Monomers, polymers and carbohydrates
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is a monomer?
A smaller unit that joins with other small units to create a large molecule
What is a polymer?
A long chain of monomers
What happens in a condensation reaction?
Water is removed to form a chemical bond
What happens in a hydrolysis reaction?
Water is added to break a chemical bond and separate molecules
Name three hexose monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose, galactose
What is the molecular formula of the three hexose monosaccharides?
C6H12O6
What type of bonds are formed when monosaccharides bond?
Glycosidic bonds
Name 3 disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
what is an isomer?
has the same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms
what are the two isomers of glucose
Alpha and Beta
What is the structure of an a-glucose and b-glucose
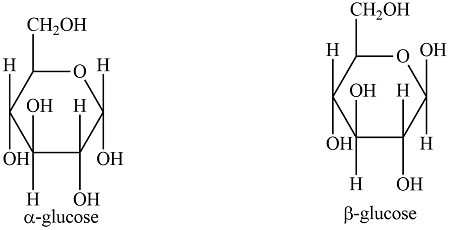
Describe function of starch
used to store a-glucose in plant cells
insoluble - no osmotic effects
large - does not diffuse out of cells
Describe the structure of starch
Amylose - 1,4 glycosidic bonds, helix with intermolecular hydrogen bonds=compact
Amylopectin - 1,4 & 1,6 glycosidic bonds, branched = many terminals ends for hydrolysis into glucose
Describe the functions of glycogen
Used to store a-glucose in animal cells(can be found in plant cells)
insoluble = no osmotic effect & and does not diffuse out of cells
Describe the structure of glycogen
1,4 &1,6 glycosidic bonds, branched = many terminal ends for hydrolysis into glucose, compact
Describe th function of cellulose
To give rigidity to plant cell walls to offer structure and support
Describe the structure of cellulose
polymer of b-glucose, 1.4 glycosidic bonds, straight chain, unbranched, alternate glucose molecules are rotated 180, h-bonds crosslinks between parallel strands form microfibrils = high tensile strength
Describe the benedict’s test for reducing sugars
Add equal volume of benedicts to the sample
heat the mixture in a boiling water bath for 5 mins
positive result = orange and brick red precipitates
Describe the benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars
would give a negative result = blue
hydrolyse the non-reducing sugars in their monomers by adding HCL
heat in a boiling baths for 5 mins
neutralise the mixture using sodium carbonate solution
proceed with the benedict’s test as usual
Describe the test for starch
Add iodine solution
positive result = from orange to blue/black