Physiological optics
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Principles of optics applied to the diagnosis and management of refractive errors in orthoptics..
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the refractive power of the cornea?
~+40D - this makes up around 2/3 of the total refractive power of the eye.
True or false - the total refractive power of the eye is approximately +60D?
True. This includes contributions from both the cornea (+40D) and the lens (+20D).
What are the three factors which affect the eye’s refractive ability?
Corneal power, lens power, and axial length. A more curved surface has a higher dioptric power.
Emmetropia
A state wherein the power of lens and cornea match the axial length, meaning there is no refractive error. Light is focussed directly onto the retina.
Ametropia
A state of refractive error caused by a mismatch between the eye’s refractive power and its axial length. This causes a blur circle to be projected onto the retina.
True or false - presbyopia is a type of refractive error.
False - presbyopia is not a true refractive error, but instead a natural part of the aging process wherein the lens gradually loses its ability to adjust its power to near objects.
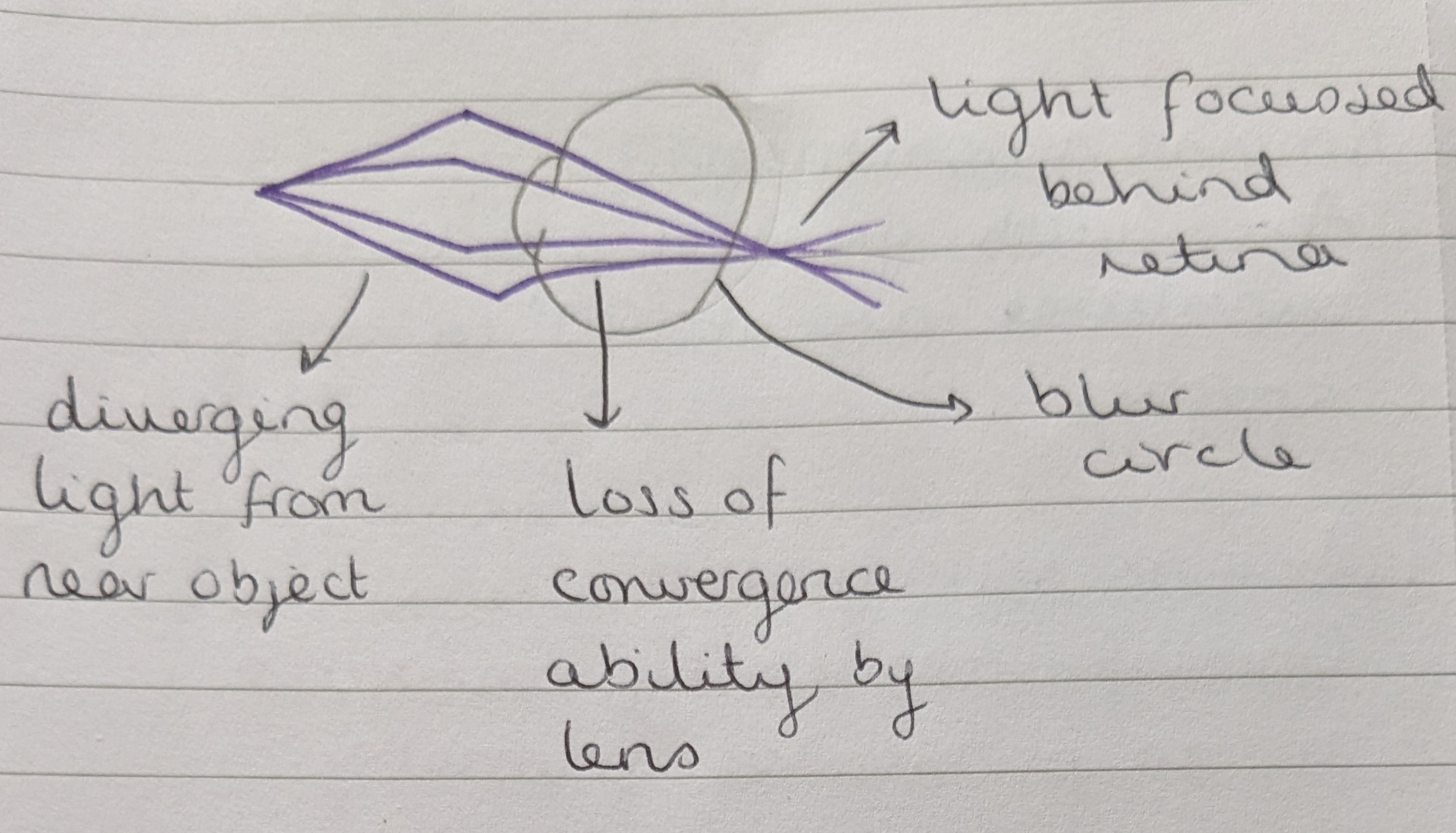
What is the difference between refractive myopia and axial myopia?
Refractive myopia refers to the eye being too long, causing the image to be formed in front of the retina.
Axial myopia refers to either the lens or the cornea being too powerful.
In myopia, near vision is clear while distance vision is blurred.
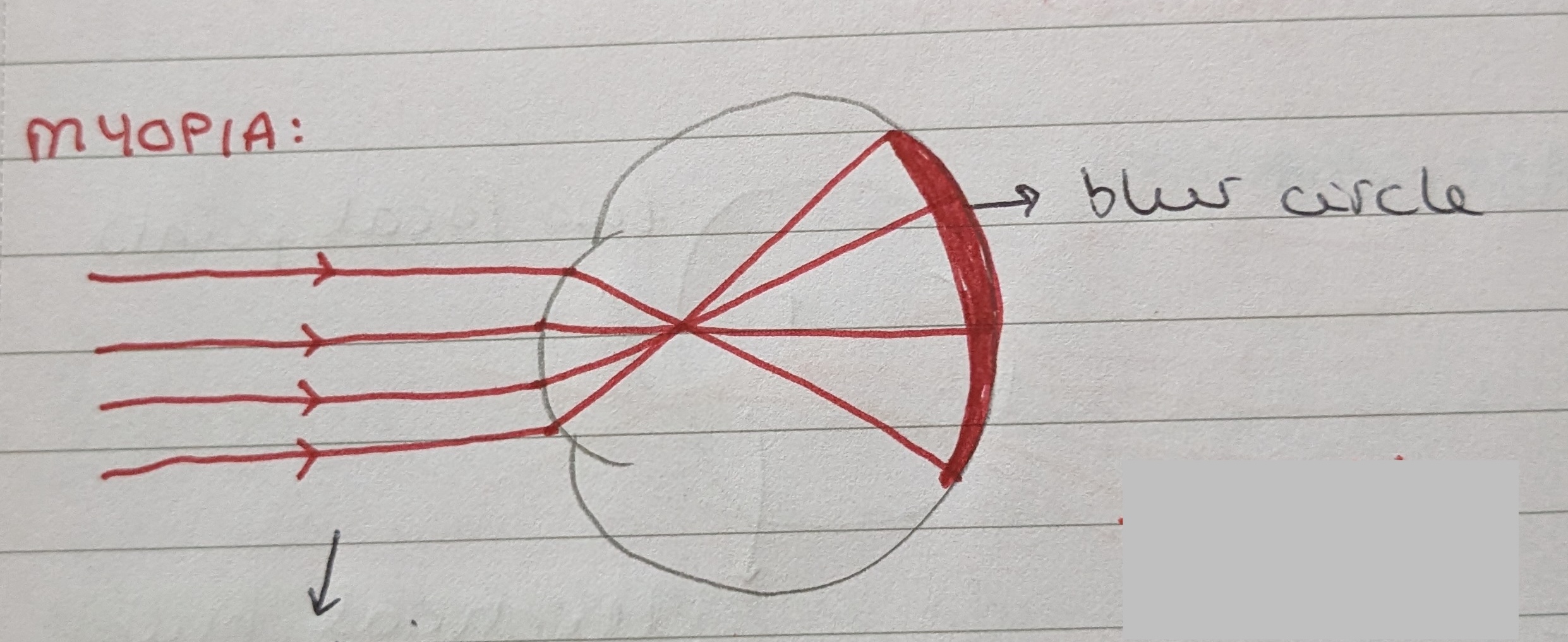
What type of lens is used to correct myopia?
A concave, negative, or diverging lens, which pushes the image back onto the retina.
What type of squint patient would you not want to be myopic?
A patient with intermittent exotropia, as the diverging lens will exacerbate their deviation even further.
In what type of squint patient would you expect a myopic prescription to correct their deviation?
A patient with a fully accommodative esotropia, as their glasses prescription will relax their accommodation and thus reduce accommodative convergence.
True or false - axial hypermetropia is caused by the eye being too long.
False, axial hypermetropia is caused by the eye being too short.
What are the two types of hypermetropia?
Axial hypermetropia, which is caused by the eye being too short.
Refractive hypermetropia, which is caused by either the cornea or the lens being too flat or too weak.
This results in the image being formed behind the retina.
In hypermetropia, distance vision is clear while near vision is blurred.
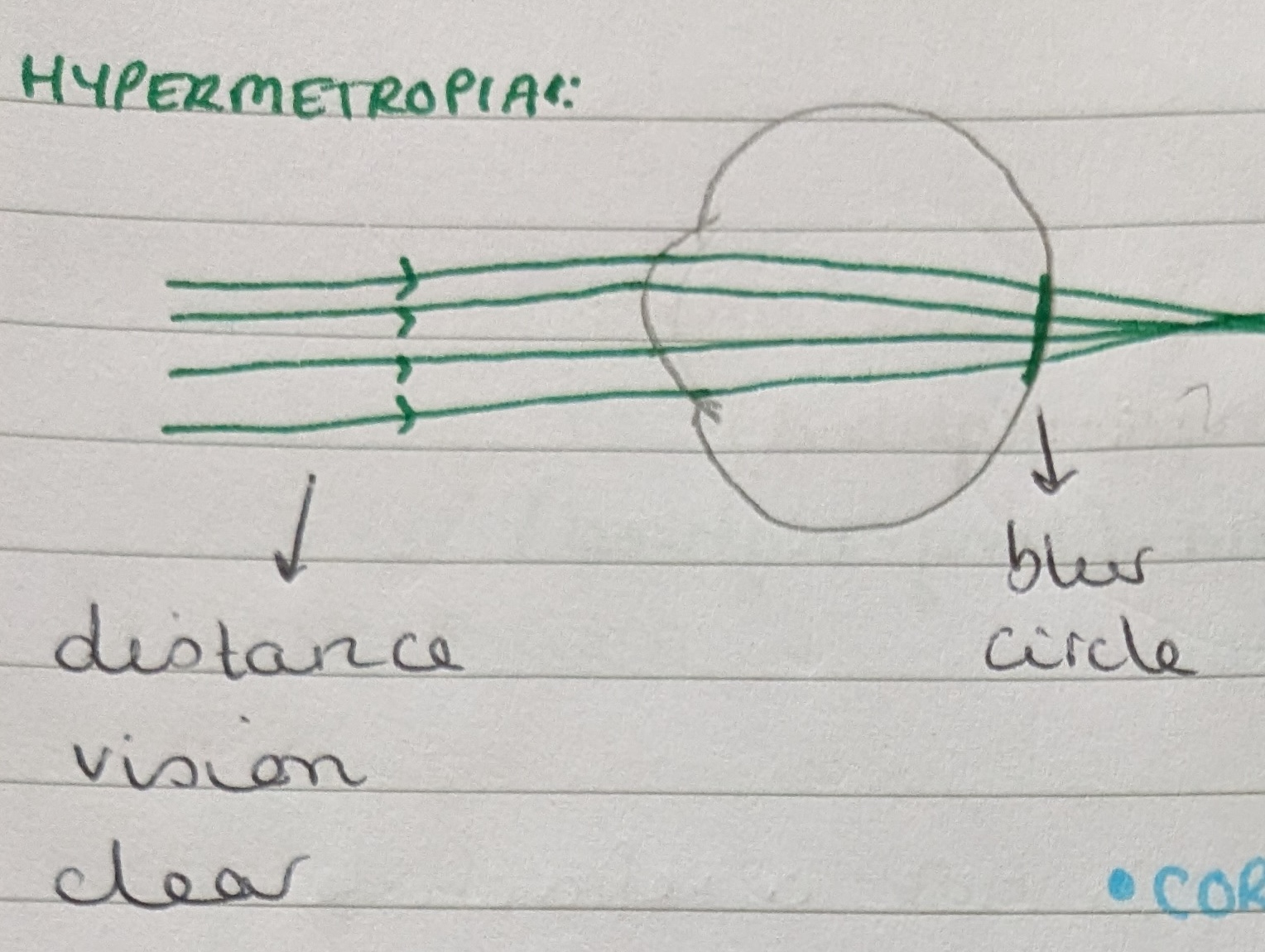
What type of lens is used to correct hypermetropia?
A convex, converging, or positive lens as this converges the light and allows it to fall onto the retina.
What type of squint patient would you not want to also be hypermetropic?
A patient with esotropia, as the increased accommodation caused by a plus lens prescription will exacerbate their deviation.
What type of squint patient could benefit from a hypermetropic prescription?
A patient with exotropia, as they may improve their alignment with the use of plus lenses.
Why can young children with hypermetropia often cope without a prescription?
Because young children have a much higher lens power capacity than adults, and so they have more ability to converge distance objects appropriately onto the retina using their accommodative effort. However, this may result in asthenopic symptoms as they age.
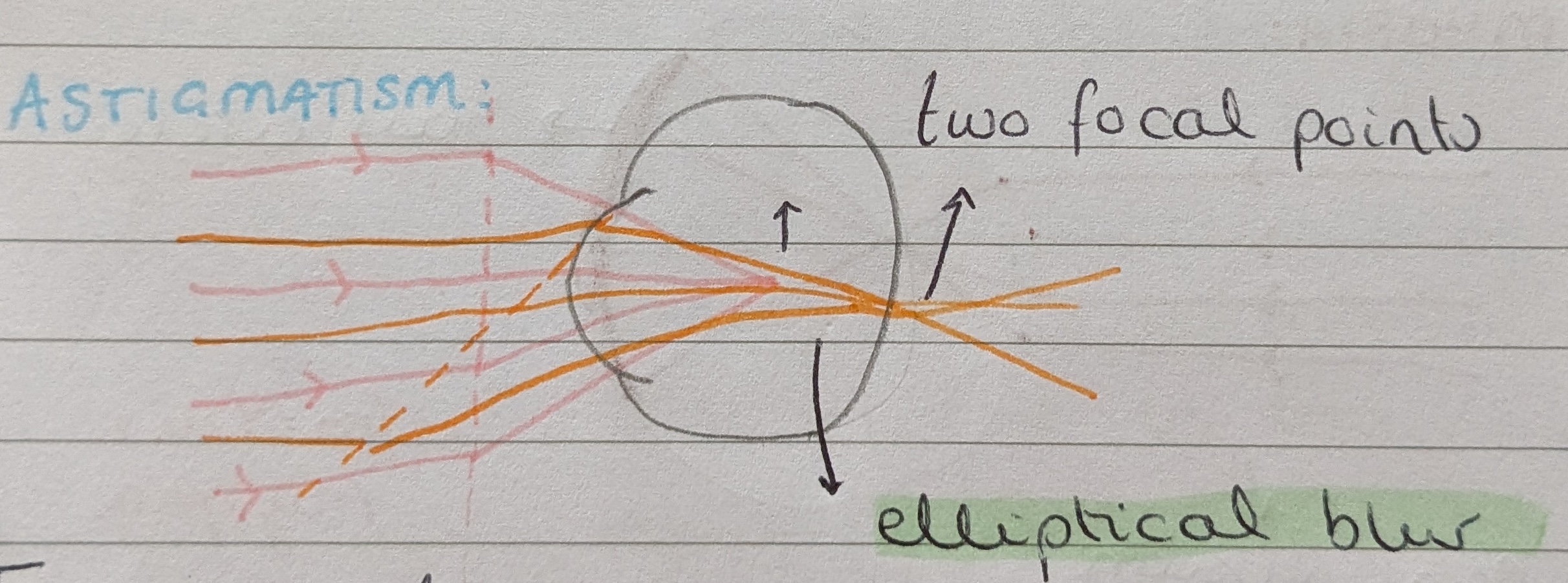
What is astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error caused by the cornea and lens having different curvatures in different meridians. This results in the image forming two focal points, creating an elliptical blur on the retina. The patient may complain of a characteristic stretched distortion to their vision, especially when looking at lights.
In regular astigmatism, these curvatures are at 90o to each other and can be corrected with lenses.
In irregular astigmatism, the curvatures do not conform to any particular geometry and so cannot be corrected with lenses. This is seen in keratoconus.
What type of lens is used to correct astigmatism?
Cylindrical lenses can be used to correct astigmatism. They compensate for the uneven curvature of the cornea or lens, allowing for clear vision. Toric lenses can also be used for astigmatism correction, as they are designed with different powers in different meridians.
Other than glasses, what methods can be used to correct refractive errors?
Contact lenses
Laser refractive surgery
Clear lens extraction
What are the risks associated with contact lens wear?
Risks associated with contact lens wear include eye infections, corneal abrasions, and allergic reactions. They also reduce oxygen supply to the cornea and may lead to dry eye symptoms. Other negative aspects of contact lens wear are the difficulty of use, ongoing cost, and environmental impacts.
When might contact lenses be indicated?
Contact lenses may be indicated for patients with refractive errors who prefer not to wear glasses, or those who require corrective lenses for active lifestyles. They may also be used in babies who have undergone cataract surgery and are aphakic, although this carries an infection risk.
Contact lenses do not cause image magnification or minification, so they may be suitable for patients with significant anisometropia or antimetropia.
How is laser eye surgery performed?
The corneal epithelium and Bowman’s layer are lifted to create a flap, and the laser is then applied to the stroma to change its curvature. The flap is then replaced. This procedure reshapes the cornea to correct vision.
What are the risks associated with laser eye surgery?
This procedure carries a risk of diplopia, glare, dry eye, and loss of binocular vision if only one eye is treated.
True or false - laser eye surgery can be used to correct amblyopia.
False, as amblyopia treatment involves addressing the underlying visual deficiencies rather than reshaping the cornea. Prisms will be required to treat amblyopia even in patients who have undergone laser eye surgery to correct a refractive error.
Anisometropia
A difference in the refractive error between the two eyes.
Antimetropia
A condition wherein one eye is myopic and the other eye is hypermetropic.
True or false - anisometropia and antimetropia carry a risk of amblyopia development in children.
True, these conditions can lead to amblyopia if left untreated. This is because they lead to images of different sizes being formed on the retina, which prevents fusion and leads to the brain ignoring the image being received from the weaker eye.
How can you measure refractive error?
Using the formula F = 1/f where F is the refractive error in diopters and f is the focal length in meters.
For example, if the patient has clear vision to a distance of 50cm, they have a refractive error of +2.00 diopters.
What is the refractive error? The patient is young, with clear distance vision but difficulty at near.
The patient likely has hypermetropia, as this condition results in blurred vision at near. They may be able to overcome their hypermetropia through accommodative effort, though the presence of symptoms indicates that a prescription would likely be helpful.
What is the refractive error? The patient is older, has clear distance vision but difficulty at near.
The patient likely has presbyopia, a condition associated with aging that causes a gradual loss of the eye's ability to focus on nearby objects, typically due to a decrease in the elasticity of the lens. This patient could be effectively treated using plus lenses for reading or varifocal glasses.
What is the refractive error? The patient is young, has difficulty with their distance vision, but clear vision at near to a distance of 50cm.
The patient likely has myopia (-2.00D), which causes blurred vision at distance while maintaining clarity for near objects. This condition can be treated with minus lenses.
F = 1/0.5 = -2.00D
What is the refractive error? The patient is young, has difficulty with their distance vision, but clear near vision to a distance of 80cm.
The patient likely has myopia (-1.25D), which causes blurred vision at distance while maintaining clarity for near objects. This condition can be treated with minus lenses.
F = 1/0.8 = -1.25D