222 exam one
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
erik erikson
Psychosocial theory
Lifelong development
Influenced by common
cultural demands
Each stage requires the
solution to a crisis
Healthy development
requires a favorable ratio of
positive to negative.
psychosocial theory Basic trust v. mistrust
Birth to 1 year
psychosocial theory Autonomy v. shame and doubt
1-3 yrs
psychosocial theory Initiative v. guilt
3-6 years
psychosocial theory Industry v. inferiority
6-11 yrs
Identity v. role confusion
adolesence
Intimacy v. isolation
early adulthood
Generativity v. stagnation
Middle adulthood
Ego integrity v. despair
late adulthood
classical conditioning
Watson
stimulus response
operant conditioning
skinner
reinforcers and punishments
social learning
Bandura
modeling
Jean Piaget
Cognitive-Developmental
Theories
Child-centered education philosophy
piagets stages
1. Sensorimotor
2. Preoperational
3. Concrete Operational
4. Formal Operational
sensorimotor
Infants use their senses of sight, touch, smell, taste, and hearing to explore their surroundings
preoperational
a period of early childhood when children develop language and symbolic representation, but still struggle with logic and abstract thought.
concrete operational
describes how children develop logical thinking skills. It's the third stage of Piaget's theory and usually occurs between the ages of 7 and 11.
formal operational
the final stage, typically beginning around age 11 or 12, where individuals develop the ability to think abstractly, logically, and systematically, allowing them to solve complex problems, consider hypothetical situations, and test hypotheses through deductive reasonin
Sociocultural Theory person
Lev Vygotsky
sociocultural theory
Transmission of culture to a new generation
• Values, beliefs, customs, and skills
Complex forms of thinking have their origin in social
interactions.
Children’s learning of new cognitive skills is guided by
a skilled social partner.
• Zone of Proximal Development
• Scaffolding
scaffolding
a teaching method that helps students learn new material by breaking it down into smaller chunks
Zone of Proximal Development
the space between what a learner can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance and support from a more knowledgeable person, like a teacher or peer, essentially representing the ideal range of challenge for optimal learning;
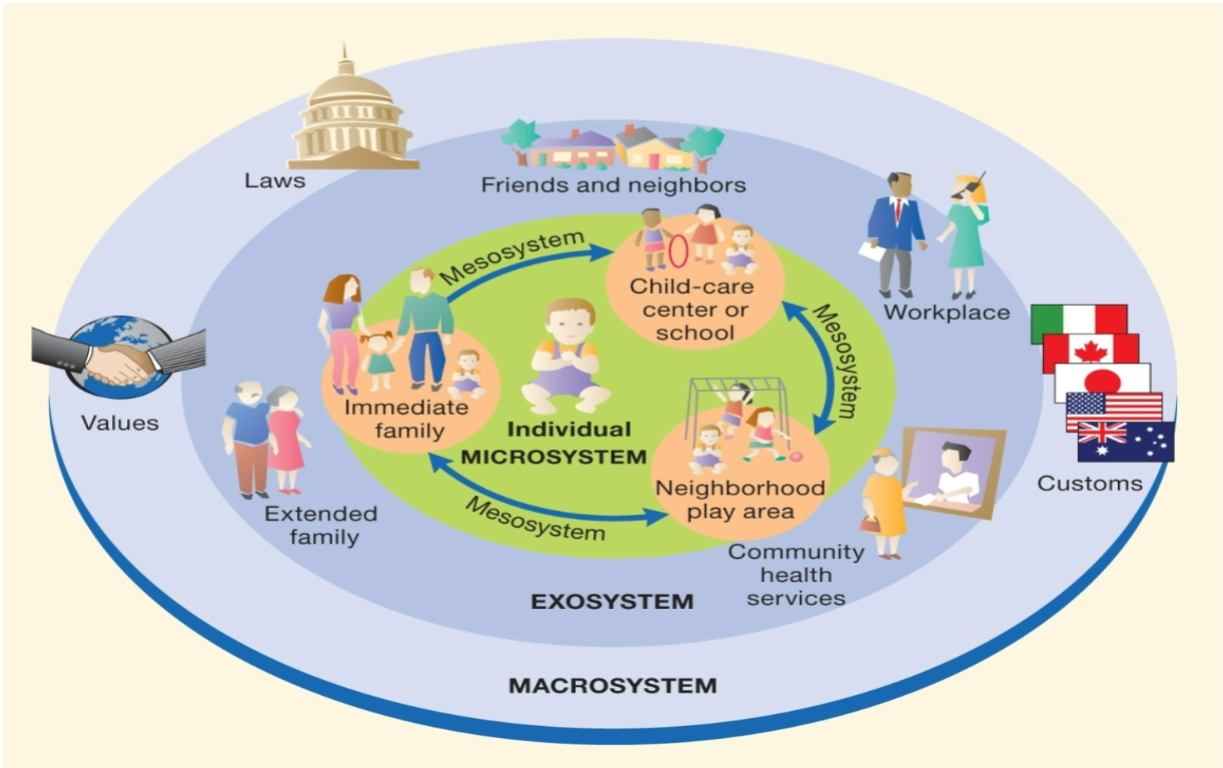
Ecological Theory
Urie Bronfenbrenner
Explains development in terms of relationships
between people and their environments.
Contexts
• Microsystem
• Mesosystem
• Exosystem
• Macrosystem
• Chronosystem
Ecological Theory graph
Eclecticism
Multiple Theoretical Approaches
Build on ideas from several sources.
Avoids rigid adherence to a single theory.
Allows deeper probing of behavior using better
research.
Prenatal
Conception to birth
The one-celled organism transforms into a human baby with remarkable capacities to adjust to life in the surrounding world.
Infancy and toddlerhood
Birth–2 years
Dramatic changes in the body and brain support the emergence of a wide array of motor, perceptual, and intellectual capacities and first intimate ties to others.
Early childhood
2–6 years
During the “play years,” motor skills are refined, thought and language expand at an astounding pace, a sense of morality is evident, and children establish ties with peers.
Middle childhood
6–11 years
The school years are marked by improved athletic abilities; more logical thought processes; mastery of fundamental reading, writing, math, and other academic knowledge and skills; advances in selfunderstanding, morality, and friendship; and the beginnings of peer-group membership.
Adolescence
11–18 years
Puberty leads to an adult-sized body and sexual maturity. Thought becomes abstract and idealistic and school achievement more serious. Adolescents begin to establish autonomy from the family and to define personal values and goals.
Early adulthood
18–40 years
Most young people leave home, complete their education, and begin full-time work. Major concerns are developing a career, forming an intimate partnership, and marrying, rearing children, or pursuing other lifestyles.
Middle adulthood
Many people are at the height of their careers and attain leadership positions. They must also help their children begin independent lives and their parents adapt to aging. They become more aware of their own mortality.
Late adulthood
65 years–death
People adjust to retirement, to decreased physical strength and health, and often to the death of an intimate partner. They reflect on the meaning of their lives.
Freud’s Psychosexual Stage
Birth–1 year
Oral: If oral needs are not met through sucking from breast or bottle, the individual may develop such habits as thumb sucking, fingernail biting, overeating, or smoking.
psychosexual 1–3 years
Anal: Toddlers and preschoolers enjoy holding and releasing urine and feces. If parents toilet train before children are ready or make too few demands, conflicts about anal control may appear in the form of extreme orderliness or disorder.
psychosexual 3-6
Phallic: As preschoolers take pleasure in genital stimulation, Freud’s Oedipus conflict for boys and Electra conflict for girls arise: Children feel a sexual desire for the other-sex parent. To avoid punishment, they give up this desire and adopt the same-sex parent’s characteristics and values. As a result, the superego is formed, and children feel guilty when they violate its standards.
psychosexual 6-11
Latency: Sexual instincts die down, and the superego strengthens as children acquire new social values from adults and same-sex peers.
psychosexual 11-18
Genital: With puberty, sexual impulses reappear. Successful development during earlier stages leads to marriage, mature sexuality, and child rearing.
erikson view on freud
Erikson emphasized that in addition to mediating between id impulses and superego demands, the ego makes a positive contribution to development, acquiring attitudes and skills that make the individual an active, contributing member of society.
What are the three main stages of prenatal development?
Germinal Period, Period of the Embryo, and Period of the Fetus
What is the germinal period, and when does it occur?
The germinal period is from conception to implantation, lasting from week 0 to week 2. During this time, cells specialize to support development, including the formation of the blastocyst, placenta, umbilical cord, yolk sac, and amnion
What happens during the period of the embryo, and when does it occur?
The period of the embryo occurs from week 3 to week 8. During this time, cells specialize to form the foundations of all body organs. The neural tube develops and by week 7, the Y chromosome directs the development of the penis with the help of testosterone. Organogenesis also occurs
What occurs during the period of the fetus, and when does it occur?
The period of the fetus occurs from week 9 to week 38-40. During this stage, there is growth and refinement of all organ systems, with the fetus growing from 1/4 ounce and 1 inch to 7 1/2 pounds and 20 inches in length. Surfactant and vernix develop and the age of viability is reached between 22 to 26 weeks.
What are autosomes?
The 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes
What are sex chromosomes and what are the combinations for each sex?
The 23rd pair of chromosomes determines sex. XX = female, XY = male
What are gametes?
Sex cells: Sperm and ova
What is a zygote?
A sperm and ovum united
What are the two types of twins?
Identical (monozygotic), from one zygote that divides into two individuals, and fraternal (dizygotic), from two zygotes, or fertilized ova
What are the developmental principles?
Cephalocaudal (head to tail) and proximodistal (center to extremities)
What are some potential problems during prenatal development?
Genetic disorders, chromosomal errors, and teratogens
What is a teratogen?
Environmental substances that can cause damage during prenatal development. Factors affecting harm include dose and age at the time of exposure. Examples of teratogens include drugs, tobacco, and alcohol
What are some examples of autosomal recessive disorders?
Phenylketonuria (PKU), sickle-cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease
What is an example of a dominant gene disorder?
huntington’s disease
What are some sex-linked disorders?
Red-green colorblindness, hemophilia, and fragile-X syndrome, which are caused by a recessive gene and more often affect boys than girls
What is Down Syndrome?
Also known as Trisomy 21, it is a chromosomal error involving problems with the twenty-first chromosome, resulting in intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, and physical abnormalities. Maternal age is a major factor
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
A condition caused by prenatal exposure to alcohol, and is associated with a range of problems including physical and cognitive impairments
low birth weight
smaller head (microcephaly)
short
smaller brain
flat midface
flat philtrum
folds in eyes
angle saw different
mild to severe intellectual disablities
shorter attention span
hyper activity
What is the Apgar Scale?
Used to assess a neonate using Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, and Respiration
What are some maternal factors that affect development?
Prenatal care, nutrition, and ag
What are the stages of Erikson's Psychosocial Theory?
Basic trust vs. mistrust (birth to 1 year), autonomy vs. shame and doubt (1-3 years), initiative vs. guilt (3-6 years), industry vs. inferiority (6-11 years), identity vs. role confusion (adolescence), intimacy vs. isolation (early adulthood), generativity vs. stagnation (middle adulthood), ego integrity vs. despair (late adulthood)
What are some key concepts in Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory?
Zone of Proximal Development and Scaffolding . the transmission of culture to a new generation
What are the systems in Bronfenbrenner's Ecological Theory?
Microsystem, Mesosystem, Exosystem, Macrosystem, and Chronosystem
Microsystem
: Immediate environment
Mesosystem
: Interactions between microsystems
Exosystem
: External social settings that affect the individual
Macrosystem
: Culture and societal values
Chronosystem
: Time and historical influences
What is Eclecticism in the context of developmental psychology?
An approach that builds on ideas from several sources and avoids rigid adherence to a single theory, allowing for a deeper understanding of behavior using better research
What are the three stages of birth?
Stage 1: Dilation and effacement of the cervix. Stage 2: Pushing and birth of the baby. Stage 3: Delivery of the placenta
What is considered Low Birth Weight (LBW)?
Below 2,500 grams (5.5 pounds)
What does it mean if a baby is preterm
Born before week 38
What is meant by a small-for-date neonate?
A baby that is smaller than expected for their gestational age
Psychosocial Theory (Erikson) pros and cons
Pros:
It covers the entire lifespan, unlike some other theories that primarily focus on childhood
It acknowledges the influence of social and cultural factors on development
It provides a framework for understanding how identity develops across different stages
Cons:
It can be difficult to empirically test all aspects of the theory.
It may be too broad and vague to account for the complexities of individual development.
The stages are presented as sequential, but individual development may not follow such a neat pattern.
Behaviorism and Social Learning Theory pros and cons
Pros:
It is based on observable behaviors, which makes it relatively easy to test empirically.
It has led to practical applications in areas such as education and behavior modification.
It highlights the important role of learning and environmental influences on development.
Cons:
It may not fully account for the role of cognitive factors in development.
It may underestimate the individual's active role in their own development.
It may oversimplify complex behaviors.
Cognitive-Developmental Theory (Piaget) pros and cons
Pros:
It provides a detailed framework for understanding cognitive changes that occur during childhood.
It emphasizes the active role of children in constructing their own understanding of the world.
It has significantly influenced educational practices.
Cons:
The stages are presented as fixed and universal, but individual development can vary.
It may not fully account for the influence of culture and social interactions on cognitive development.
It may underestimate the cognitive abilities of younger children.
Sociocultural Theory (Vygotsky) pros and cons
Pros:
It highlights the critical role of social and cultural factors in shaping cognition
It has practical implications for education, emphasizing guided learning.
It accounts for the variations in development that can occur across different cultures.
Cons:
It may not fully explain individual differences in cognitive development.
It may underestimate the role of biological factors in development.
It may be less easily tested empirically compared to some other theories.
Ecological Theory (Bronfenbrenner) pros and cons
Pros:
It provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex influences on development.
It acknowledges the importance of both immediate and broader contexts in shaping development3.
It is useful for understanding how various systems interact to influence an individual's development.
Cons:
It is difficult to empirically test all aspects of the theory due to its complexity and its numerous levels of analysis.
It may lack a clear set of specific predictions about how different systems influence specific outcomes.
It may not fully explain how specific mechanisms work within each context to influence development.
Eclecticism pros and cons
Pros:
It allows for a more flexible and comprehensive understanding of development.
It can integrate strengths from multiple theories to provide a fuller picture.
It encourages better research by considering multiple theoretical perspectives3.
Cons:
It may lack a unified framework and can lead to a piecemeal approach to understanding development.
It requires careful consideration of how different theoretical concepts can be integrated without conflict or redundancy.
Surfactant
A substance that is necessary for breathing and that develops in the fetal stage
Vernix:
A protective coating that develops in the fetal stage
Ectopic Pregnancy
A pregnancy where the zygote implants outside of the uterus
Preeclampsia/Eclampsia
Conditions involving high blood pressure during pregnancy
Period of the embryo
During this period all the ground work is laid out for all body structures and organs. The remaining weeks, fetus, are really for growth and completing the processes.
Sensitive periods in prenatal development
The embryonic period is the most sensitive period for prenatal development (weeks 3-8). This is where they are most susceptible to tetragons and developmental errors.
Emotional stress during pregnancy
Severe Stress can cause a wide variety of difficulties to the baby: miscarriage, low birth weight, respiratory and digestive illness, colic, and etc.
"Flight or Fright" hormones are produced causing excess blood to flow to arms, legs, heart, brain and deprives the uterus and baby of blood supply(oxygen and nutrients).
Fetal stress hormones can be triggered through the placenta causing stress to fetal heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose, and activity level.
effect of teratogens
Effects of teratogens depend on: dose, heredity, other negative influences, and age of the fetus.
Lead
High exposure is lead to prematurity, low birth weight, brain damage, and a wide variety of physical defects.
Mercury
Over exposure can cause disruption in the migration of neurons causing brain damage.
Tobacco
Low birth weight is best know defect. But there are other likelihood's such as clef lip, miscarriage, prematurity, and breathing during sleep.(infant death, cancer, and asthma)
Infants to smoking mothers also have bad effects.
Tobacco effects the fetus because of the nicotine and addictive substances constricting blood flow to the uterus to other places.
Passive smokers (HUSBANDS OR RELATIVE DO IT AROUND THEM) have the same risks as pregnant women who smoke.
Stages of Childbirth
Stage #1 Dilation: Longest stage, average 12 to 14 hours with first birth and 4 to 6 with others. Contractions of the uterus cause dilation (effacement of the cervix). Transition is reached when strength and frequency of contractions are at their peak.
Stage #2: Delivery: Pushing with each contraction forces baby down birth canal. Near the end of stage 2 the shoulders emerge followed by the rest of the body.
Stage #3 Delivery of the placenta: Final contractions cause placenta to separate from the wall of the uterus about 5 to 10 minutes after birth.
Implantation
Between the 7th and the 9th day this occurs. The blastocyst burrows deep into the uterine lining. amnion forms (membrane that encloses the developing organism in amniotic fluid to keep temperature constant and cushion it).
Yolk sac emerges that produces blood cells until the liver, spleen and bone marrow emerge.
30% of zygotes do not survive by preventing implantation nature eliminates a lot of prenatal abnormalities.
CNS sensitive period
3-38
heart sensitive period
3-8
upper limbs sensitive period
4-8
lower limbs sensitive period
4-8
ears sensitive period
4-16
eyes sensitive period
4-38
teeth sensitive period
6-38
palate sensitive period
6-9
external genitals sensitive period
7-38
First trimester
Weeks 0-10