1) Molecules and Fundamentals of Biology
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
any substance that takes up space and has mass
matter
A pure substance
Has specific physical and chemical properties
Can’t be broken down into a simpler substance
element
the smallest unit of matter
retains all the chemical properties of an element
atom
can an atom break-down into something smaller, while still retaining the properties of the original element?
no
two or more atoms join together
Molecule
molecules that contain more than one element
compounds
strong attractive forces that hold atoms within the a molecule
intramolecular forces
an attractive force that exists between separate molecules
intermolecular forces
Type of force determines physical properties
intermolecular force
Are single molecules with the capability of polymerizing
molecules that have the potential of bonding to other identical molecules through chemical reactions
monomers
The process by which monomers bond together
polymerization
Substances made of many monomers linked together
polymers
polymerization reaction that results in loss of H2O
Two molecules are joined together into one molecule
Dehydration (condensation) reaction
Depolymerization reaction which utilizes water to break bonds
water is added
One molecule is broken into 2 molecules
Hydrolysis
fuel
structural support
Uses of Carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen, oxygen
All carbohydrates contain
3 categories of carbohydrates
monosaccharides; disaccharides; polysaccharides
Energy storage polysaccharide of glucose monomers used by plants
strach
Energy storage polysaccharide of glucose monomers used in animals
glycogen
structural support polysaccharides made of many glucose monomers.
important component of plant cell walls
structural support deters cell lysis
cellulose
ribose is a _____ (shape) sugar
pentose (five carbon)
glucose and fructose are _____ (shape) sugars
hexose (six carbon)
glucose and fructose are of each other
isomers
What carbohydrate results when 2 monosaccharide monomers bond/join together?
disaccharide
monosaccharide monomers join together via what type of reaction?
dehydration/condensation reactions
what type of bond is formed and what is released in a dehydration/condensation reaction?
covalent bond formation; release of H2O
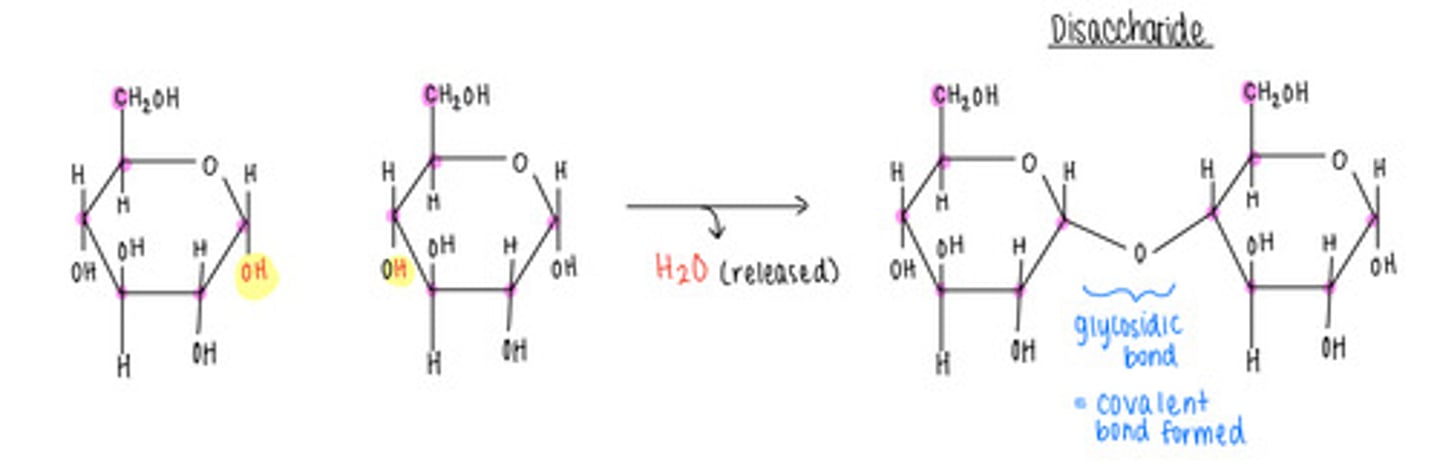
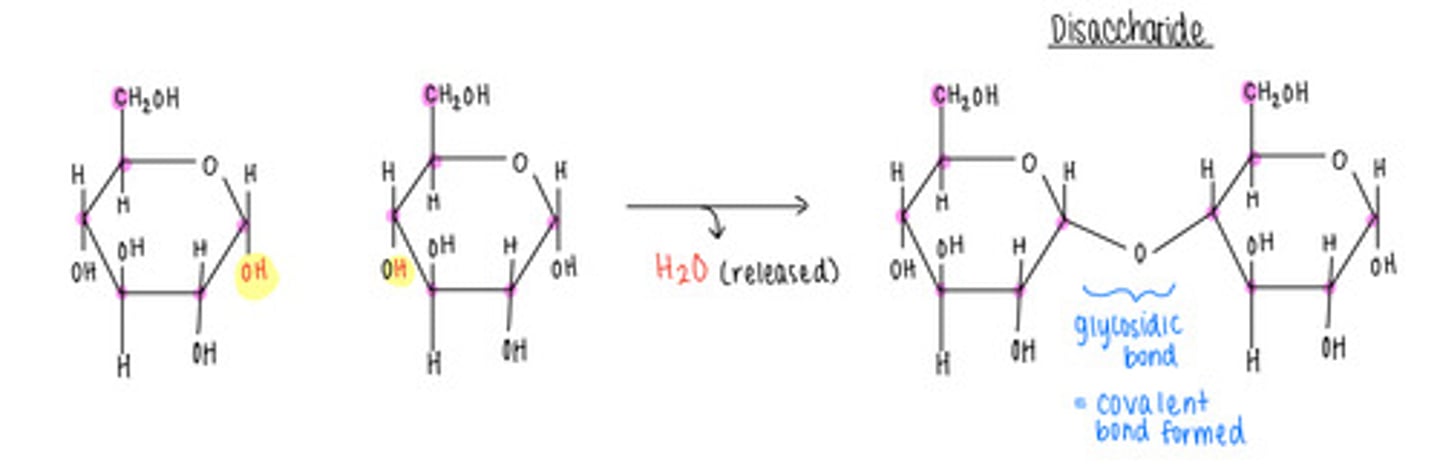
what is the opposite of a condensation/dehydration reaction - why?
A hydrolysis reaction; adds H2O to a covalent bond and splits monomers apart
what is the name of the bond that forms when a carbohydrate attaches to another molecule?
glycosidic
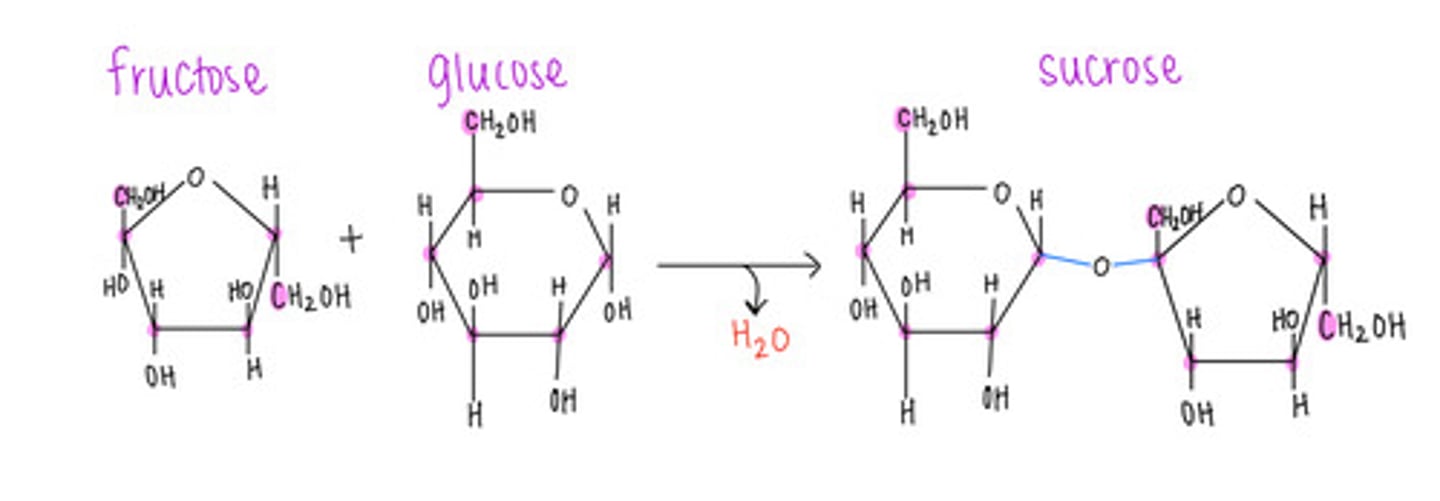
which disaccharide contains 1 glucose and 1 fructose?
sucrose (table sugar)
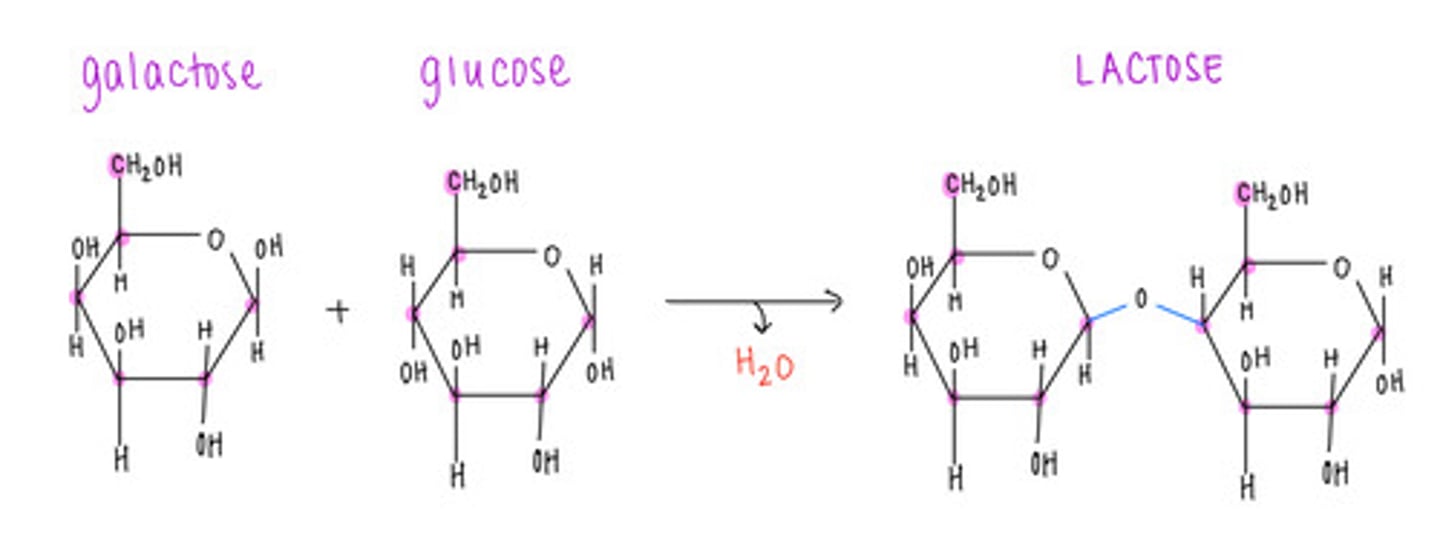
which disaccharide contains 1 galactose and 1 glucose?
lactose
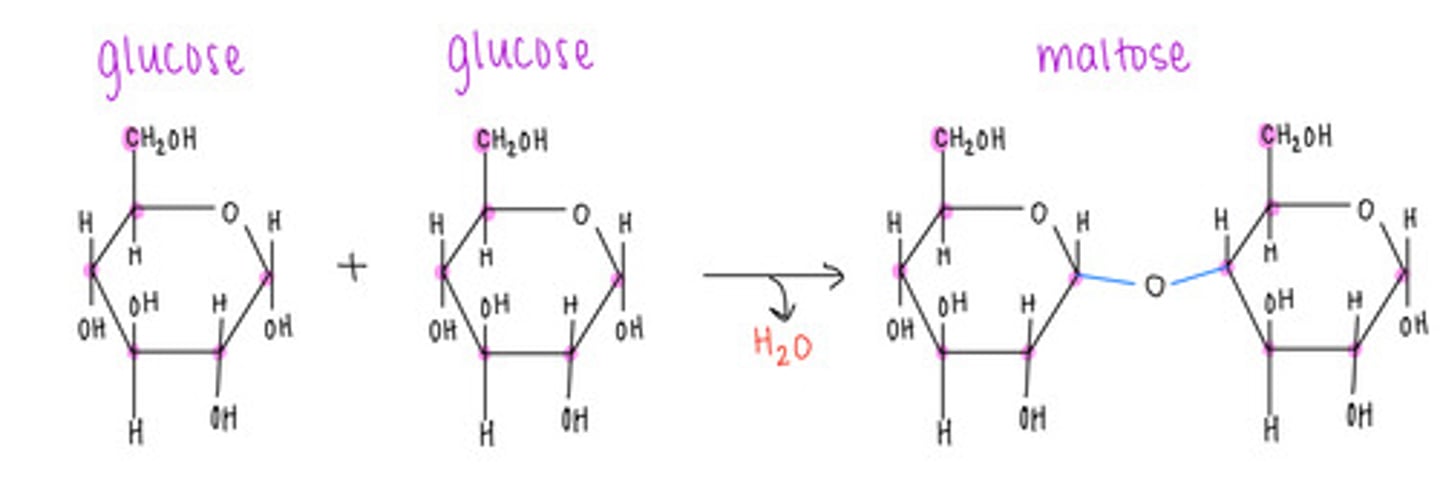
which disaccharide contains 2 glucoses linked together?
maltose
polysaccharides are long polymers of _____
monosaccharides
_____ may or may not have branching
polysaccharides
some polysaccharides are for _____, and others are for _____.
storage, structure
_____ is a crucial storage polysaccharide in plants
starch
starch contains many _____ monomers in linear forms as well as branched forms
glucose
linear plant starch is called _____
amylose
what is amylopectin?
branched form of plant starch
_____ is a storage polysaccharide found in humans
glycogen
glycogen contains many _____ monomers
glucose
is amylopectin or glycogen more branched?
glycogen
what type of bonds does glycogen have?
α-1,4-glycosidic (linear)
many α-1,6-glycosidic (branches)
name two alpha-glucose polysaccharides
starch (ex. amylose, amylopectin); glycogen
_____ is a structural polysaccharide
found in plant cell walls, wood, and paper
cellulose
cellulose is a polymer made up of what monomer?
glucose
what type of bonds does cellulose contain
Beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds;
cellulose has high ____ due to its structure
rigidity
chitin is a polysaccharide used for?
structural
chitin is found in the cell walls of _____
fungi
chitin is found in the exoskeletons of ____
insects
chitin is a structural polysaccharide with _____ added to each monomer
Nitrogen
what type of bonds are in chitin?
β-1,4-glycosidic
proteins contain polymers called _____, and each of these polymers contain monomeric subunits called ______.
polypeptides; amino acids
in an amino acid, what 4 things is the central (alpha) carbon bonded to?
hydrogen atom (H), amino group (NH2), carboxyl group (COOH), and an "R group"
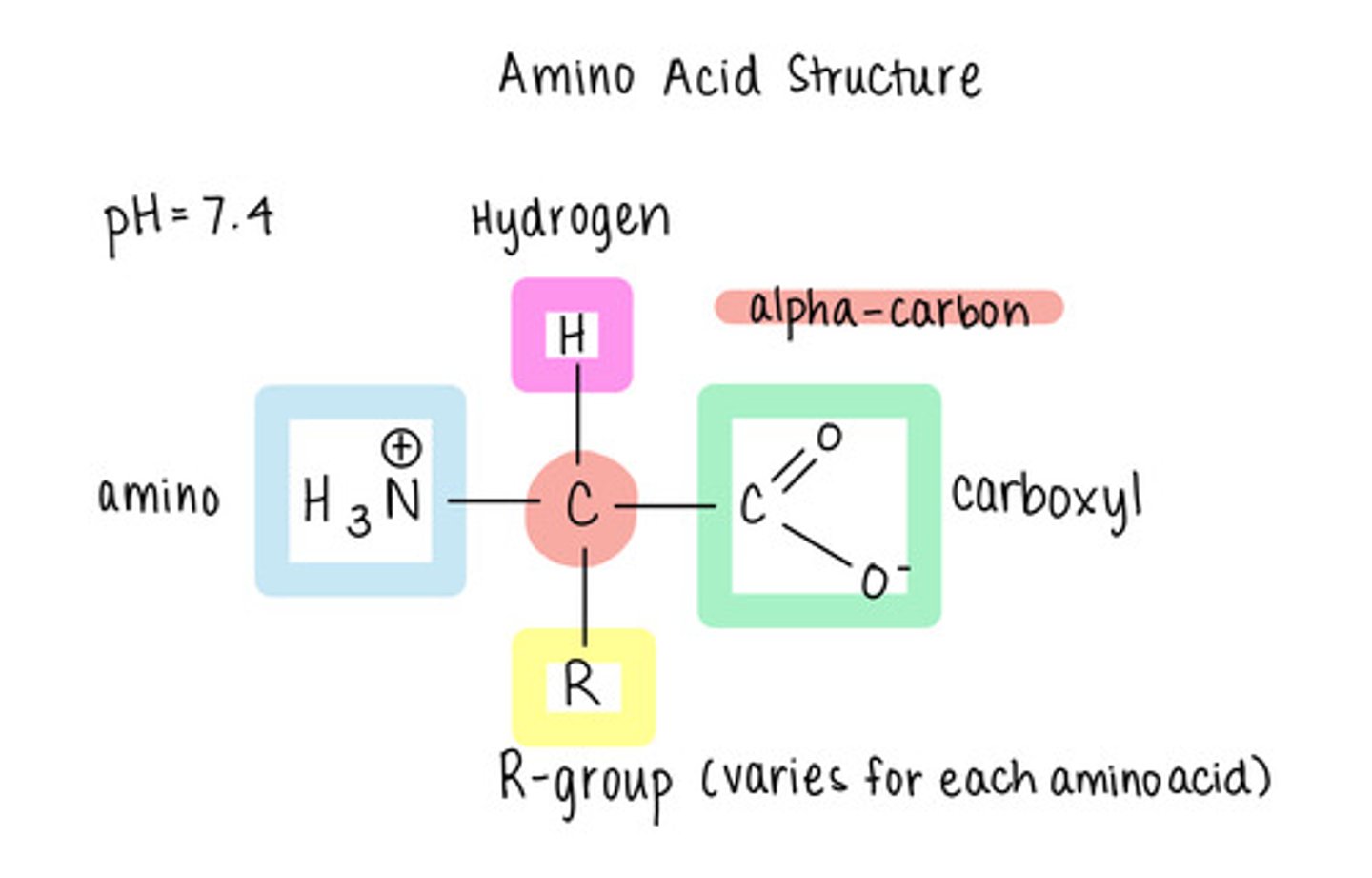
how many amino acids are there?
20
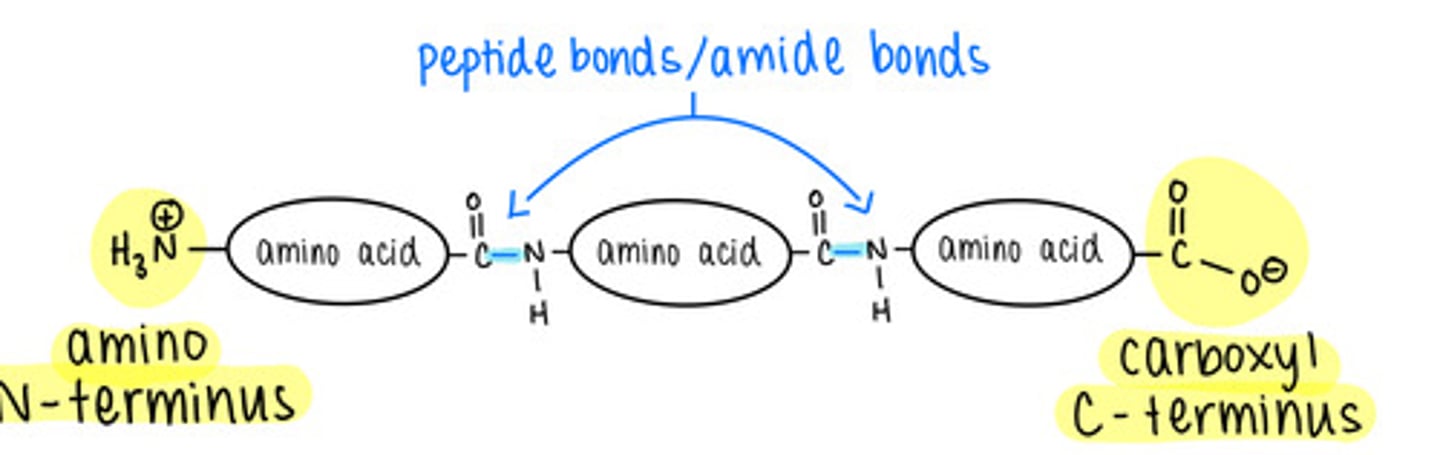
amino acids in a polypeptide are linked together via a covalent bond called a ______ bond
peptide
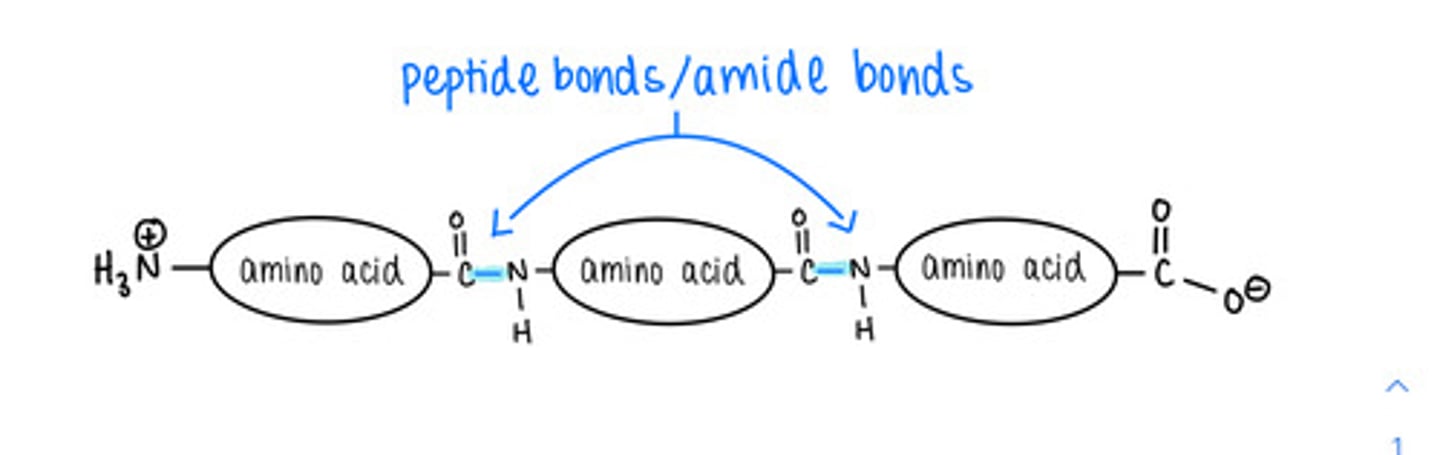
how do amino acids form peptide bonds with one another?
dehydration/condensation reactions
which type of reactions separate the amino acids of a polypeptide?
hydrolysis
polypeptides have an _____ terminus and a _____ terminus
amino (N-); carboxyl (C-)
the _____ structure of a protein is its amino acid sequence
primary
all proteins have _____ structure
primary
the _____ structure of a protein are folds that occur in a polypeptide chain due to intermolecular forces between atoms of the polypeptide backbone
Alpha Helix
Beta Pleated Sheet
secondary
the _____ is the amino acid structural features other than the R-group
polypeptide backbone
does the secondary structure include interactions between R-group atoms?
no
which level of protein structure includes alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets?
secondary
the _____ structure is the 3D structure of larger polypeptide chains due to (usually) non-covalent interactions between amino acid R-groups
tertiary
what are the common interactions between R-groups in tertiary structure?
ionic bonding; hydrogen bonding; dipole-dipole interactions; London dispersion forces; hydrophobic interactions; disulfide bonding
usually tertiary structures involve non-covalent interactions; however, ______ bonds are the "covalent exception"
disulfide
which amino acids allows disulfide bond formation?
cysteine
the _____ structure refers to large proteins that have multiple subunits (i.e. contain multiple polypeptide chains)
quaternary
while there are multiple polypeptide chains in a quaternary structure, the entire structure is considered to be _____
1 protein
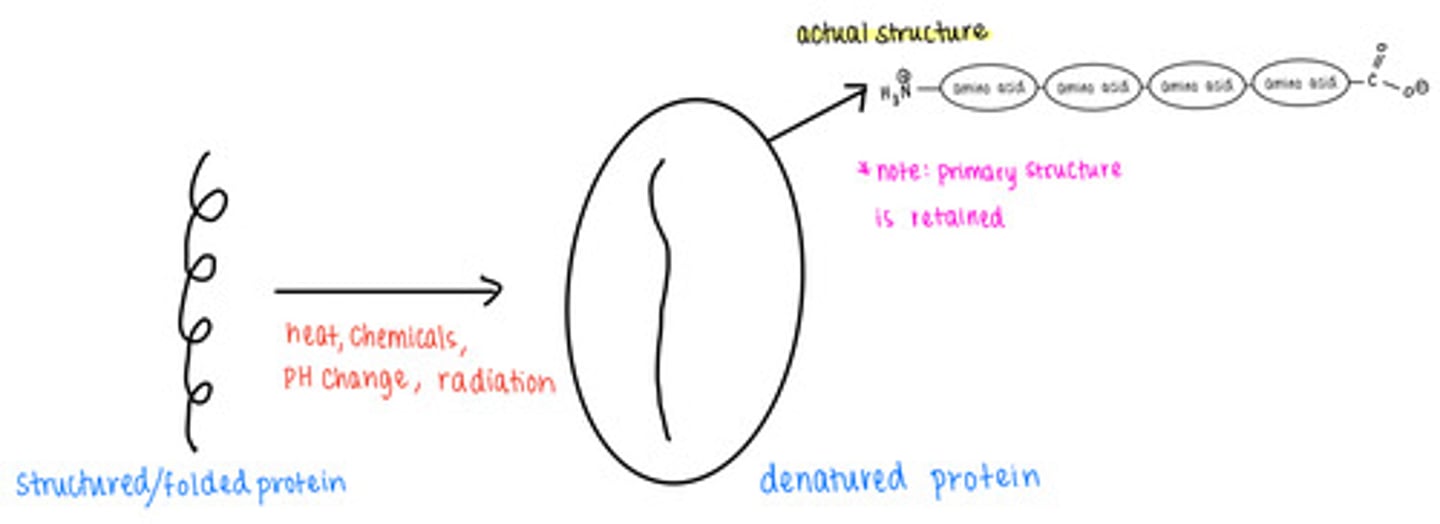
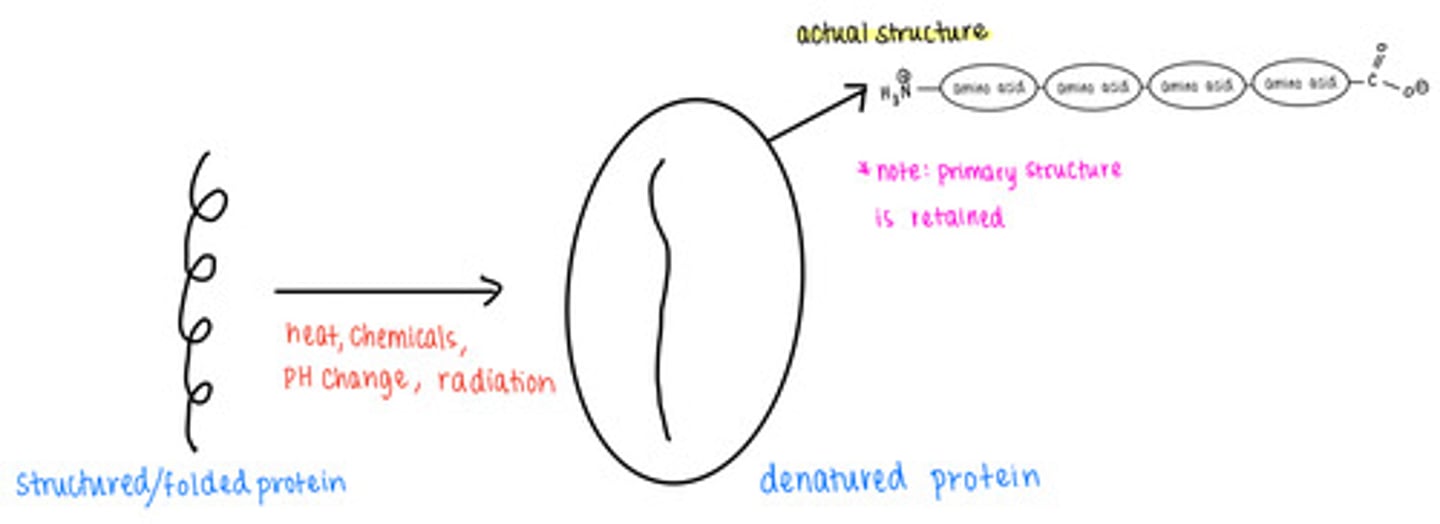
_____ causes proteins to lose their secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures
protein denaturation
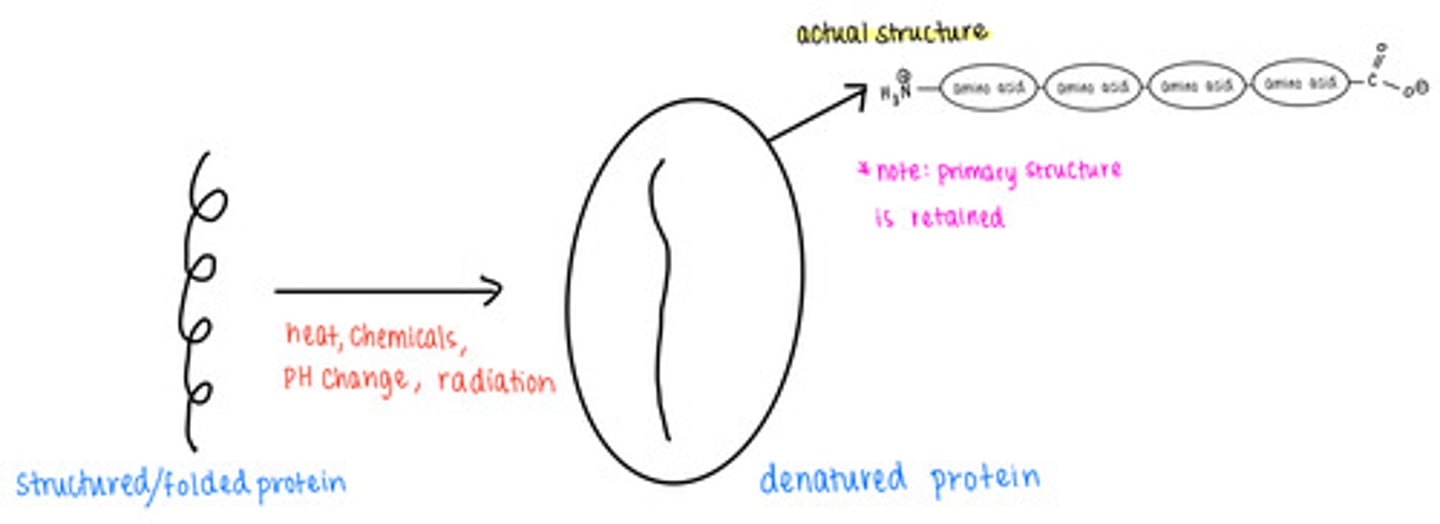
denatured proteins retain their _____ structure
primary
Composed of amino acids and non-protein components
Conjugated Proteins
Metalloproteins
Proteins which contain a metal ion cofactor
Glycoproteins
Proteins that contain a carbohydrate group
loss of _____ leads to a loss of protein function
shape
(denaturation)
what are some causes of protein denaturation?
excess temperature, chemicals, pH changes, radiation
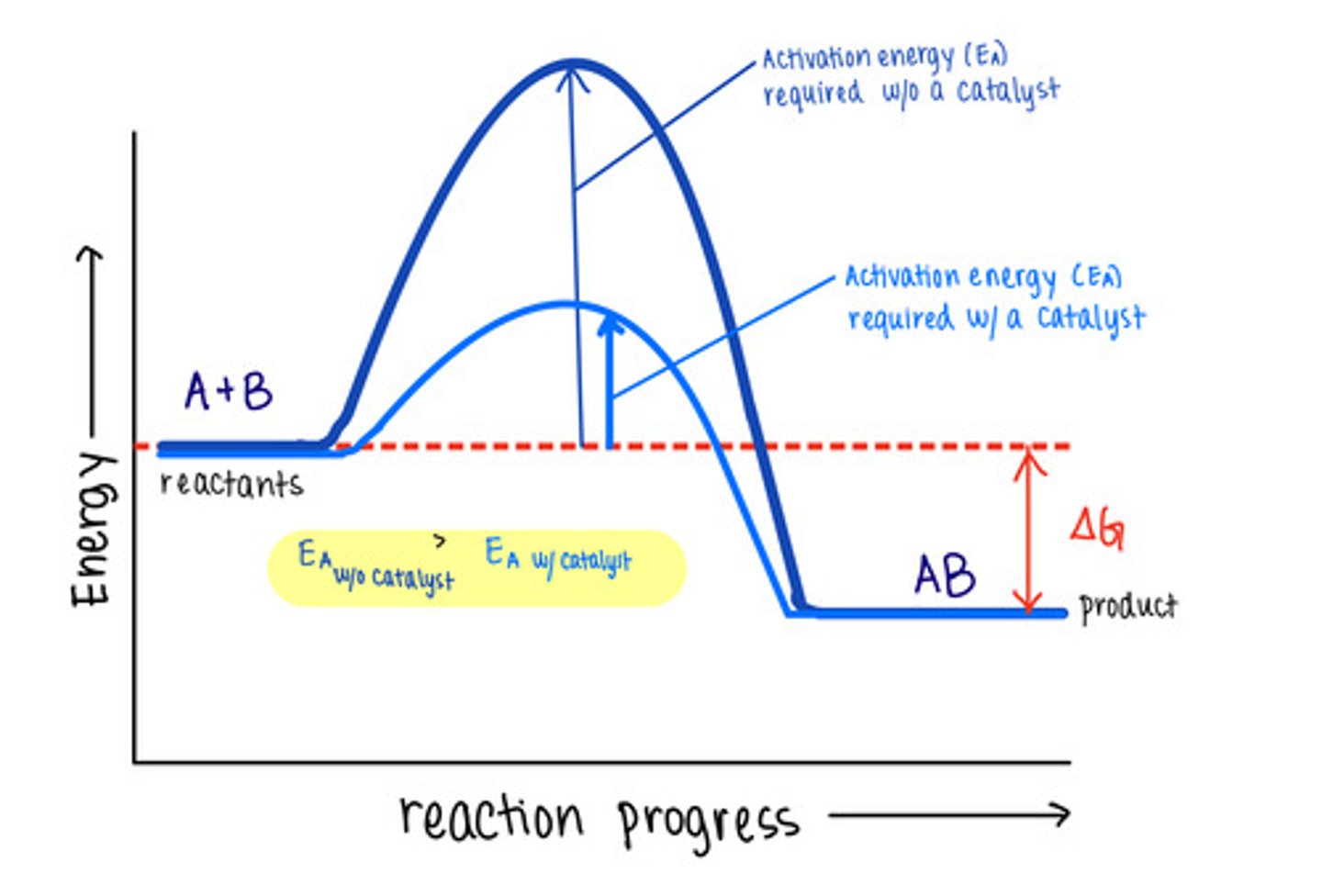
_____ are molecules that increase reaction rates
catalysts
despite speeding up reactions, catalysts do not affect the _____ of a reaction
spontaneity
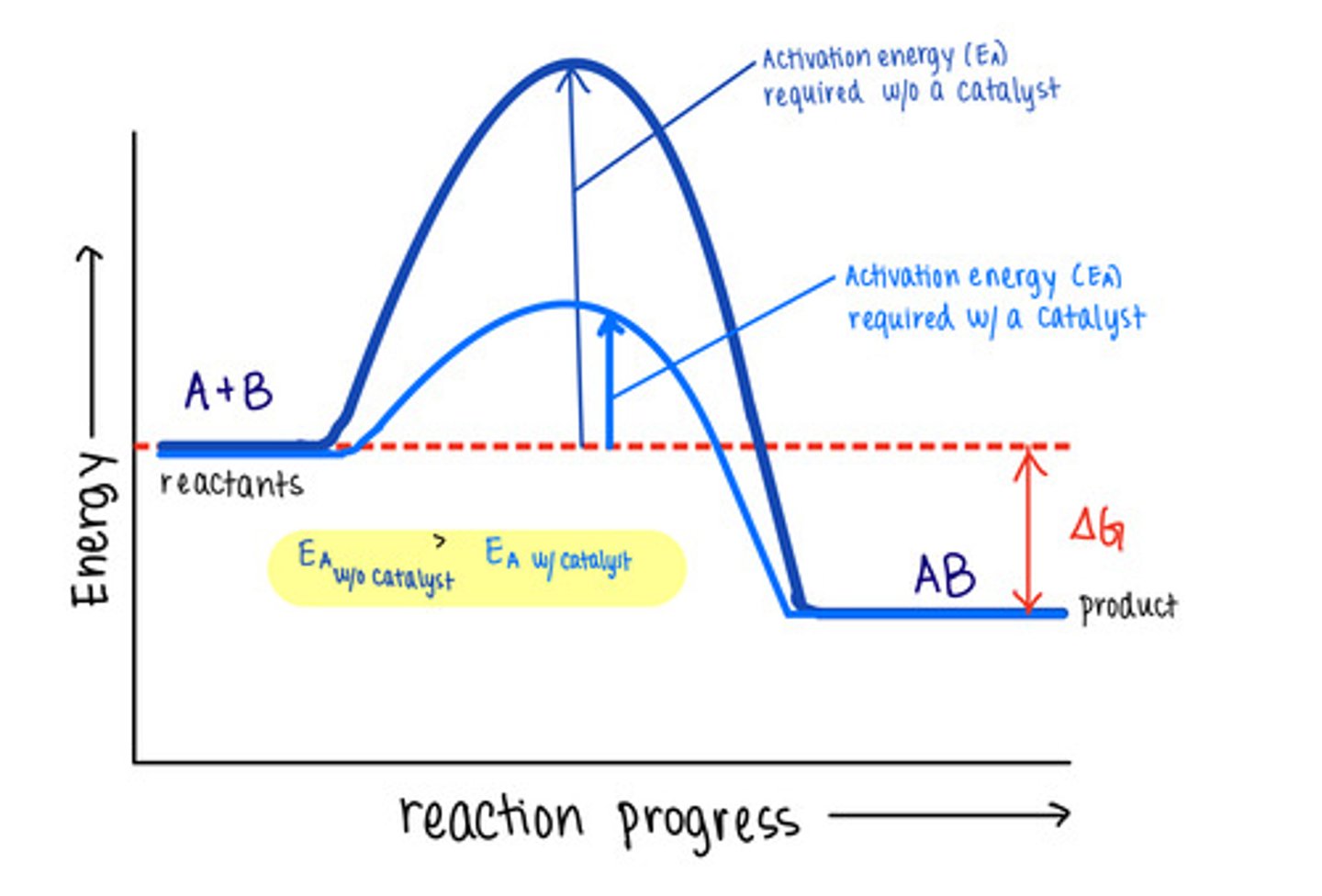
_____ are not used up by the reactions they manipulate, meaning the reaction does not change them
catalysts
catalysts lower _____ to speed reactions
activation energies/transition state energies
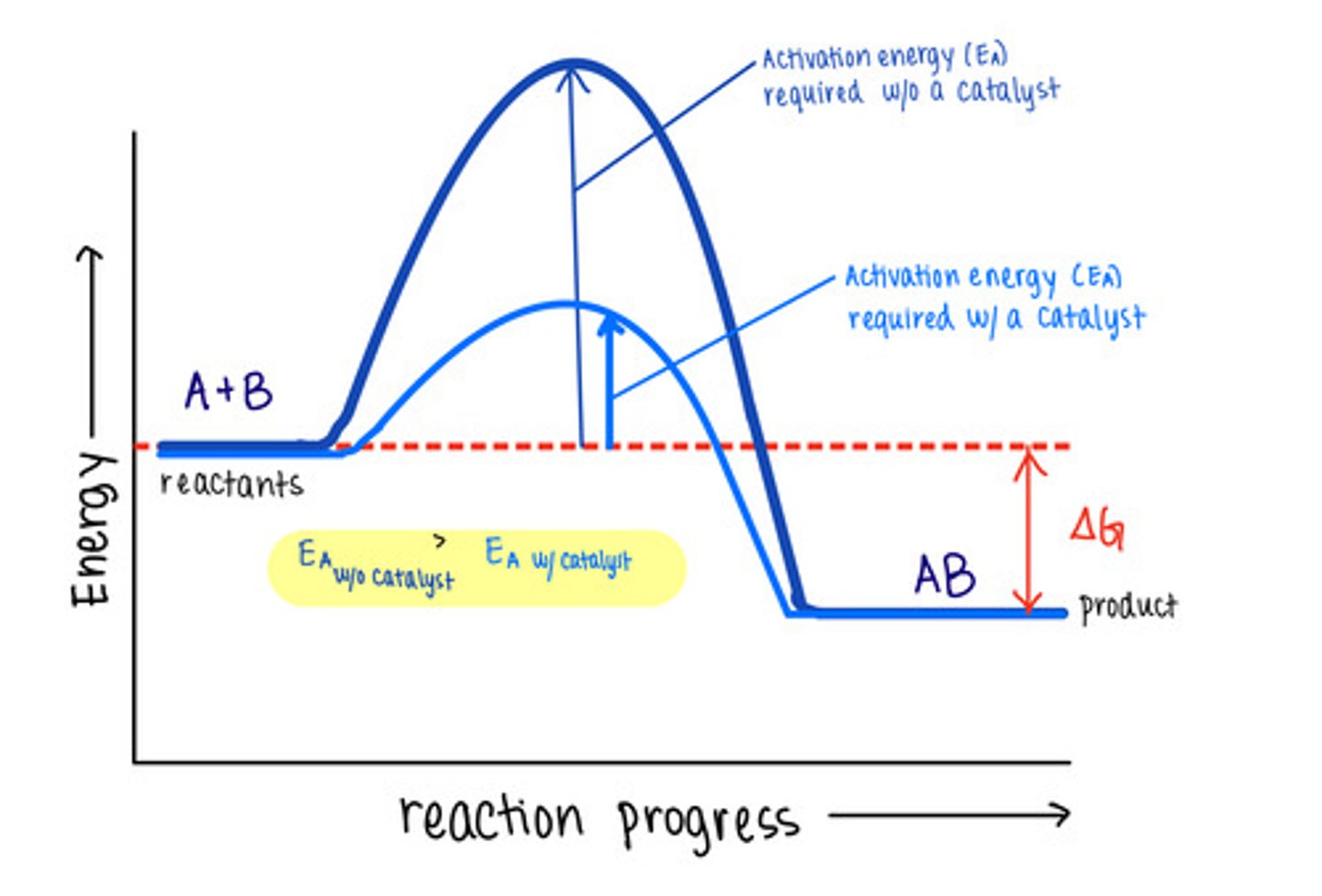
_____ do not change energy absorbing reactions to energy releasing ones, or vice versa
catalysts
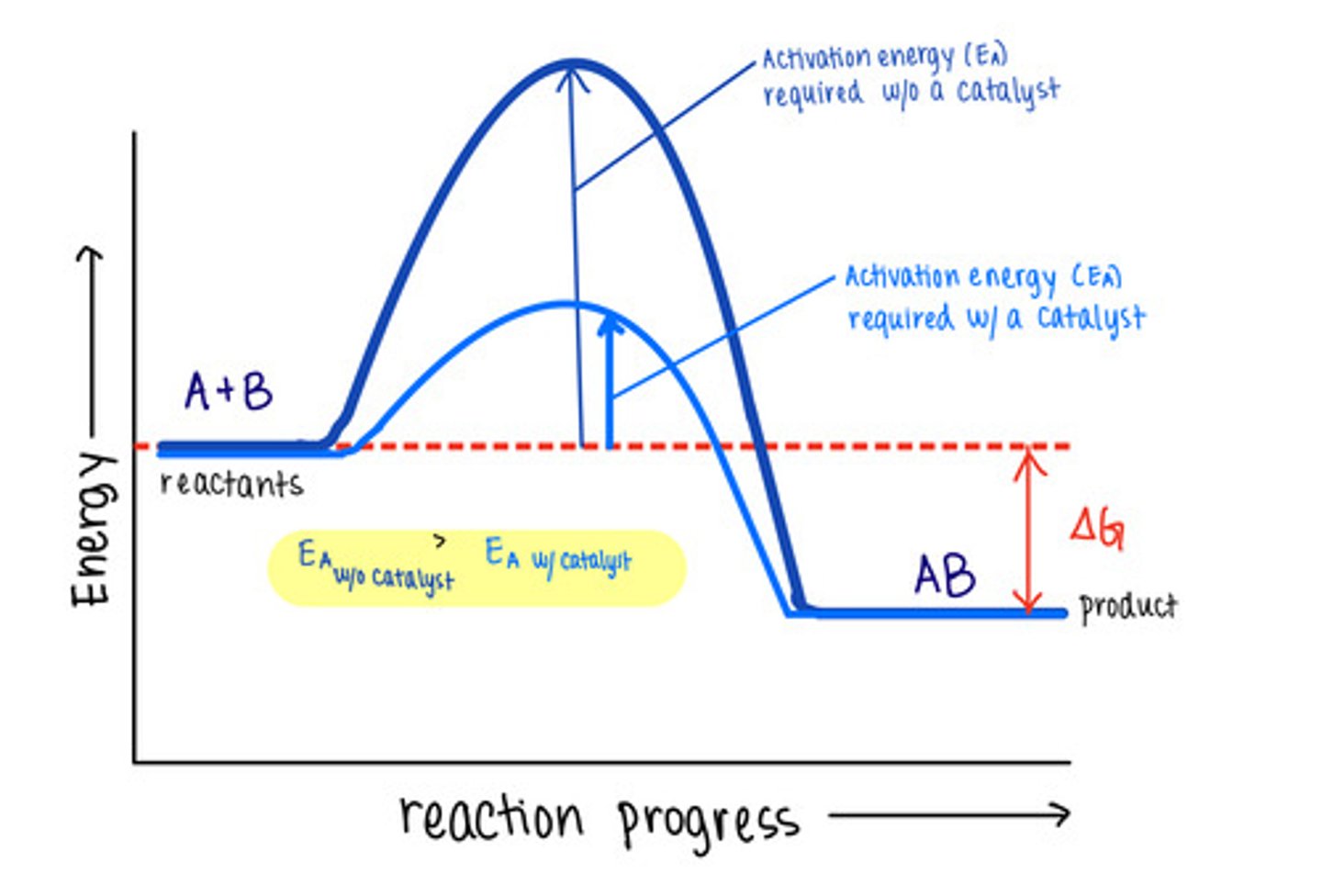
catalysts do not affect the energy of _____ or _____
reactants; products
_____ are biological protein catalysts
enzymes
substrates bind to enzymes at the _____ (location)
active site
the _____ measures how efficient an enzyme is in converting substrate to product
specificity constant
enzymes bind at the active site via the _____ model
induced fit
not all enzymes are proteins - give an example of an RNA enzyme:
ribozymes
______ are non-protein molecules that assist enzymes
cofactors
________ are organic cofactors (e.g. vitamins)
coenzymes
inorganic cofactors are usually _____
metal ions
e.g. iron (Fe2+) or magnesium (Mg2+)
_____ refer to enzymes that are bound to their cofactor
holoenzymes
what is an apoenzyme?
an enzyme that is lacking (not bound to) its cofactor
cofactors that tightly/covalently bind to their enzyme in a holoenzyme are known as _____
prosthetic groups
Protein enzymes have optimal _____ and _____ ranges in which they have the highest enzymatic activity.
pH; temperature
(temperature ranges at the upper end of a normal physiological range generally increase enzyme function)
_____ is a form of enzyme regulation, where inhibitors compete with substrates for active sites
competitive inhibition
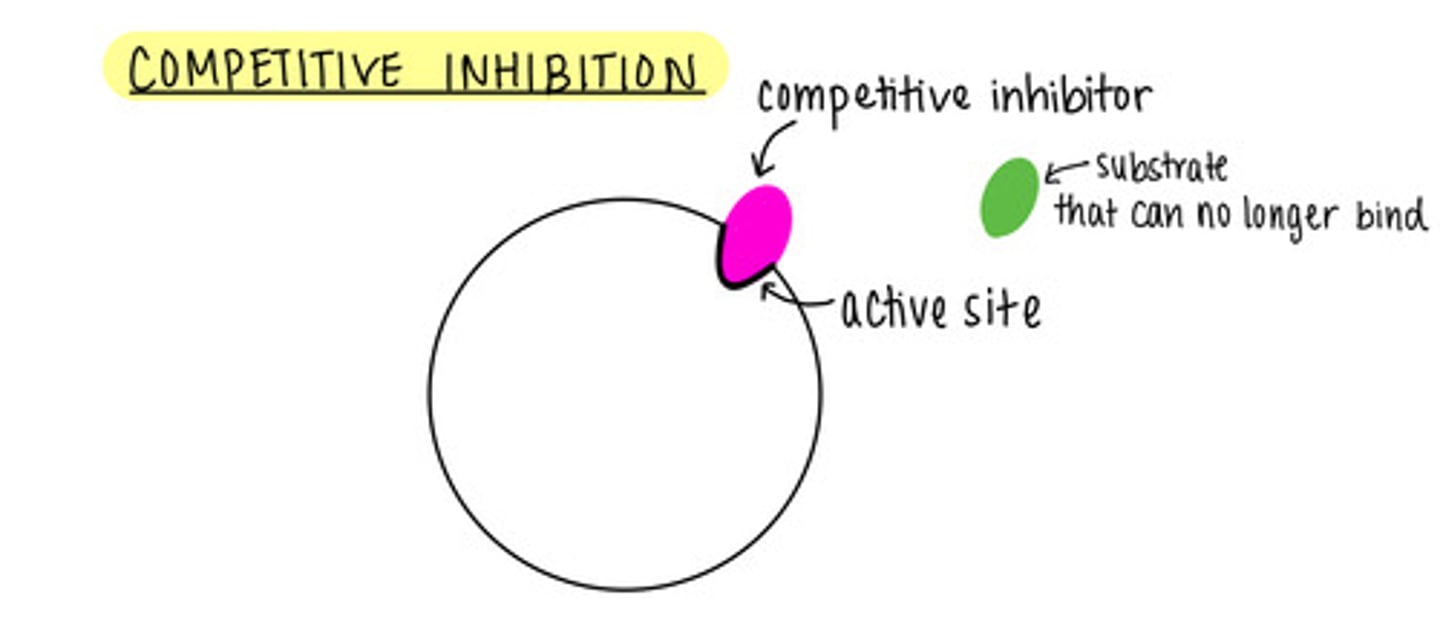
we can outcompete a competitive inhibitor by adding more _____
substrate
what is enzyme saturation?
all active sites are occupied
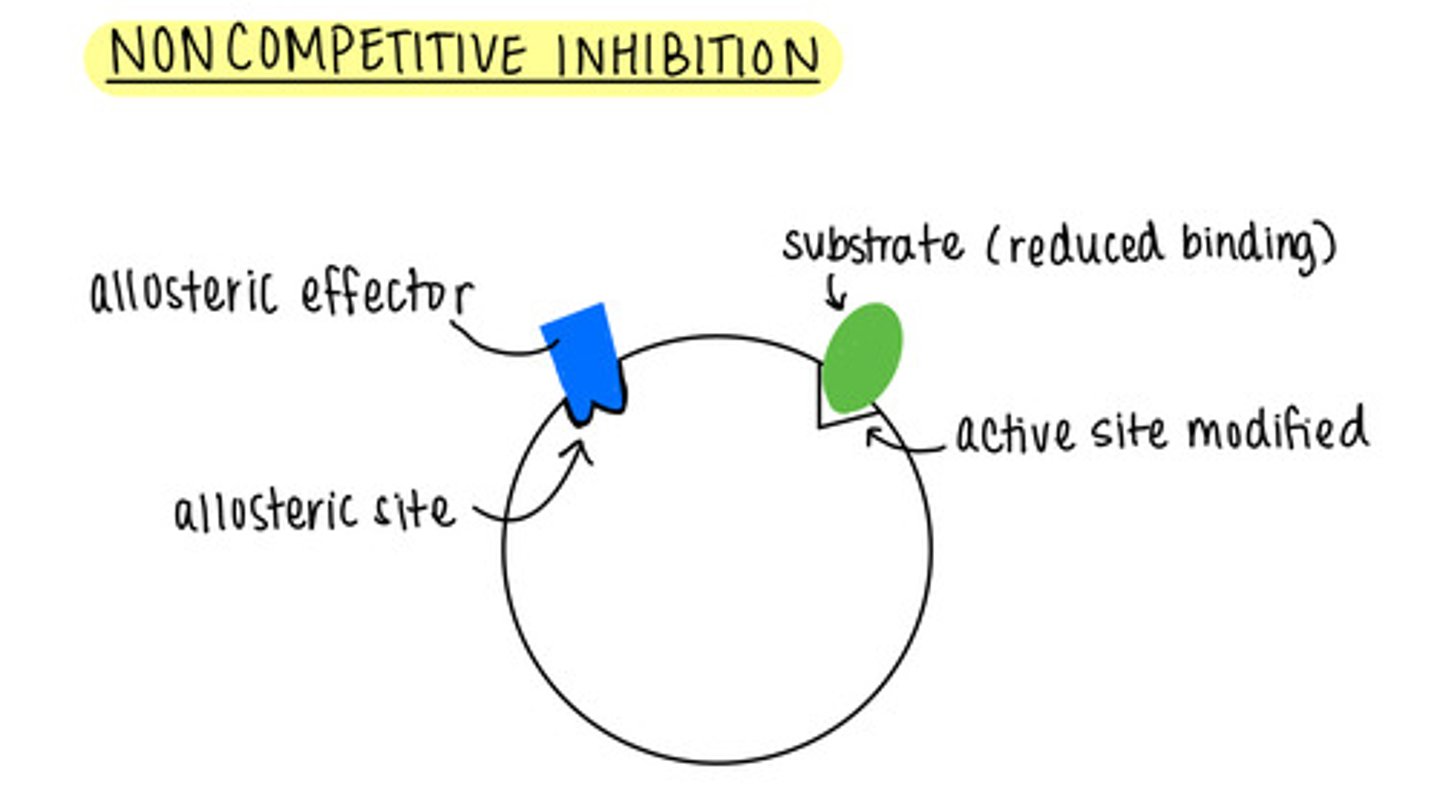
_____ is when an inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of an enzyme
noncompetitive inhibition