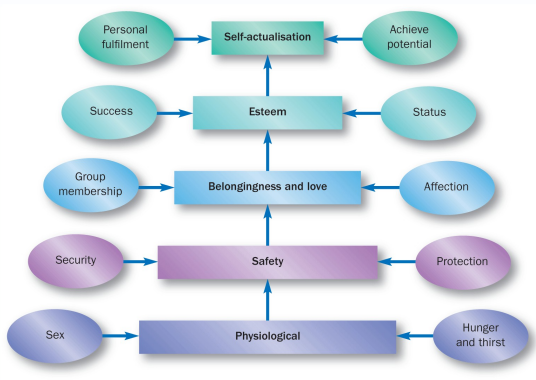
Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour - PSYCHOLOGICAL:
What is the self-concept theory?
What is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Self concept theory = theory that people often engage in behaviours that are aimed at maintaining/increasing positivity of one’s self concept
3 things:
Motivation
Belief
Attitudes
Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour - PSYCHOLOGICAL:
What is the self-determination theory?
3 basic psychological needs:
Autonomy
Competence
Relatedness
All 3 are essential for continued personal growth & wellbeing
What are the 4 broad types of buying behaviour?
***worth noting****
HDCV
Complex buying behaviour
Dissonance reducing buying behaviour
Habitual buying behaviour
Variety seeking buying behaviour
What is complex buying behaviour?
Requires high involvement
E.g. might be expensive, a big purchase, or risky
Buyers learn as they go > get others opinions, develop beliefs/attitudes to make informed choices
What is dissonance reducing buying behaviour?
Requires high involvement BUT consumers see less difference among brands
E.g. may still be expensive but hard to pinpoint between brands at a certain point (e.g. carpets)
Afterwards may feel post purchase dissonance - where they see other options OR people say something about their purchase > OFTEN RETURN THINGS
(as a marketer need to have sale care to persuade them they have made right decision)
What is habitual buying behaviour?
Requires low involvement + little difference in brands
E.g. tends to be low cost, frequently bought items like groceries
Don’t tend to search for information about brand/weight decisions
Don’t tend to regret decision (as not highly involved)
(as a marketer need to promote price/sales promotion more than product to promote brand overall)
What is variety seeking buying behaviour?
Requires low involvement BUT significant perceived brand differences
E.g. McDonalds & Burger King
Market leaders encourage habitual behaviour to limit variety seeking behaviour but challenger firms encourage this to try and win customers
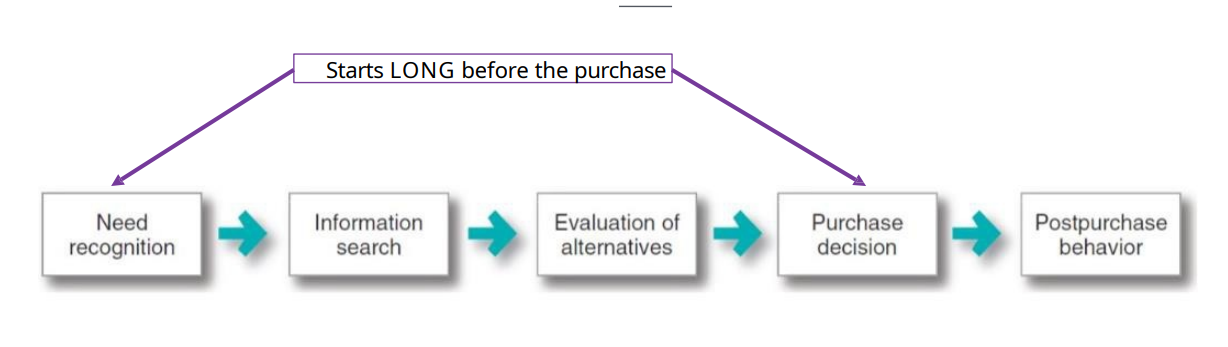
What are the steps to the decision making process?
BUYER BEHAVIOUR - B2B (BUSINESS TO BUSINESS)
BUYER BEHAVIOUR - B2B (BUSINESS TO BUSINESS)
What is B2B marketing and who are the customers?
Study of the processes involved when businesses purchase, use or dispose of products/ideas to satisfy their needs
Customers:
Commercial enterprises
Governmental bodies
Institutions
What are the 4 steps to the buyer decision-making process (Hill and Hiller)?
PPSP
Precipitation - internal & external triggers (realisation there is a need)
Product specification - importance of precisely specifying what is needed
Supplier selection - supplier search, established vs new suppliers, existing relationships, nature of purchase, etc.
Commitment - importance of monitoring & relationship building
What are the similarities between B2B and B2C buying processes?
(2)
Both buying processes built upon trust
Both are complex processes (take time)
What are the differences between B2B and B2C buying processes?
(4)
B2B customers proactively identify needs to meet their business strategy (whereas B2C customers are often swayed by advertisement/marketing so may not always be a ‘need’ but a ‘want’)
B2B buy products that meet certain specifications (more strategic, less emotional) - B2C more emotionally driven so more flexible
B2B buying process longer than B2C
B2B customers care about post-sales service - B2C only want care for after sale if they are experiencing a problem
What is B2B social media?
Corporate social media
MARKET SEGMENTATION
MARKET SEGMENTATION
What is the model that simplifies market segmentation?
(STP)
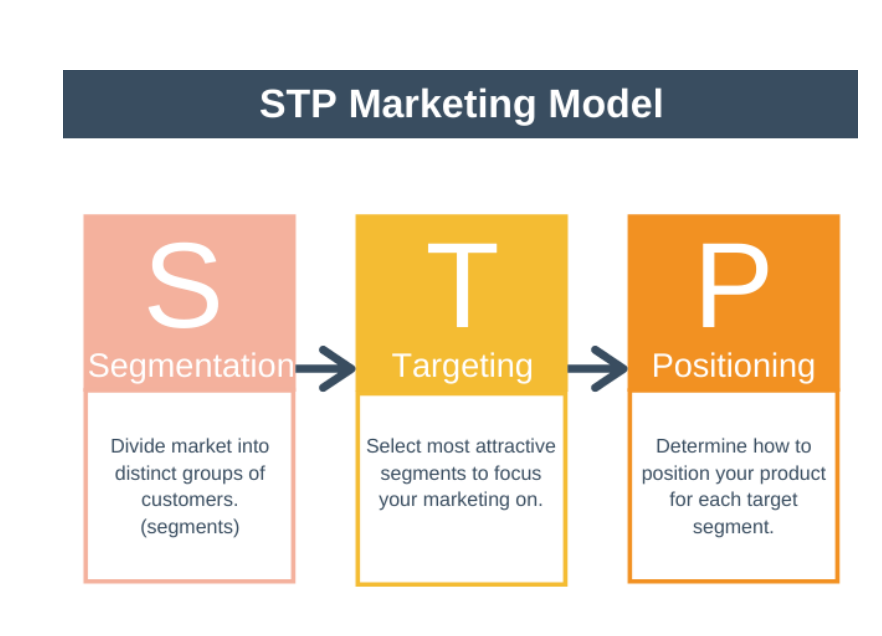
What are the 4 key ways a business can segment the market?
Geographical segmentation
Demographic segmentation (age, gender, religion, income, education, social status) *MOST POPULAR*
Psychographic segmentation (lifestyle, personality, attitudes, values) - difficult to do
Behavioural segmentation (buyer stage, usage, engagement, benefit) - best starting point especially with digital world
Demographic = statistical data
Psychographic = psychological factors (activities, opinions, interests)
How do firms geographically segment markets?
Localising their products to fit the needs of different geographical units
What is the relationship between brand loyalty and age (when market segmenting)
increasing age = increasing brand loyalty > due to being more emotionally attached to brands
What is one problem of using age to market segment?
Stereotyping
> can be a poor predictor to which stage of the lifecycle customers are at
What marketing strategy can be used to target high income customers?
High touch marketing strategies
What approach is needed to segment people psychographically?
Multi level approach
Psychographic - what is the big 5 personality trait/big five taxonomy?
The Big Five taxonomy organizes traits into the five broad domains:
extraversion (assertive v introverted)
agreeableness (kind v cruel)
conscientiousness (responsible v undependable)
emotional stability (calm v anxious)
openness to experience (creative v closedminded)
What are the 4 psychological stages to buy a product?
Awareness > Interest > Desire > Action
When using multivariable segmentation, what should market segments be like? (5)
MASDA
Measurable
Accessible
Substantial
Differentiable
Actionable
Taking away unconscious bias in segmentation is important to increase success
Taking away unconscious bias in segmentation is important to increase success
TARGETING AND POSITIONING
TARGETING AND POSITIONING
What is your ideal target segment?
(3)
Actively growing
High profitability
Low cost of acquisition
What are the 3 key targeting areas when choosing which areas to target?
Size and growth - Larger segments with more growth potential usually better (but relative to firm, e.g. luxury brands don’t)
Competitive position - if there’s lots of competitors (substitutes) or not
Objectives & resources - should only enter a segment if can gain a competitive advantage
Market targeting strategies - target market:
What are the different types
Where are they on the spectrum (broad or narrow marketing)
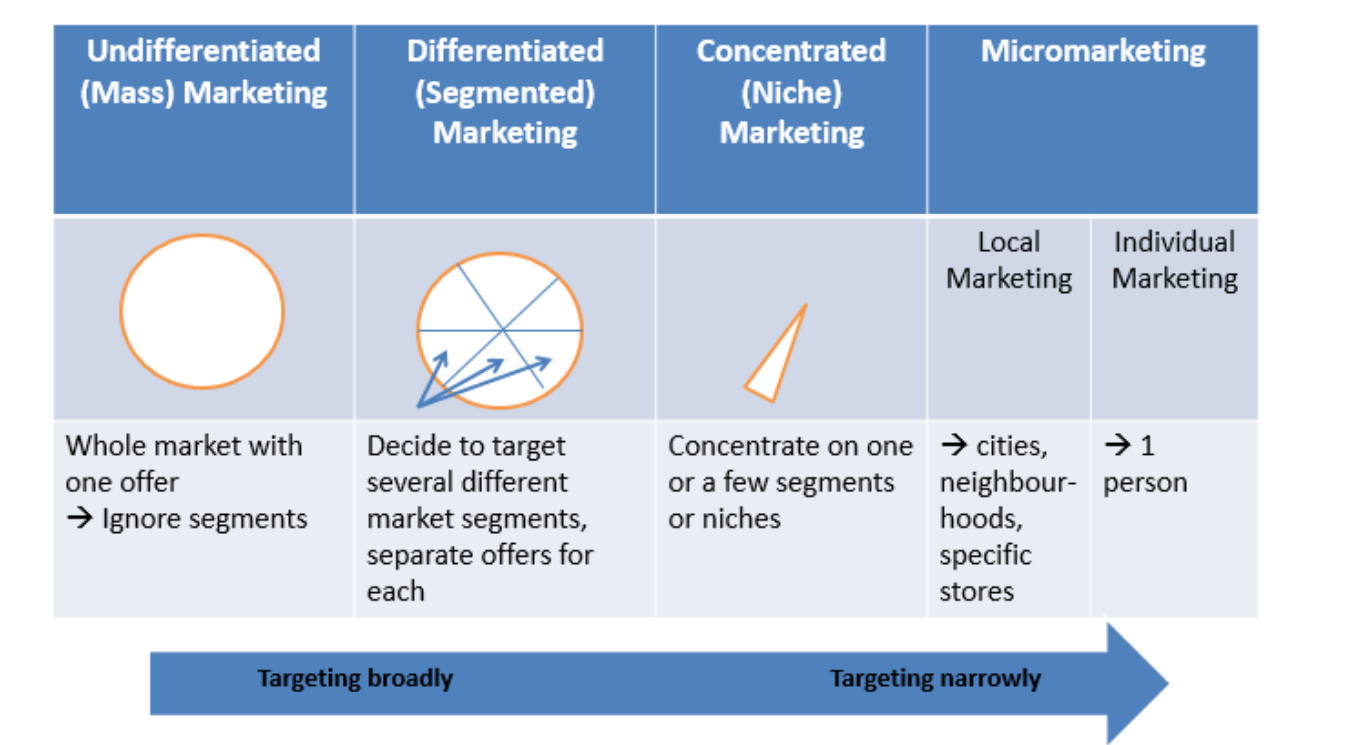
Undifferentiated (mass) marketing:
Product
Price
Promotion
Disadvantage
Product = designed for everyone - focuses on what’s common in segment (not different)
Price = single pricing structure - doesn’t consider willingness to pay of different segments
Promotion = e.g. billboards, tv adverts
Disadvantage > not strategic (can’t gain a competitive advantage over firms who segment)
Differentiated (segmented) marketing:
Product
Price
Advertising type
Product = target several markets and offer separate products for each
Price = premium prices > can boost sales & have stronger position in segment
Promotion = differentiated marketing, different pricings for ages, etc.
Disadvantage > more costly (extra market research, costs, communication, production, etc.)
Concentrated (niche) marketing:
Approach
Most focused approach > involves specialising in ONLY 1 SEGMENT (whereas differentiated marketing involved lots of different segments)
Micromarketing, describe:
Local marketing
Individual marketing
Local marketing = tailor to local people (personalised messages, etc.) but can be costly as reduces EOS
Individual marketing = extreme tailoring to 1 person, customised marketing & hyper personalisation
A retailer with a value proposition is most likely to …
Offer consumers a balanced combination of product quality at a fair price
What are different types of differentiation:
Product
Service
Channel
People
Image
Product = different features, designs, performance, quality
Service = speedy convenient service
Channel = distributing products in innovative ways that give the product added value
People = hiring & training better people than competitors
Image = strong, visible, memorable logo/image identity
Pre-emptive meaning
Competitors cannot easily copy the difference
MARKETING MIX - PRODUCT
MARKETING MIX - PRODUCT
What are the 5 different types of products?
(Kolter conceptualisation)

4 User based classification methods?
1 - Convenience products - frequently bought, minimal comparison/buying effort, immediate
2 - Shopping goods - less frequent, lots of comparison/buying effort, more risk, limited problem solving e.g. cars
3 - Speciality goods - infrequent, high risk, expensive, extensive problem solving, e.g. designer clothes
4 - Unsought goods - doesn’t know/think about often, e.g. insurance, funeral services
What is a product line?
Group of brands/products that are closely related in terms of their functions and the benefits they provide, e.g. range of Apple phones, Dell’s range of computers
What does the depth of a product line depend on?
pattern of customer requirement (e.g., number of segments),
product depth being offered by competitors
company resources
What is the product mix?
Product mix is the total set of brands marketed in a company: the sum of the product lines offered
What is the new product development (NPD)?
What are the 6 steps?
IPPDVC
NPD is the original products, improvements and new brands developed from the firm’s own R&D
Ideation
Product definition
Prototyping
Detailed design
Validation/testing
Commercialisation
What is the product life cycle?
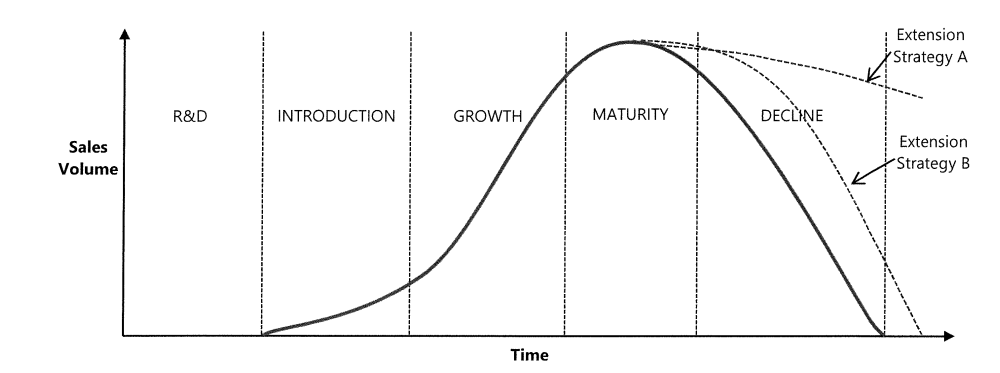
What is the diffusion theory?
Rate at which a market adopts an innovation - consumers adapt to new products at different speeds

SERVICES
SERVICES
What are the 4 features of a service?
Intangibility
Perishability - cannot be stored for future
Variability (heterogeneity) - depends upon provider (customisation)
Inseparability - can’t separate from provider + customers involved in production process
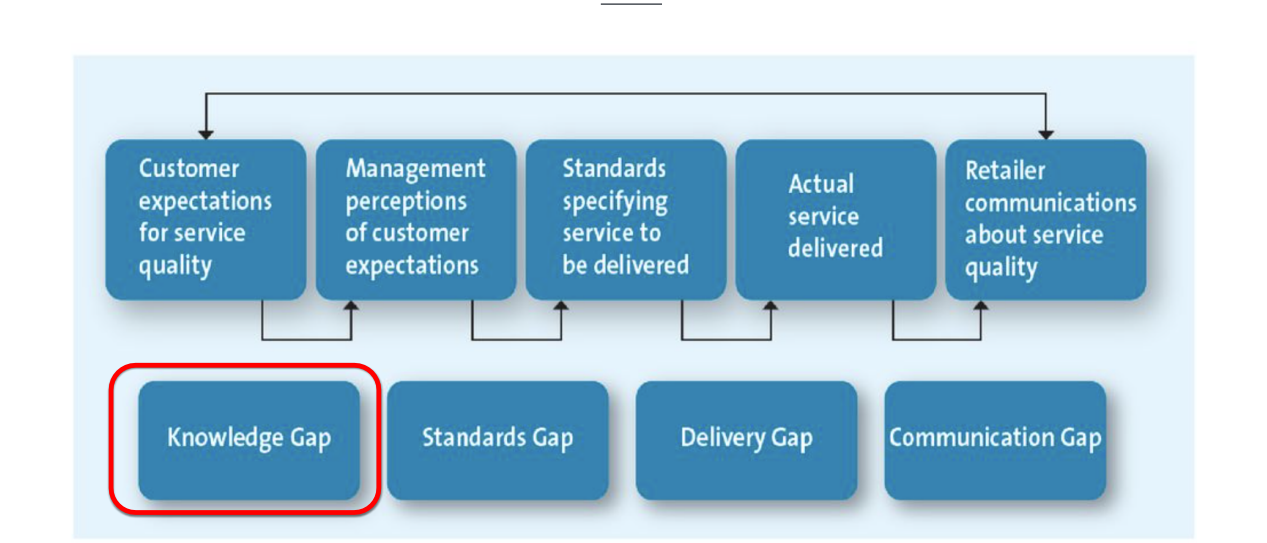
What is the gaps model?
Knowledge gap - what customers expect vs what management think customers expect
Standards gap - what management think customers expect vs actual standards
Delivery gap - experience specification vs actual results
Communication gap - delivery of experience vs what was communication to customer
PLACE
PLACE
Channel distribution - B2C
direct channel
short channel
long channel
(longest & indirect channel)
(as goes along is more indirect)
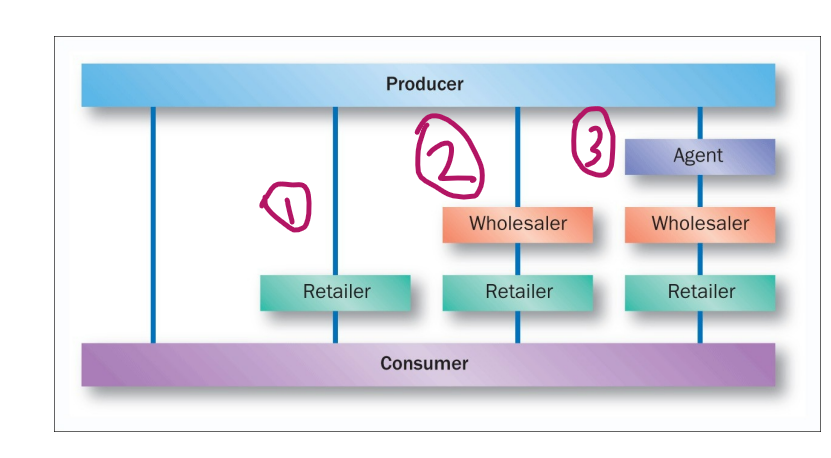
intermediary = mediator (bring 2 things together)
e.g. agents, wholesalers and retailers
intermediary = mediator (bring 2 things together)
e.g. agents, wholesalers and retailers
Why use an intermediary?
increases efficiency & reduces the cost of individual transactions
Categories of adding value by using an intermediary? (3)
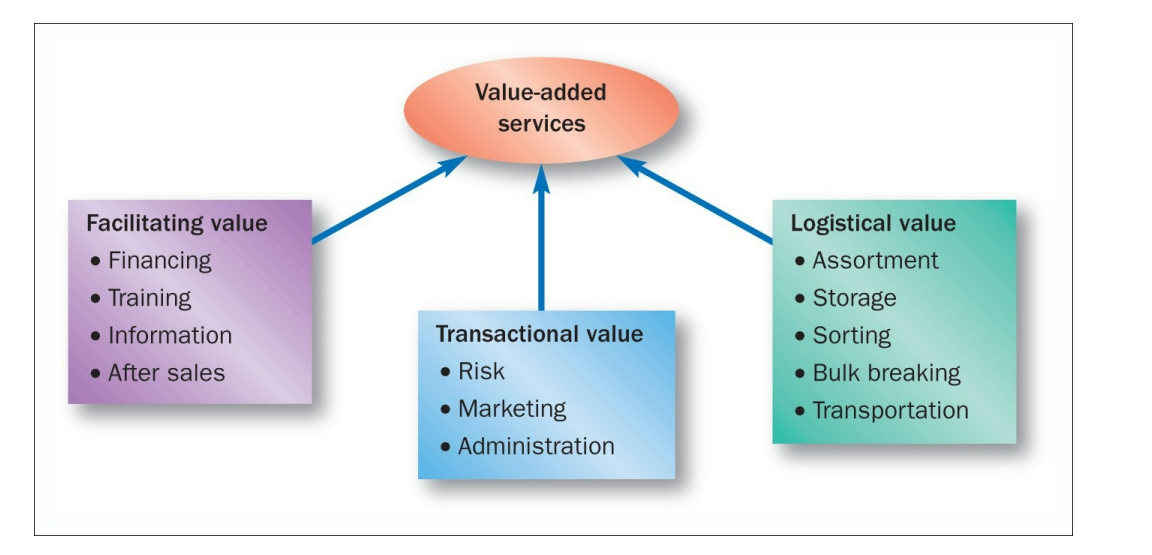
What are the 4 key elements of consistency?
access, search, possession, transaction
PROMOTION
PROMOTION
Intergrated maketing communication is..?
The management process of integrating all marketing communications activities across relevant audience points to achieve greater brand coherence