HTHSCI 2H03 - potency, efficacy and the therapeutic index
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is pharmacokinetics
Study of drug movement through the body - what the body does to the drug
What is pharmacodynamics
Study of how the drug changes the body - what the drug does to the body
- relationship b/w plasma drug concentrations and therapeutic response
- mechanisms of action of drugs
T/F Pharmacokinetic processes impact pharmacodynamics
True
Quantal effects - frequency distribution curve
Measure a specific, yes/no response to a specific dose
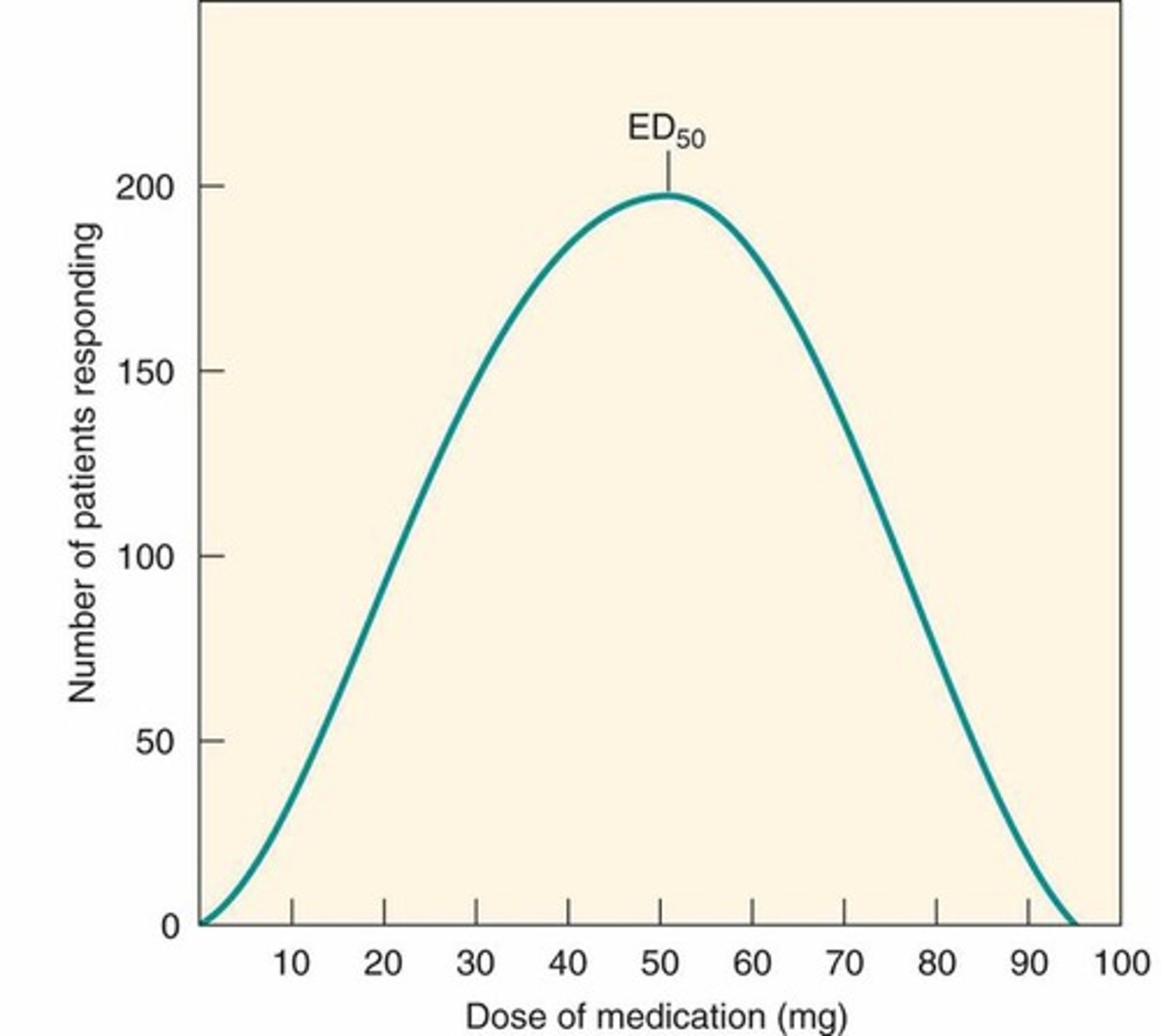
ED50 (median effective dose)
- Dose required to produce a specific therapeutic response in 50% of patients
- Often referred to as the standard dose

Therapeutic Index
- Ratio of a drug's LD50 (or TD50) to its ED50
- Median Lethal Dose (LD50)
-> Dose of drug that will be lethal in 50% test animals
- Median Toxic Dose (TD50)
-> Dose that will produce a given toxicity in 50% of patients
- Drugs with a narrow therapeutic index are considered high alert medications
Therapeutic window
Range based on the minimum effective therapeutic concentration and the minimum toxic concentration for a specific toxic effect
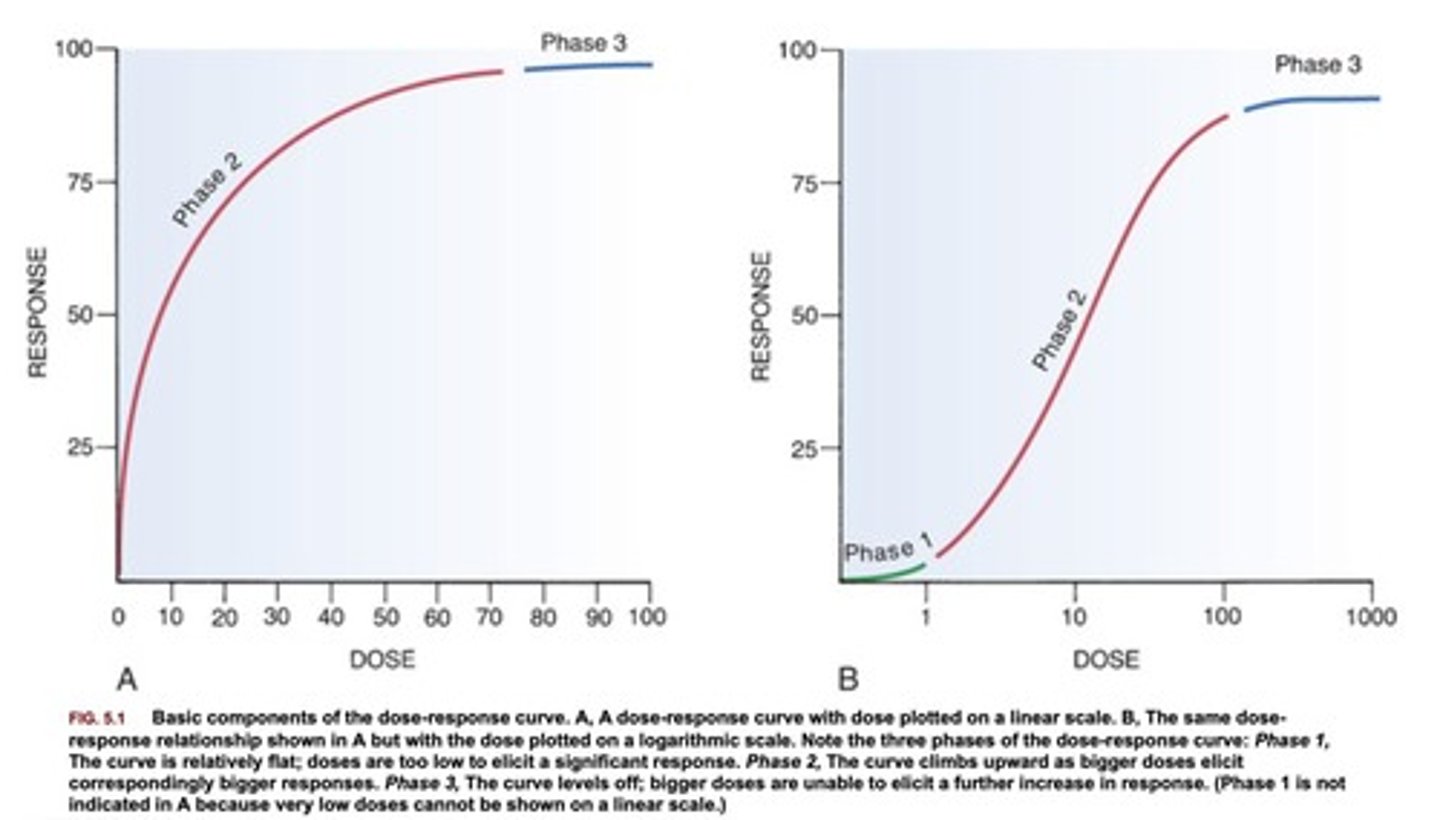
Graded effects: Dose response curves and what is it used to determine
- Demonstrates the magnitude of biological response to a drug
- Obtained by observing and measuring patient responses at different doses of drug
Used to determine
- Therapeutic range of a drug
- Efficacy of a drug
- Potency of a drug
What are the phases of the dose-response curve?
1 - few target cells being affected by the drug
2 - linear relationship between amount of drug administered and degree of client response
3 - plateau, increasing dose has no therapeutic effect. may produce adverse effects
look only on second chart
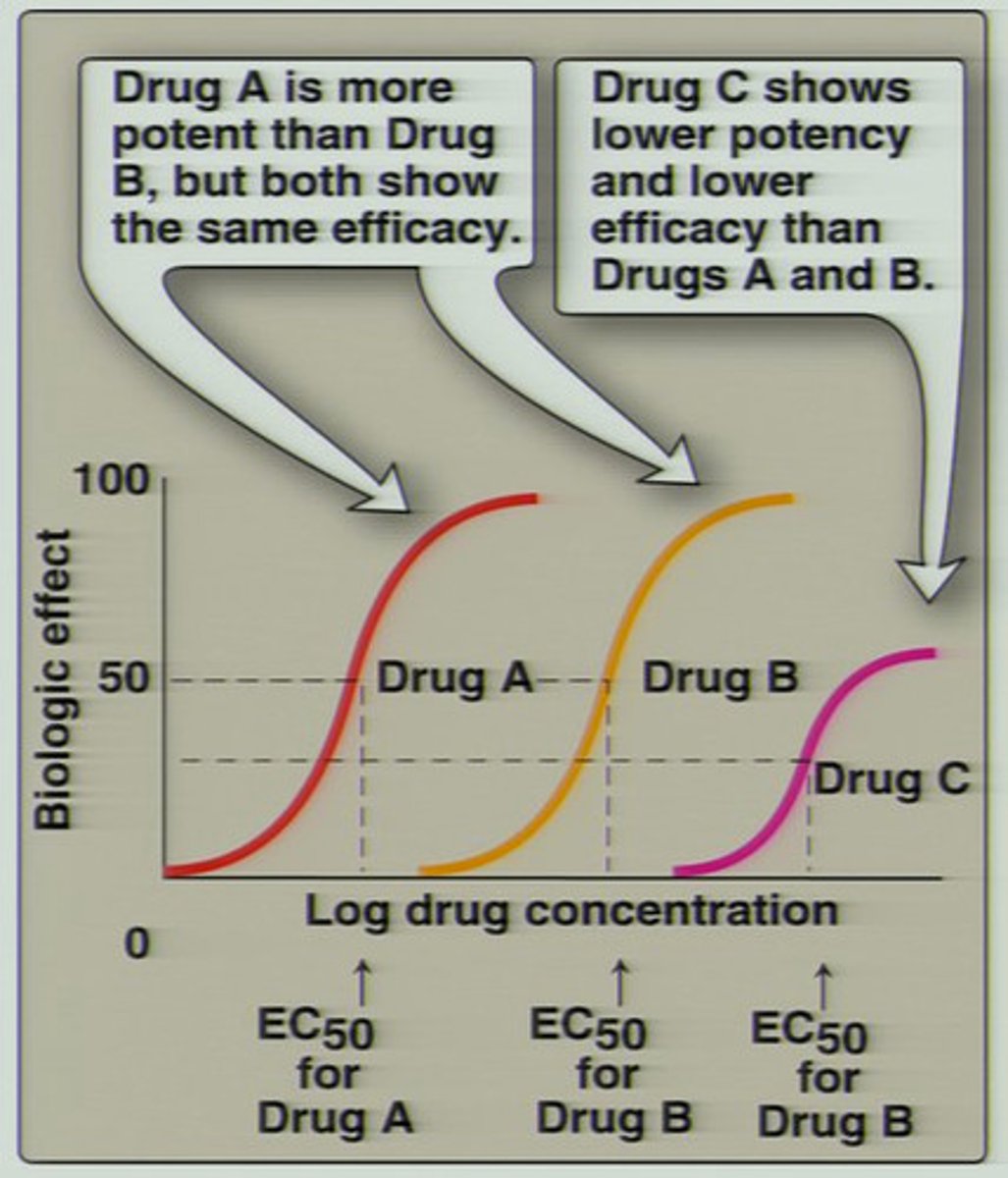
Potency
Compares the doses of two or more drugs with respect to how much drug is needed to produce a specific response
- usually based on the median effective dose or median effective concentration (ED50/EC50)
- If a drug is highly potent, it will not take much drug to produce a therapeutic response
- Potent drugs typically have a high affinity for the receptor binding site
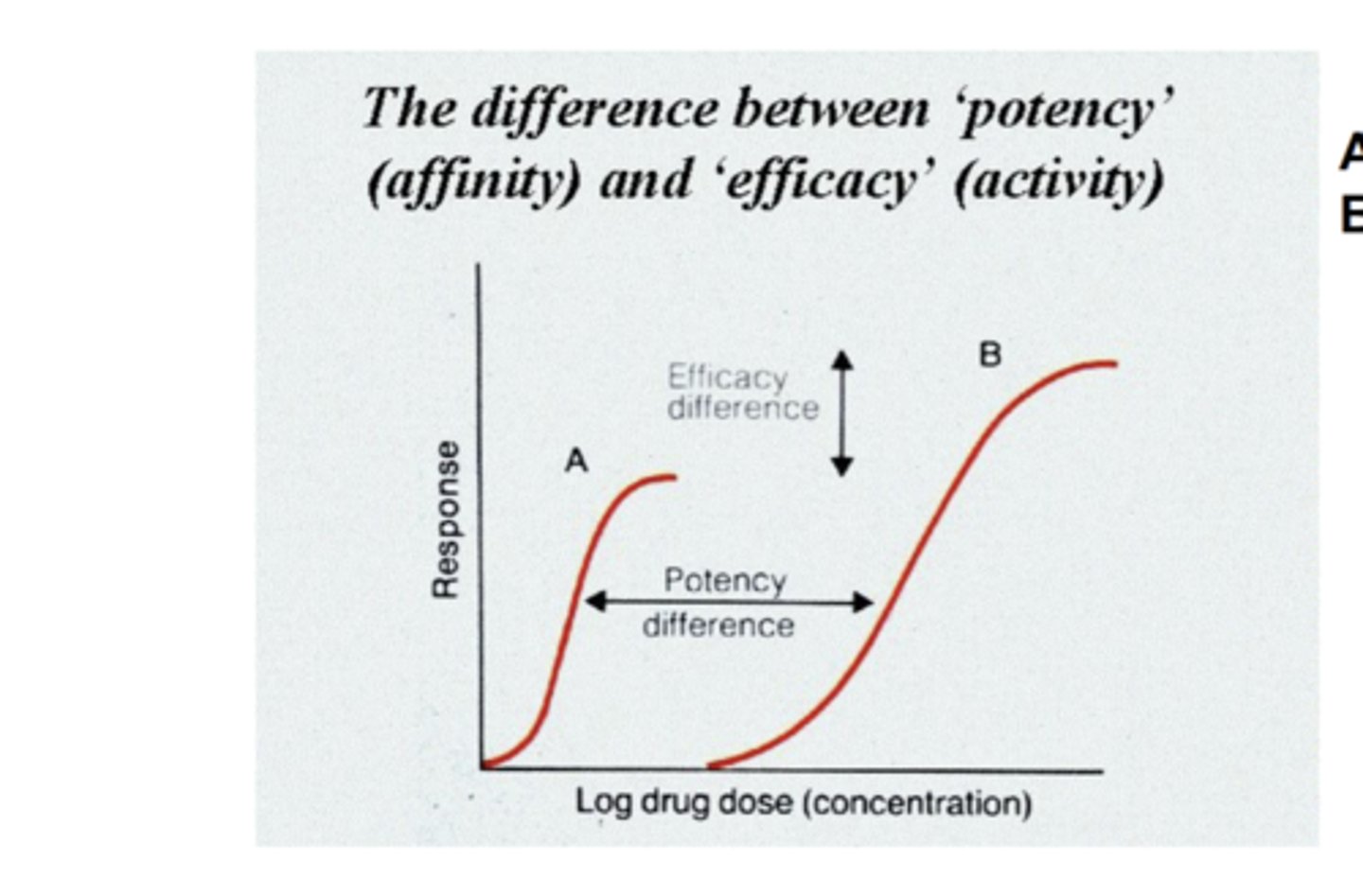
Efficacy vs potency on graph
Association vs dissociation
Association
- Drug binds to the receptor
- Rate of drug-receptor complex formation (k1)
Dissociation
- Drug dissociates from receptor
- Rate of drug-receptor complex dissociation (k-1)
High vs low affinity
high affinity
- drug rapidly binds to the receptor and then slowly dissociates
low affinity:
- The drug quickly dissociates from the receptor
- k1 is slow and k-1 is fast
You are treating a patient for hypertension. you have a choice between 2 equally effective antihypertensive medications. drug a has a higher therapeutic index than drug b. which drug do you choose?
a) drug a because its safer
b) drug b because its safer
c) makes no difference
Drug A
- drugs with a higher therapeutic index are safer - the magnitude between a therapeutic dose and a toxic dose is larger. room for error and individual differences (pharmacokinetics) is greater