partial pressures and mechanisms of ventilations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what are the functions of the lung
allow exchange of oxygen between inspired air and blood
help regulate acid base balance
play a role in metabolism of substances
allow elimination of co2
what is the atmospheric pressure or PB
760 mmhg
how does gas move from alveolus to blood
diffusion
what method of gas movement is independent of composition of gas
bulk flow
what method of gas movement is dependent on composition of gas
diffusion
what is the normal PAO2
105 mmhg
why is PAO2 105 mmhg when oxygen is 21% of the barometric pressure
because of water vapor and left over co2 already present in the alveolus
what is a normal PaO2
80-100 mmhg
what would cause an increase in PAO2
decreased metabolic rate
When metabolic rate is decreased less oxygen is utilized meaning less needs to be taken from the alveolus and given to the blood which _______ PAO2
increases
what would increase PACO2
decreases alveolar ventilation
increased metabolism
decreased cardiac output
at rest a dogs interpleural pressure is usually ________
negative
the negative interpleural pressure prevents the alveolus from expanding, but to prevent it from collapsing the transpulmonary pressure exerted is equal and ________ to the interpleural pressure
opposite
Transpulmonary pressure is equal to what
PA- PIP
as you breathe in your thoracic volume increases which leads you intrapleural pressure to _________
decrease
Once intrapleural pressure decreases what increases
Transpulmonary pressure
transpulmonary pressure and _______ are positively corelated
volume
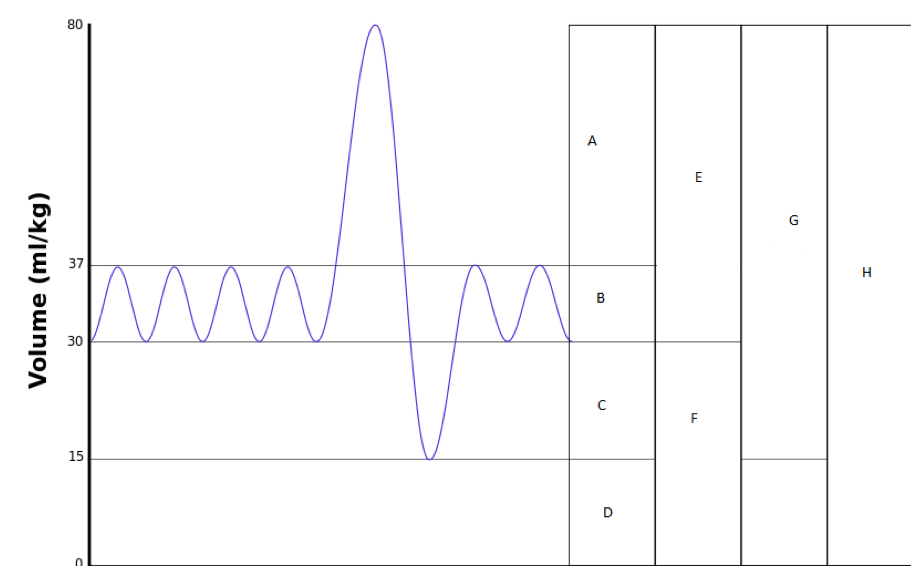
label the graph of lung volumes
a. inspiratory reserve volume
b. tidal volume
c. expiratory reserve volume
d. residual volume
e. inspiratory capacity
f. functional residual capacity
g. vital capacity
h. total lung capacity
the amount of air that enters and exits the lung on a normal breath would be called the _______
Tidal volume(VT)
the maximum amount of extra air you can inhale after a normal breath is called what
inspiratory reserve volume
the maximum amount of extra air you can exhale after a normal breath out is called what
expiratory reserve volume
the air left over in the lung after breathing out all possible is called the what
residual volume
air left in the lungs after a normal breath out is called the what
functional residual capacity
the max amount of air a person can inhale is called the
inspiratory capacity
the maximum a person can exhale after an maximum inhalation is called the what
vital capacity